
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume:12Issue:04|Apr 2025 www.irjet.net



International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume:12Issue:04|Apr 2025 www.irjet.net

Dr Parameswaran T 1 , Sheshadri M O 2 , Bindushree N 3 , Greeshma N 4 , Shraddha N 5
1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, CMR University, Bengaluru. 2345 UG Student, Dept. of Computer and Communication Engineering, CMR University, Bengaluru.
Abstract - The increasing population and rapid urbanization have led to challenges in the waste management systems, particularly in densely populated areas. Traditional waste collection systems are facing issues such as inefficiency, overfilled bins, and delays in waste collection, which can result to environmental hazards. To state these issues, the Smart Waste Dustbin System was developed using Internet of Things (IoT) technology.Thissystemintegratesvarioussensors(IR,rain, andultrasonic)withanESP32microcontrollertocreatean intelligent waste management solution capable of sorting waste, monitoring bin fullness, and providing real-time locationtracking.
The sensor is often used to measure the level of waste in the bin, providing data on whether the bin is empty, halffilled, or full. The servo motor is activated to sort waste into the appropriate compartment based on the type detected.ThesystemalsointegratesGPStechnologytotrack thelocationofthebininreal-time,whichisusefulforwaste collectionservicesandtrackingwastedisposalactivities
Key Words: SmartWasteDustbin,Wastedetector,IRSensor, ultrasonic, ESP32 microcontroller, Internet of Things, GPS location
Withtherapidgrowthofurbanpopulationsandtheincreasing rate of waste generation, efficient waste management workhasbecomeasignificantchallengeincitiesworldwide. Traditional waste management methods, such as manual collection and sorting, are often inefficient, timeconsuming,andpronetohumanerror.asaresult,wastebins frequentlyoverflowcausingsanitationissues,environmental pollution,andhighercostsformunicipalities
Inthiscontext,theSmartWasteDustbinSystempresents aninnovativesolutionbyutilizingInternetofThings(IoT) technologies to automate waste detection, sorting, and monitoring. By incorporating sensors, a microcontroller, and wireless communication, this system enhances the efficiencyofwastemanagementinsmartcities.
Thesystemisdesignedtoachievethefollowing goals:
Automated Waste Sorting: Using IR sensors and rain sensors, the system identifies and classifies the waste as eitherdry(non-biodegradable)orwet(biodegradable).The wasteisautomaticallysortedintoappropriatecompartments viaaservomotor,thussimplifyingtherecyclingprocess.

