

Content I Inhalt
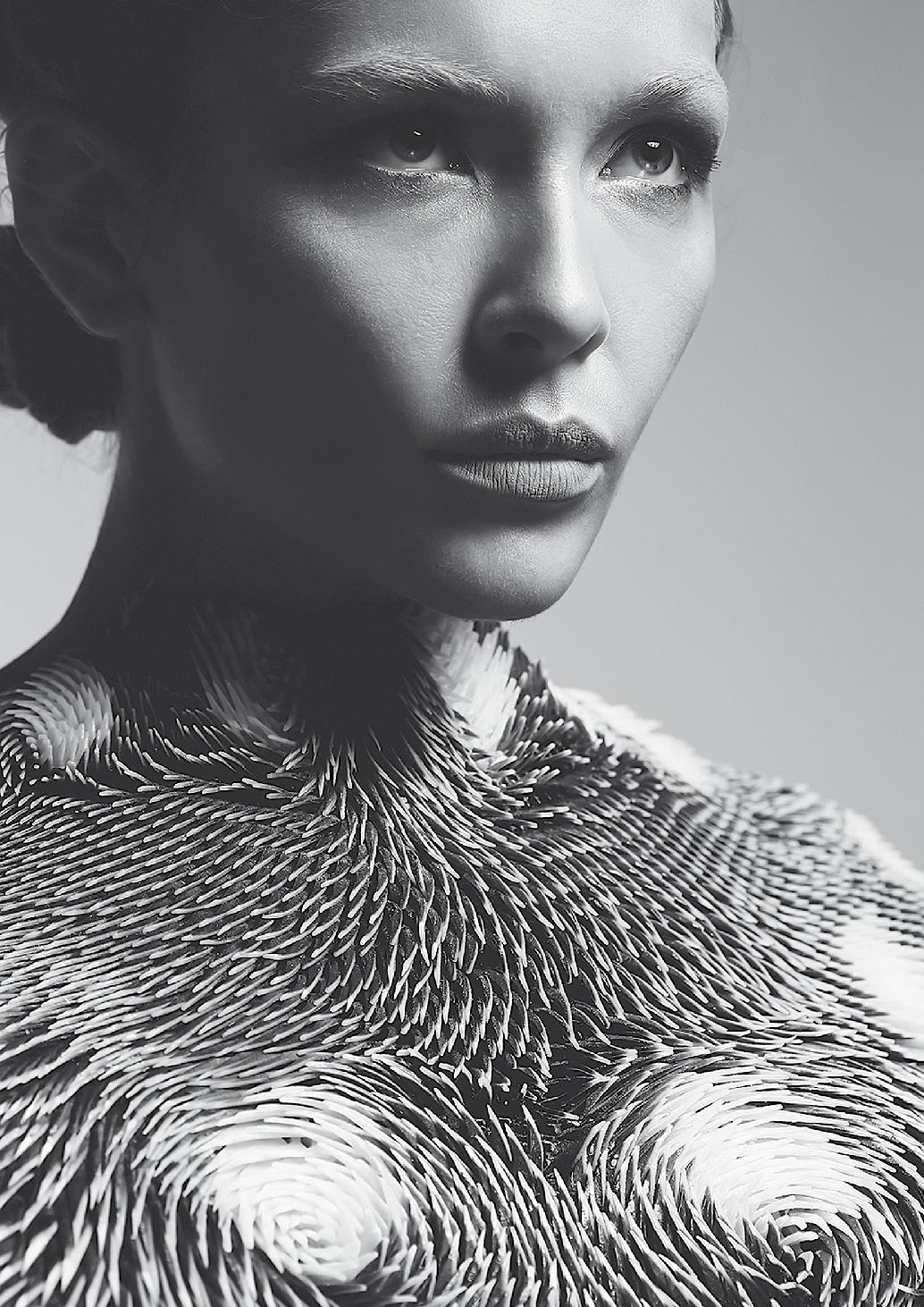


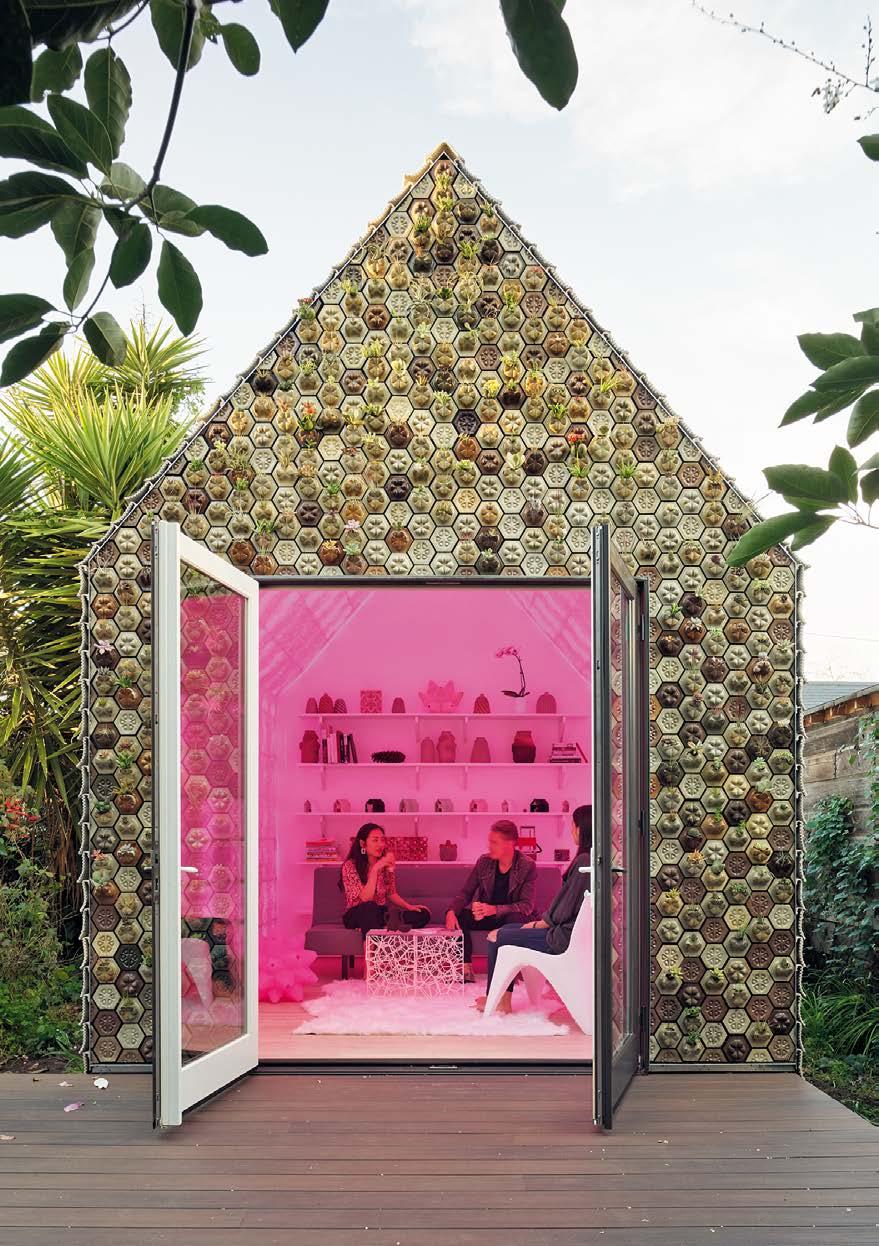
FashionTech
The fusion of human and machine becomes tangible in the FashionTech sector. The merging of design, fashion and new technologies makes it possible to turn visions into reality by developing not only material innovations but also new production processes.
This sector covers a wide range of explorations –including inspiration