Macroeconomics, 4Ce (Hubbard)
Chapter 1 Economics: Foundations and Models
1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, and optimal decisions are made at the margin
1) Changes in global weather patterns can lead to
A) more Canadians drinking coffee.
B) Canadians having to pay more for coffee.
C) wage increases for coffee shop employees.
D) the destruction of the Canadian coffee harvest.
E) Canadians demanding more coffee.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Scarcity
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Chapter Opener: You versus Caffeine?
2) The study of economics arises due to A) money.
B) scarcity.
C) greed.
D) unlimited resources.
E) unemployment.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Scarcity
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
3) Scarcity refers to the situation in which A) unlimited wants exceed limited resources.
B) unlimited resources exceed limited wants.
C) a country's population is larger than its resource base.
D) a nation's poverty level increases faster than its population.
E) our needs and wants are finite.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Scarcity
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
4) The basic economic problem of ________ has always existed and will continue to exist.
A) scarcity
B) efficiency
C) inflation
D) recession
E) unemployment
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Scarcity
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
5) Economics is the study of the ________ people make to attain their goals, given their ________ resources.
A) purchases; unlimited
B) choices; scarce
C) income; available
D) decisions; household
E) output; time
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Scarcity
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
6) An economic ________ is a simplified version of some aspect of economic life used to analyze an economic issue.
A) market
B) trade-off
C) variable
D) model
E) opportunity cost
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Economic Models
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
7) The term "market" in economics refers to
A) a place where money changes hands between institutions and the arrangements they make.
B) a legal institution where exchange can take place between a group of buyers and sellers.
C) a group of buyers and sellers and the arrangement by which they come together to trade.
D) an organization which sells goods and services to a group of buyers who make decisions at the margin.
E) a place where stocks are traded between a group of international buyers and sellers.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Markets
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
8) The term ________ in economics refers to a group of buyers and sellers of a product and the arrangement by which they come together to trade.
A) collective
B) cooperative
C) market
D) trade-off
E) monopoly
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Markets
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
9) Economists assume that
A) individuals behave in unpredictable ways.
B) consumer behaviour is explained by the existence of unlimited resources.
C) people put other people's interests ahead of their own.
D) optimal decisions are made at the margin.
E) society's output should be equally distributed.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
10) Economists assume that rational behaviour is useful in explaining choices people make
A) because irrational people do not make economic choices.
B) even though people may not behave rationally all the time.
C) because individuals act rationally all the time in all circumstances.
D) even though people rarely, if ever, behave in a rational manner.
E) because economic choices are not needed by rational people.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: People Are Rational
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
11) Economists assume that rational people do all of the following except A) use all available information as they act to achieve their goals.
B) undertake activities that benefit others and hurt themselves.
C) weigh the benefits and costs of all possible alternative actions.
D) respond to economic incentives.
E) do things to make themselves better off.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: People Are Rational
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
12) Economics does not study correct or incorrect behaviours but rather it assumes that economic agents behave ________, meaning they make the best decisions given their knowledge of the costs and benefits.
A) equitably
B) rationally
C) emotionally
D) selfishly
E) erratically
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: People Are Rational
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
13) Consider the following statements:
a. Car owners purchase more gasoline from a gas station that sells gasoline at a lower price than other rival gas stations in the area.
b. Banks do not take steps to increase security since they believe it is less costly to allow some bank robberies than to install expensive security monitoring equipment.
c. Firms produce more of a particular DVD when its selling price rises.
Which of the above statements demonstrates that economic agents respond to incentives?
A) a only.
B) b only.
C) c only.
D) a and b.
E) a, b, and c.
Answer: E
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: People Respond to Incentives
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
14) As professors and teachers get closer to retirement age they typically spend more time reading and thinking about the financial planning as well as the stock market. By gathering and using all available information as they act to achieve their goals, these teachers are exemplifying the economic idea that
A) people are rational.
B) people respond to economic incentives.
C) optimal decisions are made at the margin.
D) equity is more important than efficiency.
E) people make identical choices.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: People Are Rational
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
15) Suppose your provincial government encouraged new medical school graduates to take over rural and small town practices from doctors wishing to retire by paying both the new and retiring doctors
$100,000. These doctors would be exemplifying the economic idea that
A) people are rational.
B) people respond to economic incentives.
C) optimal decisions are made at the margin.
D) equity is more important than efficiency.
E) people make identical choices.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: People Respond to Incentives
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
16) Obesity is one of the biggest health challenges facing Canadians, with few Canadians getting the recommended amount of daily physical activity. Economists would expect
A) people who value physical appearance to exercise less than others.
B) people will exercise more when the cost of skipping exercise increases.
C) people who agree to pay a fine for skipping exercise sessions will be less healthy.
D) there is no correlation between fines for skipping exercise and how often people will go to the gym.
E) the cost of gym memberships will decrease as people join gyms and demand increases.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: People Respond to Incentives
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Apply the Concept: Does Canada's Health Care System Contribute to Obesity?
17) By charging users that skip workouts, the designers of a gym are
A) increasing the marginal cost of exercise.
B) increasing the marginal benefit of exercise.
C) increasing both the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of exercise.
D) decreasing the marginal cost and the marginal benefit of exercise.
E) assuming gym members are rational.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: People Respond to Incentives
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Apply the Concept: Does Canada's Health Care System Contribute to Obesity?
18) In economics, the term ________ means "additional" or "extra."
A) allocative
B) marginal
C) equity
D) optimal
E) absolute
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
19) A grocery store sells a bag of potatoes at a fixed price of $5.50. Which of the following is a term used by economists to describe the money received from the sale of an additional bag of potatoes?
A) marginal revenue
B) gross earnings
C) pure profit
D) marginal costs
E) net benefit
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
20) Economists reason that the optimal decision is to continue any activity up to the point where the
A) marginal benefit is zero.
B) marginal benefit is greater than the marginal cost.
C) marginal cost is zero.
D) marginal benefit equals the marginal cost.
E) marginal benefit starts declining.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
21) Marginal analysis involves undertaking an activity
A) until its marginal costs start declining.
B) only when its marginal benefits are positive.
C) until its marginal benefits equal marginal costs.
D) only if its marginal costs are greater than its marginal benefits.
E) until its marginal cost is zero.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
22) The revenue received from the sale of ________ of a product is a marginal benefit to the firm.
A) an additional unit
B) the total number of units
C) no units
D) only profitable units
E) all the units
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
23) Making optimal decisions "at the margin" requires
A) making decisions according to one's whims and fancies.
B) making consistently irrational decisions.
C) weighing the costs and benefits of a decision.
D) making borderline decisions.
E) advanced knowledge of economics.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
24) Making "how much" decisions involves
A) calculating the total benefits of the activity and determining if you are satisfied with that amount.
B) calculating the total costs of the activity and determining if you can afford to incur that expenditure.
C) calculating the average benefit and the average cost of an activity to determine if it is worthwhile undertaking that activity.
D) determining the additional benefits and the additional costs of that activity.
