Macroeconomics, 10e (O'Sullivan/Sheffrin/Perez)
Chapter 1 Introduction: What Is Economics?
1.1 What Is Economics?
1) Economics is best defined as the study of
A) financial decision-making.
B) how consumers make purchasing decisions.
C) the choices made by people faced with scarcity.
D) inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
2) Economics is the study of
A) how to invest in the stock market.
B) how society uses limited resources.
C) the role of money in markets.
D) how government officials decide which goods and services are produced.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
3) Scarcity can best be defined as a situation in which
A) there are no buyers willing to purchase what sellers have produced.
B) there are not enough goods to satisfy all of the buyers' demand.
C) the resources we use to produce goods and services are limited.
D) there is more than enough money to satisfy consumers' wants.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
4) An arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things is called
A) a contract.
B) a market.
C) money.
D) efficient.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
5) Because resources are limited
A) only the very wealthy can get everything they want.
B) firms will be forced out of business.
C) the availability of goods will be limited but the availability of services will not.
D) people must make choices.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
6) A trade-off refers to
A) allowing the government and other organizations to choose for us.
B) sacrificing one thing for another.
C) deciding who consumes the products produced in an economy.
D) holding other variables fixed.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
7) Resources are all of the following EXCEPT
A) unlimited and in abundance.
B) the things we use to produce goods and services.
C) limited in quantity and can be used in different ways.
D) scarce and therefore require choices to be made.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
8) The knowledge and skills acquired by a worker through education and experience is a description of which factor of production?
A) physical capital
B) human capital
C) labor
D) entrepreneurship
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
9) The physical and mental effort people use to produce goods and services is a description of which factor of production?
A) physical capital
B) human capital
C) labor
D) entrepreneurship
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
10) The effort used to coordinate the factors of production is a description of
A) physical capital.
B) human capital.
C) labor.
D) entrepreneurship.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
11) All of the following are considered natural resources EXCEPT
A) a coral reef.
B) gold.
C) labor.
D) a redwood forest.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
12) Normative economics
A) is the focus of most modern economic reasoning.
B) answers the question "What ought to be?"
C) predicts the consequences of alternative actions.
D) answers the question "What is?"
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
13) Which of the following is an example of a normative question?
A) How will an increase in the inheritance tax affect tax revenues?
B) What fraction of an income tax cut will be spent on imported goods?
C) Should Florida implement a state income tax to reduce its deficit?
D) How will an increase in unemployment benefits affect the unemployment rate?
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
14) Which of the following is a question answered with positive economic analysis?
A) Should the college reduce tuition for out-of-state residents?
B) Should the college charge higher tuition for part-time students?
C) If the college increased its eligibility requirements for enrollment, will class sizes decline?
D) Should the college eliminate its athletic program to cut its costs?
Answer: C
Diff: 2
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
15) Which of the following is a question answered with normative economic reasoning?
A) If the college offers free textbooks for students, will more students read their textbooks?
B) If the college provided less financial aid for out-of-state students, would more in-state students benefit?
C) If the college increased its enrollment requirements, would class size decline?
D) Should the college increase tuition to fund its athletic programs?
Answer: D
Diff: 2
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
16) The 3 key economic questions include all of the following EXCEPT
A) "what products do we produce?"
B) "how do we produce these products?"
C) "where should these products be produced?"
D) "who consumes the products?"
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
17) Deciding how a society's products are distributed among its citizens answers the economic question of
A) "who consumes the products produced?"
B) "what products will be produced?"
C) "where will the products be consumed?"
D) "how will the products be produced?"
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
18) Deciding if a company will produce automobiles by robotics or manual labor answers the economic question of
A) "who consumes the products produced?"
B) "what products will be produced?"
C) "where will the products be consumed?"
D) "how will the products be produced?"
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
19) Deciding if a power company will generate electricity from wind power or coal answers the economic question of
A) "who consumes the products produced?"
B) "what products will be produced?"
C) "where will the products be consumed?"
D) "how will the products be produced?"
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
20) An economic model is a
A) realistic version of an economic environment.
B) detailed version of an economic issue.
C) fictional representation of an entire economy.
D) simplified representation of an economic environment.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Economic Models
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
21) Economic models are used to
A) explain every detail of an economic theory.
B) explore decision making by individuals, firms and other organizations.
C) build physical renditions of government construction projects.
