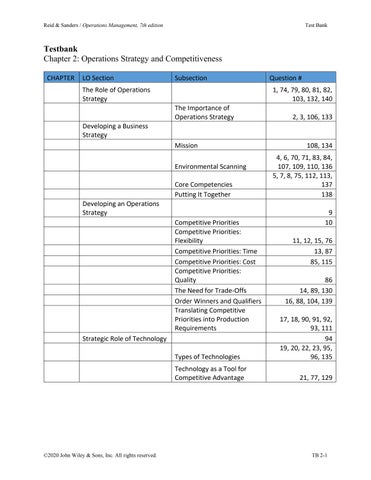
2: Operations Strategy and
The Role of Operations Strategy 1, 74, 79, 80, 81, 82, 103, 132, 140
Importance of Operations Strategy 2, 3, 106, 133 Developing a Business
108, 134
6, 70, 71, 83, 84, 107, 109, 110, 136
7, 8, 75, 112, 113,
85, 115
Need for Trade-Offs 14, 89, 130 Order
and Qualifiers 16, 88, 104, 139 Translating Competitive Priorities into Production
17, 18, 90, 91, 92, 93, 111
20, 22, 23, 95, 96, 135
77, 129
Productivity
Measuring Productivity
24, 25, 26 , 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 45, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 72, 73, 78, 97, 98, 99, 101, 116, 117, 118, 121, 122, 123, 124, 128, 131
Interpreting Productivity Measures 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 46, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 119, 120, 125, 126, 127
Productivity and Competitiveness 105, 114
Productivity and the Service Sector 102
Operations Strategy within OM: How It All Fits Together 100
© John Wiley & Sons, Inc. or the author. All rights reserved. Instructors who are authorized users of this course are permitted to download these materials and use them in connection with the course. Except as permitted herein or by law, no part of these materials should be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise.
Multiple Choice
1. Which of the following operations decisions did FedEx make to support its business strategy of competing on time and providing dependability of deliveries?
a) have its own fleet of tractor trailers and use a sophisticated bar code technology
b) have its own fleet of tractor trailers and have a large warehouse in every state
c) have its own fleet of airplanes and have a large warehouse in every state
d) use a sophisticated bar code technology and have a large warehouse in every state
e) have its own fleet of airplanes and use a sophisticated bar code technology
Ans: e
Solution: To provide spend of delivery, FedEx acquired its own fleet of airplanes. To provide dependability of deliveries, FedEx invested in a sophisticated bar-code technology to track all packages.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
2. Operational efficiency is
a) driving the business strategy
b) ensuring the right tasks are performed.
c) decreasing the firm’s input requirements.
d) increasing the firm’s output.
e) performing operations tasks well
Ans: e
Solution: Operational efficiency is performing operations tasks well, even better than competitors.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: The Importance of Operations Strategy Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
3. During the 1970s and 1980s, firms from which country provided the MOST serious competitive threat to U.S. companies?
a) Germany
b) Canada
c) Mexico
d) Japan
e) United Kingdom
Ans: d
Solution: During the 1970s and 1980s, Japanese companies began offering products of superior quality at lower cost, and the U.S. companies lost market share to their Japanese counterparts.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: The Importance of Operations Strategy
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
4. The process of monitoring the external environment is called what?
a) environmental examination
b) environmental inspection
c) environmental scrutiny
d) environmental perusal
e) environmental scanning
Ans: e
Solution: Environmental scanning is the process of monitoring the external environment for changes and trends to determine business opportunities and threats.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
5. Which of the following would NOT be considered a core competency that a company might have?
a) a highly trained workforce
b) an inefficient distribution system
c) skills in attracting and raising capital
d) use of information technology
e) quality control techniques
Ans: b
Solution: Core competencies are the unique strengths of an organization. The examples include special skills of workers, financial know-how, knowledge of production and information technology, etc. An inefficient distribution system is weakness of the business.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Core Competencies
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
6. Environmental scanning would NOT provide information on a) changes in customer wants and expectations.
b) the firm’s internal inefficient distribution system.
c) opportunities and threats.
d) changes in information technology
e) changes in global competition.
Ans: b
Solution: Environmental scanning looks at external environmental trends that can affect the business and allows a company to identify business opportunities and threats. It does not focus on a company’s own strengths and weakness (e.g., the internal inefficient distribution system).
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
7. Which of the following is NOT typically considered to be a core competency?
a) workforce
b) mission
c) market understanding
d) technology
e) facilities
Ans: b
Solution: Core competencies are the unique strengths of a business. A company may have core competencies in workforce, facilities, market understanding, financial know-how, and technology. Mission is a statement indicating what business the company is in.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Core Competencies
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
8. What term describes the process of obtaining goods or services from an outside provider?
a) outproviding
b) transferization
c) outsourcing
d) subsourcing
e) supersourcing
Ans: c
Solution: Outsourcing is obtaining goods or services from an outside provider.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Core Competencies
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
9. Once a business strategy has been developed, a) service prices must be established
b) competition must be identified.
c) an operations strategy must be formulated. d) contracting with external sources must begin e) insourcing will be conducted
Ans: c
Solution: Once a business strategy has been developed, an operation strategy must be formulated.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
10. Which of the following is NOT considered one of the four broad categories of competitive priorities?
a) technology
b) cost
c) quality
d) flexibility
e) time
Ans: a
Solution: The four broad categories of competitive priorities: cost, quality, time, and flexibility.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
11. Which of the following competitive priorities typically requires the use of more generalpurpose equipment?
a) technology
b) cost
c) quality
d) flexibility
e) time
Ans: d
Solution: Flexibility is a competitive priority focusing on offering a wide variety of products and services and meeting unique customer requirements. It typically requires the use of more general-purpose equipment that can be used to make many different kinds of products.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Flexibility
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
12. Highly skilled hourly workers would be MOST needed by companies employing which of the following competitive priorities?
a) location
b) cost
c) flexibility
d) development speed
e) time
Ans: c
Solution: Workers in flexible companies tend to have higher skill levels and can often perform many different tasks in order to meet customer needs.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Flexibility Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
13. How does Federal Express maintain its ability to compete on time during peak demand periods?
a) It subcontracts overload to other firms.
b) It purchases more planes.
c) It schedules full-time employees to work overtime
d) It uses a very flexible part-time workforce.
e) It purchases more vans
Ans: d
Solution: FedEx relies on a very flexible part-time workforce, such as college students, to cover workforce requirements during peak periods without having to schedule full-time workers.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Time
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
14. When making competitive priority decisions the firm needs to a) select the correct supply chain.
b) ensure the PWP is correctly established.
c) focus on the one competitive priority at the exclusion of all others. d) make trade-off decisions.
e) isolate the competing internal departments
Ans: d
Solution: The operation function must place emphasis on those priorities that directly support the business strategy. Thus, it needs to make trade-offs between the different priorities.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: The Need for Trade-Offs Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 1 min
15. Howard Plastics makes a variety of products out of plastics, ranging from plastic trays to body guards for cars. The company’s claim is: “We are ready to meet your custom plastics needs.” This is an example of a company that competes based on a) time.
b) cost c) quality.
d) flexibility e) efficiency.