Bin Fullness Monitoring: The ultrasonic sensor continuously measuresthedistancetothe wastelevel insidethe bin,determining whetherthebinisempty,half-filled,orfull.Thisdatahelpsoptimize the waste collection process by preventing overflows and reducingunnecessary wastecollectiontrips
Real-tine Status Updates: Through integration with the Blynk app,userscanmonitorthestatusofthewastebin. Theycanreceive real-timeupdatesregardingthetypeofwaste,binfullness,and eventhelocationofthebinusingGPStechnology.
Location Tracking: The GPS module provides precise location coordinates of the bin, making it easier for waste collection teams to locate bins that require attention. This feature is particularly useful for urban areas with numerous waste bins spreadacrosslargeregions.
The core components of the system include the ESP32 microcontroller, which serves as the brain of the system, IR and rain sensors for detecting waste type, ultrasonic sensors for monitoring bin fullness, servo motors for sorting waste, and the GPS module for location tracking. These components workinconjunctiontoensurethesystemoperatesseamlessly, sending real-time data to the Blynk app and triggering alerts whennecessary.
This system provides an efficient and automated approach to managing urban waste, contributing to cleaner cities and more sustainable waste practices. By implementing IoT solutions,itreducesthedependencyonmanualandoptimizes the waste
collectionprocess,makingitbothcost-effectiveandenvironmentally friendly.Furthermore,thereal-timedataandmonitoringcapabilities allow for better decision-making and planning in waste managementoperations.
In summary, the Smart Waste Dustbin System is designed to modernizewastemanagementbyincorporatingautomation,realtime monitoring, and location tracking. It exemplifies the potentialofIoTtechnologytosolvepressingurbanissuesand plays a vital and important role in the development of smart cities where technology is integrated into everyday life for greaterconvenience,sustainability,andefficiency.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume:12Issue:04|Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
The subject of utilizing Internet of Things (IoT) in waste managementhasgainedsignificantattentioninrecentand forthcoming years as urbanization has rapidly increased, creating challenges in waste disposal and management. Smart waste management and disposal systems aim to automate waste collection, sorting, and monitoring, improving the overall efficiency of the process. Numerous studies and projects have explored the integration of IoT, sensors,andcloudplatformsinwastemanagement.Below isanoverviewofthemostrelevantliteratureinthisarea.
IoT (Internet of Things) is transforming the way we will managewastebyconnectingsmartdeviceslikesensorsto the Wi fi internet. This helps us collect and sort waste more efficiently. For example, V. M. R. R. S. Manogar and his team (2016) came up with a smart system that uses ultrasonic sensors for checking how full trash bins are, temperature sensors to spot potentially hazardous materials, and RFID tags to track bins in real-time. All the data from these devices is sent to a central server, where it’s analyzed to find the best roots for waste collection, savingtimeandresources.
Similarly,T.ShankarandS.R.K.Jadhav(2020)developed the system that uses ultrasonic sensors to monitor bin fullness and send alerts when the bins are full. They even added solar-powered bins to make the system more ecofriendly and energy-efficient, helping to lower electricity costs. These systems aim to reduce unnecessary waste collection trips, optimize collection routes, and cut down onthecostsassociatedwithmanualwastecollection.