from lifestyle and art – which can influence applications such as workwear, personal safety wear and wearables that support the interaction with belongings, comfort, safety, and surroundings. Not to forget it offers concepts that rethink the actual fashion industry in regards to its overproduction and the throwaway society towards sustainable solutions.
Left page: Caress of the Gaze, Behnaz Farahi
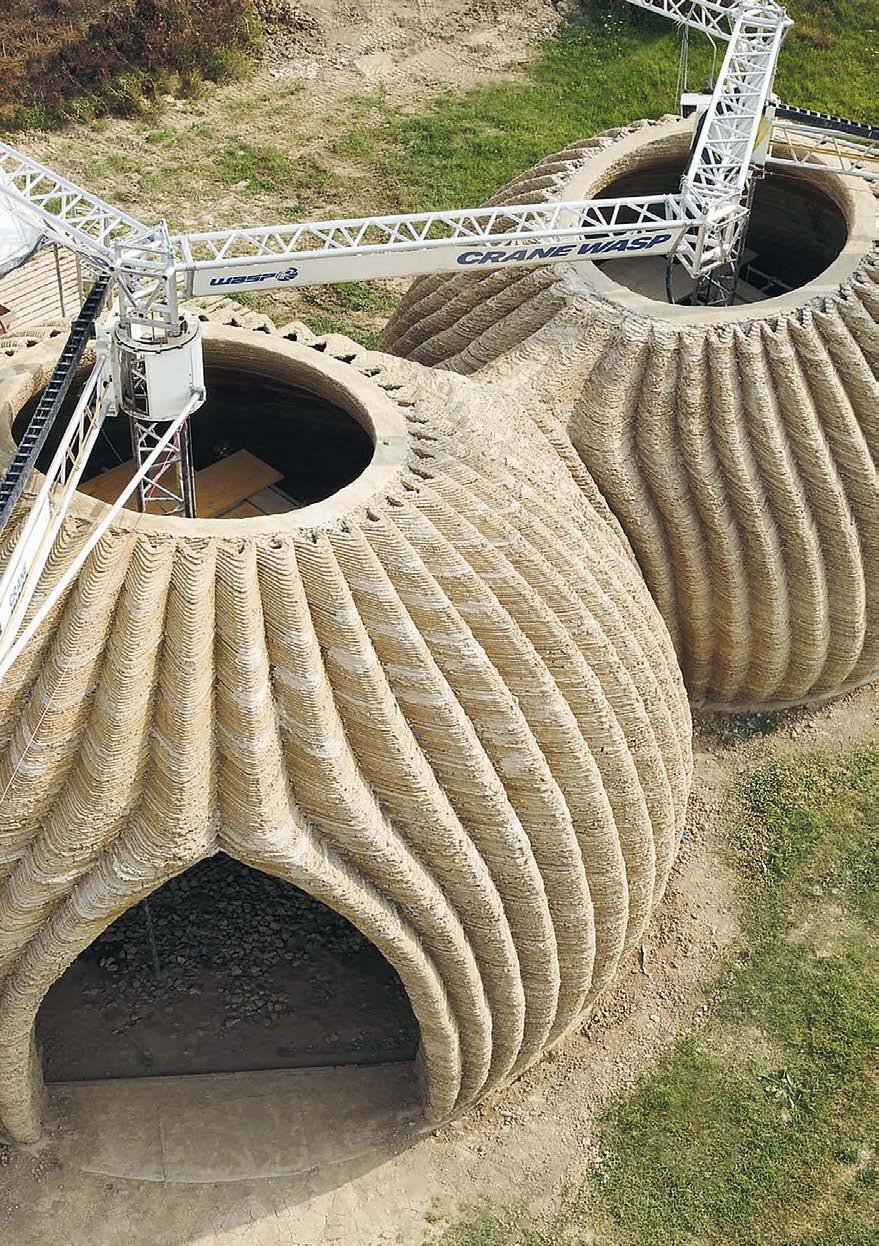


