International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 |Sept-2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 |Sept-2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1PG Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering, Dr. Sau. Kamaltai Gawai Institute of Engineering & Technology, Darapur, Amravati, Maharashtra, India 2 Assistant Professor, Dr. Sau. Kamaltai Gawai Institute of Engineering & Technology, Darapur, Amravati, Maharashtra, India -*** -
Abstract - Significant work has been put into developing digital relaying algorithms becauseofthemanyadvantagesof digital relaying in terms of economy, performance, dependability, flexibility, and system interaction. In thisstudy, numerous methods established for the differential protection of three-phase transformers are surveyed and compared. The algorithms introduced for digital relaying are described after a brief examination of the concept, the issues with differential protection of transformers, and the existing solutions as implemented with conventional (electromagnetic) relays.
The article discusses boththemostcontemporarytechnologies for transformer protection, such as artificial neural networks (ANN) and fuzzy logic, as well as more traditional ways. The use of ANN and fuzzy approaches for the safety of power transformers is stressed more than the use of conventional methods, which are just briefly mentioned.
Key Words: Differential Protection, Power Transformer
Beingoneofthemostexpensivepartsoftheelectricalpower system, the power transformer needs to be well secured from internal problems. Transformers frequently incur transient faults, which can overwhelm the differential protection'swindingcurrenttransformers(CTs).Throughfaults with a saturated CT might cause the transformer breakers to trip and the differential protection to operate improperly.
About 11.62% of power transformer failures are due to windingdefects,accordingtoa CIGREtechnical paper[2]. Duetoitseaseofuseandspeedyfunctioning,thedifferential relayisthemainpieceofprotectiveequipmentinbigpower transformers[3].Inrushcurrent,whichisatransientcurrent with an 8–10 times bigger magnitude than the full load current, can flow in the transformer windings when a transformerisfirstpoweredorencountersarapidshift[4].
Inrush current and internal faults cannot always be distinguishedbydifferentialrelay[3,5].Variousapproaches andstrategies,whichmaybecategorisedintothreegroups, havebeenpresentedtodifferentiatetheinrushcurrentfrom
internal defects. The first category consists of signal processing techniques that extract the spectral and wave shapecharacteristicsofdatausingfeatureextractorslikethe wavelet transform(WT)andfastFourier transform(FFT) [6]–[9]. These approaches' drawbacks include a heavy computing cost, susceptibility to noise, and a particular tendencytobeaffectedbythresholdsettings.
Trialanderrorshouldbeusedtodeterminethethreshold values since otherwise the protection system's generality and dependability would suffer, especially in the face of outsideinfluences.Thesecondsetoftechniquesaremodelbasedtechniquesthataimtodetermineanexactestimation of the primary winding current by utilizing estimation techniques like the Kalman filter (KF) to find the magnetizinginrushcurrents[9].
Findingaquickandeffectivedifferentialrelaymethodthat separates the transformer from the system inflicting the leastharmisthekeyproblemintransformerprotection.As the algorithm distinguishes between the operating situations,itshouldalsoavoidperformingimproperly. An enhanced differential protection system for power transformersispresentedinarticleone.Thesuggestedplan isbasedonaratiooftheprimaryandsecondarycurrentsof eachphase'sabsolutedifferenceandabsolutesum,plusthe primary and secondary terminal voltages of each phase's absolute difference and absolute sum. The proposed algorithm aims to prevent improper operation that could result from transient phenomena like magnetic inrush current,simultaneousinrushwithinternalfault,andfaults with current transformer saturation. This mal-operation couldoccurwiththeconventionalthree-phasetransformers differential protection scheme. The suggested differential protectiontechniquehasbeeninvestigatedutilizingcurrent andvoltageratios,andtheresultsindicatethatitcandeliver a quick, precise, safe, and reliable relay for power transformers.
It is possible to distinguish between inrush and fault circumstancesusingthecurrentratio.However,transformer
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 |Sept-2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
energizationduetoaninternalproblemisidentifiedusing voltageratio.Additionally,thesuggestedrelayisrestrained usingthecurrentdirectioncriterionduringexternalfaults and heavy energization. Numerous fault- and non-faultrelated situations have been simulated. The suggested method successfully distinguishes between magnetising inrush and fault circumstances in less than a half power frequency cycle, as shown in article [1]. In many circumstances, itisalsoanalyzedif faultresistance and ct saturationexist.
