

序 Preface
在全球產業面臨數位轉型與永續發展的雙重壓力下,設計的角 色正逐漸從傳統的美學與服務功能,轉變為推動創新與系統整 合的關鍵動能。《臺灣企業設計應用動態發展》報告以「設計 驅動科技與商業的雙軸創新」為核心議題,採取理論與實證並 重的研究方法,系統性分析臺灣企業如何透過設計實踐,強化 組織韌性、提升技術轉化效能,並建構具有文化識別性的品牌 價值體系。
本研究以2020至2024年間共2,835件金點設計獎Golden Pin Design Award(GPDA)入選作品為主要分析樣本,結 合量化語彙分析與15位企業決策者及設計主管的深度訪談, 歸納出設計介入企業發展的兩大驅動軸——科技與商業——以 及對應的十項核心策略架構。此方法論有助於揭示設計在技術 應用、倫理實踐、品牌經營與市場溝通等層面的關鍵作用,並 進一步論證設計作為企業創新治理核心引擎的潛力與價值。
研究結果顯示,設計的核心價值體現在其轉譯與整合能力。在 科技驅動面向,設計有助於將抽象技術轉化為具體且可感知的 使用體驗,進而促進數位轉型與永續技術的落實;在商業驅動 面向,設計則能強化品牌一致性、優化顧客互動機制,並協助 重構價值主張與提升市場韌性。可見,設計已不再僅是產品開 發末端的附加功能,而是連結技術創新、商業模式與社會價值 之間的關鍵策略中介,具備引導跨領域創新與推動永續發展的 系統性能力。
本報告的重要洞察指出:臺灣企業的設計實踐正逐步從「設計導 入」階段,邁向「設計治理」的制度性轉型階段。相關研究成果 可為企業經營者、政策制定者與設計專業實踐者提供具體的決策 依據,並為未來產業創新策略的規劃提供明確的行動框架,有助 於推動設計成為臺灣創新體系持續演化的核心驅動力量。
財團法人台灣設計研究院 劉世南研發長
As industries worldwide face the dual pressures of digital transformation and sustainable development, the role of design is gradually shifting from traditional functions of aesthetics and service to a key driver of innovation and system integration. The report “ Dynamic Development of Design Application among Taiwanese Enterprises ” centers on the theme of “Driving Dual Innovation of Technology and Business through Design”, adopting a research approach that integrates theory and empirical analysis. It systematically examines how Taiwanese enterprises leverage design practices to enhance organizational resilience, improve technological translation efficiency, and build culturally distinctive brand value systems.
The study analyzes 2,835 winners of the Golden Pin Design Award (GPDA) between 2020 and 2024 as its primary dataset. By combining quantitative lexical analysis with in-depth interviews of 15 corporate decision-makers and design executives, the research identifies two major driving axes—technology and business—and establishes a corresponding framework of ten core strategies. This methodology helps to uncover the critical functions of design in technological application, ethical practice, brand management, and market communication, further demonstrating its potential and value as a central engine for corporate innovation governance.
The findings reveal that the core value of design lies in its ability to translate and integrate. In terms of driving technology, design facilitates the transformation of abstract technologies into tangible and perceivable user experiences, thereby promoting the implementation of digital transformation and sustainable technologies. As a business driver, design strengthens brand consistency, optimizes customer interaction mechanisms, and helps reconstruct value propositions while enhancing market resilience. Evidently, design is no longer a final-stage function in product development; rather, it serves as a strategic intermediary that connects technological innovation, business models, and social value, endowing it with the systemic capability to guide cross-disciplinary innovation and drive sustainable growth.
A key insight of the report highlights that Taiwanese enterprises are evolving from the stage of “design adoption” toward a phase of institutionalized “design governance.” The research outcomes offer concrete decision-making references for business leaders, policymakers, and design practitioners alike. Moreover, they provide a clear action framework for future industrial innovation planning, contributing to the advancement of design as a core driver in the continual evolution of Taiwan’s innovation ecosystem.
Taiwan Design Research Institute (TDRI) Shyhnan Liou - Vice President, R&D
前言 Introduction
近年來國際情勢、環境變遷,以及科技的發展,都為產業帶來 深遠的影響。全球的產業都在積極回應環境、社會與公司治理 的指標(ESG) 或是永續發展目標(SDGs)。面對新興技術 發展,也積極透過人工智慧(AI)、物聯網(IoT)與大數據 分析等技術佈局、角逐市場,而這樣的產業環境,讓具備彈性 與應變能力的企業,開啟無限機會。然而,相較僵化或規模較 小之企業,則可能因難以跟上變化而被市場淘汰,而設計正是 幫助企業面對挑戰的重要策略資產。
從各大國際設計獎項,例如iF設計獎(iF Design Award) 以及紅點設計獎(Red Dot Design Award)的趨勢來看, 設計除了被用以提升視覺美感外,更多時候是透過設計進行 思維整合,以及企業價值主張的深化。而企業除了透過科技 實力的提升、營運模式的優化壯大發展之外,甚至可藉由設 計的策略價值,替開發的產品、提供的服務為企業本身提供核 心的力量。金點設計獎(Golden Pin Design Award)創立 自1981年,起初以建立臺灣人重視優良設計產品角度出發, 運行至今達39年,至今已廣納許多國內及國際企業的傑出設 計案例。本計畫考量數據完整性、趨勢有效性,以其近五年 (2020–2024)獲獎案例為研究樣本,透過了解設計作品之 理念,以及與設計團隊的訪談,歸納出臺灣企業應用設計之策 略以及趨勢。受訪團隊主要來自「製造業」、「通訊業」及「設 計服務業」,為相關產業之企業進一步提供參照,瞭解其策略 行動與思維。
本研究報告設定的讀者為國內外企業主管、專案負責人,以及 設計團隊。企業主管及專案負責人可藉本研究拓展設計資源導 入的視野,輔助設計投資規劃與跨部門資源整合;設計團隊則 能透過跨產業學習,重新思考設計角色定位與影響力,推動創 意思維落地並促進產業發展。臺灣企業若欲有效發揮設計潛 能,建議可從三個方向深化應用:首先,讓設計參與企業策略 前端,從市場洞察、商業模式規劃到技術研發,形成以使用者 需求為核心的決策機制;再者,運用設計促進跨部門協作與系 統整合,將設計視為協調營運與創新流程的關鍵手段;最後, 導入價值導向思維,將科技倫理、文化因素與永續指標納入設 計評估架構,使設計成為實現企業社會責任與品牌承諾的實踐 路徑。透過本報告,期望能促進臺灣企業設計應用知識的交 流,鼓勵產業與企業透過設計並肩前行,進而協助企業提升韌 性;也期盼讓國際讀者更瞭解臺灣企業的應用設計的走向,藉 以促進與國際市場的連結。
In recent years, global geopolitical shifts, environmental changes, and advances in technology have profoundly impacted industries. Around the world, businesses are actively responding to indicators of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance, as well as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Companies are also using technological tools such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics to expedite deployment. Flexible enterprises can take advantage of such opportunities, while those that are not may risk being eliminated from the market. In this time of change, design has become a critical strategic asset of enterprises.
Trends reflected in major international design awards, such as the iF Design Award and the Red Dot Design Award, reveal that, in addition to enhancing aesthetics, design increasingly serves as a means of integrating thinking and deepening value. Beyond technological advancement and operational optimization, companies can also drive product and service innovation through design. Since its inception in 1981, the Golden Pin Design Award (GPDA) has accumulated a wealth of outstanding domestic and overseas cases. This study takes the award-winning works of the Golden Pin Design Award from the past five years (2020–2024) as its research sample. Through conceptual analysis and interviews, it identifies the strategies and trends of design application among Taiwanese enterprises. The interviewees include teams from the manufacturing, communications, and design service industries.
The report is intended for corporate executives, project leaders, and design teams. For the former, it aims to broaden perspectives on design introduction and resources integration; for the latter, it provides opportunities for crossindustry learning, helping them redefine the role of design and translate creativity into tangible results. Ultimately, this study seeks to foster design knowledge exchange among Taiwanese enterprises, strengthen industrial resilience, and showcase the distinctive characteristics and capabilities of Taiwan’s design on the international stage.
1.1
1.2
4
GPDA 臺灣案例設計應用洞察 Insight from GPDA Taiwan Cases and Design Applications
4.1 GPDA 案例 Golden Pin Design Award Cases
4.2 設計發展應用總結 Summary of Design Development and Application
4.3 設計應用實踐與資源鏈結建議 Design Application Practice and Resource Connection Recommendations
Conclusion and Future Outlook
附錄 Appendix
1設計如何為企業創 造策略價值?
How Does Design Create
Strategic Value for Enterprises?
企業能否有效運用設計資源、進而提升組織競爭力,這些前提 乃自於對設計的理解與應用。
本章旨在鋪陳本報告的背景脈絡,說明設計在產業與社會情境 中的角色轉變,並探討其作為策略工具如何回應企業在科技創 新,與市場轉型過程中所面臨的挑戰與機會。
基於對國內外設計趨勢、產業策略與實務案例的分析,首先透 過本章引導讀者釐清「何謂設計」,以及設計在企業發展中可 發揮的潛在價值。隨著永續轉型、數位轉型與社會創新等議題 漸成全球主流,設計不僅是美學或表層裝飾的代名詞,而是一 種跨領域的整合能力與價值創造機制,能夠引導企業重新思考 產品、服務、系統設計,甚至擴展到組織的運作模式。
本章將從設計的多重角色出發,釐清其如何轉化為企業內部的驅 動力,並結合既有研究文獻,對應科技(Technology)、商業 (Business)和社會(Society)三項發展動能,為後續分析科 技所驅動的設計策略,以及商業所驅動的設計策略形成後續分析 設計策略基礎。
An enterprise’s understanding of design forms the foundation for effectively utilizing design resources and enhancing competitiveness.
This chapter aims to establish an analytical framework and value system to illustrate the evolving role of design in contemporary industries and society. It further explores how design, as a strategic tool, responds to the challenges and opportunities brought by technological innovation and market transformation.
With sustainability, digital transformation, and social innovation becoming mainstream, design has transcended its traditional function of aesthetic enhancement. It now emphasizes the critical abilities of cross-disciplinary integration and value creation, guiding enterprises to rethink their products, services, systems, and organizational models.
This chapter will outline the multifaceted roles of design and, through a review of relevant literature, connect these roles to the three major drivers of development—technology, business, and society. This serves as the foundation for the subsequent analysis of how technology and business can drive design strategies.
設計的角色
The Role of Design
因個人經驗差異,以及所屬設計領域類別的不同,「設計」在理 解上往往多元且存在落差,正如國際設計委員會(International Council of Design)所言,它難以用單一定義涵蓋1。
近年來,設計的應用範疇,更持續朝人們既有的認知之外擴 展。隨著科技的快速崛起,以及社會與環境議題的推動,設計 被賦予了龐大的任務,協助人們回應低碳永續、高齡照護,以 及提升生活品質,甚至影響了政策制定等,以回應複雜的公共 議題與挑戰 3。
The concept of “design” encompasses diverse interpretations shaped by individual experience, and—as noted by the International Council of Design—it cannot be confined to a single definition. In recent years, design applications have continued to expand beyond traditional understandings1
With the rise of technology and the growing urgency of social and environmental issues, design has been tasked with addressing goals such as low-carbon sustainability, elderly care, urban–rural connectivity, and quality of life, while also permeating fields such as finance, healthcare, and technology3
這些延伸的新角色,使設計在建築、產品、時尚、數位、視覺 等熟知領域之外,進一步滲透到金融、醫療、科技等產業。義 大利《設計經濟報告》(Design Economy Report)便以米 蘭設計週等案例指出,設計是帶動跨產業整合的重要力量,能 夠串聯文化創意產業、製造業與數位產業,並創造可觀的產值 與效益。這顯示設計不僅承載文化與美學意涵,更同時肩負提 升社會道德責任與整體經濟成長的潛能。
設計也是一種創意思考與問題解決的方法,強調同理心、使用 者體驗,並以系統化的角度來提供解方。尤其在面對當今科技 快速崛起、社會環境挑戰與市場不確定性的局勢下,設計已超 越邊陲性的輔助角色,在跨域交流溝通與關係建立上,扮演了 不可忽視的角色,並逐漸朝企業之核心商業策略靠攏,影響企 業最終決策。
According to Italy’s Design Economy Report, which cites Milan Design Week as an example, design serves as a connective force linking the cultural, creative, manufacturing, and digital industries—generating substantial economic value and impact. This demonstrates that design carries not only cultural and aesthetic significance but also embodies social responsibility and economic potential.If viewed merely as a tool for aesthetic enhancement, design’s full potential cannot be realized.
Rather, design is a methodology of creative thinking and problem-solving, emphasizing empathy and systemic thinking. Amid rapid technological development and mounting societal and environmental challenges, design has shifted from the periphery to the core, emerging as a vital force for cross-disciplinary communication and strategic decision-making within enterprises.
驅動企業發展的三要素
Drivers of Enterprise Development
企業在面對日益複雜的全球變局與產業創新挑戰時,需具備 清晰的成長動能與調適能力。Ross Dawson曾在2009年 MegaTrend研討會中提出:科技(Technology)、商業 (Business)和社會(Society)三要素是驅動整體經濟發展 的力量,能夠帶給企業宏觀視野應對變局 6。這三個因素構成 了企業營運環境的核心動態,影響其應對挑戰與創造價值的方 式,設計,正是在這之間扮演關鍵的整合角色。
In the face of global transformations and innovation challenges, enterprises must possess clear growth drivers and adaptive capabilities. At the 2009 Mega Trend Conference , Ross Dawson identified “technology, business, and society” as the three core forces driving development, offering enterprises a macroscopic perspective 6 . These three factors form the key dynamics of the operating environment, influencing how companies respond to challenges and create value—where design plays an integrative role.
● 科技因素
指涉如通訊技術、運算能力、人工智慧,與自動化等新興技術 的快速演進。透過對這些新興技術的掌握,可替產業帶來生產 效率根本性的改變,並塑造前所未有的市場機會。
然而,由於專業技術的複雜度與導入門檻高,對於非科技產業 與企業來說不易理解應用,科技領域中熟知新興技術的企業也 因為其專業性造成跨域交流難度高。因此設計扮演「技術轉 譯」的角色,將抽象的科技潛力轉化為人們易理解、易使用的 產品與服務體驗,進而提升技術落地的速度,讓科技要素之驅 動力真正發揮作用。
● 商業因素
意指商業資訊的快速流通、獲利模式的快速複製,以及效率持 續提升等作為,塑造商品化的產品,並提供相應的服務,幫助 企業快速適應以及提高市占率。
然而產業經濟體系一端是商品化導向,另一端則是偏向高價值 的供給。市場商品化的競爭,背後的低成本是關鍵之一,而要 避免價格戰便不可忽視建立跨域關係與創新所帶來的力量。而 「設計」涵蓋價值導向、跨領域合作,以及將未來情境概念化 等能力 4,因此可驅動企業的商業發展。
● 社會因素
說明人們對生活的期待,推動著產業與經濟的變革,體現消費 者不同時期的需求與價值觀的轉變。例如:對生活品質的渴望, 推動貧困人口邁向中產階級、較富裕的人口追求更高層次的精 緻體驗;網路技術的進步提升人們對政策與制度參與的期待, 這使得企業必須背負社會角色與責任。
「設計」以人為本,係落實社會責任的工具,幫助企業將價值 導入科技與商業層面,回應群眾期待。同時,國際社會也透過 永續發展目標與「環境、社會與公司治理」等指標,對企業提 出更高的責任標準與要求。
● Technology
Emerging technologies—such as telecommunications, computing power, artificial intelligence, data storage, and automation—are rapidly advancing, bringing fundamental changes in efficiency and market opportunities across industries.
However, their high complexity and implementation thresholds often make it difficult for non-technology sectors to adopt them effectively.Even technology companies, due to their specialization, face challenges in crossdisciplinary communication. In this context, design serves as a “technology translator,” transforming the abstract potential of technology into understandable and usable products and service experiences, thereby accelerating its implementation and maximizing its impact.
● Business
The rapid flow of business information, replication of profit models, and improvements in operational efficiency have fueled the commodification of products and services, enabling enterprises to seize markets swiftly.
However, competition driven by commodification often depends on low cost, leading to potential price wars. To avoid this, companies must emphasize cross-sector collaboration and innovation. Design—with its valueoriented approach, cross-disciplinary integration, and capacity for future scenario thinking 4 — can enhance a company’s business drivers.
● Society
Shifts in people's“expectations”of life continually drive industrial and economic transformation, reflecting changing needs and values over time. For instance, the pursuit of a better quality of life has enabled lowincome populations to enter the middle class, while affluent groups seek more refined experiences. The advancement of internet technology has also raised public expectations for participation in policy and institutional processes, compelling enterprises to assume greater social responsibility.
Design, being human-centered, serves as a key instrument for realizing social responsibility, helping enterprises introduce value into technology and business to respond to collective expectations. At the same time, the international community, through the SDGs and ESG frameworks, has placed higher expectations and sustainability responsibilities on enterprises.
圖1.企業發展驅動力(本研究依Ross Dawson 提出之概念重新繪製)
Figure 1. Drivers of Enterprise Development (Redrown for this study)
本節旨在釐清設計在企業發展中的關鍵角色與潛在價值,指出 設計逐漸成為企業應對環境變遷、科技創新與市場競爭的重要 策略工具。設計能夠透過創意思維與系統性分析,連結技術開 發、商業價值與社會需求,進一步擴張企業的組織能動性與策 略縱深。
引用Ross Dawson提出的三大驅動力模型(科技、商業、 社會),說明設計如何在其中扮演中介與整合角色。在科技面 向,設計協助企業將抽象技術轉化為具體、可感知的產品與體 驗,降低科技落地門檻,提升使用接受度;在商業面向,設計 則能清晰傳遞品牌價值、強化顧客連結,並引導企業跳脫價格 競爭,轉向創新驅動;在社會面向,設計透過以人為本的介入, 回應日益升高的社會責任與永續要求,並與SDGs、ESG等 全球性指標接軌。
設計於企業發展的角色不僅具策略性,更具跨域整合與價值創 造的潛能。後續以「科技驅動力」與「商業驅動力」兩大主軸 作為設計策略應用分析基礎,並引導企業與設計團隊重新思考 設計的應用價值與未來潛力,強化其在不確定環境中的應變能 力與長期韌性。
This chapter aims to clarify the key role and potential value of design in contemporary enterprise development while establishing a theoretical and practical foundation for subsequent analysis. In recent years, design has transcended its traditional focus on form and aesthetics, evolving into a strategic tool that enables enterprises to respond to environmental change, technological innovation, and market competition. Through creative thinking and systems analysis, design bridges technology, business, and societal needs, expanding an enterprise’s agency and strategic depth.
Drawing on Ross Dawson’s model of the three drivers (technology, business, and society), this chapter highlights design’s mediating and integrative role. On the technological front, design transforms abstract technologies into tangible user experiences, reducing barriers to implementation. On the business front, design strengthens brand value and customer connection, helping enterprises shift from price competition to innovation. On the social front, design adopts a human-centered approach to address social responsibility and sustainability imperatives, aligning with the SDGs and ESG frameworks. Design is not only strategic but also possesses the potential for cross-disciplinary integration and value creation. It lays the foundation for subsequent analyses of “technologydriven” and “business-driven” design strategies, helping enterprises and design teams expand the boundaries of application and strengthen their resilience.
2
研究方法與流程 Research Methodology
「金點設計獎 Golden Pin Design Award(GPDA)」是由臺灣 主辦的國際設計獎項,前身為「國家設計獎」,自2009年更 名運行至今長達16年之久,已累積相當龐大的資料庫,收錄 橫跨不同產業的優秀設計作品。
本研究建構於「金點設計獎 Golden Pin Design Award (GPDA)」的案例基礎之上,涵蓋量化數據分析和以半結構式 訪談取得之產業第一線的實際回應,藉此整理出設計應用策略趨 勢之變化以及設計價值供給的觀點,讓企業主管、專案經理與設 計團隊能快速領會、檢視,或者思考下一步該如何調整策略,使 設計發揮影響力並驅動整體經濟發展。整體研究流程如圖2。
The Golden Pin Design Award (GDPA) is an international design competition organized in Taiwan.Since its renaming from the “National Design Award” in 2009, it has operated for 16 years, accumulating a wealth of outstanding crossindustry cases.
This study combines international trend literature with GPDA case studies, employing quantitative analysis and semi-structured interviews to examine changing trends and value perspectives in design application strategies. The researchprocess is as follows:
圖2.研究流程圖
Figure 2. Research Process Diagram (Source: Compiled by this study)
01 | 研究範圍確立 首先,本研究以「設計作為策略工具」的視角出發,聚焦於「科 技」與「商業」兩大範疇,探討企業內部發展的兩大面向:「設 計介入科技驅動力」以及「設計介入商業驅動力」。基於近年 設計趨勢與產業趨勢文獻,彙整出兩大範疇、共十大設計應用 策略。除了設定本研究下一階段「設計應用策略 趨勢研究」 的研究框架以外,也系統性地掌握前述兩面項下設計應用的策 略。
02
| 設計應用策略-趨勢研究 研究進一步檢視近五年共2,835件的設計獎作品設計理念詞 彙,這些作品一半來自臺灣(1,417 件),一半來自國際(1,418 件)。透過分析詞彙得出臺灣企業常見的設計應用策略,加以 歸類整理成趨勢,以具體瞭解到哪些策略對臺灣企業來說具有 突出的落地機會,幫助企業發揮「科技」和「商業」發展驅動 力;也反映臺灣設計應用在國際市場上的特殊性與定位,和臺 灣整體產業現況的核心需求及未來創新的風險。
03 | 設計應用策略-觀點梳理
本研究透過對臺灣GPDA獲獎作品中的設計理念進行系統性 剖析,精選11件具代表性的企業案例,以「半結構式訪談」 訪談企業內部推動設計應用的關鍵人物共15位,受訪者涵蓋 品牌策略總監、設計師、專案經理等角色。透過這些第一線的 實踐經驗與策略分享,本研究得以掌握企業導入設計的組織機 制、部門間協作流程,以及設計決策如何在實務中轉化為可見 的商業與社會價值。目標對象的訪談內容不僅讓本研究得以描 繪出企業應用設計的行動,也揭示設計如何成為驅動轉型與創 新發展的核心策略。
最後,本研究整理出具共通性的設計應用思維與模式,期望能 為其他企業與設計團隊提供參照與啟發,加速設計在不同產業 場域中的落地實踐。
01 | Establishing Research Scope
From the perspective of design as a strategic tool, this study focuses on the two main domains of “technology” and “business,” examining “Design Intervention in Technology Drivers” and “Design Intervention in Business Drivers.” Based on recent literature on design and industry trends, ten design application strategies were identified to serve as the foundation for subsequent analysis.
02 | Design Application Strategies – Trend Study
The design concepts of 2,835 Design Award winners from the past five years were examined—1,417 from Taiwan and 1,418 international entries—to summarize common strategies and trends among Taiwanese enterprises. This analysis helps companies identify potential strategies to leverage “technology” and “business” drivers, while revealing Taiwan’s positioning in the international market, industry demands, and innovation risks.
03 | Design Application Strategies – Perspective Study
Focusing on 11 representative enterprise cases, 15 key personnel (strategy directors, designers, and project managers) were interviewed to analyze organizational mechanisms, collaboration processes, and decision-making transformations related to design implementation. These frontline insights reveal how design functions as a core strategy for transformation and innovation.
Finally, the study identifies common patterns of application thinking to serve as references and inspiration for enterprises and design teams, accelerating the realization of design value.
十大設計策略
與整體變化 趨勢
Ten Design Strategies and Overall Trend Changes
本章節將聚焦於設計如何回應企業發展中的兩大核心驅動 力——「科技驅動力」與「商業驅動力」,並進一步解析 設計所衍生的具體設計策略。透過金點設計獎 Golden Pin Design Award(GPDA)獲獎案例的觀察與剖析,本章揭 示臺灣在設計應用上具有代表性的企業其策略實踐的亮點和特 色。
這些案例展現企業如何運用設計回應技術創新與市場變化,也 反映出臺灣產業面對國際競爭下的核心需求與未來挑戰。這些 成功經驗可提供企業與設計團隊得以借鏡的策略思維與實踐模 式,進而強化設計在組織轉型、價值創新與市場定位中的關鍵 作用。透過本章節的解析,讀者能更具體理解設計如何作為企 業永續成長的策略引擎。
This chapter focuses on how design responds to the two core drivers of enterprise development —“technology” and “business”— by analyzing the specific design strategies they generate. Drawing on empirical observations from awardwinning cases of the Golden Pin Design Award (GPDA), it highlights the distinctive strategic practices of Taiwanese enterprises that are leading in design application. The chapter demonstrates how companies leverage design to address technological innovation and market shifts, while also reflecting the core needs and future challenges of Taiwanese industries facing international competition.
It provides enterprises and design teams with strategic thinking and practical models to learn from, thereby reinforcing design’s critical role in organizational transformation, value innovation, and market positioning. Through the analysis presented in this chapter, readers can gain a concrete understanding of how design functions as a strategic engine for sustainable enterprise growth.
3.1
十大設計策略
Ten Design Application
Strategeis
本研究整理設計作用於「科技」與「商業」這兩大範疇的十項 關鍵策略,並說明各項應用策略的功能與帶來的效益。在「設 計介入科技驅動力」以及「設計介入商業驅動力」兩大類別中, 分別收斂出五項設計策略(見圖3、圖4 )。
This study organizes ten design strategies, with five strategies each under the two domains of “technology” and “business.”
● 設計介入科技驅動力
在科技驅動的創新過程中,設計扮演著銜接人與技術之間的關 鍵角色:從使用者與系統的角度出發,識別問題、整合跨部門 需求,並協助企業回應日益複雜的市場與技術挑戰。更重要的 是,設計具有將技術轉化為具體價值的能力,使創新不僅止於 技術本身,而能真正落實於使用體驗與商業成果。透過設計對 跨域協作的推動與介面整合,科技帶來的生產效率得以被充分 發揮,進一步擴大其在組織層面的影響力。
● Design Intervention in Technology Drivers
Design plays a critical role in this domain by approaching challenges from both the user and system perspectives. It identifies problems, integrates cross-departmental requirements, and helps enterprises respond to complex market and technological scenarios. More importantly, design has the ability to translate technology into tangible value, ensuring that innova tion goes beyond the technical itself and is realized in user experiences and business outcomes. By facilitating cross-disciplinary collaboration and interface integration, design enables the full potential of technology-driven productivity gains to be realized, further amplifying its impact at the organizational level.
圖3.「設計介入科技驅動力」應用策略(資料來源:本研究整理)
Figure 3. Design Application Strategies – Technology Drivers (Source: Compiled by this study)
① 強化技術敏銳性
在產品開發前期階段,設計師需具備高度的技術感知能力,如 掌握AI 、IoT、生物科技、再生材料等前沿技術的發展趨勢, 並透過分析預測科技技術對使用者體驗、社會行為與文化脈絡 的潛在影響。技術敏銳性有助於設計引導創新方向,提升科技 的創新融合與應用,以回應社會價值與需求的方向。設計從被 動支援的角色轉向主動驅動創新的力量,將科技轉化為有意義 且具文化關聯性的創新應用。
② 人機協作優化
在人與科技的互動過程中,設計扮演了關鍵的調節角色。介於 產品與服務的開發及後期原型測試階段之間,設計透過反覆的 原型驗證與使用者測試,使科技所創造的成果得以持續被修正 與優化,最終達成人與系統之間高品質的協作關係。從使用流 程的流暢度、感官體驗的自然性,到心理層面的信任建立,設 計讓科技更可感、可親與可信。以人為中心的協作設計,使技 術創新兼具功能效益與易用性,成為提升科技應用品質的關鍵。
① Technology Sensitivity
In the early stages of product development, designers need to possess a high level of technological awareness, keeping abreast of cutting-edge trends in AI, IoT, biotechnology, and renewable materials. By analyzing and predicting how these technologies may impact user experiences, social behaviors, and cultural contexts, designers can guide innovation toward addressing societal values and needs, enhancing the integration and application of technology. This sensitivity allows design to shift from a passive support role to an active driver, transforming technology into meaningful innovative applications with cultural relevance.
② Human-Tech
During the mid-to-late stages of product and service development, as well as in the later prototype testing phase, design plays a crucial role through iterative prototyping and validation. This process ensures that technologydriven outcomes are continuously analyzed and refined to achieve high-quality interactions between humans and technology. From user workflows and sensory experiences to building psychological trust, design helps make technologies like AI and IoT more tangible, approachable, and reliable, increasing people’s willingness to embrace the fundamental changes these technologies bring.
③ 推動數位轉型
設計協助企業在數位轉型中扮演關鍵橋接角色。無論是服務流 程再設計、資料驅動的互動優化,或系統平台整合,設計皆能 化解跨領域合作的溝通隔閡,促進不同專業協同運作。透過設 計介入,數位轉型不僅止於技術更新,更能在體驗與組織層面 達成一致,使產品與服務更具親和力,並提升整體營運效能。
同時,隨著人工智慧的導入,企業得以重新定義組織、流程與 商業模式,以靈活回應市場變化與顧客需求。
④ 導入永續技術
企業的永續發展需同時兼顧社會責任、環境影響與經濟效益。
設計師以其對材料的敏感度、系統思維與人本導向,能協助企 業將永續目標轉化為具體可行的設計行動。透過設計導入,永 續不再停留於概念層面,而能落實於產品與服務的開發過程 中,例如材料選擇、能源效率、產品壽命與回收再利用等策略。
此過程不僅提升產品的環境適應性,也使企業能以更可持續的 方式回應市場與社會的期待。
⑤ 實踐技術倫理
每項新興技術應用的背後,都須考量商業價值與道德倫理間的 平衡。設計以人為本的核心價值,使其具備將倫理觀點整合進 產品與服務系統規劃的獨特能力。透過設計的介入,不僅能預 見並修正可能導致偏誤的演算模型或不公平的使用情境,也能 協助企業在創新之餘兼顧使用者權益與社會責任,促進更包容 與負責任的發展方向。
③ Design for Digital Transformation