Architecture
Advanced Technologies can affect architectural innovation at numerous scales! It can happen in every part and detail, as well as 3D printing complete buildings – from the interior to the façade, all the way up to the way digital construction is being imagined.
This vertical highlights how some of the latest technologies, material innovations and tools like computational design or robotics are being used to disrupt the architectural designbuild process, and how it can support topics like the digital side of construction.
Left page: TECLA, the eco-sustainable 3D-printed habitat by WASP
Backstage Pass

Behind the scenes and beyond – preparations, jury sessions, exhibitions, trade fair booths, award ceremonies, even virtual moments during the COVID years, gala evenings, panel talks and after-show Gimlet parties. Following snapshots capture the spirit, energy, and people who have shaped the 3D Pioneers Challenge.
A special highlight: The iconic 3DPC Trophy (designed by Ross Lovegrove, Hyperganic and Materialise) awarded to the main winners since 2020. And a glimpse of images of how the spirit of innovation traveled the world every year on its global roadshow, bringing the innovations and their stories to audiences worldwide.
Photo credits A-D: See Appendix

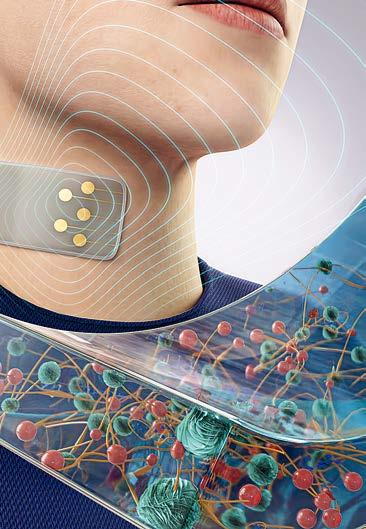
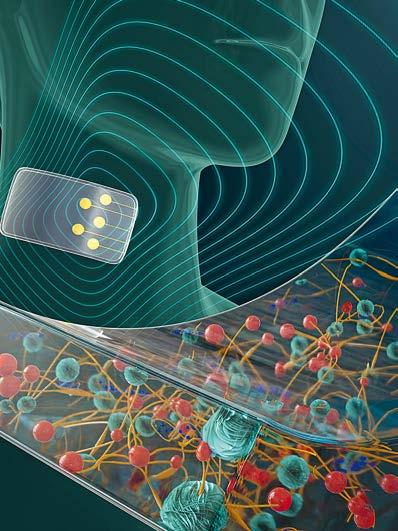
3D-Printed Electronic Skin
Institution: Texas A&M University
Team: Shounak Roy, Kaivalya A. Deo, Hung Pang Lee, John Soukar, Myeong Namkoong, Limei Tian, Amit Jaiswal, Akhilesh K. Gaharwar
Country: USA
Electronic skin6 (E-skin) mimics the flexibility and sensitivity of human skin, offering promising applications in robotics, wearable technology, and healthcare. Key challenges include developing flexible, durable materials with integrated biosensing, and advanced manufacturing methods for wearable and implantable systems. Wearables in this context are body-worn electronic devices designed to measure, monitor, or interact, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, or smart textiles.
A major breakthrough is the development of 3D-printed E-skin using nanoengineered hydrogels with tunable electronic and thermal sensing capabilities. These hydrogels leverage shear-thinning behavior to enable the fabrication of complex electronic structures while maintaining excellent flexibility, stretchability, adhesion, moldability, and conductivity.
This E-skin can accurately detect strain, pressure, and temperature changes, and also functions as a motion tracker, touchpad, voice recognition interface, and thermometer – marking a significant step forward in flexible electronics and the advancement of human-machine interfaces.