Ans: d
Solution: Lee Plastics competes based on flexibility, i.e., offering a wide variety of products and customize them to the unique customer requirements.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Flexibility
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1 min
16. Order winners and qualifiers
a) are consistent between manufacturing and service organizations. b) only matter when responding to formal competitive bid requests. c) remain constant over time.
d) change over time
e) only apply to quasi-manufacturing firms.
Ans: d
Solution: Order winners and order qualifiers change over time.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Order Winners and Qualifiers
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
17. Which of the following is an operations decision related to the structure of the production process?
a) organization of operations
b) facilities
c) worker pay
d) quality control measures
e) management policies
Ans: b
Solution: The structure of the production process involves operations decisions related to the design of the production process, such as characteristics of facility used, selection of technology, and flow of goods and services through the facility.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Translating Competitive Priorities into Production Requirements
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 1 min
18. Which of the following is an operations decision related to the infrastructure of the production process?
a) quality control approaches
b) characteristics of facilities
c) robots
d) flow of goods and services through the facility
e) flexible manufacturing system (FMS) machines
Ans: a
Solution: The infrastructure of the production process involves operations decisions related to the planning and control systems of the operations, such as organization of the operations functions, skills and pay of workers, and quality control approaches.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Translating Competitive Priorities into Production Requirements
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 1 min
19. What are the three primary types of technology?
a) product technology, process technology, and information technology
b) product technology, process technology, and environmental technology
c) product technology, process technology, and safety technology
d) information technology, environmental technology, and safety technology
e) environmental technology, information technology, and process technology
Ans: a
Solution: The three primary types of technologies are: product technology, process technology, and information technology.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Types of Technologies
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology
Time on Task: 1 min
20. Teflon, the material used in no-stick fry pans, is an example of ________ technology. a) process
b) information
c) environmental d) safety
e) product
Ans: e
Solution: Product technology is any new technology developed by a firm. One example of this is Teflon, the material used in no-stick fry pans. Teflon became an emerging technology in the 1970s and is currently used in numerous applications.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Types of Technologies
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology
Time on Task: 1 min
21. Technology should be acquired because the new technology
a) is fun
b) keeps the employees happy.
c) doesn’t cost very much.
d) always improves productivity
e) supports the company’s chosen competitive priorities.
Ans: e
Solution: The technology a company acquires should not be decided on randomly. Rather, the selected technology needs to support the organization’s competitive priorities.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Technology as a Tool for Competitive Advantage Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology Time on Task: 1 min
22. Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) is an example of ______ technology.
a) process
b) information
c) environmental
d) safety
e) product
Ans: a
Solution: Process technology is the technology used to improve the process of creating goods and services. Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) is a technology that uses computers to assist engineers in the way they manufacture products.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Types of Technologies Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology Time on Task: 1 min
23. Which type of technology has had the greatest impact on business?
a) process technology
b) information technology
c) environmental technology
d) safety technology
e) product technology
Ans: b
Solution: Information technology enables communication, processing, and storage of information. It has grown rapidly over recent years and has had a profound impact on business.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Types of Technology
Level: Easy Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology
AACSB: Technology
Time on Task: 1 min
24. When does productivity increase?
a) Inputs increase while outputs remain the same.
b) Inputs decrease while outputs remain the same
c) Outputs decrease while inputs remain the same.
d) Inputs and outputs increase proportionally.
e) Inputs and outputs decrease proportionally.
Ans: b
Solution: Productivity = Outputs / Inputs. Productivity increases when using less inputs to produce the same amount of outputs.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 1 min
25. Which of the following is a valid productivity measure?
a) multi-output productivity measure
b) partial productivity measure
c) multi-part productivity measure
d) multi-component productivity measure
e) imperfect productivity measure
Ans: b
Solution: Productivity measures include: total productivity measures, partial productivity measures, and multifactor productivity measures.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 1 min
26. Consider a pizza parlor. Which of the following would NOT be a valid productivity measure?
a) pizzas produced / number of workers used
b) pizzas produced / number of ovens
c) pizzas produced / cost of workers and ingredients
d) pizzas produced / cost of all inputs used
e) labor hours / pizzas produced
Ans: e
Solution: Productivity = Outputs / Inputs. Labor hours / pizzas produced = Inputs / Outputs is not a valid productivity measure.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 1 min
27. If inputs increase by 30% and outputs decrease by 15%, what is the percentage change in productivity?
a) 100% decrease
b) 11.54% increase
c) 34.62% decrease
d) 15% increase
e) 15% decrease
Ans: c
Solution: P = O / I. New productivity = (1-0.15) / (1+0.3) = 0.85 / 1.3 = 0.6538, so the productivity is decreased by 1-0.6538 = 0.3462, or 34.63%.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 3 mins
28. If inputs increase by 6% and outputs increase by 24%, what is the percentage increase in productivity?
a) 400.00%
b) 16.98%
c) 0.25%
d) 4.00%
e) 18.00%
Ans: b
Solution: P = O / I. New productivity = 1.24 / 1.06 = 1.1698. The productivity is increased by 1.1698 –1 = 0.1698 or 16.98%.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 3 mins
29. An airline has determined that its baggage handlers can handle 12,000 bags when 3 baggage handlers are on shift. What is the baggage handler productivity?
a) 4,000 bags/shift
b) 4,000 bags/handler
c) 14,000 bags/shift
d) 12,000 bags/shift
e) 2,000 bags/handler
Ans: b
Solution: P = O / I = 12000 / 3 = 4000 bags/handler
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 1.5 mins
30. If inputs increase by 10% and outputs increase by 4%, what is the percentage change in productivity?
a) 5.45% increase
b) 250.00% increase
c) 5.45% decrease
d) 5.77% increase
e) 5.77% decrease
Ans: c
Solution: P = O / I. New productivity = 1.04 / 1.10 = 0.9455. Since inputs were higher than outputs, this represents a loss or negative; the productivity is decreased by 1.00 –. 9455 = .0545, or 5.45%.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 3 mins
31. If inputs increase by 10% and outputs increase by 5%, what is the percentage change in productivity?
a) 4.55% decrease
b) 4.55% increase
c) 4.76% increase
d) 4.76% decrease
e) 50.00% increase
Ans: a
Solution: P = O / I. New productivity = 1.05 / 1.10 = .9545. Since inputs were higher than outputs, this represents a loss or negative; the productivity is decreased by 1.00 –.9545 = .0455, or 4.55%