Through its capabilities in aesthetics and information translation, design plays a pivotal role in the midto-late stages of product / service development and implementation. Whether it involves redesigning service workflows, optimizing data-driven interactions, or planning system platform integration, design intervention not only bridges the communication gap inherent in crossdisciplinary collaboration but also translates abstract technologies (such as code) into understandable language. This facilitates cross-departmental coordination, the integration of diverse technologies, and enhances the accessibility and appeal of products / services to end users.
④ Sustainable Tech Adoption
Sustainable enterprise development requires balancing social responsibility, environmental concerns, and profitability. Design—with its sensitivity to materials, systems thinking, human-centered approach, and crossdisciplinary integration—can transform the abstract goals of “environmental, social, and economic” value into actionable strategies. It helps companies incorporate green practices into the development process, including material selection, energy efficiency, product lifespan, and recycling mechanisms, thereby enabling businesses to meet societal expectations.
⑤ Techno-Ethics
Behind every application of emerging technology lies the need to balance business value with ethical considerations. With its human-centered core, design possesses a unique ability to integrate ethical perspectives into the planning of products and service systems. Through design intervention, companies can not only anticipate and correct potentially biased algorithms or unfair usage scenarios but also ensure that innovation respects user rights and social responsibility, fostering a more inclusive and responsible path of development.
● 設計介入商業驅動力
在競爭激烈的市場中,商品化導向的產品與服務固然有助於企 業迅速拓展市場規模、提升營運效率,卻往往僅能滿足使用者 的基本需求。當企業長期倚賴標準化與量產的邏輯,容易陷入 「快速供給、快速替代」的循環,導致市場出現高度同質化、 價格競爭惡性化的現象,最終削弱品牌的價值與顧客黏著度。
此時,設計的介入能使企業突破商業困局、重申價值主張,設 計不僅強調形式與功能的整合,更著眼於服務體驗、文化共鳴 與情感價值的建構。藉由重新定義產品與顧客之間的關係,設 計協助企業從「滿足需求」轉向「創造價值」,將同質化的商 品提升為差異化的品牌體驗。
● Design Intervention in Business Drivers
In highly competitive markets, commoditized products and services can help enterprises quickly expand market share and improve operational efficiency. However, they typically address only users’ basic needs. When companies rely heavily on standardization and mass production, they risk falling into a cycle of “rapid supply, rapid replacement,” resulting in high market homogenization, intensified price competition, and ultimately weakening long-term brand value and customer loyalty. Design intervention enables enterprises to break free from commercial deadlocks and redefine their value propositions. Beyond integrating form and function, design emphasizes user experience, cultural resonance, and emotional value creation. By redefining the relationship between products and customers, design helps companies shift from merely “meeting needs” to “creating value,” transforming commoditized offerings into differentiated brand experiences.
圖4.「設計介入商業驅動力」應用策略(資料來源:本研究整理)
Figure 4. Design Application Strategies – Business Drivers (Source: Compiled by this study)
① 提升價值主張明確性
設計在產品與服務開發的前期扮演關鍵角色,協助企業釐清品 牌優勢、整合顧客洞察,並以具體的溝通語言轉化為清晰的價 值主張。透過設計的策略介入,企業能在定位階段明確界定核 心差異,使後續的產品開發與市場傳遞方向一致,讓消費者在 接觸產品時能迅速理解品牌所提供的獨特利益與意義,從而強 化品牌辨識度與信任感。
② 確保品牌體驗一致性 品牌體驗涵蓋視覺風格、語言表達和互動等層面,在所有顧客 接觸點都應呈現一致的品牌核心價值,讓使用者在不同媒介中 感受到連續性與熟悉感。
一致性不只是外觀形式的統一,藉 由設計更在於將品牌理念滲透至產品、服務與策略之中。當品 牌形象、價值主張與使用者體驗高度對齊時,企業不僅能強化 辨識度,更能建立長期信任與忠誠度。
① Value Proposition Clarity
In the early stages of development, design intervention plays a crucial role in shaping an enterprise’s value proposition, clarifying competitive advantages, and planning how value is communicated and delivered. This forms the foundation for differentiated positioning of products and services, enabling them to stand out in the market against homogeneous offerings and allowing consumers to perceive their core distinctions and value.
② Brand Experience Consistency
Brand experience, from visual style and language to interaction, should consistently convey the core values of the brand across all customer touchpoints, allowing users to feel continuity and familiarity across different mediums. Consistency goes beyond mere visual uniformity; through design, brand philosophy is embedded into products, services, and strategies. When brand identity, value proposition, and user experience are highly aligned, enterprises can not only strengthen recognition but also build long-term trust and customer loyalty.
③ 實現顧客需求
設計以使用者為中心,透過共創、原型測試與反覆驗證等方 法,協助企業在開發階段即掌握顧客的真實需求與行為脈絡。
這種以設計驅動的協作過程,讓產品逐步貼近使用者期待,同 時累積品牌互動與情感連結。當設計參與需求驗證與決策過程 時,企業能持續優化體驗品質,並在市場中建立更高的接受度 與信任基礎。
④ 增強市場適應性
面對不同市場環境與文化脈絡,設計能協助企業以在地化視角 進行調整與再詮釋,使產品與服務更貼近使用者的生活方式與 文化習慣。設計思考的介入有助於快速洞察區域差異、縮短調 整週期,並透過原型化與用戶測試機制,持續驗證市場回饋。
這種靈活的設計策略使企業能在多元市場中同時維持品牌一致 性與在地共鳴,提升整體競爭韌性。
⑤ 確保商業可行性
設計思維協助企業在創意與營運之間取得平衡,將以人為本的 價值導向融入商業模式、資源配置與流程設計。透過設計的 系統化方法,企業可在滿足顧客需求的同時,確保產品具備 可執行與可持續的營運結構。設計不僅強化創新落地的效率, 也使創意成果能轉化為具高市場回報率與具長期影響力的商 業價值。
③ Customer Needs Fulfillment
From the early development to the prototype design stage, co-creation with customers can enhance product acceptance, brand loyalty, and overall experience quality, creating a positive feedback loop. This process lies at the heart of innovation: through design thinking and iterative trade-offs, products gradually align with customer needs while strengthening brand interaction and emotional connection.
④ Market Adaptability
Products and services must demonstrate flexibility to adapt to different markets and cultural contexts. By considering cultural sensitivity and making localized adjustments, they become better aligned with users’ habits, enhancing acceptance. Design thinking supports this process by enabling a deep understanding of local needs, rapid iterative adjustments, and the creation of differentiated value, allowing products and services to establish viable paths for survival and growth across diverse markets.
⑤ Business Viability
Creating value-driven products allows enterprises to break free from the pressures of commoditized competition. However, companies must still consider factors such as business models, cost efficiency, and resource allocation to ensure sustainable profitability and support ongoing development. Through design thinking, creativity can be embedded into corporate strategy and operations, closely aligning with customer needs while maintaining operational feasibility. This approach enhances the practical implementation of products and generates longterm market impact.
“
本章節透過前述十項設計策略,回應全球社會環境變遷 與科技崛起所帶來的挑戰,並探討企業可採取的策略, 以提升整體的組織韌性和應變能力。從「科技」與「商 業」兩大企業發展內部驅動力為視角,為企業主管、專 案經理與設計團隊提供系統性的檢視框架,協助掌握設 計資源的投入重點、應用機會與價值定位。下一章節, 本研究將透過設計應用前端的企業案例,揭示設計策略 的實踐樣貌。
In this chapter, the report uses the ten design strategies outlined earlier to address the challenges posed by global social and environmental changes as well as the rise of technology, showing how enterprises can enhance their flexibility and adaptive capabilities. By examining the two internal drivers of enterprise development—“technology” and “business”—it provides corporate executives, project managers, and design teams with a systematic framework to identify key areas for design resource investment, application opportunities, and value positioning. The next chapter will present frontend enterprise case studies of design application, revealing how these design strategies are implemented in practice.
Summery 小結 ”
3.2
臺灣企業設計策略應用動態
Dynamics of Design Strategy Application in Taiwan
本章節旨在分析過去五年間(2020–2024)臺灣企業於設計 策略應用上的發展趨勢,透過對GPDA入圍與得獎作品的量化 統計,觀察設計在企業經營與創新活動中所扮演的角色變化。
分析將聚焦於兩個主要面向:其一為科技驅動力,探討設計如 何參與技術導入、倫理實踐與人機協作優化等議題;其二為商 業驅動力,分析設計在品牌、價值主張與市場策略中的應用特 性。本節將以量化數據為基礎,呈現臺灣近年設計應用的整體 變化趨勢,並進一步詮釋其背後的產業動向與策略意涵。
This section analyzes the trends in design strategy application by Taiwanese enterprises from 2020 to 2024. By quantitatively examining the terminology used in the design concepts of Golden Pin Design Award winners, it observes how design’s role in business management and innovation has evolved.
The analysis focuses on technology drivers (technology adoption, ethics, human–machine collaboration) and business drivers (brand, value proposition, market strategy), with charts illustrating industry trends and strategic implications.
設計應用策略發展動態:科技驅動力 從設計策略的詞彙使用頻率來觀察,科技驅動面向的設計策略 關注度在近五年間整體顯著上升(見圖5),顯示設計在面對 技術快速演進與數位轉型挑戰中,扮演愈來愈關鍵的角色。以
「人機協作優化」為例,其關注度從2020年的40%上升至 2024年的59%,增幅達19%,成為近五年中最受矚目的策 略項目,說明企業與設計團隊已深刻意識到設計在提升科技親 和力與使用者互動體驗中的關鍵作用。
此外,「強化技術敏銳性」與「實踐技術倫理」同樣呈現顯著 成長,分別從29%與23%成長至45%與42%。前者突顯 設計領域對於新興技術的敏感度;後者則顯示設計在人工智 慧、大數據、穿戴式裝置等技術導入過程中,逐步承擔起倫理 監督與社會責任的角色。「推動數位轉型」與「導入永續技術」 則分別成長13%與15%,反映企業期望透過設計,將技術具 體落實於營運流程與永續實踐中。
這些趨勢指出設計在協助企業面對技術浪潮、提升系統韌性與 社會適應力方面,反映出設計思維的延伸與深化,再顯示設計 已由技術應用的外部輔助角色,轉變為驅動企業創新的引擎, 正積極介入企業決策核心,往更具前瞻性的方向推進。
● Design Application Strategy Dynamics –Technology Drivers
Analyzing the frequency of design strategy terminology reveals that attention to technology-driven strategies has increased significantly over the past five years (see Figure 4), highlighting design’s growing role in addressing the challenges of rapid technological evolution and digital transformation. For example, “Human-tech Inetraction Optimization” rose from 40% in 2020 to 59% in 2024, a 19% increase, making it the most prominent strategy over the five-year period. This indicates that enterprises and design teams have increasingly recognized design’s critical role in enhancing technology affinity and user interaction experiences.
Similarly, “Technology Sensitivity” and “Techno-Ethics Consideration” also showed notable growth, increasing from 29% to 45% and 23% to 42%, respectively. The former underscores design’s ability to quickly respond to and integrate emerging technological trends, while the latter highlights design’s role in assuming ethical oversight and social responsibility during the adoption of AI, big data, and wearable technologies. “Design for Digital Transformation” and “Sustainable Tech Adoption” grew by 13% and 15%, respectively, reflecting enterprises’ desire to leverage design to embed technology into operational processes and sustainability practices.
These trends demonstrate that design not only helps companies navigate technological waves and enhance system resilience and social adaptability, but also signals a shift from an external support role to a core engine of systemic innovation. Design now actively participates in enterprise decision-making, guiding forward-looking and responsible transformation.
圖5.企業發展科技驅動力-近五年設計策略應用趨勢圖
Figure 5. Enterprise Development Technology Drivers – Design Strategy Application Trends Over the Past Five Years
設計應用策略動態-商業驅動力 為進一步掌握設計於商業驅動力中的應用樣貌,本章聚焦於金 點設計獎得獎案例中,與市場價值、品牌建構,以及顧客關係 強化相關的策略表現。分析結果顯示(見圖6),企業對於商 業導向的設計策略投入顯著提升,特別是在「實現顧客需求」 與「提升價值主張明確性」兩項指標上,分別自2020年的 29%與30%,成長至2024年的49%,分別提高了20% 與19%。
這顯示設計已成為企業建立市場定位與顧客關係的核心工具, 是創新驅動(innovation-driven)的核心,進一步取代傳統 以效率驅動(efficiency-driven)的商業思維。「確保品牌 體驗一致性」雖整體變化幅度較小,但仍維持穩定關注,顯示 品牌體驗一致性已被視為基本要求,並持續透過設計來維護。 相對而言,「增強市場適應性」與「確保商業可行性」則分別 有13%成長幅度,指出設計除了強化產品差異化,也被期待 協助企業靈活因應市場波動與建立可持續的商業架構。
這些趨勢顯示,企業積極將設計應用於早期策略制定階段,強 化價值主張的溝通效果、精準回應顧客需求,並透過共創與驗 證機制提升產品與服務的市場契合度。設計不只是行銷與品牌 的延伸工具,更逐步轉化為企業營運與商業創新的中介機制, 有效串聯顧客洞察、產品定位與服務系統,協助企業在競爭激 烈的市場環境中獲得長期優勢。
● Design Application Strategy Dynamics –Business Drivers
To better understand design’s role in business drivers, this chapter focuses on Golden Pin Design Award-winning cases related to market value, brand building, and customer relationship enhancement. The analysis (see Figure 6) shows that enterprises have significantly increased investment in business-oriented design strategies, particularly in “Customer Needs Fulfillment” and “Value Proposition Clarity,” which rose from 29% and 30% in 2020 to 49% in 2024, representing increases of 20% and 19%, respectively.
This indicates that design has become a core tool for establishing market positioning and customer relationships, serving as the centerpiece of innovation-driven thinking, gradually replacing the traditional efficiency-driven business mindset. While “Brand Experience Consistency” shows relatively smaller overall change, it remains a stable focus, reflecting that consistency in brand experience is now considered a basic requirement and is continually maintained through design. In contrast, “Market Adaptability” and “Business Viability” grew by 13%, suggesting that design is expected not only to strengthen product differentiation but also to help enterprises respond flexibly to market fluctuations and build sustainable business frameworks.
Overall, the trends indicate that companies are increasingly applying design in early-stage strategic planning, enhancing the communication of value propositions, and accurately responding to customer needs. Through co-creation and validation mechanisms, design improves the market fit of products and services. Design is no longer merely an extension of marketing or branding; it is gradually becoming an intermediary for business operations and innovation, effectively linking customer insights, product positioning, and service systems, and helping enterprises achieve long-term advantages in highly competitive markets.
圖6.企業發展商業驅動力-近五年設計策略應用趨勢圖
Figure 6. Enterprise Development Business Drivers – Design Strategy Application Trends Over the Past Five Years
整體而言在「設計介入科技驅動力」層面,設計專業透過人機 互動優化、實踐技術倫理、推動數位轉型與導入永續科技等關 鍵策略,協助企業重新界定技術與人、社會、環境之間的關係, 不僅提升科技的社會適應力與落地價值,更深化企業在未來導 向發展上的敏捷回應能力。
在「設計介入商業驅動力」的層面,設計也展現出更高的滲透 力與整合力,不再侷限於美學或形式優化,而是成為連結顧客 需求洞察、價值主張與市場契合度的中介機制。藉由設計策略 的導入,企業得以強化其產品與服務的差異化定位,並在高度 競爭與變動的市場環境中建立具韌性與永續性的經營架構。
Overall, in the technology drivers domain, design professionals leverage key strategies such as human–tech interaction optimization, techno-ethics consideration, design for digital transformation, and sustainable technology adoption to help enterprises redefine the relationship between technology, humans, society, and the environment. This not only enhances the social adaptability and practical value of technology but also strengthens the enterprise’s agility in future-oriented development.
In the business drivers domain, design demonstrates greater penetration and integration. It is no longer limited to aesthetics or form optimization but serves as an intermediary linking customer insights, value propositions, and market fit. Through the introduction of design strategies, enterprises can reinforce differentiated positioning of their products and services and establish resilient and sustainable operational frameworks in highly competitive and dynamic market environments.
3.3
臺灣與全球設計策略應用異同
Similarities and Differences in the Application of Design Strategies between Taiwan and Global Trends
為了更深入理解臺灣設計應用的定位與發展方向,本節進一步 將臺灣近五年的設計策略趨勢與全球(不含臺灣)案例進行對 照分析。透過橫向比較,可觀察兩者在設計作為科技驅動與商 業驅動工具時的差異,並探討這些差異如何反映出不同產業結 構、政策環境與設計文化背景下的策略選擇。本小節目的在於 從國際視角檢視臺灣設計實踐的整體輪廓,辨識其應用特質與 發展潛力,並為後續提出的設計發展建議提供比較基礎與參照 框架。
To gain a deeper understanding of the positioning and development direction of design in Taiwan, this section compares Taiwan’s design strategy trends over the past five years with global cases (excluding Taiwan). By conducting a horizontal comparison, we can observe the differences in how design is applied as a technology-driving and business-driving tool, and examine how these differences reflect variations in industrial structure, policy environment, and design culture. The purpose of this analysis is to provide an international perspective on Taiwan’s design practices, identify their distinctive characteristics and development potential, and offer a comparative basis and reference framework for the design development recommendations presented in subsequent sections.
● 設計應用策略比較-科技驅動力 從全球趨勢觀察,可發現設計領域普遍展現出對永續技術與人 機協作議題的高度重視(見圖7)。國際上在「科技驅動力」 的設計策略中以「人機協作優化」為最高(56%), 其次為「導 入永續技術」(47%),「推動數位轉型」與「強化技術敏銳性」 同為43%,「實踐技術倫理」為37%。臺灣方面,僅「導入 永續技術」以48%略高於全球的47%;其餘四項皆低於全 球平均,其中「人機協作優化」為42%,與全球相比落差最 大(-14%),「實踐技術倫理」為28%(-9%)、「強化技術 敏銳性」為34%(-9%)、「推動數位轉型」為38%(-5%)。
整體顯示臺灣在科技導入的設計應用,在跨情境的「人機協作 優化」與「實踐技術倫理」的投入稍嫌不足;特別是在人機協 作與倫理之間形成「互動要求提高、倫理投入偏低」的斷層, 限制了從體驗到制度的整合創新。另一方面,永續技術的採用 略優於全球,推測與 ESG 指標、綠色製造規範與淨零政策的 內外部壓力相關,但若要有效回應智能化、自動化等趨勢,仍 需同步強化設計對組織轉型,以及隱私管理。
● Comparison of Design Application Strategies –Technology Drivers
Observing global trends, the design industry shows strong emphasis on sustainable technology and human–tech interaction in technology-driven strategies (see Figure 6). Globally, design strategies for “Technology Drivers,” “Human–Tech Interaction Optimization” ranks highest at 56%, followed by “Sustainable Technology Adoption” at 47%. “Design for digital transformation” and “Technology Sensitivity” are both at 43%, while “Techno-Ethics Consideration” is at 37%. In Taiwan, only “Sustainable Technology Adoption” slightly exceeds the global average at 48%. The remaining four strategies fall below the global average. “Human–Technology Interaction Optimization” is 42% (-14%); “Techno-Ethics Consideration” is 28% (-9%); “Technology Sensitivity” is 34% (-9%); and “Design for Digital Transformation” is 38% (-5%).
Overall, Taiwan’s design applications in technology adoption are primarily focused on implementation and operational optimization, with relatively less investment in cross-scenario human–tech interaction and ethical governance, revealing a gap of “high interaction demand, low ethical input.” This limits the potential for integrated innovation from user experience to institutional design. Sustainable technology adoption slightly exceeds the global average, reflecting the effectiveness of ESG investments, green manufacturing regulations, and net-zero policies. However, in the face of trends such as AI, IoT, and data governance, there remains a need to strengthen systematic design approaches in organizational transformation, privacy and bias management, and forward-looking sensitivity. This would better link technology adoption with long-term value for people, society, and governance, addressing gaps in ethical frameworks and risk management.
圖7.臺灣對比國際設計介入科技應用趨勢差異(資料來源:本研究整理)
Figure 7. Taiwan vs. International Trends in Design Intervention for Technology Applications (Source: Compiled by this study)
● 設計應用策略比較 - 商業驅動力 在「設計介入商業驅動力」的比較上可見(見圖8)全球正將 設計視為推動企業成長、強化市場差異化與提升顧客體驗的關 鍵工具。臺灣除了「確保商業可行性」之外,其他四項設計策 略上的應用都高於全球平均,顯示出臺灣設計應用前端的企 業,重視設計在市場定位,與價值傳遞中的實質作用。其中, 最顯著的差異出現在「提升價值主張明確性」,高達47%, 遠高於全球的35%。這些數據反映出臺灣企業,普遍將設計 視為溝通品牌差異與聚焦核心利益的重要工具,協助在高度同 質化的市場中建立明確且可感知的價值識別。其次,「確保品 牌體驗一致」與「增強市場適應性」在臺灣的比重亦分別達 34%與28%,也明顯高於全球的24%與18%。
此外,在體驗經濟的時代下,臺灣設計應用前端的企業,也擅 以設計維繫品牌體驗的一致性,同時運用設計作為快速回應市 場變化的策略手段,藉此提升目標群眾的黏著度與市場敏捷 度。整體而言,與全球相比,臺灣在商業驅動力的設計策略, 應用更趨活躍,且以市場為導向,設計被視為協助企業成長、 升營運效益,與強化品牌競爭力的核心資產。
● Comparison of Design Application Strategies –
Business Drivers
Observing international trends, design is widely recognized as a key tool for driving business growth, enhancing market differentiation, and improving customer experience. In the comparison of “Business Drivers” (see Figure 8), Taiwan exceeds the global average in all four design strategies except for “Business Viability.” This indicates that Taiwanese design cases generally place greater emphasis on the practical role of design in market positioning and value communication. The most significant difference appears in “Value Proposition Clarity,” which reaches 47% in Taiwan, far above the global average of 35%. This reflects that Taiwanese companies commonly view design as an essential tool for communicating brand differentiation and focusing on core benefits, helping establish clear and perceptible value in highly commoditized markets. Additionally, “Brand Experience Consistency” and “Market Adaptability” account for 34% and 28% respectively in Taiwan, noticeably higher than the global averages of 24% and 18%.
The chart shows that Taiwanese companies tend to use design to maintain brand experience consistency while also leveraging it as a strategic tool to quickly respond to market changes, thereby enhancing user engagement and market agility. Taiwan slightly exceeds the global average in “Customer Needs Fulfillment” and “Business Viability,” reflecting that Taiwanese design practices are generally user-centered while also considering the cost and feasibility of business execution, allowing design to deliver stable and sustainable value within corporate operations. Overall, compared to global trends, Taiwan’s design strategies for business drivers are more pragmatic and marketoriented, with design regarded as a core asset for business growth, operational efficiency, and brand competitiveness.
Figure 8 Taiwan vs. International Trends in Design Intervention for Business Applications (Source: Compiled by this study)
全球趨勢顯示,設計正同時回應技術創新與市場轉型的挑戰, 發揮連結科技、使用者與價值創造的關鍵作用。相較之下,臺 灣在科技導向上仍以操作與導入為主,對倫理治理與長期策略 的關注較少;但在商業導向上表現突出,特別在價值主張與品 牌一致性上顯示高度成熟度。這說明臺灣設計在企業端主要扮 演強化市場與溝通的角色,在引導科技轉型與制度創新的潛力 上仍有發揮空間。未來若能整合科技前瞻與商業策略,使設計 同時成為「創新驅動器」與「價值整合者」,將有助於推動臺 灣設計從應用導向邁向策略導向,並在全球設計經濟體中,更 具競爭優勢。
Global trends indicate that design is increasingly addressing the challenges of technological innovation and market transformation, serving as a critical connector between technology, users, and value creation. In contrast, Taiwan remains technology-focused on implementation and operational optimization, with less attention to ethical governance and long-term strategic considerations. However, Taiwanese design excels on the business side, showing high maturity in value proposition clarity and brand consistency. This suggests that in Taiwanese enterprises, design primarily strengthens market positioning and communication, while its potential to guide technological transformation and systemic innovation remains underdeveloped. Looking ahead, integrating technological foresight with business strategy could enable design to act as both an “innovation driver”and a “value integrator,” helping Taiwan’s design to transition from applicationdriven to strategy-driven and establish a more forwardlooking competitive advantage in the global design economy.
4 GPDA 臺灣案例 設計應用洞察 Insight from GPDA Taiwan Cases and Design Applications
延續前一章節對臺灣與全球設計應用趨勢的比較可發現,臺灣 設計實踐在本地企業中已成為強化價值溝通與市場連結的核心 工具。
本章節進一步聚焦於臺灣具代表性的金點設計獎 Golden Pin Design Award(GPDA) 得獎作品,透過深入的質化分析,提供 企業思考脈絡與決策邏輯,揭示企業如何在實際專案中整合科 技創新與商業策略,形塑設計導向的競爭優勢。
受訪團隊主要來自製造業、通訊業與設計服務業,涵蓋臺灣設 計與技術創新鏈中最具代表性的產業類別。這些企業不僅在產 品與技術層面展現出高整合度,更透過設計驅動的商業策略, 探索如何在永續發展、品牌建構與使用者體驗之間取得平衡。
透過對其設計決策與專案運作過程的分析,可為相關產業提供 具體參照,理解設計如何在不同組織架構與市場脈絡中轉化為 策略應用。
研究團隊篩選出11件GPDA得獎作品,並訪談設計團隊及業 主。這些案例不僅呈現設計如何協助企業以科技驅動創新、以 商業邏輯落實價值,更提供國際理解臺灣設計應用特質的重要 參考,展現臺灣設計在全球價值鏈中的能見度與發展潛力。
Building on the previous chapter’s comparison of Taiwanese and global design application trends, it is evident that design practice in Taiwan has become a core tool for enhancing value communication and market connectivity within local enterprises.
This chapter further focuses on representative Golden Pin Design Award-winning works in Taiwan, conducting indepth qualitative analyses to provide insight into enterprise decision-making processes and reveal how companies integrate technological innovation and business strategy to shape design-driven competitive advantages.
The interviewees primarily come from manufacturing, communications, and design service industries, covering the most representative sectors of Taiwan’s design and technological innovation chain. These companies demonstrate high integration at the product and technology levels while leveraging design-driven business strategies to explore the balance between sustainability, brand development, and user experience. By analyzing their design decision-making and project operation processes, the study provides practical references for related industries, illustrating how design can be translated into strategic applications across different organizational structures and market contexts.
The research team selected 11 Golden Pin Design Awardwinning works and conducted interviews with both design teams and clients. These cases not only demonstrate how design supports enterprises drive innovation through technology and realize value through business logics, but also offer international insight into the characteristics of Taiwanese design practice, highlighting Taiwan’s visibility and potential in the global value chain.
屾屾市‧台南來了 she n market Poster
WVM-410 UT 五軸立式綜合加工機 COMPACT CNC 5 AXIS MILL TURN MACHINING CENTER WVM-410UT 3
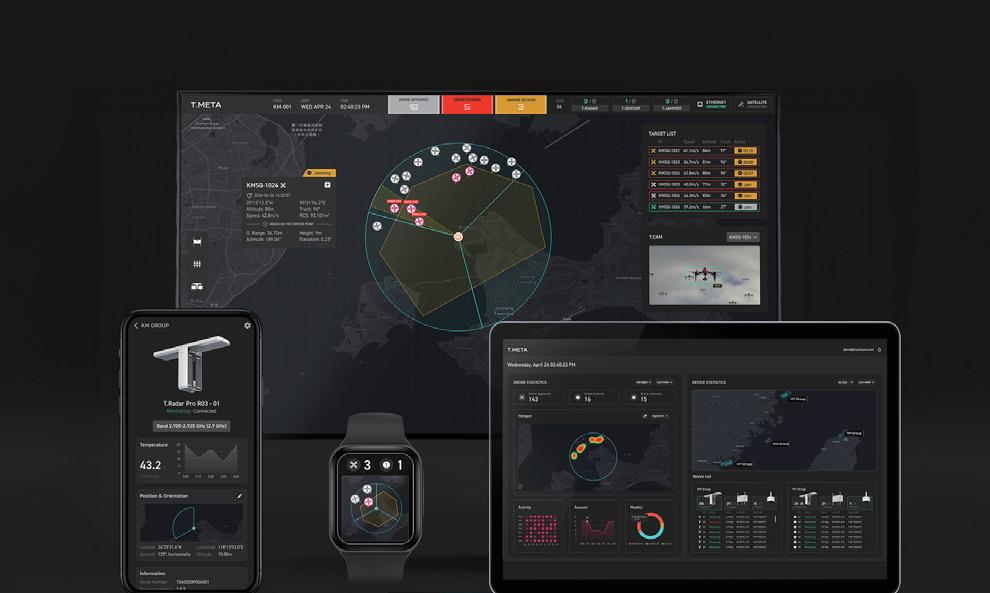
T.Meta 無人機反制系統 T.Meta Anti-Drone System 2
灼器 Scorchware 4 PEGATRON AC EVSE 電動車電源設備 5
永續感知計劃 Invisible Senses in sustainability 6
漿紙業的最後一哩路 Pulp Industry's lasting legacy 7
共居之家 Co-living Home 11 1
泉場 QUAN 8 (beanroom) 9
麥麥親子共讀區 Happy Meal Readers Area Themed Space Design 10
屾屾市‧台南來了 she n market Poster
#提升價值主張明確性 #增強市場適應性
#Value Proposition #Market Adaptability
設計類別 Design Category
視覺傳達設計
Communication Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
仰角視覺整合/屾屾市 ANGLE visual integration / shen shen market
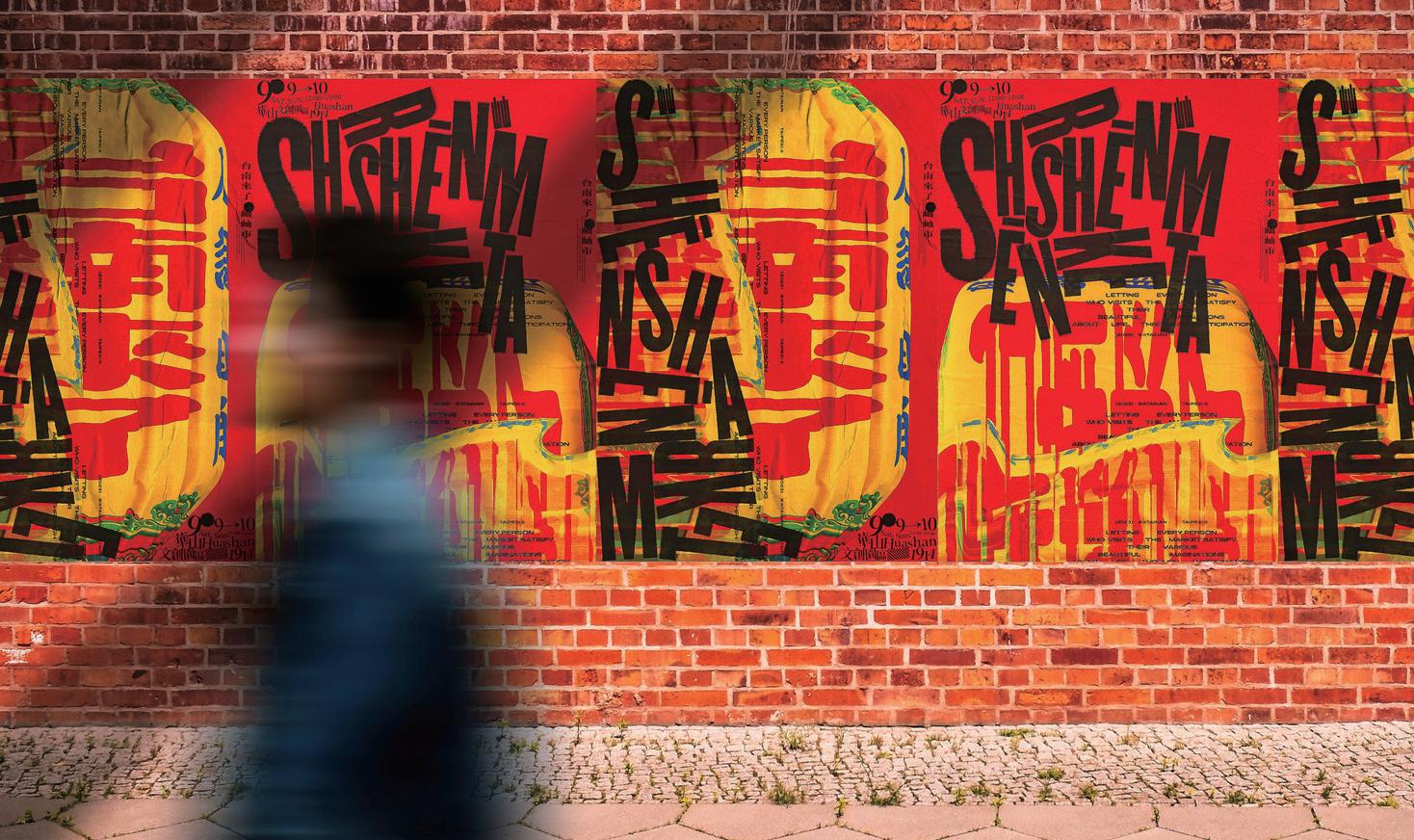