D) represent the complexities of economic environments.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Economic Models
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
22) Talking about alternatives is the first step in a process that helps us make better choices about how we use our resources.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
23) In the past few centuries, choices have led to a substantial decline in the standards of living around the globe.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
24) Scarcity is a situation in which resources are unlimited in quantity and can be used in different ways.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
25) Positive economics answers the question, "What ought to be?" Normative economics predicts the consequences of alternative actions, answering the questions, "What is?" or "What will be?"
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
26) Normative economics answers the question, "What ought to be?" Positive economics predicts the consequences of alternative actions, answering the questions, "What is?" or "What will be?"
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
27) Most modern economic analysis is normative in nature, but involves questions with positive aspects.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
28) Economists will always reach the same conclusion in their positive analyses. Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
29) One of the key economic questions is "where should products be produced?"
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
30) One of the key economic questions is "who consumes the products?"
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who? Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
31) An economic model is a detailed version of an economic environment.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who?
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
32) Economic models explore decision making by individuals, firms and other organizations. Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
33) Would an economist consider clean air a scarce resource? Explain.
Answer: Yes, because the air has alternative uses. We can choose to use it to either breathe or to undertake activities that pollute it. The more we want to breathe clean air the more we must limit the production of pollutants. The more we pollute the air the less we can breathe clean air.
Diff: 2
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
34) List and briefly describe the five factors of production.
Answer: Natural resources those resources provided by nature. Labor the physical and mental effort used by people to produce goods and services. Physical capital the infrastructure, equipment, machines and structures used to produce goods and services. Human capital the knowledge and skills obtained by workers through education and experience. Entrepreneurship the organizing and coordination of the other four factors of production needed to produce and sell products.
Diff: 2
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
35) Give an example of something that is scarce in your life and explain the choices you've made because of scarcity.
Answer: Responses are numerous and will vary by students.
Diff: 1
Topic: What Is Economics?
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
36) Positive economic analysis answers what question?
Answer: Positive economic analysis answers the question "what is" or "what will be."
Diff: 1
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
37) Normative economic analysis answers what question?
Answer: Normative economic analysis answers the question "what ought to be."
Diff: 1
Topic: Positive versus Normative Analysis
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
38) Richard runs a pizza delivery restaurant. List the three basic types of decisions studied in economics and give an example from Richard's restaurant.
Answer: How to produce? With what resources will the pizzas be produced? What to produce? What sorts of pizza do people order? Who consumes the products? Which people decided to come to the restaurant on a given day?
Diff: 2
Topic: The Three Key Economic Questions: What, How, and Who?
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
1.2 Economic Analysis and Modern Problems
1) According to the Texas Transportation Institute, the typical U.S. commuter wastes approximately how much time per year due to traffic congestion?
A) 47 hours
B) 22 hours
C) 42 hours
D) 96 hours
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Economic View of Traffic Congestion
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
2) In the U.S., which of the following government programs assist workers find jobs when they lose their jobs due to trade?
A) Trade Adjustment Assistance program
B) Social Security
C) workers' compensation
D) Obamacare
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Trade-offs from International Trade
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
3) When Canada buys lemons from Mexico instead of growing lemons in heated greenhouses
A) Canadian consumers will gain because lemon prices will drop.
B) Canadian lemon producers will gain because lemon prices will drop.
C) Canadian consumers will gain because lemon prices will rise.
D) Mexican lemon producers will lose because lemon prices in Canada will rise.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Trade-offs from International Trade
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-3: Discuss different types of market systems and the gains that can be made from trade
4) When countries trade with each other, does it result in a gain for everybody?
A) No. Producers of a good that is imported would be hurt.
B) No. Consumers of a good that is imported would be hurt.
C) No. Producers of a good that is exported would be hurt.
D) Yes. All producers and consumers from both exporting and importing countries will gain.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Trade-offs from International Trade
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-3: Discuss different types of market systems and the gains that can be made from trade
5) The financial crisis and recession which began in 2007
A) impacted only high-income countries.
B) did not impact the United States.
C) impacted many countries in the world.
D) impacted only low-income countries.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Economic View of the Managing the U.S. Economy
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
6) To combat the financial crisis and recession which began in 2007, governments worldwide made it
A) easier for firms and households to borrow money for investment and consumer goods.
B) easier for other countries to borrow money for infrastructure projects.
C) easier for firms to pay their taxes by providing a tax amnesty.
