

Safe Moving and Handling
Safe Moving and Handling
1. Open the Cameraor QR code scanner to scan the code.



2. If QR code scanner is not available, pleasevisit the weblinkprovided below.


Handling




Moving and Handling




Who is…

• A family-run business, employing over 300 staff worldwide, including internationally recognised subject matter experts
• Over 2 million people are trained every year using Highfield products
• Over 45,000 trainers and training centres delivering Highfield qualifications
Our services…
Qualifications
Products
Assessments
E-learning.
• Customers include the world’s leading brands
• Internationally recognised accredited qualifications.
International brand recognition – adds value
Why choose…

Validated, relevant, up to date training materials
Quality, value and consistency
High quality trainers
Quality assurance and compliance with regulatory standards - trustworthy
Everything we do centres around our core values:
Quality, value, service & integrity
Authenticity of certificates via check cert facility
Outstanding customer service Integrity – invigilated exams
Expert technical advice
Dedicated centre managers to provide support.
Competency and CPD
• A qualification provides knowledge and assists career progression
• Applying/Implementing the knowledge leads to competency
• To maintain competency you need to keep your knowledge up to date
• This requires: continual professional development (CPD).





Further enhance your knowledge and skills
Free Highfield CPD webinars
Benefits:
• continuing professional development (CPD) certificates for live attendance
• delivered by leading SMEs
• time inconvenient? Watch later
• throughout the year
• a library of past events
To access our events:
• visit www.highfieldqualifications.com
• select ‘online solutions tab’
• select event.




Ground rules
● Fire escapes
● Toilets
● Smoking
● Drinks
● Breaks
● Lunch
● Questions
● Talking over others
● Respect others’ points of view
● Timekeeping
As a courtesy to others, please set your mobile phone to
SILENT MODE
Mobile phones must be SWITCHED OFF and removed from the desk during the examination.







Module 1
Introduction to safe manual handling

What do you understand by the term ‘manual handling’?
The supporting and transporting of a load by hand or by bodily force
Lifting/lowering
Carrying
Pulling
Pushing.

What do you understand by the term ‘manual handling’? (cont.)
List all the manual handling tasks you do in your workplace.

Moving and handling – the bigger picture
Year on year, manual handling injuries are a significant cause of workplace injuries
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are among the leading causes of occupational ill health issues in Great Britain
There are targeted inspections by the enforcing authorities.



Outline the benefits to employers when manual handling risks are controlled
Production/contracts maintained
Quality of products maintained
Competent employees
Positive safety culture
Insurance costs maintained or reduced
Good reputation with customers.

Outline the benefits to employers when manual handling risks are controlled (cont.)
Avoid injuries at work
Avoid pain, suffering and stress (along with their families)
Retain jobs and earnings
Maintain lifestyles and leisure activities.
Costs to society
• Acute healthcare
• Rehabilitation
• Welfare Injuries caused by incorrect moving and handling place a large cost burden on society
All these are met through tax and National Insurance contributions. KEY POINT

How much do you know?
What is the legal definition of ‘manual handling’?




The supporting and transporting of a load by hand or bodily force
Any moving of objects that does not involve equipment
Lifting, carrying and lowering, but not pushing or pulling
Moving objects and equipment over long distances



How much do you know?
Every year, manual handling injuries cause a _______ number of workplace injuries.




Minor



How much do you know?
Which of the following is a benefit to the employee of using safe moving and handling techniques?




Cost of personal injury claim
Time lost to physiotherapy appointments

Good reputation
Retain lifestyle and employment


How much do you know?
Which of the following is a consequence to a business of incorrect manual handling?




Loss of production
Better reputation


Potential hazards, injuries and ill health Module 2

Manual handling
Which parts of the body are injured by unsafe manual handling?
Back
Fingers and thumbs
Arm
Hand/wrist
Rest of torso
Other.

What
are sprains and strains?
Sprain
Injury to a ligament that has been stretched too far, for example, a twisted ankle

Strain
Injury to a tendon/muscle that has been pulled too far, for example, a back injury caused by poor technique.