Electronic Skin6 (E-Skin) ahmt die Flexibilität und Sensitivität menschlicher Haut nach und eröffnet neue Anwendungen in Robotik, Wearables und Gesundheitswesen. Wearables sind körpernah getragene, elektronische Geräte wie Smartwatches oder Fitnessarmbänder, die Daten messen und überwachen. Eine zentrale Herausforderung ist die Entwicklung flexibler, langlebiger Materialien mit integrierten Biosensoren sowie geeigneter Fertigungsmethoden für tragbare oder implantierbare Systeme.
Ein technologischer Durchbruch ist die Herstellung von 3D-gedruckter ESkin3 aus nanooptimierten Hydrogelen, deren elektronische und thermische Eigenschaften präzise anpassbar sind. Diese Hydrogele verflüssigen sich unter Druck oder Bewegung, was sie ideal für den 3D-Druck komplexer Strukturen macht. Zugleich bieten sie hohe Flexibilität, Dehnbarkeit, Haftung und Leitfähigkeit.
Die E-Skin kann Veränderungen in Dehnung, Druck und Temperatur zuverlässig erfassen und dient zusätzlich als Bewegungssensor, Touchpad, Sprachsteuerung und Thermometer –ein bedeutender Schritt für smarte, körpernahe Technologien und die Mensch-MaschineInteraktion.
Strain / Pressure sensing
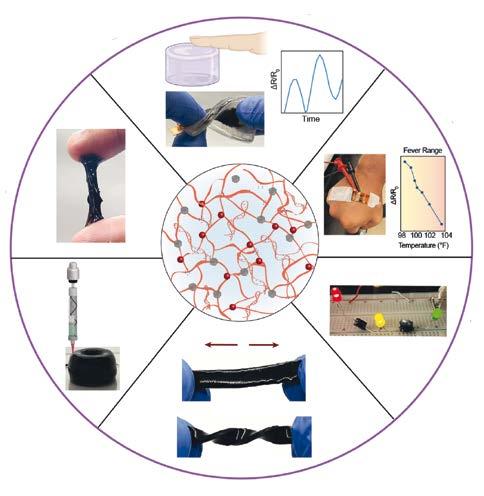
/ Strechable
Material: Nanoengineered hydrogels and bioinks with electronical properties
Process: Direct Ink Writing (DIW), Digital Light Processing (DLP), custom bioprinting
Left page: E-skin visualisation showing nanoengineered hydrogels
Right: Chart showing E-skin characteristics


Material
The development of materials is a basic column and promises to be a main driver for innovations in Advanced Technologies.
The use of wellknown industrial materials is challenging for the 3Dprinting processes but just as much a part of this vertical as the development of new alloys, matrices and processes or the processing of meta, nano or biomaterials. The focus is on how specific material choices contribute to improved functionality or performance and where material developments open up new opportunities. Regarding regulations and standards, new material developments either meet current existing or may require the creation of new standards to find their way into industrial use. Especially in this category, a look at sustainability is of great added value. There is great potential to include and push the topic of sustainability, not only for the transparency in material passport for a circular economy.
Left page: 4,500 3D-printed ceramic shingles clad the walls and roof of the cabin
Protomycokion
Institution: Lund University
Team: Ana Goidea, David Andréen
Country: SWEDEN
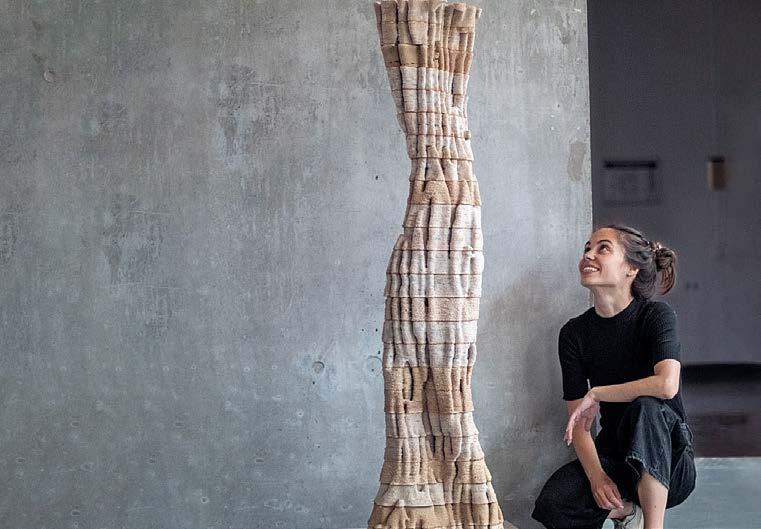