D) easier for workers to purchase health insurance through their employers.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Economic View of the Managing the U.S. Economy
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-12: Explain how monetary policy influences interest rates, aggregate demand, real GDP and inflation
7) Congestion taxes tend to cause an increase in traffic volume during rush hours.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Economic View of Traffic Congestion
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
8) Economic expansion and growth are the only objectives that U.S. policymakers consider when they implement tax, spending and financial policies that affect the U.S. economy.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Economic View of the Managing the U.S. Economy
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
1.3 The Economic Way of Thinking
1) Who is associated with the following summary of the economic way of thinking: "The theory of economics does not furnish a body of settled conclusions immediately acceptable to policy. It is a method rather than a doctrine, an apparatus of the mind, a technique of thinking which helps its processer draw correct conclusions."
A) John Maynard Keynes
B) Alfred Marshall
C) Adam Smith
D) President Harry Truman
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: The Economic Way of Thinking
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
2) To make things simpler and focus attention on what really matters, economists
A) use assumptions.
B) ignore all variables.
C) think at the margin.
D) respond to incentives.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Use Assumptions to Simplify
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
3) A variable measures
A) something that always has the same value.
B) something that can take on different values.
C) factors that occur with high degrees of uncertainty.
D) the degree to which something varies over time.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Isolate Variables - Ceteris Paribus
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
4) The Latin phrase ceteris paribus means that when a relationship between two variables is being studied
A) both are treated as unpredictable.
B) neither of those two variables is allowed to change.
C) all other variables are held fixed.
D) we recognize that some factors are unknown.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Isolate Variables - Ceteris Paribus
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
5) To think at the margin means to consider
A) how nothing remains constant over time.
B) how a small change in one variable affects another variable.
C) how people behave in their own self-interest.
D) how people will decide what to purchase.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Think at the Margin
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-20: Apply the concepts of opportunity cost, marginal analysis, and present value to make decisions
6) Jerome has a "C" average in his philosophy course and a "B" average in his economics course. He decides to study an extra hour for his philosophy exam. This is an example of
A) thinking at the margin.
B) using assumptions to simplify.
C) ceteris paribus.
D) caveat emptor.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Think at the Margin
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
7) A small change in a variable is
A) an average change.
B) a ceteris paribus change.
C) an efficient change.
D) a marginal change.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Think at the Margin
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-20: Apply the concepts of opportunity cost, marginal analysis, and present value to make decisions
8) Adam Smith
A) is considered the founder of economics.
B) introduced the concept of ceteris paribus to the discussion of supply and demand.
C) is responsible for refining the model of supply and demand.
D) is the author of this text.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Rational People Respond to Incentives
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
9) When economists assume that people are rational and respond to incentives, they mean
A) people act with kindness.
B) people are altruistic.
C) people act in their own self-interest.
D) people are selfish.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Rational People Respond to Incentives
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
10) When deciding to implement a congestion tax, economists and the government would use the elements of the economic way of thinking to primarily determine
A) if the tax would be allocated equitably.
B) what congestion tax amount should be charged.
C) who should be exempt from the tax.
D) where to spend the revenue generated.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Example: Southern California addresses its Congestion Problem
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
11) The book cites a result where after of the implementation of the congestion tax in Stockholm, Sweden of $1.50-$3.00, traffic volume was reduced and travel time for cars and buses was cut in half. This is an example of
A) responding to incentives.
B) the role of pricing in allocating resources.
C) caveat emptor
D) comparative advantage.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Example: Southern California addresses its Congestion Problem
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
12) To reduce traffic congestion, the Southern California Council of Governments (SCAG) advocate the implementation of
A) a congestion tax.
B) a gas tax
C) a bus subsidy
D) a car sales tax.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Example: Southern California addresses its Congestion Problem
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
Recall the Application about the incentives to install rooftop solar panels to answer the following question(s).
13) According to the Application, a 10 percent increase in the tax credits for solar panels results in an increase in the number of households that install solar panels by 7.6 percent. The increase in sales due to this subsidy is an example of which element of the economic way of thinking?
A) responding to incentives
B) isolating variables
C) thinking at the margin
D) using assumptions to simplify
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Application 1, Incentives to Install Rooftop Solar Panels
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
14) According to the Application, another factor that was responsible for solar power deployment was the rising price of electricity. The increase in sales due to higher electricity prices describes the economic concept of
A) using assumptions to simplify.
B) ceteris paribus.
C) rational self interest.
