
Myeloma 101: The Big Picture Perspective with Q&A
Joseph Mikhael, MD, MEd, FRCPC, FACP, FASCO, Chief Medical Officer, International Myeloma Foundation



Joseph Mikhael, MD, MEd, FRCPC, FACP, FASCO, Chief Medical Officer, International Myeloma Foundation


Joseph Mikhael, MD, MEd, FRCPC, FACP

• Professor, Applied Cancer Research and Drug Discovery, Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen), City of Hope Cancer Center
• Chief Medical Officer, International Myeloma Foundation
• Consultant Hematologist and Director, Myeloma Research,
Phase 1 Program, HonorHealth Research Institute
• Adjunct Professor, College of Health Solutions, Arizona State University
Teresa S. Miceli RN BSN OCN
Mayo Associate, Assistant Professor of Nursing
Myeloma Research RN Navigator, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
International Myeloma Foundation
InfoLine Advisor, Nurse Leadership Board, Support Group Leader
NCI Myeloma Steering Committee


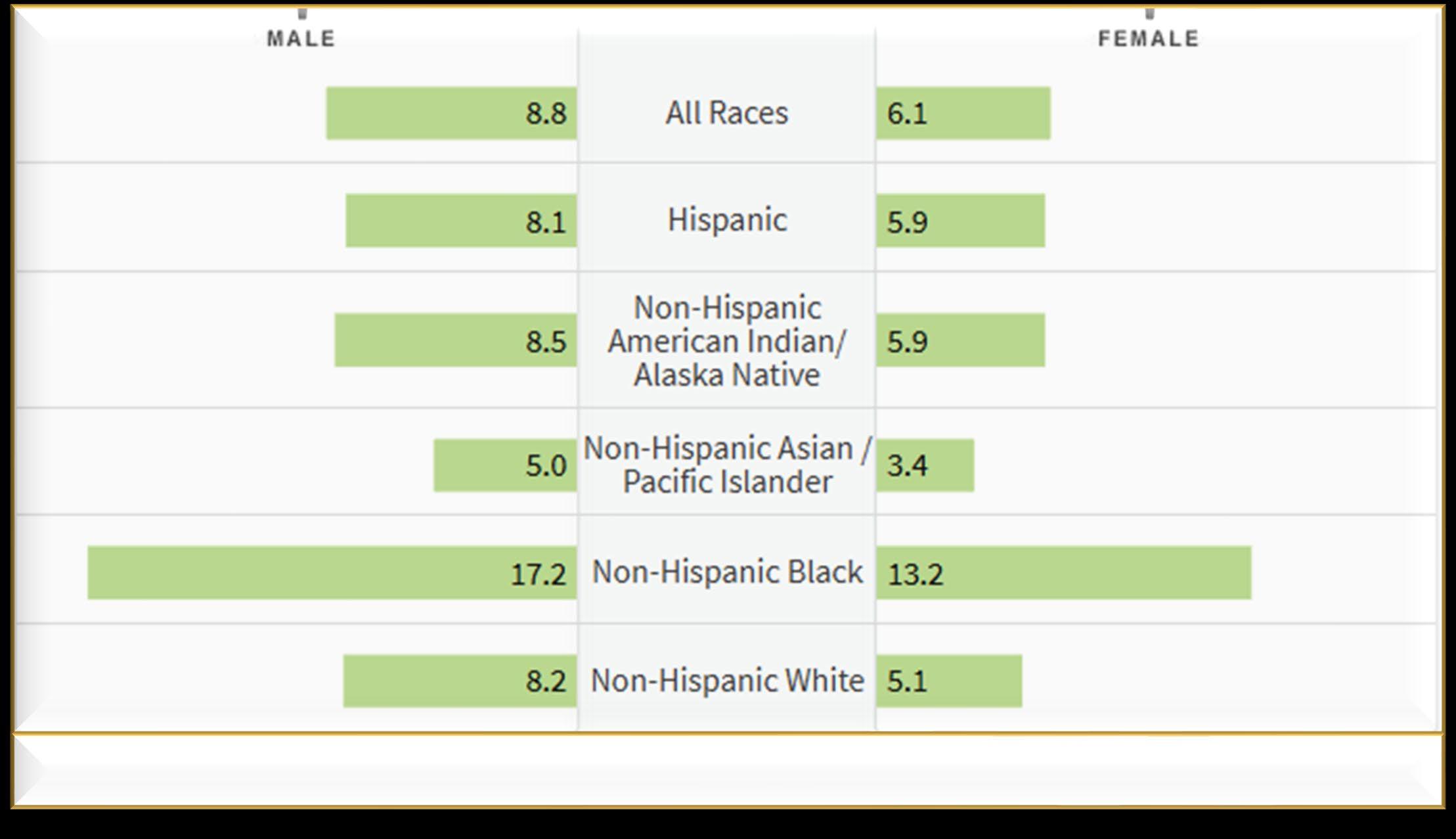



Environmental Factors:
• Exposure to some chemicals
• Radiation exposure
Examples:
Agent Orange
Burn pits
Pesticides, Herbicides
Firefighter/First Responder exposures
Individual Factors:
• Age
• Family History of related disorders
• Personal History of MGUS or SMM
• Obesity
VA Study Documents Health Risks for Burn Pit Exposures
Leukemia and Multiple Myeloma Set to Be Added to List of Conditions Linked to Burn Pits
In most cases, the honest truth
WE DON’T KNOW














