







Academic Authors: Jatinder Kaur, Ayushi Jain, Chandani Goyal, Kashika Parnami, Anuj Gupta, Simran Singh
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited First edition 2026
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Tekie.AI ICSE Computer Science 8
ISBN: 978-93-89789-26-3
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
91Springboard, 3rd Floor
145, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Printed by: Printpro Solutions
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Standing at the forefront of the digital and AI revolution, the importance of coding, computational thinking, and artificial intelligence has reached unprecedented heights. In today’s professional landscape—be it medicine, space exploration, education, science, or business—AI is transforming every sector.
Recognising this imperative, the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has strongly recommended the integration of coding, computational thinking, AI awareness, and problem-solving abilities into the curriculum. Moreover, future-ready subjects like Artificial Intelligence, Data Science, and emerging technologies are now at the core of education reforms. It is evident that AI will soon become an integral part of learning even at the elementary level.
Uolo has introduced an innovative 360-degree program for an AI-driven computer science curriculum, known as Tekie.AI, spanning grades 1 to 8. Tekie.AI is a significant stride towards STEM and AI education, empowering learners with skills needed to excel in an intelligent, technology-driven world.
Tekie.AI adopts a captivating and engaging approach to learning, in line with the recommendations of the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023 and NEP 2020. The curriculum is ingeniously woven into the thrilling adventures of Mel and Conji, fictional characters from the enchanting land of Avora. Their journey now explores not only the wonders of coding but also the incredible world of AI—how machines learn and assist humans.
The Tekie.AI series represents a modern way of acquiring AI concepts along with computer science knowledge and honing computational and critical thinking skills. Every chapter features AI Connect, real-world applications, and hands-on activities that make artificial intelligence simple, relatable, and fun. The package comes with digital content, provided free of cost, to ensure a seamless and holistic learning experience for children.
Tekie.AI is a technology-powered curriculum that encompasses the following components:
• Main Content Books: These introduce learners to core computer science concepts, AI fundamentals, and computer tools. Every theory chapter includes an AI Connect section, while each Tools chapter offers hands-on AI activities that make artificial intelligence easy to understand, relatable, and fun.
• Coding Books: Specifically designed to nurture coding skills, these booklets align with experiential and contextual learning, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
• Digital Platform: Tekie.AI offers a digital platform with Computer Science, Coding, and AI assignments that help students practice, explore, and apply concepts in real-world ways.
• Animated Learning Videos: The program is powered with high-quality animation-based videos that deliver learning in an engaging manner.
• Teacher Manual: This valuable resource supports classroom instruction, ensuring that educators effectively deliver the curriculum.
Welcome to the captivating realm of Tekie.AI! We hope you enjoy this educational journey as it equips you with the skills to thrive in an exciting, intelligent, and ever-changing 21st-century world.
Tekie is an interactive, engaging, and experiential computer science program. It enables learners to attain mastery in computer science theory, new-age computer tools and coding. These are delivered through a storytelling-based coursebook and an experiential learningoriented coding book.
The learning experience is augmented by a digital platform that gives learners access to learning videos and experiential activities and projects that are rooted in the curriculum.
Engaging Textbooks
Comic Stories
Teacher Manual
Test Papers
Additional Projects
Test-paper Generator

Student and Teacher Platform
Learning Videos
Interactive Classroom and Homework Assignments
Byte-size Lesson Modules

The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It aims to create a more holistic, dynamic and multidisciplinary approach to education. The NEP highlights the need for early development of computational thinking, coding, and digital literacy as vital skills for students’ holistic growth. UOLO is fully committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.











1. Focus on conceptual understanding
2. 21st century skills, values, and dispositions
3. Computational and critical thinking
4. Application in real life
5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Experiential learning
7. Enjoyable and engaging
8. Artificial intelligence and coding concepts
9. Digital literacy and emerging technologies
10. Factoids on India
Competency-based Education
NEP Pages 12, 17 and 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 5, 11, 12 and 56
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16 and 43
11. Assessment of core concepts and application skills Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18 and 22
Engaging hands-on projects encouraging practical application of computer science and coding
Story-based Approach
Enchanting tales that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure 5 7
Equipping the students with future-ready skills through exposure to the latest tools and technologies
Engaging chapters to deepen students’ understanding and engagement with AI concepts
Test papers designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills 3 4 11
Projects on the digital platform to deepen understanding and develop essential practical skills

Invites learners to discuss in small groups and present different perspectives
Story-style learning videos that deliver concepts to students.
Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical, and evaluative thought process
Interactive quizzes that reinforce learning and assess students’ understanding
Probing question related to the concept that arouses curiosity
Tool to create customised assessments that align with the curriculum and help evaluate students’ progress effectively.
7 Enjoyable and engaging
8 Artificial intelligence and coding concepts
9 Digital literacy and emerging technologies
10 Factoids on India
11 Assessment of core concepts and application skills
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions, and learning approaches necessary for students to thrive in the 21st century. This textbook identifies and incorporates these elements throughout its content, activities, and exercises. Referred to as “NEP Tags”, they are defined as follows:



INTEGRATED




Art Integration
Bringing creativity and fun into learning by combining music, drama, and art with other subjects
Sports Integration
Using games and sports in daily life to enrich computer-related activities
Holistic & Integrated Learning
Cross-curricular linkages to make the learning experience more holistic, joyful and meaningful
Critical Thinking
Coding opportunities to apply higher-order skills like algorithmic and computational thinking, and problem-solving

SDG
Hands-on Activity
Step-by-step activities to enable learners put theoretical knowledge into practice
Sustainable Development Goals
Applied computer science activities related to real-world issues and sustainable development

SEL Social Emotional Learning
Developing the skills to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships with others and make responsible choices

The curriculum is thoughtfully mapped to introduce tools and technologies at each grade level, ensuring a smooth and progressive learning experience for students. Beginning with basic concepts in junior grades, the curriculum gradually incorporates more advanced tools and concepts in higher grades. This structured approach enables students to build on their knowledge each year, equipping them with essential skills in computer science and technology as they progress from grade 1 through grade 8. By the time they reach the higher grades, students are well-equipped to tackle complex projects, think critically, and apply their skills in real-world scenarios. The curriculum not only fosters technical proficiency but also encourages creativity, problem-solving, and a deeper understanding of the digital world.










































Advantages
Theme Page: Lists the chapters covered under a unit


Comic Story: To introduce key concepts in a fun way
Discuss: A multi-faceted probing question related to the concept that arouses curiosity






4
a
b

Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic



c
Computers are very useful but they also have some disadvantages. Some of them are:



Explore More: Short videos to find out more about the topic


Explore More!




Discuss! How can computers help us in doing homework and creating


Do It Yourself: Short exercises between the











Let


Open Paint and click on the Shapes group.
2. Click on the Oval shape.
Project-based Learning: A project-based learning approach employed to foster an engaging and interactive learning experience


3. After selecting the shape, go to the drawing area.


4. Hold the left mouse button, drag the mouse, and then release the mouse button. You will see that an oval has been drawn.
Points to Remember: Summary of the chapter
Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Apply your learning: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for higher-order thinking and analysis
Have you ever given a command to the speaker at your home to play a song, and it plays it? Do you know what these speakers are known as?






These special speakers, which follow your voice commands, are smart speakers Smart speakers can do this because of AI.
What is AI?


Artificial Intelligence: Chapters on Artificial Intelligence to explore the fundamentals of AI, including its principles and applications in various fields
AI stands for Artificial Intelligence It gives machines the ability to learn and do things on their own, just like humans do
• Learning Games: These are educational games that you play on your computer. Some of them use AI to adjust the difficulty level as you play. For example, Quick, Draw!
AI Around Us
Fun with AI: Using Quick, Draw!

AI devices are all around us. There are many types of machines that use
1. Visit this link with the help of your teacher: https://quickdraw.withgoogle.com/
Artificial Intelligence (AI) to perform tasks or respond to us. Some examples of such AI devices are:
2. Click on the Let’s Draw! button to start.

• Talking Toys: Some toys use AI to understand your voice and respond with sounds, songs, or even short sentences. These speakers respond to your voice commands. They use AI to understand your voice commands, like when you ask them to play music or tell

• Robot Helpers: daily tasks at home. They can clean floors, cook food, etc. They do work in the same way as a human does.


Click on

AI Connect: Linking the topics in theory chapters to real-life applications of Artificial Intelligence
3. The AI will ask you to draw something like a cat, mug, house, church, remote control, etc., in under 20 seconds.
AI helps teachers and children in many ways at schools:
01
• Selfie Magic: Some phones use AI to edit your selfies. The AI can adjust lighting, smooth out backgrounds, or add fun filters. 01

• It listens when you read and helps you say words correctly.
• It checks your spelling and gives better words.
• It plays learning games that change to help you learn better.
• It can look at pictures you draw or write and tell what they are.
AI Activity: Engaging, hands-on activities in every Tools chapter based on an AI-related extension of the topic Magic Sketchpad

a We can talk to our friends using a computer.
Test Paper 1 (Based on Chapters 1 to 3)
b We can smell a flower shown on a computer.
A. Fill in the blanks.
c We can learn to dance using a computer.
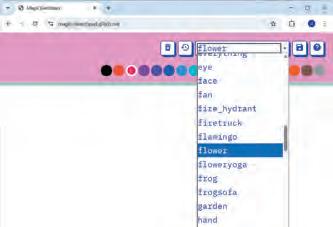
Magic Sketchpad is a website that uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) to help complete your drawings. When you start drawing something, the computer guesses what you are trying to make and adds to it.
Objective: The aim of this activity is to help students understand that AI can learn from drawings and try to guess what we are making. As students draw, they will see how the computer watches their lines, makes a smart guess, and then helps complete the picture.
Test Papers: Designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills
1 Open the following website with the help of your teacher: https://magic-sketchpad.glitch.me
1 Things that are present in nature are called things.
Tick () the things for which computers can be used at a school.
a To teach and learn.
2 Some machines need to work.
b To book tickets.
2 You will see a blank white area in the centre.
3 A list of object names appears at the top showing “cat,” “car,” “tree,” etc. options.
3 Computers are used in to keep information of patients.
c To play on the field.
4 At restaurants, computers are used to order and pay for B. Tick () the correct answer.
1 Which of the following is a human-made thing? a Mountains

Cars
2 Which machine helps us keep our food











• Sorting
• Grouping of Data
• Filtering Data
• Charts
• Sheet Tabs

• Understanding Databases
• Database Management System
• Structured Query Language
• More SQL Queries

• Creating a Video in Canva
• Components of Video Editor in Canva
• Adding Videos in Canva
• Basic Video Editing Tools
• Applying Effects on Videos
• Downloading and Sharing a Video









AI refers to a technology that allows computers or machines to do tasks that usually require human intelligence, like learning, solving problems, making decisions, and understanding language. AI systems can recognise patterns, answer questions, or recommend things (like videos or songs) by learning from large amounts of data. Real-life examples include self-driving cars, voice assistants, and smart robots in industries and hospitals.


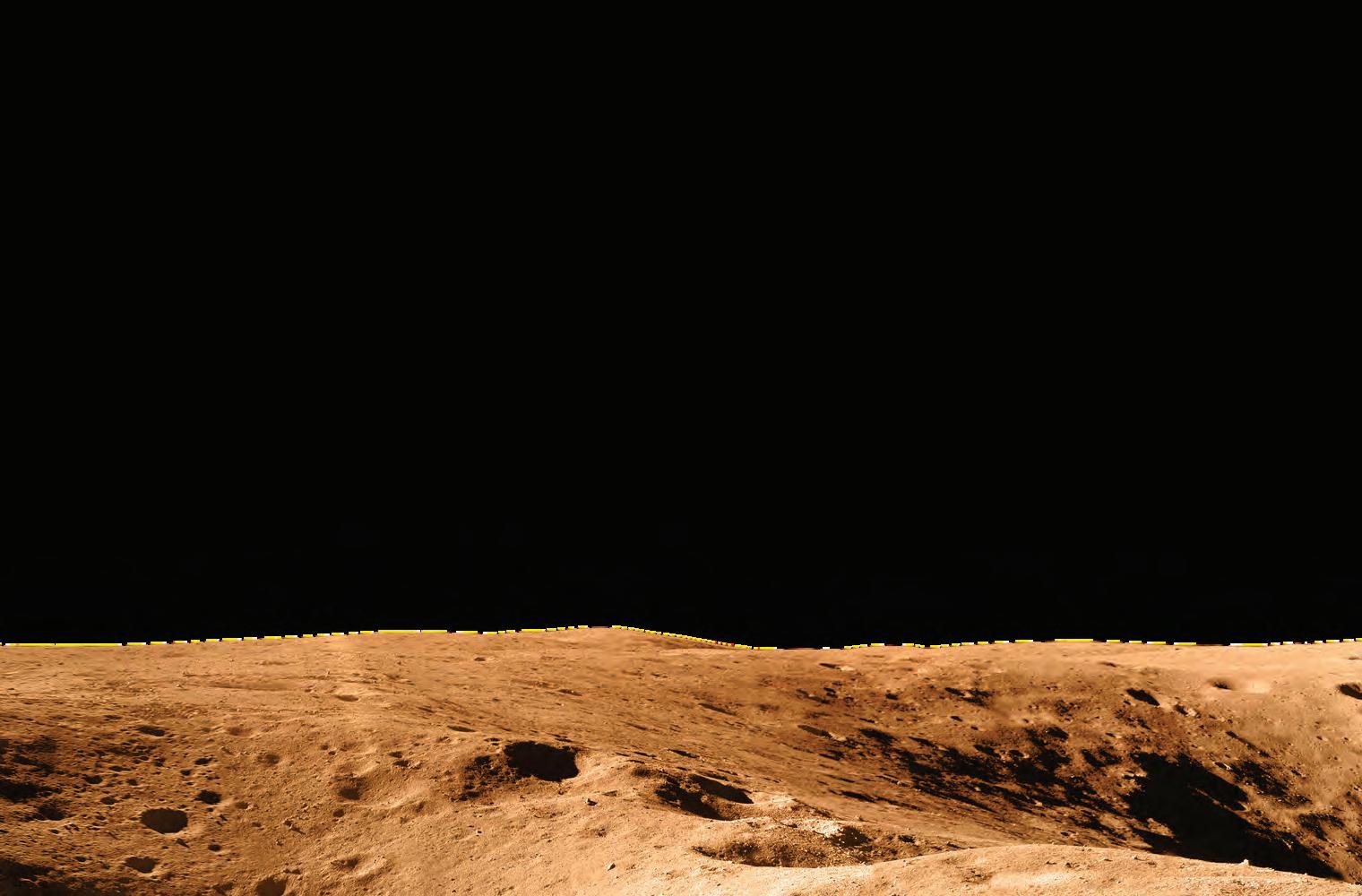
AI helps spacecraft and space robots navigate safely and make smart decisions on their own.
It guides Mars rovers in avoiding obstacles and choosing which rocks or places to study.




AI analyses huge amounts of space data from satellites and telescopes to help scientists make discoveries.
AI supports automatic docking, safe landings, and deep-space missions without needing humans to control every step.
Because of AI, space exploration is now faster, safer, and more efficient for astronauts and robots.








Steve Chien is a leading AI scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
He led the development of ‘Autonomous Sciencecraft’ software used on satellites and Mars rovers.
His AI helps robots and spacecraft plan their science tasks and explore places with less help from humans.
Steve Chien’s work allows space missions to run more independently and is recognized around the world.







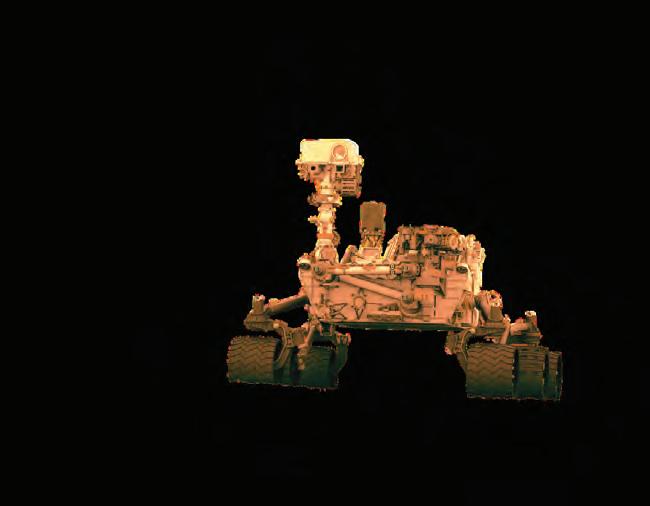
NASA uses AI in Mars rovers like Perseverance and Curiosity to explore the red planet.
AI-powered robots such as "Astrobee" help astronauts with chores on the International Space Station (ISS).
SpaceX rockets use AI for safe landings and navigation
The Dragon spacecraft from SpaceX docks with the ISS automatically using AI.
SpaceX’s Starship will use advanced AI for future missions to Mars and beyond.







An operating system (OS) is an important component of a computer. It is a program that controls and manages computer hardware. An OS acts as an interface between a user and a computer system. The OS lets users run programs — for example, games, word processors and web browsers — smoothly. The operating system controls various activities like organising and storing files on your computer’s storage device effectively and efficiently.




An operating system ensures that users can work on multiple programs simultaneously. It also helps you interact with the computer through devices like mouse, keyboard, printer, and monitor. Some examples of operating systems include Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux, and Unix. Each of these operating systems has its own features, user interfaces, and characteristics, but they all serve the fundamental purpose of managing computer resources and providing an environment for running applications smoothly.
The original name of Microsoft Windows was “Interface Manager”. Microsoft eventually changed the name to “Windows” because of the rectangular windows that were a prominent feature of the graphical user interface (GUI).

An operating system is like the boss of the computer that makes sure everything runs smoothly, keeps things organised, and helps us use the computer easily and safely.
Operating system handles the following responsibilities:
It controls and manages all the computer resources.
It provides an interface to users.
It hides the complexity of software.
It supports multiple execution modes.
It monitors the execution of user programs to prevent errors.
The first computer operating system called General Motors-North American Aviation Input/Output System (GM-NAA I/O) was created in 1956.


An operating system carries out various important functions that help in the smooth running of a computer. Here are a few functions of an operating system:
An operating system manages everything on a computer. It makes sure that all the games, apps, programs, applications, and files work together.
It allocates and deallocates memory space to running processes, ensuring efficient use of RAM.
It is easy to use. You can click icons and buttons because the operating system gives you a friendly way to talk to the computer.
An operating system helps protect a computer from unauthorised access by managing user permissions and security settings.
An operating system detects and handles errors or crashes, preventing a single application or hardware issue from crashing the entire system.
Write T for True and F for False.


Scan the QR code to learn how operating system works.
1 An operating system controls who is allowed to use the system.
2 An operating system deallocates memory space to running processes, ensuring efficient use of RAM.
Following are the different types of operating system:
A single-user operating system is designed for personal use and allows one person to use the computer at a time. This operating system provides a user-friendly interface, supports various applications, and can be customised to suit individual preferences. It is the type of operating system most people use on their personal laptops or desktop computers. Following are the functions of a single-user OS.
1. In a single-user operating system, only one individual can log in and use the computer at a time. This ensures that the computer’s resources, such as the CPU, memory, and storage, are dedicated to a single user’s tasks and processes.
2. The user of a single-user operating system has the authority to install and run software, manage files and folders, and configure system settings according to their preferences.
A multiuser operating system is a computer system that allows multiple users that are on different computers or terminals to access shared resources and data at the same time. Following are the functions of a multiuser OS.
Unlike single-user systems where only one user can use the computer at a time, a multiuser operating system allows several users to log in and work on the same machine simultaneously. Each user has their own login credentials and can perform tasks independently.
The operating system efficiently manages and allocates computer resources to different users and their respective processes. This ensures that every user gets a fair share of the available resources.
To maintain privacy and security, a multiuser operating system ensures that one user’s data and activities are isolated from others. Users cannot access each other’s files without proper authorisation.


Scan the QR code to learn the differences between single-user and multiuser operating systems.
Fill in the blanks.
1 In an operating system, many users can access the resources of the computer simultaneously.
2 A operating system can be customised to suit individual preferences.
A multitasking operating system is a type of operating system that allows a computer to run and manage multiple tasks or processes simultaneously. In context to multitasking operating system, some key points are:
1. In a multitasking operating system, simultaneous tasks are like a computer juggling multiple activities at once, such as running different programs or serving multiple users, ensuring everyone can work without interruption.
2. This type of operating system helps your computer effectively manage its resources such as the CPU and memory. The operating system ensures that these resources are used wisely, so your computer can switch between tasks quickly without slowing down.
3. Multitasking operating systems boost your computer’s productivity. They allow you to work more efficiently, making it easier to complete multiple tasks and get things done faster.


Scan the QR code to learn more about multitasking operating systems.

Multitasking operating systems are the reason you can listen to music, browse the web, and chat with friends on your computer or smartphone all at the same time, just like having multiple superpowers for your device!

A real-time operating system (RTOS) is a specialised computer operating system designed for tasks that require extremely precise and predictable timing and responsiveness. In context to RTOS, some key points are:
1. An RTOS gives quick and steady responses to tasks. It makes sure important actions happen without delay, which is useful for systems that need perfect timing, like machines and control devices.
2. An RTOS is designed to finish tasks on time. This is important in systems that collect or control data, where actions must happen at regular times.
3. An RTOS makes sure that certain important actions happen on time. Such systems are used in places where even a small delay can cause problems, like in traffic lights, robots, or medical machines.