D) marginal thinking.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Application 1, Incentives to Install Rooftop Solar Panels
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
15) According to the Application, the value of the federal tax credits equaled 30 percent of solar panel installation costs. If you purchase a rooftop solar panel for $20,000, then on the year you installed your solar panels, you should expect a decrease in your liabilities to the federal taxes by
A) $6,000.
B) $12,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $1,500.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Application 1, Incentives to Install Rooftop Solar Panels
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
Recall the Application about housing prices in Cuba to answer the following question(s).
16) According to the Application, in 1960 the Cuban government
A) confiscated most housing in the country.
B) did not allow people to sell or rent their homes.
C) caused a large shortage of housing as a result of its policies.
D) all of the above.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Application 2, Housing Prices in Cuba
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
17) Recent housing reforms in Cuba should give homeowners ________ incentives to repair their homes and therefore ________ construction of new homes.
A) more; decrease
B) more; increase
C) fewer; decrease
D) fewer; increase
Answer: B
Diff: 2
Topic: Application 2, Housing Prices in Cuba
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
18) Using assumptions to make things simpler and focus attention on what really matters is like using a road map to plan a trip.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Use Assumptions to Simplify
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
19) Ceteris paribus means "Let the buyer beware."
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Isolate Variables - Ceteris Paribus
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
20) Ceteris paribus is the same as rise / run.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Isolate Variables - Ceteris Paribus
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
21) A small, one-unit change in value is called a marginal change.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Think at the Margin
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-20: Apply the concepts of opportunity cost, marginal analysis, and present value to make decisions
22) A key assumption of most economic analysis is that people act rationally, meaning they respond to incentives.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Rational People Respond to Incentives
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
23) A key assumption of most economic analysis is that people are altruistic, meaning that they act in their own self-interest.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Rational People Respond to Incentives
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
24) Economists assume that individuals make informed decisions and act in their own selfinterest.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Rational People Respond to Incentives
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
25) The congestion tax implemented in Stockholm reduced traffic volume and cut travel time for cars and buses by 20%.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Example: Southern California addresses its Congestion Problem
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
26) To determine an appropriate congestion tax, an economist has to assume that people respond to incentives.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Example: Southern California addresses its Congestion Problem
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
Recall the Application about housing prices in Cuba to answer the following question(s).
27) According to the Application, recent reforms in Cuba have relied less on the free market in determining prices in the housing market.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Application 2, Housing Prices in Cuba
Skill: Fact
AACSB: Reflective Thinking Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
28) What is meant by the term "marginal change"?
Answer: A marginal change is a small, one unit change in value.
Diff: 1
Topic: Think at the Margin
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking Learning Outcome: Micro-20: Apply the concepts of opportunity cost, marginal analysis, and present value to make decisions
1.4 Employability: Economic Logic on the Job
1) Which of the following occupations would a major in economics be useful for?
A) management-analyst
B) real estate appraiser
C) financial analyst
D) all of the above are correct.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Employability: Economic Logic on the Job
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
2) Which of the following occupations would use economic analyses in their real world jobs?
A) store manager
B) teacher
C) environmental regulator
D) all of the above are correct.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Employability: Economic Logic on the Job
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
3) Which of the following skills would the study of economics help promote?
A) problem solving
B) memorization
C) critical thinking
D) A and C only.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Employability: Economic Logic on the Job
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
4) Which of the following occupations would a major in economics be least useful for?
A) management-analyst
B) real estate appraiser
C) financial analyst
D) medical doctor
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Employability: Economic Logic on the Job
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
5) Why does economics fit well as a liberal arts education?
Answer: A liberal arts education provides broad knowledge and thinking skills, so a worker is more flexible in responding to changes in the workplace. Economics fits naturally into the liberal arts because it provides a framework for problem-solving that can be applied everywhere, from making a personal decision about where to live, to a national decision about when to stimulate the economy with a tax cut, to a global decision about how to respond to climate change.
Diff: 1
Topic: Employability: Economic Logic on the Job
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
1.5 Preview of Coming Attractions: Macroeconomics
1) Macroeconomics is best described as the study of
A) very large issues.
B) the choices made by individual households, firms, and governments.
C) the nation's economy as a whole.
D) the relationship between inflation and wage inequality.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Macroeconomics
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
2) Which of the following is a macroeconomic question?
A) Should we have a constitutional amendment requiring the government to implement a national consumption tax to replace the current income tax?
B) Why did a leading computer manufacturer establish call centers in India?
