

� Artificial Intelligence in 2025: Regulation, Jobs & Global Impact
Introduction: AI at a Turning Point
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has entered 2025 as one of the most transformative forces in human history. Over the last decade, its progress has accelerated at an exponential rate moving from narrow, task-specific models to advanced, general-purpose systems that can reason, plan, and adapt. Generative AI tools such as OpenAI’s GPT series, Google’s Gemini, and Anthropic’s Claude have become mainstream in workplaces, homes, and educational institutions.
The year 2025 marks a critical turning point:
• Governments are racing to implement regulations that balance innovation with public safety.
• Businesses are integrating AI into core operations to cut costs and boost productivity.
• Workers are navigating a rapidly changing job market where entire professions are being redefined.
The stakes are high. Proper governance could usher in an era of unprecedented prosperity. Poorly managed, AI could deepen inequality, destabilize economies, and erode public trust in information.
By Shoroc.com
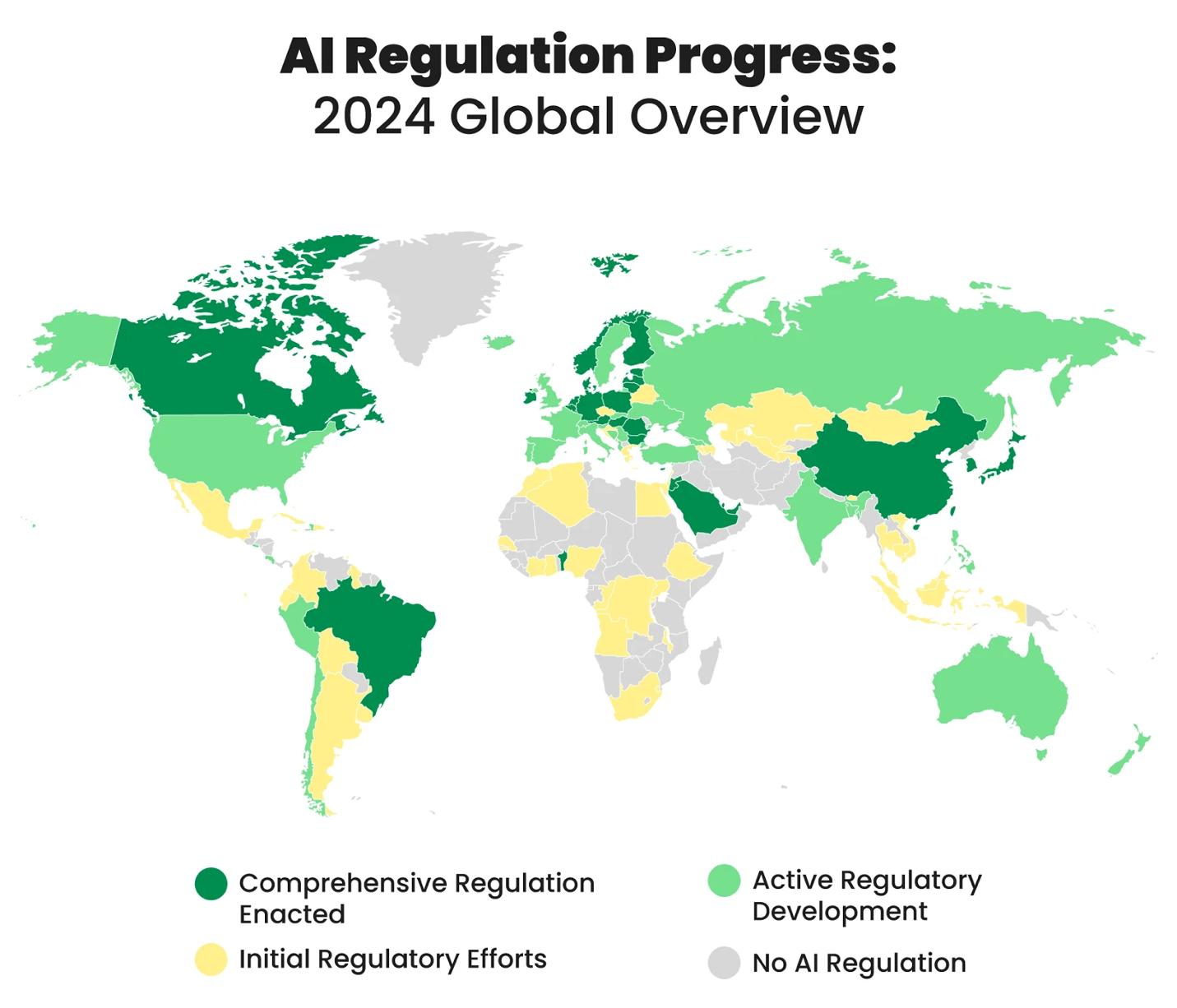
The Global AI Regulatory Landscape
Why Regulation is
Urgent
Unregulated AI poses risks in several domains:
1. Bias & Discrimination – AI systems trained on flawed data can perpetuate or amplify societal biases.
2. Privacy Violations – Generative AI models can infer personal information from seemingly harmless queries.
3. Misinformation – Deepfakes and AI-generated propaganda threaten democratic processes.
4. Economic Disruption – Sudden job losses without retraining programs can harm economic stability.
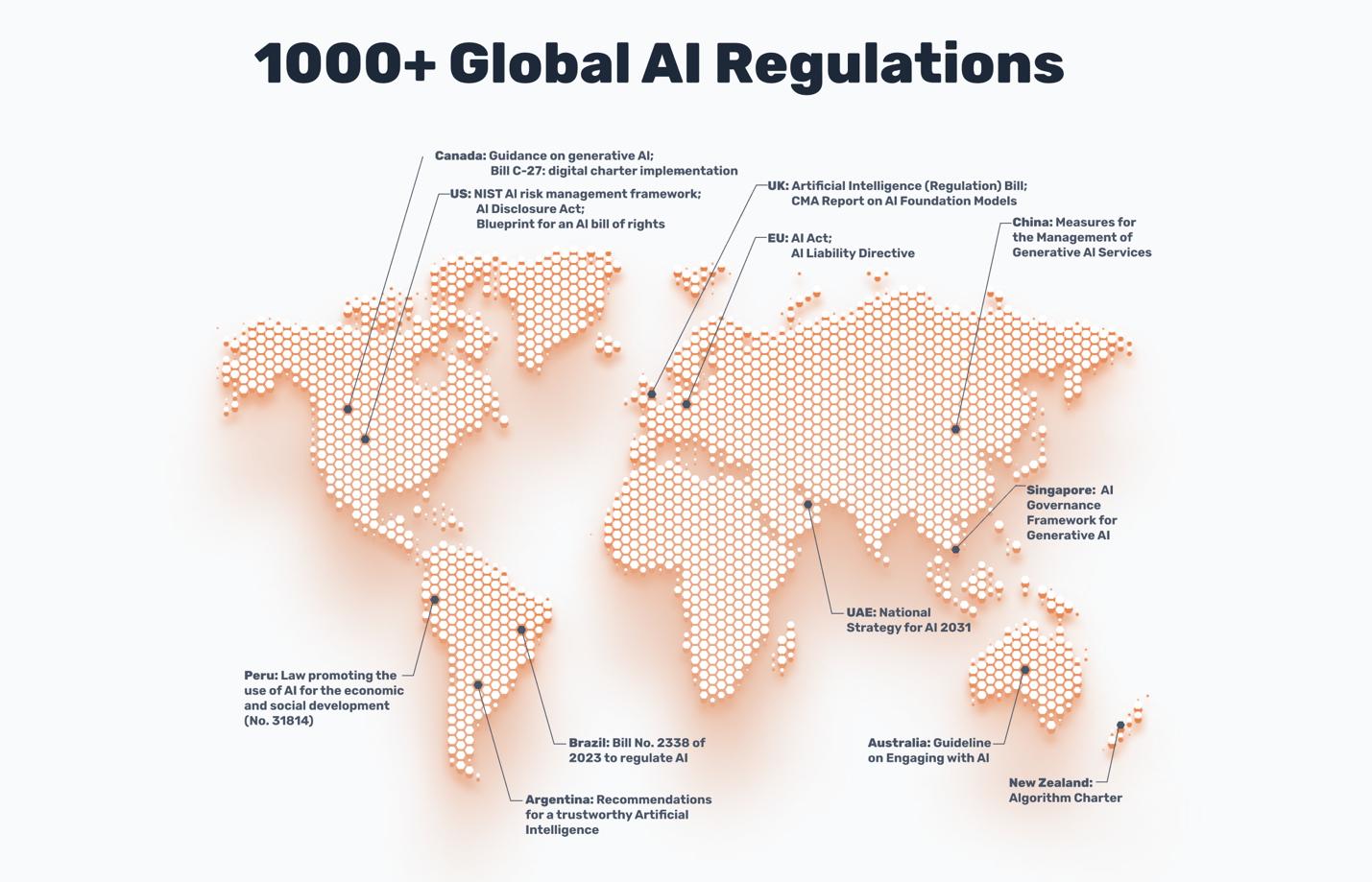
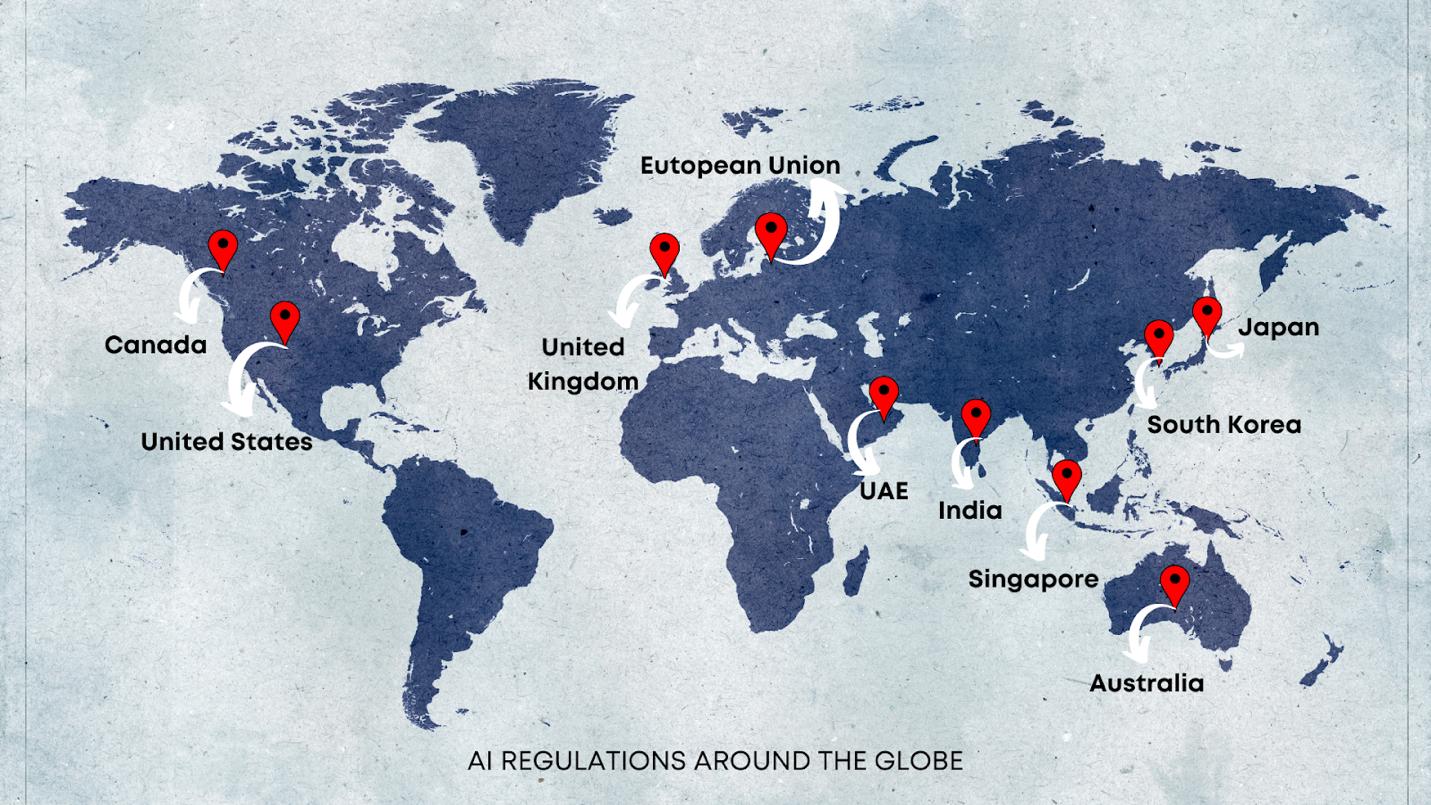
Key Players & Their Approaches
European Union (EU) – AI Act
The EU AI Act, formally enforced in February 2025, is the most comprehensive regulation to date. It adopts a risk-based classification:
• Unacceptable Risk – Banned outright (e.g., social scoring, manipulative AI in toys).