圖9. 屾屾市‧台南來了(圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 9. she n market Poster (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
此視覺傳達設計展現高度的文化底蘊,以老宅、廟宇與懷舊電 影元素轉譯地方文化,在台北市場成功引發共鳴。設計不僅保 留文化精神,也靈活調整語境,並在不同接觸點維持一致形 象,強化品牌識別與文化傳播,突顯設計作為文化溝通與市場 策略工具的價值。
This communication design showcases a deep cultural foundation, translating local culture through elements of old houses, temples, and nostalgic films, successfully resonating with the Taipei market.
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 解決文化與市場溝通落差
設計團隊展現出高度的文化感知能力,能將如廟宇、燈籠等具 在地色彩的元素,轉化為具國際視覺語彙的設計語言,讓傳統 文化得以跨越地域與語境限制,在不同市場中被辨識與接受。
這種轉譯不僅體現形式創意,更深入文化語境的結構與情感 面,使設計成為品牌與使用者之間有效連結的溝通橋梁,賦予 文化資產當代性與市場生命力。
02 | 回應不同產業之規模與需求
設計團隊依據客戶規模與產業屬性,靈活調整設計的介入深度 與參與模式,從品牌策略、內部流程到使用者觸點提出整合性 建議。這樣的操作彈性,讓設計不僅作為創意解決方案的提供 者,更成為協助企業在不確定市場中穩定轉向的策略夥伴,展 現對變動環境的高度適應能力。
03 | 強化落地可行性
在數位技術與AI工具持續變化的背景下,設計師需兼具創新 構想與落地可行性的平衡,快速回應市場需求及變動,並確保 創意構想在多方協作的情況下維持一致性。這種調整力正可帶 來「增強市場適應性」的結果,讓設計從創意供給,進化為整 體營運與創新管理的重要推動力量。
01 | Bridging Cultural and Market Communication Gaps
The design team leveraged strong cultural awareness to transform local elements such as temples and lanterns into an internationally recognizable visual language. This approach allowed the culture to transcend geographic boundaries, serving as a bridge between the brand and users, and giving cultural assets contemporary relevance and market appeal.
02 | Responding to Diverse Industry Scales and Needs
By adapting the depth and mode of intervention according to client size and industry characteristics, the team provided integrated recommendations spanning brand strategy to user touchpoints. Design became a strategic partner for enterprises navigating uncertain markets.
03 | Enhancing Implementation Feasibility
Amid rapid changes in digital and AI tools, design balanced innovation with practical execution, ensuring consistency across multiple collaborators. This strengthened market adaptability and positioned design as a driver for both operational and innovation management.