1 I am specially designed for tasks that require extremely precise and predictable timing and responsiveness. 2 I allow a computer to run and manage multiple tasks or processes simultaneously.
A distributed operating system is a type of operating system that manages multiple computers or devices that are connected to each other through a network (using multiple communication links). These computers communicate and coordinate over the network to function as a single unified system. In context to a distributed operating system, some key points are:
A distributed operating system allows computers to cooperate on tasks, share resources, and communicate over a network. This networked collaboration enhances the efficiency and capabilities of the entire system.
It facilitates the sharing of computing resources such as CPU power, storage, and data across various computers within the network.
It ensures efficient communication between various computer systems, enabling them to work in harmony and perform tasks that would be challenging for a single computer.
Fill in the blanks.
1 A distributed operating system enables computers to work together seamlessly.
2 There is a communication channel in a distributed operating system.
A user interface (UI) works as a bridge that allows people to communicate with computers, smartphones, and various digital devices in a manner that is simple and easy to use. A UI encompasses all the elements and design components that users see and interact with on their monitor screens.
A UI includes various graphical and interactive elements, such as buttons, menus, forms, icons, text, images, and more. Its primary purpose is to make user interactions with the software efficient.
The smiley face emotion “:-)” created in 1982 is considered one of the earliest forms of user interface design.
Let us discuss the following UIs in this chapter.
Character user interface
Graphical user interface


A character user interface, also known as a command line interface (CLI) is a user interface that requires users to type text commands to interact with the computer system. These commands are handled by command-line interpreters.
Examples of operating systems that use CUI are DOS, Windows Command Prompt, and Unix.
A GUI is a user interface that employs graphical elements such as icons, buttons, windows, and menus, to enable users to interact with computers and software applications. It provides an intuitive and visual based means of navigating, controlling, and accessing digital content, making computing more user-friendly for individuals who may not have extensive technical knowledge.
Microsoft Windows is one of the most widely used GUI-based operating systems for personal computers.
Let’s learn about the striking differences between the two interfaces.
Appeal
Ease of Learning
Interaction Elements
Attractive and appealing Relatively less appealing
Easier to learn and user-friendlyRequires expertise
Icons, menus, buttons, etc.Text-based commands
Command Learning No need to learn complex commands Requires memorisation of commands
Multitasking Supports multitasking with windows Limited multitasking capability
Input Devices
Supports mouse and keyboardKeyboard only
Feedback Provides immediate visual feedback of the action performed Limited or no visual feedback of the action performed
Have you ever wondered why a computer mouse is called a ‘mouse’? Well, it is because the inventor, Douglas Engelbart, thought the cord of the first mouse looked like a tail. So, just like a mouse scurrying around with its tail, the computer mouse helps you move things around on a computer screen! Did You Know?



Artificial Intelligence (AI) is now a part of the operating systems in our smartphones. It helps our phones learn our daily habits — like when we usually charge them or which apps we open most — and adjusts settings to save battery and speed up performance. AI also powers features like voice typing, face unlock, and photo suggestions in the gallery. This makes our phones feel more personal and helpful, almost like they understand us! AI can even predict what we might want to do next, such as suggesting replies to messages or reminding us about upcoming events. It also helps in improving camera quality by recognising scenes and adjusting lighting automatically. With AI, smartphones are not just tools — they are becoming smart companions that learn and grow with us.

Write T for True and F for False.
1 A CUI includes various elements like buttons, menus, and icons.
2 A GUI does not provide feedback to the user.
1 Operating system is a program that controls and manages computer hardware. It acts as an interface between the user and computer system.
2 There are different types of operating systems like the single-user, multiuser, multitasking, real-time, and distributed operating systems.
3 In a single-user operating system, one user has exclusive control over the computer’s resources.
4 A multiuser operating system allows multiple users to work on the same computer simultaneously.
5 A multitasking operating system allows a computer to run and manage multiple tasks or processes simultaneously.
6 A real-time operating system (RTOS) is designed for tasks that require extremely precise and predictable timing.
7 A distributed operating system manages multiple computers that are connected to each other through a network.
8 A character User Interface, also known as a Command Line Interface (CLI), is a user interface that requires the user to type text commands to interact with a computer system.
9 A GUI is a type of user interface that employs graphical elements such as icons, buttons, windows, and menus, to enable users to interact with computers and software applications.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints complex multitasking operating system GUI single-user
1 is a program that controls and manages computer hardware.
2 The user of the operating system has the authority to install and run software according to their preferences.
3 operating systems boost your computer’s productivity.
4 A is a type of user interface that employs graphical elements such as icons, buttons, windows, and menus.
5 A graphical user interface doesn’t require you to remember commands.
B. Who am I?
1 I have the authority to install and run software, manage files and folders, and configure system settings according to my preferences.
2 I can get you anything at a click of a button, you don’t need to remember any complicated commands.
3 I ensure efficient communication between various computers so that they can work in harmony.
4 I am deployed in applications where split-second timing and timely-responsiveness are paramount.
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 The distributed operating system doesn’t allow computers to share resources.
2 A GUI is simple and doesn’t require knowing a lot of computer technicalities.
3 An RTOS makes sure that certain important actions happen on time.
4 Microsoft Windows is an example of an operating system.
5 A GUI does not provide feedback to users to let them know what is happening.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 What is the need of an operating system?
2 What is UI?
3 What is GUI? How does it make our work easier?
4 Give one difference between the single and multiuser operating systems.
5 What are the features of a real-time operating system?




E. Apply your learning.
1 Mohini’s mother got herself a new computer. Mohini excitedly interacts with the computer through its graphical elements such as icons, buttons, and menus. What type of interface is she using?
2 Shehnaz is working on a device that allows her to only type the commands using a keyboard. Name the interface that she is working on.
3 Rohit has an operating system on his laptop that is designed for personal use and allows one person to use the computer at a time. Name the type of operating system he has on his system.







Computer networks are systems of interconnected computers, devices, or nodes that share resources and information with each other. These computers are linked with each other through transmission media, such as cables, telephone lines, radio waves, or infrared light beams.
The network size may vary from small to large depending on the number of computers it connects.
A data communication system consists of the following parts:
1. Sender: A sender, also known as a source, is any device or computer that starts communication by creating and sending data, messages, or signals. This can be a computer, smartphone, or any other electronic device which is capable of sending data.
2. Receiver: The receiver is the device or computer that receives the data, messages, or signals sent by the sender. The recipient processes this information and takes appropriate actions based on the data received.
3. Medium: A medium is also called a communication channel or communication media. It is the physical path or method through which data is conveyed from a sender to a receiver. This can include various types of transmission media, which are wired connections such as television cables, telephone cables, and optical fibre, or wireless technologies such as radio waves and infrared signals.
4. Message: The message is the actual information being sent from the sender to the receiver. It could be a text, a picture, a video, or any other type of data. In the context of a letter, it’s the content of the letter itself. On a network, the message is what the sender wants to share with the receiver.
5. Protocols: These are the set of rules and guidelines that ensure seamless and standardised communication between devices on a network. When your computer wants to send a message to another computer, they both need to use the same protocol, just like speaking the same language. These protocols make sure the information travels correctly, gets received properly, and can be understood, creating a reliable way for computers to share data.

Network architecture refers to the design and structure of devices used in computer networks. These devices such as routers, switches, and modems are built with specific components and connections to enable data exchange between computers. These include the central processing unit (CPU), memory for storage, network interfaces for connections, and the operating system for managing tasks.

1. Personal Area Network (PAN): A PAN stands for a personal area network. It includes devices like smartphones, tablets, and accessories which are connected through technologies like Bluetooth. Two smartphones communicating through Bluetooth is an example of a PAN. It can be wired or wireless.
2. Local Area Network (LAN): LAN stands for a local area network. A LAN is a network that connects devices in a limited area, for example, homes, offices, or schools. This network allows devices to share files, printers, and shared accounts. LANs are widely used in homes and small organisations to connect computers and other devices for smooth communication. A school lab is an example of LAN.
3. Campus Area Network (CAN): CAN stands for a campus area network. It connects multiple LANs within a specific area. CAN is a special type of network that covers a small area, such as a school campus or a big office building. For example, it helps to easily share information between the classrooms of a school.
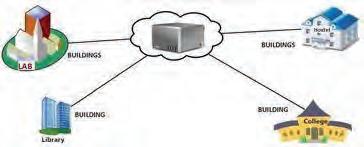
4. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A MAN stands for a metropolitan area network. A MAN covers a large area like a city. It connects multiple LANs within that area which enables communication between various locations. MANs are essential for universities or within cities to connect municipal offices for data exchange and communication. Cable TV networks are an example of MAN.
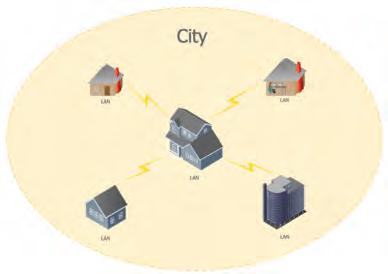
5. Wide Area Network (WAN): A WAN stands for a wide area network. It connects LANs and MANs over long distances that cover cities, nations, or continents. The internet is the most significant WAN that enables global communication.


Networking concepts include various networking devices, terminologies, protocols, and topologies. Let us discuss about them in detail.
Networking devices are the hardware devices that are used to connect computers together to share files or printers. These devices perform different tasks at different segments of a computer network.
MODEM: MODEM stands for MOdulator-DEModulator. A modem is a device that converts digital data from a computer into analog signals that can travel over telephone or cable lines, and converts incoming analog signals back into digital data.




Switch: A switch is a device on a network that connects multiple devices (like computers) and directs data only to the device that needs it. A switch improves network efficiency.
Hub: A hub is a central device or place that connects multiple devices on a computer network. It allows various devices, such as computers, printers, or other gadgets, to share information and communicate with each other. It sends data to all connected devices, which can lead to inefficiencies.






Router: A router is a device used in computer networks that directs data traffic efficiently between different computer networks. This device ensures that the data reaches the correct destination.
Gateway: A gateway connects two different computer networks and allows them to communicate and share information with each other.

Internet: The internet is a global network of networks that connects millions of computers worldwide. It provides a variety of information and communication facilities. It consists of the interconnected networks that communicate via standardised communication protocols.
Intranet: An intranet is a private network within an organisation that is accessible only to its members. It is used for file sharing, internal communication, and other purposes.
URL: URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. A URL is a web address used to locate and access specific content or websites on the internet. For example ”www.examplе.com” is a URL.
ISP: ISP stands for internet service provider. An ISP is a company that provides internet access services to individuals and businesses, connecting them to the internet.

IP Address: An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique number assigned to every device on a network. The most common version is IPv4, written as four numbers separated by dots (for example: 192.168.1.1).
DNS: DNS stands for Domain Name System. DNS is like the internet’s phone book. It translates humanfriendly domain names (e.g., “google.com”) into IP addresses that computers use to find websites.
Web Page: A web page is a single document displayed in a web browser. It can contain text, images, videos, and links to other pages.
Web Server: A web server is used to store and deliver the contents of a website to clients such as web browsers.
Website: A website is a collection of related web pages that are stored on a web server and can be accessed through the internet. It is the space where individuals, businesses, or organisations can share information, products, services, or entertainment with people from all around the world. To access a website, one has to type the address of the website (URL) in the address bar of a web browser.
Web Portal: A web portal is a special website that gathers lots of useful things at one place. This portal provides easy access to various services, information, and tools.
Link: A link is a connection between two things on the internet, such as web pages, documents, or websites. For example, when you click a hyperlink on a web page, it redirects you to another page or resource. It can be text or an image.
Hyperlink: A hyperlink is a clickable link in a website or document that directs users to another website or resource. A hyperlink makes navigation easy.
Hypertext: Hypertext is a way of organising and connecting information in digital documents, such as web pages. It allows you to click the words or phrases (called hyperlinks) to jump to the related information or various sections within the same document or on other web pages.
Bandwidth: Bandwidth is the capacity of a network connection. It is measured in bits per second (bps) or Bytes per second (Bps). This capacity determines how much data can be transmitted over the network at a given time. More bandwidth means faster data transmission.
Unscramble the following words.
In computer networks, protocols are a set of rules and conventions that govern how data is transmitted, received, and processed between devices.
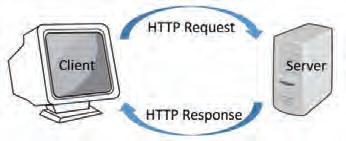
1. HTTP: HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It is the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web. It is a request-response protocol used for transmitting information and files on the internet. When you type a website address in your browser and press Enter, your browser uses HTTP to request the web page from the server where the website is stored.
Another form of HTTP is HTTPS, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. It is used for secure communication over a network.
2. FTP: FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. FTP is a protocol for transmitting files over the internet. It is commonly used by web developers to upload files to a website’s server. FTP allows the user to upload, download, and manage files on a remote server.
3. TCP/IP: TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol. It is a set of rules and protocols that govern how devices communicate over a network. This protocol provides the fundamental framework for internet communication, allowing computers and devices to share information and resources across the globe.
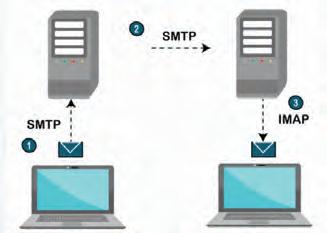
4. IMAP: IMAP stands for Internet Message Access Protocol. It is an email protocol that allows you to access and manage emails stored on a mail server. IMAP enables the user to view, organise, and delete emails on the server while keeping copies of messages on the server.
5. SMTP: SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It is used for sending emails. It works by sending outgoing emails from the sender’s email client to the recipient’s email server.


Network topologies refer to the arrangement of devices and connections on a computer network. Various topologies define how devices are linked and communicate with each other.
Following are the different types of network topologies:
In a bus topology, all devices share a single communication line. In this type of topology, messages travel along the line and only the intended recipient device processes the message. It is simple and inexpensive but can slow down as more devices are added.
In a star topology, all devices are connected to a central hub or switch. All communication passes through the central hub which makes it efficient and easy to troubleshoot. The disadvantage of the star topology is that if the hub fails, the whole network will be disabled.
In a ring topology, each device is connected to two other devices by forming a circular network. Data travels in one direction through the ring until it reaches the intended recipient. Although it runs smoothly, it can be slow at times; and if one device breaks, the whole network may get affected.


















In the mesh topology, every node is directly connected to every other node forming a mesh. The disadvantage of the mesh topology is that the network is costly, due to the large number of cables used and it is difficult to find a faulty node.
A hybrid topology is a combination of two or more types of topologies. It integrates elements from the bus, star, ring, and mesh topologies. It is often used on large networks to enhance performance and reliability.
Do It Yourself 2C
Complete the classification diagram.
Network Topologies

Cloud computing is the process of manipulating, configuring, and accessing online applications. We can use various services and resources over the internet by using it. Cloud computing offers an online data storage facility; one can access them through the internet on remote servers. This means that data can be stored, applications can be run, and tasks can be performed online without needing powerful computers. Cloud computing offers convenience, scalability, and accessibility, allowing users to access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. Google Drive, Microsoft OneDrive, Dropbox, and Apple iCloud Drive are some of the common examples of cloud computing.
1. On-demand Self-service: Cloud services are available whenever needed. Resources like storage and software can be accessed based on requirements without waiting for any approval or assistance.

2. Broad Network Access: Cloud services can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, whether it’s a computer, smartphone, or tablet.
3. Resource Pooling: Resource pooling involves gathering all computer resources, such as storage, processing power, and networks from various computers, and using them together.
4. Rapid Elasticity: Rapid elasticity allows quick scaling up or down of computing resources in response to demand. This means that resources like storage, processing power, or bandwidth can be increased or decreased rapidly according to needs.
5. Measured Services: In cloud computing, services are billed only for what is used. This ensures precise charges for the services needed, avoiding unnecessary expenses.
1. Cost-efficiency: Money is saved because there’s no need to buy and maintain physical supplies or software. Payment is made only for the services used, making it budget-friendly.
2. Scalability: Resources can easily grow or shrink. If a business expands, the cloud grows accordingly. If less is needed, there’s no obligation to use more capacity.
3. Flexibility: Work can be done from anywhere with an internet connection, whether it’s at home, in a cafe, or while travelling. This accessibility supports remote work.
4. Automatic Updates: Cloud services handle updates and maintenance, ensuring the latest features and security without manual installations.
5. Data Security: Cloud service providers prioritise the safety and protection of data. They use encryption and other measures to secure data, making it more reliable than traditional methods.
6. Collaboration: Cloud platforms make it easier to work together. Multiple people can edit files simultaneously, promoting teamwork and improving productivity.
7. Disaster Recovery: Cloud services automatically back up data. Even if a computer crashes, files remain safe and can be recovered.
Storing and sharing data using cloud computing means saving your files, documents, and information on the internet, rather than on your computer’s hard drive. Cloud computing allows you to access these resources from anywhere using an internet connection. Additionally, you can easily share this data with others which enables collaboration and makes it convenient for remote work or sharing information with colleagues or friends. Such storing and sharing eliminates the need for physical storage devices and offers flexibility and accessibility to your data. The process of storing data from your computer to cloud storage is called uploading, and the process of copying files from cloud storage to a system is called downloading.

Discuss the concept of storing and sharing data using cloud


Artificial Intelligence (AI) helps cloud services like Google Photos and YouTube organise our pictures and videos automatically. AI can recognise faces, places, and even objects in photos to group them neatly into albums without us doing anything. It can also tag videos by topic or suggest what we might want to watch next. This smart use of AI makes it easier for people to find, share, and enjoy their memories online.
Network security involves the implementation of strategies, protocols, and tools to protect computer networks, systems, and data from unauthorised access, attacks, and damage. It includes measures like firewalls, antivirus software, encryption, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard sensitive information from cyber threats. Network security ensures that only authorised users can access specific data.
Cyber ethics refers to responsible and ethical behaviour on the internet. These ethics involve being respectful, honest, and considerate in online interactions. This includes avoiding cyberbullying, respecting others’ privacy, and giving credit to original content providers for using their online content. By following cyber ethics, we create a safe and positive online space for all.
1 Computer networks are interconnected devices that share resources and information.
2 Essential components of a network: sender, receiver, medium (communication channel), message and protocol.
3 Network devices include routers, switches, modems, etc.
4 Types of networks are PAN, LAN, CAN, MAN, and WAN.
5 IP address is a unique numerical label assigned to devices on a network for identification and communication.
6 Protocols are rules governing data transmission between devices in a network, including HTTP, FTP, TCP/IP, IMAP, and SMTP.
7 Network topologies refer to the arrangement of devices and connections in a computer network.
8 Cloud computing enables accessing services and resources over the internet, offering scalability, accessibility, and convenience.
9 Network security involves strategies like firewalls and encryption to protect computer networks, systems, and data from unauthorised access and attacks.
10 Cyber ethics refers to responsible online behaviour, including avoiding cyberbullying and respecting others’ privacy, ensuring a positive digital environment.

A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints structure telephone ethical router source capacity
1 A sender, also known as a , is any device or computer that starts communication by creating and sending data, messages, or signals.
2 Network architecture refers to the design and of devices used on computer networks.
3 A modem is a device that connects your computer to the internet and translates digital data into signals that can travel over lines.
4 A is a device used on computer networks that directs data traffic efficiently between various computer networks.
5 Bandwidth is the of a network connection.
6 Cyber ethics refers to responsible and behaviour on the internet.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 What does LAN stand for in computer networks?
a Large area network
c Long access network
2 Which network type covers a city and connects multiple LANs?
a LAN
c WAN
3 What does URL stand for in the context of the internet?
a Uniform resource locator
c Unified resource link
4 What is the role of a switch in a network?
a Connects devices and directs data only to the intended device
b Connects multiple LANs within a specific area
c Connects two different computer networks
d Sends data to all connected devices in the network
b Local area network
d Limited area network
b PAN
d MAN
b Universal recording language
d User related link
5 Which characteristic of cloud computing allows quick scaling up or down of computing resources?
a On-demand self-service
c Rapid elasticity
b Broad network access
d Measured service
C. Who am I?
1 I am the physical path or method through which data is conveyed from a sender to a receiver in a network.
2 I translate human-friendly domain names into IP addresses that computers use to find websites on the internet.
3 I connect two different computer networks and allow them to communicate and share information with each other.
4 I am a connection between two things on the internet, such as web pages, documents, or websites.
5 I am a special website that gathers various services, information, and tools in one place for easy access.
6 I am an email protocol that allows users to access and manage emails stored on a mail server.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 A sender is a device that receives data, messages, or signals sent by the receiver.
2 In a bus topology, all devices are connected to a central hub.
3 Cloud computing services are billed based on the resources you actually use.
4 IMAP is an email protocol that allows you to access and manage emails stored on a mail server.
5 WAN stands for Wide Area Network and covers a limited area like a city or a campus.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 Mention any two points of difference between PAN and CAN.
2 Define Hypertext and its purpose in digital documents.
3 What do you understand about the term “Cloud Computing”?
4 Name one characteristic of Cloud Computing.

5 What is Cyber Ethics, and why is it important?
6 What does ISP stand for, and what is its role in internet connectivity?




F. Apply your learning.
1 Jashan wants to understand the role of protocols in computer networks. Choose one protocol (e.g., HTTP, FTP) and explain it to him.
2 Harpreet is trying to explain computer networks to her younger brother. How would you explain the concept of LAN (Local Area Network) to a younger sibling in simple words?
3 Deepak is at home and needs to share a large presentation file with his classmate who lives in another city. Which type of network would be most suitable for this task, and why?
4 Sakshi is planning to run a cloud-based software business. Explain to her the characteristics of cloud computing, like “on-demand self-service” and “measured service”.






Computational thinking (CT) is the process of conceptualising problems in such a way that the resulting solutions can be viewed as computational operations and algorithms. In simple words, it’s like turning a big problem into small, easy-to-understand pieces that you can solve. It’s the first thing you do before you start telling a computer what to do. You break the problem into tiny steps, like giving the computer a recipe to follow. Using computational thinking, you can solve puzzles, play games, do homework, break big problems into smaller steps, or find patterns.

In order to carry out computational thinking, there are four essential skills/pillars that must be acquired. Let us discuss them one at a time.
• Decomposition
• Pattern recognition
• Abstraction
• Algorithmic design
4 Pillars of Computational Thinking
Decomposition
Decomposition is the process of dividing a difficult activity or problem into smaller, easier-to-solve components or sub-problems
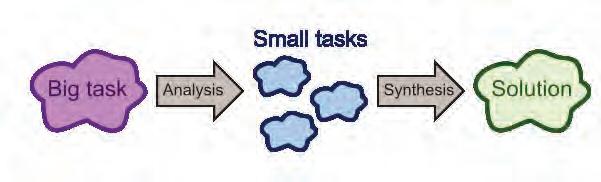
Through independent analysis and treatment of each smaller component, this method makes problemsolving more feasible.

The stages you usually take while decomposing a problem are as follows:
Identify the Problem Clearly state the objectives and conditions of the issue you are trying to solve. Break It Down
Separate the main issue into smaller issues or jobs. Each minor issue ought to be a stand-alone solution that aids in resolving the main issue.
Suppose you want to go on a trip to Nainital. Before the trip, you need to ensure that everything is arranged.
Here, the problem statement is to check if all the arrangements for a trip to Nainital are done.
Now, let us break down this problem into smaller subproblems:
1. How many travellers are there?
2. When is the departure date?
3. When is the arrival date?
4. How long will the trip last?
5. What are the places to visit?
Pattern recognition is a data analysis method that uses machine learning algorithms to automatically recognise patterns and regularities in data. This data can be anything from text and images to sounds or other definable qualities. Pattern recognition systems can recognise familiar patterns quickly and accurately.
Now, to identify the places to visit in Nainital, we need to identify the pattern of people frequently visiting places.
The technique we use to identify the most visited places is pattern recognition. Pattern recognition is also applied when we observe our current problems and check if a previously identified solution can solve them.
Abstraction means focusing on the most important parts and ignoring the details that don’t matter.
Imagine you want to go on a hike during your trip. You can bring a map of the hiking route with you. Maps are a great example of abstraction. You can just focus on the hiking route you will take. This way, you can leave out all the unnecessary details on the map that you don’t need to know to go on this hike.
In computer science, the set of steps that solves a specific problem is called an algorithm.
Algorithmic design is a critical problem-solving skill. It strengthens the ability to create a process for finding a solution as opposed to focusing on the answer itself.