Thefindingsdemonstratethat,dependingonthefaultcase, thesuggestedapproachmayquicklyidentifyandcategorize faultsituationsfromneutralendswith3%ofwindingsand higher. This method is determined to be straightforward, trustworthy,secure,andreliablefordifferentiatingbetween inrushcurrentsandfaultcurrents.
Awell-knownmethodforprotectingtransformers,motors, generators, buses, and other types of power equipment having input and output current measurements is the currentdifferentialprinciple.Theconceptisalsoutilizedto createpercentdifferentialprotectionthatmaybetunedtoa certainsensitivityfordetectingin-zonefaultsandsecurity duringexternalfaults.Thetypicalmethodforachievingthis protectivereliabilityistosimulateadifferential-restraining featurewithtworegions oneworkingandtheothernot while monitoring the actual differential restraint ratio during faults. The installed current transformers (CTs) would quickly get saturated by some external faults with large dc offset and high X/R system time constant, which wouldthenresultinhighdifferential/restraintratiosover thesetcharacteristicintheworkingzone.Thedifferential protectionwouldactivateinthesecircumstances,resulting inanunintendedtransformertrip.
Thearticlefocused[2]oncertainimprovementsmadetothe primary differential protection's differential concept and provided instructions on how to set up the protection for increasedsecurityandsensitivity.
faults, there may be instances in which dangerously high differential/restraint ratios cross the characteristic and causeanundesiredtrip.Itisessentialfortheprotectionto giveextrasecurityduringexternalfaultswiththeaidofearly CT saturation detection and directionality check. To configuretheprotectionforbestperformance,a thorough investigationofthesystem,includingthepowertransformer andcurrenttransformers,isrequired.
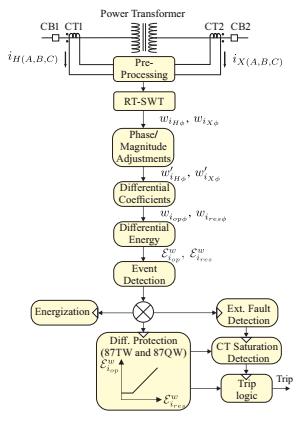
One of the primary issues with the power transformer differentialprotectionhasbeenthecurrenttransformer(CT) saturationphenomena,whichresultsininaccuratecurrent readings and improper relay functioning. In order to stabilize the relay during external faults and accurately distinguishCTsaturationfromcross-countryinternalfaults, one of the authors proposed [3] a quick and effective transformerdifferentialprotectionschemewithadditional differentialCTsaturationandcross-countryfaultdetection modules after the external fault detection. All of these moduleswerebasedonthedifferentialwaveletcoefficient energywithborderdistortions.
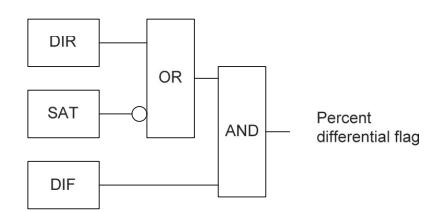
Fig-1: 87Tsecuritylogic[2]
If the differential/restraint feature is the only factor providing security, the transformer percent differential protectionisnotsufficientlydependableduringanexternal malfunction.DuetothesaturationofCTscausedbyexternal
Fig-2: Theproposedwavelet-basedtransformer differentialprotection[3]
With typical simulations of internal faults, transformer energizations, and external faults with CT saturations followedbycross-countryinternalfaults,theperformanceof the proposed technique was evaluated. While a phasor-
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 |Sept-2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
based conventional protection scheme only guaranteed 92.60%ofsuccessratewithanaveragerelayoperatingtime of19ms,theproposedwavelet-baseddifferentialprotection withonly87TWand87QWunitspresentedasuccessrateof 100%fordetectinginternalfaultswithanexpressiveaverage relayoperatingtimeof214s.Thesuggestedapproachwas themoststraightforward,efficient,andpreciseone.
Both the suggested and the traditional procedures were resistanttotheCTsaturationwithregardtothemanyevents tothepowertransformer.However,comparedtotheusual method, the suggested CT saturation detection module is simpler, needing simply the incorporation of a wavelet coefficientenergyincrement/decrementcounterasopposed tothestandardharmonic-basedfunctions.Additionally,the suggested approach guaranteed a 100% success rate in identifying cross-country internal problems from the database 4, as opposed to the standard approach's 89% successrateemployingbothindependentandcross-blocking modes.Incomparisontotheconventionaltechniqueusing the independent and cross-blocking modes, which had success rates of 100% and 87.05%, respectively, the suggestedmethodfordatabases5and6ensuredadetection successrateof99.11%forcross-countryinternalproblems. As a result, the suggested technique demonstrated high reliabilityinidentifyingcross-countryinternaldefectsand wasimmunetoCTsaturation.