周雨衛 Viter Chou|負責人
雖然設計在某些細節會受到日本或其他文化影響,但越在地越國際是我們的設計理念,我們重視過程 中,如何以地方自身的語言與脈絡轉譯出具文化底蘊與當代感的視覺表達。
T.Meta 無人機反制系統
T.Meta Anti-Drone System
#人機協作優化 #強化技術敏銳性 #Human-Tech #Technology Sensitivity
設計類別 Design Category
服務系統設計 Service Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
創未來科技股份有限公司(企業內部設計團隊) Tron Future Tech (In-house Design Team)

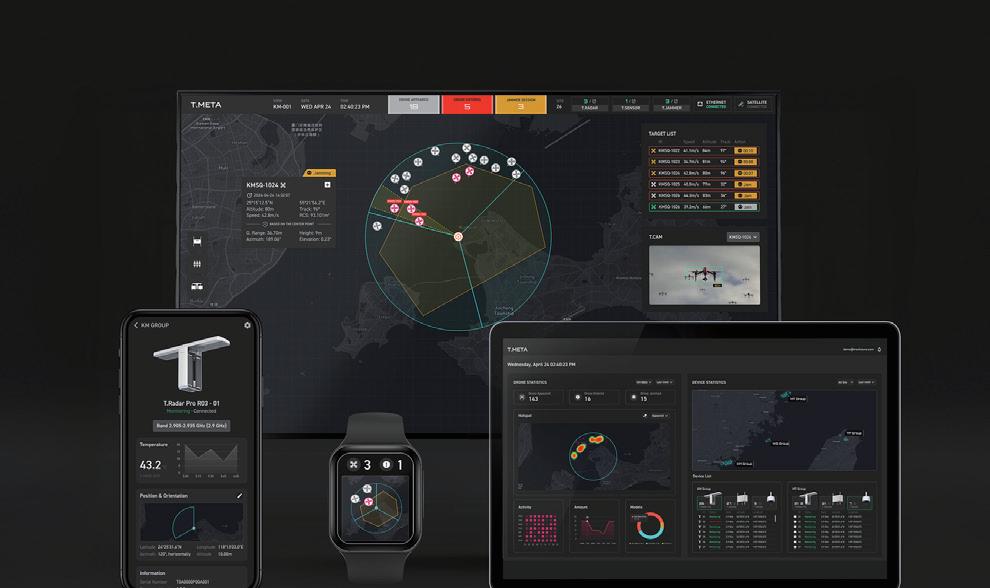
圖10. T.Meta 無人機反制系統(圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 10. T.Meta Anti-Drone System (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
〈T.Meta 無人機反制系統〉為軍事應用服務系統設計,適用 多種戰術情境。為保障軍事操作安全,系統涉及高度複雜的偵 測干擾技術。經過轉化複雜科技,使直覺與透明化之操作介面 與任務導向流程,讓操作者即使在高壓情境或未受充足訓練條 件下,也可以快速判斷並做出決策及行動。
This military system design transformed complex detection technologies into intuitive and transparent interfaces with task-oriented workflows, enabling personnel to make rapid decisions and take action even under high-pressure conditions or with limited training.
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 強化系統性思維的前後端整合 設計團隊從規劃前期,需求定義階段即積極參與,並將AI工 具視為策略夥伴,輔助參數模擬與技術風險控管。設計師運用 系統性思維,整合前端的操作需求與後端感測模組及知識庫邏 輯,提升整體使用之流暢性,強化了產品使用邏輯。
02 | 提升跨部門協作
設計團隊建立跨部門的密切協作流程,與工程、製造與業務單 位反覆驗證每項設計細節。設計師需快速吸收技術語彙,並轉 化為高效可行的設計方案,有效整合多方觀點,致力於提升系 統易用性,在保障軍事安全的情況下,促進軍工技術的創新。
03 | 化解技術複雜性打造直覺的使用體驗
設計團隊將複雜的程式語言轉譯為直覺且易於理解的操作體 驗。透過有層次的視覺設計與流程調整,團隊有效提升了使 用介面的辨識度與親切感,同時在品牌形象與產品價值之間 建立明確連結。這樣的設計策略不僅強化了產品的實用性, 也協助企業在國際市場中展現差異化,進一步形塑獨特性與 競爭定位。
01 | Strengthening Systemic Thinking Across Frontend and Backend
The design team was involved from the requirements definition stage, treating AI tools as strategic partners to assist with parameter simulation and risk management. Using systemic thinking, they integrated frontend user needs, backend sensor modules, and knowledge bases, improving workflow fluency and product logic.
02 | Enhancing Cross-Department Collaboration
The team established collaborative processes across engineering, manufacturing, and business units, repeatedly validating design details. Designers quickly absorbed technical terminology and translated it into feasible solutions, effectively integrating perspectives to enhance system usability and drive defense technology innovation.
03 | Mitigating Technical Complexity
The design team translated complex programming into intuitive experiences, using layered visual and workflow design to improve interface recognizability and brand association, thereby strengthening product usability and differentiation in international markets.

Marcus | 設計總監Design Director
以前我們在找工業設計師時,重視的是繪圖能力;但現在,畫圖只占整個工作量的 30%,前期的思考 與策略才是關鍵。
龔家正
WVM-410 UT 五軸立式綜合加工機
COMPACT CNC 5 AXIS MILL TURN MACHINING CENTER WVM-410UT
#人機協作優化 #強化技術敏銳性
#Human-Tech #Technology Sensitivity
設計類別 Design Category
產品設計類 Product Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
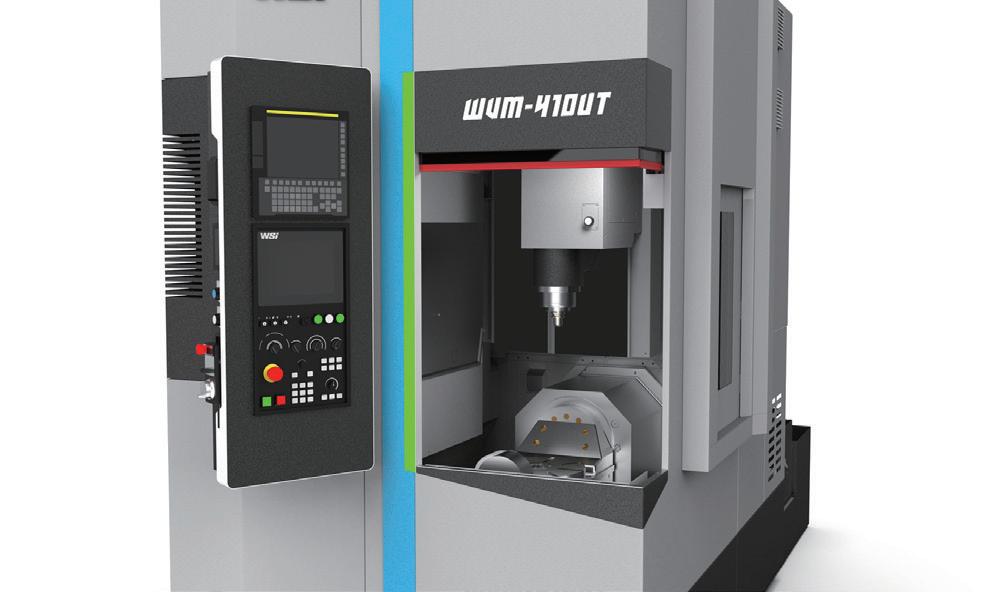



偉詳工業股份有限公司(企業內部設計團隊) WAYSIA INDUSTRAIL CO., LTD. (In-house Design Team) 圖 11. WVM-410
Figure 11. COMPACT CNC 5 AXIS MILL TURN MACHINING CENTER WVM-410UT (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
本產品使用於高度複雜的金屬加工需求,將切削工藝進行整 合,整併多站加工工序,適用於工業、汽機車零件和醫療產業 等精密製造產業。設計不僅關注機械性能,更進一步搭載智慧 化操作介面、人工智慧物聯網,強化操作便捷性與工作辨識 度,此整合設計策略讓產品在功能性、效率與使用者體驗三者 之間達成平衡。
A highly complex metalworking machine integrating milling and turning processes, tailored for precision manufacturing industries. The intelligent interface combined with AIoT enhances operational convenience and recognizability, balancing functionality, efficiency, and user experience.
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 提供技術整合能力
面對智慧製造與自動化需求,設計團隊不僅負責外觀,更深入 機構設計、系統整合與介面設計。透過設計,有效解決複雜問 題,提升模組協同與作業效率。設計在此成為驅動系統整合與 創新的關鍵角色,而非附加功能。面對高度工程導向的產品邏 輯,設計團隊善於將艱澀技術術語轉譯為直觀、可辨識的操作 語言。透過色彩標示、圖形使用者介面與資訊分層等策略,提 升使用親和力與操作精準性。此舉不僅優化了工作流程,更強 化品牌識別,讓產品在國際市場中展現高度競爭力。
02 | 貼近使用者需求
設計師從實際使用情況出發,觀察並回應產線數位轉型過程中 的關鍵痛點。聚焦使用者需求,調整介面流程與知識庫導入方 式,降低技術門檻,提升操作效率與能源管理表現。設計在此 不只是形式上的加值,而是實質促進技術落地與現場應用的關 鍵媒介,協助企業邁向永續與轉型目標。
01 | Providing Technical Integration Capability
Faced with smart manufacturing and automation requirements, the design team went beyond aesthetics to engage in mechanical design, system integration, and interface development. They enhanced module coordination and operational efficiency, translating complex engineering terminology into intuitive, recognizable operational language. Strategies such as color coding, graphical user interfaces, and layered information presentation increased user-friendliness and operational accuracy.
02 | Aligning Closely with User Needs
Designers observed key pain points in real usage scenarios. By focusing on user requirements, they adjusted interface workflows and knowledge base integration, lowering the technical threshold, improving operational efficiency, and optimizing energy management performance.