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 3 mins
32. If Joe’s Diner serves 150 meals in one day using 3 kitchen staff, what is the kitchen staff daily productivity?
a) 40 meals/staff
b) 45 meals/staff
c) 50 meals/staff
d) 55 meals/staff
e) 60 meals/staff
Ans: c
Solution: P = O / I =150 / 3 = 50 meals per staff
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1 min
33. If inputs increase by 30% and outputs increase by 15%, what is the percentage change in productivity?
a) 50.00% decrease
b) 88.46% increase
c) 88.46% decrease
d) 11.54% increase
e) 11.54% decrease
Ans: e
Solution: P = O / I. New productivity = 1.15 / 1.30 = .8846. Since inputs were higher than outputs, this represents a loss or negative. The productivity is decreased by 1.00 –.8846 = .1154, or 11.54%
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 3 mins
34. Suppose that on Monday the cost of inputs sums to $1000, and the value of outputs sums to $4000. For which of the following values on Tuesday would productivity increase?
a) inputs = $1100, outputs = $4000
b) inputs = $1100, outputs = $4200
c) inputs = $850, outputs = $3600
d) inputs = $1000, outputs = $3900
e) inputs = $2000, outputs = $8000
Ans: c
Solution: Calculate the P= O/I for each. “Inputs = $850 and outputs = $3,600” leads to the productivity of 3,600/850 = 4.235, which is the only one higher than the productivity on Monday (4000/1000 = 4)
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 2 mins
35. Suppose that a plant has a daily productivity of 200 parts per employee. What can we conclude?
a) The daily productivity is excellent.
b) The plant can hire more workers and still earn profits.
c) The plant is not earning profits
d) The plant must be highly automated.
e) No specific conclusion can be made.
Ans: e
Solution: No specific conclusion can be made. To interpret the meaning of a productivity measure, it must be compared with a similar productivity measure. The number by itself does not tell us very much.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
36. Suppose that a plant has a daily productivity of 0.85 parts per employee. What can we conclude?
a) The plant must be very labor-intensive.
b) The plant is not earning profits.
c) The plant must be highly automated
d) The plant should lay off workers.
e) No specific conclusion can be made.
Ans: e
Solution: No specific conclusion can be made. To interpret the meaning of a productivity measure, it must be compared with a similar productivity measure. The number by itself does not tell us very much.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 1.5 mins
37. Suppose that a plant has a total productivity measure of 0.85. What can we conclude?
a) The plant is not earning profits
b) No specific conclusion can be made.
c) The plant should lay off workers.
d) The plant is highly automated
e) The daily productivity is excellent.
Ans: a
Solution: Productivity = Outputs / Inputs. A plant cannot earn profit if its productivity is < 1 (i.e., inputs > outputs).
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
38. Suppose that last month the cost of inputs summed to $100,000, and the value of outputs summed to $800,000. For which of the following values this month would productivity increase?
a) inputs = $110,000, outputs = $800,000
b) inputs = $50,000, outputs = $400,000
c) inputs = $200,000, outputs = $1,600,000
d) inputs = $100,000, outputs = $820,000
e) inputs = $300,000, outputs = $1,600,000
Ans: d
Solution: Calculate the P= O/I for each; “inputs = $100,000, outputs = $820,000” is the only one higher than last month, i.e., 820,000 / 100,000 = 8.2 > 800,000/100,000 = 8, indicating a productivity increase.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 2 mins
39. Suppose that in week 1 a company produced 1,000 units using 60 labor hours. For which of the following values in week 2 would labor productivity decrease?
a) units = 2,000, hours = 120
b) units = 1,500, hours = 95
c) units = 1,000, hours = 58
d) units = 500, hours = 30
e) units = 2,000, hours = 100
Ans: b
Solution: Calculate the P= O/I for each; “units = 1,500, hours = 95” is the only one with the productivity lower than week 1, i.e., 1,500/95 =15.789 < 1,000/60 = 16.67 units/hour, indicating a decrease in labor productivity.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 2 mins
40. Suppose that on Wednesday the cost of inputs summed to $4,000, and the value of outputs summed to $10,000. For which of the following values on Thursday will productivity stay the same?
a) inputs = $2,000, outputs = $5,000
b) inputs = $5,000, outputs = $10,000
c) inputs = $4,000, outputs = $8,000
d) inputs = $10,000, outputs = $4,000
e) inputs = $12,000, outputs = $40,000
Ans: a
Solution: Calculate the P= O/I for each; “inputs = $2,000 and outputs = $5,000” = 5000/2000 = 2.5 is the only one that equals to Wednesday’s (10,000/4,000 = 2.5).
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
41. Vericol, Inc. manufactures drugs using workers and automated machines. The firm has decided to replace two workers with a new machine, while the output per day is not expected to change. Which of the following cannot be true?
a) Labor productivity will increase.
b) Machine productivity will decrease
c) Labor productivity will decrease.
d) Multifactor productivity will increase
e) Multifactor productivity will decrease.
Ans: c
Solution: Labor productivity = Output / Labor. If replacing 2 workers with a new machine while keeping the same level of output, the labor productivity will increase (fewer hours used), not decrease. Since no further information about machines available, multifactor productivity and machine productivity cannot be computed, so no conclusive statements can be made. That is, they may increase or decrease.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 3 mins
42. A manager has just replaced three workers with a machine that is cheaper to operate than the cost of the three replaced workers. Output is expected to remain the same. Which of the following is true?
a) Labor productivity will decrease
b) Machine productivity will increase.
c) Multifactor productivity will decrease.
d) Multifactor productivity will increase.
e) The value of output will decrease.
Ans: d
Solution: Total inputs will decrease since the machine is cheaper to operate. While the output remains the same, multifactor productivity will increase.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
43. Suppose that in January a company produced 5,000 units using 1,000 labor hours. For which of the following values in February would labor productivity decrease?
a) units = 5,000, hours = 900
b) units = 10,000, hours = 1,500
c) units = 10,000, hours = 2,000
d) units = 2,500, hours = 500
e) units = 5,000, hours = 1,100
Ans: e
Solution: Calculate the P= O/I for each; “units = 5,000, hours = 1,100” is the only one less than January, i.e., 5,000 / 1,100 = 4.54 < 5,000 / 1,000 = 5, indicating a labor productivity decrease.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
44. Suppose that in year 1 a company produced $100 million worth of outputs while inputs totaled $50 million. For which of the following values in year 2 would productivity decrease?