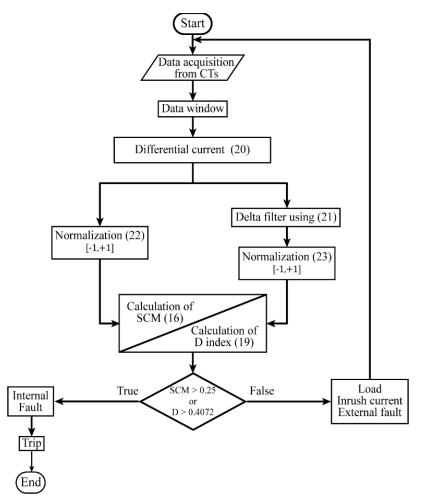
Fortheprotectionofathree-phasetransformer,author[4] offers a differential algorithm to distinguish between transient events such inrush currents and external faults fromsolidandturn-to-turnfaults.Todeterminethetypeof event,thealgorithmisbasedonthebehaviorofthesecond centralmoment(SCM).Instantaneousdifferentialcurrents are filtered and normalized before being used as input signalsbythealgorithm.Tosuccessfullyidentifytheevent, the system compares the SCM's magnitude with a predeterminedthresholdbasedonthebinomialdistribution. Thealgorithmrecognizestheoccurrenceasafaultsituation iftheSCMmagnitudeexceedsthelimit.Ifnot,theeventis classifiedasasteady-statesituationoratransitoryevent.If the transformer's settings are altered or the harmonic makeupofthedifferentialcurrentchanges,thethresholdis setting-free.Ifthepowersystemischanged,thethreshold doesnotneedtoberecalculated.Whencurrenttransformers undergosaturation,theDindexwasdevelopedtospeedup faultdiagnosis.ThisindexcomparestheSCM'smagnitudeto a certain limit in order to identify the fault current. Both indicesoperatesimultaneously,andifanyofthemcrosses eitheroftheirthresholds,afaultsituationisidentified.The techniqueisbuiltinMATLABandevaluatedusingareal-time digitalsimulator(RTDS).
ThemagnitudeoftheSCMandtheDindexforeachphase were determinedusingthe suggestedtechniqueusing the differentialcurrent.Todistinguishbetweendistincttypesof
events,bothindiceswerecomparedtotheircorresponding thresholds.Detectionofaninrushcurrentoranincidentthat doesnotnecessitateurgentprotectiveactionwasmadeifthe SCMorDindexdidnotmeetthesetrequirements.Ifnot,it wasseenasaninternalproblem.Comparedtothe89.95% accuracy of the traditional technique, the algorithm's accuracywas99.63%.Atypicaldefectdetectiontimesmaller than a cycle of 60 Hz was also revealed by the suggested approach. These findings demonstrated that a novel differentialprotectionforthree-phasepowertransformers maybebuiltusingthealgorithm.
Authorwastaskedwith[5]creatingadifferentialprotection strategy to distinguish between internal faults and power transformer magnetizing current in order to reduce the likelihood of false tripping. A method based on an acceleratedconvolutionneuralnetwork(CNN)isdeveloped todistinguishbetweeninternaldefectsandinrushcurrent. Theproposedalgorithm'sprimarycompetitiveadvantageis its ability to combine the fault detection and feature extractionblocksintoasingledeepneuralnetwork(DNN) blockbyallowingthenetworktoautomaticallyidentifykey features.
Fig-3: Flowdiagramofsecondcentralmoment-based transformerdifferentialprotection[4]
This leads to the algorithm being faster, more hardwarefriendly,andmoreaccurateasaconsequence.Theproposed method is applied to a simulated 230kV network and an experimental prototype. Different cases with various externalfactorsaresimulatedtocalculatereliabilityindexes.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 |Sept-2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Comparison between the accelerated CNN, conventional CNN,andninewidelyusedmethodsdemonstratesthefaster andmorereliableperformanceoftheproposedalgorithm.
