
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Sreejith.S
1 , Godwin Jacob Andews2 , Vishnu Sajan3 ,
Shijina
.B4 ,
Abhijith.M
5
12345Department of Computer Science and Engineering, TOMS College of Engineering Mattakara, India 4Assistant Professor
Abstract -Safe, transparent, and impenetrable elections are a big job in today's time. Traditional voting systems suffer from common issues of vote manipulation, security vulnerabilities, and the absence of transparency. To enhance election security, prevent fraud, and maintain voter anonymity, this research proposes a blockchainbased election system that utilizes decentralized ledger technology.Theprocesseliminatesfraudulentorduplicate votes by combining fingerprint and iris recognition to verify voter identities. Due to the immutability of blockchainandcryptographicencryption,votescannot be altered or deleted once they are cast. The process also enablespublicverificationandreal-timecountingofvotes, which enhances trust in the democratic process. In comparison with traditional voting systems, our process not only enhances security but also accessibility and speed.
Key Words: Blockchain, Voting System, Decentralized Ledger, Fingerprint Authentication, Iris Recognition, Cryptographic Security, Election Transparency, Realtime Vote Tallying
1.INTRODUCTION
To provide secure authentication, biometric technologies scan and analyse unique human characteristics such as fingerprints and iris scans. Biometrics are a reliable security method since they cannot be hacked, forgotten, or stolen like passwords or PINs can. Biometric authentication is increasingly widely used in secure applications as a result of its increasing usage in the public and corporate realms. For enhanced electionsecurity,preventionoffraud,andassuranceofan open and unhackable voting system, this research recommends a biometric voting system based on blockchaintechnologyusingfingerprintandirisscan.
The proposed system uses blockchain technology to create a secure and unchangeable voting history, safeguarding it from corruption and unauthorized access. Itensuresaccuracyandpreventsduplicatevotingthrough the use of fingerprint and iris recognition. Online vote counting simplifies election administration, while an interactive graphical user interface improves usability. Thissolutionboostselectionintegrityandstreamlinesthe voting process by combining blockchain's decentralized framework with biometric authentication. By addressing long-standing issues in voting systems and providing a
secure, efficient, and transparent democratic process, this technologyenhancesvoterconfidence.
Fingerprint-based voting systems increase the verification of voters through biometric technology, making the electoral process more efficient and secure. Fingerprint-based, these systems prevent fraud in voting and ensure that every vote is counted. If the voter is already registered and there are fingerprint details in the system, the voter can only vote when their fingerprint is successfullyverified.Iftheirfingerprintisnotthesame,the process is halted by the system, thus avoiding any illegal voting. This technology enhances voter integrity and simplifiesandacceleratesthevotingprocess.Asfingerprint identification is simple and fast, it shortens waiting times and simplifies the process. Fingerprint-based systems are less expensive than other biometric technologies and can be interfaced with current electronic voting machines (EVMs).
Butissueslikesensormalfunction,dirtyorharmedfingers, and attempt at manipulation must be tackled. Ongoing advancements in biometric technology and attempts at voter education are paramount to building broad confidenceandtrustworthinessinsuchsystems.
Voting systems based on iris recognition provide a secure and reliable way of verifying the voter's identity throughscanningandrecognitionoftheuniquepatternsin a person's iris. There is a wider margin of error in fingerprint identification due to finger wear. And like fingerprintauthentication,irisrecognitionisadeterrentto voter fraud, ensuring electoral integrity. If a voter is preregisteredandtheiririsdatamatchesinthedatabase,they will be allowed to vote; otherwise, they will be barred. Integrating these systems with Temasek's biometric databaseensuresthatonlythoseeligibletovotecandoso, thusfreeandfairelectionsinIndia.
A good number of errors are eliminated, and the system becomes immune to illegitimate use, giving a high degree of security to voting. The second strong point is that the featuresthatconstitutetheirisdonotchangeoverashort span, making it suitable for different age groups. The methodusedremainsthesameanddoesnotalterwiththe change of external conditions, unlike fingerprints.Besides, irisscanningisahygienictouch-freesolution,hencemakes