a) outputs = $90 million, inputs = $50 million
b) outputs = $400 million, inputs = $200 million
c) outputs = $250 million, inputs = $100 million
d) outputs = $50 million, inputs = $25 million
e) outputs = $60 million, inputs = $25 million
Ans: a
Solution: Calculate P= O/I for each; “output = $90 million, inputs = $50 million” is the only one less than year 1 (i.e., 90/50 = 1.8 < 100/50 = 2), indicating a productivity decrease.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
45. If the telecommunication company sold $10,000,000 of Internet service using $50,000 of labor, $25,000 of leased bandwidth, $45,000 service fees, and $80,000 or replacement parts, what is the telecommunication multifactor productivity?
a) 35
b) 40
c) 45
d) 50
e) 55
Ans: d
Solution: Multifactor productivity = 10,000,000 / (50k + 25k + 45k + 80k) = 10,000,000 / 200k = 50
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
46. Suppose that on Thursday a company produced 80 units using 160 labor hours. For which of the following values on Friday would daily labor productivity increase?
a) units = 70, hours = 160
b) units = 80, hours = 180
c) units = 240, hours = 500
d) units = 160, hours = 300
e) units = 40, hours = 100
Ans: d
Solution: Calculate the P= O/I for each; “units = 160, hours = 300” is the only one more than Thursday (160 / 300 = 0.5333 > 80 / 160 = 0.5), indicating a productivity increase.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
47. A firm produces 100 units using 800 labor hours. What is its labor productivity?
a) 0.125 units/hour
b) 8 units/hour
c) 100 units/hour
d) 800 units/hour
e) –0.125 units/hour
Ans: a
Solution: Labor productivity = O / I = 100 / 800 = .125 units / hr
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
48 A firm produces 2000 products using 10 workers on an eight-hour shift. What is the labor productivity per worker?
a) 200 units/hour
b) 25 units/hour
c) 250 units/hour
d) 20 units/hour
e) 0.04 units/hour
Ans: b
Solution: Labor productivity = 2000 units / (10*8 hr) = 25 units/hr
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
49. A machine shop produces metal frames on two different machines. The average daily production on machine 1 is 300 frames, and the average daily production on machine 2 is 180 frames. What is the daily machine productivity?
a) 480 frames/machine
b) 330 frames/machine
c) 240 frames/machine
d) 160 frames/machine
e) 300 frames/machine
Ans: c
Solution: Daily machine productivity = (300 + 180) /2 = 240 frames/machine
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
50. A machine shop produces metal brackets on two different machines. Machine 1 can produce a bracket every 10 minutes. Machine 2 can produce a bracket every 4 minutes. What is the average productivity per machine?
a) 4.3 brackets/hour
b) 8.6 brackets/hour
c) 10.5 brackets/hour
d) 21.0 brackets/hour
e) 7.0 brackets/hour
Ans: c
Solution: Average machine productivity = (60 mins /10 mins + 60 mins /4 mins) / 2= 21 /2 = 10.5 brackets / hour per machine
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
51. A firm produces handbags using three workers. On Tuesday, Jane completed 60 bags in 6 hours, Ron completed 50 bags in 7 hours, and Mary completed 80 bags in 5 hours. What was the overall productivity of the firm?
a) 7.92 bags/hour
b) 11.05 bags/hour
c) 10.00 bags/hour
d) 10.56 bags/hour
e) 61.67 bags/hour
Ans: d
Solution: Overall labor productivity = Total bags / Total labor hours = (60+50+80) / (6+7+5) = 10.56 bags / hour
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
52. Suppose that output is worth $400, and labor and materials costs are $200 and $100, respectively. What is the materials productivity?
a) 2.00
b) 1.33
c) 0.25
d) 0.75
e) 4.00
Ans: e
Solution: Materials productivity = 400 / 100 = 4.00
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1 min
53. A firm produces 500 units per day using five workers on a five-hour shift. On average, 15% of the units produced are defective and must be scrapped. What is the labor productivity for nondefective units?
a) 17 units/hour
b) 3 units/hour
c) 20 units/hour
d) 85 units/hour
e) 15 units/hour
Ans: a
Solution: Labor productivity = Nondefective units / Total labor hours = (500*0.85) / (5*5) = 17 units/hour
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
54. Suppose that weekly output is worth $1000, and labor and materials costs are $300 and $200, respectively. What is the multifactor productivity ratio?
a) 1000
b) 8
c) 2
d) 3
e) 0.5
Ans: c
Solution: Multifactor productivity = 1000 / (300 + 200) = 1000 / 500 = 2
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
55. Each day a firm produces 50 products worth $40 each. Raw materials cost per unit are $12. The firm uses 4 workers on an eight-hour shift earning $10 per hour each. What is the multifactor productivity ratio?
a) 1.82
b) 0.77
c) 3.16
d) 0.12
e) 2.17
Ans: e
Solution: Multifactor productivity = Total outputs / Total inputs = (50*40) / (50*12 + 4*8*10) = 2.17
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
56. A bakery bakes bread in two different ovens. Oven 1 can bake a loaf every 30 minutes. Oven 2 can bake a loaf every 15 minutes. What is the average productivity per oven?
a) 6.00 loaves/hour
b) 3.00 loaves/hour
c) 2.67 loaves/hour
d) 1.33 loaves/hour
e) 0.38 loaves/hour
Ans: b
Solution: Oven 1 can bake 2 per hour. Oven 2 can bake 4 per hour. Total 6 loaves per hr / 2 ovens = 3 loaves per hour.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
57. Johnny employs five painters. He collected the following data from last week.
Painter Hours
Julius 40
Suzy 36
Fawn 44 74
Which painter was LEAST productive last week?
a) Julius
b) Margaret
c) Dave
d) Suzy
e) Fawn
Ans: a
Solution: Calculate by dividing walls completed by the hours; Julius was LEAST productive with 1.5 walls per hour
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
58. A bakery uses five ovens to bake muffins. Yesterday’s data are provided below.
Oven Hours Muffins
Oven 1 5 600
Oven 2 10 1500
Oven 3 8 1280
Oven 4 8 800
Oven 5 6 780
Which oven was the MOST productive?
a) Oven 1
b) Oven 2
c) Oven 3
d) Oven 4
e) Oven 5
Ans: c
Solution: Calculate by dividing muffins baked by the hours; oven 3 was most productive with productivity of 160 muffins per hour
Oven Hours Muffins
1 5
2 10
3 8
4 8
Muffins per
5 6 780 130
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
59. The state government utilizes five workers to stamp license plates. Last month’s data are provided below.
Worker Days
Pete 30
Tommy 20
Laura 24
Julie 28
Susan 29
Which worker was the LEAST productive?
a) Pete
b) Tommy
c) Laura
d) Julie
e) Susan
Ans: e
Solution: Calculate by dividing units stamped by the days; Susan was least productive with productivity of 41.38 units per day.
Worker
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 2 mins
60. A firm uses five plants to produce its products. Each final product has a value of $100. The following table provides last week’s output, labor hours used (at $15 per hour), and materials cost per unit.