While trekking, when we reach the top, we need to set up a tent to spend the night there.
Let us look at the steps to set up the tent:
1. Find a clean, flat spot.
2. Lay out the tent and its parts.
3. Connect the sticks and put them through the tent.
4. Attach the cover and secure it with pegs.
5. Double-check everything to make sure it’s set up right.
This set of steps makes the task of building the tent much easier.
One of the main reasons that algorithmic thinking is important for students is because it enhances a student’s ability to think critically. It broadens their minds to the additional capabilities of a particular solution and helps them see a problem more holistically.
After understanding the computational thinking approach and its usage for problem-solving, let’s explore algorithms and flowcharts.

In what ways can computational thinking be integrated into various subjects, such as mathematics, science, or social studies, to enhance problem-solving skills and critical thinking?


An algorithm is a step-by-step process to complete a task or solve a particular problem.
The key characteristics of a good algorithm are:
Clear Inputs and Outputs: A good algorithm specifies what information is needed at the beginning (inputs) and what it will produce at the end (outputs).
No Ambiguity: Its instructions must be crystal clear, avoiding any confusion.
Precise Steps: It should offer specific steps for problem-solving, eliminating uncertainties.
Efficiency: A good algorithm should solve problems quickly and efficiently.
Termination: It must end after a finite number of steps, preventing endless loops.
Universal: Algorithms should work across various programming languages, ensuring versatility.
These qualities make algorithms effective and reliable for solving a wide range of problems.


To learn more about computational thinking, scan the QR code.


Imagine you have a box of colourful crayons. You want to arrange them in a pattern, but you can use only two colours at a time. How would you create a beautiful pattern using your crayons?
The steps to develop an algorithm are:
1. Understanding the Problem: Clearly understand the problem to be solved.

2. Defining Inputs and Outputs: Identify what information the algorithm will take as an input and what it will produce as an output.
3. Designing the Algorithm: Plan the step-by-step process to solve the problem.
4. Testing and Debugging: Testing is the process of evaluating a software application or code to identify and fix issues or bugs. Debugging is the process of identifying, analysing, and fixing errors or bugs in the code that cause the software to behave incorrectly.

How can computational thinking concepts, such as algorithms and problem-solving, be applied to everyday life situations outside the classroom?
Here is an example of an algorithm.
Example: Algorithm to go to school:
Step 1: Wake up.
Step 2: Get ready.
Step 3: Have breakfast.
Step 4: Check your bag.
Fill in the blanks.

Step 5: Keep your lunch and bottle.
Step 6: Leave home.
Step 7: Travel to school.
Step 8: Stop.
1 Computational thinking involves breaking down complex problems into steps.
2 is a process of simplifying a problem by removing unnecessary details.

Algorithms can be written in various forms, including natural language, pseudocode, or programming languages like Python. Some samples of how an algorithm can be expressed in various forms are:
Algorithm: Calculate the sum of two numbers
Step 1: Start
Step 2: Get the first number
Step 3: Get the second number
Step 4: Add the first number to the second number
Step 5: Display the result as the sum
Step 6: Stop
Algorithm: Calculate the sum of two numbers. START
INPUT firstNumber
INPUT secondNumber
result = firstNumber + secondNumber
OUTPUT result END
Algorithm: Calculate the sum of two numbers
# Input
num1 = float (input (''Enter the first number: ''))
num2 = float (input (''Enter the second number: ''))
# Calculate the sum sum_result = num1 + num2
# Display the result
print (''The sum of'', num1, ''and'', num2, ''is:'', sum_result)

These samples illustrate how the same algorithm, which calculates the sum of two numbers, can be expressed in natural language, pseudocode, and the Python programming language. Each form provides a way to describe the steps involved in solving a problem, catering to various levels of detail and specificity.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a technology that helps computers process data, recognise patterns, and make predictions. To do this, AI also uses the same steps as computational thinking.
Decomposition (Breaking down problems): When AI translates a sentence from English to Hindi, it does not do it all at once. Instead, it breaks the sentence into smaller parts—words, grammar, and meaning—before building the translation.
Pattern Recognition: AI learns by finding patterns in data. For example, a face recognition system compares new faces with stored patterns of eyes, nose, and mouth to identify a person.
Abstraction (Focusing on important details): A self-driving car ignores unnecessary details like the colour of a building. Instead, it focuses only on what matters—traffic lights, road signs, and pedestrians.
Algorithmic Design (Step-by-step solutions): Virtual assistants like Siri or Google Assistant follow algorithms to answer your questions. For example, if you ask, “What’s the weather today?”, the AI follows steps: detect your voice → understand the question → fetch data → give an answer.
A flowchart is a visual representation of an algorithm or process, using symbols and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps.


To learn more about algorithmic thinking, scan this QR code.
Think and Tell
Imagine you are a chef, and your job is to bake a perfect chocolate cake. Just like following a recipe, you have to follow a set of step-by-step instructions. What do you think would happen if you mixed up the steps or left some out? How important is it to follow the ‘algorithm’ (recipe) correctly when baking a cake?

Flowcharts use symbols such as rectangles, diamonds, ovals, and arrows to represent various elements and actions, such as processes, decisions, and the flow of control of an algorithm.
The following figure shows the symbol, its name, and its description:
SymbolSymbol Name
Description
Start/stop terminalThis symbol is used to represent the start and stop of the flowchart.
Input/outputThis symbol is used to represent the input and output of the flowchart.
ProcessingThis symbol is used to represent the processing like arithmetic operations, data assignments, etc.
Decision This symbol is used to check whether condition is true (yes) or false (no).
Flow lines (arrows) This symbol is used to connect the symbols. It indicates the direction of the flow.
From simple calculations to complex decision-making processes, flowcharts are employed to address a wide range of problems. They help visualise solutions and dissect challenges into manageable steps. Here is an example of a flowchart that calculates the sum of two numbers.
= num1 + num2

If you want to determine whether the sum of two numbers is even or odd, you need to use a decision block (often represented by a diamond shape in flowcharts). Here is an updated flowchart that includes a decision block:
Input variables num1, num2, and sum
Read num1 and num2
sum = num1 + num2
In a real-world scenario, think about how you would apply computational thinking elements like decomposition, pattern matching, abstraction, and algorithm design to plan and organise a school event, such as a science fair. Describe how you would use these elements to ensure that the event runs smoothly and efficiently.
1 Computational thinking is a strategy for solving problems that is used to handle complex problems.
2 Decomposition is the process of breaking problems into smaller ones in order to make them easier to solve.
3 To establish detailed problem-solving techniques, algorithms are built.
4 A fundamental idea is an abstraction, which focuses on important aspects while discarding unimportant details.
5 Pattern recognition simplifies the identification of recurring themes within problem solutions.
6 Algorithmic thinking is a component of computational thinking. It emphasises creating step-by-step algorithms to solve specific problems.
7 An algorithm is a step-by-step process to complete a task or solve a particular problem.
8 A flowchart is a visual representation of an algorithm or process using symbols and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps.
Hints pattern algorithmic simpler solving flowchart
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 Computational thinking is a strategy for problems that is used to handle complex problems.
2 A is a visual representation of an algorithm or process using symbols and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps.
3 The four pillars that define computational thinking are decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and design.
4 Decomposition is the process of breaking down complex problems into parts.
5 recognition simplifies the identification of recurring themes within problem solutions.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 What is computational thinking?
a A type of computer programming language
c A hardware component of a computer
2 Algorithmic thinking involves:
a Creating random steps to solve a problem
b Developing a step-by-step process for problem-solving
c Drawing pictures to represent solutions
d Ignoring data and patterns
3 Which of the following is NOT a pillar of computational thinking?
a Decomposition
c Abstraction
b A strategy for solving problems
d A type of computer virus
b Pattern recognition
d Flowchart
4 When you break down a complex problem into smaller, manageable parts, you are using:
a Pattern recognition
c Decomposition
5 An algorithm must be:
a Ambiguous and open to interpretation
c Well-defined and unambiguous
b Abstraction
d Algorithmic design
b Written in natural language
d Complex and lengthy

C. Who am I?
1 I focus on the most important parts and ignore the details that don’t matter.
2 I am a step-by-step set of instructions for solving a specific problem.
3 I involve recognising patterns and similarities in data to make sense of information.
4 I am a fundamental concept in computer science, involving the development of efficient problem-solving strategies.
5 I am the visual representation of an algorithm or process using symbols and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Abstraction is one of the key pillars of computational thinking.
2 An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem.
3 Algorithms should work across various programming languages, ensuring versatility.
4 Computational thinking is only applicable to computer science and programming.
5 A good flowchart should solve problems quickly and efficiently.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 What is computational thinking, and how does it differ from algorithmic thinking?
2 Why do you use the decision box in a flowchart? Explain.
3 Write the names of any two symbols that are used in a flowchart. Also, draw their symbols and write their functions.
4 Write any three characteristics of an algorithm.
5 What is the benefit of using an algorithm and a flowchart together?




1 Pari wants to design a step-by-step algorithm to plan a trip. Help her do so.
2 Roop has been given the task of drawing a flowchart to calculate the area of a circle. How can she do it?
3 Lakshay wants to create a flowchart for calculating the average of a list of numbers. Help him by discussing all the symbols used to create a flowchart.
4 Shaurya wants to display a condition X < Y while creating a flowchart. Suggest her the correct shape to put the statement.
5 Pihu has drawn a flowchart, but she used a wrong shape to display the statement Z = A + B + C. Suggest her a correct shape to put the statement.








Suppose you are ordering food for dinner tonight. You will fetch your phone, use a food ordering app, and place the order. It is that simple!
Your smartphone must have a variety of apps. Do you ever realise how these apps are created and how they work? Well, you will learn about apps in this chapter.
Apps or Applications are software programs or mobile applications that can be downloaded and installed on electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and computers. These apps serve various purposes and can be used for playing games, accessing social media, learning, productivity, communication, and many other activities. You are likely to be familiar with popular apps and may use them regularly for entertainment, education, or communication.


In short, an app refers to a program or software application designed to perform specific tasks or functions on a computer, smartphone, tablet, or other kinds of digital devices.
The first mobile app store was launched by Apple in July 2008, alongside the release of the iPhone 3G. It was called the “App Store,” and it initially featured 500 apps.
1. Social networking apps: Social networking apps are apps that help people connect and share with others online. They let you make friends, post updates, and chat. Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Snapchat, and X (formerly known as Twitter) are some of the commonly used Social Networking Apps.


2. Productivity apps: Productivity apps are apps that help you get things done and be more organised. Microsoft Word, Google Drive, Snapseed, Analytics, and YouTube Studio are a few examples of productivity apps.

3. Educational apps: Educational apps are digital apps designed to support learning and education across various subjects and skill levels. They include interactive learning platforms which offer engaging lessons; quiz apps, language learning tools, and educational games for younger learners. These apps enhance learning by providing interactive, accessible, and flexible educational experiences.

4. Gaming apps: Gaming apps are apps where you can play fun games. These apps provide entertainment and challenges, allowing you to explore virtual worlds, solve puzzles, or compete with others. Temple Run, Angry Birds, Spotify, Minecraft, and Fruit Ninja are a few examples of gaming apps.

5. Food delivery and cooking apps: Food and cooking apps are apps that help you discover recipes, cook delicious meals, learn about food, and order food. Zomato, Swiggy, DoorDash, Insta Mart, and Zepto are few examples of food delivery and cooking apps.










You can access apps from your mobile phone, desktop, or directly from the web. Let us learn all these methods to access the apps.





Think and Tell
What are the most popular apps according to you?

Desktop apps are like the computer version of the apps you use on your phone, but they are designed to work on your computer and do all sorts of different things, from writing documents to playing games or editing pictures.
Desktop apps are software applications that you can use on your computer or a laptop where they are installed and run locally. Desktop applications do not require an internet connection to run. For example, Microsoft Word is a desktop app that helps you write essays and stories on your computer. There are also games like Minecraft that you can play on your computer. Skype, Microsoft PowerPoint, Paint, Microsoft Excel, and iTunes are a few examples of desktop apps.

A web app is a software application that operates on web servers and is accessed by users through web browsers over the internet.
Web apps, short for web applications, are software applications that run on web servers and are accessed through web browsers over the internet. These applications provide a user interface and functionality similar to traditional desktop applications but are designed to be used within a web browser. Since web apps are hosted on web servers, users can access them from anywhere, using various devices, without the need for installation. This ease of accessibility is a significant advantage for both users and developers. Web apps can be accessed from any device with a web browser and an internet connection. They are not tied to a specific operating system, making them platform-independent. Padlet, YouTube, Gmail, and Google Drive are a few examples of web apps.




Mobile apps are programs you install on your phone to make it more fun or helpful for whatever you want to do.















A mobile app is a tiny computer program that you can download and use on your smartphone or tablet. It makes your phone do fun or useful things beyond making calls or sending texts. Mobile apps can be games you play, tools that help with homework, maps that show you where to go, or even things like filters that make your photos look improved. Mobile apps can be downloaded from the app stores available on your mobile. An app store can host large numbers of mobile apps. You can check the various features of the app you want to download and compare it with other related mobile apps available on the app store. Instagram, Camera, Telegram, iMusic, and Google Maps are a few examples of mobile apps.

















































































































To know more about web apps, scan this code.
1 Match the different types of apps with their suitable examples:
of App






































2 Fill in the
a and are social media apps.
b Apps can be and installed on electronic devices.
c run on web servers and are accessed through web browsers over the internet.
d You can download a mobile app from available on your phone.
Apps can be classified based on the technology used to create them, and their usage.
There are two types of apps based on how they are made. They are:
Native apps are specifically designed for a particular type of phone, such as iPhones or Android phones. They are known for their high speed and excellent performance because they are designed exclusively for your phone. Examples of native apps include Camera, Gallery, Clock, Maps, and Settings.

You Know?
Native apps can sometimes be used even without an internet connection! That is because they are installed directly on your device, and many of them store information on your phone. It is like having a little piece of the internet right on your device!
Hybrid apps can work on different types of phones and use web technologies, allowing them to work on multiple platforms and access device features. They are compatible with both iPhones and Android phones and can be downloaded and installed from their respective app stores, such as the Google Play Store for Android phones and Apple Music for iPhones. Although they may not match the speed and smoothness of native apps, they offer versatility by running on a wide range of smartphones. Examples of hybrid apps include Uber, Zomato, Instagram, Telegram, and X (formerly known as Twitter).

Native apps are built specifically for one type of mobile operating system, such as iOS (for Apple devices) or Android (for Android devices).
They typically offer the best performance and responsiveness because they are optimised for the particular device and its features.
Native apps have complete access to device features, like the camera, GPS, and sensors, allowing them to take full advantage of these capabilities.
They are distributed through platform-specific app stores like the Apple App Store and Google Play Store.
There are many apps based on their usage. They are:

Hybrid apps are developed using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and can run on multiple platforms (iOS, Android, etc.) with some modifications.
Hybrid apps might not feel as fast or quick as regular apps because they use a part that is like a web browser to show things, and that can be a bit slow.
Hybrid apps can access device features to some extent using plugins, but not as exclusively as native apps.
Hybrid apps can be distributed through web browsers as web applications. They can also be distributed through app stores.

Educational apps are software applications designed to facilitate learning and provide educational content on various subjects and skills. These apps are developed to make learning more engaging, interactive, and accessible for users of all ages, from children to adults.






How can we get hybrid apps onto our phones? Is it similar to how we get native apps?


Social networking apps are like virtual platforms where you can meet and talk to your friends and even make new ones. They are special apps on your phone or computer that help you connect with people, share things about your life, and see what your friends are up to.


Did you know that the "Like" button on Facebook was originally going to be called the "Awesome" button? Facebook's founder, Mark Zuckerberg, considered different names for it before settling on "Like". So, every time you click "Like" on a post, you are giving it a little touch of awesomeness!
Entertainment apps are online portals for having fun and enjoyment on your phone or tablet. They are special apps that offer all sorts of things to make you happy and have a great time.























Banking apps are like a virtual bank branch on your phone or tablet. They are the special apps provided by your bank to help you do immediate money transactions without going to the bank in person.








Name four native apps and four hybrid apps. Which one between the two categories do you use the most?
a These apps can help users develop a wide range of skills, including reading, writing, maths, and problem-solving.
b These apps are like virtual platforms where you can meet and talk to your friends.
c These apps provide you with help when you do important financial transactions.
d These apps let you shop for all sorts of things without having to go to a physical store.
e These apps are the portals for fun and enjoyment on your phone or tablet.
MIT App Inventor is a visual development platform that allows users to create mobile applications for Android devices without the need to write traditional codes. It is designed to make app development more accessible to a wide range of people, including those who do not have extensive programming experience. MIT App Inventor provides a visual, drag-and-drop interface for designing the user interface and functionality. Users can assemble components and connect blocks to create the app’s logic.
Let us create a simple app using MIT App Inventor.
The name of this app will be Magic_Button
The app will have the following components:
1. A button
2. An image (Download any image from the internet and save it on your computer for later use.)
These two components will be added to the app design. Initially, the image will not be visible. The idea is to display the image only after the user clicks on the button. Let us design the app now.
Visit the following link to open MIT App Inventor: https://appinventor.mit.edu/
The given screen appears:

Click on the Create Apps! Button.
A sign-in screen appears. You can use your Gmail ID to login, or you can create a new one as well.
After signing in, the Welcome to MIT App Inventor pop-up box appears. Click on the Continue button at the bottom of the screen.
Another screen appears, from which you can choose to view the tutorials or start a new blank project.
Click on START A BLANK PROJECT.
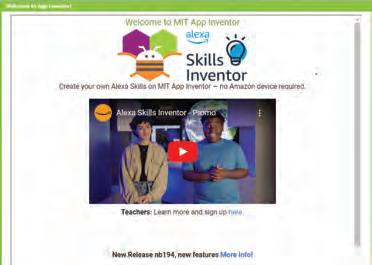
Continue Button
The Project View window appears.
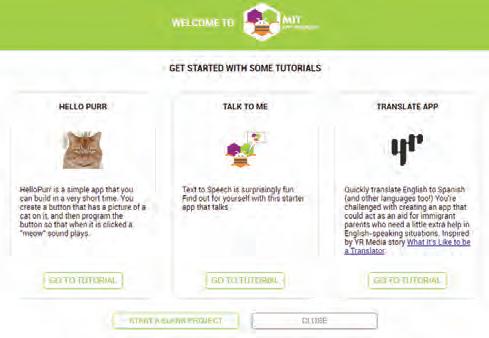
Click here to start a blank project
A dialog box appears, asking you to give a project name to your project.
Give an appropriate name to your project, for example, Magic_Button and click on OK
A new project with the same name will be created.
The Project View window will open.
The Project View window is divided into four sections:
Palette: Various components are presented under different categories in the palette.
Viewer: You can select any component from the palette and drag and drop it onto the screen in the Viewer section.
Components: The Components section shows the various components that are placed in the Viewer.
Properties: The Properties section shows the properties of the selected components.
Let us now create the interface of the app.
From the Palette section, click on the Layout tab.
Drag the VerticalArrangement component and place it on the screen in the Viewer section.
Now, click on the VerticalArrangement1 component in the Components section and go to the Properties section.

Scroll down to the Height property and click on it.
Select the Fill parent option and click on OK.
Similarly, select the same option for the Width property. The VerticalArrangement component will fill the whole screen.
Now, from the User Interface tab, drag the Button component and drop it on the screen.
You can also observe that the Button1 component is added under the Components section.
Now in the Properties section, scroll down to the Text property of the button. Replace the text “Text for Button1” with “Magic_Button”.
From the Palette section, drag the Button component and place it in the Viewer section on Screen1.
Now, change some more properties of the button in a similar way from the Properties section:
o Font Size: 20
o Background Colour: Cyan
o Text Colour: Blue
o Shape: Rounded
o Height: 10 percent
o Width: Fill parent
Now, drag an Image component from the User Interface section and place it on the screen.
From the Components section, select Image1 and click on the Picture option in the Properties section. A drop-down will appear. Click on the Upload File option.
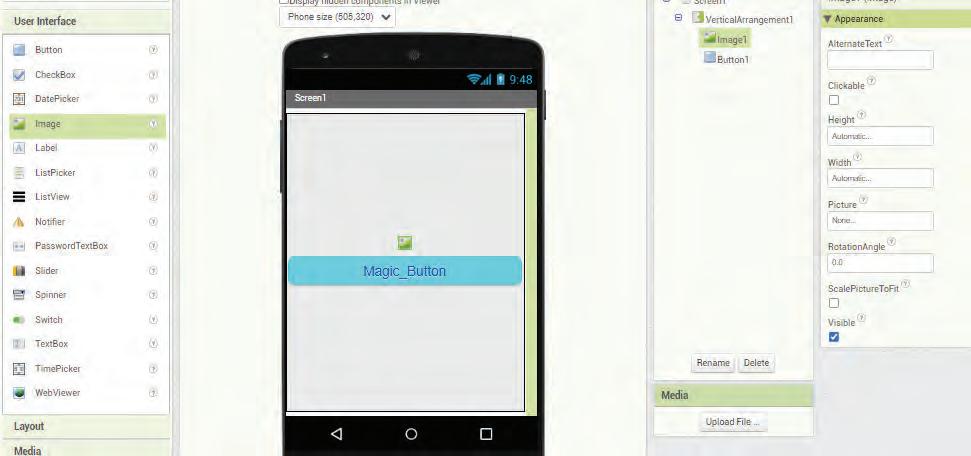
The Upload File dialog box will open. Click on the Choose File button.

An Open dialog box appears. Select the picture that you have downloaded from the internet and click on Open.
The image will appear on the screen.
You can now set the properties of the image.
o Height: Fill parent
o Width: Fill parent
o Visible: Uncheck (to hide the image initially)
After setting all the properties of both objects, the screen will look as shown here:


Once you have arranged the components on the screen, you can proceed to create the code for the app.
Coding in MIT App Inventor is very easy and user-friendly. You can create code for your app by using various blocks present in the Blocks Editor.
To create code for your app, follow the given steps:
Click on the Blocks Editor button on the right-hand upper corner of the Project View window.
The Blocks Editor will open with the Blocks section on the left and the Viewer section on the right.
Click on Screen1 > Button1 from the Blocks pane.
The blocks related to Button1 will appear.
Drag when Button1.Click block from the Blocks drawer and drop it in the Viewer pane.
Now, click on the Image1 component in the Blocks panel. The blocks related to the image are displayed.
Drag set Image1.Visible to block and drop it inside the when Button1.Click block.
Now, from the Built-in > Logic drawer, drag the true block and snap it together with the set Image1. Visible to block.
The code for your app is complete.
Now, when you click on the Magic_Button on your mobile app, you will see a picture of a flower.
To test your app, you will need a mobile phone.
Go to the Google Play Store of your android phone and search MIT AI2 Companion App.
Install the app by clicking on “Install”.
After installation, open the app. You have to provide a six-character code to connect.
Now, to get the code, go to your computer where you have created your app.
Go to the Connect menu and select the AI Companion option.