Sorting waste properly is key to reducing landfill waste andpromotingrecycling.Inonestudy,K.P.Ramachandran and his team (2018) created an automatic waste sorting system using infrared sensors, color sensors, and servo motors.Thesystemsortsmaterialsintodryandwetwaste categories, making it easier to recycle. Their research highlights how crucial accurate sorting is for improving recyclingefficiency.
S. S. Hossain and his colleagues (2021) took it a step further by combining infrared sensors with moisture sensors to differentiate between wet and dry waste. They also added artificial intelligence (AI) to help the system learn and improve its sorting capabilities. This combination of IoT and AI can help make waste sorting faster and more accurate, reducing the effort required for manualsorting.
Automatedsortingsystemscouldsaveusalotoftimeand energy,makingrecyclingeasierandmoreefficient.
1.3.
Ultrasonicsensorsaregreatformonitoringhowfulltrash binsare,helpingoptimizewastecollection.In2017, S.R.Sahasrabuddheandhisteamdevelopedasystemthat


usedultrasonicsensorstomeasurewastelevels.Thedatawas sent to a cloud server where the collection schedule was adjusted based on real-time information. This means waste management companies should avoid wasting resources by collectingwastefrombinsthataren’tfull.
M.A.H.Tarek(2018)builtasimilarsystem,whereultrasonic sensors detected the waste level in bins and transmitted that data to a cloud platform. This not only helped with waste monitoring but also made it easier to optimize the routes of waste collecting vehicles, which cuts unnecessary trips and loweringtheimpactofwastecollection.
1.4GPSIntegrationforWasteTracking
GPStechnologyisalsoplayingabigroleinmodernwaste management. By tracking the exact location of bins, waste management companies can plan and optimize collection routesmoreeffectively.AstudybyA.S.Shuklaandhisteam (2016)demonstratedhow GPScoordinatescouldbeusedto identifythebestrootsforwastecollectiontrucks,helpingsave timeandfuel.
H. R. M. Poona (2016) took this even further by integrating GPS with IoT systems. This allowed for precise, real-time trackingofbins,improvingthelogisticsofwastecollection.In large cities where bins are spread far apart, this level of precision helps ensure that collections happen in time and in themostefficientwaypossible.
1.5. CloudIntegration and Remote Monitoring
Cloud platforms like Blynk, Thing Speak, and AWS IoT are becoming the backbone of many IoT-based waste management systems. They allow waste management teams to store, process, and analyze data from all the sensors in a central place. For example, M. S. Khan and his team (2020) developed a cloud-based system using Blynk to track the fullness of waste bins. The system sent alerts to waste management teams when bins were full, helping them collect wastepromptly.
Cloud integration makes it easy to monitor waste systems in real-time, even from a distance. Plus, it supports scalability, meaning the system will grow as the quantity of bins and sensors increases, making it adaptable to both small and large-scalewastemanagementneeds.
1.6.Challenges and Future Directions
While IoT-based waste management systems have many benefits, there are still challenges to overcome. Issues like sensor accuracy, power consumption, and the cost of implementing these systems on a larger scale in urban areas canmakeitintacttofullyrealizetheirpotential.Plus,systems thatrelyoncontinuousinternetconnectivitymightstrugglein areaswithweaknetworksignals.
In the future, researchers could focus on developing lowpower sensors and more energy-efficient systems. AI and machine learning could also play a bigger role, helping to predict and optimize waste collection based on patterns and trends. By addressing these challenges, we can make waste management even more sustainable and reduce its environmentalimpact.