C) Why does a pharmaceutical manufacturer try to lower its production costs?
D) Should the government put a tax on alcohol in an attempt to assist in the funding of support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous?
Answer: A
Diff: 2
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Macroeconomics
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
3) Which of the following is NOT a macroeconomic question?
A) Should we have a constitutional amendment requiring the federal government to balance the budget each year?
B) Should restaurants be required to list the number of calories for each product on their menus?
C) How does a fiscal stimulus package affect gross domestic product?
D) Should Congress enact tougher immigration laws to reduce unemployment?
Answer: B
Diff: 2
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Macroeconomics
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
4) We can use macroeconomic analysis to
A) learn how to balance a checkbook.
B) study the choices made by households.
C) understand marginal changes in the macroeconomy.
D) understand why economies grow.
Answer: D
Diff: 2
Topic: Using Macroeconomics to Understand Why Economies Grow
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
5) Macroeconomics involves the study of the decision-making of individual firms or individuals.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Macroeconomics
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
6) Macroeconomics helps explain economic fluctuations, why the economy shrinks and expands and why some of the economy's resources are idle.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Using Macroeconomics to Understand Economic Fluctuations
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
7) Define the field of economics known as macroeconomics.
Answer: Macroeconomics is the study of the nation's economy as a whole. Macroeconomics focuses on the issues of inflation, unemployment and economic growth.
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Macroeconomics
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
8) Identify and explain the three ways we can use macroeconomic analysis.
Answer: Macroeconomics explains why some resources increase over time and how an increase in these resources translates into a higher standard of living. In the fastest-growing countries, citizens save a large fraction of the money they earn. Firms can then borrow the funds saved to purchase machinery and equipment that make their workers more productive. The fastest growing countries also have well-educated workforces, allowing firms to quickly adopt new technologies that increase worker productivity. All economies, including ones that experience a general trend of growth, are subject to economic fluctuations including periods when the economy shrinks. During an economic downturn, some of the economy's resources are idle. Many workers are unemployed, and many factories and stores are closed. By contrast, sometimes the economy grows too rapidly, causing inflation. Macroeconomics helps us understand why these fluctuations occur, why the economy sometimes cools and sometimes overheats and what we can do to moderate the fluctuations. A third reason for studying macroeconomics is to make informed business decisions. A manager who intends to borrow money for a new factory or store could use her knowledge of macroeconomics to predict the effects of current public policies on interest rates and then decide whether to borrow the money now or later.
Diff: 2
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Macroeconomics
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Macro-1: Define macroeconomics and identify its basic concerns
1.6 Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
1) The study of the choices made by individual households, firms, and government is called A) macroeconomics.
B) microeconomics.
C) managerial economics.
D) market economics.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
2) Microeconomics is best described as the study of
A) the choices made by individual households, firms, and governments.
B) inflation, unemployment, gross national product, and the nation's economy as a whole.
C) how markets interact in the aggregate economy.
D) marginal changes in the economy.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
3) Which of the following is a microeconomic question?
A) Should companies pay for employees' health insurance?
B) Why do some countries have higher economic growth rates than other countries?
C) Should Congress and the president take action to reduce the unemployment rate?
D) Should the Fed attempt to influence the interest rate to control potential inflation?
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Using Microeconomics to Evaluate Public Policies
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
4) Which of the following is a microeconomic question?
A) Should the government decrease unemployment benefits to reduce the unemployment rate?
B) Why do some countries have higher inflation rates than other countries?
C) Should the government subsidize corn farmers to encourage the production of ethanol?
D) Should congress decrease taxes to help stimulate the economy?
Answer: C
Diff: 2
Topic: Using Microeconomics to Evaluate Public Policies
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
5) Microeconomics helps explain economic fluctuations, why the economy shrinks and expands and why some of the economy's resources are idle.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
6) Microeconomics is the study of aggregate behavior in the economy.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
7) One example of a microeconomic question is, "How will prices in the clothing industry change if the government bans imports from China?"
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
8) One example of a microeconomic question is, "Should unemployment benefits be increased?"
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
9) Describe the field of economics known as microeconomics.
Answer: Microeconomics is the study of the choices made by individual households, firms and government and how these choices affect the markets for goods and services.
Diff: 1
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
10) Identify and explain the three ways we can use microeconomic analysis.
Answer: 1. To understand markets and predict changes: One reason for studying microeconomics is to better understand how markets work. Once you know how markets operate, you can use economic analysis to predict how various events affect product prices and quantities.