• High Risk – Strict compliance required (e.g., AI in healthcare, law enforcement).
• Limited Risk – Transparency requirements only.
• Minimal Risk – Largely unregulated.
The EU Act mandates third-party audits for high-risk AI and imposes fines up to €35 million or 7% of global turnover for violations.
United States
The U.S. has no single AI law, but the AI Bill of Rights Blueprint and sector-specific rules from agencies like the FTC and NIST are shaping corporate behavior. States such as California and New York have passed AI bias laws targeting hiring and credit-scoring algorithms.
China
China’s Generative AI Provisions require all AI outputs to align with “core socialist values” and undergo security assessments. AI must be registered with government authorities before public release.
By Shoroc.com
Other Regions
• Canada: Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA) pending approval.
• Japan: Soft law guidelines focusing on ethical AI.
• Gulf States: UAE and Saudi Arabia investing heavily in AI infrastructure, with lighttouch regulation to attract innovation hubs.
� Suggested Table:

Country/Region Regulation
EU AI Act Yes Very High 2025
USA AI Bill of Rights (nonbinding) No Medium Draft
China Generative AI Provisions Yes High 2024
Canada AIDA No Pending 2025

� Suggested Map: Color-coded heatmap of AI regulation status by country.
By Shoroc.com
AI’s Impact on Employment
The Automation Wave
AI adoption is automating routine, repetitive, and data-heavy work:
• Legal: Contract analysis, discovery.
• Finance: Fraud detection, algorithmic trading.
• Retail: Inventory management, automated checkouts.
• Healthcare: Diagnostic imaging, patient triage.
World Economic Forum data (2025):
• Jobs displaced by AI by 2030: ~92 million globally.
• Jobs created by AI by 2030: ~78 million.
• Net change: –14 million jobs.
The New Jobs
Emerging roles include:
• AI Prompt Engineers – crafting effective prompts for generative AI tools.
• MLOps Engineers – managing AI deployment pipelines.
• AI Ethics Officers – ensuring compliance and fairness in AI applications.
• Synthetic Data Specialists – generating artificial training data for privacy-preserving AI.
� Suggested Table:

Job Title Avg Salary (US) Growth Rate (2023–2030)
Prompt Engineer
$120,000 +45%
AI Ethics Officer
$110,000 +39%
MLOps Engineer
$125,000 +41%
� Suggested Graph: Bar chart comparing jobs lost vs. jobs created from 2020–2035.

Economic Ripple Effects
AI’s economic influence extends beyond automation:
• Productivity Boost: IMF projects AI could add $7 trillion to global GDP by 2035.
• Cost Savings: McKinsey reports AI can cut operational costs by up to 25% in certain industries.
• Inequality Risks: Countries without AI infrastructure risk widening the economic gap the “AI Divide.”
Case Study: Germany has integrated AI into manufacturing (Industry 4.0), leading to efficiency gains but also triggering labor strikes over job losses.
By Shoroc.com
Future Scenarios
1. Optimistic – AI complements human labor, boosts GDP, and improves quality of life through better healthcare, education, and governance.
2. Pessimistic – Poor regulation leads to massive unemployment, disinformation crises, and concentration of AI power in a few corporations.
3. Mixed Reality – Gradual adaptation; some industries thrive, others collapse.
By Shoroc.com
Conclusion
AI in 2025 stands at a regulatory, economic, and social crossroads. Governments, businesses, and individuals must act now to ensure that this transformative technology is deployed ethically and inclusively. The future will not be determined solely by the sophistication of AI models, but by how we choose to govern and integrate them into human society.
By Shoroc.com