Protomycokion demonstrates the potential of 3D printing with biomaterials in a “new paradigm of manufacturing”: working with nature and biology both as inspiration and as the actual driver of transformation. This Bio-FDM process involves 3D printing with living fungi that bind wood particles after extrusion through their biological growth. In this way, the mycelium grows within the wood composite and fibers it anew while it reaches for nutrients.
Fungi are the archetype of the circular economy: They are the most important decomposers in our world, transforming waste into new organisms. Here, fungi become “agents of transformation,” bringing us closer to a more sustainable material culture. The complex geometries of 3D printing allow oxygen to flow through the structure due to their large surface area, which promotes fungal growth. As a result, more efficient materials can be produced than was previously possible.
Protomycokion demonstriert das Potenzial des 3D-Drucks mit Biomaterialien in einem „new paradigm of manufacturing“: die Arbeit mit der Natur und der Biologie sowohl als Inspiration als auch als eigentlicher Motor der Transformation. Bei diesem Bio-FDM-Verfahren wird mit lebenden Pilzen 3D-gedruckt, die durch ihr biologisches Wachstum nach der Extrusion Holzpartikel binden. Auf diese Weise wächst das Myzel innerhalb des Holzverbunds und fasert ihn neu, während es nach Nährstoffen greift.
Pilze sind der Archetyp der Kreislaufwirtschaft: Sie sind die wichtigsten Zersetzer unserer Welt, die Abfälle in neue Organismen umwandeln. Hier werden Pilze zu „Agents of Transformation“, bringen uns einer nachhaltigeren Materialkultur näher. Die komplexen Geometrien des 3D-Drucks ermöglichen durch die große Oberfläche der Pilze eine Durchströmung der Struktur mit Sauerstoff, was das Pilzwachstum fördert. Dadurch können leistungsfähigere Materialien produziert werden, als es bisher möglich war.
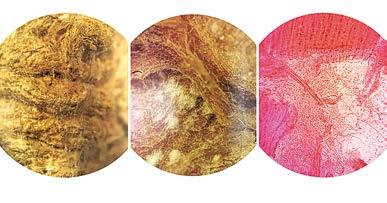
Material: Mycelium inoculum, sawdust, water, clay, cellulose fiber, xanthan gum
Process: Bio-FDM 3D printing, biofabrication
Left page: Ana Goida with the Protomycokion pillar
Top: Fungi as “agents of transformation”
Right top & bottom: Complex geometries promote fungal growth





3DTI
Company: What The Future
Founder: Janne Kyttanen and Eduard Zanen
Country: THE NETHERLANDS
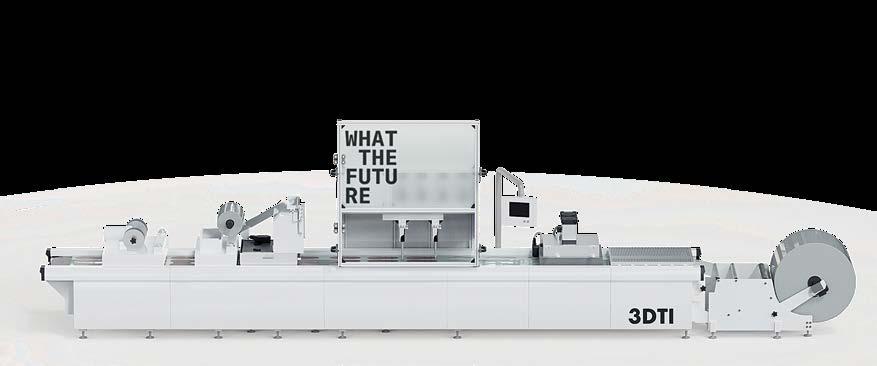
What the Future is redefining the manufacturing landscape with 3DTI – a breakthrough technology that combines 3D printing, thermoforming, and injection into a single, seamless process. By replacing traditional CNC-milled tooling with 3D-printed molds, 3DTI enables rapid design iteration, same-day production, and unprecedented agility in manufacturing.
3DTI is transformative for the footwear industry, enabling brands to bring products to market faster and to manufacture closer to the customer, using planet-friendly materials. This innovation supports scalable, sustainable mass production – significantly reducing costs and supply chain risk and complexity.