洪泳沅 Kai Hung | 設計師 Designer
我們透過設計整合與空間佈局優化,在有限的廠房空間內提升機台容納密度與產能,進而賦予產線高 度彈性,以兼顧『少量多樣』訂單與『高複雜度』產品外觀的精密加工需求。
灼器 Scorchware
#增強市場適應性 #提升價值主張明確性 #確保商業可行性
#Market Adaptability #Value Proposition #Business Viability
設計類別 Design Category
產品設計類 Product Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
安達陶瓷藝術有限公司(企業內部設計團隊)
Anta Pottery Art Co., Ltd. (In-house Design Team)


圖 12. 灼器(圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 12. Scorchware (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
〈灼器〉展現餐具設計從造型、釉色到手感質地,皆呼應品牌「直 接、單純、純粹」的理念。純手工製作的獨特痕跡,強調職人精 神,讓每件餐具都傳遞品牌態度。設計更延伸至餐桌、空間與服 務流程,讓顧客在多層次感官體驗中感受到一致的品牌語言,顯 現設計如何將品牌價值落實於體驗並建立市場辨識度。
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 協助應對轉型壓力
設計團隊在面對傳統產業數位轉型趨勢下,並未採取破壞式創 新,而是從工法與流程中找出可以調整的切點。他們理解陶瓷 產業長年依賴手工經驗與人工作業的特性,因此不從頭翻轉流 程,而是提出材料替換建議(如改用低耗能釉料、優化乾燥與 燒製階段的能源配置),採信消費行為數據基礎。這種微調式 創新的設計應用策略,降低了現場技術人員的學習門檻,也讓 永續製程能夠逐步落地。設計團隊的角色不僅是規劃者,更是 現場與企業內部團隊之間的協調者與實驗者。
02 | 強化產品的情感價值
設計團隊在產品視覺與包裝上,針對陶瓷在生活中扮演的角色 進行再定義。包裝材料選用環保紙纖材,連結品牌的永續承 諾。從材質、色彩到內文,團隊確保品牌語言的一致性。從「產 品接觸點」出發的策略,讓使用者能更輕易地將產品與品牌核 心價值連結起來,進而提升品牌信任與回購意願。
03 | 轉化為可參與的生活實踐
面對品牌在地文化的傳達需求,設計團隊主動挖掘品牌原鄉的 文化資產,不直接複製紋樣,而是轉化為可使用、可參與的日 常細節。例如將製陶工具的形狀轉化為把手細節,或將裝飾符 號以壓印的方式呈現在產品底部,創造一種「細節中的文化在 場」。這樣的策略讓產品即使進入國際市場,也能保有文化辨 識度,並展現品牌對土地的情感連結。設計因此不再只是裝飾, 而是一種具體可感、可傳遞的文化實踐。

Tableware designed to embody “direct, simple, and pure” through form, glaze, and tactile feel. Handcrafted traces reflect artisan spirit, extending to table settings and service to create a consistent sensory experience and brand recognizability.
01 | Supporting Transformation Pressure
Facing digital transformation challenges in a traditional industry, the design team leveraged production knowledge with micro-adjustments. They optimized processes with low-energy glazes, improved energy allocation, and integrated simple monitoring modules. This approach lowered the learning curve, gradually implemented sustainable production, and allowed design to function as both coordinator and experimental facilitator.
02 | Enhancing Product Emotional Value
The design team redefined the role of ceramics in daily life through product visuals and packaging. Environmentally friendly paper fiber was used for the packaging, connecting it to the brand's commitment to sustainability.
03 | Translating into Participatory Cultural Practice
Designers integrated local cultural heritage into details—handle shapes, base imprints with local language—making culture tangible. This elevated international recognizability and emotional brand connection, creating a concrete and engaging cultural experience.
孫盈馨 Ying-Hsing Sun|總監Director
從消費者不只在意功能,也在意物件的情緒連結及帶來的生活氛圍;未來應該會從品牌策略、行銷至 使用體驗,朝向更深層的整合;讓物件走進生活場景,而不只是藝術品。
PEGATRON AC EVSE 電動車電源設備 PEGATRON AC EVSE
#強化技術敏銳性 #實踐技術倫理性
#Technology Sensitivity #Techno-Ethics
設計類別 Design Category
產品設計類 Product Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
和碩聯合科技(企業內部設計團隊) PEGATRON (In-house Design Team)



圖 13. PEGATRON AC EVSE
Figure 13. PEGATRON AC EVSE (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
此電動車電源設備,展現了設計如何在技術整合與系統協調中 扮演關鍵角色。此設備結合高度直覺化的操作介面,如通過 NFC卡/App完成身分識別,而直覺的燈號指示設計,讓使用 者能清楚辨識充電狀態,提升整體使用效率與便利性。同時, 產品支援不同國際充電標準,並滿足隨插即充功能,亦符合歐 美市場需求,此充電樁設計回應標準尚未統一的全球性問題。
An EV charging device using NFC cards and a mobile app for customer identification. Light indicators improve operational efficiency, and the device supports multiple international standards with plug-and-charge functionality, highlighting design’s role in technology integration and global adaptability.
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 建立公平可及的使用關係
設計團隊從能源轉型與智慧交通的社會挑戰出發,思考技術介 入對人與環境的實質影響。透過導入 NFC 身分識別、燈號引 導與即插即充等功能,設計師不僅關注操作效率,更從「誰能 使用技術」與「如何讓技術被公平使用」的倫理視角出發,確 保不同年齡與技術熟悉度的使用者皆能順利操作。此設計實踐 使能源科技從專業領域走向公共日常,體現以人為本的系統思 維,並在快速演變的智慧電網環境中維持友善性與高適應性。
02 | 克服國際規範差異實現技術普及
面對國際市場充電介面尚未統一的現況,設計團隊以「公平使 用」為核心目標,發展出兼容多國標準的模組化結構。此策略 不僅提升產品在不同城市治理與政策條件下的適用性,也反映 企業對全球能源基礎設施不平衡現象的主動回應。高度通用化 的介面設計與可擴充的模組架構,讓產品能靈活對應各地規範 與技術變化,確保電動車充電的普及性與可持續性。設計師在 此過程中成為企業創新與社會責任之間的協調者,使設計成為 推動永續轉型與技術普惠的重要策略媒介。
01 | Establishing Fair and Accessible Usage
The design team approached the project from the perspective of energy transition and smart transportation. By integrating NFC, light guidance, and plug-and-charge functions, they balanced efficiency with equitable access. They also considered the ethical questions of “who can use the technology” and “how to ensure fair use,” embedding social responsibility into everyday energy practices.
02 | Overcoming International Standards for Technology Adoption
Facing diverse cross-national standards, the team adopted “fairness” as a guiding principle. They developed a modular structure compatible with multiple countries, enhancing global applicability and adoption. Design thus served as a critical mediator for corporate innovation and social responsibility.
邱榆皓Yuhao Chiu | 設計主任
以電動車智慧充電樁為例,設計不僅在滿足使用者需求,更要將永續價值帶入開發的思維脈落與策略 之中,從營運管理系統到城市環境議題,讓整體更有效的運作。
永續感知計劃 PEGATRON AC EVSE
#導入永續技術 #提升價值主張明確性
#Sustainable Tech Adoption #Value Proposition
設計類別 Design Category
整合設計類 Integration Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
周育潤設計工作室/恆隆行貿易股份有限公司 KEV Design Studio /HENG LEONG HANG CO.,LTD.



圖14. 永續感知計劃(圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 14. Invisible Senses in Sustainability (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
案例以企業廢棄資源為基礎,透過材料再生與再設計,賦予廢 棄物新生命,並轉化為具市場潛力的多件產品,體現循環設計 思維的核心價值。同時,團隊透過跨界合作,將再生材料導入 實際場域,從通路展示到居家應用,實現「材料到體驗」的永 續整合。〈永續感知計劃〉強調負責任創新,在設計決策中兼 顧環境影響與社會價值,並以設計提升消費者對永續議題的意 識,不僅呼應SDGs目標,更示範了設計如何結合品牌策略與 生活美學,推動產業轉型與永續發展。
Designed diverse products using recycled waste materials, integrating cross-sector collaboration to achieve sustainability from material to experience. The project raised consumer awareness of sustainability, aligned with the SDGs, and promoted industry transformation.
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 轉化抽象永續理念為具體溝通策略 此案例給予廢棄濾網與報廢器具第二生命,使得看不見的永續 價值得以感知、理解,進而產生共鳴。設計於此扮演的是傳遞 者與詮釋者的角色,協助企業找到非語言式、非產品導向的溝 通方式,以深化品牌永續主張,促進讓社會大眾共同響應。
02 | 提升企業永續行動的可能性
設計師在永續材料導入過程中,不應僅限於材質美學與功能轉 譯,更需協助企業重新定位其永續角色,即便是非製造型產業 亦同(如金融與服務業)。這代表設計師需具備策略性思維與 溝通能力,能將既有預算導向永續議題,促使企業擴大投入 「非直接收益」,但具長遠意義的永續創新行動。
03 | 建立共享知識基礎與使用者理解力
永續設計的推進需從需求理解與知識對齊開始。設計團隊於前 期即投入回收廠、處理場域的研究與訪談,確保與企業在知識 與目標上的共識,進而提高設計效率與落地品質。這種「設計 先行於理解」的過程,大幅提升了使用者同理心與企業內部推 動力,也為設計團隊與業主建立共識與問題敏感度,這點顯示 設計作為橋接產學與社會的關鍵角色。
01 | Translating Abstract Sustainability into Tangible Communication
By repurposing discarded filters and tools, the team gave them a second life, making intangible sustainability values perceivable and understandable. Design acted as a communicator, helping the company convey sustainability claims in non-verbal and non-product-centric ways that resonate with audiences.
02 | Enhancing the Feasibility of Corporate Sustainability Actions
Designers not only focus on the aesthetics of materials but also help companies redefine their roles in sustainability, guiding existing resources toward long-term sustainable innovation. This encourages businesses to increase their investment in “non-immediate returns” yet deeply meaningful sustainable initiatives.
03 | Building Shared Knowledge and User Understanding
Early in the project, designers conducted field research in recycling sites to align with corporate goals. This strengthened empathy, consensus, and implementation quality, establishing a bridge between academia, industry, and society.

周育潤 Yu-Jui Chou|總監Director
就永續感知計劃來說,雖然產品設計是重點,但我更加在意如何理解企業需求方向;而設計師的角色 不只在執行產品包裝,也包含找出企業核心價值,並提出有創意以及企業可實踐的方案。
漿紙業的最後一哩路
Pulp Industry's lasting legacy
#增強市場適應性 #導入永續技術
#Market Adaptability #Sustainable Tech Adoption
設計類別 Design Category
整合設計類 Integration Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
中華紙漿股份有限公司 Chung Hwa Pulp Corporation



圖15. 漿紙業的最後一哩路 (圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 15. Pulp Industry's lasting legacy (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
此案例橫跨材料研發、產品再生、空間設計與社區共創等層面, 展現設計作為整合驅動器的策略角色。該專案不僅著眼於漿紙 業的廢棄物轉化,更藉由與成大永續環境實驗所與澤木設計等 在地團隊合作,打造出一套以地方為本,並串起在地企業、社 區、職人、技術研發與空間設計者共同成就的創新能量。
Factory space integrated material research, product recycling, spatial design, and community co-creation. Through industry-academia collaboration, recycled paper pulp was transformed, connecting local businesses, communities, and design teams, showcasing design’s integrative and driving role.
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 提升材料創新與數位轉譯的系統鏈結 設計團隊以設計為驅動核心,回應環境永續的轉型壓力,重 新思考傳統產業中廢棄資源的再生價值。透過導入循環材料、 材料模組設計與現場應用,並串聯數據監測、製程優化與敘 事傳播等流程,團隊建構出橫跨研發、製造與文化溝通的整 合系統。
02 | 推動跨域整合與轉型落地 專案從一開始便以開放協作為前提,設計團隊與工班、學研機 構、在地社群密切合作,進行材料測試與應用模擬。透過跨部 門、多知識系統的交織,深化在地材料語境的轉譯與再造。這 種設計驅動的協作模式,是一種嵌入地方經驗、文化價值與產 業技術的融合策略。
03 | 建構企業與社會的文化共感場域 本案以「不再是圍牆的圍牆」作為象徵語彙,設計團隊重新定 義企業設施的公共角色。相較於常見以數位自動化為主的轉型 方案,團隊更聚焦於人與場域的關係重構,將工廠邊界轉化為 文化實驗場,讓設計成為企業與社會之間的情感介面與價值共 構平台。這樣的策略不僅強化地方認同,也拓展企業永續轉型 的實踐深度與社會影響力。
01 | Enhancing Material Innovation and Digital Translation Across Systems
Starting from environmental sustainability, the team explored the value of recycling traditional industrial waste. They introduced circular materials, modular material design, and on-site applications while integrating data monitoring, process optimization, and narrative communication. The design team connected R&D, manufacturing, and cultural communication systems, linking production logic with local storytelling.
02 | Driving Cross-Domain Integration and Transformative Implementation
Based on open collaboration, designers worked with workshops, academic research, and community partners to conduct material testing and application simulations. The intersection of diverse knowledge deepened strategies embedded in local experience, enabling practical transformation.
03 | Building Cultural Empathy Between Enterprise and Society
Symbolized by the concept of “walls no longer being walls,” the project redefined the relationship between the company and society. The factory boundary became a cultural experimental space, serving as an emotional interface and co-creation platform, strengthening local identity while expanding the depth and social impact of corporate sustainable transformation.

沈昀靚 Lauren Shen|總經理室主任
不論再怎麼高科技發展,最基本的還是「人」。我們與在地職人及設計師合作,強調「回到人本」, 希望花蓮廠多與地方互動、連結並闡述在地故事,是永續、共好、和地方共創的概念整合。
泉場 QUAN
#提升價值主張明確性 #推動數位轉型 #確保品牌體驗一致性
#Value Proposition #Design for Digital Transformation #Brand Experience
設計類別 Design Category
空間設計類 Spatial Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
共序工事建築設計事務所/泉承國際股份有限公司 Üroborus_studioLab / CHIUAN CHENG INTERNATIONAL CO., LTD.
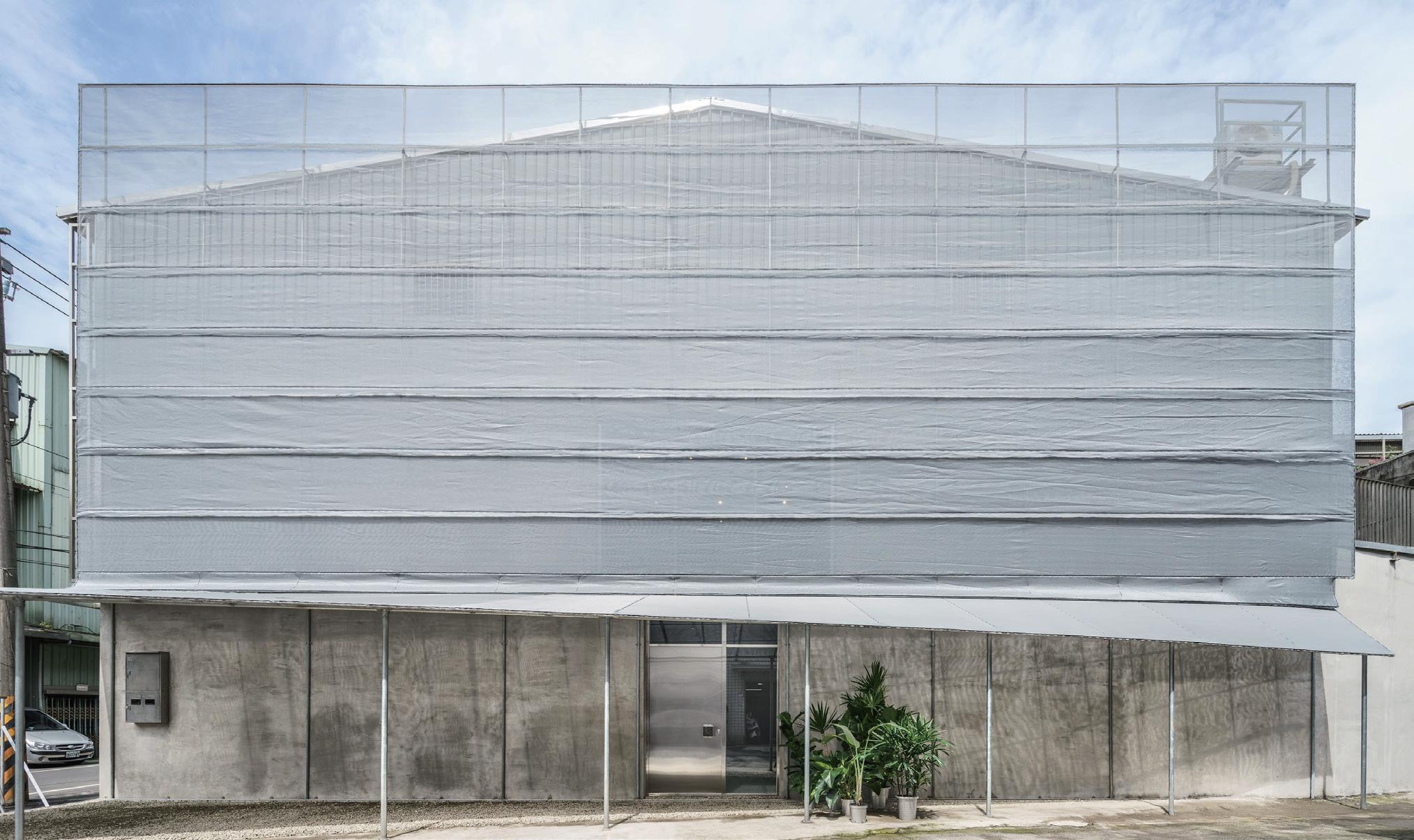



圖16. 泉場(圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 15. Pulp Industry’s Lasting Legacy (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
〈泉場〉清楚展現致力於提升空間美學,將工廠的形象轉化為 能展示、能交流與產生連結的未來場域,並導入智能化聲控系 統,已強化整體自動化形象。透過展覽與社區互動,〈泉場〉 成功傳達企業創新與社會責任,並以獨特材料與敘事手法建立 差異化定位,突顯設計作為產業轉型與文化轉譯的核心價值。
The elevator factory space leveraged aesthetic design and incorporated a voice-controlled system to reinforce its automated image. By integrating exhibitions and community interactions, the project demonstrated the company’s innovation, social responsibility, and cultural translation value.
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 引導產業轉型,重塑品牌價值主張 設計團隊從企業主的核心需求出發,跳脫傳統工廠空間的侷 限,重新構思空間作為品牌願景延伸的介面。透過「未來工廠」 的整體構想,設計不再僅止於物理環境的改善,而是協助企業 由生產導向,轉向體驗與形象導向。藉由形塑空間語彙與設計 敘事,團隊清晰勾勒出品牌對外溝通的價值立場,實質重構其 市場定位與文化意義,使設計成為品牌策略轉型的推進工具。
02 | 連結技術與永續力,強化品牌差異化 本案導入聲控電梯、在地材料的再設計,以及可回收的展覽裝 置,不僅展現企業對創新與永續的實踐承諾,也使抽象的品牌 理念轉化為具象的使用者體驗。設計團隊將這些元素整合為一 致的品牌語言,透過材料、技術與場域的整合,強化品牌的價 值識別,並建立其在產業與市場中的差異化優勢。
03 | 打造協作平台,促進共創與品牌認同 團隊透過展覽、講座與虛實整合的互動體驗,將設計轉化為使 用者參與品牌共建的介面,使價值不再是單向傳遞,而是在共 感與對話中累積的集體認同。設計的實踐深化品牌與社群的連 結,也讓企業的價值主張更具可感知性與影響力。設計的介 入,不僅只於成果的表現形式,也是串聯內外部利害關係人、 促進共創與價值共構的重要平台。
01 | Guiding Industry Transformation and Reshaping Brand Value Proposition
The design team addressed core corporate needs and traditional industry transformation. Moving beyond conventional factory limitations, the “Future Factory” concept transformed the space into an interface extending the brand vision, helping the company shift from production-driven to experience- and image-driven, thereby reconstructing market positioning and cultural significance.
02 | Integrating Technology and Sustainability to Strengthen Brand Differentiation
Voice-controlled elevators, redesigned local materials, and recyclable installations were introduced, turning innovation and sustainability into tangible experiences. These elements were integrated into a coherent brand language, enhancing value recognition and market differentiation.
03 | Creating a Collaborative Platform to Promote Co-Creation and Brand Recognition
Through exhibitions, lectures, and interactive experiences introduced into the factory space, a co-creation interface is formed, deepening the connection between the brand and its community. It serves as an important platform that links stakeholders and fosters co-creation and shared value.