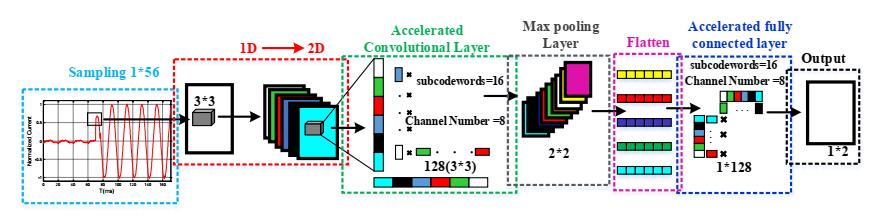
Fig-4: Procedureoftheproposeddifferentialprotection schemeofthepowertransformers[5]
The computational cost, dependence on the model, and preset threshold of existing approaches in differential protectiontodifferentiateinternaldefectsfromtheinrush currentinpowertransformersreducethedependabilityand generality of this critical operation. With the help of the enormousquantityofdatacapturedbycontemporarydata gathering systems, the suggested solution represents a significant advancement in the practical intelligent automationofpowertransformerprotection.Byemploying the product quantization approach to accelerate the convolutionandFCNlayers,wecreatedanacceleratedCNN. TheacceleratedCNNrunsfourtimesquickerthanthebasic CNN,improvingaccuracybyaround1%whilemaintaining accuracy. Furthermore, once the CNN structure is established,thesuggestedmachinelearning-basedsecurity mechanismmaybeusedwithmanysystemsindependentof the system characteristics. Both simulated and actual scenarios of applying the suggested strategy to a system wereused.Tenadditionalapproaches,includingeightdatadrivenandtwosignalprocessingmethods,werecompared totheoutcomesoftheacceleratedCNNmethod.
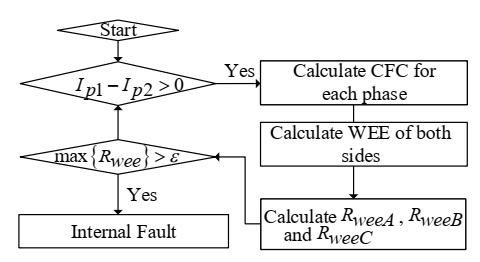
WhenaninternaldefectdevelopsduringDCbiasorinrush current, the converter transformer's current differential protection stops working. In order to create a new differential protection system, a new criteria is therefore provided in [6]. The new criterion is determined by the wavelet energy entropy (RWEE) of the primary fault component to the secondary fault component. Once an internal fault occurs, the energy entropy (WEE) of the primarysideismuchlargerthanthatonthesecondaryside, andthenalargeRWEEcanbeobtained.Otherwise,WEEof both sides are similar, and RWEE is around one. The simulation results show that the proposed criterion can perform well under inrush current, CT saturation, and DC biasconditions.It candiscriminatethe internal faultfrom external fault. Most importantly, it avoids the refusal of trippingwhenaninternalfaultoccurs.
Fig-5: FlowdiagramofRWEEbasedtransformer protection[6]
In [6], a brand-new WEE-based criterion for converter transformer differential protection is put forward. On the otherhand,becauseaninternalfaultonlycausesachangein thedirectionofCFContheprimaryside,itisusedasamajor fault characteristic to separate internal fault from other disturbances.
Inordertoestablishcriteria,theratioofWEEonthemain side to that on the secondary side is used. The new protection strategy is offered based on the suggested criterion.Theeffectivenessofthesuggestedsystemandits improvement of TDP dependability under various disturbance circumstances have been confirmed by simulation. It demonstrates that the suggested technique performsasintendedregardlessofinternalorexternalfault and that it is unaffected by noise and fault impedance. Results are unaffected by inrush current, DC bias, or CT saturation. In contrast to the majority of wavelet-based techniques,itresolvestheissueoftrippingrejectingwhen internalproblemsarise.
Energization and internal fault circumstances need to be adequatelyseparatedinordertoincreasethereliabilityand security of transformer differential protection. For differentiatingbetweenthetransformerinrushcurrentand internal defects, a novel approach with a low computing overhead and excellent resilience against measurement noises is suggested in article [7]. The recursive extended least-squares(RELS)algorithmisusedtofitsinewavesto thesamplepointsofthenormalizeddifferentialcurrentsfor variousphasesinthesuggestedtechnique.Theapproachcan efficientlypredictthedynamicsofthemeasurementnoises thankstotheexpandedkernel.Asadecision-makingfactor, three residual signals defined as the variations between fitted sine wave signals and normalized differential currents are taken into consideration. In roughly a halfcycleofthepowersystemfrequency,theenergizationstate is determined based on the chosen criteria. To show the efficacy of the suggested strategy, several simulation and experimental test scenarios are employed. The findings demonstratethatthesuggestedmethodhasa98%accuracy
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 |Sept-2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
rate, operates quickly, and has a comparatively little computingloadforembeddedimplementation.