2.

Volume:12Issue:04|Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
The Smart Waste Dustbin system, integrating sensors, servos, ultrasonic technology, and IoT features, has various potential applications in multiple domains. The following are some of the prominent applications of the system:
2.1. SmartCitiesandUrbanmanagement
Waste Management Optimization: The Smart Waste Dustbin system can play a role in the smart city initiative by automating waste segregating and monitoring bin fullness levels. It helps authorities optimize waste collectionrootandschedulesbasedontherealtimestatus of waste smart bins, minimizing manual intervention and improvingoperationalefficiency
ReducingOverflows:Bynotifyingtheauthoritieswhenthe bins are full through the Blynk app, the system prevents wastebinoverflows,whicharecommonincrowdedurban areas.Thisresultsincleanerpublicspacesandareduction inwaste-relatedhealthhazards.
Efficient Resource Allocation: City waste management departments can use the real-time data provided by the system to allocate resources (trucks, workers) more effectively.Thiscanreduce fuel consumption,lowercosts, andensurewasteiscollectedinatimelymanner
2.2. Environmental Protection
Waste Segregation and Recycling: The Smart Waste Dustbin system helps in sorting dry and wet waste at the source itself. This leads to improved waste segregation, which is vital for recycling processes. With accurate sorting, recyclable materials such as paper, plastic, and metal can be easily separated from organic waste, promoting sustainability and reducing, decreasing the environmentalimpactoflandfills
PromotingEco-FriendlyPractices:Byencouragingusersto dispose of waste in the right category (wet or dry), the system can help raising awareness about environmental responsibility. The real time data got by the system will also be used to generate reports and insights, promoting betterwastemanagementpractices.
2.3. Residential andCommercial Use
Home and Office Waste Management: For households and offices, the system can be deployed as a smart waste disposal solution. The automatic sorting of wet and dry waste ensures that the waste is organized and ready for recycling or composting, thus promoting eco- friendly living.
Alert system for Full Bins: The built-in buzzer and Blynk app alerts inform residents or facility managers when the bin is full and needs emptying, eliminating the inconvenience of overfilled bins and maintaining cleanliness.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072
Customized Waste Sorting: With adjustable servo positions and sensor thresholds, users can customize the sorting mechanism for different types of waste, enabling more personalizedandefficientwastedisposalpractices.
2.4. CommercialEstablishments and PublicSpaces
Public Parks, Malls, and Schools: In public spaces like parks, malls, or educational institutions, this system can be used to ensure proper waste management, keep track of bin status remotely, and maintain cleaner, morehygienic environments. Italsohelpsinautomatingwastecollection,allowingfacilities toreducecostsandmanagewaste efficiently.
Hotels and Restaurants: These businesses generate a significant amount of waste daily. The Smart Waste Dustbin system can be implemented in kitchens and dining areas to automate waste categorization and make sure that waste is sorted before being collected. This can help businesses with regulations on waste segregation and contribute to sustainabilitygoals
2.5. Industrial and ManufacturingFacilities
Waste Management in Factories: Industrial facilities produce varioustypesofwaste,includingdrywaste(likeplastic,metal, and paper) and wet waste (like organic matter and liquids). TheSmartWasteDustbin systemcanautomatewastesorting andmonitorbinfullness,ensuringthatthefacilityadheresto environmental standards and reduces waste management costs.
Improved Recycling Programs: The accurate detection and segregation of waste at the source can boost the facility’s recycling initiatives, improving sustainability and helping businessesmeettheirsocialresponsibility(CSR)goals
2.6.Environmental Monitoring andDataAnalytics
Waste Generation Analysis: The data generated by the Smart Waste Dustbin system can be used to analyze the volume of waste produced in specific areas. This data can help environmental researchers, municipalities, or businesses makeinformedand efficient decisions aboutwastereduction, recyclingprograms,andtheoverallenvironmentalfootprint.
IoT-BasedSmartWasteSystems:Thesystemservesaspart of a larger IoT based waste management network, where waste bins are interconnected with central servers that monitor real time data from various locations. This type of connectedsystemenablesmunicipalitiestomanagewasteina moreefficient,data-drivenway.
2.7. IntegrationwithSmartTechnologies
Smart Home Automation: The Smart Waste Dustbin system can be integrated with other smart home devices, suchaslights,smartthermostats,andhomeassistantslike Google Hone or Amazon Alexa, for a seamless and automated home management experience. For example, a voice command could be used to check the status of the wastebinortotriggeranalertwhenthebin isfull.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume:12Issue:04|Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
Fleet Management: The system could also be integrated with waste collection fleet management systems. The GPS tracking feature in the dustbin will allow authorities or waste collection agencies to efficiently route garbage trucksbasedonthereal-timestatusofwastebins.
Automated Waste Collection Robots: In the future, this system could be integrated with robotic waste collection units that move around and autonomously collect trash from differentlocations. Thesystem’sdata on bin fullness and waste type can guide these robots to the nearest full bin,improvingefficiency.
Smart Waste Processing: With advancements in technology, smart dustbins could also be linked to automated waste processing systems for recycling and composting.Thesystemcouldautomaticallysort,process, and even manage the waste disposal process end-to-end, makingitmoreeffectiveandenvironmentallyfriendly.
2.9.
Disaster Relief Operations: In the aftermath of natural disasters, the Smart Waste Dustbin system can be deployed in disaster relief zones to efficiently handle the waste generated from relief operations and help manage sanitaryconditionsindisaster-strickenareas.
CloudplatformslikeBlynk,ThingSpeak,andAWSIoTare becoming the backbone of many IoT-based waste management systems. They allow waste management teams to store, process, and analyze data from all the sensorsinacentralplace.Forexample,M.S.Khanandhis team (2020) developed a cloud-based system using Blynk to track the fullness of waste bins. The system sent alerts to waste management teams when bins were full, helping themcollectwastepromptly.
Cloudintegrationmakesiteasytomonitorwastesystems in real-time, even from a distance. Plus, it supports scalability,meaningthesystemcangrowasthenumberof bins and sensors increases, making it adaptable to both smallandlarge-scalewastemanagementneeds.