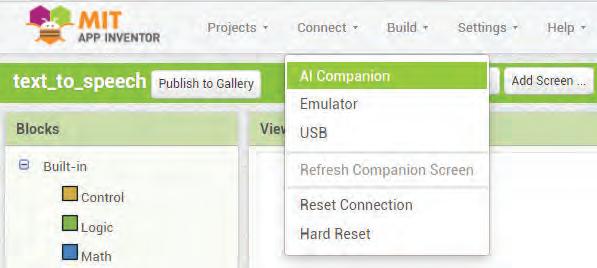
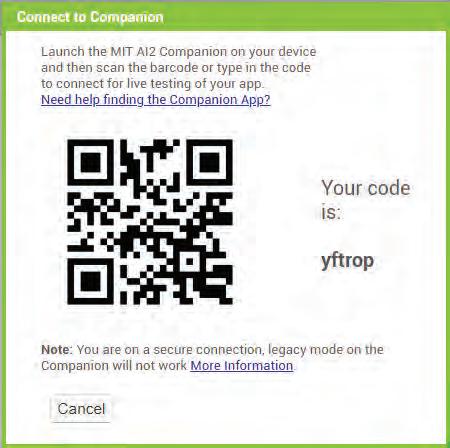


A Connect to Companion window will open with a six-character code.
You can now fill in this six-character code on the mobile phone app.
The app will now open on your mobile.
Click on the button that you have created, which is the Magic_Button.
You will be able to see an image of the flower.
Create an app on MIT App Inventor to show your name when you click on a button.

1 Apps or applications are software programs or mobile applications that can be downloaded and installed on electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and computers.
2 Social networking apps, productivity apps, gaming apps, food delivery and cooking apps are different types of apps.
3 You can access apps from your mobile phone, desktop, or directly from the web.
4 Desktop apps are software applications that you can use on your computer, just like you use games or apps on your smartphone.
5 Web apps, short for web applications, are software applications that run on web servers and are accessed through web browsers over the internet.
6 A mobile app is a tiny computer program that you can download and use on your smartphone or tablet.
7 Native apps are specifically designed for a particular type of phone, such as iPhones or Android phones.
8 Hybrid apps can work on different types of phones and use web technologies, allowing them to work on multiple platforms and access device features.
9 MIT App Inventor is a visual development platform that allows users to create mobile applications for Android devices without the need to write traditional codes.
A. Fill in the blanks.
An is a computer program that you can download and use on your smartphone or tablet. are special apps that let you shop for all sorts of things without having to go to a physical store. apps are developed using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript and can run on multiple platforms.
In MIT App Inventor, various components are present under different categories in apps are apps that help people connect and share with others online.
Who am I?
I am like a virtual bank branch on your phone or tablet.
I can assist you to design and make the app of your dreams.
I am a computer program that you can download and use on your smartphone.
I can show the properties of the selected components.
I am a type of app that can work on different types of phones, like both iPhones and Android phones.
C. Write T for True and F for False.
Apps are software programs that can be installed on your desktop.
There are two types of apps: hybrid and native.
Web apps do not operate on web servers and are not accessed by users through web browsers.
Native Apps provide the best performance as they are optimised for the particular device.
The Components section shows the various components that are placed in the Viewer.
D. Answer the following questions.

E. Apply your learning.
Ramesh wants to learn how to design an app on MIT App Inventor. Which website should he visit?
Tia wants to understand the e-commerce apps and know a few examples. Can you explain it to her?
Umang wants to download a specific app for his iPhone. Where can he get the app?
Geet is using her computer and wants to learn about web apps. Can you help her understand about them?
Meher has installed an app on her phone that was not a pre-loaded app. What type of app has she downloaded?







Do you help your parents to plan the household budget? Suppose your mother wants you to learn budget planning. So you decide to assist her in maintaining the monthly budget. Which application do you think is the most suitable for this task?
Yes, you can use a spreadsheet.
A spreadsheet is a tool that helps you organise data in rows and columns and do calculations. Spreadsheets also allow you to analyse and visualise data.









There are many spreadsheet software options available, such as Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets.
While Excel is a licenced software, you can use Google Sheets without purchasing any licence. Google Sheets allows you to create and collaborate on spreadsheets online.
Let us create a spreadsheet to plan the monthly budget. To do this, follow the given steps:
1. Open the Google Chrome browser and visit the link: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/
2. The home page appears, as shown below. Click on the plus ‘+’ sign to open a blank spreadsheet.
3. In your new spreadsheet, click on the Rename textbox given at the top left corner of the sheet and rename the file as, “Monthly Budget”.

A spreadsheet consists of a grid-like structure. The various components of a spreadsheet are discussed as follows:
Row: A horizontal line of boxes is called a row or record.
Column: A vertical line of boxes is called a column or field.
Cell: An intersection of a row and a column is called a cell.
Column/Field
Row/Record
Cell
A cell is a rectangular block in a spreadsheet that can hold data.
Data can be numbers, strings, or symbols.
To refer to a cell, we use cell names. A cell name is a combination of letters and numbers. Letters represent the column, and numbers represent the row.
For example, look at the adjoining image. The first cell will be called A1, where A stands for the column and 1 stands for the row.

Now, let us start entering the data in the sheet. Follow these steps:
1. Select a cell where you want to add data using the mouse or the arrow keys.
2. Enter numbers, text, or any other information you want to add data to the cell.
3. Press the Tab key to move to the next cell in a row.
4. Press the Enter key to move to the next cell in a column.
Now, type the data as shown in the given image.
In Google Sheets, a formula is an expression used to perform calculations and obtain results within the cells of the spreadsheet. Formulas always begin with an equal sign (=) followed by the mathematical expression. Now that you have added the details of your expenses, let us apply a formula to find the total expense.
Follow the given steps to do so:
1. Select the cell where you want the total to appear, for example, cell B13.
2. Type the equals sign ‘=’.
3. Now, click on the cell B3, type a plus ‘+’ symbol, and click on cell B4.
4. Repeat this process up to cell B12 and then press the Enter key. The sum of cells B3 to B12 will appear in cell B13.


To know how you can also insert images in the cell, scan this QR code.



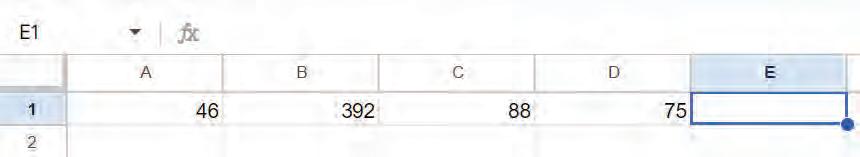

You have learnt in the previous section how to calculate the total amount using formulas. Now, you will see how using functions can make your work even easier and faster.
Functions allow you to calculate more efficiently using cell ranges instead of typing out the name of each cell
A cell range is a group of cells selected together. You can use cell ranges in the functions instead of selecting individual cells.
Functions are like built-in formulas in Google Sheets. They perform calculations, handle data, and analyse information.
Functions work with cell ranges. This saves time because you do not need to type each cell name separately. To type a cell range, first we type the name of the first cell, then a colon (:), and then the name of the last cell. For example, A1:A4.
To use a function, first type the ‘=’ sign, then the function name, followed by cell names or cell ranges inside the brackets.
For example, =SUM(A1:A4)
Let us try functions in place of formula to find the total monthly expense.
The SUM function is used to add the values given in a specific cell range. To use the SUM function, follow the given steps:
1. Click on the cell where you want the sum to appear, for example, cell B13.
2. Type an equal to symbol ‘=’ and then the function name SUM
3. Type the opening parentheses ‘(‘ after the function name.
4. Inside the brackets, add the cell range for which you want to calculate the total. For example, B3:B12.
5. Press Enter to complete. You can see the result in the cell B13.
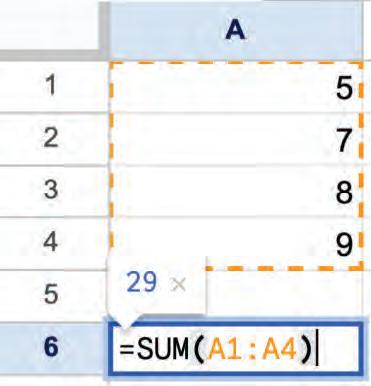
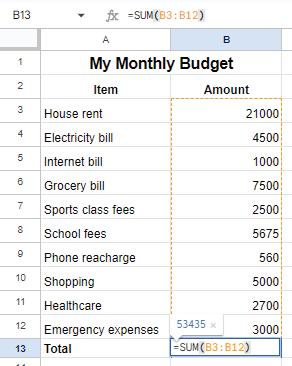
A group of friends went on a trip. Their individual expenses are given in the table below. Use a spreadsheet function to find the sum of all individual expenses (cells B2 through B8) and display the result in cell B10.
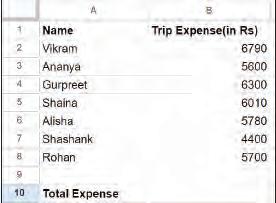
The Average function calculates the average of a range of numbers. To find the average monthly expense, you can use the average function as shown here:
=AVERAGE(B3:B12)
This function finds the average of all values in cells B3 through B12.
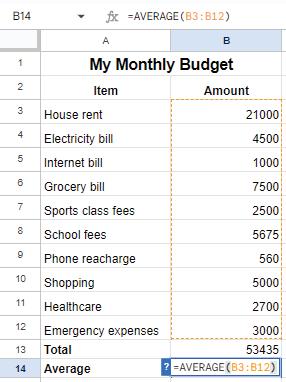

The Max function finds the maximum value in a range of numbers. To find the highest monthly expense, use the Max function as given here:
=MAX(B3:B12)
This function returns the highest value from cell B3 to B12.
You can use the Min function in a similar way to find the minimum value in a range of numbers. To find the lowest monthly expense, use the Min function as given below:
=MIN(B3:B12)
This function returns the lowest value from cell B3 to B12.
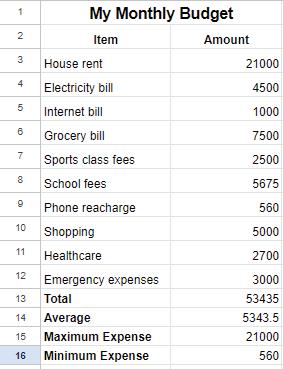
The Count function tells you how many cells contain numerical values. To find the number of cells that contain numbers in a given range, use the Count function as given here:
=COUNT(B3:B12)
This function counts the number of cells with numeric values from B3 to B12.
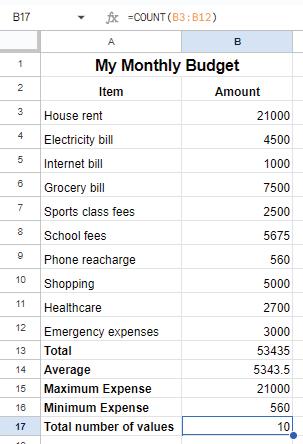
Let us learn about some more functions used in Google Sheets.
Apart from the functions used in the previous section, there are many functions that you can use to perform mathematical calculations.
Let us learn more about these functions.
This function gives you the remainder after dividing the dividend by the divisor.
Syntax: =MOD(Dividend, Divisor)
Example: =MOD(23, 5)
Result: 3
This function returns the square root of any number.
Syntax: =SQRT(Value)
Example: =SQRT(100)
Result: 10
This function rounds a given number down to the nearest integer.
Syntax: =INT(Value)
Example: =INT(5343.5)
Result: 5343
This function is used to raise a number to a specified power.
Syntax: =POWER(base, exponent)
Example: =POWER(10, 3)
Result: 1000
This function returns the absolute or non-negative value of a given number.
Syntax: =ABS(Value)
Example: =ABS (-243)
Result: 243

Apart from the mathematical functions, there are several text functions that can be used in Google Sheets. Let us learn about some commonly used text functions.
The CONCATENATE function is used to join multiple text strings into a single string. This is helpful when you want to combine information from different cells.
Syntax: =CONCATENATE(“text_string1”, “text_string2”)
Example: =CONCATENATE(“Hello”, “World”)
Result: HelloWorld
This function counts all characters in a cell, including letters, numbers, spaces, and punctuation marks.
Syntax: =LEN(“text_string”)
Example: =LEN(“Hello”)
Result: 5
This function converts all the text in a cell to uppercase letters.
Syntax: =UPPER(text)
Example: =UPPER(“Hello”)
Result: HELLO
This function converts all the text in a cell to lowercase letters.
Syntax: =LOWER(text)
Example: =LOWER(“Hello”)
Result: hello
You are tracking the number of hours you study, for different subjects, in a Google Sheet. Which function would you use to find the subject that you have studied the longest? Think and Tell
In order to work with dates and time, Google Sheets provides two important functions. Let us see how these functions work.

This function returns the current system date.
Syntax: =TODAY()
Example: = TODAY()
Result: 01/08/2024
This function returns both today’s date and the current time.
Syntax: =NOW()
Example: = NOW()
Result: 01/08/2024 10:30
Label the parts of the given function.
a b What will be the output of the following functions?
a MAX(12, 34, 87, 32, 52, 43)
b CONCATENATE(“My “, “ “, “Rules “)
c ABS(-23)
d POWER(20, 2)

How are formulas and functions

When we write a formula in Google Sheets, we often refer to other cells. This is called cell referencing. It helps Google Sheets know which cell’s value to use in a calculation. Let us learn about the three types of cell references.
• A relative reference is the default type of cell reference in Google Sheets. It means that when you copy a formula from one cell to another, the cell references in the formula automatically change based on their new position.
• Example: If you write =A1+B1 in cell C1 and copy it to C2, it becomes =A2+B2.
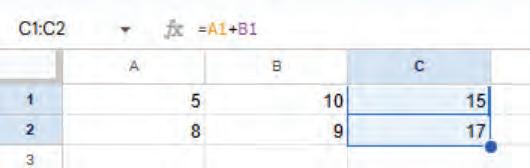

• An absolute reference keeps the cell address fixed even when you copy the formula to another cell. It is created by adding a ‘$’ sign before the column letter and row number (for example, $A$1). This ensures that the formula always refers to the same cell.
• Example: =$A$1+$B$1 will always refer to A1 and B1, no matter where you copy it.
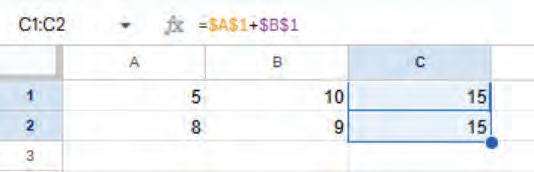
• A mixed reference is a combination of relative and absolute referencing. In this case, either the column or the row remains fixed, while the other changes when the formula is copied.
• $A1 fixes the column A only.
• A$1 fixes the row 1 only.
These references help when you want some parts of a formula to change and others to remain constant.
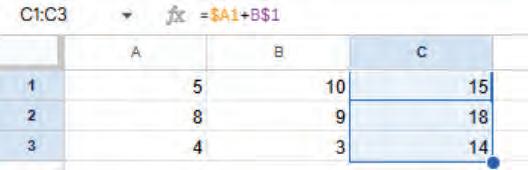
1 A spreadsheet is a tool that helps you organise data and do calculations.
2 A cell is a rectangular block in the sheet that can hold data.
3 A cell name is a combination of letters and numbers.
4 Functions are pre-built formulas that you can use to perform various calculations or operations on your data.
5 A cell range is a group of cells selected together.
6 Some common functions used in Google Sheets are: SUM (adding numbers), AVERAGE (finding the mean value), MAX (finding the highest value), MIN (finding the lowest value), and COUNT (counting the number of cells with numbers).
7 Some common text functions are: CONCATENATE(joining text strings), LEN(finding length of string), LOWER(converting string to lowercase), and UPPER(converting string to uppercase).
8 Two important date and time functions are: TODAY(returns today’s date) and NOW(returns today’s date and current time).
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints Max Average cell Now numbers
1 A is a rectangular block in a spreadsheet that can hold data.
2 To refer to a cell in a spreadsheet, we use a combination of letters and .
3 The function finds the maximum value in a range of numbers.
4 The function is used to find the average of a range of numbers.
5 The function returns the current date and time.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Which function is used to find the minimum value in a range of numbers?
a MAX
c AVERAGE
2 How do you create a cell range for cells A1 to A4?
a A1,A4
c A1-A4
3 Which function would you use to join text strings together?
a UPPER
c LEN
b MIN
d COUNT
b A1:A4
d A1 to A4
b CONCATENATE
d SUM
4 To get the current system date in a cell, which function would you use?
a NOW()
c DATE()
5 The function =SQRT(16) returns:
a 4
c 16
C. Who am I?
1 I return the highest value from a set of numbers.
b TODAY()
d TIME()
b 8
d 2
2 I count the number of cells that contain numeric values in a range.
3 I add all values in a specified cell range together.
4 I convert all text in a cell to lowercase letters.
5 I provide the current date and time.

D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Google Sheets is a licensed software like Microsoft Excel.
2 The COUNT function counts the number of cells that contain text.
3 The SUM function adds up all the values in a specified cell range.
4 The MOD function returns the remainder when one number is divided by another.
5 The LOWER function converts all the text in a cell to uppercase letters.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 What is the purpose of the LEN function in Google Sheets?
2 How do you move to the next cell in a row after entering data?
3 What is a cell range in Google Sheets?
4 Which function calculates the square root of a number?
5 Describe the process to find the total expense using the SUM function.
6 What is an absolute reference in a spreadsheet?
F. Apply your learning.
1 You have a list of your monthly grocery expenses in cells C3 to C10. Create a formula to calculate the total amount spent using the SUM function.
2 Sunny recorded the daily high temperatures for a week in cells D5 to D15. How can he find out the average temperature for that week?
3 Smriti has entered a value in a cell, E2, with the name “john smith.” Which function can she use to convert this name to uppercase?
4 Raima wants to find out how many apples are left after each person takes 3 apples from a total of 20 apples. Which function can she use?
5 Seema needs to add the current date to a report. Which function will be useful for her?
Objective: To understand how Google Sheets’ AI can suggest correct formulas when students work with data.
Activity: Enter marks data in Google Sheets and use AI-powered formula suggestions to calculate totals and averages.
Solution: Follow the given steps:
1 Open a new Google Sheet and type this data:
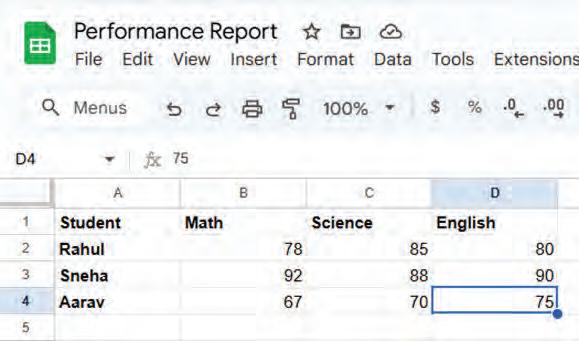

2 Add a new column named Total
3 Click in Rahul’s Total cell (E2).
4 Start typing ‘=’.
5 Google Sheets AI will suggest =SUM(B2:D2).
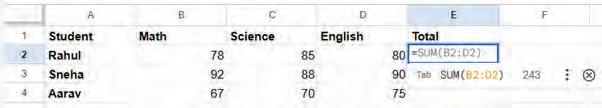
6 Press Tab/Enter to accept the suggestion.
7 Autofill the formula for other students.
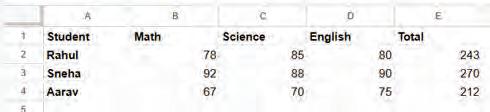
8 Similarly, add a new column: Average.
9 Click in Rahul’s Average cell (F2).
10 Start typing ‘=’.
11 Google Sheets will suggest =AVERAGE(B2:D2).
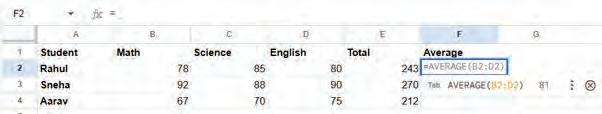
12 Press Tab/Enter to accept.
13 Autofill for other students.
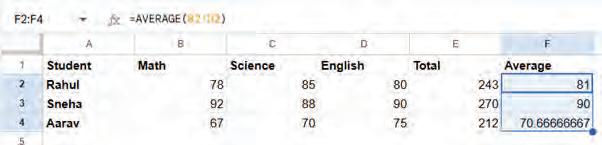





Data Visualisation Using Spreadsheets


You have created a Google spreadsheet in the previous chapter for your monthly budget. However, analysing and drawing conclusions from the numbers in the sheet can be challenging. What if you could ‘see’ the data visually to help analyse and interpret the results? Yes, that is possible in Google Spreadsheets. You can organise your data, group sheets, filter information, and create charts based on the data in your spreadsheet. In this chapter, we will explore these concepts in detail.
Sorting means to arrange data in a particular sequence based on specific criteria. It allows us to reorganise data in rows or columns, making it simpler to locate, analyse, and understand. Let us again consider the example of the monthly budget sheet. Suppose you want to find out which item is the most expensive. Then, you can sort the data of the sheet in descending order. To do so, follow the steps:
1. Choose the range of cells that contains the data you want to sort.
2. Go to the Data menu.
3. Select Sort range > Advanced range sorting options from the menu.
4. A dialog box appears. In the Sort by drop-down, select Column B and then check Z to A checkbox to arrange data in column B in the descending order.
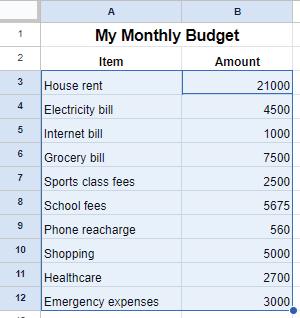
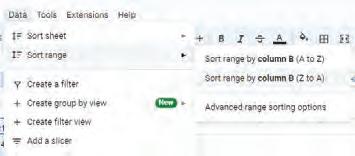
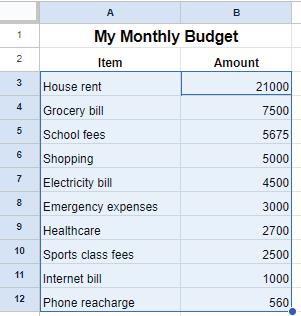
Suppose you are interested in finding out how many entries for bills are there in the monthly budget sheet. This way, you can display each bill entry just once, without repeating it multiple times. This is done with the help of grouping of data.
Grouping in Google Sheets means combining rows or columns into a collapsible section. It keeps the sheet tidy but does not remove duplicate entries.
Follow the steps to group data in the monthly budget sheet:
1. Select the rows that you want to group. Then, go to the View menu.
2. Select the Group option > Group rows 4-6.
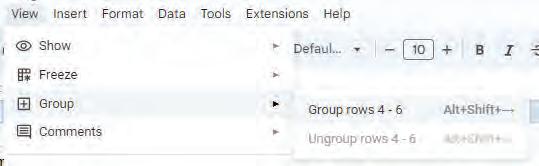
3. Use the plus ‘+’ button to show the group and the minus ‘−’ button to hide the group.
Suppose you want to see only those items that cost more than ₹5000. To resolve this, we use the Filters. Filters in Google Sheets allow you to display only the data that meets specific criteria. Filters can help narrow down the options to what we want and hide the rest. Filtering allows us to focus on specific parts of our data that meet certain conditions.
By using filters in spreadsheets, you can easily find specific data, answer specific questions, and understand information in a better way. Let us try to filter data to find items that cost more than ₹5000 in the monthly budget sheet.
1. Select the range to which you want to apply the filter.
2. Go to the Data menu and choose Create a filter option.


