Year 7
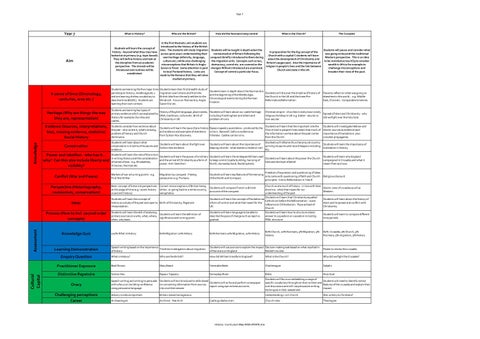
Year 7
Aim
A sense of time (Chronology, centuries, eras etc.) Heritage (Why are things the way they are, representation)
Knowledge
Evidence (Sources, interpretations, bias, missing evidence, statistics) Social History Conservation Power and rebellion - who has it… why? Can this also include liberty and visibility? Conflict (War and Peace) Perspective (Historiography, revisionism, conservatism) Ideas
Assessment
Process (How to incl. second order concepts)
Knowledge Quiz
Who are the British?
How did the Normans keep control
What is the Church?
The Crusades
In the first thematic unit students are introduced to the history of the British Studnets will learn the concept of Isles. The students will study migration Students will be taught in depth aobut the Students will pause and consider what history - beyond what they may have In preparation for the big concept of the across 5000 years understanding their normanisation of Britain following the was going on beyond the traditional looked at at primary (e.g. topic based). Church with a capital C students will learn own heritage (ethnicity, language, conquest (briefly introduced to them during Western perspective. This is an idea They will define history and look at about the development of Christianity and culture etc.) while also challenging the migration unit). Concepts such as tax, to be revisited across KS3 to consider the discipline from an academic Britain's pagan past. Also the importance of misconceptions that Britain is Anglodemocracy, conrol etc. are covered as the wealth in Africa for example to perspective. The strands will be religion in people's lives and the link between Saxon or fixed. Some attention is paid changes William introduced are examined. challenge misconceptions and introduced and routines will be Church and state in the UK. to local Fenland history. Links are Concept of control a particular focus. broaden their vista of the past. established. made to the Romans that they will ahve studied at primary.
Students are learning the five major time periods (pre-history, middle ages etc.) and are learning the key vocabulary to describe time (BC/DC). Students are learning their own context.
Students learn their first breadth study of migration over time to and from the British Isles from the early settlers to the Windrush. Focus on 'Roman Era, Anglo Saxon Era' etc.
Students learn in depth about the Norman Era Students will discover the timeline of history of and the beginning of the Middle Ages. the Church in the UK and the times PreChronological events during the Norman Reformation/Reformation. Invasion.
Students are learning key types of History of English language, place names, Students will learn about our castle heritage primary evidence which are explained by DNA, traditions, culture etc. Birth of including Framlingham and others and History for example churches and Christianity in UK problem of ruins castles. Students consider how we know about the past - who wrote it, what's missing, problem of literacy and Church dominance
Christian empire - churches in every town (visit), Spread of Islam and Christianity - why religious holidays in UK e.g. Easter - secular vs did we fight over the holy land. non-secular.
Students will learn that the important role the Students will learn the issue of pre-history Bayeux tapestry as evidence - produced by the Church had in people's lives meant that much of and evidence and examples of eveidence victors. Beowolf, Celts no evidence as the information we have about the past comes from Sutton Hoo discovery. illiterate. Castles can be ruins. from the Church.
Students will learn about what Students will learn about the fight over conservation is in terms of museums and Sutton Hoo evidence. evidence.
Studnets will reframe Churches around country Students will learn about the importance of as living museums and record keepers including keeping records - what statistics reveal or not! Ely.
Students will learn the role of the victors Students will learn the power of a military Students will learn the strategies William used in writing History and the consideration Students will learn about the power the Church and the arrival of Christianity as a form of to keep control (caslte building, harrying of of names of eras - e.g. Elizabethan, held and the level of belief. power. Anti-Semitism. North, domesday book, feudal system). Victorian, Norman etc. Markers of war as turning points - e.g. First World War
Migration by conquest. Fleeing persecution e.g. Puritans.
Basic concept of historical perspectives - Correct misconceptions of Britain being at this stage of time (e.g. recent history white - or going back to a white country, vs ancient history) xenophobia Studnets will learn the concept of history as a study of the past and open to Birth of Chrisianity, Paganism interpretation.
Pause to reflect on what was going on elsewhere in the world… e.g. Middle East, China etc. Comparable timelines.
Freedom of expression and questioning of ideas Studnets will learn key features of the Harrying only came with questioning of faith and Church of the North and its impact. principles - link to Reformation in Year 8 Church wrote much of history - in line with their doctrine - what that means for our understanding of the past Students will learn that Christianity equalled Students will learn the concept of Feudalism as Catholicsm before the Reforemation - some a form of control and what that meant for the reference to Orthodoxism. Pope as head of UK. Church Students will compare French vs British accounts of the conquest.
Students will investigate Hebrew and Islamic sources as evidence (and importance of translation)- plus consider propaganda. Studnets will learn the importance of translation in history. Students will learn why England campaigned in Crusades and what it meant then and now.
Religious discourd
Islamic view of crusades as wll as Western. Students will learn about the history of Islam and its spread and conflict with Christianity.
Students will learn the skill of analysing Students will learn the definition of primary sources on a who, what, where, significance and turning point. when, why basis.
Students will learn language to be able to describe the pace of change such as rapid vs. gradual.
Students will learn how to structure a basic answer to a question on causation including PEEL structure.
Students will learn to compare different time periods.
100% What is History
80% Normans 10% Migration, 10% History
80% Church, 10% Normans, 5% Migration, 5% History
80% Crusades, 5% Church, 5% Normans, 5% migration, 5% History
80% Migration 20% History
Speech writing based on the importance Timeline investigation about migration of history
Students will use sources to explain the impact Decision making task based on what resulted in of Normans on England Becket's murder.
Poster to review the crusades
What is History?
Who are the British?
How did William transform England?
What is the Church?
Why did we fight the Crusades?
Practitioner Exposure
Basil Brown
Mary Beard
Venerable Bede
Charlemagne
Saladin
Distinctive Repetoire
Sutton Hoo
Bayeux Tapestry
Domesday Book
Bible
Holy Grail
Learning Demonstration Enquiry Question
Cultural Capital
What is History?
Oracy Challenging perceptions Career
Speech writing and writing to persuade Students will be introduced to skills based Students will write and perform a newpaper with a focus on building confidence on converting information from sources report using eye-witness accounts. using persuasive language into a written answer
Students will focus on embedding a range of Students will need to identify certain specific vocabulary throughout their written and features of the crusades and explain their oral discussions and will use persuasive writing impact. techniques in their assessment.
History is old/unimportant.
Britain is/was homogenous.
Understanding c vs C church
War unholy to Christians?
Archaeologist
Archivist - Nat Arch
Church roles
Theologian
Castle guide/tourism
History - Curriculum Map WEB UPDATE.xlsx