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
it most appropriate for mass-use elections. But challenges will be the initial installation costs, lighting conditions for scanningaccuracy,andoperabilityofthesystemforpeople with varying technical know-how. Ongoing technological advancements and voter education will be pivotal in enhancing acceptability and usability at large within irisbasedvoting.
Blockchain voting systems should be conducted fairly automatic election processes for citizens. The votes are impartially recorded in an unchanging and unavoidable digital record. This guarantees the safety of each voting document and makes loopholes impossible, thus affording the citizen a high level of trust in the entire process. Moreover, when coupled with specific biometric techniques,blockchainoffersasupremesystemofsecurity whereonlyeligibleandregisteredvotersareabletoverify andcasttheirvotes.
Notably, blockchain technology provides the additional benefit of audit facilities. The resistant and open record kept by a blockchain makes it extremely reasonable to verifyagainst:thisincreasescorpustoelectionresults.The hope that implementation can be made modern election techniques is obstructed with practicality-and further, realism-real challenges that remain. These might include, therefore, certain issues such as scalability and accessibilityandthedigitalbackbonerequired.Finally,the issue of energy consumption and the resistance from the traditional voting systems implies that cautious planning and development in stages are then critically required. By leveraging the complete information technology evolution andworkingtowardsresolvingallotherissues,blockchain votingmayverywelltransformtheelectoralprocessintoa safer,moretransparentsystemandonethattheworldcan relyupon.
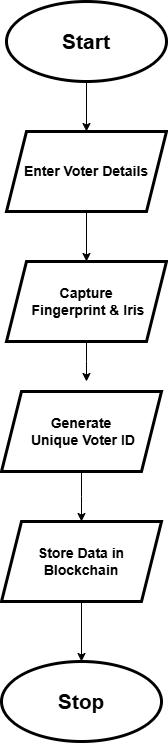
The biometric voting system has two levels, namely Admin and Booth levels. The admin level manages the registering of voters, the election dates, and securing the database of voters and their fingerprint and iris data through blockchain. Blockchain ensures that all stored informationisimmutableandcan'tbetamperedwith,thus enhancing security and reliability. The information can therefore be edited anytime it must be retrieved in line withtheverificationofthevoteratthetimeofelection.
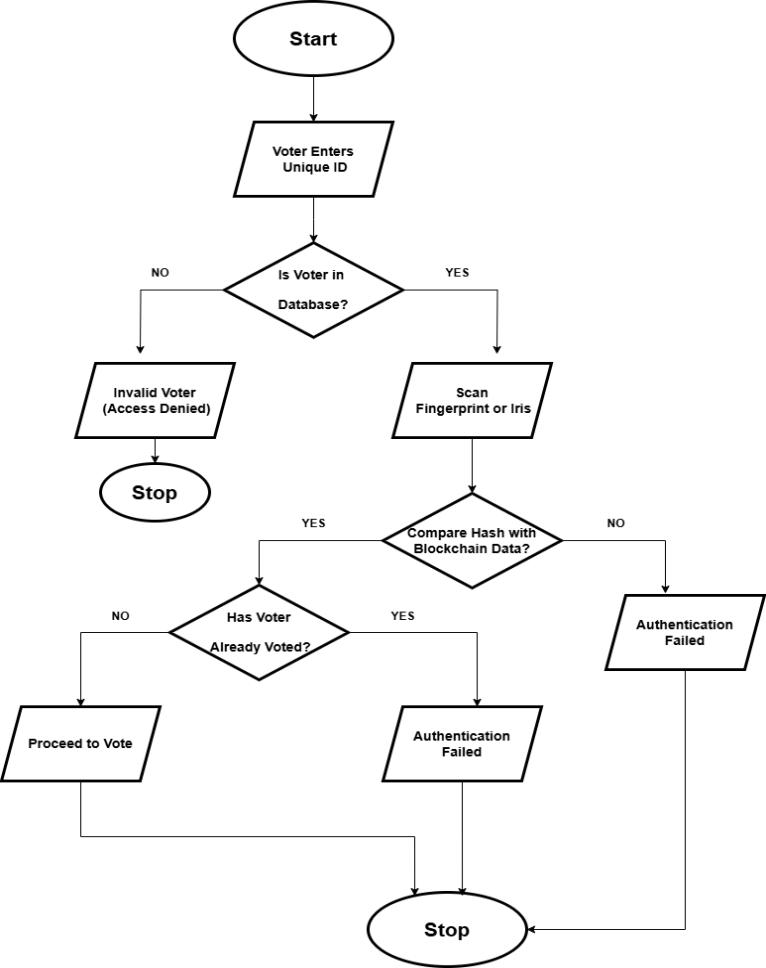
At Booth level, voters are notified about the election date and time and are asked to authenticate fingerprint or iris scans.Thebiometricdata isscannedandhashed,and this hash is then compared with hashes of previously stored biometric data on the blockchain. To make sure this biometric information can't be accessed by any unauthorizedparty,itisunspeakablyassignedthroughthe technique of hashing. After a unique voter ID is verified with him/her, the system goes ahead to verify his/her
biometric information and ascertain him/her as being eligible to vote; this proves that voting by those same individual takes place only once to eliminate duplicity of votes.
Thebiometricdata ofa votershouldperfectlymatchwith those stored; hence, the voter will be allowed to mark his vote. Otherwise, an "Invalid Vote" message is displayed, and it cancels the possibility of treaty any unauthorized voting. The district election administration would not permit any unauthorized votes; however, this system will place an integrated lockdown on monitoring in real-time through biometrics that allows consistent checks on the security and integrity of the voting process in favour of transparent,accurate,andfairelectionsleadingtowardsa safe,fraud-proof,andefficientvotingexperience.
3.1.
3.1.1.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
3.1.2.Voter Verification & Authentication
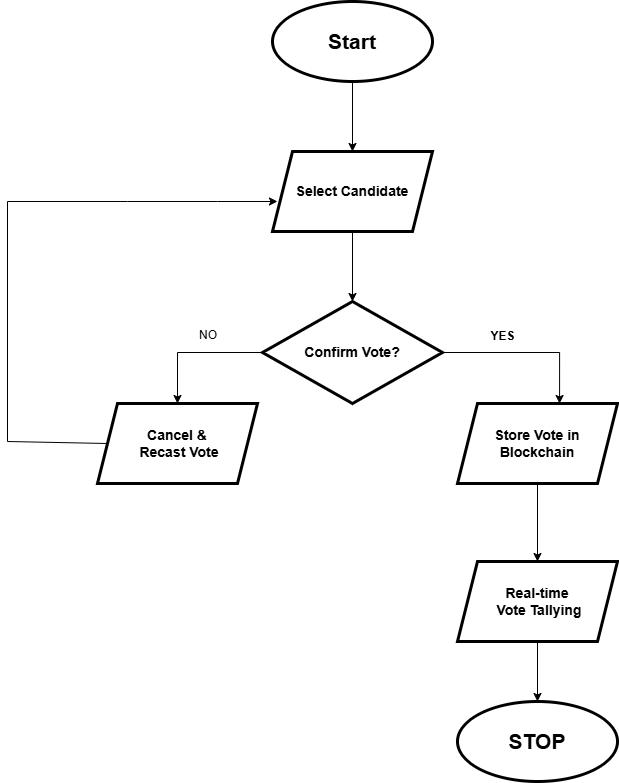
3.1.3. Vote Casting & Result Processing
4. RESULT
Fig -1:VoteIDVerificationPage