3. Click on the Filter symbol and select Filter by condition and choose your rule.
4. Here, we must select the Greater than condition and put 5000 in the Value or formula box.
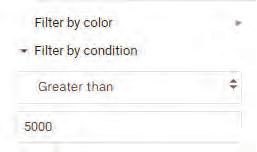
5. After selecting the required rule, click OK.
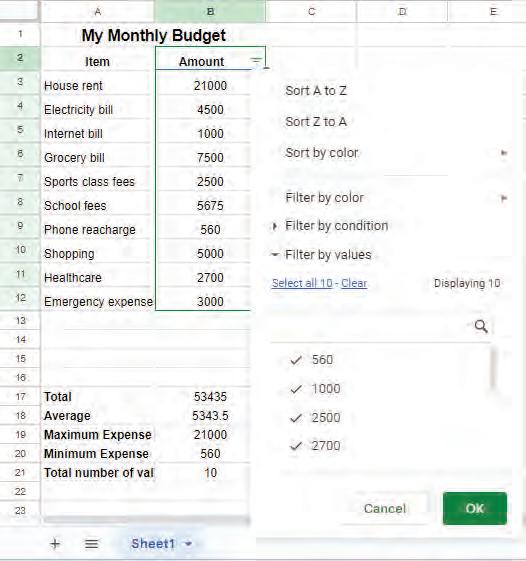
6. The spreadsheet hides unmatched rows, showing only the data that fits the selected criteria.
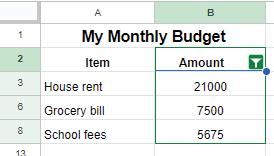



You have a list of animals in a spreadsheet, and you want to see only the ones that are mammals. What should you use?
a Sorting
b Filtering
c Formatting
d Deleting
Write T for True and F for False.
List of Animals
Animals Class
Lion Mammals
Crocodile Reptiles
Shark Fish
Tortoise Reptiles
Giraffe Mammals
Elephant Mammals
Kangaroo Mammals
a You have created a list of cars and their speeds in a Google Sheet. You can use the sorting feature to put them in order from the highest to the lowest speed to view the fastest car at the top.
b Grouping data is only useful when working with numbers, and it does not apply to other types of information.
Charts help us look at data in the form of pictures. This helps us to understand the data in a better way.
Charts are common in everyday life, such as weather forecasts on TV. These charts use colourful images and symbols to display daily temperatures or chances of rain. Just like looking at the weather without too many numbers, charts help us see information in pictures, making it easier for our eyes and brains to quickly understand.
In Google Sheets, there are various types of charts available to visually represent data. Let us explore some common types of charts:
Column Chart: It uses vertical bars for comparing data or showing quantities. Each bar represents a category, and its height shows the value or amount.
Bar Chart: It is similar to a column chart but with horizontal bars. Each bar represents a category, and its length shows the value or amount.
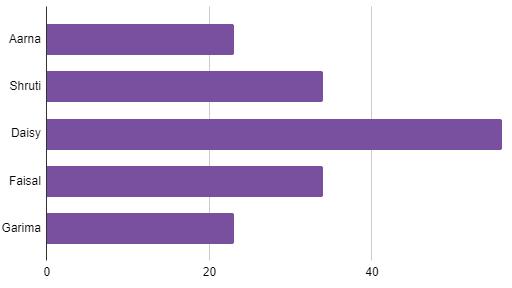
Pie Chart: It displays parts of a whole as slices of a pizza. Each slice represents a category, and its size shows the proportion or percentage.
Line Chart: A line chart shows how data changes over time by connecting dots. This helps us spot trends, such as temperature changes throughout a year or the progression of a plant’s growth.

Follow the given steps to create a chart:
1. Choose the cells that contain the data you want to present in the chart.
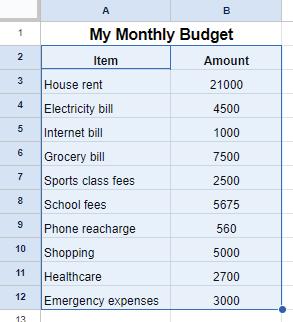
2. Go to the Insert tab and select the Chart option.
3. A chart will appear along with a Chart editor menu on the right-hand side of the page.
4. Select the appropriate type of chart from the Chart editor menu. In this example, we are creating a column chart.
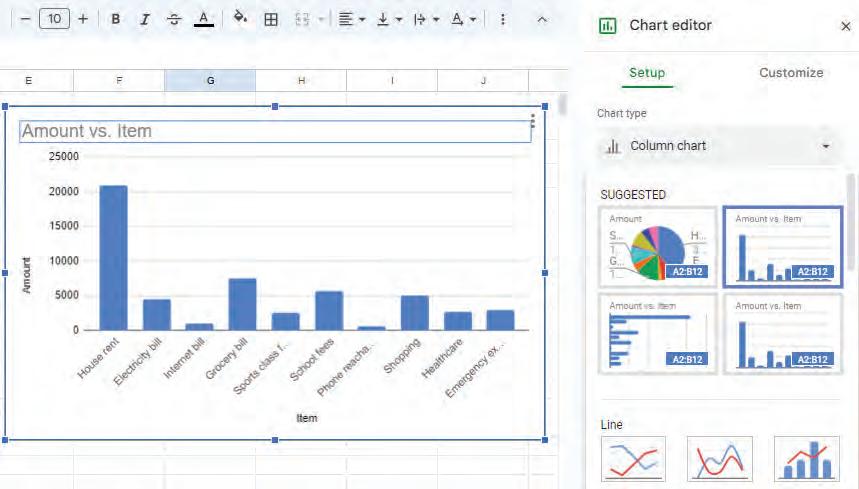
5. Once you have selected a chart type, you can customise it from the Customize tab in the Chart editor menu. As you can see in the image, the background is changed to light yellow, and the 3D version of the chart is enabled.
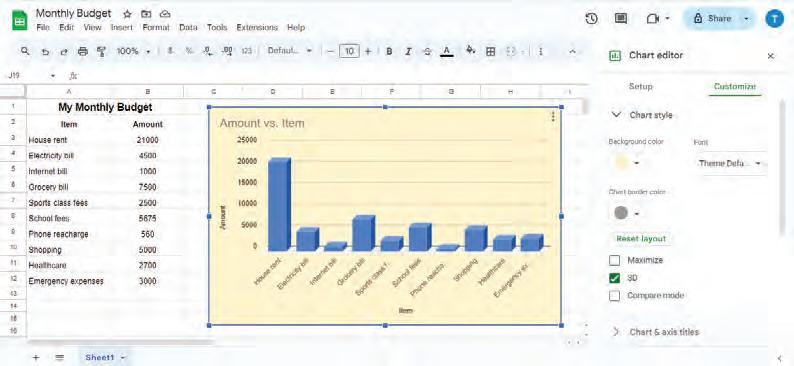
So far, you have been working on the monthly budget sheet. If you want to track your subject marks throughout the year, you do not need to create a new spreadsheet. Instead, you can keep adding new sheets in the same spreadsheet.


Scan this QR code to know about plenty of different types of charts in Google Spreadsheets.
To add a new sheet tab in Google Sheets, follow the given steps:
1. Click on the plus ‘+’ symbol at the bottom left corner of the Google sheet.
2. A new sheet tab will appear, ready for you to work on.
Colouring sheet tabs in a Google Spreadsheet means giving different colours to the names of the sheets.
Let us colour-code the sheet tabs to organise the spreadsheet, making it easier to find the information you need.
The steps for colouring sheet tabs are:
1. Right-click on the tab you want to colour.

2. Click on the Change color option.
3. A palette of colours will be displayed. Select the colour you like by clicking on it. The sheet tab will be coloured.

In Google Sheets, every file can have multiple sheet tabs. Naming them properly helps keep your data organised.
To name or rename a sheet:
1. Double-click the sheet tab (like Sheet 1), type a new name, and press Enter.
2. You can also right-click the sheet tab and choose Rename from the menu.
To delete a sheet:
1. Right-click the sheet tab, select Delete, and click OK to confirm.
Tick () the correct answer.
1 Why do we use charts in Google Sheets?
a To make the data look fancy
b To make the numbers bigger
c To help understand and analyse data more easily
d To hide the data from others
2 Which type of chart looks like a pizza divided into slices?
a Bar chart b Line graph c Pie chart d Scatter plot
Sorting refers to arranging data in rows and columns based on specific criteria.
Grouping means putting related rows or columns together to keep the sheet tidy.
Filters in Google Sheets allow you to display only the data that meets specific criteria.
Charts visually represent data to make it easier to understand.
Column Chart uses vertical bars for comparing data or showing quantities.
A bar chart uses rectangular bars to compare quantities.
Pie Chart displays parts of a whole as slices of a pizza.
A line chart shows how data changes over time by connecting points.
Colouring sheet tabs in a Google Spreadsheet means giving different colours to the names of the sheets.
A. Fill in the blanks.
A bar chart is like a graph made up of colourful rectangular bars, where each bar represents a category, and its shows the value or amount.
data helps to organise data in rows or columns based on specific criteria.
Charts are representation of data.
data means putting similar things together to keep the data tidy.
A chart uses lines to show how something changes over time by connecting dots.

B. Tick () the correct option.
Which type of chart would you use to display the progression of a plant’s growth?
a Column chart
c Pie chart
Grouping in spreadsheets refers to:
a Colouring sheet tabs
c Combining related rows or columns together
What do charts do in spreadsheets?
a Perform calculations
c Sort data alphabetically
b Bar chart
d Line chart
b Arranging data in a specific order
d Creating formulas to perform calculations
b Show data visually and help understand it
d Change the font style of the spreadsheet
What symbol is used to show a grouped set of rows in Google Sheets? a ‘*’
What feature in Google Sheets helps you display only items that meet certain conditions?
a Sorting
b Grouping
c Filtering d Charts
C. Who am I?
I help you to reorganise data to make it simpler to locate and understand.
I put similar items together to keep things tidy in a spreadsheet.
3
I am a type of chart that uses colourful and rectangular vertical bars to compare quantities or values.
I am a process in spreadsheets that enable you to display data according to a specific criteria.
I am a symbol used to add sheet tabs in Google Sheets.
D. Write T for True or F for False.
Pie charts are suitable for comparing quantities or values, while line graphs are used to show changes over time.
Filtering data in spreadsheets permanently removes hidden rows or columns from the dataset.
Sorting in spreadsheets refers to arranging data in a specific order based on certain criteria, making it easier to locate and analyse.
You can colour sheet tabs in Google Sheets to organise different sheets better.
Grouping data helps you to display items without repeating them multiple times.
E. Answer the following questions.
How does grouping data help in organising a spreadsheet?
What is a line chart used for?
Describe the steps to apply a filter in Google Sheets.
How can you add a new sheet tab in Google Sheets?
Which type of chart is best for showing the names of different sports and the number of students who like each sport?

F. Apply your learning.
Ishita has to organise a list of words in dictionary order. What methods should she use to convert List 1 into List 2?
Arjun has recorded the prices of various canteen items in a spreadsheet. Which option can he use to find out the most expensive item in the list?
Ravi is a sales person in an organisation. He maintains the sales data in a Google spreadsheet. Which feature of spreadsheets should he use to display only those items that have sold more than 50 units.

Suppose you are creating a mathematics project based on distances of different places from your school. You are recording the data in a spreadsheet. Now, you want to create a similar type of project for science subject where you have to record the distance of different planets from the Sun.
How will you add a new sheet in the same spreadsheet?
Akhil owns a grocery shop. He wants to see how many items in his shop share the same price. Which option can he use to do so?
Objective: To observe how Google Sheets’ AI automatically suggests different chart types for different kinds of data.
Activity: Enter different datasets in Google Sheet and compare the AI-suggested charts.
Solution: Dataset 1: Categories (Pie Chart)
1 Enter the data:
2 Choose the cells that contain the data you want to present in the chart.
3 Go to the Insert tab and select the Chart option.
4 Google Sheets usually suggests a Pie Chart, since data represents parts of a whole.
Dataset 2: Column Chart (Comparisons)
1 Similarly, enter the following data and observe which chart type the AI suggests.
2 Google Sheets usually suggests a Column Chart (good for comparisons).
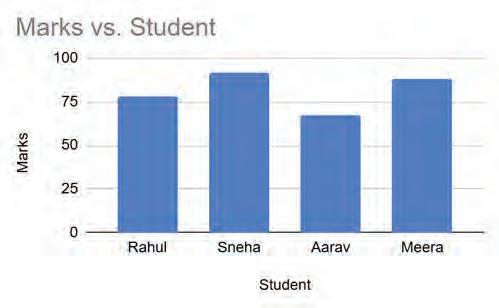
3 Remember, AI tools don’t always suggest the perfect option. They make guesses based on patterns in the data, but sometimes the choice may not be the most suitable.






When you visit your school library, you can observe that the books are organised in a very systematic manner. You go to the particular bookshelf and fetch the book that you need. Then you ask the librarian to issue it to you. How do you think these books are organised in such a manner?
Yes, they have been given a unique number, and then they are arranged according to their genre, author, date of publication, etc.
Now, think of the same data being organised on a computer. This data can be maintained on a computer, also known as a database.
When we maintain data in an organised and structured manner in digital form on a computer, it is called a database.
It is a group of related facts organised together so that they can be accessed, controlled, and modified. It is an organised method of saving and finding information.
Where have you seen the use of a database in your daily life?
A database is a collection of tables, where each table consists of rows and columns. Each row represents a single record, and each column denotes a single piece of information surrounding that record.

A table is a grid-like structure consisting of rows and columns. In a database, the columns are referred to as fields and the rows are referred to as records.
Field: It is the title at the top of each column, describing what kind of data is in the column. It is also referred to as an attribute.
Record: It is a row in the table, containing all the information for one entry.
Shreya Delhi 998877665512-03-2010
Asmi Noida 334455667723-09-2011
Aarna Gurgaon 786756453404-04-2011
Records
In the above table, Student_Name, Location, Phone Number, and Date of Birth are the fields in the table and [Shreya, Delhi, 9988776655, 12-03-2010], [Asmi, Noida, 3344556677, 23-09-2011], [Aarna, Gurgaon, 7867564534, 04-04-2011] are the three records in the table.

Databases are used to store several types of information, such as customer records, product data, and medical records. They are used by almost all organisations, governments, and businesses to keep their records in a systematic manner.

In the 1960s, the first databases emerged with hierarchical models. Relational databases, introduced in the 1970s by E.F. Codd, revolutionised data management, leading to modern database systems.
Here are some of the advantages of using a database:
It can carry vast quantities of data.
It can organise data in a manner that makes it easier to retrieve.
It can be used to modify and erase data rapidly.
It can be used to share data with others. Is it important for data to be


A database management system (DBMS) is a software application that enables you to construct, operate, and interact with databases. Some common examples of DBMS are MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and Oracle.
Here are some of the key roles or functions of a DBMS:
Storing Data: A DBMS can retain a huge amount of data in an organised form. This makes it easy and simple to access and recover the data when necessary.
Managing Data: A DBMS can manage the data in a database, such as adding, removing, modifying, and restoring data. It may also help to ensure that the data is genuine and consistent.
Protecting Data: A DBMS can protect the data in a database from unauthorised entry, change, or loss. It can do this by applying security measures such as user login and encryption.
Querying Data: You can access a specified piece of information from the database by making use of queries. This means that users may ask questions about the data, and the DBMS will deliver the results of the query.

A database is a structured data storage system used to store, organise, and retrieve information. It has evolved from manual systems to digital databases, playing a crucial role in modern data management.
Here are the various types of DBMS systems:
Hierarchical Database Management System (HDBMS) keeps data in a tree-like structure. Each record may have one or more child records, and each child record might have one or more grandchild records. HDBMS are well-suited for maintaining data that has a natural order, such as the structure of a corporation or the arrangement of plants and animals. Some examples of HDBMSs include IBM’s Information Management System (IMS) and the Integrated Data Store (IDS).
Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) are the most commonly used type of DBMS. They hold data in the form of tables, which are made up of rows and columns. Each row represents a record, and each column indicates a field. RDBMS are highly efficient in preserving and locating data, and they are also quite adaptable. Some notable RDBMSs include MySQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
Object-Oriented Database Management System (OODBMS) stores data in the form of objects. Objects are like records, but they may also have methods, which are like functions. OODBMS is well-suited for keeping complicated data, such as data that is tied to things in the real world.
Network Database Management System (NDBMS) stores data in a network-like structure. Each record may have one or more parent records, and each parent record might have one or more child records. NDBMS are well-suited for maintaining data that involves a complicated connection between records, such as airline routes between cities.
Do you think that a person with special knowledge of databases is required to handle it?
Database Management System consists of six main components.
These are:
• Data
• Hardware
• Software
• Users
• Procedures
• Database Access Language

Data: This is the most significant component of a database. It is a collection of fundamental facts and figures that are recorded in the database.
Hardware: The hardware consists of the real computers that store and manage data in the database. This includes the computer, the hard disk drive, and the RAM.
Software: The software is the tool that operates the information. It is responsible for storing, obtaining, and managing data. The most common database application is termed a database management system (DBMS).

Users: The users are the individuals who connect with the database. They might be end-users who use the database to see data or database managers who operate the database.
Procedures: A procedure is a form of general instructions or guidelines for using a DBMS. These instructions include how to set up the database, install it, log in and out, manage it, create a backup, and generate reports from the database.
Database Access Language: Database Access Language is a language that allows users to give commands to a database to operate the data stored. You can use this language to ask the database to do many things, such as getting data, modifying it, or removing it.

Your favourite streaming service, like Netflix, uses big data and databases to recommend movies and shows to you.
Answer the following questions.
Name the components of a DBMS.
Name the different types of DBMS. 1 2
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is a powerful tool used for managing and manipulating data in databases. SQL provides a way to communicate with and manipulate databases through the following main operations:
• Data Querying: Allows users to retrieve specific data from databases.
• Data Manipulation: Includes commands to insert, update, and delete data.
• Data Definition: Enables users to define and modify the structure of the database objects, such as creating, altering, and dropping tables.
SQL statements are classified into the following two categories:
Data Definition Language (DDL): The SQL statements or commands that are used to create or delete tables are called DDL commands. These are necessary for creating, altering, and deleting the table. For example, create database, create table, add, modify, drop, etc.
Data Manipulation Language (DML): The SQL statements or commands that are used to insert, delete, or update data in the table of the database are called DML commands. For example, insert, delete, update, etc.
In the previous class, you learnt about creating tables, inserting data, and using the SELECT command with the WHERE clause. In this chapter, you will be introduced to more advanced SQL commands and concepts.
Before learning about SQL queries, let us first quickly learn about the various data types and keys used in SQL.
There are the following main data types used in SQL:
Data Type Description
Number Numeric data types are used to store a numeric value in a field column. It may be decimal, integer or real value.
Character (Fixed Length) This data type is used to store fixed-length character strings. If the string is shorter than the specified length, it is padded with spaces.
Varchar (Variable Length) It is used to store variable length alphanumeric data.
NUMBER(n, d) where n specifies the number of digits and d specifies the number of digits to right of the decimal point.
CHAR(size) where size represents the maximum (255 Characters) number of characters in a column.
VARCHAR(size) / VARCHAR2(size) where size represents the maximum (2000 characters) number of characters in a column.
Roll_number int (2)
Salary int (6, 2)
Name char(20)
Address Varchar(50)
Date It is used to store date in columns. The standard date format is YYYY-MM-DD.
Time It is used to store time in columns. The standard time format is hh:mm:ss.
Date
Time
dob Date
joining_time Time

Keys in a database are used to define any constraints on the table. We know a database can have multiple tables. Keys are also used to establish and identify relationships between tables.
There are many keys that can be defined for a table. A table can have multiple keys also.
Primary Key The primary key is the attribute or set of attributes in a table that uniquely identifies a row in that table. There should be only one primary key in a table.
Candidate KeyThere might be multiple attributes that can uniquely identify a row in a table. Candidate key is the attribute that uniquely identifies a row in the table, but is not considered as the primary key.
Composite KeyWhen a primary key consists of more than one attribute, it is called a composite key.
Foreign key Foreign keys help us to establish a relationship between multiple tables in a database.
Let us now revise some of the basic SQL commands that you have learnt in the previous grade.
The Create Table command is used for creating tables.
Create Table table_name (
column_name_1 data_type_1, column_name_2 data_type_2,
column_name_n data_type_n );
CREATE TABLE Students (
Student_ID VARCHAR(6), Student_Name VARCHAR(50), Grade INT, Section CHAR(1), Roll_Number INT, Library_ID VARCHAR(7), House_ID VARCHAR(4), Enrollment_Date DATE );
The Create Table command is used to create a new table in a database. When defining a table, you can set a primary key to ensure each record is unique.
Syntax Example
Create Table table_name ( column_name_1 data_type_1 PRIMARY KEY, column_name_2 data_type_2, ………
………
column_name_n data_type_n );
CREATE TABLE Students ( Student_ID VARCHAR(6) PRIMARY KEY, Student_Name VARCHAR(50), Grade INT, Section CHAR(1), Roll_Number INT, Library_ID VARCHAR(7), House_ID VARCHAR(4), Enrollment_Date DATE );
Insert table command is used to insert values in the created table.
Syntax Example
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, ...);
INSERT INTO Students (Student_ID, Student_Name, Grade, Section, Roll_Number, Library_ID, House_ID) VALUES (‘STU001’, ‘Riya Das’, 7, ‘A’, 23, ‘LIB007’, ‘H001’, ‘24-07-2024’);
The SELECT statement is used to query the database and retrieve specific data.
Syntax
SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE condition;
Examples Output
SELECT * FROM Students;Gives all the records entered in the table
SELECT Student_Name, Grade FROM Students; Gives only two columns Student_ Name and Grade
SELECT * FROM Students WHERE Grade = 7; Gives all the records of the students who study in grade 7.
Let us now learn about some more SQL queries.
You have seen that we can use the SELECT statement with WHERE clause. There are some more clauses which can be used with the SELECT statement. Let us learn about them.