E) advanced knowledge of economics and product markets.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
25) The extra cost associated with undertaking an activity is called
A) net loss.
B) marginal cost.
C) opportunity cost.
D) foregone cost.
E) activity cost.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
26) DeShawn's Detailing is a service that details cars at the customers' homes or places of work.
DeShawn's cost for a basic detailing package is $40, and he charges $75 for this service. For a total price of $90, DeShawn will also detail the car's engine, a service that adds an additional $20 to the total cost of the package. What is DeShawn's marginal benefit if he sells a basic detailing package?
A) $35
B) $75
C) zero dollars
D) He makes a marginal loss of $15.
E) The marginal benefit cannot be determined.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
27) DeShawn's Detailing is a service that details cars at the customers' homes or places of work.
DeShawn's cost for a basic detailing package is $40, and he charges $75 for this service. For a total price of $90, DeShawn will also detail the car's engine, a service that adds an additional $20 to the total cost of the package. What is the marginal cost of adding the engine detailing to the basic detailing package?
A) $20
B) $30
C) $60
D) $60 plus the value of his time
E) $0
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
28) DeShawn's Detailing is a service that details cars at the customers' homes or places of work.
DeShawn's cost for a basic detailing package is $40, and he charges $75 for this service. For a total price of $90, DeShawn will also detail the car's engine, a service that adds an additional $20 to the total cost of the package. Should DeShawn continue to offer the engine detailing service?
A) Yes, he still makes a profit by selling the engine detailing service with the basic detailing package.
B) Yes, but only if he raises the price of the basic detailing package.
C) Yes, because he will increase sales of the basic detailing package.
D) No, his marginal benefit is less than his marginal cost.
E) More information is needed for DeShawn to make this decision.
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
Scenario 1.1
Suppose a cell phone manufacturer currently sells 20,000 cell phones per week and makes a profit of $5,000 per week. A manager at the plant observes, "Although the last 3,000 cell phones we produced and sold increased our revenue by $6,000 and our costs by $6,700, we are still making an overall profit of $5,000 per week so I think we're on the right track. We are producing the optimal number of cell phones."
29) Refer to Scenario 1.1. Using marginal analysis terminology, what is another economic term for the incremental revenue received from the sale of the last 3,000 cell phones?
A) gross earnings
B) marginal revenue
C) sales revenue
D) explicit revenue
E) net benefit
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
30) Refer to Scenario 1.1. Using marginal analysis terminology, what is another economic term for the incremental cost of producing the last 3,000 cell phones?
A) a marginal cost.
B) an opportunity cost
C) an explicit cost
D) a foregone cost
E) a loss
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
31) Refer to Scenario 1.1. Had the firm not produced and sold the last 3,000 cell phones, would its profit be higher or lower, and if so by how much?
A) Its profit will be $6,700 higher.
B) Its profit will be $700 higher.
C) Its profit will be $700 lower.
D) Its profit will be $6,000 lower.
E) Its profit will be unchanged.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
Lydia runs a small nail salon in the town of New Hope. She is debating whether she should extend her hours of operation. Lydia figures that her sales revenue will depend on the number of hours the nail salon is open as shown in the table above. She would have to hire a worker for those hours at a wage rate of $10 per hour.
32) Refer to Table 1.1. Using marginal analysis, how many hours should Lydia extend her nail salon's hours of operations?
A) 2 hours
B) 3 hours
C) 4 hours
D) 5 hours
E) 6 hours
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
33) Refer to Table 1.1. What is Lydia's marginal benefit if she decides to stay open for two hours instead of one hour?
A) $25
B) $50
C) $75
D) $125
E) $150
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
34) Refer to Table 1.1. What is Lydia's marginal cost if she decides to stay open for two hours instead of one hour?
A) $10
B) $20
C) $25
D) $40
E) $50
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
35) Soo Jin shares a one-bedroom apartment with her classmate. Her share of the rent is $700 per month. She is considering moving to a studio apartment which she will not have to share with anyone. The studio apartment rents for $950 per month. Recently, you ran into Soo Jin on campus and she tells you that she has moved into the studio apartment. Soo Jin is as rational as any other person. As an economics major, you rightly conclude that
A) Soo Jin did not have a choice; her roommate was a slob.
B) Soo Jin figures that the additional benefit of having her own place (as opposed to sharing) is at least $250.
C) Soo Jin figures that the benefit of having her own place (as opposed to sharing) is at least $950.
D) the cost of having one's own space outweighs the benefits.
E) you made an error in assuming that Soo Jin is rational.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
36) McCain Foods Ltd. is one of the largest producer s of frozen French fries in the world. If the marginal cost of producing an extra million kilograms of French fries is $1 million, then McCain Foods Ltd. should produce the extra French fries
A) only if the marginal benefit is greater than $1 million plus an acceptable profit margin.
B) as long as the marginal benefit the firm receives is just equal to or greater than $1 million.
C) as long as the marginal cost does not rise.
D) until the marginal benefit the firm receives reaches zero.
E) More information is needed for McCain Foods to make this decision.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Solved Problem: Binge Watching and Decisions at the Margin.
37) The approximately 12 seconds between episodes on Netflix means that binge watching is
A) the result of a series of marginal decisions.
B) something every one plans to when they first login to Netflix.
C) something Netflix forces viewers to do.
D) an indication of how quickly Netflix users can make decisions.
E) a rational decision.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Solved Problem: Binge Watching and Decisions at the Margin.
38) Scarcity refers to a situation in which unlimited wants exceed the limited resources available to fulfill those wants.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Scarcity
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
39) Scarcity is a problem that will eventually disappear as technology advances.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Scarcity
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
40) An economic model is a simplified version of reality used to analyze real-world economic situations. Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Economic Models
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
41) The sales revenue a seller receives from the sale of an additional unit of goods is called the marginal benefit.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
42) Optimal decisions are made at the point where marginal cost equals zero.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
43) If it costs Sinclair $300 to produce 3 suede jackets and $420 to produce 4 suede jackets, then the difference of $120 is the marginal cost of producing the 4th suede jacket.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
44) Suppose the extra cost of producing an extra million kilograms of French fries is $1 million. Then, McCain Foods Ltd. should make the extra French fries if they generate additional revenue of $1 million.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 2 Type: TF
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
Special Feature: Solved Problem: Binge Watching and Decisions at the Margin.
45) Explain the economic assumption that "people are rational."
Answer: "People are rational" means that economists assume consumers and firms will use all available information as they act to achieve their goals. Rational individuals weigh the benefits and costs of each action, and they choose an action only if the benefits exceed the costs.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: People Are Rational
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
46) Explain the economic idea that "people respond to incentives."
Answer: Human beings act from a variety of motives, including religious belief, envy, and compassion. "People respond to incentives" means that people will act if they feel it is in their best economic interest to do so.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: People Respond to Incentives
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
47) What is meant by the statement that "optimal decisions are made at the margin"?