Plant Output (in units) Labor Hours Materials Cost per Unit
Plant 1 2000 400 $20
Plant 2 5000 900 $18
Plant 3 9000 2000 $20
Plant 4 1000 150 $30
Plant 5 2000 440 $18
Which plant was MOST productive last week?
a) Plant 1
b) Plant 2
c) Plant 3
d) Plant 4
e) Plant 5
Ans: b
Solution:
Plant 1 = 2000/(400x15 + 20x2000) = .043
Plant 2 = 5000/(900x15 + 18x2000) = .048
Plant 3 = 9000/(2000x15 + 20x2000) = .042
Plant 4 = 1000/(150x15 + 30x2000) = .031
Plant 5 = 2000/(440x15 + 18x2000) = .047
Plant 2 was most productive with the highest productivity ratio of 0.048.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
61. A firm uses five plants to produce its products. Output value and total input cost for last week are provided below.
Plant Output Value Total Cost
Plant 1
Plant 2
Plant 3
Plant 4
Plant 5
$20,000 $25,000
$50,000 $60,000
$40,000 $42,000
$80,000 $99,000
$25,000 $29,000
Which plant was LEAST productive last week?
a) Plant 1
b) Plant 2
c) Plant 3
d) Plant 4
e) Plant 5
Ans: a
Solution:
Plant 1 = 20000/25000 = .800
Plant 2 = 50000/60000 = .833
Plant 3 = 40000/42000 = .952
Plant 4 = 80000/99000 = .808
Plant 5 = 25000/29000 = .862
Plant 1 was least productive with the lowest productivity ratio of 0.800.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
62. Last week Jason painted 11 houses in 4 days. This week he painted 14 houses in 5 days. What was his percent productivity increase?
a) 1.82%
b) 1.79%
c) 27.27%
d) 25.00%
e) 5.00%
Ans: a
Solution:
Last week: 11 / 4 = 2.75
This week: 14 / 5 = 2.8
2.8 / 2.75 = 1.01818.
The productivity was increased by 0.01818 or 1.82%
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
63. Last month a plant produced 10,000 units using 2000 labor hours. This month it produced 12,000 units using 3000 labor hours. What is the percent productivity decrease?
a) 200%
b) 100%
c) 50%
d) 25%
e) 20%
Ans: e
Solution:
Last month: 10000 / 2000 = 5
This month: 12000 / 3000 = 4
Percentage of productivity change = (4 – 5) / 5 = –0.2, or 20% decrease
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Analysis
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 1.5 mins
64. On Tuesday George produced 100 units in 8 hours. On Wednesday he produced 120 units in 10 hours. What was his percent productivity change?
a) 0.50%
b) 4.17%
c) 4.17%
d) 4.00%
e) 4.00%
Ans: d
Solution:
Tuesday: 100 / 8 = 12.5
Wednesday: 120 / 10 = 12
Percent productivity change = (12 – 12.5) / 12.5 = –0.04, or 4% decrease
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
65. Last month Stacy sold 10 houses while working 20 days. This month she sold the same number of houses in 22 days. What is her percent productivity change?
a) 10.00%
b) 9.1%
c) 9.1%
d) 10.00%
e) 4.55%
Ans: b
Solution:
Last month: 10 / 20 = 0.5
This month: 10 / 22 = 0.4545
Percent productivity change: (.4545 – 0.5) / 0.5 = –.0.091, or 9.1% decrease
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
66. Yesterday, John produced 100 units in 8 hours. Today he produced the same amount in 6 hours. What is his percent productivity change?
a) 33.33%
b) 0.00%
c) 25.55%
d) 25.00%
e) 4.67%
Ans: a
Solution:
Yesterday: 100 / 8 = 12.5
Today: 100 / 6 = 16.666
Percent productivity change: (16.666 – 12.5) / 12.5 = 0.3333, or 33.33% productivity increase
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
67. A company used to produce 500 units every 2 days, but 10% of the units were defective. After installing a new process, defects have been eliminated while output has remained the same. What is the percent increase in productivity due to installing the new process?
a) 10.00%
b) 25.00%
c) 11.11%
d) 0.00%
e) 5.56%
Ans: c
Solution: Productivity = Outputs / Inputs
Old process: (500 * 0.9) / 2 = 225 units per day
New process: (500) / 2 = 250 units per day
Percent productivity increase = (250 – 225) / 225 = 0.111, or 11.11%
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
68. A company used to produce 300 units every day, but 20% of the units were defective. After installing a new process, the defect rate has been reduced to 5%, while output has remained the same. What is the percent increase in productivity due to installing the new process?
a) 15.79%
b) 0.00%
c) 15.00%
d) 18.75%
e) 75.00%
Ans: d
Solution:
Old process: Nondefective output = 300 – 20%*300 = 240 units
New process: Nondefective output = 300 – 5%*300 = 285 units
With the same amount of inputs, the % productivity change = (285 – 240)/240 = 0.1875, or 18.75% increase
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
69. Last month a plant produced 1200 units using 150 labor hours. This month it produced 1500 units using 300 labor hours. What is the percent productivity decrease?
a) 37.50%
b) 60.00%
c) 100.00%
d) 300.00%
e) 200.00%
Ans: a
Solution:
Last month: 1200 / 150 = 8 units / hour
This month: 1500 / 300 = 5 units / hour
Percent productivity decrease = (5 – 8) / 8 = –0.375, or 37.5%
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
70. Which of the following has used the Internet to conduct a fashion show in order to boost sales?
a) The Gap
b) Eddie Bauer
c) Fruit of the Loom
d) Victoria’s Secret
e) Sears
Ans: d
Solution: Victoria’s Secret uses the Internet to conduct fashion shows in order to boost sales.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Technology
Time on Task: 1 min
71. Which of the following is NOT described in the chapter as one of the major environmental trends that firms should monitor?
a) marketplace trends
b) global climate trends
c) economic trends
d) political trends
e) social trends
Ans: b
Solution: Environmental scanning does not monitor global climate trends. It monitors trends in the market and some other types of trends that can affect business, such as economic, political, and social trends.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 1 min
72. Suppose that a plant manager is only evaluated based on the partial productivity measure: output/(number of employees). If she replaces 10% of the workforce with robots (one robot per replaced worker), and output remains the same, what will be the percent change in this measure of productivity?
a) 10% increase
b) 10% decrease
c) 11.1% increase
d) 11.1% decrease
e) No change in productivity
Ans: c
Solution: Partial labor productivity = O / I = 1 / (1*0.9) = 1.111, or 11.1% increase in labor productivity
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
73. Productivity is essentially
a) something to fill out managers’ reports.
b) a measure of resource effectiveness.
c) a scorecard of how efficiently resources are used
d) a balance scorecard metric.
e) the current business fad
Ans: c
Solution: Productivity is a measure of how efficiently an organization converts inputs into outputs.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
74. Happy Donuts is a U.S.–based bakery company. Recently, the company opened its first store in China. Which of the following is most likely to be one of the reasons for this movement?
a) It helps the company to be a cost leader.
b) It helps the company to compete on differentiation.
c) It supports the company’s business strategy.
d) It facilitates the implementation of TQM within the company.