The Order By clause allows us to sort the results in ascending or descending order. For example, To list students by age in ascending order:
SELECT * FROM Students ORDER BY Age; To sort by age in descending order, use DESC:
SELECT * FROM Students ORDER BY Age DESC;
Distinct Clause
The Distinct keyword helps eliminate duplicate values. For example, to list unique cities where students live:
SELECT DISTINCT City FROM Students;
The Update command modifies existing records. To update the address of a student: UPDATE Students
SET Address = ‘1010 Elm Street’ WHERE StudentID = 1;
The Delete command removes records from a table. To delete a student from the database:
DELETE FROM Students WHERE StudentID = 3;
Aggregate functions perform calculations on a set of values and return a single value. Common aggregate functions include:
• COUNT(): Returns the number of rows.
Example: Count the number of students in each grade level:
SELECT Grade, COUNT(*) FROM Students GROUP BY Grade;
• SUM(): Returns the sum of a numeric column.
Example:
SELECT SUM(salary) FROM Employees;
• AVG(): Returns the average value of a numeric column.
Example:
SELECT AVG(price) FROM Products;
• MAX(): Returns the maximum value.
Example:
SELECT MAX(age) FROM Employees;
• MIN(): Returns the minimum value.
Example:
SELECT MIN(quantity) FROM Orders;
To search for specific data in a MySQL database, you can use SQL queries by specifying some conditions.
The where clause is used to filter the rows returned by a query based on specified conditions.
Syntax:
select * from table_name where condition;
Example:
select Student_Name from Student where Gender = ’F’;
This SQL statement retrieves the Student_Name of the girl students.
Output Diksha Payal
Shreya
Wildcard operators in SQL are special characters for pattern matching in text data. They help in finding data that matches a pattern, not just an exact value. They are used with the 'like' clause in an SQL query. Two main wildcard characters used in SQL are '%' (matches multiple characters) and '_' (matches a single character). Let us look at their usage.
Using '%' Character: The percent sign (%) represents zero, one, or multiple characters.
Syntax:
select column_name from table_name where column_name like '%pattern';

Example:
select Student_Name from Student where Student_Name like '%s%';
Using '_' Character: The underscore (_) represents a single character.
Syntax:
select column_name from table_name where column_name like 'pattern_pattern'; Example:
select Student_Name from Student where Student_Name like 'P_yal';
Match the following.
Create
Descending order
Distinct Filter rows
Where
Create a new table
Desc Eliminates duplicate values
A database is a structured collection of related data that can be easily accessed and managed.
Databases use tables to organise data, with rows for individual records and columns for specific information. Components of a DBMS include data, hardware, software, users, procedures, and database access language.
Advantages of databases include handling large data volumes, efficient data organisation, quick data changes, and data sharing.
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that helps create, operate, and interact with databases. SQL is the language used to interact with the database.
Two types of SQL statements are Data Definition Language (DDL) and Data Manipulation Language (DML).
Keys in a database are used to define any constraints on the table.
The primary key is the attribute or set of attributes in a table that uniquely identifies a row in that table.
Wildcard operators in SQL are special characters for pattern matching in text data.
A. Fill in the blanks.
A database is a structured collection of .
In a database, each piece of information is stored in a
The software used to manage and organise databases is called a
The sign represents zero, one, or multiple characters in a value.
To retrieve specific information from a database, you can use a special language called .
B. Tick () the correct option.
What is a database?
a A place to store variables
c A storehouse for variables
Which of the following is an example of RDBMS?
a IDS
c Oracle
Which of the following is NOT a component of DBMS?
a Users
c Hardware
What is a record in a database?
a A collection of data
c A row in a database table
b A collection of organised information
d A kind of tree structure
b IMS
d None of these
b Data
d Network
b A collection of books
d A column of information
What is a primary key called when it consists of more than one attribute?
a Primary key
c Foreign key
b Composite key
d Candidate key

C. Match the following.
1 Wildcard operator
A column in a database table
2 DBMS Relational, hierarchical, and network
3 Different types of DBMS
4 Components of a DBMS
5 Attribute
D. Write T for True or F for False.
A software application that helps users create, manage, and access databases
A special character for pattern matching in text data
Data, hardware, software, users, procedures, and database access language
A database is a collection of data organised in a way that makes it easy to retrieve, manage, and update.
In a database, information is stored in tables, which are made up of rows and columns.
The where clause is used to filter the rows returned by a query based on specified conditions.
Databases are only used by businesses and organisations; they have no relevance in our everyday lives. Two main wildcard characters are % and &.
E. Answer the following questions.
How is data stored in RDBMS?
What do you mean by DML commands?
What are the advantages of using a database?
What is a database management system (DBMS)?
What are the wildcard operators used in SQL? Explain them.
F. Apply your learning.
Consider the following Employee table and answer the queries given below:
Display the IDs and names of all the employees.
Display the names of the employees whose salary is less than ₹23000.
Display the names and IDs of the employees whose salaries are more than ₹23000. Display the


Objective: To help students practice writing basic SQL commands and ask Microsoft Copilot (or another AI tool) to convert plain English questions into SQL queries.
Activity: Create a Books database on the Tekie digital platform, then ask Microsoft Copilot to convert plain English questions into SQL queries and run them on the Tekie platform.
Microsoft Copilot is an AI-powered assistant from Microsoft that helps users boost productivity by automating tasks, generating content, and offering intelligent suggestions across apps like Word, Excel, PowerPoint, etc.
Solution:
1 Create the Books database using Tekie digital platform.
2 Now use AI assistance (Microsoft Copilot):
a. Open Microsoft Edge browser.
b. Click the Copilot icon in the search bar.

c. You will be directed to a web page as shown.

d. Type the following prompt into Copilot:

e. Your task is to ask Microsoft Copilot the following questions in plain English and get SQL queries as responses.
The questions are:
i. Show all the books in the database.
ii. List the titles of books that cost less than 300.
iii. Display all books in order of their price, from cheapest to costliest.
iv Add a new book: Book_ID = 5, Title = Ikigai, Price = 270.
v. Update the price of Harry Potter to 420.
vi. Delete the book with Book_ID = 2.
f Copy the AI-suggested queries, paste them into your Tekie digital panel, and observe the results in the Output window. Compare the SQL results with your expectations to verify correctness.
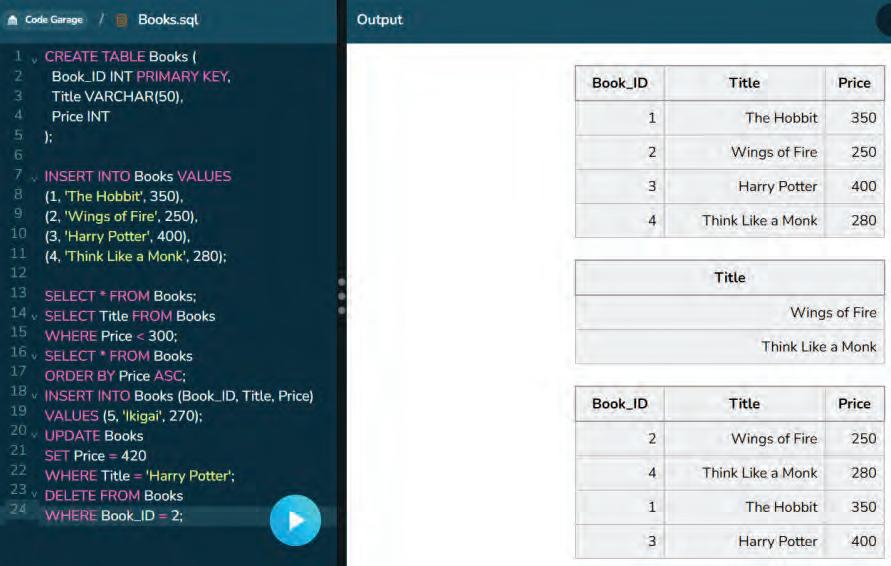






Video editing is the process of arranging and modifying video clips to create a video project. It involves cutting, adding, and enhancing clips to make the video more interesting and effective. Video editing is used to create presentations and reports in schools and offices, producing stories for series and movies and to create content for social media platforms.
Let us start a video project from scratch.
Follow the given steps to create a blank video in Canva:
1. Log in to www.canva.com and create an account if you do not have one.
2. Click on the Create a design button on the home page.
3. A drop-down list of options will appear.
4. Click on the Video option.


You can also click on the Video icon on the home page and select from the various options.
Let us discuss the various components of Canva window as marked in the above image.
1. Canvas: The canvas is your workspace, where you build and design your video. Here you can add and arrange all the elements of your video project, including text, images, videos, and audio.
2. Timeline: The timeline is a critical component that allows you to control the timing of your video. You can arrange elements on the timeline to determine when they appear and for how long. It helps you arrange objects like text, images, and videos in the desired sequence.
3. Zoom controls: Canva offers zoom controls that allow you to zoom in and out of your canvas. This feature helps you focus on specific details while working on your video.
4. Grid view: Grid view provides an overview of all the pages in your video project, helping you visualise the structure and flow of your video. It is a useful tool for organising your content effectively.
5. Preview: The Preview option allows you to see how your video will appear to your audience. It is a valuable tool for reviewing your video before finalising it, ensuring everything looks and sounds right.
6. Elements: The Elements option offers a wide range of design elements, including photos, videos, stickers, shapes, and icons. You can search and browse for elements to enhance the visual appeal of your video project.
7. Text tool: Text tool enables you to add text to your video. You can choose from various fonts, colours, sizes, and styles to customise your text elements. This is essential for creating titles, captions, and onscreen messages.
8. Uploads: This feature allows you to upload your own media files, such as images, videos, and audio clips, to incorporate them into your video project. It is a way to personalise your content and add unique elements.
9. Draw: You can draw any shape in your video by using the tools present under this drawer.

10. Projects: You can view all your projects that you have created up to now under this option. You can select any one of them to work upon.
11. Notes: You can add notes to your project to keep track of ideas, reminders, or specific instructions. Notes are useful for collaborating with others on your video project.
12. Canva assistant: This is an artificial intelligence tool that helps you with your queries during the project. You can ask any query by clicking on the Canva Assistant button.

You can use Canva’s Timeline feature to precisely control when each video element appears and disappears.
Match the features with its correct descriptions.
Canvas Lets you zoom in and out of your canvas to focus on details.
Timeline Enables you to add and customize text in your video.
Zoom Controls Your workspace where you build and design your video.
Preview Helps you control the timing of your video by arranging when elements appear.
Text Tool Lets you see how your video will appear to your audience before finalising it.
You can add videos to your project using various options. Let us discuss them one by one.
You can upload your videos to Canva and add them to your project. Follow the given steps to add video from your device.
1. Click on the Uploads option in the side bar.
2. Click on Upload files and select the video files from your device. Wait for the upload to complete.
3. Drag and drop the uploaded video onto the timeline.
2 1
Follow the given steps to add videos to your video project in Canva:
1. Click on the Elements option in the side bar.
2. Type keywords related to the type of video you need in the Search bar (e.g., ‘nature,’ ‘city,’ ‘people’).
3. Go to Videos section, click on the video you want and drag it to the timeline.
4. You can resize it from the ends of the video to fit it according to the dimensions.
5. You can also add a new page and then add the video to that page.
Let us discuss some basic video editing tools.
To trim and split your videos, follow these steps:
1. Click on the video in the timeline to select it.
2. Hover over the beginning or end of the video clip and drag the edge to trim the video to the desired length.
3. Move the playhead (the vertical line) to the point where you want to split the video. Click on the Split button that appears above the timeline.


To resize or crop your video, follow the given steps:
1. Click on the video in the timeline.
2. Drag the corners of the video to resize it.
3. Crop the video by clicking on the Crop button above the canvas. Drag the edges of the video to crop it to the desired size. Click Done when finished.
You can add music or sound effects to your video:
1. Click on the Elements option in the side bar and go to Audio section.
2. Type keywords in the Search bar to find the type of music or sound effect you want.
3. Click on the audio track and drag it to the audio timeline.
4. Click on the audio track in the timeline to adjust the
You can enhance your video in Canva using the following effects.
Follow the given steps to apply filters and effects in your video:
1. Click on the video in the timeline.
2. Click on the Edit video button above the canvas.
3. In the tools tab, go to the Filters section. Select the filter of your choice.
4. Use the slider to adjust the intensity of the filter.
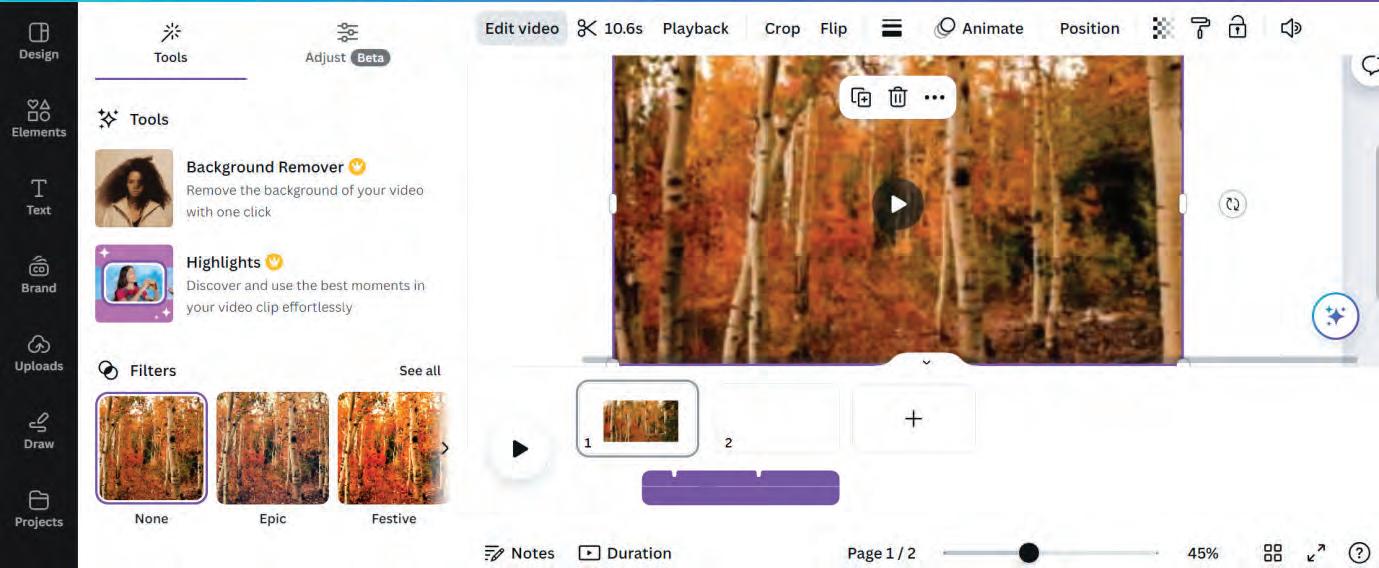

You can add text and graphics to your video by following the given steps:
1. Click on the Text option in the side bar.
2. Select a text style and click on it to add it to the canvas.
3. Double-click on the text box to edit the text. Change the font, size, colour, and position as needed.
4. Click on the Elements option in the side bar. Search for graphics or stickers and drag them onto the canvas.
You can make your video more dynamic by adding animations to it. Follow the given steps:
1. Click on the text or graphic you want to animate.
2. Click on the Animate button present above the canvas.
3. Select an animation style from the options.
4. Customise the animation duration and delay if needed.
5. Your video is ready. Click on the Play button to watch your video.
Downloading lets you save your video, while sharing helps you show it to others or collaborate on it.
Follow these steps to export your finished video:
1. In the top right corner, click on the Share button.
2. Select Download from the dropdown menu.
3. Choose the video format (MP4 is recommended).
4. Wait for the video to process and download to your device.
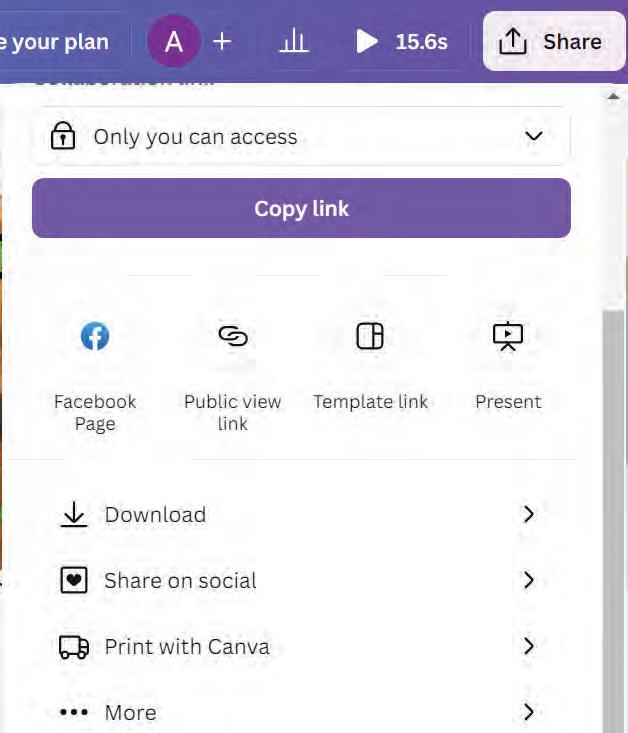
Now that your video is ready, you can share it with others by following the given steps:
1. In the top right corner, click on the Share button.
2. Set the sharing options, like who can see your video and if they can edit it.
3. Click on Copy link to get a shareable link or choose how you want to share it, like through email or social media.
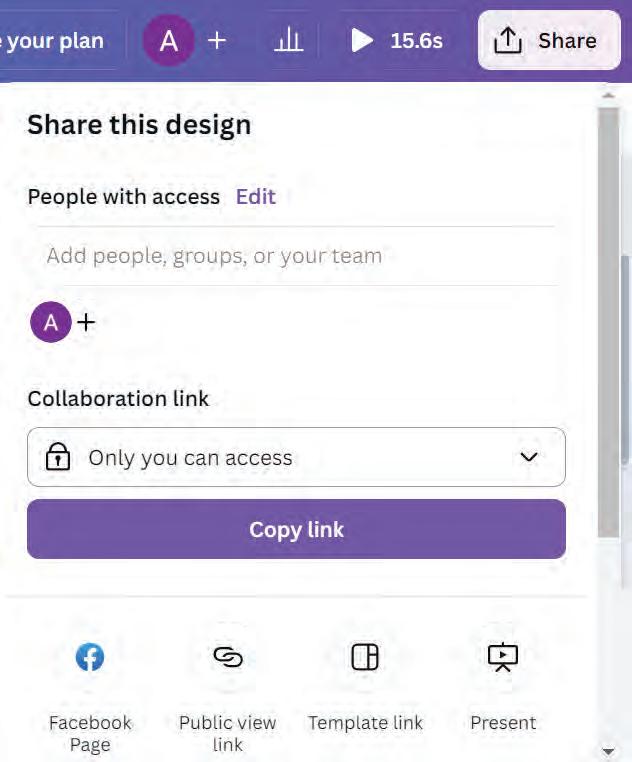
Have you ever used the Preview option in any application before finalizing your video?






1 Fill in the blanks.
a To upload a video, click on tab in the side bar.
b Drag the video to the after uploading.
c Find videos by clicking on and using the Search bar.
d Trim a video by dragging the or .
e To share your video, click on the button in the top right corner.
2 Solve the following crossword using the given hints.
Across
1. The button you click to adjust the visual appearance of your video with different styles.
4. A tool used to cut a video into segments.
6. The button you click to start watching your edited video.
Down
2. To change the size of a video.
3. The section where you upload your own video files
5. The format recommended for downloading videos.
1 Video editing involves arranging, modifying, and enhancing video clips to create a project.
2 Key components of Canva’s video editor include the canvas, timeline, text, elements, uploads, and audio controls.
3 You can add text in your video to express your thoughts along with the video.
4 You can add pictures to your video in Canva to enhance the presentation of the video.
5 Adding videos in Canva brings motion to your project, with options to resize and preview.
6 You can insert audio in Canva for background music with volume control.
7 Applying filters and effects can enhance the visual appeal of your video.
8 Animations make your video more dynamic by adding movement to text and graphics.
9 After finishing, you can download or share your video using the Share button.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints Create a design Preview Canvas Uploads trim split
1 The option in Canva lets you upload your own videos, images, and audio files.
2 To start a video project in Canva, you first click on the button on the home page.
3 The feature helps you see how your video will look before finalizing it.
4 You can and your videos using basic editing tools in Canva.
5 The is your workspace where you build and design your video in Canva.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 What does the Timeline in Canva allow you to control?
a The colour of the text
b The timing of video elements
c The size of the canvas d The type of filters used
2 Which option in Canva helps you add animations to your video?
a Uploads b Elements
c Animate d Text
3 What file format is recommended when downloading your video from Canva?
a JPG
b MP4
c PNG d GIF
4 To add your own video file to a project in Canva, which option should you use?
a Elements
b Uploads
c Video Library d Timeline
5 What feature helps you focus on specific details of your video while editing?
a Zoom controls
b Filter options
c Canvas d Grid view
C. Who am I?
1 I help you organise the timing of your video elements in Canva.
2 I am the workspace where you build and design your video.
3 I help you add motion to text and graphics in your video.
4 I let you see an overview of all the pages in your video project.
5 I offer a variety of design elements like stickers, shapes, and icons to enhance your video project.

D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 The Timeline in Canva allows you to control when elements appear in your video.
2 The Elements option in Canva is used to add text to your video.
3 You cannot resize or crop videos in Canva.
4 Canva’s Video Library offers a wide range of pre-existing video clips.
5 You can download your finished video directly from Canva.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 What do you mean by video editing?
2 How does the timeline help you control the timing of your video?
3 Write the names of basic video editing tools.
4 Why is the Preview option important in Canva?
5 How can you add text to your video?
F. Apply your learning.
1 Neha is enhancing her Canva video by adding photos. What are the steps she should follow to resize the video clips effectively?
2 Kavita wants to add background music to her Canva video. Where can she find the audio option to do so?
3 Rahul wants to add captions to his Canva video. Which option should he use to add text?
4 Ravi needs to ensure that his video elements appear at the right times. What tool in Canva will help him manage the timing of these elements?
5 Arjun is an artist. He wants to create a drawing using his imagination. Which option can he use to do so?