Fig -2:BiometricVerificationPage

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

Fig -3:SelectaCandidatePage
Fig -4:ConfirmPage
Fig -5:AdminmanagementPage

Fig -6:ResultPage

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 02 | Feb 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thisprojectprovidesavotingmodelbasedonbiometrics and blockchain technology that, ideally, will improve security, transparency, and efficiency in elections. Fingerprint and iris authentication of the voter will make itimpossibleforanyoneelsetovoteinplaceofthat voter, thereby ensuring only eligible voters actually vote. Aside from that, the backend of the blockchain guarantees that thedataremainsimpeccablebecausethereisnoroomfor vote tampering, thereby permitting a verifiable, tamperproof election process. Added to that is the further simplicity with which this voting system is operated that now makes voting even simpler but also retains the utmost levels of security. The success of this novel approach presents the way biometric and blockchain technologies can be underpinning the delivery of a trustworthy secure digital voting system, thus propelling furtherdevelopmentsine-governance.
1. *Shrushti Sankhe, Pratiksha Kute, Mayuri Kokane, Runali Dhaygude, Prof. Sujay Pawar (2022).* Biometric VotingSystem.
2. *S. Abimanyu, R. Anbarasan, S. Dhinkaran (2021).* Iris DetectionBasedAuthenticationforSecureVotingSystem.
3. *Shubha P., Padmasree P., Sowndharya Lakshmi R. (2021).*VotingSystemBasedonBlockchainandUsingIris Recognition.
4. *Rajapandian B., Rajeswari Jayakumar, Rishika S., VaishnaviM.(2019).*Iris-BasedE-VotingSystem.
5.*Ms.BhavanaC.L.,Ms.BhumikaN.,Ms.BindhuH.S.,Ms. MaduriR.,Ms.Asha A.(2018).*AnAdvancedandSecured BiometricVotingSystem.
6. *Rajesh M. Gandhi, Priyanka S. Shelar (2017).* Online VotingSystem.
7. *Rudrappa B.Gujanatti, Shivaram N. Tolanur, Murughendra S. Nemagoud, Shanta S. Reddy, Sangameshwar Neelagund (2015).* A Fingerprint-Based VotingSystem.
8.*K.Prathyusha,P.Raja(2020).*SecureBiometricVoting SystemUsingBlockchainTechnology.
9. *M. Zareapoor, K. K. R. Choo, K. R. Choo (2021).* Enhancing E-Voting Security with Blockchain and BiometricAuthentication.
10.*A.V.Deshmukh,M.D.Khandagle,P.S.Nikam(2019).* Biometric Voting Machine Using Fingerprint Scanner and Blockchain.
11. *V. S. Jadhav, M. R. Shinde, A. P. Kulkarni (2020).* Blockchain-Based Voting System with Multi-Factor Authentication.
12. *A. Sharma, S. Sharma (2021).* Security Challenges in Electronic Voting: A Biometric and Blockchain-Based Approach.
13. *S. Mahajan, R. Patel (2020).* Decentralized Voting UsingBlockchainforTransparentElections.
14. *P. Kumar, T. Singh (2019).* A Comparative Study of Biometric-BasedE-VotingSystems.
15.*J.Smith,D.Brown(2022).*IrisandFingerprint-Based VoterIdentificationforSecureElections.