Answer: In economics, the word "marginal" means "extra" or "additional." Economists reason that the optimal decision is to continue any activity up to the point where the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost, so optimal decisions are made at the point where the extra benefit received from an activity is equal to the extra cost associated with that activity.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
48) Suppose that watching one more episode of your favourite NetFlix show is worth $ 200 to you. Suppose that studying for that same amount of time will boost your mark enough to get you a bursary. What is the smallest size of the bursary that would cause you to study instead of watching another episode (assuming you are rational)?
Answer: The bursary would have to be at least $200 for a rational person to choose to study instead of watching the next episode assuming there are no other benefits to studying.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: People Are Rational
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytic Skills
Special Feature: Solved Problem: Binge Watching and Decisions at the Margin.
49) Consider the following statements:
a. Soda drinkers purchase more soda from a grocery store that sells soda at a lower price than other rival grocery stores in the area.
b. Homeowners do not take steps to increase security even though they believe it is more costly to allow burglaries than to install security monitoring equipment.
c. Manufacturers produce less of a particular cell phone when its selling price rises.
Which of the above statements demonstrates that economic agents respond to incentives?
A) a only
B) b only
C) c only
D) a and b
Answer: A
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: People Respond to Economic Incentives
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Scenario 1.2
Suppose a cigar manufacturer currently sells 1,500 cigars per week and makes a profit of $3,000 per week. The plant foreman observes, "Although the last 500 cigars we produced and sold increased our revenue by $7,500 and our costs by $7,000, we are only making an overall profit of $3,000 per week so I think we need to cut back on production."
50) Refer to Scenario 1.2. Using marginal analysis terminology, what is another economic term for the incremental revenue received from the sale of the last 500 cigars?
A) gross earnings
B) marginal revenue
C) sales revenue
D) gross profit
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
51) Refer to Scenario 1.2. Using marginal analysis terminology, what is another economic term for the incremental cost of producing the last 500 cigars?
A) marginal cost
B) operating cost
C) explicit cost
D) Any of the above terms are correct.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
52) Refer to Scenario 1.2. Had the firm not produced and sold the last 500 cigars, would its profit be higher or lower, and if so by how much?
A) Its profit would be $500 higher.
B) Its profit would be $1,000 higher.
C) Its profit would be $500 lower.
D) Its profit would be $1,500 lower.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Table 1.3
Ivan runs a custom jewelry shop in Sparkle City. He is debating whether he should extend his hours of operation. Ivan figures that his sales revenue will depend on the number of additional hours the jewelry shop is open as shown in the table above. He would have to hire a worker for those hours at a wage rate of $25 per hour.
53) Refer to Table 1.3. Using marginal analysis, how many hours should Ivan extend his hours of operations?
A) 2 hours
B) 3 hours
C) 4 hours
D) 5 hours
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
54) Refer to Table 1.3. What is Ivan's marginal benefit if he decides to stay open for six hours instead of five hours?
A) $10
B) $20
C) $30
D) $91.67
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
55) Refer to Table 1.3. What is Ivan's marginal cost if he decides to stay open for six hours instead of five hours?
A) $10
B) $20
C) $25
D) $91.67
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
56) Fiona shares an office with her ex-husband. Her share of the rent and utilities is $625 per month. She is considering moving to a home office which she will not have to share with anyone. The home office will not cost her anything as far as extra rent or utilities. Recently, you ran into Fiona at the gym and she tells you that she has moved into her home office. Fiona is as rational as any other person. As an economics major, you rightly conclude that
A) Fiona did not have a choice; her ex-husband was a jerk.
B) Fiona figures that the additional benefit of having her own office (as opposed to sharing) is at least $625.
C) Fiona figures that the benefit of having her own office (as opposed to sharing) is zero, since she is no longer paying rent and utilities.
D) the cost of having one's own space outweighs the benefits.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
Table 1.4
Sofia runs a small candy store. She is debating whether she should extend her hours of operation. Sofia figures that her sales revenue will depend on the number of additional hours the candy store is open as shown in the table above. She would have to hire a worker for those hours at a wage rate of $15 per hour.
57) Refer to Table 1.4. Using marginal analysis, how many hours should Sofia extend her hours of operations?
A) 2 hours
B) 3 hours
C) 4 hours
D) 5 hours
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
58) Refer to Table 1.4. What is Sofia's marginal benefit if she decides to stay open for six hours instead of five hours?
A) $10
B) $15
C) $25
D) $210
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
59) Refer to Table 1.4. What is Sofia's marginal cost if she decides to stay open for six hours instead of five hours?
A) $10
B) $15
C) $25
D) $210
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
60) Raul restores old motorcycles. Raul has just spent $9,000 purchasing a 1920 Indian Scout motorcycle which he expects to restore and sell for $25,000 once the work is completed. After having spent $9,000, Raul realizes that he will need to spend an additional $5,000 on materials to complete the restoration. Alternatively, he can sell the motorcycle without restoring it for $11,000. What is his marginal benefit if he sells the motorcycle without restoring it?
A) $2,000
B) $5,000
C) $11,000
D) $14,000
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
61) Raul restores old motorcycles. Raul has just spent $9,000 purchasing a 1920 Indian Scout motorcycle which he expects to restore and sell for $25,000 once the work is completed. After having spent $9,000, Raul realizes that he will need to spend an additional $5,000 on materials to complete the restoration. Alternatively, he can sell the motorcycle without restoring it for $11,000. What is his marginal cost to complete the restoration?
A) $2,000
B) $5,000
C) $11,000
D) $14,000
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
62) Raul restores old motorcycles. Raul has just spent $9,000 purchasing a 1920 Indian Scout motorcycle which he expects to restore and sell for $25,000 once the work is completed. After having spent $9,000, Raul realizes that he will need to spend an additional $5,000 on materials to complete the restoration. Alternatively, he can sell the motorcycle without restoring it for $11,000. What should he do?
A) He should not restore the motorcycle and sell it now to make the most profit.
B) It does not matter what he does; he is going to take a loss on the project.
C) He should finish the restoration and then sell the motorcycle.
D) He should sell the motorcycle back to the party he purchased it from and cut his losses.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Optimal Decisions Are Made at the Margin
Learning Outcome: 1.1 Explain these three key economic ideas: People are rational, people respond to incentives, optimal decisions are made at the margin
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produce
1) The three fundamental questions that any economy must address are
A) What will be the prices of goods and services; how will these goods and services be produced; and who will receive them?
B) What goods and services to produce; how will these goods and services be produced; and who receives them?
C) Who gets jobs; what wages do workers earn; and who owns what property?
D) How much will be saved; what will be produced; and how can these goods and services be fairly distributed?
E) How can the economy's output be equally shared; who are the decision makers; and what is the optimum output?
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: The Economic Problems
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
2) The idea that because of scarcity, producing more of one good or service means producing less of another good or service refers to the economic concept of
A) optimization.
B) efficiency.
C) trade-off.
D) equity.
E) consumption.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Trade-offs
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
3) Society faces a trade-off in all of the following situations except
A) when deciding who will receive the goods and services produced.
B) when deciding what goods and services will be produced.
C) when deciding how goods and services will be produced.
D) when some previously unemployed workers find jobs.