Objective: To explore and use the AI tools available in Canva.
Activity: Use the AI tools in Canva to design an image.
Solution: Follow the given steps:
1 Open www.canva.com. You will see the homepage as shown below.

2 Click on the Canva AI option.
3 You will see various options such as 'Design for me,' 'Create an image,' 'Draft a doc,' and more.
2 Click on the Canva AI option.
3 You will see various options such as 'Design for me,' 'Create an image,' 'Draft a doc,' and more.
4 Select any of these options and write a simple prompt for Canva to perform the desired task for you.
4 Select any of these options and write a simple prompt for Canva to perform the desired task for you.
5 Here, the option Draft a doc is selected. Enter a simple prompt and Canva will begin creating your document.
5 Here, the option Draft a doc is selected. Enter a simple prompt and Canva will begin creating your document.
6 Canva’s AI will then generate a draft based on your prompt.
6 Canva’s AI will then generate a draft based on your prompt.

7 Experiment by changing your prompt in different ways to explore the variety of documents Canva can produce.

7 Experiment by changing your prompt in different ways to explore the variety of documents Canva can produce.




You may have noticed that while texting a friend using your smartphone, the predictive text fills in the rest of the phrase even before you get to the end of the sentence. Similarly, while shopping online, you get product recommendations based on your shopping history. Or when you are out for a jog, your smartwatch helps you track your fitness goal by giving useful information like the number of steps. All of this is possible because of Artificial Intelligence (AI), a technology that has transformed how we live, work, and interact with machines around us.
AI can be defined as a branch of computer science concerned with creating intelligent machines that can learn from data, solve problems, and make decisions. It involves the study of principles, concepts, and technologies that enable machines to exhibit human-like intelligent behaviour.

Be it in your classroom, in the marketplace, or at home, you can find applications of AI everywhere. Some prominent fields where AI has made a significant impact are given as follows:
Healthcare Detecting diseases, discovering new drugs, doing remote surgery
Business Preventing fraud, helping us shop by giving recommendations
Education Smart content that helps us learn
Banking Managing money and bank accounts, preventing fraud
Transport Autonomous vehicles, ride-hailing apps, navigation system
Social media Face recognition, content filtration
Security Data security, identification of fraud, threats, etc.
Robotics Heavy industry, robotic surgeries, home assistants
Smart homes Smart devices and connectivity to mobile applications
Artificial Intelligence depends on data for its effectiveness. The quality and type of data fed into AI systems determine how smart they become. AI has three main domains based on the type of data they use:
Data: Data is the foundation of data science. It works with numeric and alpha-numeric data.
Computer Vision: Computer vision works with image and visual data.
Natural Language Processing: NLP works with textual and audio/speech-based data.

Every domain of AI uses a specific type of data that acts as input to the machine and requires a specific method to handle and utilise it.
What is the difference between data science and data analytics?
Data science is an important field in today’s world because we create a lot of data every day—way more than ever before. Whether it is from our phones, computers, or other devices, there is a massive amount of information coming in constantly. To make sense of all this data, we need special methods and tools to process, analyse, and understand it.
Data science is a domain of computer science that helps us learn things from data by using scientific methods, algorithms, and statistics.


Data science combines ideas and methods from statistics, maths, data analysis, and computer science to dig out useful information from huge piles of data collected over time. This makes it easier for us to study all kinds of data—both organised and messy—and turn it into something that we can understand and use in the real world.

Did You Know?
In data science, various data formats, such as CSV (Comma-Separated Values), JSON (JavaScript Object Notation), Excel (XLSX), XML (Extensible Markup Language), SQL (Structured Query Language) are used to represent and store different types of data.
Data science can be considered the study of data. It involves the following processes:
• Collecting the data
• Analysing the data
• Using data to solve problems or make data-driven decisions
The problem can be anything from predicting the weather, recommending films on Netflix, finding the fastest route, or even understanding trends on social media. So, data science encompasses various disciplines that focus on data analysis and finding the best possible solution.
Let us take a simple example: Suppose your school wants to find out which sports or games students like the most. Here are the steps they could follow.
Collecting data: The school distributes a survey to every student, asking about their favourite sport.
Analysing data: After collecting responses, they examine the survey results to identify the most popular sport.
Making data-driven decisions: With this information, the school can decide which sport or game to organise more frequently.
This process ensures that decisions are based on data, leading to better outcomes that align with students’ preferences.

Every time you watch a video on YouTube or scroll through Instagram, data science algorithms are working in the background to recommend what you see next. These algorithms analyse millions of pieces of data in seconds — far faster than any human could!
There are different components of data science, which include:
Statistics
The science of collecting and analysing numerical data in large quantities in order to gain helpful insights.
A tool used to interpret large amounts of data easily through visual representations.
The study and development of algorithms that enable machines to make predictions or decisions based on data.
A subset of machine learning focused on algorithms that automatically learn and determine the best models for data analysis and prediction.

Data science is everywhere in our daily lives. Here are a few reasons why it is important:
1. Making Informed Decisions: Whether it is a business deciding which products to sell, a doctor determining the best treatment for a patient, or a school planning a new curriculum, data plays a crucial role. It helps people make smart, evidence-based decisions.
2. Solving Problems: Data science helps us find solutions to complex problems. For example, by analysing weather data, scientists can predict hurricanes and help people prepare for them.
3. Creating New Opportunities: Companies like Google, Amazon, and Facebook use data science to develop new technologies and services that enhance our lives, making things easier and more enjoyable.
Collect and analyse data from your classmates about their favourite snacks and drinks. Then, use the data to recommend healthy and popular options for a school event. Identify and write the three processes of data science as per the given scenario:
Collecting data:
Analysing data:
Making data-driven decisions:
Data science is used in many fields and impacts our daily lives in many ways. Let us learn about the applications of data science.
Data science plays an important role in education. It enables personalised learning for students, which improves student outcomes. Additionally, data science algorithms use feedback from students and teachers to enhance personalised learning experiences.
Data science is also used in other aspects of education, such as designing curriculum based on student performance and optimising administrative tasks. For example, identifying students struggling in certain subjects can inform school administration to hire additional tutors and get more learning resources, etc.

Data science plays an important role in the healthcare sector. Data science algorithms analyse medical images to detect symptoms of diseases with high accuracy, helping doctors diagnose their patients in the early stages of a disease. It uses patient data, such as their medical history, to predict which patients are at risk of developing chronic diseases and recommends preventive measures for these diseases. It also helps analyse real-time health data collected through wearable devices to monitor conditions like heart disease. Data science also optimises hospital operations by predicting patient admissions, managing resources better, and reducing wait times. This helps improve overall healthcare services for patients.



Data science makes the entertainment sector more personalised by analysing data to understand what people like or dislike. For example, streaming services like Netflix use data on what films or shows you watch to recommend new films and shows you might enjoy. Music apps like Spotify create personalised playlists by analysing what you listen to more frequently. Video games also use data science to tailor game experiences to your preferences.
Data science has transformed the sports industry by enhancing performance analysis, strategy development, and fan engagement. It helps study players’ performances in terms of various parameters, like speed and technique, to optimise training and game strategies. For example, data on batting patterns and defensive moves in cricket helps coaches develop better game plans. Smart wearable devices help to track athletes’ health and fitness data in real time to personalise training needs and prevent injuries.

Data science helps analyse extensive environmental data to understand patterns, make predictions, and inform policy decisions. For example, data scientists use satellite images and sensor data to monitor deforestation, detect illegal fishing activities, and track wildlife populations. Climate scientists analyse historical weather data to predict climate change impacts and help policymakers plan to decrease its effects. Air quality data collected from sensors helps identify pollution sources and develop strategies to improve air quality. Data science also optimises resource management by predicting water demand and managing renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, contributing to more sustainable environmental practices.

Data science plays an important role in helping stores understand customer preferences and how to improve the shopping experience. For example, when you shop online, have you noticed how websites suggest other items you might like? It is possible through data science. The website uses data science to analyse your previous purchases and suggest similar things. Data science also helps stores maintain stock so they do not run out of items. It also helps to fix prices based on data on what people are willing to pay.






Data science helps make travel safer, more efficient, and more convenient. For example, when we use a navigation app, like Google Maps, data science helps us calculate the fastest route by analysing traffic data from many drivers. Data science also predicts jams and suggests alternate routes to avoid delays in reaching the destination.
Data science helps transport companies optimise their routes and schedules by analysing passenger demand and vehicle availability data. For example, airlines use data science to forecast flight demand and adjust ticket prices accordingly. Data science improves safety by analysing data from vehicle sensors to prevent accidents.


































































































































































Data science is used in banks and financial institutions to detect fraud and make smarter money decisions. Banks use data science to analyse transaction patterns or financial data to detect fraud. For example, when using a credit card, data science looks for unusual spending patterns that could indicate fraud. Data science helps predict how much money a company might make in the future based on its past sales data, which helps investors decide whether to invest or not.
Data science also helps banks decide whether to lend money or not by analysing a person’s credit history and money-spending habits. This ensures that the bank is lending money to someone who is likely to pay it back.

Data science helps to make our experiences more personalised and engaging on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, etc. For example, when you use Facebook or Instagram, data science analyses your previous likes, comments, and shares to show you posts from friends and pages you are interested in. Data science helps detect fake social media accounts and harmful content to make social media safer. Data science helps social media platforms target advertisements to specific groups of people based on their online activities.
AI Movie Selector – How AI Learns Your Preferences
Objective: To understand how AI learns from user data and makes decisions based on preferences, just like online movie recommendation platforms (Netflix, Amazon Prime, etc.)
Follow the given steps to explore how this application works.
Steps to Perform the Activity:
1. Visit the website https://www.whatismymovie.com/. This website uses AI to recommend movies based on the descriptions.
2. The following web page appears.
3. Type a few words about a movie you like (for example, “A Bollywood comedy movie”) in the text box. Then click on the Search button.

4. Now, see what movies AI suggests.
5. Try using different keywords and observe how AI makes changes to its recommendations.
6. Analyse How AI Learns:
• The more specific details you provide, the more accurate AI’s recommendations will be.
• AI uses past user data, keywords, and patterns to improve its decision-making.
• If you watch the movie and rate it highly, AI learns and improves the future recommendations.
Do It Yourself 9B
Match the applications of data science with its correct description.
Application
Education
Environment Protection
Sports
Finance
Healthcare
Description
Optimising player training and injury prevention through data analysis.
Improving diagnoses and treatments by analysing medical images and patient data.
Personalising learning experiences and improving administrative tasks using student data.
Monitoring pollution, managing resources, and predicting climate impacts.
Detecting fraud and analysing spending habits for better investment decisions.
1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to creating intelligent machines capable of learning, problem-solving, and decision-making like humans.
2 AI applications are prevalent in various fields, including healthcare, business, education, banking, and social media.
3 Data science involves processing and analysing data to extract meaningful insights and support decision-making.
4 The main processes in data science include collecting data, analysing data, and using data to make informed decisions.
5 Data science helps solve complex problems and create new opportunities across industries such as education, healthcare, and entertainment.
6 Data science applications are essential in modern technologies like autonomous vehicles, smart homes, and fraud detection systems.
7 Understanding and leveraging data science is crucial for optimising operations and enhancing the user experience in multiple sectors.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints medical images social media transport math intelligent
1 Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science concerned with creating machines.
2 In healthcare, data science algorithms analyse to detect symptoms of diseases.
3 Data science helps companies optimise their routes and schedules.
4 AI applications in include content filtration and detection of fake accounts.
5 Data science combines ideas and methods from statistics, , and computer science.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Which of the following is a component of data science? a Healthcare
Visualisation
vision

2 Which of the following is NOT an application of data science in education?
a Designing curriculum based on student performance
b Predicting weather patterns
c Personalising learning experiences
d Optimising administrative tasks
3 Data science in sports helps analyse players’ to optimise training. a Salaries b Performances
c Diets d Social media profiles
4 Data science in transport improves safety by analysing data from a Vehicle sensors b Social media posts
c TV advertisements d Roadside advertisements
5 Data science in retail helps stores understand customer preferences and maintain a Inventory b Customer relationships
c Security cameras d Loyalty programs
C. Who am I?
1 I help businesses prevent fraud and provide shopping recommendations.
2 I use data science to create personalised playlists and recommend new songs.
3 I am a data science application that helps predict flight demand and adjust ticket prices.
4 I analyse traffic data from drivers to calculate the fastest route and avoid jams.
5 I use data science to monitor deforestation and illegal fishing activities.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Data science algorithms can help identify pollution sources to improve air quality.
2 AI is limited to use in social media and does not apply to healthcare.
3 Data science in education helps in optimising administrative tasks.
4 AI and data science cannot be used in banking due to security concerns.
5 Data science can help in developing new technologies and services by analysing data.
E. Answer the following questions.
1 What is artificial intelligence (AI)?
2 How does data science contribute to the healthcare sector?
3 Explain the processes of data science.
4 What role does data science play in the sports industry?
5 Describe how data science is used in the entertainment industry.
F. Apply your learning.
1 Your school wants to reduce electricity usage. How could data science help achieve this goal?
2 A hospital wants to improve patient wait times. How can data science contribute to this improvement?
3 A sports team wants to improve their training regimen. How can data science assist them?
4 An e-commerce platform wants to increase customer satisfaction. How can data science be utilised?
5 A city wants to implement a smart traffic management system. How can data science aid in this implementation?


Have you ever wondered how AI assistants like Alexa or Siri listen to your commands and respond? It is possible with the help of a domain of AI, that is called Natural Language Processing.
Imagine a situation where you are talking to a computer or a robot. As it is a machine, it will not be able to understand your language. Here, NLP plays its role. NLP makes the machine understand your language and respond to you in a way that makes sense.
NLP helps computers understand us and talk to us like people.
Imagine you have a computer that has NLP. How would you use it to make your daily life easier?

With its wide range of useful applications, NLP transforms our day-to-day interaction with technology. Some of these are given as follows.

Virtual Assistants: This is one of the most common applications of NLP. A virtual assistant is an AI tool that understands and responds to voice commands or text inputs, such as questions and requests, or performs tasks for you. Virtual assistants come in the form of applications or combinations of devices loaded with applications. Siri on the iPhone, Alexa on the Amazon Echo device, and Google Assistant on the Android phone are some of the popular virtual assistants. You can ask a virtual assistant to set alarms, check the weather, play your favourite songs, or even tell you jokes.
Search Engines: Search engines are websites and applications that help you find information on the internet. Google, Bing, Yahoo, etc., are some of the popular search engines. These search engines use NLP to understand the words you type into the search bar and then direct you to relevant web pages. NLP helps search engines comprehend the meaning and context of your search and help you find what you are looking for.



Sentiment Analysis: NLP can be used to analyse the sentiment or emotion expressed in the text. For example, businesses might use sentiment analysis to analyse customer feedback and preferences for their products and services across reviews on social media platforms and product remarks on online stores. This insightful data can help companies enhance their products, services, or customer experiences.
Spam Detection: NLP helps keep your email inbox free from unwanted mails, also known as spam. Spam-detecting algorithms employ NLP to identify patterns or characteristics common to spam emails, such as certain keywords or phrases, and then filter spam from reaching your inbox.


Autocorrect: Autocorrect is a handy tool featured on devices, such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, etc., that allow users to automatically correct misspelt words as they type them. Autocorrect algorithms employ NLP to analyse the context of the text being typed and suggest corrections based on frequently used words and phrases. This is particularly useful when typing on small touchscreen devices.
Speech Recognition: NLP algorithms analyse audio input from speech and transcribe it into text, enabling hands-free interaction with devices, such as smartphones or voice-controlled appliances. Speech recognition technology is used in applications like voice search, home automation, voice dictation, voice biometric, etc. The ‘Read Aloud’ feature in Microsoft Word makes use of NLP algorithms to read all or part of your document, highlighting each word as it is read. You may also dictate your documents in Word. Dictating within Microsoft Word automatically translates your spoken words into text.


Education: Chatbots and virtual assistants that are powered by NLP engage with students in natural conversations, providing guidance and support. NLP enables automated assessment of students’ work and provides them with instant feedback and assistance in identifying areas for improvement, saving educators’ time. ChatGPT, for example, offers personalised learning experiences by adapting to individual learning styles. NLP-powered tools like Grammarly analyse written text for grammatical errors or inappropriate word usage.
Language Translation: NLP facilitates the translation of text from one language to another. A popular example is Google Translate, which uses artificial intelligence to provide instant translations. NLP algorithms analyse the structure and meaning of text and capture the patterns and probabilities of word sequences. This allows them to provide suggestions for improving translations, detecting errors, or offering alternative translations.

1. Visit this link with the help of your teacher: https://www.squibler.io/ai-story-generator
2. You will arrive at this page.
3. Write the idea of your story in the Story Plot section. For example, ‘A librarian finds a book that brings stories to life.’
4. Pick the Creativity Level: Choose between “Realistic” for grounded stories or “Inventive” for imaginative tales. You can also balance the two by placing the slider in the centre.
5. Pick the Length: Select your story’s length from the dropdown menu: Short or Medium.
6. Advanced Settings: Fine-tune your story by adjusting ‘Narrative perspective,’ ‘Genre,’ ‘Character names,’ ‘Setting description,’ and ‘Character description.’
7. Click Generate Story: Click ‘Generate Story’ and enjoy.
Let us look at the example given below;
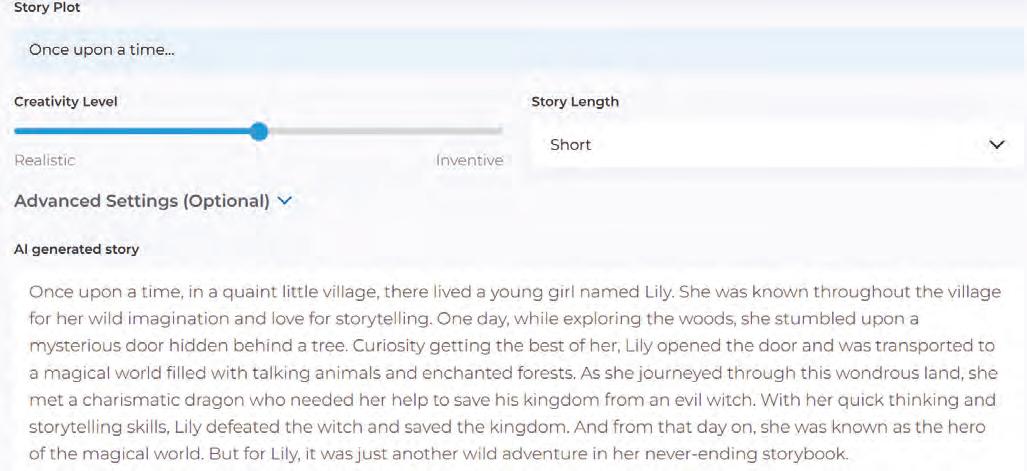


When we read a book or a story, we understand the meaning from the sentences. But for a computer, text is just a collection of characters. Computers cannot “understand” text like humans do, so we need a way to turn words into numbers. One simple method for this is called the Bag of Words (BoW) model.
The Bag of Words is a NLP model which helps in extracting features from the text, which can be helpful in machine learning algorithms. In this model, text (like a sentence or document) is shown as a collection of words without worrying about grammar or the order of the words. In this model, we count how often each word appears in the provided text and create a vocabulary for the entire text collection.
The Bag of Words (BoW) is a NLP model which helps in extracting features from the text, which can be helpful in machine learning algorithms. In this model, text (like a sentence or document) is shown as a collection of words without worrying about grammar or the order of the words. In this model, we count how often each word appears in the provided text and create a vocabulary for the entire text collection, or corpus.
The following figure gives a simple explanation of how the bag of words works. In this figure, the text on the left side is a collection of words that we have processed and cleaned up. When we run this entire text collection through the bag of words algorithm, it picks out all the unique words and counts how often each word appears. The list on the right shows these unique words and the number of times each word shows up in the text.
The following figure gives a simple explanation of how the bag of words works. In this figure, the text on the left side is a collection of words that we have processed and cleaned up. When we run this normalised corpus through the bag of words algorithm, it picks out all the unique words and counts how often each word appears. The list on the right shows these unique words and the number of times each word shows up in the text.
In the field of computer science, the development of computer systems is crucial. Computer systems play a significant role in processing data and performing tasks efficiently.

So, the bag of words method gives us:
So, the bag of words method gives us:
1. A list of all the unique words (vocabulary) in the text.
1. A list of all the unique words (vocabulary) in the text.
2. The number of times each word appears (frequency).
2. The number of times each word appears (frequency).
The steps in the process of implementation of the bag of words algorithm are as follows:
1. Normalise the text: Collect data and pre-process it.
2. Create a dictionary: Next, you make a list of all the unique words in the corpus. This is called vocabulary.
3. Create document vectors: For each document in the corpus, find out how many times the word from the unique list of words has occurred.
1. Computers cannot understand text like humans. Bag of Words gives them a simple way to “read” text by turning it into numbers.
4. Repeat: Create document vectors for all the documents.
2. It helps find patterns in text. For example:
• If the word “free” appears many times in an email, it might be spam.
Let us understand the concept of the bag of words algorithm with the help of an example. Suppose there are three documents with one sentence each.
1. Document 1: I love to play football.
• If the word “great” appears often in a review, the review is probably positive.
3. It powers everyday tools we use:
2. Document 2: Football is a great game.
3. Document 3: I love to watch football games.
• Search engines: When you type “volcano project”, the search engine checks which documents contain these words most often.
• Spam filters: Emails with too many words like “prize, winner, lottery” get blocked.
• Recommendations: Apps like YouTube or Netflix can compare your text searches with other users’ words.
To understand the concept of NLP practically, let us create an app which will convert the input text to speech. For this, we will use the MIT App Inventor. This app will process the input text and convert it to speech.
App based on NLP
The MIT App Inventor is an online platform for creating apps for mobile phones and tablets. It is a very easy and simple platform to learn app creation and coding. This platform focuses on teaching everyone, especially young children, to create their own apps.
Follow the given steps to create an app:
1. Visit the following link to open MIT App Inventor: https://appinventor.mit.edu/
2. The following screen appears:
3. Click on the Create Apps! button.
4. A sign-in screen appears. You can use your Gmail ID to login, or you can create a new one.
5. After signing in, the Welcome to App Inventor pop-up box appears. Click on the Continue button at the bottom of the screen.

6. Another screen appears, from where you can choose to view the tutorials or you can start a new blank project.
Continue button
1. Click on START A BLANK PROJECT.
2. The Project View window appears.
3. A dialog box appears asking to give a project name to your project.
4. Give an appropriate name to your project, for example, text_to_speech and click on OK.

Click here to start a blank project
5. A new project with the same name will be created.
6. Click on it. The Project View window will open.
The Project View window is divided into four sections:
Palette: Various components are present under different categories in the palette.
Viewer: You can select any component from the palette and drag and drop it on the screen in the Viewer section.
Components: The Components section shows the various components that are placed in the Viewer.
Properties: The Properties section shows the properties of the selected component.

