responses, and the risks that have materialized or are imminent. These risks include an increase in nonperforming loans and financial sector distress; a lack of options for households and businesses to discharge debts incurred during the pandemic through formal insolvency; tighter access to credit; and elevated levels of sovereign debt. With the goal of directing countries toward options that can support an equitable recovery, this Report then highlights policies that respond to some of the adverse impacts of the crisis and mitigate spillovers of financial risks.
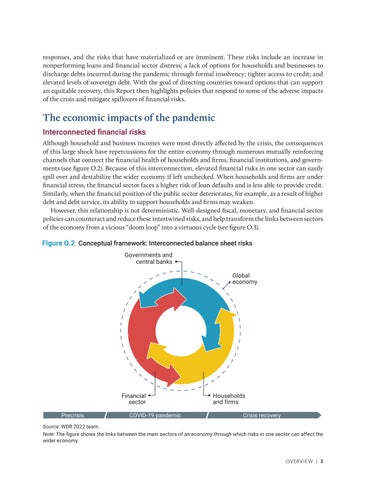
The economic impacts of the pandemic Interconnected financial risks Although household and business incomes were most directly affected by the crisis, the consequences of this large shock have repercussions for the entire economy through numerous mutually reinforcing channels that connect the financial health of households and firms, financial institutions, and governments (see figure O.2). Because of this interconnection, elevated financial risks in one sector can easily spill over and destabilize the wider economy if left unchecked. When households and firms are under financial stress, the financial sector faces a higher risk of loan defaults and is less able to provide credit. Similarly, when the financial position of the public sector deteriorates, for example, as a result of higher debt and debt service, its ability to support households and firms may weaken. However, this relationship is not deterministic. Well-designed fiscal, monetary, and financial sector policies can counteract and reduce these intertwined risks, and help transform the links between sectors of the O.2 economy from a vicious “doom loop” into a virtuous cycle (see figure O.3). Figure
Figure O.2 Conceptual framework: Interconnected balance sheet risks Governments and central banks Global economy
Financial sector Precrisis
/
COVID-19 pandemic
Households and firms
/
Crisis recovery
Source: WDR 2022 team. Note: The figure shows the links between the main sectors of an economy through which risks in one sector can affect the wider economy.
OVERVIEW | 3