E) when making a trade-off because of scarcity.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Trade-offs
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
4) Which of the following statements is true?
A) Anytime you have to decide which action to take you are experiencing economic equity.
B) Trade-offs do not apply when the consumers purchase a product for which there is excess supply, such as a stock clearance sale.
C) Every individual, no matter how rich or poor, is faced with making trade-offs.
D) Economics is a social science that studies the trade-offs we are forced to make because resources are unlimited.
E) Producing more of one good means more of another good can be produced.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Trade-offs
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
5) Which of the following is not an example of an economic trade-off that a firm has to make?
A) whether it is cheaper to produce with more machines or with more workers
B) whether it is to outsource the production of a good or service
C) whether or not consumers will buy its products
D) whether it should produce more of its product
E) whether it should produce less of its product
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Trade-offs
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
6) The highest valued alternative that must be given up to engage in an activity is the definition of
A) economic equity.
B) marginal benefit.
C) opportunity cost.
D) marginal cost.
E) economic stability.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Opportunity Cost
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
7) The Coffee Nook, a small cafe near campus, sells cappuccinos for $2.50 and Russian tea cakes for $1.00 each. What is the opportunity cost of buying a cappuccino?
A) 2 1/2 Russian tea cakes
B) 2/5 of a Russian tea cake
C) $2.50
D) $1.00
E) $0.40
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Opportunity Cost
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytic Skills
8) Arlene quits her $125,000-a-year job to take care of her ailing parents. What is the opportunity cost of her decision?
A) zero, since she will no longer be earning a salary
B) It depends on the "going rate" for home-care providers.
C) at least $125,000
D) the value she attributes to the satisfaction she receives from taking care of her parents
E) the total value of all alternatives that must be given up to engage in taking care of her parents
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Opportunity Cost
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytic Skills
9) The distribution of income primarily determines which of the fundamental economic questions?
A) What goods and services are to be produced?
B) How the goods and services are to be produced?
C) Who will receive the goods and services produced?
D) How to plan the economy?
E) How to redistribute the goods and services?
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Who Will Receive the Goods and Services Produced?
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
10) Automobile manufacturers produce a range of automobiles such as sports utility vehicles, luxury sedans, pickup trucks and compact cars. What fundamental economic question are they addressing by making this range of products?
A) How to produce goods that consumers want?
B) Why produce a variety of automobiles?
C) What to produce?
D) Who to produce automobiles for?
E) What price to charge for each range of products?
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: What Goods and Services Will Be Produced?
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
11) Consider the following economic agents:
a. the government
b. consumers
c. producers
Who, in a centrally planned economy, decides what goods and services will be produced with the scarce resources available in that economy?
A) the government
B) producers
C) consumers
D) consumers and producers
E) the government, consumers and producers
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Centrally Planned Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
12) The decision about what goods and services will be produced made in a market economy is made by
A) lawmakers in the government voting on what will be produced.
B) workers deciding to produce only what the boss says must be produced.
C) producers deciding what society wants most.
D) consumers and firms choosing which goods and services to buy or produce.
E) consumers dictating to firms what they need most.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: What Goods and Services Will Be Produced?
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
13) Central planning relies on ________ to determine what types of products to make.
A) government employees
B) consumers' choices
C) individual businesses
D) consumers' wants
E) collective decisions
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Centrally Planned Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Apply the Concept: Central Planning Leads to Some Odd Products
14) Which of the following statements about the economic decisions consumers, firms, and the government have to make is false?
A) Governments face the problem of scarcity in making economic decisions.
B) Only individuals face scarcity; firms and the government do not.
C) Both firms and individuals face scarcity.
D) Each faces the problem of scarcity which necessitates trade-offs in making economic decisions.
E) Both firms and individuals have to make choices.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: What Goods and Services Will Be Produced?
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
15) Why is it necessary for all economic systems to not only provide people with goods and services, but also restrict them from getting as much of these goods and services as they wish?
A) Failure to do this could reduce the efficiency of the system by producing some goods and services that are not as highly valued as others.
B) Failure to do this could lead to an inequitable allocation of goods and services produced.
C) Failure to do this could lead to drastic shortages of good and services.
D) Failure to do this could reduce efficiency and lead to an inequitable allocation of output.
E) Failure to do this could lead to an equal allocation of goods and services produced.
Answer: A
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Who Will Receive the Goods and Services Produced?
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytic Skills
16) Who receives the most of what is produced in a market economy?
A) lawmakers and other politically favoured groups
B) those who are willing and able to buy them
C) everyone receives an equal amount
D) people who earn the highest incomes
E) those who need them the most
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Who Will Receive the Goods and Services Produced?
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
17) How are the fundamental economic decisions determined in North Korea?
A) Individuals, firms, and the government interact in a market to make these economic decisions.
B) These decisions are made by the country's elders who have had much experience in answering these questions.
C) The government decides because North Korea is a centrally planned economy.
D) The United Nations decides because North Korea is a developing economy.
E) North Korean firms decide as they determine production.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Centrally Planned Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
18) How are the fundamental economic questions answered in a market economy?
A) The government alone decides the answers.
B) Individuals, firms, and the government interact in markets to decide the answers to these questions.
C) Households and firms interact in markets to decide the answers to these questions.
D) Large corporations alone decide the answers.
E) Wealthy individuals alone decide the answers.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Market Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
19) Which of the following is a problem inherent in centrally planned economies?
A) Households and firms make poor decisions in choosing how resources are allocated.
B) There is too little production of low-cost, high-quality goods and services.
C) Production managers are more concerned with satisfying consumer wants than with satisfying government's orders.
D) Exports tend to exceed imports.
E) Those who are willing and able to buy what is produced determine what is produced.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Centrally Planned Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
20) All of the following contributed to the downfall of the Soviet Union in 1991 except
A) public dissatisfaction with low living standards and political repression.
B) an inability to produce low-cost consumer goods that households wanted.
C) lack of high-quality goods and services.
D) lack of a strong dictator who can coordinate economic activities.
E) all of the above contributed to the downfall.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Centrally Planned Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
21) ________ is a situation in which a good or service is produced at the lowest possible cost.
A) Allocative efficiency
B) Productive efficiency
C) Equity
D) Optimal marginalism
E) Equality
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
22) Productive efficiency is achieved when
A) firms add a low profit margin to the goods and services they produce.
B) firms produce the goods and services that consumers value most.
C) firms produce goods and services at the lowest cost.
D) there are no shortages in the market.
E) there are no surpluses in the market.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
23) When production reflects consumer preferences, ________ occurs.
A) allocative efficiency
B) productive efficiency
C) equity
D) efficient central planning
E) scarcity
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
24) Allocative efficiency is achieved when firms produce goods and services
A) at the lowest possible cost.
B) that consumers value most.
C) at the lowest opportunity cost.
D) at a marginal cost of zero.
E) at the highest possible price.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
25) Markets promote
A) equity and competition.
B) voluntary exchange and equality.
C) equity and equality.
D) competition and voluntary exchange.