Ans: c
Solution: Business strategy is a long-range plan for a business. Opening a store supports the company’s long-range plan for its business.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 1 min
75. Juan is a high school graduate entering a university. He is particularly good in verbal communication and persuasion but not as good in mathematics. Taking advantage of his core competencies means that Juan should major in a) engineering.
b) science.
c) economics.
d) marketing.
Ans: d
Solution: Core competencies are the unique strengths of a business. Studying a major in marketing would give Juan an advantage, since his strengths, or core competencies, are verbal communications and persuasion.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Core Competencies
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 1 min
76. Fusion Gourmet Cookery is a restaurant offering a range of dishes from India and the Middle East. The slogan of the restaurant is “We will personalize any dish.” This suggests that the restaurant competes based on a) cost.
b) quality.
c) time.
d) flexibility.
e) efficiency.
Ans: d
Solution: The slogan suggests that the restaurant’s competitive priority is flexibility. That is, it can offer a variety of foods to the customer specifications.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Flexibility
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1 min
77. After identifying various types of technologies that her company could acquire, Lisa and her team list a set of key critical success factors to evaluate each. Which of the following is least likely to be considered?
a) Gain a competitive advantage.
b) Improve current processes
c) Maintain up-to-date standards.
d) Follow the latest fad
Ans: d
Solution: The technology a company acquires should not be decided on randomly, such as following the latest fad or industry trend. Technology should be acquired to help gain a competitive advantage, maintain up-to-date technology, and improve processes.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Technology as a Tool for Competitive Advantage Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1 min
78. The IT workshop at a state university is open from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. Monday through Friday. It uses 4 part-time student technicians per day with each of them working a 4-hour shift. On average, the workshop solves 50 computer hardware- and software-related requests per day. What is the student productivity ratio?
a) 50 requests per day
b) 25 requests per shift
c) 6.25 requests per hour
d) 3.125 requests per hour
e) 1.5625 requests per hour
Ans: d
Solution: Student productivity = value of output / labor-hours of input = 50 / (4 * 4) = 3.125 requests per hour.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
True/False
79. An operations strategy covers a relatively short time horizon, whereas a business strategy covers a relatively long time horizon.
Ans: False
Solution: A business strategy is a long-range plan of a business. An operation strategy is a longrange plan for the operations function that specifies the design and use of resources to support the business strategy.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 0.5 mins
80. To provide speed of delivery, Federal Express invested in a sophisticated bar code technology.
Ans: False
Solution: To provide speed of delivery, FedEx acquired its own fleet of airplanes. To provide dependability of deliveries, FedEx invested in a sophisticated bar code technology to track all packages
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 0.5 mins
81. To provide dependability of deliveries, Federal Express acquired its own fleet of airplanes.
Ans: False
Solution: To provide dependability of deliveries, FedEx invested in a sophisticated bar code technology to track all packages It acquired its own fleet of airplanes to ensure speed of delivery.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
82. Operations strategy is developed before the business strategy so the company knows what it will be producing before establishing a long range business strategy
Ans: False
Solution: The operation strategy is a long-range plan developed for the operations function that specifies the design and use of resources to support the business strategy. It must be aligned with the company’s business strategy and enable the company to achieve its long-term plan.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 0.5 mins
83. Victoria’s Secret has used the Internet to conduct a fashion show in order to boost sales.
Ans: True
Solution: Victoria’s Secret uses the Internet to conduct fashion shows in order to boost sales.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Technology
Time on Task: 0.5 mins
84. Market research represents a type of environmental scanning.
Ans: True
Solution: Market research represents a type of environmental scanning that monitor marketplace trends, e.g., changes in customer wants and expectations and ways in which competitors are meeting those expectations.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 0.5 mins
85. Companies that compete on cost generally also allow a lot of product customization.
Ans: False
Solution: Companies that compete on cost usually offer a narrow range of products and product features and allow for little customization.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Cost Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
86. Firms that focus on quality as their primary competitive priority usually implement either product design quality or process quality, but not both.
Ans: False
Solution: Firms that compete on quality need to address both product design quality and process quality. The product must be designed to meet customer needs and the process must produce the product exactly as it is designed.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Quality Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
87. To ensure speed of deliveries, Federal Express subcontracts its work overload to other firms during peak demand periods.
Ans: False
Solution: FedEx uses a very flexible part-time workforce, such as college students, to cover workforce requirements during peak periods.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Time Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 0.5 mins
88. As long as the firm meets the order qualifier classification it will always be competitive and win competitive bid opportunities
Ans: False
Solution: Order qualifiers are the business standards that a company has to meet if it wants to do the business. Yet to be successful in the marketplace, the company must further focus on order winners, the competitive priorities that will differentiate the company from the others.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Order Winners and Qualifiers
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
89. Companies that compete based on flexibility often cannot compete on cost.
Ans: True
Solution: A company that competes based on flexibility will likely not be able to compete on cost. It often takes more resources to customize a product or a service.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: The Need for Trade-Offs
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
90. Facilities decisions are part of the production process infrastructure.
Ans: False
Solution: Facility decisions are related to the structure or the design of the production process.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Translating Competitive Priorities into Production Requirements
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
91. Decisions regarding flow of goods and services through the facility are part of the production process structure
Ans: True
Solution: The structure of the production process involves operations decisions related to the design of the production process, such as facilities, technology, and flow of goods and services through the facility.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Translating Competitive Priorities into Production Requirements
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
92. Worker pay decisions are part of the production process structure.
Ans: False
Solution: Worker pay decisions are related to the infrastructure of the production process (the planning and control systems of the operations).