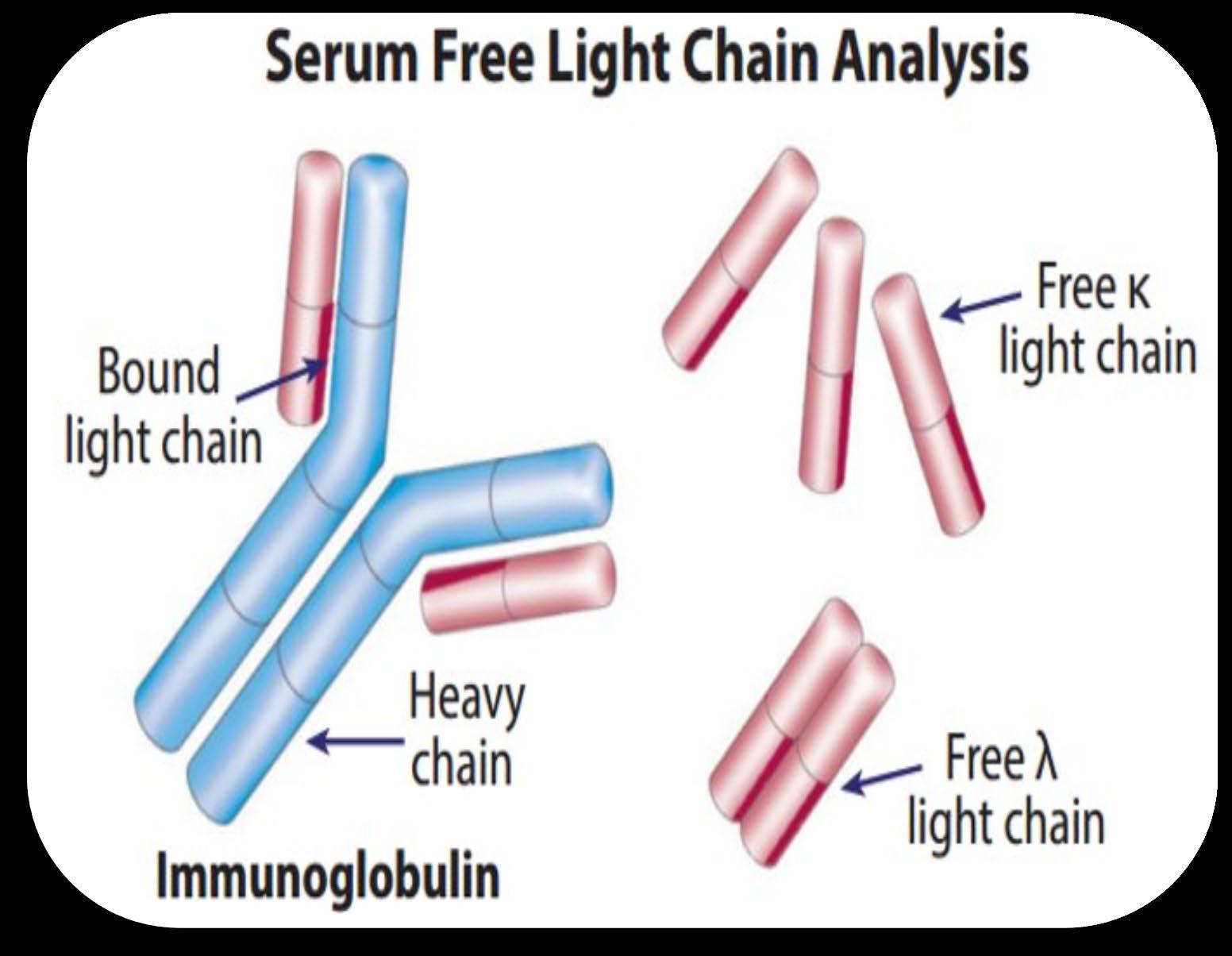
Heavy Chain = M-Spike

65% IgG – most common
20% IgA – associated with AL Amyloid
5% to 10% light chain-only (kappa, lambda)
Less common: IgD, IgE, IgM


• AL-Amyloid
• POEMS
• Light or Heavy Chain Deposition Disease
• MGCS = Clinical
• MGRS = Renal
• MGNS = Neuro
Condition
Clonal plasma cells in bone marrow
MGUS1-4 (Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance)
SMM1-5,8 (Smoldering Multiple Myeloma) Active Multiple Myeloma6-8
Presence of Myeloma
Defining Events
Likelihood

* In clinical trial






Test Name
CBC + differential
Complete metabolic panel
Beta-2 Microglobulin (B2M)
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
Serum Immunofixation and Protein
electrophoresis (SPEP+IFE)
Immunoglobulins (G, A, M, D, E)
Free light chain assay with kappa/lambda ratio
Urine immunofixation & protein electrophoresis (UPEP+IFE)
What it means