E) competition and equality.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Market Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
26) Which of the following statements is true about competition in a market?
A) Competition forces firms to outsource the production of their labour-intensive products.
B) Competition forces firms to undercut their selling price, thus benefiting consumers who will be able to purchase products at the lowest price possible.
C) Competition forces firms to produce and sell products as long as the marginal benefit to consumers exceeds the marginal cost of production.
D) Competition forces firms to add only low profit margins to their costs of production.
E) Competition forces firms to add only high profit margins to their costs of production.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Market Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
27) ________ increases economic efficiency because it forces firms to produce and sell goods and services as long as the additional benefit to consumers is greater than the additional cost of production.
A) Competition
B) Voluntary exchange
C) Equity
D) A centrally planned economy
E) Equality
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Market Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
28) Which of the following generates productive efficiency?
A) competition among sellers
B) competition among buyers
C) government inspectors
D) government production rules
E) government regulations
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
29) Voluntary exchange between buyers and sellers generates ________ in a market economy.
A) scarcity
B) allocative efficiency
C) productive efficiency
D) equity
E) equality
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
30) Which of the following is a result of a market economy?
A) environmental protection
B) an equal income distribution
C) agreement on equity
D) voluntary exchange
E) scarcity
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Market Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
31) Political candidates often hold fund raisers by charging "per plate" for dinner. Wendy purchased four tickets to a $1,000 per plate dinner for a local city council candidate. Is this transaction economically efficient?
A) No, political candidates should never be allowed to overcharge for a fund raising dinner.
B) Yes, it was a voluntary exchange that benefited both parties.
C) No, Wendy paid too much for four dinners.
D) Yes, it is efficient only from the perspective of the candidate but not from the perspective of Wendy.
E) Yes, it is efficient only from the perspective of Wendy but not from the perspective of the candidate.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Market Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytic Skills
32) In economics, the term "equity" means
A) everyone has an equal standard of living.
B) the hardest working individuals consume all they want.
C) only elected officials have high standards of living.
D) economic benefits are distributed fairly.
E) economic benefits are distributed freely.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Equity
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
33) Which of the following is motivated by an equity concern?
A) Some provinces and municipalities have transferred funds to food bank programs in order to increase benefits to lower-income families.
B) Following the implementation of subsidies for energy conservation, household demand for rooftop solar panels increased quite significantly in BC.
C) Some provinces allow automotive insurance companies to charge men and women different rates for insurance.
D) Canada offers patent protection to pharmaceutical manufacturers to prevent others from duplicating their products.
E) Following the removal of subsidies in urban water use, household demand for water decreased quite significantly in Bogor, Indonesia.
Answer: A
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Equity
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking, Ethical Reasoning
34) Which of the following is motivated by an efficiency concern?
A) In 2013 the Alberta government handed out pre-paid credit and debit cards to flood victims.
B) The right to purchase tickets to the Grey Cup is decided by a lottery.
C) Organ transplant waiting lists rationing scarce kidneys that would favour young patients over old in an effort to wring more life out of donated organs.
D) The federal government Equalization program which makes larger transfers to poor provinces than to wealthy ones.
E) Some university scholarships have been cut back since these programs siphon money from need-based programs, thus harming lower-income students with greater financial need.
Answer: C
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking, Ethical Reasoning
35) Which of the following is an example of an efficiency-equity trade-off faced by economic agents?
A) Provincial health programs are not cost effective. Instead of focusing on universal access to the health care system, money should be spent on programs that prevent disease first and treating disease second.
B) Concerned about the falling birth rate, the French government has pledged more money for families with three children, in an effort to encourage working women to have more babies.
C) Some Canadian universities are actively recruiting foreign students for their technology-based programs.
D) Municipal sports programs must charge all participants the same price, even when participants don't live in the municipality.
E) The growing demand for corn by ethanol producers has led to a surge in the price of tortillas, a staple in the Mexican diet. To quell public outcry over rising tortilla prices, the Mexican government released government corn stocks at prices well below the market, and pressured states to impose price ceilings on tortillas.
Answer: A
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytic Skills, Ethical Reasoning
36) Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between economic efficiency and economic equity?
A) They are both automatically achieved in a free market economy.
B) They always call for opposite outcomes.
C) There is no conflict between the two goals.
D) There is often a trade-off between the two.
E) There is no trade-off between the two.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
37) Allocative efficiency best explains ________, and productive efficiency best explains ________.
A) how something will be produced; when something will be produced
B) when something will be produced; why something will be produced
C) why something will be produced; what will be produced
D) what will be produced; how something will be produced
E) what will be produced; when something will be produced
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
38) Assume an economics instructor want to promote equity in their classroom. To do this, announce that all students will receive a final grade equal to the class average. Based on the equity-efficiency tradeoff, what is a likely outcome?
A) Most students will spend their time on other courses, resulting in little learning and a low class average.
B) Freed from competition, students will fully apply themselves to an economics course causing the class average to rise.
C) Student behaviour will not change, but everyone in the class will have the same mark.
D) Students will put extra effort into this economics course solely to help other students do well.
E) Students will demand the same grade allocation in all their other courses.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Trade-offs
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytic Skills, Ethical Reasoning
Special Feature: Apply the Concept: The Equity-Efficiency Trade-off in the classroom.
39) How are the fundamental economic decisions determined in Canada?
A) Individuals, firms, and the government interact in a market to make these economic decisions.
B) These decisions are made by the country's elders who have had much experience in answering these questions.
C) The government decides because Canada is a centrally planned economy.
D) The United Nations decides because Canada is a developing economy.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Mixed Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
40) The government makes all economic decisions in a mixed economy.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Mixed Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
41) When voluntary exchange takes place, both parties gain from the exchange.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Market Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
42) A university must decide if it wants to offer more Internet-based classes. This decision involves answering the economic question of "what to produce."
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: What Goods and Services Will Be Produced?
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
43) One desirable outcome of a market economy is that it leads to a more equitable distribution of income.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Market Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
44) What is equity, and how does it differ from efficiency?
Answer: Equity refers to the fair distribution of economic benefits. In economics, efficiency refers to least cost production (productive efficiency) and producing according to human preferences (allocative efficiency).
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Equity
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
45) What is opportunity cost?
Answer: Opportunity cost refers to the highest-valued alternative that must be given up to engage in an activity. For example, the opportunity cost of taking this economics class is what you are giving up to take the class, which may be taking another class such as accounting or psychology, working extra hours at your job, or extra sleep (whichever is your highest-valued alternative).
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Opportunity Cost
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
46) Define productive efficiency. Does productive efficiency imply allocative efficiency? Explain.
Answer: Productive efficiency is an efficiency criterion that describes a situation in which goods and services are produced at the lowest possible cost. It does not imply allocative efficiency which is a criterion associated with producing goods and services that consumers value most. For example, a manufacturer may be able to produce typewriters at the lowest possible cost of say, $200, but this does not necessarily mean that consumers are willing to pay $200 for a typewriter.
Diff: 3 Type: ES
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytic Skills
47) What is a centrally planned economy?