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Translating Competitive priorities into Production Requirements
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
93. Quality control approaches are part of the production process infrastructure.
Ans: True
Solution: Quality control approaches are part of the production process infrastructure.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Translating Competitive priorities into Production Requirements
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
94. Studies have shown that companies that invest in new technologies tend to improve their financial position over those that do not
Ans: True
Solution: Studies have shown that companies that invest in new technologies tend to improve their financial position over those that do not.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology Time on Task: 0.5 mins
95. Operations management is only concerned with information technology applications within the firm.
Ans: False
Solution: The three primary types of technologies (product, process, and information) are differentiated based on their application, but all are important to operations managers.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Types of Technologies Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology Time on Task: 0.5 mins
96. Process technology is the technology that has grown the MOST rapidly and has had the greatest impact on business.
Ans: False
Solution: Information technology has grown rapidly over recent years and has had a profound impact on business.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Types of Technology Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology Time on Task: 0.5 mins
97. A measure of how efficiently inputs are being converted into outputs is called utilization.
Ans: False
Solution: Productivity is a measure of how efficiently an organization converts inputs into outputs.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
98. Productivity = Input / Output
Ans: False
Solution: Productivity = Output / Input
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
99. Output / (all inputs used) is called total productivity.
Ans: True
Solution: Total productivity measure = Output produced / all inputs used
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
100. An operations strategy should NOT impact the firm’s supply chain design.
Ans: False
Solution: Decisions regarding operations strategy directly impact decisions on organizational structure and infrastructure of the company. This includes the design of supply chain.
Section Ref: Operations Strategy Within OM: How It All Fits Together
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
101. Output / (labor + capital) is an example of a partial productivity measure.
Ans: False
Solution: Partial productivity is computed as a ratio of output to only one input (e.g., labor, materials, and machines)
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
102. Productivity gains in the service sector have been much lower than that of manufacturing.
Ans: True
Solution: Employment in the service sector of the U.S. economy has grown rapidly. However, productivity gains in this sector have been much lower than those of manufacturing.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Productivity and the Service Sector
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
103. Marketing strategy defines marketing plans to support the business strategy.
Ans: True
Solution: Marketing strategy defines marketing plans to support the business strategy.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
104. McDonald’s and pizzerias compete on the same “order winners ”
Ans: False
Solution: McDonalds competes on consistency; pizzerias compete on homemade taste.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Order Winners and Qualifiers
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
105. A nation’s productivity is NOT directly related to its standard of living.
Ans: False
Solution: Increases in productivity are directly related to increases in a nation’s standard of living.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Productivity and Competitiveness Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 0.5 mins
106. Describe the difference between operational efficiency and strategy.
Ans: Operational efficiency is the ability to perform operations more efficiently than competitors. Strategy, on the other hand, is a plan for competing in the marketplace.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: The Importance of Operations Strategy Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
107. Define “environmental scanning.”
Ans: Environmental scanning is monitoring the external environment for changes and trends in the market, in the economic and political environment, and in society in order to determine business opportunities and threats.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
108. A mission statement answers what three overriding questions?
Ans: (1) What business is the organization in? (2) Who are the customers? (3) How will the company’s core beliefs shape its business?
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Mission Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
109. What are some general technological trends in the marketplace?
Ans: point-of-sale scanners, automation, computer-assisted processing, electronic purchasing, electronic order tracking, and e-commerce
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 3 mins
110. How have U.S. tobacco companies responded to public awareness of the dangers of smoking?
Ans: Many have changed their strategy to focus on customers overseas where smoking is still socially acceptable, or have diversified into other product lines.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
111. Discuss how the operations strategy categories of structure and infrastructure determine the nature of the company’s operations function.
Ans: Structure is the operations decisions related to the design of the production process while infrastructure is operations decisions related to the planning and control systems of the operations. Together they define how the firm will pursue its long range plan.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Translating Competitive Priorities into Production Requirements Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
112. Suggest some core competencies that companies may have.
Ans: Examples may be: highly trained workforce, responsive in meeting customer needs, flexible in performing a variety of tasks, strong technical capability, creative in product design, flexible in producing a variety of products, technologically advanced, an efficient distribution system, skilled in understanding customer wants and predicting market trends, skilled in attracting and raising capital, use of latest production technology, use of information technology, and quality control techniques.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Core Competencies
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
113. What outsourcing activities does Total Logistics Control perform for Meijer?
Ans: TLC is responsible for all deliveries, route scheduling, and all activities involved in maintaining a fleet of trucks, allowing Meijer to focus on its core competencies.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Core Competencies
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
114. At the national level why is it important to measure productivity?
Ans: The economic success of a nation and the quality of life of its citizens are related to the competitiveness in the global marketplace. Increases in productivity are directly related to increases in a nation’s standard of living. Understanding the nation’s productivity helps to define how the nation is performing as a whole.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Productivity and Competitiveness
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
115. Describe how Southwest Airlines competes on cost.
Ans: Facilities are streamlined: only one type of aircraft is used, and flight routes are generally short. This serves to minimize costs of scheduling crew changes, maintenance, inventories of parts, and many administrative costs. Unnecessary costs are completely eliminated: there are no meals, printed boarding passes, or seat assignments.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Competitive Priorities Cost Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 3 mins
116. For what entities can productivity be measured?
Ans: individuals, inputs (e.g., labor, materials, machines, etc.), departments, organizations, industries, or even countries
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge: Time on Task: 3 mins
Problems
117. If a company’s inputs for producing a certain product increase by 10% and the output increases by 25%, what is the percentage productivity increase for that product?
Ans: 13.6%
Solution: New productivity = Output / Input = (1 + 0.25) / (1+0.1) =1.136. This results in a productivity increase of 0.136, or 13.6%.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
118. If a company’s inputs for producing a certain product increase by 50% and the output increases by 90%, what is the percentage productivity increase for that product?
Ans: 26.7%
Solution: New productivity = Output / Input = (1+0.9) / (1+0.5) = 1.267. This results in a productivity increase of 0.267, or 26.7%.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 2 mins
119. The school’s cafeteria has three service lines (pizza, salads, and sandwiches). The pizza line has one server and serves 90 pizzas per hour. The salad line has two servers and they handle 140 customers in 70 minutes. The sandwich line has three servers and they supply 360 sandwiches in 90 minutes. Which service line has the highest hourly productivity?
Ans: Pizza line at 90 pizzas/server/hour
Solution: Productivity = Output / Input
Productivity (Pizza line) = 90 pizzas / hour or 90 / 60 = 1.5 pizzas/server/min
Productivity (Salad line) = 140 / 70 / 2 = 1 salad/server/min
Productivity (Sandwich line) = 360 / 90 / 3 = 1.33 sandwiches/server/min
Pizza line has the highest productivity at 90 pizzas/server/hour
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic
Time on Task: 3 mins
120. A new milling machine can process 2,000 jobs in 8 hours. What is the productivity of the machine?
Ans: 250 jobs/hour
Solution: Machine productivity = 2,000/8 = 250 jobs/hour
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
121. A firm produces 6,000 products using 12 workers on a nine-hour shift. What is the labor productivity per worker?
Ans: 55.6 units/hour
Solution: Labor productivity = 6,000 units / (12 workers * 9 hours) = 55.6 units/hour per worker
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1.5 mins
122. A machine shop produces hangers on two different machines. Machine 1 can produce a hanger every 15 minutes. Machine 2 can produce a hanger every 10 minutes. What is the average productivity per machine?