What are the functions of the spine?
Allows movement Provides support and stability
Protects the internal organs
Provides the attachment of muscles and ligaments.
Anatomy of the spine
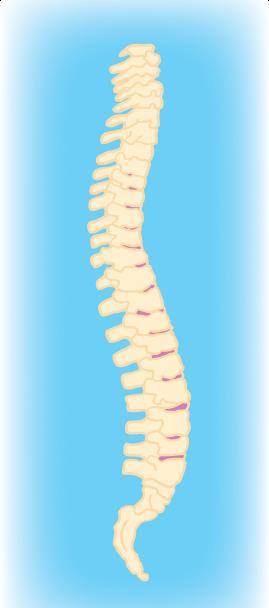
Cervical spine (neck)
Thoracic spine (mid back)
Lumbar spine (low back)
Sacrum (tail bone).
The vertebrae
Facet joints in motion
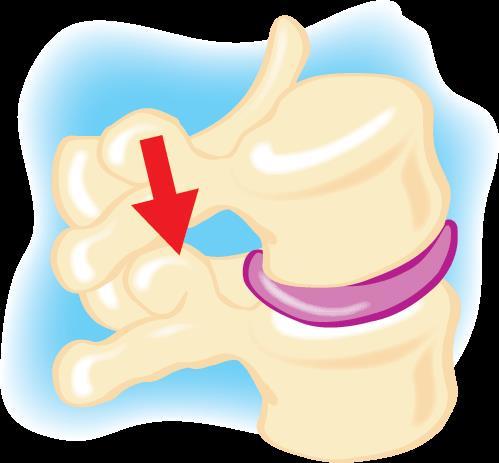

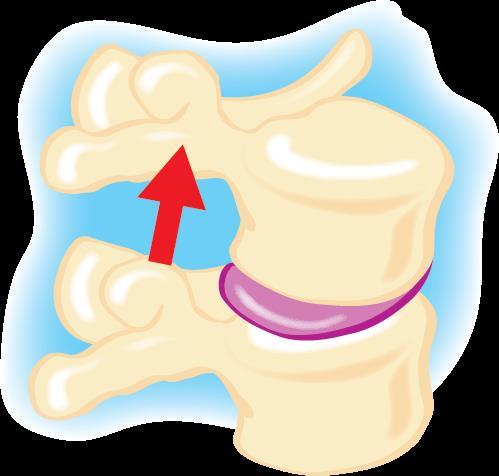
Flexion (bending forward) Extension (bending backward).
Vertebral body Disc
The spinal joint and intervertebral disc
Nerve root
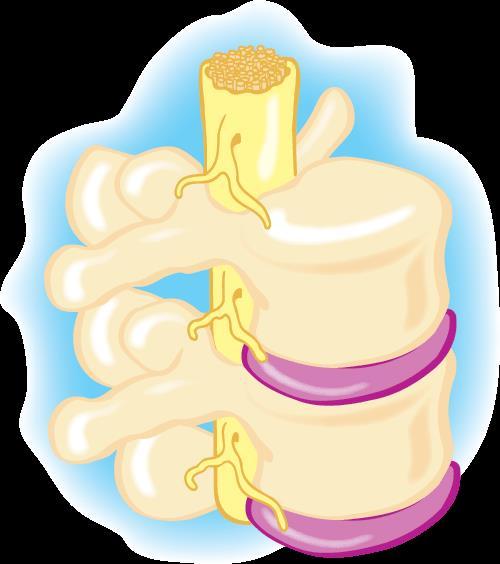
Spinal cord
Vertebrae
Spinal nerves
Intervertebral disc
Facet joints.
The spinal joint and intervertebral disc
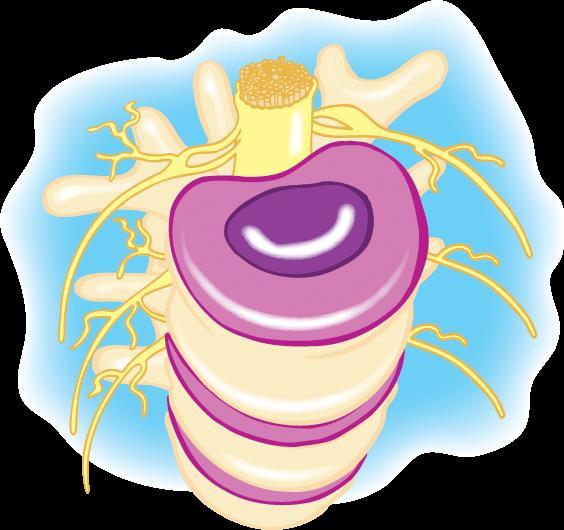
The spinal unit, showing the Intervertebral disc in good health
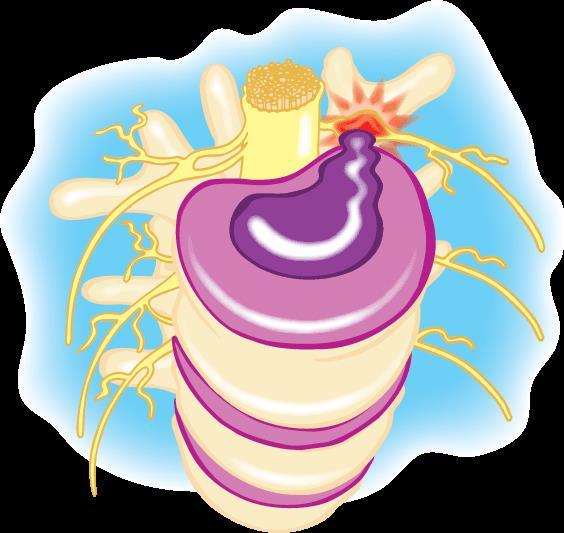
The spinal unit showing a prolapsed intervertebral disc.