2. To make personal and managerial decisions: On the personal level, we use economic analysis to decide how to spend our time, what career to pursue, and how to spend and save the money we earn. As workers, we use economic analysis to decide how to produce goods and services, how much to produce, and how much to charge for them.
3. To evaluate public policies: While societies use markets to make the most of decisions concerning production and consumption, the government has several important roles in a marketbased society. We can use economic analysis to determine how well the government performs its roles in the market economy. We can also explore the trade-offs associated with various public policies.
Diff: 2
Topic: Preview of Coming Attractions: Microeconomics
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-1: Identify the basic principles of economics and explain how to think like an economist
1.7 Appendix: Using Graphs and Percentages
1) There is a positive relationship between two variables if
A) they move in opposite directions.
B) they move in the same direction.
C) one variable changes and the other does not.
D) neither variable moves.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Two Variables
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
2) There is a negative relationship between two variables if A) they move in opposite directions.
B) they move in the same direction.
C) one variable changes and the other does not.
D) neither variable moves.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Two Variables
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
3) The slope of a curve measures
A) the change in the vertical variable in response to the change in the horizontal variable.
B) the length of the curve.
C) only the change in the horizontal variable.
D) only the change in the vertical variable.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
4) Slope is calculated as the
A) change in the vertical variable divided by the change in the horizontal variable.
B) change in the horizontal variable divided by the change in the vertical variable.
C) the vertical axis divided by the horizontal axis.
D) change in the vertical variable.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
5) The slope of a straight line
A) is constant.
B) is negative.
C) is zero.
D) changes along the curve.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
6) If the variable on the vertical axis increases by 20 and the variable on the horizontal axis increases by 5, the slope of the line is
A) 0.25.
B) 4.
C) 15.
D) 100.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
7) If the variable on the vertical axis increases by 24 and the variable on the horizontal axis decreases by 3, the slope of the line is A) -24.
B) -8.
C) 3.
D) 72.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
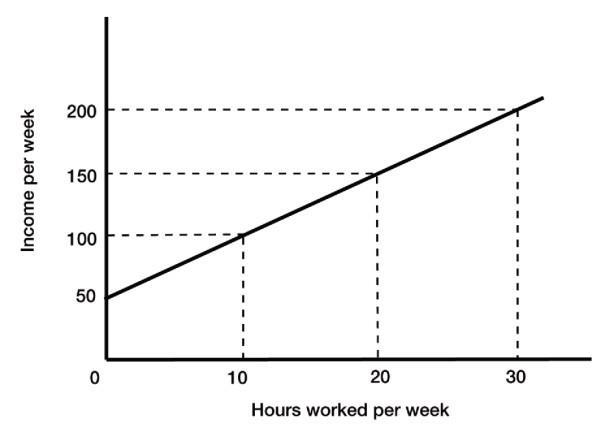
8) Refer to Figure 1A.1. If the hours worked per week are 20, the income per week is A) 50. B) 100.
C) 150.
D) 200. Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Two Variables, graphing
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
9) Refer to Figure 1A.1. If the hours worked per week are 30, the income per week is A) 50. B) 100.
C) 150.
D) 200. Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Two Variables, graphing
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
Figure 1A.1
10) Refer to Figure 1A.1. The slope of the line between the points where income equals 50 and income equals 200 is A) 0.2.
B) 5.
C) 10.
D) 50. Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope, graphing
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
11) Refer to Figure 1A.1. The slope of the line between the points where hours worked per week are 20 and hours worked per week are 30 is A) 0.2.
B) 5.
C) 10.
D) 50. Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope, graphing
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
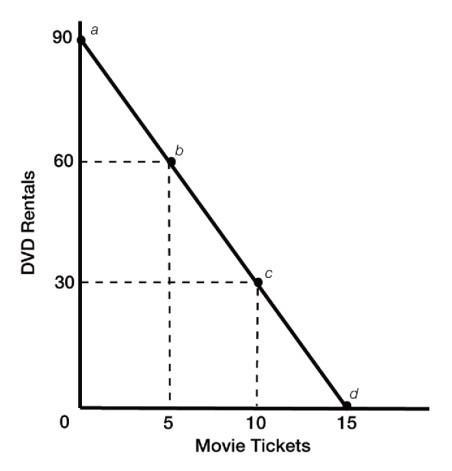
1A.2
12) Refer to Figure 1A.2. If this consumer rents zero DVDs, how many movie tickets will she purchase?