What The Future Food utilises the same technology to power the production of frozen confections on-demand, in any quantity, shape and flavour. 3DTI enables the production of custom food products with the immense scale of mass manufacturing and the intricate detail of hand production, at a fraction of the complexity and cost.
What the Future definiert die Fertigungsindustrie mit 3DTI neu. Die bahnbrechende Technologie vereint 3D-Druck, thermoplastische Formgebung und Spritzguss in einem einzigen, nahtlosen Prozess. Herkömmliche CNCgefräste Werkzeuge werden dabei durch 3D-gedruckte Formen ersetzt, wodurch schnelle Design-Iterationen, Produktion am selben Tag und eine beispiellose Flexibilität in der Fertigung ermöglicht werden.
3DTI revolutioniert damit die Schuhindustrie – Marken können ihre Produkte schneller auf den Markt bringen sowie näher am Kunden fertigen und dabei umweltfreundliche Materialien verwenden. Diese Innovation unterstützt eine skalierbare, nachhaltige Massenproduktion, die die Kosten, das Risiko und die Komplexität der Lieferkette erheblich reduziert.
What The Future Food nutzt dieselbe Technologie, um tiefgefrorene Süßspeisen, wie Eiscreme, in jeder beliebigen Menge, Form und Geschmacksrichtung direkt nach Bedarf zu produzieren. 3DTI ermöglicht die Herstellung individuell gestalteter Lebensmittel in großer Stückzahl – mit der feinen Detailgenauigkeit handwerklicher Produktion, aber bei deutlich geringerer Komplexität und zu einem Bruchteil der Kosten.


Material: Low-cost ABS molds, recycled PET films
Process: 3D printing, Thermoforming, and Injection (3DTI)

Left page: A vast variety can be produced on demand, also the 3DPC strawberry ice-pops
Left: No need for traditional CNC-milled tooling
Top: Sustainable impetus for the footwear industry
Bottom: 3DTI = 3D printing + Thermoforming + Injection
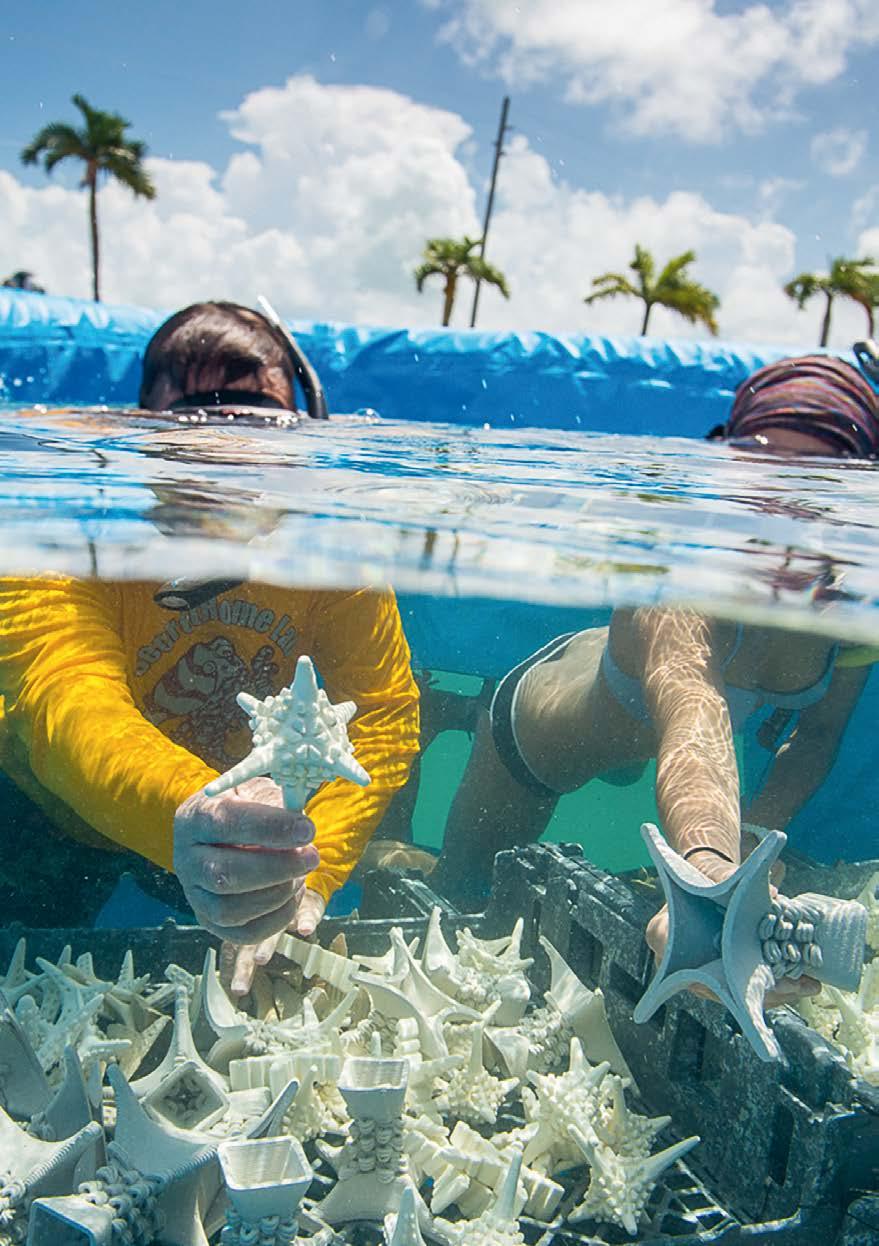