What are acute and chronic conditions?
Acute

Sharp and of short duration. Illnesses that are acute appear quickly and can be serious or life-threatening. When the illness ends, the patient usually recovers fully
Chronic

Of long duration and slow progression. Illnesses that are chronic develop slowly over time and do not end. Symptoms may be continual or intermittent, but the patient usually has the condition for life.
High-risk activities



High-risk activities

Stretching upwards


Poor posture.
Guideline for maximum handling loads (HSE)

How much do you know?
What could cause an intervertebral disc to rupture?




Carrying a load
Lifting a load to shoulder height
Repetitive lifting and carrying

Holding a load close to the trunk


How much do you know?
Which type of injury is a twisted ankle?







How much do you know?
What is the name of the interlocking joint found in the spine?




Interspinal
Compound
Disc
Facet



How much do you know?
Which of the following is a high-risk activity?




Reaching above head height
Carrying a load
Moving a load at chest height

Pushing a handcart

Legal duties and responsibilities Module 3
Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974
“
Every employer must ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, the health, safety and welfare at work of all employees Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974.
”
Number of people exposed What is ‘reasonably practicable’?
Reduction in risk
Severity
Likelihood
Materials
Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 (HASWA)
An employer’s duties are to:
• provide and maintain safe equipment
• provide safe systems of work
• provide information, instruction, supervision and training
• provide a safe place of work
• provide a safe working environment
• consult employees
• have a health and safety policy (written when there are 5 or more employees).
Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
Employers must provide comprehensible and relevant information on:
• risks to their employees’ health and safety
• control measures
• emergency procedures
KEY POINT
This must be done using a language that is understood.

Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
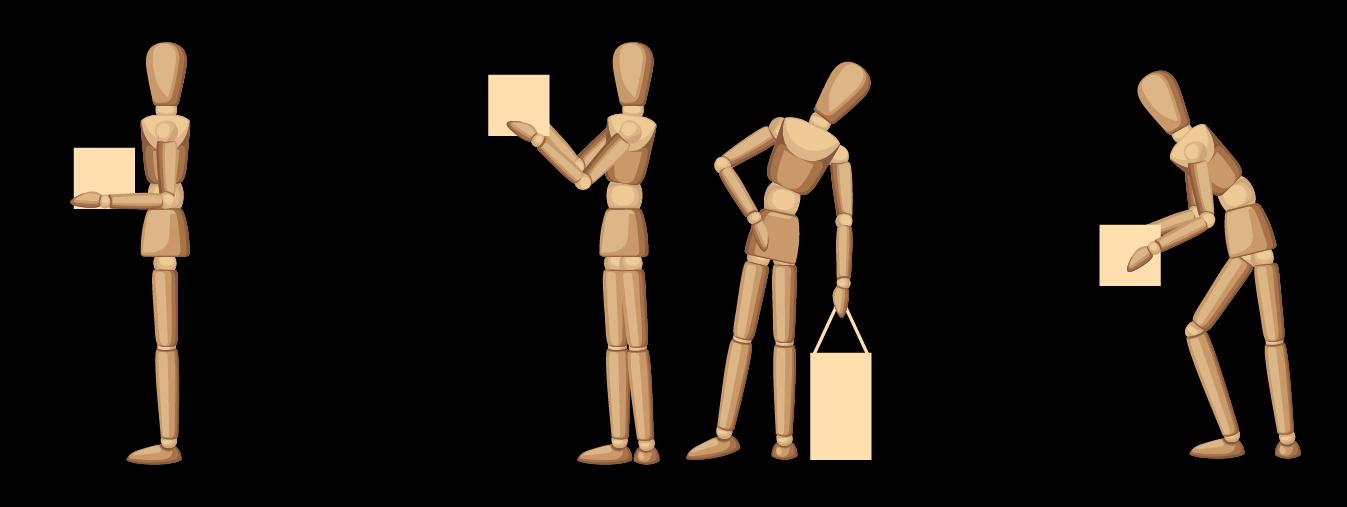
Employers must take into account the capability of any employee before giving them a task to complete.

Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
KEY POINT
Employers must ensure that employees are provided with adequate health and safety training:
• on recruitment
• on being exposed to increased risk
• on a change of job or equipment
• from time to time (refresher training).
Employers’ responsibilities under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992
AVOID manual handling operations where possible
ASSESS the risk of injury from any manual handling operation that can’t be avoided
REDUCE the risk of injury from manual handling operations, so far as is reasonably practicable.
Employers’ responsibilities under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992
REVIEW all manual handling assessments according to the risk or whenever any significant change occurs
RECORD significant assessments. These must be recorded when there are 5 or more employees.
Employees’ duties and responsibilities
• Cooperate with the employer
• Take reasonable care of themselves and others
• Do not alter the equipment provided and use it as instructed
• Report any faults or defects
• Inform the employer if they identify hazardous handling activities
• Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 (HASWA)
• Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
• Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992.
Enforcement of the law
Local authority environmental health officers
• Shops, offices, residential homes, warehousing and entertainment
Health and Safety Executive (HSE)
• Factories, hospitals, nursing homes, mines, schools and construction sites.
Consequences and penalties of non-compliance
Enforcement action hierarchy
Informal advice given during an inspection
A formal letter or advice issued after an inspection
An improvement notice is served
A prohibition notice is served
Prosecution commences.





How much do you know?
Which regulations provide guidance on how to reduce the risks associated with manual handling activities?




Handling and movement regulations
Manual handling in the workplace regulations
Lifting, lowering and carrying regulations
Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992



How much do you know?
According to the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974, the employee must take _________ care of themselves and others.







How much do you know?
Who must provide a safe place of work as defined in the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974?




The employer
The employee
The safety officer
The competent person


Risk assessments

What is a hazard?

Hazard Something that has the potential to cause harm.

What is a risk?
Risk
The likelihood of harm occurring.



Who undertakes a manual handling assessment?
A competent person
Competent person
Has appropriate skills, knowledge and experience

Knowledge
Skills
Has qualifications in health and safety relating to that type of workplace Is able to implement that knowledge in the workplace effectively
Experience
Has experience in the employer’s type of work
Other qualities
Has good communication skills and attitude.

Load
What would you need to know about a load before moving it?
Is the load:
• heavy?
• difficult to manage?
• bulky?
• unstable or likely to move unexpectedly, for example, if it contains animals or liquids?
• harmful, for example, hot or sharp?
• awkwardly stacked?
• too large to see over?

Individual capability (you)
What do you need to consider about yourself before
carrying out manual
handling?
• Are you fit enough (fatigue level)?
• Are you ill?
• Any past/present injuries to consider?
• Have you been trained with this load?
• What are your handling skills like?
• Are you pregnant?
• Are you familiar with the equipment?
• Do you know the ability of your partner for team lifting?
• Do you need a particular level of strength or other physical requirements?

What you need to know before attempting manual handling
Does it involve:
• holding loads away from the trunk?
• introducing unsatisfactory body movements, such as twisting, reaching upwards or stooping?
• excessive lifting distances?
• moving the load a considerable distance?
• strenuous pushing or pulling?
• a risk of sudden movement?
• frequent or prolonged physical effort?
• a process-imposed work rate?

Environment
What you should know before manual handling
Are there:
• space constraints preventing good posture?
• floors that are uneven, slippery or unstable?
• obstructed floors and traffic routes?
• extremely hot or cold working conditions?
• changes in levels due to steps or ramps?
• chances of strong gusts of wind?
• poor lighting conditions?
• surfaces at different heights?
• any other hazardous conditions?