In the suggested procedure, three RSs are identified and taken into consideration as the decision criterion. The suggestedtechniqueoutperformsthecurrentonesinterms of computing complexity and resilience against measurement disturbances. The algorithm also has an operatingtimeof0.5cyclesofpowersystemfrequencyanda 98%accuracylevel.
Thetransformerprotectionmustfunctiondependablyinthe eventofaproblemforpowersystemstorunsafely.Creating a quick and precise differential protection strategy that restrains the transformer during energizing and external faultcircumstancesaswellasdisconnectsitduringinternal faultconditionsisdifficult.Forpowertransformerswithany typeofwindingconnection,starordelta,ageneralmethod basedontheratiosofprimaryandsecondaryvoltagesand currents,augmentedwithcurrentdirectionandwave-shape criteria, is proposed. The ratios are those between the terminal phase voltages and the absolute differences and sumsoftheprimaryandsecondarylinecurrents.Themain goalistopreventexteriorfaultsundercurrenttransformer saturation, energising on an existing internal fault, and improperfunctioningofthestandarddifferentialprotection strategy during energization. Performance analyses show that the suggested algorithm can safeguard a power transformerquickly,effectively,anddependablyforallkinds ofwindingtopologies.
Apowertransformerdifferentialprotectionmethodthatis applicabletoallwindingdesignsisprovided.Itisbasedon ratiosofthedifferenceandsumofthe60Hzcomponentsof thelinecurrentsandthephasevoltagesatthetransformer terminals. The voltage ratio is utilized to identify simultaneous energization under internal fault, but it restricts the relay during energization alone. The current ratioisusedtodifferentiatebetweenenergizationandfault scenarios.Additionally,thesignalrestraintduringexternal faults associated with ct saturation is provided by the currentdirectioninadditiontothewave-shaperequirement. Thesuggestedtechniquemaycorrectlydistinguishbetween energising and fault instances in less than one cycle, accordingtoanalysisofalargenumberofcasesofnormal and fault conditions. Additionally, the presence of fault resistance and ct saturation is taken into account, and its impactontheperformanceofthesuggestedsystemhasbeen assessed.
Thefindingsshowthatthesuggestedapproachcanquickly identifyanddifferentiatebetweenfaultscenariosfrom5%of thewinding.Allwindingdesignsofpolyphasetransformers maydistinguishbetweenenergisingandfaultcircumstances with the suggested method with high accuracy and efficiency.
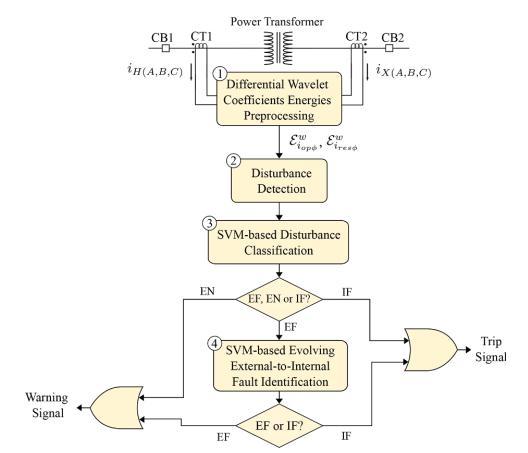
Apowertransformerdifferentialprotectionsystembasedon supportvectormachines(SVM)andhigh-frequencyfeatures retrievedusingthereal-timeboundarystationarywavelet transformwasreportedbytheauthor[9].(RTBSWT).With theuseofsyntheticdata,SVMmodelsarecreatedthattake into account a wide range of events, including inter-turn faults,externalfaultsduringCTsaturation,anddeveloping external-to-internal faults. The findings of a comparative performanceassessmentthattookoperatingtime,accuracy, andotherreliabilityindicesintoaccountwerepositive.The provided SVM-based relay's simplicity, built on the traditional differential protection framework with no difficult-to-deriveparameters,drawsattentiontopossible implementationissuesintherealworld.
TheSVM-basedprotectiontechniquehadasuccessrateof 100% in identifying external faults, internal defects, and energization events. Depending on the DSP being utilised, the relay operating period in a hardware implementation rangesfromafewhundredsecondstoafewmilliseconds.