Sustainability
This overarching category addresses the aspects of enabling "A Better World." and is of basic importance for manufacturing not only with Advanced Technologies. Always with the view to sustainability, which can be perceived as a multilayered megatrend that includes the ecological, economical, and social significance of our actions.
Key topics like climate change, energy demand, and nutrition are faced with a demand for innovations in Clean Tech, Circular Economy, Zero Waste, or Agriculture, amongst others. In terms of responsible manufacturing, topics like rethinking production, product cycles, upcycling, recycling, materiality, marketing concepts, and many more focus subjects do apply. Concepts such as the Material Passport and the Digital Product Pass play a crucial role in enhancing transparency and traceability throughout product lifecycles, supporting circularity and sustainability goals. As an essential point to allow sustainability, the demand for technical innovations is not only necessary but actively being implemented. Advanced Technologies do have the power to enable solutions to these challenges and to drive futureproof responsible manufacturing.
Left page: Design of Coral Reef Seed Units by Emerging Objects
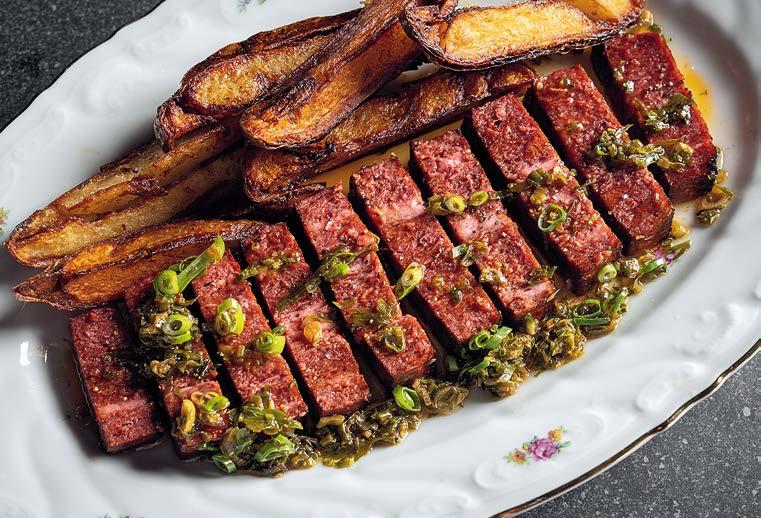
Steakholder Foods
Company: Steakholder Foods®
CO-Founder
and CEO: Arik Kaufman
Country:
ISRAEL
Steakholder Foods is a pioneering company at the forefront of food innovation, specializing in 3D-printing machinery and premium plant-based premixes. With a mission to revolutionize meat production, the company provides advanced manufacturing solutions that create delicious alternatives to traditional meat, fish, and seafood. Their cutting-edge technology includes the HD144 printer, designed for crafting fish and seafood substitutes, and the MX200 printer, tailored for producing meat alternatives. Complementing these innovations are their high-quality plant-based premixes, which serve as the foundation for a new generation of sustainable, flavorful protein products.
Steakholder Foods began its journey five years ago as a cultured meat company, pioneering advancements in cellular agriculture. In parallel, they developed proprietary 3D-printing technologies capable of producing complex textures and whole-cut formats, setting a new standard for alternative protein innovation. While cultivated meat continues to progress toward scalability and cost-efficiency, they have strategically shifted their focus to plant-based solutions. This transition has enabled to introduce a new generation of premium plant-based products that deliver an elevated sensory experience and align with evolving market demands.


Steakholder Foods ist ein Vorreiter in der Lebensmittelinnovation, spezialisiert auf 3D-
Drucktechnologie und hochwertige pflanzliche Rezepturen. Mit dem Ziel, die Fleischproduktion grundlegend zu verändern, entwickelt das Unternehmen fortschrittliche Lösungen für köstliche Alternativen zu Fleisch, Fisch und Meeresfrüchten. Zum Portfolio gehören der HD144-Drucker für Fisch- und Meeresfrüchte-Ersatz sowie der MX200-Drucker für pflanzliche Fleischalternativen. Ergänzt wird dies durch eigens entwickelte Grundmaterial-Rezepturen – die Basis einer neuen Generation nachhaltiger und geschmackvoller Proteinprodukte.
Steakholder Foods begann seine Reise vor fünf Jahren als Unternehmen für kultiviertes Fleisch und erzielte seither Fortschritte in der zellbasierten Landwirtschaft. Parallel entstand eine eigene 3D-Drucktechnologie, die komplexe Texturen und ganze Fleischstücke herstellen kann und damit neue Maßstäbe in der Produktion alternativer Proteine setzt. Da kultiviertes Fleisch wirtschaftlich noch nicht skalierbar ist, richtet sich der Fokus inzwischen auf pflanzenbasierte Lösungen. Diese ermöglichen Premiumprodukte mit intensivem Genusserlebnis, die den Bedürfnissen eines sich wandelnden Marktes entsprechen.