Answer: A centrally planned economy is an economy in which the government decides how economic resources will be allocated.
Diff: 3 Type: ES
Topic: Centrally Planned Economies
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
48) Define allocative efficiency. Explain the significance of this concept in economics. Answer: Allocative efficiency is an efficiency criterion that describes a situation where the marginal benefit (or marginal valuation) of the last unit purchased is equal to the marginal cost of producing that unit. In other words, allocative efficiency occurs when production reflects consumer preferences. This is a significant concept in that all societies face scarcity which necessitates that societies make choices about what goods and services to produce. To maximize society's wealth, resources must flow to their highest valued use. This value is determined by consumers.
Diff: 3 Type: ES
Topic: Efficiency
Learning Outcome: 1.2 Discuss how a society answers these three key economic questions: What goods and services will be produced? How will the goods and services be produced? Who will receive the goods and services produced?
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
1) Economic models do all of the following except A) answer economic questions.
B) portray reality in all its minute details.
C) make economic ideas explicit and concrete for use by decision makers.
D) simplify some aspect of economic life.
E) simplify versions of reality.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Economic Models
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
2) All of the following are part of an economic model except A) assumptions.
B) hypotheses.
C) data.
D) opinions.
E) theory.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Economic Models
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
3) Which of the following statements about positive economic analysis is false?
A) Positive analysis uses an economic model to estimate the costs and benefits of different course of actions.
B) There is much more disagreement among economists over normative economic analysis than over positive economic analysis.
C) There is much more disagreement among economists over positive economic analysis than over normative economic analysis.
D) Unlike normative economic analysis, positive economic analysis can be tested.
E) Positive analysis is concerned with what is and can potentially be disproven.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
4) Which of the following is a positive economic statement?
A) The standard of living in Canada should be higher.
B) If the price of iPhones falls, a larger quantity of iPhones will be purchased.
C) The government should restructure the health care system.
D) The Ontario government should not have bailed out Canadian auto manufacturers.
E) The government should close income tax loopholes.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
5) Which of the following is a positive economic statement?
A) People should not buy SUVs.
B) The government should mandate electric automobiles.
C) Scarcity necessitates that people make trade-offs.
D) Foreign workers should not be allowed to work for lower wages than the citizens of a country.
E) People should not buy imported fruits and vegetables.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
6) Which of the following is a normative economic statement?
A) Rising global demand for coal has led to increases in the price of coal.
B) With rising mortgage rates and rising unemployment rates, the number of unsold homes has increased.
C) Toronto is considering increasing funds for light-rail development to promote the use of public transportation.
D) Pharmaceutical manufacturers should not be allowed to patent their products so prescription drugs would be more affordable.
E) The minimum wage law causes unemployment.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
7) Which of the following is a normative economic statement?
A) The price of gasoline is too high.
B) The current high price of gasoline is the result of strong worldwide demand.
C) When the price of gasoline rises, the quantity of gasoline purchased falls.
D) When the price of gasoline rises, transportation costs rise.
E) When the price of gasoline falls, oil companies cut production.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
8) Which of the following questions or statements regarding minimum wage is normative?
A) How do changes in minimum wages affect the employment opportunities of teens?
B) People working in the retail sector deserve higher pay.
C) Wages play a role in causing someone to apply for a job.
D) Higher minimum wages will cause firms to employ fewer people.
E) The minimum wage law causes unemployment.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Apply the Concept: Should the Government of Saskatchewan Increase its Minimum Wage?
9) The economic analysis of minimum wage involves both normative and positive analysis. Consider the following consequences of a minimum wage:
a. The minimum wage law causes unemployment.
b. A minimum wage law benefits some groups and hurts others.
c. In some cities such as San Francisco and New York, minimum wage laws are necessary for lowskilled workers to stay in the city.
d. The gains to winners of a minimum wage law should be valued more highly than the losses to losers because the latter primarily comprises businesses.
Which of the consequences above are positive statements and which are normative statements?
A) a, b, and c are positive statements and d is a normative statement.
B) a and b are positive statements, c and d are normative statement.
C) Only a is a positive statement, b, c and d are normative statements.
D) a and c are positive statements, b and d are normative statements.
E) a and d are positive statements, b and c are normative statements.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Analytic Skills
Special Feature: Apply the Concept: Should the Government of Saskatchewan Increase its Minimum Wage?
10) Which of the following is part of an economic model?
A) preferences of economic agents
B) data
C) norms
D) opinions
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Economic Models
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
11) "An increase in the price of gasoline will increase the demand for hybrid vehicles." This statement is an example of a positive economic statement.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
12) "The distribution of income should be left to the market" is an example of a positive economic statement.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
13) Positive analysis is concerned with "what ought to be," while normative analysis is concerned with "what is."
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 2 Type: TF
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
14) What is the difference between positive economic analysis and normative economic analysis? Give one example each of a positive and normative economic issue or question or statement.
Answer: Positive economic analysis is concerned with what is. Positive economic analysis reaches conclusions based on verifiable statements. Normative economic analysis, on the other hand, is concerned with what ought to be. Normative analysis reaches conclusions based on opinions. (Students will give many different examples.)
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Normative and Positive Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
15) Explain why economics is considered a social science.
Answer: Economics is a social science because it studies the actions of individuals. As a social science, economics considers human behaviour, particularly decision-making behaviour, in every context.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Economics as a Social Science
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
16) What are the five steps by which economists arrive at a useful economic model?
Answer:
1. Decide on the assumptions to use in developing the model.
2. Formulate a testable hypothesis.
3. Use economic data to test the hypothesis.
4. Revise the model if it fails to explain the economic data well.
5. Retain the revised model to help answer similar economic questions in the future.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Economic Models
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
17) What is an economic variable? Give an example of an economic variable.
Answer: An economic variable is something measurable that can have different values, such as the wages of software programmers. (Students will give many different examples.)
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Economic Models
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
18) Which of the following are positive economic statements and which are normative economic statements?
a. An increase in the minimum wage causes unemployment.
b. The government should raise the minimum wage above $7.25 per hour.
c. The prolonged recession has caused the unemployment rate to reach a 30-year high.
d. Interest rates need to be lower for the economy to emerge from the recession.
e. Inflation has decreased since the onset of the recession.
f. Once the recession has ended, interest rates should increase to assure that inflation does not go up.
Answer: Statements a, c, and e are positive economic statements. Statements b, d, and f are normative economic statements.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Positive and Normative Analysis
Learning Outcome: 1.3 Understand what economic models are and aren't, and why they are a good idea
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
1) Which of the following is a microeconomics question?
A) How much will be saved and how much will be produced in the entire economy?
B) What will the level of economic growth be in the entire economy?
C) What factors determine the price of carrots?
D) What determines the average price level and inflation?
E) Why do economies experience periods of recession?
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Microeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
2) Microeconomics is the study of
A) how households and firms make choices.
B) the economy as a whole.
C) the global economy.
D) topics such as inflation and economic growth.
E) what determines the unemployment rate.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Microeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
3) Which of the following is a macroeconomics question?