Equipment and work organisation
What are the other factors to be considered before manual handling?
• Is movement hindered by work equipment?
• Is the work equipment being used unsuitable?
• Is movement hindered by personal protective equipment?
• Is there an indication of a lack of training or information from employees?
• Is the job boring?
• Is the job repetitive?
• Is communication between management and staff failing?
HSE Manual Handling Assessment
Chart ‘MAC’ tool
Hand distance from the lower back
Observe the task and examine the horizontal distance between the operative’s hands and their lower back. Always assess the worst-case scenario. Use the following to guide your assessment
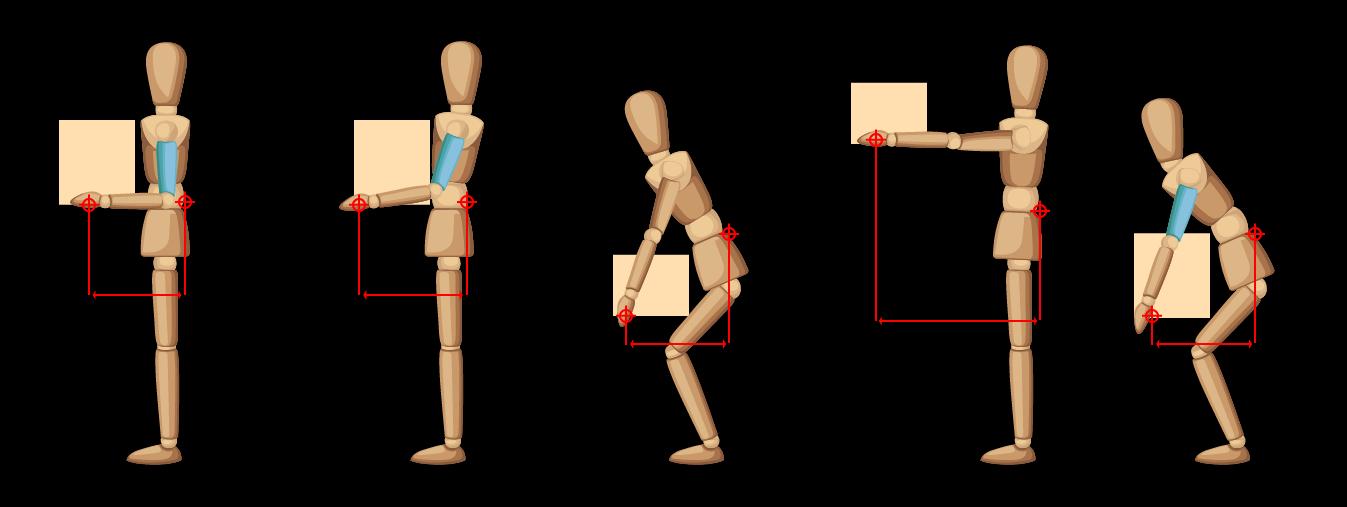
Upper arms vertical AND torso upright
Hands close to the low back G/0
Hands at moderate distance from the low back
Upper arms angled away from torso Torso bent forward G/0
Torso upright. Arms fully outstretched
Hands far from the low back
Upper arms angled away from torso AND torso bent forward R/6
HSE Manual Handling Assessment
Chart ‘MAC’ tool
Vertical lift region
Observe the position of the operative’s hands at the start of the lift and as the lift progresses. Always assess the worst-case scenario. Use the following illustrations as a guide Hands
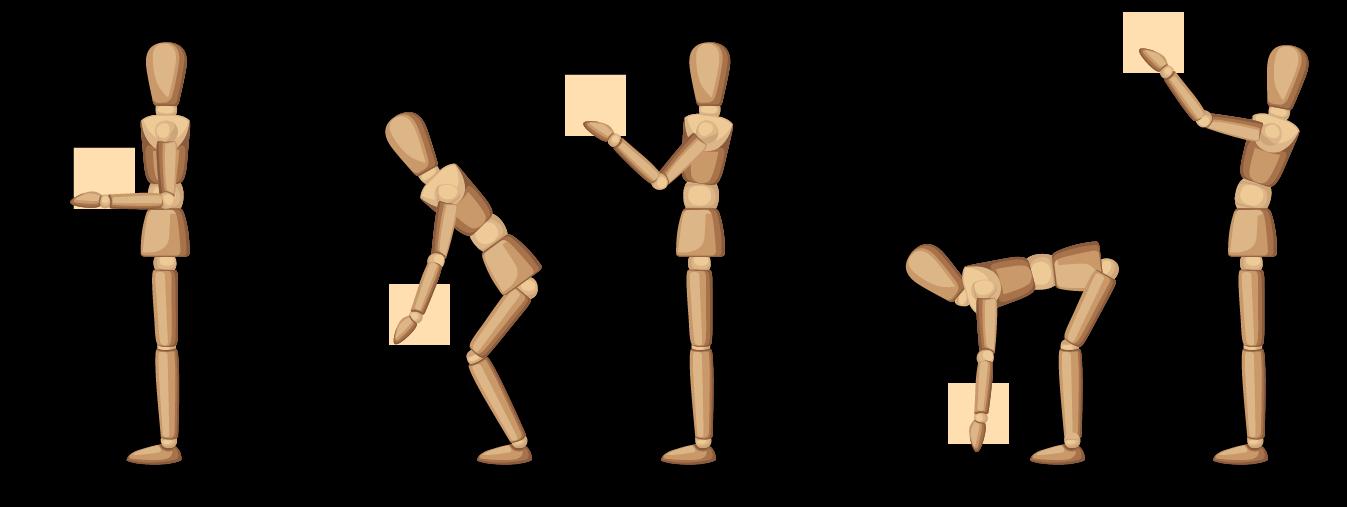
HSE Manual Handling Assessment
Chart ‘MAC’ tool
Torso twisting and sideways bending
B. Hand distance from the lower back
Observe the task and examine the horizontal distance between the operative’s hands and their lower back. Always assess the ‘worst case scenario’. Use the following to guide your assessment:

Observe the operative’s torso as the load is lifted. If the torso twists in relation to the hips and thighs or the operative leans to 1 side as the load is lifted, the colour band is amber and the numerical score is 1. If the torso both twists and bends to the side as the load is lifted, the colour band is red and the numerical score is 2 Little or no torso
HSE Manual Handling Assessment
Chart ‘MAC’ tool
G = green – low level of risk
Although the risk is low, consider the exposure levels for vulnerable groups, such as pregnant women or young workers, where appropriate.
A = amber – medium level of risk
Examine tasks closely.
R = red – high level of risk
Prompt action is needed. This may expose a significant proportion of the working population to a risk of injury.
P = purple – very high level of risk
Such operations may represent a serious risk of injury and should come under close scrutiny, particularly when the entire weight of the load is supported by 1 person.
The colour-coding helps to identify the level of risk. Which colour requires immediate action to reduce risk?


How much do you know?
Which of the following is a manual handling hazard?







How much do you know?
A _________ is something with the potential to cause harm.




Warning Danger
Hazard
Risk



How much do you know?
What is meant by the word ‘risk’?




The potential to cause harm
The danger presented by an activity
The lack of safety
The likelihood of harm occurring



How much do you know?
Before asking an individual to undertake a work activity, the employer must take into account their:






Manual handling controls Module 5

How can we reduce the risk?
The load
Can the load be made:
• lighter?
• less bulky?
• easier to grasp?
• more stable?
• less damaging to hold?
KEY POINT
Employers must ensure that employees are provided with adequate health and safety training.

How can we reduce the risk?
The individual
• Individuals’ capabilities must always be given priority
• Employees must be given full details on the tasks they will be expected to undertake
• Where higher risks of manual handling injuries are identified, specific training must be given
• Procedures to protect new or expectant mothers must be in place
• Employees must be given information on the tasks they are likely to face in the workplace
• Policies and procedures must be adjusted to address temporary capability issues
• Work clothing and personal protective equipment, when worn, must be suitable for manual handling activities.

How can we reduce the risk?
The task
• Use appropriate equipment designed to assist with lifting/handling
• Make amendments to the workplace’s layout o reduce high-risk movements, such as twisting and stooping
• Improve efficiency in the workplace by introducing changes to the layout and processes
• Avoid lifting from floor level
• Avoid lifting above shoulder height
• Vary work routines
• Reduce the activities that require repetitive handling
• Push rather than pull.

How can we reduce the risk?
The environment
• Make the workplace obstruction-free to allow a full range of movement
• Ensure flooring is suitable and does not cause slips or trips
• Improve environmental conditions, such as lighting, heating and ventilation
• Redesign work processes and procedures to avoid steps or steep ramps
• Ensure staff maintain correct posture by redesigning the workplace if necessary.

How can we reduce the risk?
Other factors
Work organisation
• Rotate tasks or make adjustments to the work routine to reduce boredom
• Reduce the number or frequency of mundane tasks where practicable
• Utilise individuals’ skills more effectively
• Make deadlines and targets achievable and safe
• Involve the entire workforce in communication and assessments
• Make manual handling training relevant to the manual handling activities carried out in the workplace.