Material: Plant-based premixes: custom paste blends mimicking meat and seafood texture and taste
Process: Drop Location in Space technology (DLS™) and Fused Paste Layering technology (FPL™)
Left page: SH™ – Beef Marbled Steak
Top: SH™ – White Fish Fillet
Middle: How it started: with cultivated meat (MeaTech)
Right: Meat Printer MX200 and Fish Printer HD144


A decade of innovation: From the first heart printed from stem cells to the first additively manufactured metal bridge, all the way to the jet suit that makes the dream of personal flight a reality. For ten years, the international competition of the 3D Pioneers Challenge has accompanied some of the most exciting milestones in Additive Manufacturing and Advanced Technologies. This book shows how these technologies are transforming industries: Architecture and Design, Fashion and Mobility, as well as Medical Technology, Digitalization, and Sustainability. International experts share insights from their perspectives, while the initiators Simone and Christoph Völcker bring together these developments and provide a forward-looking outlook toward the year 2035 and beyond. It paints a picture of what the manufacturing world of tomorrow will look like – and who will shape it. The book provides impulses for research, business, and politics – with a clear focus on sustainability, value creation, and societal transformation.
A decade of innovation: From the first heart printed from stem cells to the first additively manufactured metal bridge, all the way to the jet suit that makes the dream of personal flight a reality. For ten years, the international competition of the 3D Pioneers Challenge has accompanied some of the most exciting milestones in Additive Manufacturing and Advanced Technologies. This book shows how these technologies are transforming industries: Architecture and Design, Fashion and Mobility, as well as Medical Technology, Digitalization, and Sustainability. International experts share insights from their perspectives, while the initiators Simone and Christoph Völcker bring together these developments and provide a forward-looking outlook toward the year 2035 and beyond. It paints a picture of what the manufacturing world of tomorrow will look like – and who will shape it. The book provides impulses for research, business, and politics – with a clear focus on sustainability, value creation, and societal transformation.
A book for everyone who wants to understand how innovation emerges, how it transforms cultures and markets – and how to become part of this movement. In the true spirit of pushing boundaries.
A book for everyone who wants to understand how innovation emerges, how it transforms cultures and markets – and how to become part of this movement. In the true spirit of pushing boundaries.
Eine Dekade voller Innovationen: vom ersten gedruckten Herz aus Stammzellen über die erste additiv hergestellte Metallbrücke bis hin zum Jet Suit, der den Traum vom persönlichen Fliegen Wirklichkeit werden lässt. Der internationale Wettbewerb 3D Pioneers Challenge begleitet seit zehn Jahren die spannendsten Meilensteine von Additiver Fertigung und Advanced Technologies. Das Buch zeigt, wie diese Technologien Branchen verändern: Architektur und Design, Fashion und Mobilität ebenso wie Medizintechnik, Digitalisierung oder Nachhaltigkeit. Internationale Expert:innen beleuchten die Chancen aus ihrer Perspektive, während die Initiatoren Simone und Christoph Völcker die Entwicklungen bündeln und einen Ausblick auf das Jahr 2035 und darüber hinaus geben. Es entsteht ein Bild davon, wie die produzierende Welt von morgen aussieht – und wer sie gestaltet. Das Buch setzt Impulse in Forschung, Wirtschaft und Politik – mit einem klaren Blick auf Nachhaltigkeit, Wertschöpfung und gesellschaftliche Transformation.
Eine Dekade voller Innovationen: vom ersten gedruckten Herz aus Stammzellen über die erste additiv hergestellte Metallbrücke bis hin zum Jet Suit, der den Traum vom persönlichen Fliegen Wirklichkeit werden lässt. Der internationale Wettbewerb 3D Pioneers Challenge begleitet seit zehn Jahren die spannendsten Meilensteine von Additiver Fertigung und Advanced Technologies. Das Buch zeigt, wie diese Technologien Branchen verändern: Architektur und Design, Fashion und Mobilität ebenso wie Medizintechnik, Digitalisierung oder Nachhaltigkeit. Internationale Expert:innen beleuchten die Chancen aus ihrer Perspektive, während die Initiatoren Simone und Christoph Völcker die Entwicklungen bündeln und einen Ausblick auf das Jahr 2035 und darüber hinaus geben. Es entsteht ein Bild davon, wie die produzierende Welt von morgen aussieht – und wer sie gestaltet. Das Buch setzt Impulse in Forschung, Wirtschaft und Politik – mit einem klaren Blick auf Nachhaltigkeit, Wertschöpfung und gesellschaftliche Transformation.
Ein Buch für alle, die verstehen wollen, wie Innovation entsteht, wie sie Kulturen und Märkte verändert – und wie man selbst Teil dieser Bewegung werden kann. Ganz im Sinne von pushing boundaries.
€ 29 (D) / US $ 39.00
Ein Buch für alle, die verstehen wollen, wie Innovation entsteht, wie sie Kulturen und Märkte verändert – und wie man selbst Teil dieser Bewegung werden kann. Ganz im Sinne von pushing boundaries. € 29 (D) / US $ 39.00