A) What determines the inflation rate?
B) What determines the size of the film industry in Canada?
C) How is the production quantity of digital cameras determined?
D) What determines the wage of auto workers?
E) What factors determine the price of iPhones?
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Macroeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
4) Macroeconomics is the study of
A) how households make choices.
B) how firms make choices.
C) how households and firms make choices.
D) the economy as a whole.
E) the impact of government interventions on market outcomes.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Macroeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
5) Examining the conditions that could lead to a recession in an economy is an example of macroeconomics topic.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Macroeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
6) The decisions Apple makes in determining production levels for its iPhone is an example of a microeconomics topic.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Microeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
7) Suppose that to move more people off the wait list for organ donations, surgeons and hospitals are developing a market for organ swapping. This is an example of a macroeconomic topic.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Microeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
8) Examining the conditions that could lead to economic growth is an example of a macroeconomic topic.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Macroeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
9) The decisions General Motors makes in determining production levels for its Chevy Bolt is an example of a microeconomic topic.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Microeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
10) Which of the following are primarily macroeconomic topics and which are primarily microeconomic topics?
a. gasoline prices
b. unemployment
c. inflation
d. health care costs
e. air pollution
f. economic growth
Answer:
b, c, and f are primarily macroeconomic topics.
a, d, and e are primarily microeconomic topics.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Microeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
11) How does the study of microeconomics differ from that of macroeconomics? Give one example each of an issue studied in microeconomics and in macroeconomics.
Answer: Microeconomics is the study of how household and businesses make choices, how they interact in markets, and how the government attempts to influence their choices while macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including topics like unemployment, inflation and economic growth. (Students will give many different examples.)
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Microeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
12) Define macroeconomics.
Answer: Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including topics such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Macroeconomics
Learning Outcome: 1.4 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
1.5 Define important economic terms (It's not all Greek)
1) Which of the following statements is true about profit?
A) Profit refers to the revenue received from the sale of a quantity of goods.
B) Profit is calculated by multiplying price and quantity sold.
C) The terms "accounting profit" and "economic profit" can be used interchangeably.
D) Profit is the difference between revenue and cost.
E) A firm's revenue will increase as its costs increase.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Profit
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
2) In economics, the accumulated skills and training that workers have is known as
A) human capital.
B) entrepreneurship.
C) physical capital.
D) innovation.
E) natural resources.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Human Capital
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
3) Which of the following is an example of an activity undertaken by an entrepreneur?
A) designing your landscaping for your new home
B) holding a position as the president of a small university
C) running for Prime Minister of Canada
D) starting your own pet sitting business
E) choosing the color scheme for your renovated kitchen
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Entrepreneur
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
4) The machines workers have to work with are considered
A) human capital.
B) physical capital.
C) entrepreneurship.
D) financial capital.
E) natural resources.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Capital
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
5) Technology is defined as
A) the process of developing and revising models.
B) new innovations and creations.
C) the processes used to produce goods and services.
D) the process of recycling products.
E) the machines that workers have to work with.
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Technology
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
6) Which of the following statements about economic resources is true?
A) Economic resources include financial capital and money.
B) Economic resources are also called factors of production.
C) Economic resources are used only by businesses.
D) All economic resources are man-made.
E) All economic resources are found in nature.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Resources
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
7) As the minimum wage rises
A) the price of takeout coffee will rise.
B) the price of takeout coffee will fall.
C) there will be a shortage of coffee.
D) there will be a surplus of coffee.
E) more coffee will be exported from Canada.
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Human Capital
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Economics in Your Life and Career: How Much Will You Pay for a Cup of Coffee?
8) If climate change continues to reduce the amount of green coffee available to roasters,
A) the price of take out coffee will rise.
B) people working in coffee shops will receive higher wages.
C) more people will want to drink coffee than before.
D) more entrepreneurs will enter the roasting business.
E) demand for green coffee will increase.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Human Capital
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Economics in Your Life and Career: How Much Will You Pay for a Cup of Coffee?
9) In the market for factors of production, firms earn income by selling goods and services to households.
Answer: FALSE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Resources
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
10) One example of human capital is the amount of skills that you have.
Answer: TRUE
Diff: 1 Type: TF
Topic: Human Capital
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
11) List the five main factors of production.
Answer: The five main factors of production are labour, capital, human capital, natural resources, and entrepreneurial ability.
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Resources
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
12) What is the difference between an invention and an innovation?
Answer: An invention is the development of a new good or a new process for making a good. An innovation is the practical application of an invention. Innovation could also refer to any significant improvement in a good or in the means of producing a good.
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Innovation
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
13) Explain the difference between a firm's revenue and its profit.
Answer: A firm's revenue is the total amount received for selling a good or service. It is calculated by multiplying the price per unit by the number of units sold. A firm's profit is the difference between its revenue and its costs.
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Revenue
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
14) What are some of the reasons given for the increase in coffee prices?
Answer: The reasons include bad weather in Colombia, wages, and the actions of individual firms.
Diff: 2 Type: ES
Topic: Resources
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Special Feature: Economics in Your Life and Career: How Much Will You Pay for a Cup of Coffee?
15) What is technology and what factors does it depend on?
Answer: Technology is the processes a firm uses to produce goods and services. In the economic sense, a firm's technology depends on many factors, such as the skill of its managers, the training of its workers, and the speed and efficiency of its machinery and equipment.
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Technology
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
16) What is the difference between physical capital and human capital?
Answer: Physical capital includes manufactured goods which are used to produce other goods and services. Human capital refers to the accumulated education, training, and skills that workers possess.
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Capital
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
17) What is the difference between accounting profit and economic profit?
Answer: Profit is the difference between revenue and cost. Accounting profit excludes the cost of some economic resources that the firm does not pay for explicitly. Economic profit includes the opportunity cost of all resources used by the firm.
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Profit
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
18) What is a household? How do households interact with firms in a market?
Answer: A household consists of all persons occupying a home. Households supply factors of production used by firms to produce goods and services. Households also demand goods and services produced by firms.
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Resources
Learning Outcome: 1.5 Define important economic terms. (It's not all Greek)
AACSB: Analytical Thinking
1.6
Review the use of graphs and formulas
1) If a graph has a line that shows the amount of outsourcing in the last ten years, it is known as
A) a pie chart.
B) a time-series graph.
C) a demand curve for outsourcing.
D) a supply curve of outsourcing.
E) a flow chart.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Graphs
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
2) ________ have a horizontal and a vertical axis and are used in economics to illustrate relationships between two economic variables.
A) Two-dimensional graphs
B) One-dimensional graphs
C) Pie charts
D) Bar graphs
E) Flow charts
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Graphs
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
3) If a straight line passes through the point x = 14 and y = 3 and also through the point x = 4 and y = 10, the slope of this line is
A) negative 11 divided by 6.
B) seven tenths.
C) negative seven tenths.
D) 6 divided by 11.
E) one and seven tenths.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Slope
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
4) On a two-dimensional graph, ________ allows for the effects of additional variables.