How can we reduce the risk?
Other factors
Equipment
• Utilise competent advice to ensure the correct equipment is obtained
• Ensure the type of wheels used are suitable for the workplace flooring
• Make sure grips and handles are in good order and suitable, particularly when gloves are worn
• Ensure work equipment is suitably maintained and always fit for purpose
• Brakes should be effective and easy to use.
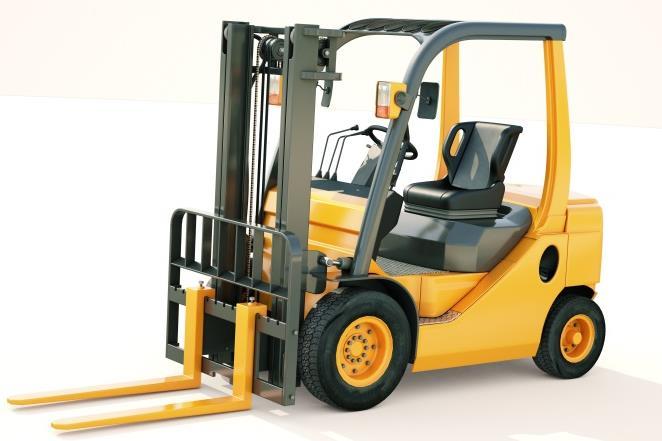
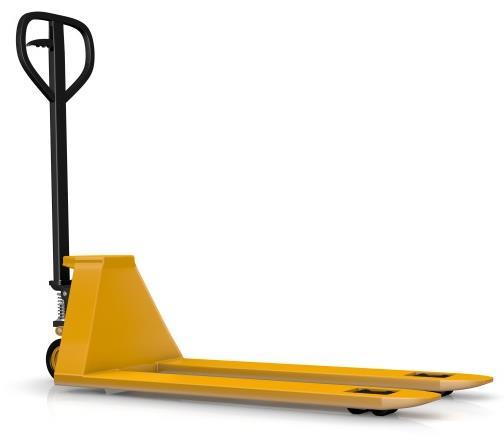
Reducing the risk
Equipment designed to handle loads.







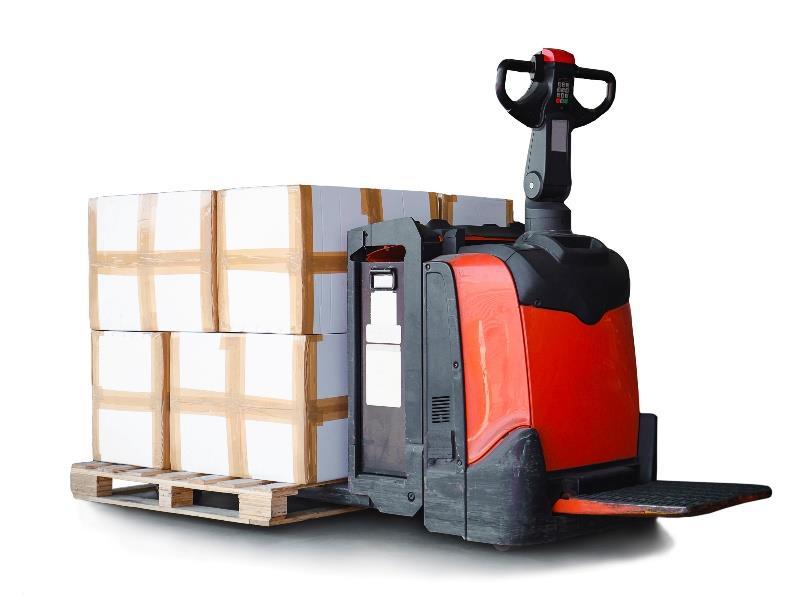
Reducing the risk
Equipment designed to carry people and loads.


The safety of lifting and handling equipment
Daily user checks – visual and manual checks for damage and that safety devices, wheels and brakes are working
The employer must maintain, service and test lifting equipment and hoists in accordance with manufacturers’ instructions
Equipment that is subject to the Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) must be tested and examined by a competent person and have a valid certificate of ‘thorough examination’
Passenger-carrying lifts and hoists – examined every 6 months
Non-passenger-carrying lifts or hoists – examined every 12 months.

How much do you know?
Which of the following control measures would reduce the risk from the load?




Avoid lifting from floor height
Make the workplace obstruction
Ensure the wheels on the equipment are suitable for the flooring

Provide hand holds on boxes


How much do you know?
Which of the equipment listed below would MOST effectively reduce the manual handling of a load?




A bucket on wheels
A conveyor belt system

A wheelchair
A hand pallet truck


How much do you know?
Equipment that is subject to the Lifting Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) requires which type of certificate?




Thorough examination
Annual examination

Six-monthly certificate
Safety certificate


How much do you know?
Which of the following control measures would reduce the risk from the TASK?