Hemoglobin, WBC, Platelets
Creatinine, Calcium, Albumin, Liver function
Part of staging and risk stratification
Measures the level of normal and clonal protein
Identifies the type of clonal protein

Measures the level of normal and clonal protein
Identifies the type of clonal protein




Imaging:
– Skeletal survey: Series of X-rays; less sensitive than other techniques
– Whole body low dose (CTWB-LD CT )
– Positron Emission Tomography (PET/CT)
– Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)

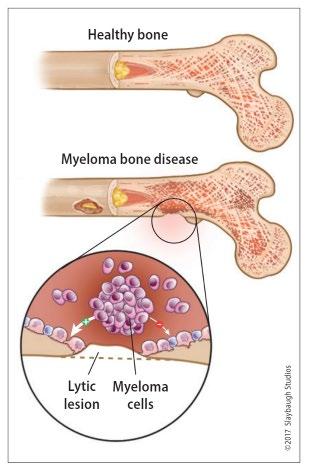
Healthy bone versus myeloma bone disease

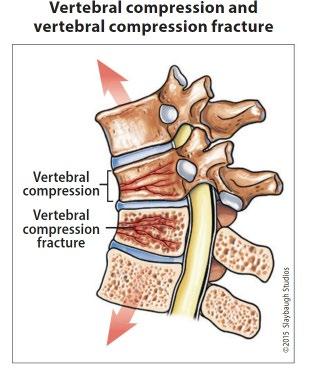


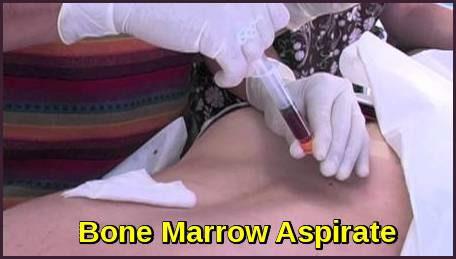

Bone marrow biopsy & aspirate • Bone marrow plasma cells (%) • Congo Red staining if concern
Bone marrow genetics
• Cytogenetics
• Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
• Next generation sequencing (NGS)