洪浩鈞 Hao-Chun Hung |創辦人
我們不只做空間設計,更透過商業策略對話引導企業二代思考『未來工廠』長相,改變傳統囤放式 的廠房運用,打造有別於同業的場域。除了幫助業主吸引目標客群,更達到他們期望推向產業轉型 的期待。
9 (beanroom)
#提升價值主張明確性 #確保商業可行性
#確保品牌體驗一致性
#Value Proposition #Business Viability #Brand Experience
設計類別 Design Category
空間設計類 Spatial Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
水相設計有限公司/木日生有限公司 Waterfrom Design / Planet-J Limited



圖 17. (beanroom)(圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 17. (beanroom) (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
此案例具體展現了設計在資源有限的情況下,如何同時兼顧商業 可行性與永續實踐。水相設計採用「商品即裝飾」的策略,讓產 品本身成為空間視覺的一部分,減少額外裝飾與材料使用,在提 升空間使用效率的同時,回應永續資源的議題。設計團隊也將 後台數據資料可視化,並公開於現場,讓資訊透明成為顧客體驗 的一環,進一步促進顧客參與及建立品牌信任感。此設計策略說 明,設計已不僅止於外觀塑造或美學表現,更是整合資料、提升 營運效率與創造顧客價值的關鍵手段。藉由將產品、空間、資訊 與品牌體驗有機結合,本案展現設計作為企業長期策略工具的潛 力,有效支撐其市場差異化與永續轉型的需求。
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 強化品牌差異化,提升市場擴展潛力
設計策略從商業模式與消費心理出發,此案例採取「先有豆、 後有店」的零售導向經營模式,透過品牌命名、包裝設計與故 事敘事的整體一致性,讓品牌形象具備高度辨識度與延展性。
這顯示設計不再僅止於美學與形象塑造,而是驅動市場區隔、 強化顧客認同與擴大商業潛力的核心資源。
02 | 提升營運效益與品牌一致性
設計團隊導入模組化展示與彈性空間配置,兼顧現場執行效率 與品牌識別一致性。此策略有效降低長期營運成本與空間更新 頻率,使品牌體驗得以穩定擴展。設計在此不僅支撐了品牌語 言的整合,也展現其作為具備成本效益,與彈性的商業策略操 作的潛力。
03 | 連結科技與市場開啟品牌轉型契機 面對消費者對「個人風格」與「自我認同」的重視,設計團隊 從品牌風格轉向、包裝細節到敘事語調的策略調整,成功串聯 情感連結與科技應用。此舉不僅提升顧客黏著度與市場接受 度,更推動產品線擴展與目標族群的多元化。設計因而成為品 牌調整與商業模式轉型的重要策略,展現其在面對快速變動的 市場,與科技情境下的靈活性與前瞻價值。
Coffee retail space designed with the strategy of “product as décor.” The project balances commercial objectives and sustainability, integrating data visualization to enhance transparency and participation, showcasing design’s strategic potential in operational efficiency and brand value integration.

01 | Strengthening Brand Differentiation and Market Expansion Potential
Based on the “beans first, store later” coffee retail model, the design ensured consistency across brand naming, packaging, and storytelling, creating a highly recognizable and extensible brand identity. Beyond aesthetics, design drove market differentiation and supported commercial growth.
02 | Enhancing Operational Efficiency and Brand Consistency
Modular product display racks with flexible layouts were introduced to balance execution efficiency with consistent brand recognition. This approach reduced operational costs and update frequency, strengthening the scalability and strategic adaptability of the brand experience.
03 | Connecting Technology and Market to Enable Brand Transformation
Targeting customer needs for “personal style” and “selfidentity,” the design aligned brand aesthetics with narrative strategies, linking emotion and technology. This enhanced customer engagement and market acceptance, facilitating diversification of the target consumer base.
李冠興Elvis Lee| 品牌總監 Integrated Planning Director
我們在消費者購買咖啡豆的過程創造許多記憶連結的機會,像是屬於咖啡豆的地景命名、配樂以及 空間設計,讓每支配方豆有故事,如此國內外消費者買豆子時,就有如把整段旅程的感覺帶回家。
麥麥親子共讀區
“Happy Meal Readers Area” Themed Space Design
#提升價值主張明確性 #實現顧客需求 #確保品牌體驗一致
#Value Proposition #Customer Needs #Brand Experience
設計類別 Design Category
空間設計類 Spatial Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
究方社有限公司 JOEFANGSTUDIO
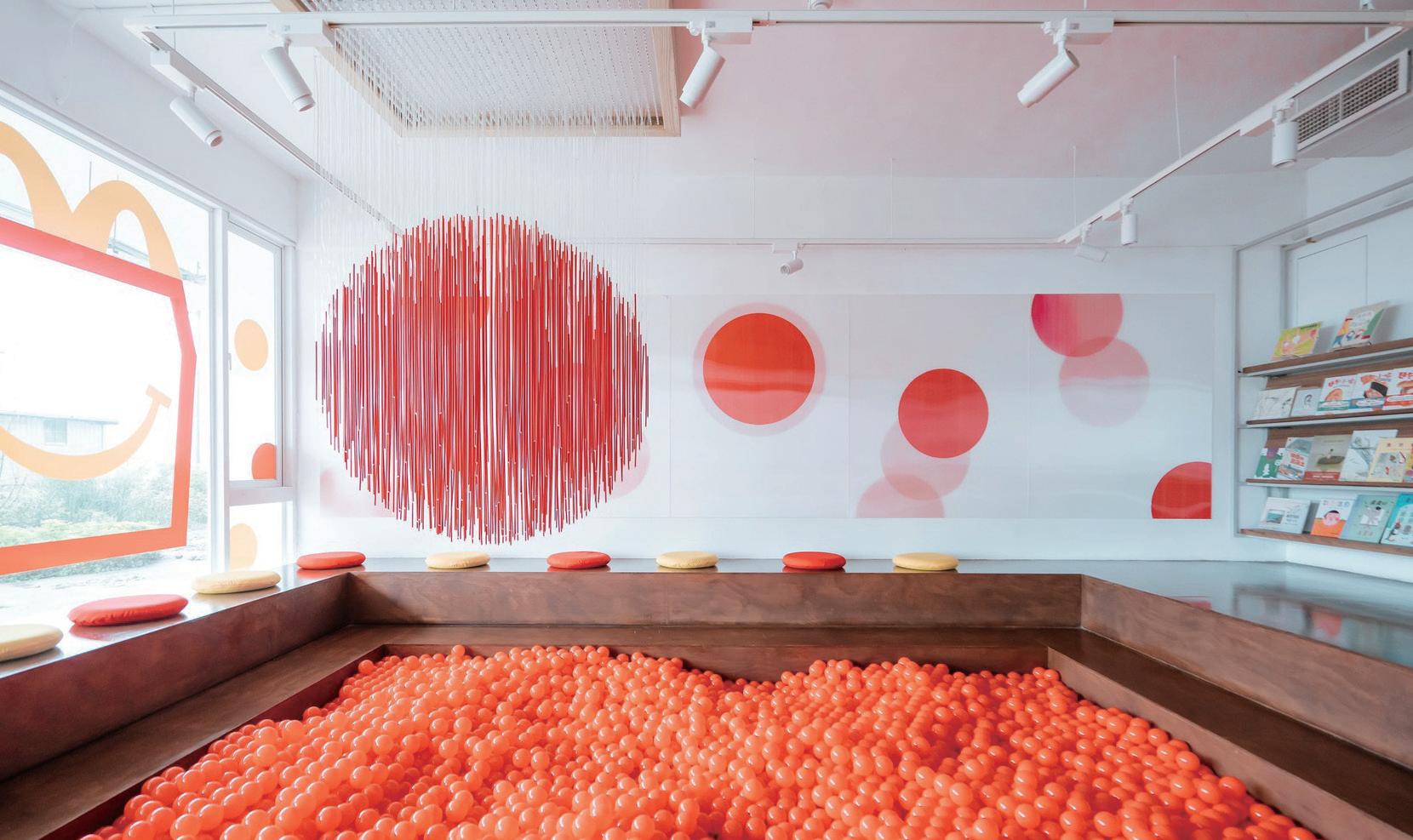
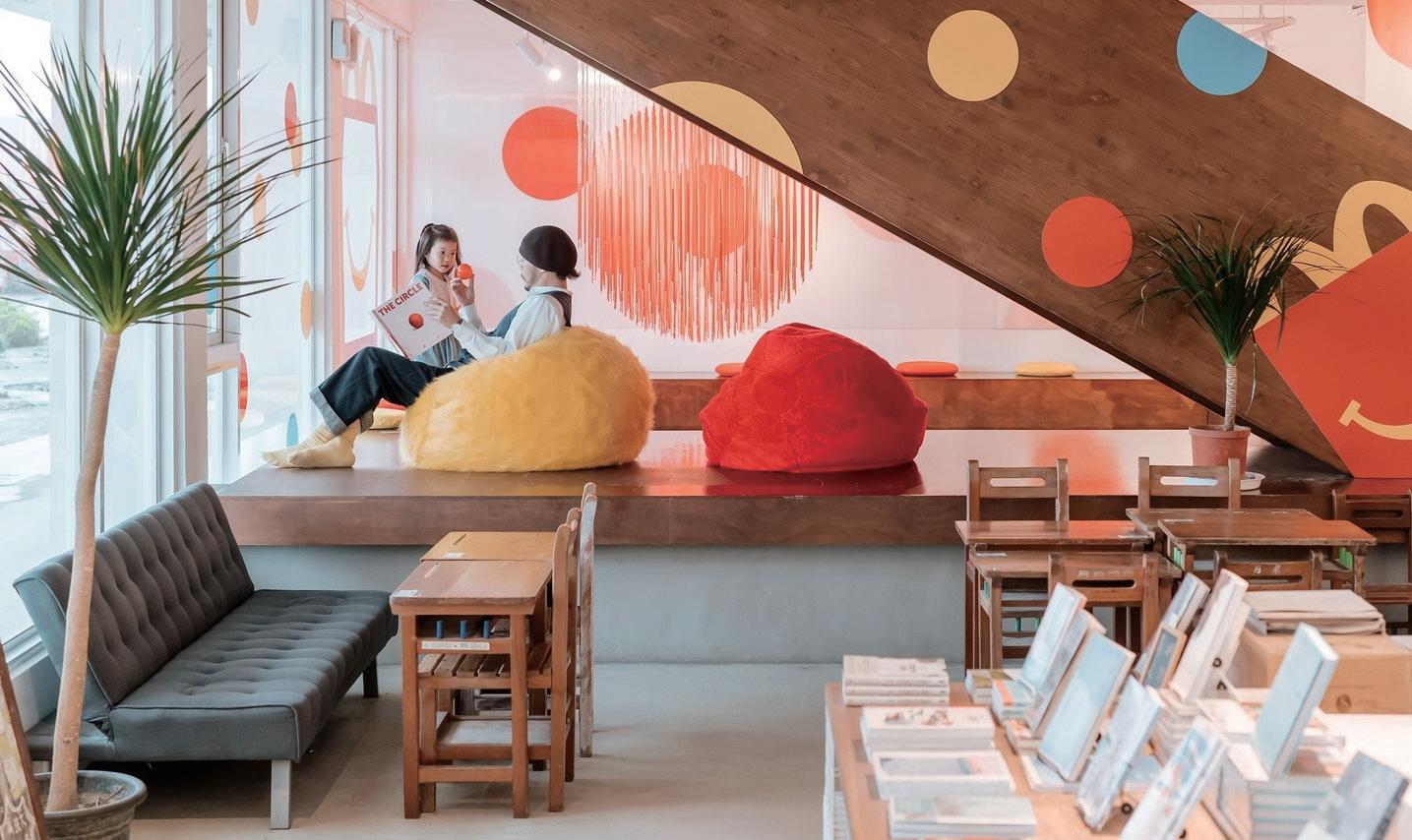



圖18. 麥麥親子共讀區(圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 18. “Happy Meal Readers Area” Themed Space Design (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
〈麥麥親子共讀區〉由設計師方序中與麥當勞合作,以繪本《不 圓的圓》為靈感,將共讀情境轉化為具教育與家庭意義的公共 場域。空間延續繪本中的圓形符號與童趣元素,營造親子共享 的閱讀與學習氛圍。此案例體現顧客共創,不僅深化品牌與使 用者的情感連結,也讓設計成為親子關係與社會教育的媒介, 展現設計連結產業、文化與使用者的策略價值。
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 建立關係並重新定義公共參與的起點 設計在此案例中不僅是視覺呈現的技術手段,更是與在地民眾 建立關係的重要媒介。設計團隊從繪本創作出發,進一步延伸 為實體親子共讀空間,讓設計直接進入家庭與生活場景。這種 從內容到場域的轉譯,使設計不再是單向的表述,而是促進社 會連結與互動的橋梁,實踐了以人為本的設計精神。
02 | 驅動共創歷程,深化使用者情感參與 團隊透過與偏鄉兒童的共讀與設計工作坊,將使用者從被動接 受者轉化為主動參與者,實踐情感共鳴的設計策略。從孩子 們對設計的喜愛,發現其背後其實來自說故事的熱情,設計 師藉此讓參與者不只是了解設計,而是共同構築內容與形式。
這種以故事為引的共創過程不僅增加使用者對空間的情感投 射,也進一步拉近品牌與在地社群之間的距離,促進長期的 使用者關係。
03 | 提升文化共感,賦予品牌真實性與深度 該案強調文化創新不應流於視覺表象,而應源於對人、情境與 生活脈絡的細膩理解。當設計深度介入教育、共讀與社群互 動,品牌形象即成為生活經驗的一部分,涵蓋從孩童到家庭、 從偏鄉到城市的多層次文化共感。透過設計導入參與式方法, 品牌不再是自我宣稱的形象,而是以真實參與深化其社會價值 與認同。
A parent-child reading space inspired by picture books, extending circular and playful elements to deepen brand emotional connections. The project demonstrates design’s ability to link industry, culture, and user experience.
01 | Building Relationships and Redefining the Starting Point of Public Participation
Design serves as a visual medium and a bridge connecting local communities. By translating picture books into a physical reading space, it facilitates social connection and embodies a human-centered approach.
02 | Driving Co-Creation Processes and Enhancing Emotional Engagement
Through shared reading and workshops, children in rural areas transition from passive to active participants. Stories guide co-creation, strengthening emotional projection and bringing the brand closer to the community, fostering longterm interaction.
03 | Enhancing Cultural Empathy to Impart Brand Authenticity and Depth
Design should not remain at the level of visual representation; it should reach into education and communities, integrating the brand into lived experiences and fostering cultural resonance from children to families, from rural areas to cities. By introducing participatory design approaches, the brand evolves from a selfproclaimed image into one that deepens its social value and identity through genuine engagement.

