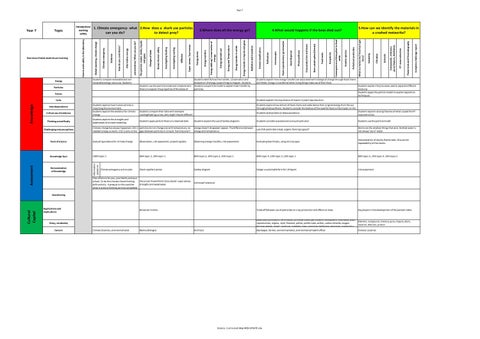
Year 7
Energy
Students compare renewable and non renewable energy resources. Students Students use the particle model and simple kinetic theory to explain the properties of the states of
Particles
Students identify how the transfer, conservation and dissipation of energy causes things to happen. Students Students use particle model to explain heat transfer by particles.
Students explore how human activity is impacting the environment. Students explore the evidence for climate change
Students analyse data on bee populations.
Students explore varying theories of what caused the KT mass extinction.
Students explore the use of Sankey diagrams
Students consider pseudoscience around pollution
Students use the particle model
Climate change has always happened, CO2 is particles do not change size with temperature, no needed to keep us warm, CO2 is only a time gaps between particles in a liquid. Particles aren't
energy doesn't disappear/ appear. The difference between energy and temperature.
use of all pesticides is bad, organic farming is good?
Atoms are the smallest things that exist. Bottled water is not always "pure" water.
Tools of science
Evaluating evidence for climate change
Observation, risk assessment, presenting data
Observing energy transfers, risk assessments
Evaluating bee threats, using microscopes
Interpretation of results; flames tests. Discuss the repeatability of the results.
Knowledge Quiz
100% topic 1
80% topic 2, 20% topic 1.
80% topic 3, 10% topic 2, 10% topic 1
80% topic 4, 10% topic 3, 10% topic 1
80% topic 5, 10% topic 4, 10% topic 2
Demonstration of Knowledge
Shark repellent poster
Sankey diagram
Design a sustainable farm for Littleport
risk assessment
Trade off between use of pesticides on crop production and effects on bees.
Key players in the development of the periodic table.
pesticides, pollination, fertilisation, photosynthesis, germination, ecosystems, food webs, plant reproduction, stigma, style, filament, pollen, pollen tube, anther, carbon dioxide, oxygen, glucose, energy, insect, producer, predator, prey, carnivore, herbivore, omnivore, community,
Element, compound, mixture, pure, impure, atom, neutron, electron, proton
Bee keeper, farmer, environmentalist, environmental health officer
Forensic scientist
Critical use of evidence Thinking scientifically Challenging misconceptions
Students explore the strengths and weaknesses of climate modelling
Climate emergency action plan
Students compare their data with exemplar cooling/heating curves, why might they be different Students apply particle theory to observed data
Plan of action for you, your family and your Voice over PowerPoint/ story board- super senses, school. Or do the climate chane thinking strengths and weaknesses skills activity. A prequal to this could be what is science thinking activity completed
Ice house? practical
Questioning
Cultural Capital
Complete challenge report
Flame tests and Chromatography
KT- mass extinction
Compounds , mixtures, pure/impure, distillation
Solvents
Students explore how almost all food chains and webs derive their original energy from the sun through photosynthesis. Students consider the balance of the need for food vs the impact on the
information poster on difference
Knowledge
Filtration
Students explain the processes used to separate different mixtures. Students apply the particle model to explain separation techniques. Students explain the importance of insects in plant reproduction.
Cells
Assessment
Solubility
Pollution/ pesticides
Invasive species
Consequences of disruption to food webs
Ecosystems
Food webs
Bees catastrophes (threats)
Crop production and issues
Photosynthesis
Seed dispersal
Plant reproduction/ germination
microscopes
Pollination
Animal classification
Students explain how energy transfers are associated with biological change through food chains and Webs. Energy is transferred when living things make use of their food.
Forces
Interdependence
What is a meteorite? How has it got here?
5.How can we identify the materials in a crashed meteorite?
4.What would happens if the bees died out?
Radiation and insulation
Energy transfer in liquids and gases
Energy transfer in solids
Energy and Temperature
Energy spreads out
Energy adds up/ conservation of energy
Energy transfers
3.Where does all the energy go?
Energy stores
Super senses. Top trumps
Diffusion
investigating cooling
investigating heating
Bunsen Burner safety
Changes of state
The particle model, Solids, liquids and gases
presentation/ What can you do?
Alternative energy
How do you contribute?
Evidence
1. Climate emergency- what 2.How does a shark use particles can you do? to detect prey?
Climate emergency
Overview of what students are learning
Introduction/ working safely
Global warming, climate change
Topic
How to work safely in the laboratory
Year 7
Applications and implications
Brownian motion.
Oracy, vocabulary Careers
Climate Scientist, environmentalist
Marine Biologist
Architect
Science - Curriculum Map WEB UPDATE.xlsx