Initial Therapy (a.k.a. Frontline, Induction)
Quad Therapy (ex. CD38+ MoAb + VRd)
HD-Melphalan + Stem Cell
Transplant (ASCT)
Maintenance
Treatment for Relapse
Consolidation
Therapy
Supportive Care and Living Well
Treatment for Relapse

Treatment for Relapse
Treatment for Relapse
Treatment for Relapse



(thalidomide)
(lenalidomide)
(pomalidomide)
Rev, Len
or Pom
(daratumumab)
(isatuximab)



Peptide Drug Conjugate* Pepaxto (Melphalan Flufenamide)
BCMA Targeted Antibody Drug
Conjugate (ADC)*
Blenrep (belantamab mafodotinblmf )
Abecma (idecabtagene vicleucel)
Belamaf, or B
Bispecific Antibodies
Carvykti (ciltacabtagene vicleucel)
Tecvayli (teclistimab)
Talvey (Talquetamab)
Elrexfio (Elranatamab)
Cevostamab, Iberdomide, Mezigdomide, Venetoclax Linvoseltamab, LCAR-B38M, ABBV-383



















Negative by next generation flow (NGF) (minimum sensitivity 1 in 10-5 nucleated cells or higher)*
mCR AND normal Free Light Chain ratio, Bone Marrow negative by flow, 2 measures
CR AND negative PCR
Complete Response: Negative immunofixation (IFE); no more than 5% plasma cells in BM; 2 measures
Very Good Partial Response: 90% reduction in myeloma protein
Partial Response: at least 50% reduction in myeloma protein
Minimal Response
Stable Disease: Not meeting above criteria
Progressive Disease: At least 25% increase in identified myeloma protein from lowest level
MRD = Minimal Residual Disease
sCR = Stringent Complete Response; BM = Bone Marrow
Kumar, S., Paiva, B., Anderson, K. C., Durie, B., Landgren, O., Moreau, P., ... & Dimopoulos, M. (2016). International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. The lancet oncology, 17(8), e328-e346.


• Not every relapse requires immediate therapy
• Each case is different
Symptomatic or extramedullary disease


Asymptomatic biochemical relapse on 2 consecutive assessments

Asymptomatic high-risk disease or rapid doubling time or extensive marrow involvement Consider Observation Monitor Carefully Consider Treatment
Patient-/Disease-Specific Monitor Carefully
Initiate Treatment


Bi-Specific Antibodies
Talvey (Talquetamab) CAR-T



Antibody Drug
Empliciti (Elotuzumab)
Bi-Specific Antibodies



Bi-Specific Antibodies
CAR-T






Monoclonal Antibodies
Daratumumab and Darzalex Faspro
Sarclisa (Isatuximab)
TAK-079 MOR202

Immune Therapies
Abecma (Ide-cel CAR-T)
Carvykti (Cilta-cel CAR-T)
Tecvayli (Teclistamab)
Elrexfio (Elranatamab)




Other CAR Ts



Other Bi Specific Antibodies





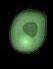
How it works:
An antibody directed at a target (BCMA) combined with a cytotoxic agent (chemotherapy)
ADC = Antibody-Drug Conjugate
BCMA = B-Cell Maturation Antigen

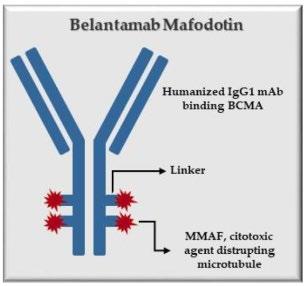
ADCP/ADCC = Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity & Phagocytosis
Image Credit: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/