Let us now create the interface of the app.
1. From the Palette section, drag the Button component and place it in the Viewer section on Screen1
Button 1 added in Components section

2. You can see that the Button1 component has also been added under the Components section.
3. Now in the Properties section, scroll down to the Text property of the button. Replace the text “Text for Button1” with “Text to Speech”.
4. Now, in the Palette section, click on the Media drawer.
5. Select the Text to Speech component and drop it on Screen1
6. It will not be visible on the screen. However, you can see it below Screen1 as a non-visible component.
The interface of the app is created. Now, let us create the code for it.
The next step is to create a code for the app. To code in MIT App Inventor is very easy and user-friendly. You can create code for your app by using various blocks present in the Blocks Editor
To create the code for your app, follow the given steps:
1. Click on the Blocks Editor button in the right-hand upper corner of the Project View window.
2. The Blocks Editor will open with the Blocks section on the left and the Viewer section on the right.
3. Click on Screen1 > Button1 from the Blocks pane.
4. The blocks related to Button1 will appear.
5. Drag the when Button1.Click block from the Blocks drawer and drop it in the Viewer pane.
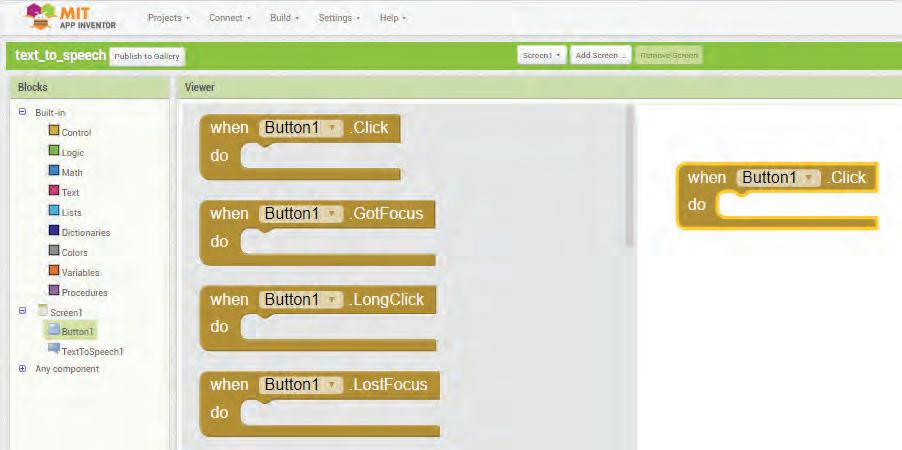

6. Similarly, click on Screen1 > TextToSpeech1.
7. The blocks related to the Text to Speech component will appear.
8. From the Blocks drawer, drag the call Text to Speech1.Speak block and drop it inside the when Button1.Click block.
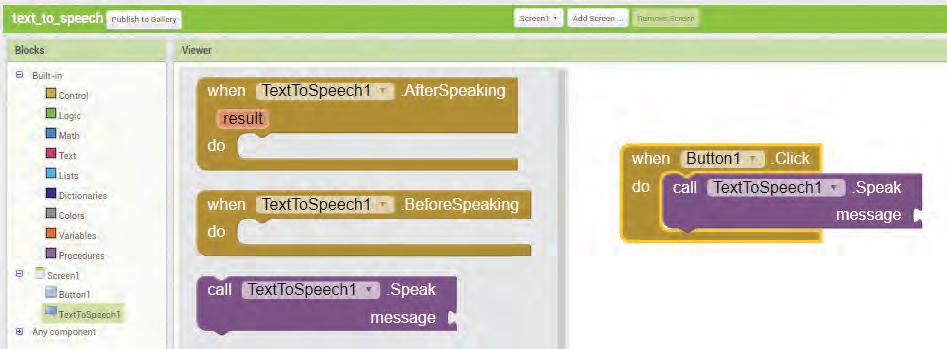
9. Now, from Built-in > Text drawer, drag the “A text string” block and plug it into the socket labelled message
10. Click inside the text string block and type your desired message. For example, “Welcome to the world of coding!”
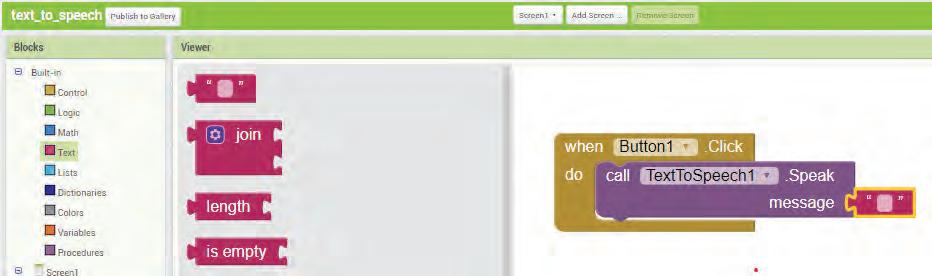
11. Your app and its code are ready to use.

1. To test your app, you will need a mobile phone.
2. Go to the Google Play Store of your Android phone and download the MIT AI2 Companion App.
3. Install the app by clicking on Install.
4. After installation, open the app. You will need to provide a six-character code to connect.
5. To get the code, go to your computer where you have created your app.
6. Go to the Connect menu and select the AI Companion option.


You can scan this QR Code to get the MIT AI2 Companion App on your mobile phone.
7. A Connect to Companion window will open with a six-character code.


You can now fill in this six-character code on the mobile phone app.
1. The app will now open on your mobile phone.
2. Click on the button that you have created.
3. You will be able to hear the message that you have provided in the app code, that is “Welcome to the world of coding!”
Welcome to the world of coding!

Answer the following questions.
1 How do search engines use NLP?
2 What is sentiment analysis and how is it used?
3 How does NLP assist in spam detection?
1 Natural Language Processing, or NLP, makes the computers understand the human language in text and spoken form.
2 A virtual assistant is an AI tool that understands and responds to voice commands or text inputs, such as questions and requests, or performs tasks for you.
3 Search engines are websites and applications that help you find information on the internet.
4 Google Translate is an AI-powered translation app that allows users to translate text into different languages.
5 NLP can be used to analyse the sentiment or emotion expressed in a text.
6 Autocorrect is a handy tool featured on devices, such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, etc., that allows users to automatically correct misspelt words as they are being typed.
7 MIT App Inventor is an online platform for creating apps for mobile phones and tablets.
8 The Project View window of MIT App Inventor is divided into four sections, Palette, Viewer, Components, and Properties.
9 The Bag of Words (BoW) is a NLP model which helps in extracting features from the text, which can be helpful in machine learning algorithms.
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 is a handy tool featured on smartphones that allows users to automatically correct misspelt words as they are being typed.
2 on iPhones is a popular virtual assistant.
3 NLP helps keep your email inbox clean and clear from unwanted mails called
4 is an AI-powered language translation tool.
5 is the domain of AI that deals with the language-based interactions between a machine and a human as well as between two machines.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 NLP helps comprehend the meaning and context of your search and find what you are looking for.
a Search Engines
b Home Automation
c Spams d Sentiment Analysis
2 Which of the following application uses speech recognition?
a ChatGPT
b Grammarly
c Spam Detection d Dictating to Microsoft Word
3 What is the full form of NLP?
a Natural Language Processor
c Natural Language Program
b Natural Language Processing
d Neuro Language Processing
4 Which of the following is a potential application of sentiment analysis using NLP?
a Chatbots tutoring students
b Autocorrecting misspelt words
c Assessing customer feedback on products
d Asking a virtual assistant to check the weather
5 You can ask to play your favourite song.
a Siri
c Google Assistant
6 Where is Bag of Words used in real life?
a Reading story books
c Detecting spam emails
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 ChatGPT is an NLP-powered tool.
2 NLP algorithms are trained on vast amounts of text data.
3 Virtual assistants come in the form of applications only.
b Alexa
d All of these
b Playing outdoor games
d Painting pictures
4 E-commerce sites make use of sentiment analysis to know customer’s preferences.
5 NLP can be used to analyse written text for grammatical errors.

D. Answer the following questions.
1 Define NLP.
2 What are virtual assistants?
3 How does NLP contribute to providing a personalised learning experience?
4 How can NLP help businesses know their customer preferences?
5 What is the purpose of the MIT App Inventor?
6 Apply the Bag of Words algorithm to the following sentence: “AI is changing the world because AI can solve problems and AI can learn from data.”
F. Apply your learning.
1 Sita’s friend Anita is visually impaired. Sita sees Anita working on MS Word and notices that the text in the file is being read aloud to Anita. What will Anita’s answer be when Sita asks her about this interesting feature in MS Word?
2 Sneha notices that whenever she makes a spelling mistake while texting, the messaging app automatically corrects the word. Which application of NLP do you think is being used here?
3 Rohan is amazed to see how his friend uses Alexa to play his favourite songs with voice command. He asks what else this virtual assistant can do besides playing his friend’s favourite songs. What do you think Rohan’s friend will tell him?

As we already know, artificial intelligence is a technology that enables machines to perform various tasks like humans. For example, voice assistants like Siri and Alexa use artificial intelligence that assist in performing any task using simple voice commands.
Artificial Intelligence has grown very quickly in recent years. Earlier, AI was mainly used for recognising speech, understanding text, or identifying objects in images. Now, AI can also be used for creating completely new content, such as stories, poems, drawings, music, or even computer programs. This creative ability of AI is called Generative AI. It is becoming popular in many areas of life, from helping people write and design, to assisting in learning and problem solving. Generative AI gives us new ways to express ideas and explore creativity, making it one of the most exciting parts of modern technology.
Generative AI is a category of artificial intelligence algorithms that learn patterns from existing data and use that knowledge to produce new, similar, or innovative content based on the patterns it has learned. Generative AI can generate different types of new content, such as text, image, code, audio, and video, in response to input.
Generative AI plays a significant role in our lives, especially through chat applications and other creative tools. Generative AI applications take input in the form of text and generate appropriate content. For example, DALL-E, a generative AI application, creates images using a description in natural language. Similarly, Google’s Gemini, formerly known as Bard, is another generative AI application that can generate code in more than 20 programming languages, including Python, C++, Java, JavaScript, etc. It also helps in debugging and code explanation.

The following points discuss the steps involved in the working of generative AI:
Generative AI learns to create new content by looking at numerous examples. In machine learning, this collection of examples is referred to as a training dataset. For example, if you want to teach a computer to draw an elephant, you will show it thousands of pictures of elephants. These images serve as the dataset, allowing the AI system to understand what an elephant looks like.
Generative AI tries to understand patterns used in the examples. For instance, when observing images of elephants, you might notice some common features such as long trunks, ivory tusks, wide ears, and huge heads. Similarly, generative AI tries to capture these patterns from the dataset related to elephants.
Once the generative AI has learnt these patterns, it can create a new image of elephants. It uses its understanding to draw something that looks like an elephant but it is not a copy of any pictures it saw before.
Generative AI does not always produce accurate content on the first attempt. Sometimes the results may look unusual or contain mistakes. To improve, Generative AI uses feedback and keeps learning from its errors. With more practice and better training data, it can create more accurate and useful results over time.
Let us learn about the applications of generative AI.
1. Content Creation: Generative AI tools can create different types of content such as articles, stories, poems, and blogs. They learn from large amounts of data and use that knowledge to produce new content. For example, GPT-4 and Jasper produce human-like content for articles, blogs, stories, and more.

2. Entertainment: Generative AI can compose music, write scripts, and generate visual content for video games and films. For example, AIVA helps students compose original music for projects and presentations.
3. Healthcare: Generative AI can improve diagnostic tools and help develop new medical treatments. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the generative AI tool AlphaFold accurately predicted the shapes of virus proteins and aided in the rapid development of vaccines


4. Fashion and Design: AI can generate new designs for clothing lines to speed up the design process. AI can create images of how clothes look on different body types and poses. For example, designers use AI tools like IBM’s Watson to analyse fashion trends and generate new clothing designs based on popular colours, patterns, and fabrics.


5. Customer Service: Generative AI can be used in chatbots to handle customer queries more effectively. It can provide human-like interactions that help to improve the customer service experience.
6. Education and Training: Generative AI enhances the individual learning experience by helping to create personalised learning materials. For example, Duolingo is a language-learning application that has lessons tailored to each user’s skill level. It adjusts difficulty based on the individual’s learning pace and ability, making language learning more effective and enjoyable.



Objective: To understand the difference between real images and AI-generated images.
Following are the key features of an AI-generated image:






















7. Scientific Research: Generative AI can provide researchers with synthetic data for experiments and analysis. Synthetic data refers to artificially generated data that is similar to real-world data but does not originate from actual observations. It is useful in fields like climate science and biology, where real-world data can be difficult and expensive to obtain.

1. AI-generated images can appear flawless, but they often lack the minute details found in real world environments. There will be inconsistencies in shadows, lighting, or reflections that would not be present as they would be in actual images.
2. AI-generated images will show unnatural smoothness in human skin, texture, and features, making the image perfect but not natural like that in the case of real images.
3. AI-generated images struggle to generate complex backgrounds. In AI-generated images, you will notice that the environment of the photos is blurred and unrealistic. It might also have repetitive patterns.
4. AI-generated images might miss details like text on shirts, brand logos, inconsistent numbers of fingers, eye and ear shapes, etc.
5. Some AI images might have watermarks on them. Look for these watermarks or logos that might suggest it is AI-generated.




Can you determine which of the following images are real and AI-generated? Also, give reasons for your answers.






It may not always be straightforward to identify AI-generated images, and it can indeed be quite challenging at first glance.
However, you can use some AI image detection tools, like Hive Moderation, to verify if the image is AIgenerated or not. Let us follow the given steps.
1. Click on the link below: https://hivemoderation.com/ai-generated-content-detection/?demo=image This link will direct you to a web page. Scroll down to find the ‘Upload’ button.
2. Click on the ‘Upload’ button to upload your image files and check the results to see if an image is AI generated or not.

3. Let us check the result for one of the images that you were asked to identify earlier. The result shows that the uploaded image is not an AI-generated image.
4. Now, similarly, you can test for other images.Generative AI vs Conventional AI
In contrast to conventional AI, generative AI is designed to create new and unique content rather than just processing or classifying existing data. Let us look at some of the differences between conventional and generative AI.
Aspect Conventional
Goal Focus on achieving high accuracy in performing predefined tasks, such as recognising objects in images.
Training Trained to recognise patterns and make decisions by learning from examples.
Output Predictions, classifications, or decisions (e.g., fraud detection, image classification).

Applications Spam detection, image recognition, and recommendation systems.
Focus on creating new data similar to training data, such as writing stories or generating realistic images.
Trained to understand patterns and generate similar new data based on large datasets.
New content such as texts, images, code, or other forms of data (e.g., story generation, music generation).
Story or poem generation, music composition, image creation, and interactive chatbots.
Did You Know?
Generative AI is used in video games to create expensive and dynamic worlds. For example, games like No Man’s Sky use AI to generate entire planets with unique ecosystems, landscapes, and creatures.
ChatGPT is an advanced Generative AI tool created by a company called OpenAI. The name “GPT” stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer, which is a type of AI model trained on a huge amount of text data. This training helps ChatGPT understand human language and generate answers that sound natural.
ChatGPT can answer questions, explain topics, compose poems, write stories, solve problems, translate languages, and even generate computer code. It does not “think” like humans but gives answers by choosing words that fit best, based on the patterns it has learned from data.
ChatGPT is a versatile tool that can support learning, creativity, and everyday activities. Some of its uses include:
• Education: Explains difficult topics in easy language, summarises lessons, and helps with essays or project ideas.
• Creativity: Generates poems, stories, songs, or even jokes to inspire imagination.
• Problem-solving: Provides answers to questions, suggests ideas, and explains solutions step by step.
• Language support: Translates sentences, corrects grammar, and suggests better vocabulary.
• Everyday tasks: Helps in drafting emails or making simple schedules.
ChatGPT can be accessed easily on the internet, and with just a few steps you can start using it.
1. Click on the link: https://chat.openai.com/. This will direct you to a web page as shown.

2. Sign up using an email address or a Google/Microsoft account.
3. Click the ‘Try ChatGPT’ button.
4. On the web page that appears, type a question or request in the text box.
5. Click the Enter button and ChatGPT will reply instantly with an answer. You can continue the conversation just like chatting with a person.
Always check important information from trusted sources, because ChatGPT can sometimes make mistakes.
Match the following.
ChatGPT
DALL·E
Makes images from text
Writes text answers
AIVA Helps in medical research
AlphaFold Gives language lessons
Duolingo Composes music
Generative AI is a category of artificial intelligence algorithms that learn patterns from existing data and use that knowledge to produce new, similar, or innovative content based on the patterns it has learned.
DALL-E, a generative AI application, creates images using a description in natural language.
There are many applications of generative AI such as content creation, entertainment, healthcare, fashion and design, customer service, education and training, scientific research, etc.
ChatGPT is an advanced Generative AI tool created by a company called OpenAI. The name “GPT” stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer.
ChatGPT can answer questions, explain topics, compose poems, write stories, solve problems, translate languages, and even generate computer code.
A. Fill in the blanks.
The application is used to create images using generative AI. refers to artificially generated data that is similar to the real-world data but does not originate from actual observations.
ChatGPT is an advanced Generative AI tool created by a company called is a language-learning application that has lessons tailored to each user’s skill level.
Google’s , formerly known as Bard, is a Generative AI application that can create computer code in many programming languages.
B. Tick () the correct option.
Which of the following can be created using generative AI?
a Images b Sounds
c Stories
d All of these
Which of the following is not a common application of generative AI?
a Music composition
c Image synthesis
b Fraud detection
d Story writing
The full form of GPT in ChatGPT is .
a General Purpose Transformer
c Global Processing Technology
b Generative Pre-trained Transformer
d Generative Programming Tool
ChatGPT can do all of the following except .
a Compose poems and stories
c Generate computer code
What is the goal of Conventional AI?
a Write poems
c Do predefined tasks accurately
b Translate languages
d Think like humans
b Generate music
d Create images

C. Write T for True and F for False.
Generative AI can improve diagnostic tools and help develop new medical treatments.
Conventional AI is trained to recognise patterns and make decisions by learning through examples.
Generative AI can be used in chatbots to handle customer queries.
ChatGPT understand human language and generate answers that sound natural.
Generative AI can only produce textual content.
D. Answer the following questions.
Name any three tools that use generative AI.
Mention any two uses of ChatGPT in everyday life.
How does generative AI improve personalised learning in education? Give an example.
Differentiate between conventional AI and generative AI.
Explain in brief how Generative AI works to create new content.
E. Apply your learning.
Samuel runs an online store and receives many customers’ queries every day. How can generative AI in chatbots help him improve customer service?
Jasreen is a student who loves drawing and is excited to learn about DALL-E, a generative AI tool that creates images based on text descriptions. Explain how DALL-E can help Jasreen visualise the kind of image Jasreen might want to generate based on her description using DALL-E.
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 An controls and manages all the computer resources.
2 A is a central device or place that connects multiple devices on a computer network.
3 A is a visual representation of an algorithm or process, using symbols and arrows to illustrate the sequence of steps.
4 apps are the programs that you install on your phone for whatever you want to do.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 A operating system manages multiple computers that are connected to each other through a network.
a Single-user
c Real Time
b Multiuser
d Distributed
2 A connects multiple LANs within that area which enables communication between various locations.
a LAN
c MAN
b CAN
d WAN
3 is a data analysis method that uses machine learning algorithms to automatically recognise patterns and regularities in data.
a Decomposition
c Abstraction
b Pattern Recognition
d Algorithmic Design
4 The function is used to add the values given in a specific cell range.
a Sum()
c Power()
b Average()
d Min()

C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 A multiuser OS allows multiple users to work on the same computer simultaneously.
2 Concatenate() function combines multiple text strings into one.
3 A good algorithm should solve problems quickly and efficiently.
4 Telegram is an example of the native app.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 Write any two differences between CUI and GUI.
2 Define sorting.
3 Name the pillars of computational thinking.
4 What is the benefit of using a banking app?
E. Apply your learning.
1 Divyansh is at home and needs to share a large presentation file with his colleague who lives in another city. Which type of network would be most suitable for this task?
2 Pihu has drawn a flowchart, but she used the wrong shape to display the statement Z = A + B. Suggest her the correct shape to put the statement.
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 is a NLP model which helps in extracting features from the text, which can be helpful in machine learning algorithms.
2 The SQL commands that are used to insert, delete, or update data in the table of a database are called commands.
3 The option offers a wide range of design elements, including photos, videos, stickers, shapes, and icons.
4 NLP helps keep your email inbox free from unwanted mails also known as .
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Which of the following is a capability of ChatGPT?
a Cooking food
c Driving a car
b Explaining topics
d Painting a wall
2 data types are used to store a numeric value in a field column.
a Number
c Date
b Character
d Time
3 A is an AI tool that understands and responds to voice commands or text inputs, such as questions and requests, and also performs tasks for you.
a Language translation
c Sentiment analysis
C. Write T for True and F for False.
b Spam detection
d Virtual assistant
1 Drones are used for tasks such as aerial photography, surveillance, and package delivery.
2 HDBMS stores data in a network-like structure.
3 Video editing involves arranging, modifying, and enhancing video clips to create a project.
4 The MIT App Inventor is an online platform for creating apps for mobile phones and tablets.

D. Answer the following questions.
1 Write any three applications of Generative AI.
2 Describe the key role of a DBMS.
3 What is data science?
4 What is speech recognition?
E. Apply your learning.
1 Urvashi wants to create and edit videos for her school project using an easy online tool. Which application should she use?
2 Anuj wants to know the difference between RDBMS and OODBMS. Explain them to him.
3 Bhavna is unaware of the role of data science in the field of sports. Write any two roles to inform her.
4 Raghav wants to translate a paragraph from English to French. Which application can he use to do this?
Tekie.AI is a pioneering Computer Science series that places Artificial Intelligence at its core, helping learners understand how AI is transforming everyday life. Compliant with NEP 2020, it blends core computer science knowledge with real-world AI applications, building skills, curiosity, and confidence for an AI-driven future. Through the thrilling adventures of Mel and Conji from the world of Avora, the series makes complex ideas engaging and relatable. More than just a book, Tekie.AI is a pathway to the future, connecting classroom learning with the technologies shaping tomorrow’s world.

• AI Connect: Linking core computer concepts with cutting-edge AI applications
• AI Activities: Engaging exercises to explore and apply AI concepts in practical ways
• Experiential Learning: Hands-on exposure through digital experiences
• In-built Triggers: Stimulating prompts and questions for classroom interaction and critical thinking
• Assessments: Tools to evaluate understanding of concepts and application of skills
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-93-89789-26-3