方序中Joe
Fang|總監Director
執行諸多的專案中,我們有許多和民眾對話的機會,像「麥麥親子共讀區」就藉機傳達故事概念,讓 親子使用空間時能有實際的啟發及參與感。
共居之家
Co-living Home
#實現顧客需求 #增強市場適應性
#Customer Needs #Market Adaptability
設計類別 Design Category
空間設計類 Spatial Design
受訪對象 Interviewees
行一建築.彭文苑建築師事務所 YUAN ARCHITECTS
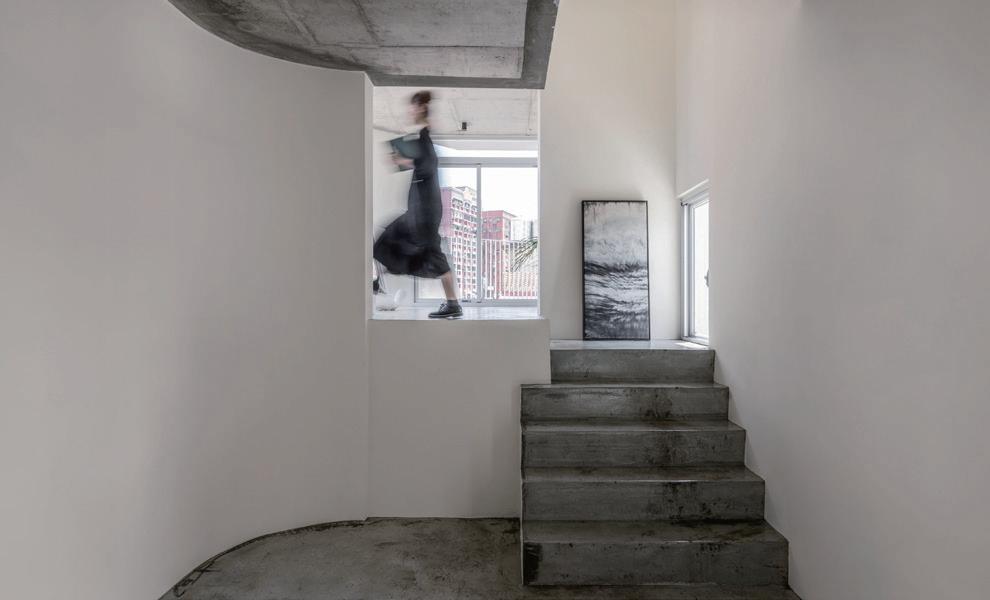
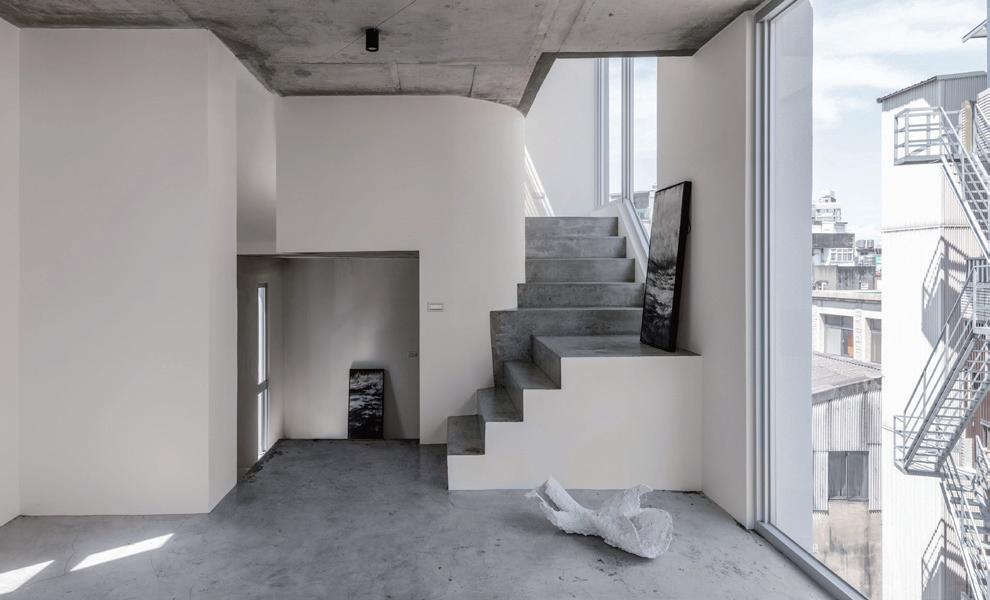