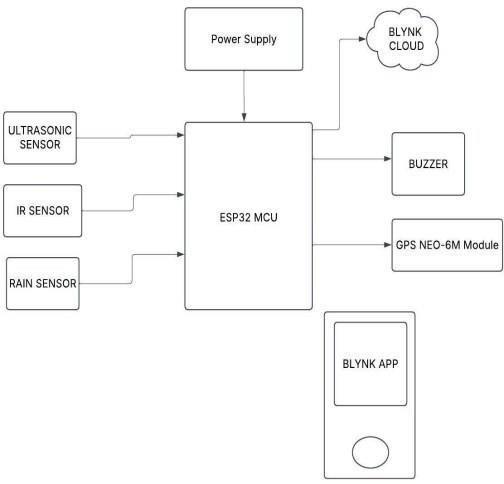

3. Block Diagram Components
A block diagram represents the major components of the Smart Waste Dustbin system and shows how these components interactwithoneanother.Ithelpsinvisualizing the system’s structure and its functionality. Below is a detailed breakdown of the block diagram, which divides the systemintothefollowingfunctionalblocks:
WasteDetectionSystem
The waste detection system is responsible for identifying thetypeofwaste(wetordry)basedonthereadingsfrom IRSensor(fordrywaste)andRainSensor(forwetwaste)
Microcontroller ESP32
The ESP32 microcontroller serves as the brain of the system. It is responsible for receiving input data and signals from the sensors, processing the data also controlling the actuators (servo motor) and also communicating with the cloud- based platform for monitoring.



International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume:12Issue:04|Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
ServoMotor
The servo motor controls the waste compartment door, directing waste into either the wet or dry compartment basedondetectedwastetype
UltrasonicSensor
The ultrasonic sensor measures and gives the distance betweenthesensor,thetopsurfaceofthewasteinthebin fordeterminingthefullnesslevel.
GPSforlocationtracking
TheGPSmoduletracksthegeographicallocation(latitude andlongitude)ofthewastebininreal-time
CloudCommunicationthroughBlynkapp
The Blynk cloud platform acts as a central hub to process and visualize the data got the sensors. It enables remote monitoring and interaction with the system through the Blynkmobileapp.
AlertSystem
The buzzer serves as an alert system for the user and wastemanagementteam
RainSensor
The rain sensor detects the presence of wet waste. It is connected to GPIO 15. When the sensor detects moisture (wetwaste),itsendsaLOWsignaltotheESP32
SoftwareImplementation
The software implementation for the Smart Waste Dustbin System involves integrating the hardware components (sensors, actuators) with the microcontroller (ESP32)andusingacloud-basedplatform(Blynk)forrealtime monitoring and control. The software is written in Arduino IDE using C++ programming language and communicates with the ESP32, utilizing libraries like Blynk,ESP32Servo,TinyGPS++,andWiFi.
The first section of the code includes the necessary libraries and sets up the required credentials for Wi-Fi and Blynk. Using credentials one can log in and manage the portal. A mobile app that is available offline could provide users with access to help and locate areas, expandingtheplatform'sreach.
FutureEnhancementsfortheSmartwastedustbin
The Smart Waste Dustbin system designed for automated waste detection, sorting, and monitoring has significant
potential for expansion and enhancement in the future. In thissection,wecandiscussthepossibleimprovementsand future scopeof system, as well as the challenges that need to be addressed for broader implementation cases as needed. Integration with Smart City Infrastructure one of the major areas for future development lies in integrating


the Smart Waste Dustbin system with broader Smart city infrastructure.Smartcitiesrelyoninterconnectedsystems that use data to improve the quality, efficiency of life for residents and optimize city services. The Smart Waste Dustbin system can be integrated with Various IT System ofthecities.
Although the present system effectively sorts dry and wet waste, future advancements in AI-based waste sorting could make it more intelligent and capable of handling a widervarietyofwastetypes.
Expansiontohandlemorecomplexwaste
Thepresentsystemprimarilyhandlessimplewaste categorization intowetanddry types. However, with ongoing advancementsinmaterialscienceandwasteprocessing,the system could evolve to manage more complex types of waste
EnhancementinSensorTechnology
The performance and quality of the current system is heavily dependent on the sensors used for waste detection (IR sensor, rain sensor, ultrasonic sensor). To improve the system’s accuracy and performance, the sensor advancementscouldbeincorporated
MobileApplicationDevelopment
Theplatform'saccessibilityandusabilitywouldbeenhanced by developing a mobile application specifically for it. A mobile app that is available offline could provide users withaccesstohelpandlocateareas,expandingtheplatform's reach.
To enhance the sustainability of the Smart Waste Dustbin system, future versions could be powered by solar panels or otherrenewableenergysources.Thiswouldmakethe system more energy-efficient and reduce its reliance on traditional powersources,especiallyforoutdoororremote installations
Asthesystemmatures,itcouldbeintegratedwithautonomous wastecollectionrobotsforfullyautomatedwastemanagement
It is possible that establishing an efficient communication channel between the platform, law enforcement agencies and NGOs could enhance its ability to handle cases. The provision of anonymous incident details to authorized organizationscouldfacilitatefasterandmorecoordinated responsetoWasteCollection