Avoid lifting above head height
Check the safe working load

Avoid steep steps or ramps
Check the individual’s capability

Principles of safe movement
Three key safe movement principles
Safe movement principles
Warm up
Check load
Is help needed?
Plan
Clothing
Grip
Repetitive strain injuries
Storage.
Safe movement principles

Stop and think.
Safe movement principles

Position the feet.
Position of feet
Safe movement principles
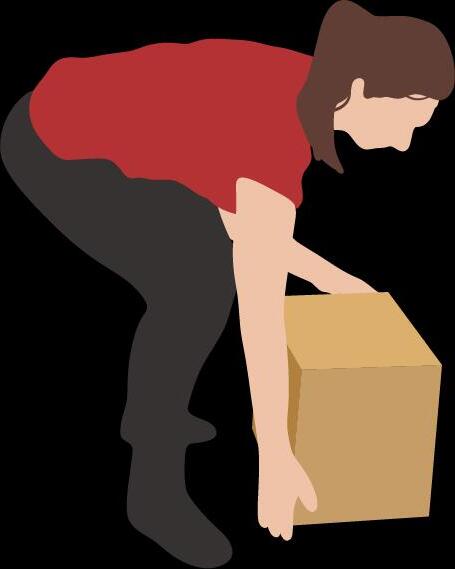

Safe movement principles
Lift with a firm grip and keep the back slightly flexed. 4
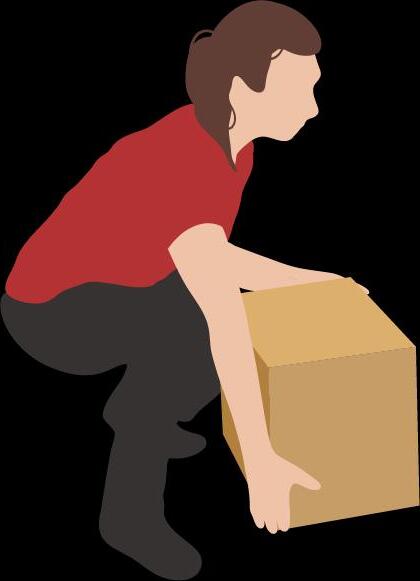

Safe movement principles

Raise the load with the legs.
Safe movement principles

Keep the load close to the body.
Carrying loads
Keep the load close to the body
Avoid changing your grip
No twisting
Look where you are going
Do not obstruct your vision
Use mechanical aids.
Unloading
Keep the direction of unloading square on
Bend the knees
Allow for slight back flexion
Watch your fingers!
Rest the load
Slide Secure.
Pushing and pulling
Tips when pushing and pulling
• Use handling aids with handles between the shoulder and waist
• Ensure the movement is within the individual’s capability
• Make efforts to remove the need to push or pull when on slopes, either up or down
• Manage uneven surfaces
• Maintain correct stance
• Maintain correct pace.
Team handling
Where there is more than 1 person involved,the risk of injury goes up, so:
assess the load
plan the movement decide who will give the orders check that all of the team is ready before beginning and that all can communicate ensure instructions are clear and incisive, for example, ‘ready, steady, go’

Remember that putting down needs just as much organisation as the lift.






2 How much do you know?
What is the correct sequence of the safe movement principles?
Position the feet
Get a firm grip and keep the back slightly flexed
Stop and think
Raise with the legs
Bend the knees
Keep the load close to the body.



How much do you know?
Which of the following is a safe movement principle?




Keep the back stiff and straight
Keep the back slightly flexed
Lift with the back
Twist the back to change direction



How much do you know?
Which of the following would be the best method of reducing the risk of manual handling injuries?




Automate the process
Provide back support belts for lifting
Instruct staff in safe lifting techniques
Use manual lifting equipment



How much do you know?
Which of the following statements is true?




When there is more than 1 person involved in a task, the risk of injury goes down
When there is more than 1 person involved in a task, the risk of injury goes up
When there is more than 1 person involved in a task, the risk of injury may go up or down

When there is more than 1 person involved in a task, the risk of injury remains the same


How much do you know?
Which of the following is correct?




Loads should be carried close to the body
Loads should be carried at arm’s
length Loads should not be carried further than 25m

Loads should not be wider than the body


1. Open the Cameraor QR code scanner to scan the code.
2. If QR code scanner is not available, pleasevisit the weblinkprovided below.
https://bit.ly/4egSxXb
“NowIt’sA
ScantheQRCodeand leaveusareviewon


Thank you for listening