圖19. 共居之家(圖片來源:GPDA官網)
Figure 19. Co-living Home (Source: Golden Pin Design Award Website)
案例說明 Case Description
〈共居之家〉坐落於新竹市中心狹窄巷弄內,於僅四米面寬的 轉角基地上,打造一棟一層一戶的五層樓住宅,為年輕世代提 供具互動性的城市居住選擇。設計重新詮釋傳統公寓的動線 與居住型態,透過錯層樓地板與穿梭樓梯創造垂直交流空間, 鼓勵住戶互動,形塑微型社區氛圍。建築外觀則將內部生活 語彙向街區延伸,以斜板陽台串連各層,回應都市紋理。〈共 居之家〉強調空間由人與生活共構,回應老舊都市更新的在 地文化脈絡,試圖在日益冷漠的城市中,打開一種嶄新的共 享住宅想像。
設計應用 Design Applications
01 | 促進連結並強化共居文化 設計不再只是形式與功能的組合,而是人與人、人與城市重新 產生關係的媒介。透過設計,原本只是通行工具的樓梯轉化為 鄰里間日常互動的場域,創造了自然發生的社會性,並形塑一 種微型社區的共居文化。此策略突顯了空間的「公共性」與 「可對話性」,並使建築成為日常生活中促進情感連結的社會 裝置。
02 | 提升空間歸屬感
設計的成形不是設計師單方面的構想輸出,而是住戶與設計團 隊共同思考與實作的過程,體現了參與式設計的價值。從三十 版的初始提案、不斷的現場討論,到因應住戶需求的動態調 整,每一個細節都源自真實生活經驗的堆疊,展現設計如何作 為「平台」而非單向輸出。這樣的策略有助於培養空間的歸屬 感,讓使用者真正成為設計成果的共同擁有者。
03 | 建構文化脈絡與在地紋理 面對都市更新與快速複製的建築生產邏輯,設計團隊選擇從個 人經驗出發,回應在地的文化紋理。拒絕「模仿式在地化」, 轉而主張生活痕跡本身就是文化的最佳詮釋,且唯有長時間觀 察與誠實對話,才能使文化自然浮現。此策略強調「文化不輸 出而是內化」,設計語言需與使用者生活真實連結,才能創造 具有在地深度與國際辨識度的作品。
A five-story residential building with one unit per floor, offering interactive urban living for the younger generation. It reinterprets traditional apartment circulation and living patterns, creating a micro-community atmosphere.
01 | Facilitating Connections and Strengthening Co-Living Culture
Design serves as a medium to foster relationships among residents and between people and the city. Staircases are transformed into social interaction spaces, shaping a micro-community co-living culture that emphasizes the space’s “publicness” and “dialogue potential,” turning the building into a social device for emotional connection.
02 | Enhancing Sense of Belonging
The design process actively involves residents and the design team. Through iterative proposals and on-site discussions, adjustments are made based on real-life experiences. This participatory approach ensures that design is not a one-way professional output but a cocreated experience, cultivating a strong sense of ownership among users.
03 | Building Cultural Context and Local Texture
In the context of rapid urban redevelopment and replicable architecture, the project draws from individual experiences to respond to local textures, avoiding imitation-based localization. Through observation and dialogue, cultural elements naturally emerge, emphasizing cultural internalization and integration with daily life, creating works with local depth and international recognition.
彭文苑Wenyuan Peng|總監 Director
那些看似微不足道的日常,其實都構成了文化的底蘊。這些經驗需要時間的累積與觀察,而不是模仿 或表面化的設計。真正的在地文化會自然浮現,只要我們夠誠實、夠忠於自己。
綜觀本研究所分析的 11 件金點設計獎案例,可清楚看出設計 策略在回應企業不同發展驅動力中的多樣角色與關鍵價值。這 些案例橫跨產品、空間、服務、整合與視覺傳達等不同設計類 型,展現出設計在科技落地、人機互動優化、製程數位化與跨 域系統整合等技術導向議題上的轉譯與整合能力,也展現出在 品牌文化建構、價值主張溝通、顧客關係經營與市場差異化等 商業導向面向中的策動潛能。
這些案例皆共同體現出一個明確趨勢:設計不再只是美學的修 飾,而是企業應對變動、激發創新與創造價值的核心資產。本 研究透過這些案例的橫向觀察與策略對照,進一步揭示設計如 何在回應科技革新與市場競爭的同時,發揮其在永續轉型、文 化傳承與社會參與中的策略意涵。
A comprehensive analysis of the 11 Golden Pin Design Award winners examined in this study clearly reveals the diverse roles and key values of design strategies in responding to different corporate development drivers. These cases span various design categories, including product, spatial, service, integration, and communication design, and demonstrate design’s capacity for translation and integration in technology-driven areas such as technological implementation, human-tech interaction optimization, digitalized production processes, and crossdomain system integration.
At the same time, they showcase the strategic potential of design in business-oriented dimensions such as brand culture building, value proposition communication, customer relationship management, and market differentiation. Collectively, these cases embody a clear trend: design is no longer merely an embellishment of aesthetics, but a core asset that enables enterprises to adapt to change, spark innovation, and create value. Through a comparative and cross-sectional analysis of these cases, this study further reveals how design— while responding to technological innovation and market competition—also plays a strategic role in advancing sustainable transformation, cultural continuity, and social engagement.
4.2
設計發展應用總結
Summary of Design Development and Application
本研究在首章節從全球設計應用的拓展脈絡切入,說明設計 已跨越單一產業領域,在影響力上逐步延伸至生活、科技、 治理與永續等面向。經過金點設計獎 Golden Pin Design Award(GPDA)的案例分析後,研究更進一步看見臺灣設計 前端企業展現成熟的設計運用能力。追求設計帶來美學成果之 外,甚至更加重視策略導向、系統導向與價值導向效益。
美學導向效益
Aesthetic Benefit
著重外觀與感官呈現,強化產品 辨識度與吸引力,提升品牌質感 與感知價值,在同質化市場中建 立直覺記憶點。
策略導向效益 Strategic Benefit
在早期規劃階段,將設計思考 納入決策過程,進而幫助企業 市場定位、商業模式驗證、技 術應用藍圖規劃等關鍵環節。
Design has transcended the boundaries of individual industries, with its influence steadily extending into areas such as everyday life, technology, governance, and sustainability. Through case analyses from the Golden Pin Design Award (GPDA), this study further reveals that Taiwanese enterprises, while pursuing the aesthetic achievements brought by design, are equally—if not more— focused on its strategic, systemic, and value-oriented benefits.
系統導向效益 Systemic Benefit
不只解決表面可見的單一問題, 而是與研發、人資、營運、法務 等單位緊密協作,從調節單一問 題背後存在根本與系統性的問 題,開拓更寬廣的市場。
價值導向效益 Value-oriented Benefit
超越 KPI,用關鍵價值指標 (KVI)的觀念,將使用者體驗、 倫理考量與環境責任納入評估架 構之中。
01
|
商業驅動力:從商品導向走向價值與關係經營
Business Drivers: From Product Orientation to Value and Relationship Management
No
On this basis, two distinct trends have emerged in how Taiwanese enterprises are incorporating design:
2
避免深陷商品化競爭的市場下,多數案例應用設計的手段,展現出從「商品導向」走向「關係型提案」的關鍵趨勢,標誌著設 計在商業體系中從附屬角色轉為協調者與整合者,成為推動產業創新的實質動能。
說明 Description
1 作為與目標使用者之間,建立長期信任與情感連 結的策略手段。
A strategic approach that uses design to build long-term trust and emotional connection.
透過品牌故事、文化轉譯與生活化體驗,設計 協助企業在高度同質化的市場中創造差異化與 認同感。
Through brand storytelling, cultural translation, and everyday-life experiences, design helps enterprises create differentiation and a sense of identity.
3
4
以「真實生活感」為核心,使品牌不再依附於 單一產品價值,而是融入使用者的日常經驗, 形成具延展性的關係網絡。
With “a sense of real life” at the core, brands are no longer tied to the value of a single product but instead become integrated into users’ everyday experiences, forming a network of relationships.
擅用「共創實踐」於組織策略與營運流程中, 發揮設計思維效益。
Effectively applying “co-creation practices” within organizational strategy and operational processes to maximize the benefits of design thinking.
5
不僅參與產品開發與空間規劃,更協助整合營 運邏輯、數據回饋與使用者洞察,促進跨部門 協作與資源整合。
Helping to integrate operational logic, data feedback, and user insights to foster crossdepartmental collaboration and resource integration.
代表性案例與相關產業 Related Cases & Industries
04 灼器:從器物觸感、開箱敘事、環保材質到用餐情境,建立可持續的品牌情感與回 購意願。#製造-餐具製造 09 (beanroom):以「商品即裝飾」與故事命名、現場數據透明,創造可被記住的 體驗節點與品牌信任。#製造-食品製造
10 麥麥親子共讀區:由繪本→共讀空間→偏鄉共讀與工作坊,讓家庭參與、情感連 結持續累積。#設計-空間設計
01 屾屾市‧台南來了:老宅/廟宇元素轉譯為「國際語彙」,在台北市場引發共 鳴,創造文化辨識度。#設計-視覺設計
04 灼器:職人痕跡+低調文化印記,讓文化成為日常可感的品牌識別。#製造-餐 具製造
08 泉場:將工廠轉化為「可展示與交流的未來場域」,用在地材料、展覽敘事建 立差異化品牌語言。#製造-電梯製造
04 灼器:
器物、餐桌、空間到服務流程一體化,讓品牌語言進入日常使用情境而 持續被觸發。#製造-餐具製造 09 (beanroom):產品空間、資訊整合,從買豆→逛店→帶故事回家,延展為多接 觸點的品牌網絡。#製造-食品製造 11 共居之家:把樓梯變成互動場域,從住戶日常交流形塑「微型社區」,讓設計成 為生活關係的媒介。#設計-空間設計
07 漿紙業的最後一哩路:和工班、學研、社群的開放協作;材料測試+應用模擬, 形成跨域共創模式。#設計-空間設計
08 泉場:以展覽、講座、虛實互動建立「品牌共建平台」,讓利害關係人一起累 積品牌認同。#製造-電梯製造
09 (beanroom):模組化展示、彈性配置+後台數據可視化公開,連動營運效率 與品牌一致性。#製造-食品製造 美學導向讓使用者「看見」價值;策略導向讓企業「選對」方 向;系統導向讓問題「被真正解決」;價值導向則讓發展「走 得長遠」。這些企業案例中展現了下列的設計應用趨勢:
10 麥麥親子共讀區:與親子、偏鄉學童透過共讀/工作坊共創內容與場域,從使用 者變「參與者」。#設計-空間設計
02 T.Meta 無人機反制系統:設計於需求定義前期介入,AI 參數模擬+前後端 (操作介面×感測模組×知識庫)整合,跨工程/製造/業務協作。#資通訊-電子 資訊
03 WVM-410 UT 五軸機:從機構、介面到系統整合;以資訊分層、色彩標示降 低門檻,直接影響作業效率與能源管理。#製造-電子資訊
06 永續感知計劃:前期走訪回收廠與處理場域,建立知識對齊與需求理解,讓永續 導入與內部推動更順暢。#製造-居家電器
02 | 科技驅動力:從問題解決走向系統思維與社會適應
Technology Drivers: From Problem-Solving to Systems Thinking and Societal Adaptation 隨多元技術與前瞻科技的發展,更加以關懷人本的細膩思維駕馭科技硬實力,設計功能超越傳統單一功能優化與介面改良,轉 向更高層次的系統思維與社會適應。
No 說明 Description
1
以人本視角介入技術發展,從使用者行為與 倫理關懷出發,重新定義「技術應該如何被 使用、為誰而設計」。
Starting from user behavior and ethical considerations, “how technology should be used, and whom is it deisgned for” is redefined. .
2 由「問題解決」邁向「價值感知」的轉變, 使科技不再僅是效率的象徵,而能轉化為富 有意義的生活體驗與社會價值。
Marking a shift from “problem-solving” to “value perception,” this approach transforms technology into a meaningful life experience and a source of social value.
3
在技術整合與永續導入上的應用,也展現出 面對不確定環境的適應能力。
Applications in technology integration and sustainability implementation demonstrate the adaptive ability of the environment.
4 設計模組化、通用化與多場域應用等設計策 略,使產品能在不同政策、文化與基礎設施 條件下靈活運作,回應企業對於永續發展與 社會公平的期望。
Design strategies such as modularization, universality, and multi-context application enable products to operate flexibly across varying policy, cultural, and infrastructural conditions, addressing the goals of sustainable development and social equity.
代表性案例與相關產業 Related Cases & Industries
02 T.Meta 無人機反制系統: 將高壓、軍事化的技術情境轉譯為直覺操作 介面,讓不同訓練程度的人都能有效使用,體現「技術為人所用」的核心。#資 通訊-電子資訊
05 PEGATRON AC EVSE 電動車電源設備:以「公平使用」為前提,整 合 NFC、燈號識別與通用操作邏輯,確保不同年齡與科技熟悉度者都能安全 上手,回應技術倫理與普惠精神。#能源與智慧基礎-運輸
灼器:不只改善材質或使用流程,而是創造「餐桌與生活情感」的價值, 使產品成為生活意義而非單純器物。#製造-餐具製造
10 麥麥親子共讀區:設計不只回應場域功能(閱讀空間),而是透過故事、 共讀儀式與陪伴需求,創造可被感知與延續的家庭與社會價值。
#設計-空間設計
06 永續感知計劃:透過再生材料導入、跨部門理解與循環應用,使永續不僅 是口號,而能靈活回應產業現場變化。#製造-居家電器
07 漿紙業的最後一哩路:於高度傳統與高不確定性的產業場域中,以共創與 跨域整合逐步調整工法與應用,面對環境與轉型壓力仍能落地。#設計-空間 設計
05 PEGATRON AC EVSE 電動車電源設備:以模組化設計對應不同國際 規格,使產品能在多國政策與技術條件下部署,回應能源公平與永續行動。 #能源與智慧基礎-運輸 03 WVM-410 UT 五軸立式綜合加工機:以系統整合與介面模組化方式降 低技術使用門檻,使產品可在不同製程、不同規模工廠環境中運作,提高設備 通用性與延展性。#製造-機械設備
綜觀臺灣近年企業的設計導入趨勢,設計正逐步成為組織策略 思維中的核心要素。無論是參與決策前端、整合跨部門系統, 或協助企業建構長期價值框架,設計皆展現出超越傳統角色的 影響力。從「策略導向設計」強化市場洞察與創新前瞻力,到 「系統導向設計」協助組織在複雜結構中梳理流程與協調資 源,再到「價值導向設計」將社會責任與品牌理念納入企業決 策,這些實踐共同顯示設計已成為企業內部治理與外部競爭的 雙重驅動力。設計的價值不僅在於解決問題,而在於引導企業 重新理解何謂「有意義的創新」與「可持續的成長」。
當設計被納入企業核心,成為連結策略、系統與價值的整合平 台時,便能協助組織在快速變化的環境中保持敏捷與韌性,並 以更全面的視野開展未來發展藍圖。
Design is gradually becoming a strategic core for Taiwanese enterprises. From participating in front-end decisionmaking and integrating cross-departmental processes to building long-term value frameworks, the role of design has transcended traditional product or brand support. It serves as a crucial driver of corporate governance and competitiveness, guiding companies toward meaningful innovation and sustainable growth, while maintaining agility and resilience in a changing environment.
設計應用實踐與資源鏈結建議
Design Application Practice and Resource Connection
在本章訪談案例分析之中觀摩到設計的導入應用趨勢與價值, 而在對高度驗動與競爭激烈的市場環境中,企業若欲有效擴大 設計的應用效益,僅依賴單一組織內部的資源投入與設計實作 往往難以發揮最大綜效益。
從11件案例之中可見,設計不僅存在於企業內部的研發與品 牌推廣部門,更透過跨企業合作、外部設計資源整合,以及上 下游供應鏈的協作機制,展現更具規模的創新能量。這些案例 顯示「企業間資源鏈結」已逐漸成為推動設計策略實踐的關鍵 動能。透過與設計服務公司、製造夥伴、新創團隊、甚至是文 化機構的合作,企業得以導入多元視角與專業技能,形塑更貼 近使用者需求與時代議題的產品與服務。本研究歸納幾項具參 考性的資源鏈結作法,以及設計應用實踐建議,提供企業、設 計團隊以及政策實踐參考。
To effectively amplify the impact of design in a highly competitive market, relying solely on internal resources is often insufficient. By connecting with design firms, manufacturing partners, startups, and cultural institutions, enterprises can gain diverse perspectives and specialized capabilities, enabling the development of products and services that better align with user needs and societal issues. Below are strategic recommendations for Taiwanese enterprises, design teams, and policymakers to promote design.
本章以金點設計獎 Golden Pin Design Award (GPDA) 臺灣 的案例,清楚展現出設計如何成為企業核心運作的重要推力。這 些案例顯示,設計不僅是產品開發或品牌包裝的輔助環節,而是 連結技術創新、商業策略與組織發展的整合中樞。設計在企業內 部扮演了決策協調、科技轉譯與體驗優化的關鍵角色,並在外部 市場中形塑了品牌價值、文化識別與社會信任。在科技層面,設 計協助企業以人本視角介入新技術應用,兼顧使用者體驗、永續 導入與倫理思考,使創新能在多變的政策與產業環境下保持穩定 性與普及性;在商業層面,設計強化品牌敘事、服務體驗與市場 差異化,促進跨部門協作與產業共創,讓企業以更靈活的方式連 結顧客並創造長期價值。
這些案例揭示出臺灣設計的策略價值正在深化——設計不僅回 應市場,更引導組織思維的革新,成為企業因應不確定環境、 整合科技與文化、實現永續競爭力的重要基石。此趨勢象徵著 臺灣設計正以更成熟且具前瞻性的姿態,從實踐經驗走向策略 層次,在全球設計版圖中展現持續的影響力與發展潛能。
結語及未來展望 Conclusion and Future Outlook
回顧近年臺灣設計應用前端的企業,臺灣優勢在於深知設計 是成為策略決策與創新驅動的重要一環,設計也多層次的介 入商業策略之中。不再侷限於產品造型或品牌視覺的修飾, 而是深入參與組織治理、顧客關係與文化建構等層面。它協 助企業在不確定的市場中重新定義價值主張,結合科技創新 與永續思維,形塑出具韌性與識別度的競爭優勢。透過對金 點設計獎 Golden Pin Design Award (GPDA)得獎案例的 研究與訪談,本研究歸納出設計已在臺灣產業中扮演兩項關 鍵角色:一方面作為商業驅動力,促進品牌差異化與市場連 結;另一方面作為科技驅動力,協助企業以人本視角整合新 技術回、應社會與環境議題。設計的影響力正體現在其跨域 整合、價值詮釋與策略引導的能力上,使其成為組織內部協 調與外部溝通的共同語言。
展望未來,臺灣企業若要借助設計的力量幫助發展,必需參 考本案案例發現,讓設計參與更早期的策略構思,從市場洞 察、商業模式建構到技術藍圖規劃皆納入設計觀點,將能形 成更具前瞻性與包容性的創新結構。設計不僅能在跨部門合 作中協調流程與整合資源,也能透過其系統性思維促進組織 學習與知識轉譯,進而強化整體競爭力。同時,面對AI、永 續與社會包容等全球議題,設計所代表的已不只是創意與美 感,而是一種以人為本的思考模式,協助企業與社會在科技 進程中保持倫理平衡與文化敏銳度。此外臺灣設計在介入科 技創新起步中,在科技發展享譽全球的支持下,更具備成長 優勢,值得積極發展。
從產業與政策的視角來看,設計已具備連結創新與治理的潛 力。若能與產業升級、地方創生、科技創新及永續治理等國 家戰略相互呼應,設計將成為推動臺灣產業轉型與文化再生 的核心引擎。這需要政府、教育機構與企業端共同重構對設 計的理解,並在資源配置與人才培育上建立支持設計研究與 跨域合作的制度基礎。GPDA在其中扮演了重要角色,它不 僅是設計成果的展示平台,更是觀察設計變遷與產業創新的 指標。透過其持續的評選與資料累積,臺灣能更精確地掌握 設計導入的趨勢與價值,並以此作為推動政策與產業升級的 實證依據。
In recent years, the application of design in Taiwanese enterprises has gradually moved toward the core of business strategy, extending from product aesthetics and brand visuals to organizational governance, customer relationships, and cultural construction. Design helps companies redefine value in uncertain markets, integrating technological innovation and sustainability thinking to create resilient and recognizable competitive advantages. Insights from Golden Pin Design Award cases show that design functions as both a business driver and a technology driver: on one hand, it promotes brand differentiation and market connectivity; on the other, it integrates new technologies from a human-centered perspective, addressing social and environmental challenges, and serving as a common language for internal coordination and external communication.
Looking ahead, enterprises that incorporate design perspectives into early strategic ideation—from market insights and business model development to technology roadmap planning—can build more forward-looking innovation structures. Through systematic thinking, design can facilitate cross-departmental coordination, organizational learning, and enhanced competitiveness. At the same time, in response to global challenges such as AI, sustainability, and social inclusion, design provides a human-centered lens that helps companies maintain ethical standards and cultural sensitivity.
From the perspectives of policy and industry, when design is integrated with industrial upgrading, regional revitalization, technological innovation, and sustainable governance, it can become a core engine driving Taiwan’s industrial transformation and cultural regeneration. Design competitions have also emerged as important platforms that support policy advancement and industrial upgrading. The future value of design lies in guiding people to reflect on “what constitutes meaningful innovation.” As it becomes a translator between people, technology, and culture, design serves as a vital force for fostering trust and realizing sustainability.
設計的未來價值不僅在於提升效率或創造差異,而在於引導企業與社會重新思考「何謂有意義的創新」。當設計 成為連結人、技術與文化的橋樑,它便不只是解決問題的手段,而是成為能啟動變革、促進信任與實現永續的核 心力量。臺灣設計的挑戰與潛能皆在於此 讓設計持續參與國家產業與文化發展的核心,並以創新與韌性共同 構築未來。 “ Conclusion 總結 ”
附錄一
GPDA案例分析結果
Results of Golden Pin Design Award Analysis
為呈現全球與臺灣五年合計之前100名高頻關鍵字在各年度的整體趨勢與相對表現,本研究進一步統計這些字詞在每一年中的排名 變化(見下表1、表2)。考量到年度排名可能因些微變動而造成分析誤差,本研究採用十分位區間進行標準化處理,以避免微小名次 差異對整體趨勢判讀造成過度影響。即可建立出每個關鍵字在五年期間的「年度表現趨勢圖」,不僅可觀察其熱度波動,也有助於 辨識長期穩定關鍵字與短期爆紅字詞之異同。此計分方式除提升橫向比較的可行性,也能作為後續趨勢聚類分析或詞彙演變路徑研 究的重要依據。圖表中呈現的便是這100個高頻關鍵字在五年間的加權排名表現視覺化結果,反映出不同詞彙在全球設計領域中的 持續能見度與關注程度。
(This appendix presents the analysis results. For the English version, please contact TDRI directly.)
表 1. GPDA五年合計前100名高頻字之「全球」歷年表現
表 2. GPDA五年合計前100名高頻字之「臺灣」歷年表現
接著,為深入理解金點設計獎五年來高頻關鍵字間的語意結構與內在關聯性,本研究進一步運用社會網絡分析法進行詞彙共現關係 的建模,係將高頻詞間的共現關係轉換為「節點(node)」與「邊(edge)」的形式,建構語意社會網絡圖,藉以呈現詞彙之 間在語料中的共現強度與互動頻率。為了簡化視覺結構並凸顯核心網絡,本研究導入Motif(語意主題)分析技術進行網絡簡化。 Motif作為一種模式辨識技術,能有效找出網絡中的重複結構與高頻互連子圖,從而辨識出在語意網絡中具中心性與結構穩定性的 關鍵詞群。本研究辨識出數個與「功能」、「文化」、「材料」等主題相關的詞彙子群,分別圍繞在特定應用領域或敘事語境中, 形成彼此緊密連結的概念群聚,顯示此一詞組在整體語意架構中具有高度連結性與策略意涵(見下表3)。此分析結果不僅揭示出 設計語境中的核心概念與語意邏輯,也為後續主題趨勢的分群、設計思維的演化路徑或跨領域應用的切入點,提供分析基礎。
表 3.五年合計Motif關聯字分組
Group Vertex
4-clique motif: "areas", "lighting", "spatial", ... areas, floor, lighting, spatial
4-clique motif: "based", "culture", "shape", ... based, culture, overall, shape
4-clique motif: "colors", "coffee", "within", ... coffee, colors, glass, within
4-clique motif: "comfortable", "surface", "human", ... achieve, comfortable, human, surface
4-clique motif: "created", "theme", "exhibition", ... created, exhibition, key, theme
4-clique motif: "easy", "small", "appearance", ... appearance, easy, small, user
4-clique motif: "energy", "development", "industry", ... development, energy, industry, sustainable
4-clique motif: "front", "whole", "side", ... combined, front, side, whole
4-clique motif: "function", "low", "reduce", ... function, integrated, low, reduce
4-clique motif: "green", "identity", "diverse", ... diverse, green, identity, red
4-clique motif: "history", "book", "music", ... book, creative, history, music
4-clique motif: "house", "center", "wood", ... center, house, wood, years
4-clique motif: "image", "addition", "quality", ... addition, free, image, quality
4-clique motif: "innovative", "water", "long", ... body, innovative, long, water
4-clique motif: "market", "paper", "packaging", ... box, market, packaging, paper
4-clique motif: "metal", "texture", "feel", ... cover, feel, metal, texture
4-clique motif: "multi", "multiple", "smart", ... intelligent, multi, multiple, smart
Group Vertex
4-clique motif: "open", "simple", "large", ... back, large, open, simple
4-clique motif: "operation", "easily", "convenient", ... convenient, easily, operation, size
4-clique motif: "present", "hand", "four", ... cultural, four, hand, present
4-clique motif: "project", "future", "elements", ... elements, future, inspired, project
4-clique motif: "provides", "providing", "outdoor", ... built, outdoor, provides, providing
4-clique motif: "screen", "performance", "better", ... better, functions, performance, screen
4-clique motif: "set", "display", "control", ... control, display, full, set
4-clique motif: "spaces", "together", "old", ... living, old, spaces, together
4-clique motif: "storage", "allowing", "meet", ... allowing, environmental, meet, storage
4-clique motif: "tea", "chinese", "around", ... around, beauty, chinese, tea community, social, urban, value
4-clique motif: "wall", "white", "room", ... interior, room, wall, white
55-clique motif: "design", "space", "different", ... allows, area, art, brand, building, city, color, concept, core, create, creating, daily, design, designed, different, environment, every, experience, features, first, form, high, home, life, light, local, main, material, materials, modern, natural, nature, original, people, power, process, product, products, provide, public, sense, series, space, structure, style, system, taiwan, technology, time, traditional, unique, users, various, visual, work
5-clique motif: "without", "children", "air", ... air, children, friendly, without, world
綜合前文的字頻統計、語義共現與主題分群結果,並對照設計創新相關理論,本研究進一步進行對標分析,建立實務與理論之間的 連結基礎。本研究歸納出兩大核心目標與應用範疇,分別是科技與商業,每一範疇皆涵蓋五個構面(衍生發展為策略),用以說明設 計在企業不同策略層級中的角色與價值(見下表4 )。
本研究依據這兩大目標所應涵蓋的設計構面與關鍵特性,回扣統計分析結果,進行交叉對照。透過此對標,本研究得以檢視金點設 計獎獲獎案例在設計語彙上的關鍵趨勢,檢視是否反映了企業運用設計作為策略工具的實踐路徑。
表 4. 文獻構面對標文本分析之字詞
構面 SNA Motif Group
強化技術敏銳性 Technology Sensitivity
特性 SNA Motif Group
前瞻洞察 Foresight Capability
趨勢感知 Trend Awareness
人機協作優化 Human-Tech
人本設計 Human-Centeredness
易用性 Usability
實踐技術倫理 Techno-Ethics
推動數位轉型 Design for Digital Transformation
倫理意識 Ethical Awareness
負責任創新 Responsible Innovation
數位素養 Digital Literacy
系統設計思維 Systems Design Thinking
關聯詞分組 SNA Motif Group
technology, intelligent, smart, innovative, system, control, provides, efficiency, integrated, operation, temperature, energy, air, recycled, plastic, sustainability, green, future
users, user, screen, front, back, body, control, functions, function, interaction, providing, allowing, enhancing, features, offers, safety, multiple, friendly
privacy, data handling, friendly, safe, ensuring, safety, offers, context-dependent
導入永續技術 Sustainable Tech Adoption
永續導向思維 Sustainability Mindset
負責任創新 Responsible Innovation
system, provides, display, screen, technology, platform, integrated, creating, creating (context: digital service), innovative, intelligent, smart, operation, visual
sustainability, recycled, plastic, reduce, recycled, green, energy, environment, friendly, reduce, waste, environment, sustainability, daily(context: daily sustainability activities)
構面 SNA Motif Group
提升價值主張明確性
Value Proposition
確保品牌體驗一致性
Brand Experience
增強市場適應性
Market Adaptability
確保商業可行性
Business Viability
實現顧客參與性 Customer Needs
特性 SNA Motif Group
價值聚焦 Value-Driven Focus
清晰溝通 Clarity in Communication
體驗一致性 Experience Consistency
品牌導向設計 Brand-Driven Design
文化敏感性 Cultural Sensitivity
在地化靈活性 Localization Flexibility
策略適配 Strategic Alignment
資源可行性 Feasibility with Resources
共創能力 Co-Creation Capability
使用者參與設計 Participatory Design
關聯詞分組 SNA Motif Group
create, creating, project, concept, value, provide, based, aims, quality, performance, offers
brand, color, visual, design, identity, concept, visual, color, create, exhibition, art, style, appearance, lines
local, taiwan, chinese, culture, cultural, traditional, diverse, city, community, public, international
market, product, project, business, efficiency, development, providing, performance, quality
user, create, creating, public, children, activities, experience, sense, festival
附錄二 感謝誌
Acknowledgements
本研究得以順利推展需感謝金點設計獎 Golden Pin Design Award (GPDA) 各受訪企業與設計團隊撥冗參與訪談,慷 慨分享第一手經驗與真知灼見。各位的寶貴意見不僅協助本 研究團隊深入理解企業在設計導入與應用上的契機,也為研 究提供了重要的實務觀點與案例參照。
同時,亦感謝研究過程中提供協助的產業夥伴、協作團隊, 使研究成果得以更趨完整。此份研究報告的完成,凝聚了眾 多參與者的智慧與心力,在此謹致上誠摯謝意。
● 單位名稱 Company Name
偉詳工業股份有限公司
WAYSIA INDUSTRAIL CO., LTD.
創未來科技股份有限公司 Tron Future Tech
屾屾市 shen shen market
仰角視覺整合 ANGLE visual integration
泉承國際股份有限公司
CHIUAN CHENG INTERNATIONAL CO., LTD.
共序工事建築設計事務所 Üroborus_studioLab
木日生有限公司 Planet-J Limited
水相設計有限公司 Waterfrom Design
恆隆行貿易股份有限公司 HENG LEONG HANG CO.,LTD.
周育潤設計工作室 KEV Design Studio
行一建築.彭文苑建築師事務所 YUAN ARCHITECTS
究方社有限公司 JOEFANGSTUDIO
和碩聯合科技 PEGATRON
安達陶瓷藝術有限公司 Anta Pottery Art Co., Ltd.
中華紙漿股份有限公司 Chung Hwa Pulp Corporation
The completion of this study was made possible with the support of the design-leading enterprise teams featured in the cases. By sharing their valuable experiences and insights, they helped the research team gain a deeper understanding of the opportunities in design implementation, providing practical perspectives and reference cases. We sincerely appreciate their wisdom and dedication, which contributed significantly to the completion of this report.
● 受訪者 Interviewee
洪泳沅 Kai Hung | 設計師 Designer
龔家正 Marcus | 設計總監Design Director
謝文侃 | 主理人
周雨衛 Viter Chou | 負責人
張朝喨 | 負責人
洪浩鈞 Hao-Chun Hung | 創辦人
李冠興Elvis Lee | 品牌總監 Integrated Planning Director
葛祝瑋 | 設計總監 Design Director
卞文俊Webster Peng | 經理 Manager
周育潤 Yu-Jui Chou | 總監Director
彭文苑Wenyuan Peng | 總監 Director
方序中Joe Fang | 總監Director
邱榆皓Yuhao Chiu | 設計主任
孫盈馨 Ying-Hsing Sun | 總監Director
沈昀靚 Lauren Shen | 總經理室主任
1. International Council of Design. (n.d.). What is design? International Council of Design. https://www. theicod.org/en/professional-design/what-is-design/ what-is-design
2. Rodgers, P. A., & Bremner, C. (2017). The concept of the design discipline. Dialectic, 1(1), 5–25. https://doi. org/10.3998/dialectic.14932326.0001.104
3. Design Council. (2022). Design Economy 2022: Full report. Retrieved from https://www.designcouncil. org.uk/fileadmin/uploads/dc/Documents/Design_ Economy_2022_Full_Report.pdf
4. iF International Forum Design GmbH. (2025). iF design trend report 2025. iF International Forum Design GmbH. https://ifdesign.com/en/trend-report
5. Fondazione Symbola. (2025). Design Economy 2025. Retrieved from https://www.salonemilano.it/en/articles/ design-economy-2025-symbola
6. Dawson, R. (2009, May 25). The MegaTrends of Technology, Business, and Society. Retrieved from https://rossdawson.com/the_megatrends
7. Norman, D. A., & Verganti, R. (2014). Incremental and radical innovation: Design research vs. technology and meaning change. Design Issues, 30(1), 78-96.
8. Auernhammer, J. (2024). Strategic design: The integration of the two fields of strategy and design. In Proceedings of the Design Research Society (DRS) Conference 2024 (pp. 1–14). DRS. https://doi. org/10.21606/drs.2024.1399。 附錄三
關於台灣設計研究院
財團法人台灣設計研究院( Taiwan Design Research
Institution , TDRI )於2020 年成立,前身為台灣創意設計中 心(Taiwan Design Center,TDC),是台灣唯一一個以 設計為核心、促進產業、社會、公共創新為目標的法人組織。
主要任務為運用「設計力」整合政府跨部會的資源,讓設計成 為我國重要施政價值與國家戰略,同時透過跨域的知識整合, 讓政府導入設計思維,以設計驅動企業賦能,在台灣打造設計 領先型企業。
免責聲明
本報告係針對文獻、公開資訊和調查結果進行資料彙整及整體 分析,並非針對特定案主表示任何意見,亦不保證本報告於未 來仍維持準確、即時與完整性。本單位不對本報告資訊正確及 完整與否負任何義務及保證責任,閱讀者因使用本報告資訊所 引發之任何損失或任何性質之費用,亦同。
發行人 | 邱求慧
總編輯 | 張基義
副總編輯 | 劉世南
作者 | 劉宛育、黃莉庭、黃雪菡、李思婷
研究顧問 | 黃莉庭
研究助理 | 郭泱萱
研究分析團隊 | 晨晰统計顧問公司 康弘毅團隊
視覺及插畫設計 | 優仕創意有限公司
執行單位|財團法人台灣設計研究院
地址 | 11072台北市信義區光復南路133號北向製菸工廠2樓
網址 | https://www.tdri.org.tw
電話 | (02) 2745-8199
傳真 | (02) 3322-9028
出版單位 |經濟部產業發展署 地址 |106242 台北市大安區信義路三段41-3號
網址 | https://www.ida.gov.tw
電話 |(02)2754-1255
傳真|(02) 2703-0160
出版年月 | 2025年12月 版 次|初版
ISBN | 978-986-533-525-0 GPN | 1011401414
定價|非賣品
經濟部產業發展署保留所有權利。
欲利用本書全部或部分內容者, 請徵求經濟部產業發展署同意或書面授權。
臺灣企業設計應用動態發展 = Dynamic development of design application among Taiwanese enterprises / 劉宛育,黃莉庭,黃雪 菡,李思婷作. -- 初版. -- 臺北市:經濟部產 業發展署,2025.12 面; 公分 ISBN 978-986-533-525-0(平裝) 1.CST:設計 2.CST:產業發展 3.CST:個案研究 4.CST:臺灣 964 114016767