A) moving along a curve
B) shifting curves
C) eliminating a curve
D) adding an additional curve
E) eliminating colour
Answer: B
Diff: 3 Type: MC
Topic: Graphs
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
5) Which of the following statements is false?
A) An inverse relationship has a negative slope value.
B) A direct relationship has a positive slope value.
C) A curved line has slope values that change at every point.
D) A straight line has a slope of zero.
E) Few economic relationships are actually linear.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Slope
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
6) The relationship between consumer spending and disposable personal income is
A) an inverse relationship.
B) a direct relationship.
C) a negative relationship.
D) independent.
E) reverse causality.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Positive and Negative Relationships
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
7) Suppose when the price of laptops fall, university students buy more laptops. This implies that
A) there is a positive relationship between laptop prices and quantities purchased by college students.
B) there is a negative relationship between laptop prices and quantities purchased by college students.
C) there is a direct relationship between laptop prices and quantities purchased by college students.
D) there is a one-to-one relationship between laptop prices and quantities purchased by college students.
E) there is no relationship between laptop prices and quantities purchased by college students.
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Positive and Negative Relationships
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
8) If the price of milk was $2.50 a litre and it is now $3.25 a litre, what is the percentage change in price?
A) 13 percent
B) 30 percent
C) 75 percent
D) 77 percent
E) 130 percent
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Formulas
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
9) In 2019, Hooverville consumed 205,000 tonnes of sugar. In 2020, sugar consumption rose to 245,000 tonnes. Calculate the percentage change in sugar consumption.
A) 8.37%
B) 11.95%
C) 19.51%
D) 26.33%
E) 53%
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Formulas
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
10) At a recent faculty meeting, Lorraine Waverly, president of Skywalker College, announced that enrollment is up by 12 percent over the previous semester. If enrollment the previous semester was 3,250 students, what is the student enrollment this semester?
A) 390
B) 2,860
C) 3,640
D) 4,030
E) 3,238
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Formulas
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills

11) Refer to Figure 1.1. Using the information in the figure above, calculate the percentage change in revenue from alcoholic beverage sales between 2013 and 2015.
A) 23.8%
B) 30%
C) 40%
D) 42.9%
E) 73.3%
Answer: A
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Formulas
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
12) Refer to Figure 1.1. Using the information in the figure above, calculate the percentage change in sales of alcoholic beverages between 2013 and 2015.
A) 23.1%
B) 23.8%
C) 30%
D) 40%
E) 42.9%
Answer: E
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Formulas
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills

13) Refer to Figure 1.2. Calculate the area of the triangle A.
A) $1.3 million
B) $2.6 million
C) $3.4 million
D) $5.2 million
E) $8.4 million
Answer: B
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Formulas
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
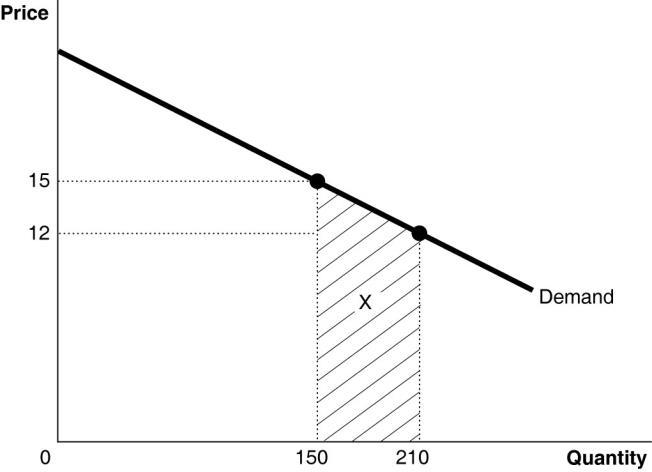
14) Refer to Figure 1.3. Calculate the area of the trapezoid X
A) $270
B) $720
C) $810
D) $2,520
E) $2,500
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Formulas
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas AACSB: Analytic Skills
15) Refer to Figure 1.4. Which of the following statements is false?
A) The slope of the tangent at E is positive.
B) The slope of the tangent at F is negative.
C) The slope of the tangent at E and the slope of the tangent at F are equal.
D) Neither the slope of the tangent at E nor the slope of the tangent at F are equal to zero.
E) The slope of the tangent at E is positive and the slope of the tangent at F is negative.
Answer: C
Diff: 1
Type: MC
Topic: Slope
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
16) What is the "omitted variable" problem in determining cause and effect?
A) It is a problem that arises when an insignificant variable is given too much weight in an economic analysis leading to skewed conclusions about cause and effect.
B) It is a problem that arises when a significant variable is not given enough weight in an economic experiment leading to skewed conclusions about cause and effect.
C) It is a problem that arises when an insignificant economic variable that should have been omitted is included in an economic experiment leading to false conclusions about cause and effect.
D) It is a problem that arises when an economic variable that affects other variables is omitted from an analysis and its omission leads to false conclusions about cause and effect.
E) It is a problem that arises when an economic variable that affects other variables is purposely omitted from an analysis and its omission leads to correct conclusions about cause and effect.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Cause and Effect
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
17) ________ is a problem that occurs when one concludes that a change in variable X caused a change in variable Y when in actual fact, it is a change in variable Y that caused a change in variable X.
A) The omitted variable
B) The positive-to-negative relationship
C) Reverse causality
D) Nonlinear slope
E) Tangent line
Answer: C
Diff: 1 Type: MC
Topic: Cause and Effect
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
18) The prevalence of Alzheimer's dementia is very high among residents living in nursing homes. A student concludes that it is likely that living in nursing home causes Alzheimer's dementia. What is the flaw in the student's reasoning?
A) The student has failed to take into account other causes of Alzheimer's disease.
B) The student is drawing a false conclusion; he is confusing cause and effect.
C) The student is using an inadequate sample size.
D) The student is drawing a false conclusion by making the mistake of omitting the age of the residents.
E) The student is drawing a false conclusion by making the mistake of omitting the gender of the residents.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Cause and Effect
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
19) You explain to your roommate Surya, who makes beaded headbands, about an economic theory which asserts that consumers will purchase more of a product at lower prices than they will at higher prices. She contends that the theory is incorrect because over the past two years she has lowered the price of her headbands and yet has seen a decrease in sales. How would you respond to Surya?
A) Surya is right; she has evidence to back her claim. The theory must be erroneous.
B) Surya is making the mistake of assuming that correlation implies causation.
C) I will explain to her that she is making the error of reverse causality: it is the decrease in demand that has caused her to lower her prices.
D) I will explain to her that there are some omitted variables that have contributed to a decrease in her sales such as changes in income.
E) Surya is making the mistake of assuming that causation implies correlation.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Type: MC
Topic: Cause and Effect
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Reflective Thinking
Table 1.5
20) Refer to Table 1.5. The table above shows the sales of DVD recorders in North America. Present the information using a bar graph.
Answer:
Diff: 1 Type: ES
Topic: Graphs
Learning Outcome: 1.6 Review the use of graphs and formulas
AACSB: Analytic Skills