Ans: 5 units/hour
Solution:
Total hourly outputs from 2 machines = 60/15 + 60/10 = 10 units
Average productivity = Total output in units / 2 machines = 10 /2 = 5 units/hour per machine
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
123. A firm produces shirts using three workers. On Wednesday, Madeline completed 110 shirts in 6 hours, Federico completed 90 shirts in 7 hours, and Susan completed 130 shirts in 9 hours. What was the overall productivity of the firm?
Ans: 15 shirts/hour
Solution: Total outputs = 110 + 90 + 130 = 330 shirts
Total inputs = 6 + 7 + 9 = 22 hours
Total productivity = Total outputs / Total inputs = 330 / 22 = 15 shirts / hour
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
124. A firm produces 1,500 units per day using four workers on a five-hour shift. On average, 12% of the units produced are defective and must be scrapped. What is the labor productivity for nondefective units?
Ans: 66 units/hour
Solution:
Total nondefective units = 1,500 * (1 – 0.12) = 1,320 units. Total input = 4*5 = 20 hours.
Labor productivity = 1,320 units / 20 hours = 66 units / hour.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
125. Last week George mowed 6 lawns in two days. This week he mowed 8 lawns in three days. In which week was George more productive?
Ans: last week
Solution: Productivity = Output / Input. Last week: 6 lawns / 2 days = 3 lawns/day. This week: 8 lawns / 3 days = 2.67 lawns/day. George was more productive last week.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 2 mins
126. During week one, on average, the aircraft cleaning staff was able to totally clean an airplane in 45 minutes using 3 cleaners. During week two the average time to clean an aircraft went to 40 minutes with one of the cleaning staff off sick. Week two productivity changed in which direction and by how much?
Ans: Week two productivity is 20 minutes / staff; productivity decreased
Solution:
Week 1: Average cleaning time per airplane = 45 minutes / 3 staff = 15 minutes / staff. Week 2: Average cleaning time per airplane = 40 minutes / 2 staff = 20 minutes / staff. The percentage change in labor productivity = (20 – 15)/15 = 0.333, or a decrease of 33.3%.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 3 mins
127. A company uses two plants to produce motorcycles. Plant A produces 200 per week using 20 workers and 4 machines. Plant B produces 250 per week using 10 workers and 10 machines.
a) Compute labor productivity ratios for Plant A and Plant B. Which one is more productive?
b) Computer machine productivity ratios for Plant A and Plant B. Which one is more productive?
c) Can the multifactor productivity ratios be computed to determine which plant is more productive? Why or why not?
Ans:
(a) Plant A has a lower labor productivity (10 units/worker) than Plan B (25 units/worker).
(b) Plant A has a higher machine productivity (50 units/machine) than Plant B (25 units/machine).
(c) The overall multifactor productivity ratios cannot be computed because the cost of labor and machines is needed.
Solution:
(a) Labor productivity (A) = 200 / 20 = 10 units/worker per week.
Labor productivity (B) = 250 /10 = 25 units/worker per week.
(b) Machine productivity (A) = 200 / 4 = 50 units/machine per week.
Machine productivity (B) = 250 / 10 = 25 units /machine per week.
(c) Total productivity cannot be computed because costs of labor and machine are unknown.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Interpreting Productivity Measures
Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 5 mins
Fill-in-the-Blank
128. Productivity is computed as a ratio of ____________________.
Ans: outputs to inputs
Solution: Productivity is computed as a ratio of outputs (goods and services) to inputs (e.g., labor and materials).
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 1 min
129. Rapid technological change includes the risk of ________________________.
Ans: obsolescence
Solution: Investing in technology can be costly and entail risks, such as overestimating the benefits of the technology or incurring the risk of obsolescence due to rapid new inventions.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Technology as a Tool for Competitive Advantage
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology Time on Task: 1 min
130. The operations function must place emphasis on those priorities that directly support the __________. Therefore, it needs to make _________ between different priorities.
Ans: Business strategy; trade-offs
Solution: The operations function must place emphasis on those priorities that directly support the business strategy. Therefore, it needs to make trade-offs between the different priorities.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: The Need for Trade-Offs
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
131. ___________ is a measure of how efficiently inputs are being converted into outputs.
Ans: Productivity
Solution: Productivity is a measure of how efficiently inputs are being converted into outputs.
Section Ref: Productivity
Sub Section Ref: Measuring Productivity
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 5: Define productivity and identify productivity measures.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
132. Operations strategy is a long range plan for the design and use of resources in support of
Ans: the business strategy
Solution: Operations Strategy is a long-range plan for the design and use of resources to support the business strategy.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
133. Mass produced standard products were the main manufacturing concern until .
Ans: the 1970s
Solution: Operations strategy did not come to the forefront until the 1970s. Up to that time, U.S. companies emphasized mass production of standard product designs,
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: The Importance of Operations Strategy Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
134. Restaurants that offer pizza to go have different ____________ than those that do not.
Ans: missions
Solution: Restaurants that offer pizza to go have different missions than those that do not. The mission defines the company’s business.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Mission Level: Medium
Bloom’s: Application
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Analytic Time on Task: 1 min
135. __________ technology is used to improve the process of creating goods and services.
Ans: Process
Solution: Process technology is used to improve the process of creating goods and services.
Section Ref: Strategic Role of Technology
Sub Section Ref: Types of Technology Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 4: Explain the strategic role of technology.
AACSB: Technology Time on Task: 1 min
136. Environmental scanning helps organizations recognize ________________________
Ans: opportunities and threats
Solution: Environmental scanning allows a company to identify opportunities and threats.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Environmental Scanning
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
137. By outsourcing noncore activities, firms can concentrate on their
Ans: core competencies
Solution: By outsourcing noncore activities, a company can focus on its core competencies.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Core Competencies
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
138. A business strategy is like an explorer’s ________________________.
Ans: compass
Solution: Without a business strategy, the company would have no overriding plan. Such a plan acts like a compass, pointing the company in the right direction.
Section Ref: Developing a Business Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Putting It Together
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 2: Explain how a business strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
139. Saying that an organization is qualified to be in its market means it has the right .
Ans: order qualifiers
Solution: Order qualifiers are those competitive priorities that a company has to meet if it wants to do business in that particular market.
Section Ref: Developing an Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Order Winners and Qualifiers
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Comprehension
Learning Objective 3: Describe how an operations strategy is developed.
AACSB: Knowledge Time on Task: 1 min
140. _________ develops financial plans to support the business strategy.
Ans: Finance strategy
Solution: Finance strategy develops financial plans to support the business strategy.
Section Ref: The Role of Operations Strategy
Sub Section Ref: Untitled Introduction
Level: Easy
Bloom’s: Knowledge
Learning Objective 1: Explain the role of operations strategy in the organization.
AACSB: Knowledge
Time on Task: 1 min