Adifficultinstanceiswhenanexteriortransformerdefect evolves into an internal fault, a CT saturation, or both. However,theapproachdemonstrateda98.7%accuracyin separating emerging external-to-internal problems from exterior faults with and without CT saturation. With an operationtimeofupto2.6ms,thesuggestedrelayiscapable ofperformingthiseventdifferentiation.
Whenitcametoimportantturn-to-turninternaldefects,the suggestedSVM-basedprotectionstrategyperformedbetter thanthetraditionaloneandhadthequickestoperatingtime. TheNI sbRIO 9637 boardhasa portion of the given datadrivenprotectionsystemimplemented.
Fig-6: ProposedSVM-basedpowertransformer differentialprotection[9]
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 |Sept-2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thisboardwasabletorunthenecessarypreprocessingand SVM 1, issuing a trip signal in about 3 ms, which is faster thanconventionalprotectionandotherexistingdata-driven powertransformersprotectionschemes.Thisisdespitethe fact that the board was not intended to run highly timeconsuming digital signal processing and machine learning algorithms.
A thorough analysis of around 7500 motors revealed that statorproblemsweretoblame.DraftreceivedonMay20; updatedonOctober28.TEC00126-2003,papernumber.A. Siddique and G. S. Yadava work at the Indian Institute of Technology'sIndustrial Tribology,MachineDynamicsand Maintenance Engineering Centre in New Delhi, India (110016). B. Singh works at the Indian Institute of Technology'sDepartmentofElectricalEngineeringinNew Delhi,India(e-mail:bsingh@ee.iitd.ernet.in).Identityofthe Digital Object 10.1109/TEC.2004.837304 responsible for 37%ofthefailures.Asaresult,diagnostictestssensitiveto thestateofthestatorwindingareneededwhenconducting predictivemaintenanceonmotorsforstatordefects.
This article does a literature review on transformer protection.Ithasbeendiscoveredthatmanymethodsand techniqueshavebeenproposedandputintopractisesince thedevelopmentofdigitalrelaysuptothispoint,butwhenit comestofullsecurityandthedevelopmentoftechniquesto meetmodernrequirements,therecentmathematicaltoolof ANNandfuzzylogicconceptseemstobedependable,quick, androbust.Butinsomecommonreal-worldscenarios,even these solutions can fall short, and digital relays can malfunction.Therefore,itappearsthatthereisahugearea for research into quick and more dependable power transformerprotectiontechniques.
[1]Ali,E.,Helal,A.,Desouki,H.,Shebl,K.,Abdelkader,S.,& Malik, O. P. (2018). Power transformer differential protectionusingcurrentandvoltageratios. Electric Power Systems Research, 154,140-150.
[2]Sevov,L.,Khan,U.,&Zhang,Z.(2017).Enhancingpower transformerdifferentialprotectiontoimprovesecurityand dependability. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 53(3),2642-2649.
[3] Medeiros, R. P., & Costa, F. B. (2017). A wavelet-based transformerdifferentialprotectionwithdifferentialcurrent transformer saturation and cross-country fault detection. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 33(2),789799.
[4]Esponda,H.,Vázquez,E.,Andrade,M.A.,&Johnson,B.K. (2019). A setting-free differential protection for power
transformers based on second central moment. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 34(2),750-759.
[5]Afrasiabi,S.,Afrasiabi,M.,Parang,B.,&Mohammadi,M. (2019).Integrationofaccelerateddeepneuralnetworkinto powertransformerdifferentialprotection. IEEETransactions on Industrial Informatics, 16(2),865-876.
[6]Deng,Y.,Lin,S.,Fu,L.,Liao,K.,Liu,L.,He,Z.,...&Liu,Y. (2019).Newcriterionofconvertertransformerdifferential protection based on wavelet energy entropy. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 34(3),980-990.
[7] Naseri, F., Samet, H., Ghanbari, T., &Farjah, E. (2019). Power transformer differential protection based on least squares algorithm with extended kernel. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 13(8),1102-1110.
[8] Ali, E., Malik, O. P., Knight, A., Abdelkader, S., Helal, A., &Desouki, H. (2020). Ratios-based universal differential protectionalgorithmforpowertransformer. Electric Power Systems Research, 186,106383.
[9] Simões, L. D., Costa, H. J., Aires, M. N., Medeiros, R. P., Costa, F. B., &Bretas, A. S. (2021). A power transformer differentialprotectionbasedonsupportvectormachineand wavelet transform. Electric Power Systems Research, 197, 107297.