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume:12Issue:04|Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
RecurrentCommunity surveyandresponsive feedback integration
A feedback mechanism could be implemented, enabling userstosharetheirexperiencesandsuggestionsforongoing enhancement.Thiswouldensurecontinuousimprovement. The platform could be able to adapt and keep pace with changing user preferences due to frequent community surveysthatprovideinsightintonewtrends.
BlockchainforSecureAccess
The technologies of Blockchain will be used for access, manage register, sign in, log in and keeps credentials Secure
IntegratingwithEnvironmentalManagingSystems
The platform, and possibly by Integrating to Environmental management authorities and Solid waste managementauthoritiesonecantrackthelevelofbin
Globaladoptionindevelopingcountries
While the systems areideal for urban environments in developed countries it has significant potential for deployment in developing countries where waste managementwasamajorchallenge.Byintroducinglowcost, low-maintenance smart waste systems, local municipalities
1) Ravi&Devarajan,A.(2017)
"Smart Waste Management System Based on IoT and CloudComputing"
IEEEInternationalConferenceonComputationalIntelligence and Communication Technology (CICT)
DOI:10.1109/CICT.2017.57
2) Pandian,R.,&KumarS.(2019)
"DesignofIoT-basedSmartWasteManagementSystemfor Urban Areas" IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Communication, and Aerospace Technology (ICECA)DOI:10.1109/ICECA.2019.8821710
3).Lee,S.,Park,Y.,&Kin,J.(2018)
"Development of the Smart Waste Collection System Using IoT and Real-Time Data Analytics"
IEEETransactions onIndustryInformatics, 14(10)
DOI:10.1109/TII.2018.2822583
4).Mousavi,S.,&Goudarzi, H.(2020)
"An IoT-based Waste Bin Monitoring System with Intelligent SortingandManagement"
DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3024
5).Javaan.S&Sadeghian,M(2021)
"A Smart Waste Management System Using IoT and AI to


Improve Efficiency in Municipalities” IEEE Transactions IndustrialElectronics, 68(5)
DOI:10.1109/TIE.2020.3035735
6).Vora,P.&PrakashA.(2020)
"IoT-based Automated Waste Segregation and Management SystemforSmartCities"
IEEE International Conference Smart Computing and Applications(ICSCA) DOI:10.1109/ICSCA49979.2020.9171559
7) Chaudhary,R.,&Agarwal,M.(2017)
"A Smart Waste Management System Using IoTs and WirelessSensors"
IEEE International Conference Computing, Communication, Control, andAutomation(ICCCCA) DOI:10.1109/ICCCCA.2017.8354702
8) Gupta,&Soni,A.(2018)
"Smart Dustbins and Automated Waste ManagementSystem using IoT"
IEEE 7th International Conference Cloud Computing, Data Science, andEngineering(Confluence). DOI:10.1109/CONFLUENCE.2018.8442557
9) Sharma,A.,&Sharma,S.(2021)
"IoT-EnabledSmart Management System forUrbanandRural Areas"
IEEE International Conference on Emerging Trends in Smart Technology (ETST)
DOI:10.1109/ETST52995.2021.00045
10). YCA Padmanabh Reddy, Parameswaran & R Sathiyaraj Publisher:IEEExplore. “SmartEnvironmentMonitoringFrameworkUsingBigDataand IoT”https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9641609