A) 0
B) 5
C) 10
D) 15
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Negative Relationships, graphing
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
13) Refer to Figure 1A.2. If this consumer rents 60 DVDs, how many movie tickets will she purchase?
A) 0
B) 5
C) 10
D) 15
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Negative Relationships, graphing
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
Figure
14) Refer to Figure 1A.2. The slope of the curve
A) is negative.
B) is positive.
C) is zero.
D) changes along the curve.
Answer: A
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope, graphing
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
15) Refer to Figure 1A.2. The slope between points a and c is
A) -5.
B) -6.
C) 10.
D) 30.
Answer: B
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope, graphing
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
16) The slope of a nonlinear curve
A) is constant.
B) is negative.
C) is zero.
D) changes along the curve.
Answer: D
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Nonlinear Relationships
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
17) If the price of monthly satellite TV service increases from $40 to $50, the percentage change is
A) 5 percent.
B) 20 percent.
C) 25 percent.
D) 45 percent.
Answer: C
Diff: 2
Topic: Computing Percentage Changes
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
18) If the price of monthly satellite TV service increases from $50 to $60, the percentage change (using the average value (or the midpoint ) is
A) 18.2%
B) 16.7%
C) 10%
D) 60%
Answer: A
Diff: 2
Topic: Computing Percentage Changes
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
19) If the price of a 32GB memory card decreases from $25 to $20, the percentage change is A) -20 percent.
B) -33 percent.
C) -50 percent.
D) -60 percent.
Answer: A
Diff: 2
Topic: Computing Percentage Changes
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
20) If the price of a 32GB memory card decreases from $25 to $20, the percentage change using the average value (or the midpoint) is
A) -22.2%
B) -20 percent.
C) -25%
D) -5%
Answer: A
Diff: 2
Topic: Computing Percentage Changes
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
Recall the Application about the government of Mexico City repainting highway lane lines to transform a 4-lane highway into a 6-lane highway to answer the following question(s).
21) When the government converted the highway from 4 lanes into 6 lanes, they claimed the capacity had increased by 50 percent. When the government switched the highway back from 6 lanes to 4 lanes, they claimed the capacity had been decreased by 33 percent. Had the government used the midpoint method, the percentage increase would have been ________ percent and the percentage decrease would have been ________ percent.
A) 33; 50
B) 33; 33
C) 40; 40
D) 50; 50
Answer: C
Diff: 2
Topic: Application 3, The Perils of Percentages
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-5: List ways in which governments intervene in markets and explain the consequences of such intervention
22) When computing percentage changes, using the simple approach results in increases and decreases which are
A) identical.
B) symmetric.
C) not symmetric.
D) more accurate than using the midpoint method.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Topic: Application 3, The Perils of Percentages
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
23) If you work 4 extra hours, and the slope of the curve showing the relationship between your income and work hours is 8, your income will increase by
A) $2.
B) $4.
C) $12.
D) $32.
Answer: D
Diff: 2
Topic: Using Equations to Compute Missing Values
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
24) To increase income by $120 when the slope of the curve showing the relationship between your income and work hours is 8, how many extra hours will you need to work?
A) 8
B) 15
C) 112
D) 960
Answer: B
Diff: 2
Topic: Using Equations to Compute Missing Values
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
25) Suppose you find that by studying one extra hour for your exam, you can increase your score by 4 points. How many hours of studying do you need it you want to increase your score from 60 to 80 points (assuming that the relationship is linear)?
A) 5 hours
B) 6 hours
C) 20 hours
D) 80 hours
Answer: A
Diff: 2
Topic: Using Equations to Compute Missing Values
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
26) The origin of a graph is the intersection of the two axes, where the value of both variables is zero.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Two Variables
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
27) Positive relationships are also referred to as inverse relationships.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Two Variables
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
28) Negative relationships are also referred to as inverse relationships.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Two Variables
Skill: Definition
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
29) Slope is calculated as rise / run.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
30) Slope is calculated as a change in the variable on the horizontal axis divided by a change in the variable on the vertical axis.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1
Topic: Computing the Slope
Skill: Analytical
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs
31) The relationship between the number of hours you study and your economics score is linear. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1
Topic: Graphing Nonlinear Relationships
Skill: Conceptual
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Learning Outcome: Micro-2: Interpret and analyze information presented in different types of graphs