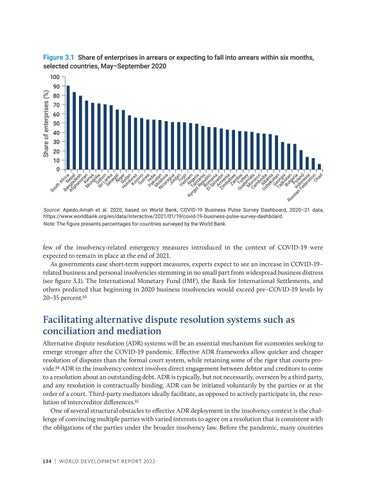
Figure 3.1 Share of enterprises in arrears or expecting to fall into arrears within six months, selected countries, May–September 2020
Share of enterprises (%)
100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10
So
ut
h A Ba Nfric a Af ngl epa gh ad l an es is h ta M Ken n on y g a G ol Sr ab ia i L on Se ank ne a g N al ig H Su er on da d n Ko ura s s Gu ovo in e Pa Ind a ki ia M st N old an ic o ar va a Jo gua rd a Vi Togn et o n N am Ky rg Ta ige yz nz ria Re an i R pu a El om blic Sa an lv ia A ad Zi rm or m en ba ia Za bw m e Gu Tu bia at rke e M m y Ca oro ala m cc bo o Uz Alb dia be an k ia G ista Ta eor n jik gia Bu ista Ru lg n a ss ia In Pol ria n do an Fe n d de es ra ia tio Ch n ad
0
Source: Apedo-Amah et al. 2020, based on World Bank, COVID-19 Business Pulse Survey Dashboard, 2020–21 data, https://www.worldbank.org/en/data/interactive/2021/01/19/covid-19-business-pulse-survey-dashboard. Note: The figure presents percentages for countries surveyed by the World Bank.
few of the insolvency-related emergency measures introduced in the context of COVID-19 were expected to remain in place at the end of 2021. As governments ease short-term support measures, experts expect to see an increase in COVID-19– related business and personal insolvencies stemming in no small part from widespread business distress (see figure 3.1). The International Monetary Fund (IMF), the Bank for International Settlements, and others predicted that beginning in 2020 business insolvencies would exceed pre–COVID-19 levels by 20–35 percent.63
Facilitating alternative dispute resolution systems such as conciliation and mediation Alternative dispute resolution (ADR) systems will be an essential mechanism for economies seeking to emerge stronger after the COVID-19 pandemic. Effective ADR frameworks allow quicker and cheaper resolution of disputes than the formal court system, while retaining some of the rigor that courts provide.64 ADR in the insolvency context involves direct engagement between debtor and creditors to come to a resolution about an outstanding debt. ADR is typically, but not necessarily, overseen by a third party, and any resolution is contractually binding. ADR can be initiated voluntarily by the parties or at the order of a court. Third-party mediators ideally facilitate, as opposed to actively participate in, the resolution of intercreditor differences.65 One of several structural obstacles to effective ADR deployment in the insolvency context is the challenge of convincing multiple parties with varied interests to agree on a resolution that is consistent with the obligations of the parties under the broader insolvency law. Before the pandemic, many countries
134 | WORLD DE VELOPMENT REPORT 2022