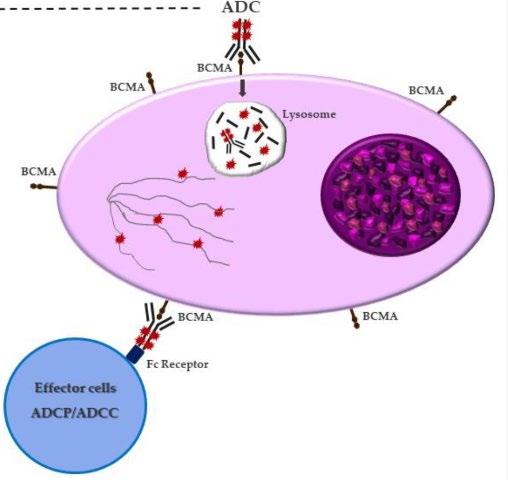
• Incorporates 2 antibody fragments to target and bind both tumor cells and T cells
• Brings target-expressing MM cells and T cells into close proximity, enabling T cells to induce tumor-cell death

FcRH5
“Off the Shelf” Advantage
• No manufacturing process, unlike CAR T-cell therapy (but like ADC/belantamab therapy)
• Thus, no delay between decision to treat and administration of drug ADC = Antibody-Drug Conjugate; BCMA = B-Cell Maturation Antigen; CD3 = Cluster of Differentiation 3; FcRH5 = Fc receptor-homolog 5; GPRC5D = G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D


CAR T therapy recommended. Insurance approved and ready to move forward.













Control is the immediate priority with active disease Cure remains the overall goal
Defining “Cure” has many considerations:
Minimal Residual Disease Negative (MRD-) Time Off Therapy
Functional Cure
Requiring Treatment Stable or Unmeasurable Disease, Receiving Treatment
Unmeasurable Disease, Receiving No Treatment Active Disease


VD
Rev/Dex
CyBorD
VTD
VRD
KRD
D-VMP
DRD
ASCT
Tandem ASCT (?)
Nothing
Thalidomide?
Bortezomib
Ixazomib
Lenalidomide
Combinations
Bortezomib
Lenalidomide
Carfilzomib
Pomalidomide
Selinexor
Panobinostat
Daratumumab
Ixazomib
Elotuzumab
Isatuximab
Belantamab mafodotin*
Melphalan flufenamide*
Idecabtagene autoleucel
Ciltacabtagene autoleucel
Teclistamab, Talquetamab
Elranatamab
D-VRD
Isa-VRD
D-KRD
Isa-VRD “More” induction?
Daratumumab?
Carfilzomib?
Lenalidomide + PI
ASCT, autologous stem cell transplant; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; Cy, cyclophosphamide; d- daratumumab; D/dex, dexamethasone; isa, isatuximab; K, carfilzomib; M, melphalan; PD-L1, programmed death ligand-1; PI, proteasome inhibitor; Rev, lenalidomide; V, bortezomib.
Speaker’s own opinions.
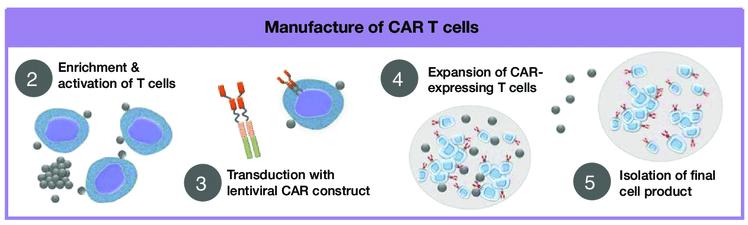
CAR T Cell Therapy
Bispecific/Tri-specific
Antibodies
Cell Modifying Agents
Venetoclax
PD/PDL-1 Inhibition?
Small Molecules
* These agents are currently off the market but available through special programs
Anito-cel
Cevostomab
Linvoseltamab
Iberdomide, Mezigdomide
Sonrotoclax

















