International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
MEDBLOCK
1Soham patkar, VESIT IT Department, Mumbai, India
2Hemantkumar yadav, VESIT IT Department, Mumbai, India
3Preet Thakker, VESIT IT Department, Mumbai, India
4Dr Shalu Chopra, HOD - VESIT IT Department, Mumbai, India
5Miss Rohini Sawant, Asst. Prof. VESIT IT Department, Mumbai, India ***
Abstract - Due to inefficient management of health records we face a critical issue with accountability, confidentiality and authenticity of medical data. Medical records are difficult to maintain and it takes time to search for a particular record in the current system which still uses a file based storage system.
In this paper, we propose MedBlock, a record management system to handle EMRs, using blockchain technology. Our system gives patients a comprehensive, immutable log and easy access to their medical information across providers and treatment sites. Leveraging unique blockchain properties like authentication, confidentiality, accountability and data sharing we aim to create a platform for the users where they can store their records securely and it is authentic. Using this technology we invite Insurance agencies to make their insurance settlement process easy and hassle free by making use of the platform to verify the records of a patient and their invoices. The user will not have access to add the data they can only view the data and grant access to hospitals to add the records and authorize the concerned insurance agency to validate the information and process the claim. Companies can use the platform to reduce the response time for insurance claiming processes and be secured from fraudulent claims.
Keywords Secure, Encrypted, Blockchain, Verification
I. INTRODUCTION
Medical records need innovation. Patients leave data scatteredacross variousjurisdictionsandtheylose easy accesstopastdata,becausetheprovider,notthepatient, generally holds the primary responsibility. We need a system where healthcare facilities are more friendly towards users and they have the right to give access to varioushospitalsanddoctors.Creatingaplatformwhere weleveragecharacteristicsofblockchaintomakethings more user centric and providing interfaces to insurance companies to get the authentic data through a trustworthysolution.
Claiming medical insurance in the current system is a tedious process and vulnerable to many frauds, hence
our aim is to create a trustworthy medium where patients can store their data and distribute it efficiently anditisauthentic.
Owing to its security features, we’ll use blockchain technology for building this system. The system should be secure and give full access control to data owners. It shouldprovideaninterface whereinall theEHRscanbe accessed containing lab reports, medical prescriptions, medical history, etc. Accountability for each data item is maintained as the address and the public key of all the concerned parties are recorded at every step. Insurance Companiescanalsoverifyinvoicesandmedicalbillsand calculatethetransactions therebyreducingtheresponse timefortheinsuranceclaim process
The main objective of this project is to build a system for storing the health records securely with access control. To provide an easy interface for medical insurance agencies for verification of records and their visualization. To minimize spoofing of data for false claiming of insurance and improve authenticity of records. We aim to create a private peer to peer blockchain with each concerned entity as a node and it willbearolebasedaccesscontroli.eallnodeswillnotbe abletoaccessthedataunlessauthorizedbyauser.
The block content represents data ownership and viewership permissions shared by members of a private, peer-to-peer network. Blockchain technology supports the use of “smart contracts”, which allow us to automateandtrackcertainstatetransition(eg,changing viewerrightsorthebirthofanewrecordinthesystem). We record patient-provider relationships through Ethereum blockchain smart contracts that associate a medical record with viewing permissions and data retrievalinstructions(essentiallydatapointers).
We include on the blockchain a cryptographic hash of the record to ensure against tampering, thus guaranteeingdataintegrity.Providerscancreaterecords for a particular patient, and patients can authorize sharing of records between providers. This keeps participants informed and engaged in the evolution of theirrecords.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
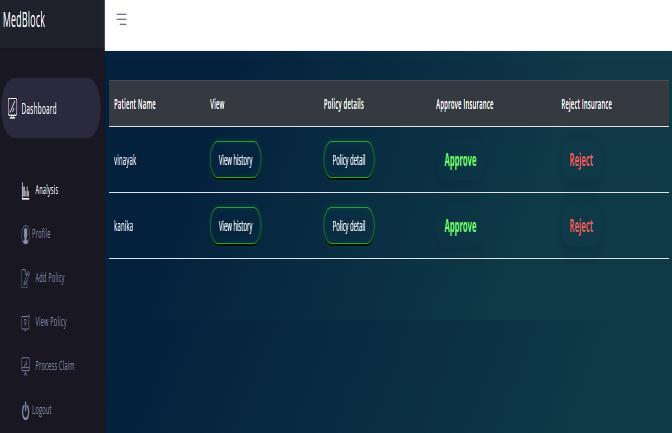
In Medblock we provide an interface to Insurance Administrators to retrieve the information of concerned patients and they can view all the invoices related to the patient as well. The authorization is given bypatientsandotherthantheauthorizedentitynoother nodewillbeabletoviewtheinformation.
Potential Benefits of the System:
SafePlacetoStoredata.
BasedontheparadigmofBlockchain.
ImprovedResponserateforClaimingInsurance.
SecureAccesscontrolmechanism.
Tamper-resistantsystemtopreventforgeddata
II. Related Work
The existing systems provide the basic functionalities and can be easily handled in a hospital environment. There is no intelligence software which supports secure patient access to healthcare records. Most of the works done in these systems are not secure andsomeofthemarenotaccurate.Therearealsofearof data breaches and missing information or records. Another huge problem in these existing systems is that the information is not fully secured enough. Any unauthorized users can access all the sensitive information of a patient and exploit it for very wrong purpose.Thetechnological advancementsareappliedto datasecuritieswhichcanreducetherisks.
[1] Medical project management
In the medical field, for a single patient, data originates from various sources and each of these sources may have a separate format to represent this data likegeneral info ofa patient,or incase ofhospitals data may be split across multiple departments. This restricts the data exchange between different stakeholders.
This paper proposes a new mediator semantic based on XML format which would help users to interact with largemedicaldataandresearchsimilarprojects.Ittakes the input data stream to provide a unified representation. Any input must first pass through the datamodulewhichconvertsalldataintometadatawhich inturnisstoredinarelationaldatabase.Thencomesthe 2nd module which runs the user queries performing simple queries like adding or deleting data or searching for particular dataset. The 3rd module consists of user data interaction and visualization. In this paper, storing of data is mostly confined to relational databases, here propose an alternative of using blockchain ledger for storingdata.
[2] Secured health records
Thispapertalksaboutsecuringthemedicaldata and making it easily accessible for later use. This paper proposesaSHA3basedsystemforsecureaccessofdata. It clearly defines the access for writing and reading of data between different users. It also addresses the issue of unifying a way to record the details of patient encounter. As the current system is quite subjective to each health care institution. This paper majorly focuses ondatasecurityfromunauthenticatedsources,buteven here data is editable from the proposed system. The needofourprojectisthedatashouldnotbeeditedonce itisuploadedinblock.
[3] Medrec
This paper proposes a decentralized storage of electronicmedicalrecordsbasedonblockchain.Thedata storedisconfidentialandwehaveaccountabilityofeach data block. It leverages the blockchain properties for sensitivedatahandling.
They have incentivized the stakeholders like researchersandpublichealthauthoritiestobecomedata minersandbea partofthis network,inreturnthey will get anonymized and aggregated data as mining rewards forstoringthenetworksecurely.Thus,itencouragesbig data for researchers and also engaging patients and providers in choice to release metadata. It defines data ownershipandviewershippermissionsinanetworkand the data is then logged into a network using hashing algorithms. They also use smart contracts to store the representation of medical records and relationships betweendifferentusers.
[4] A Blockchain-Based System for Anti-Fraud of Healthcare Insurance
The incidence of healthcare insurance fraud and the number of people involved in the frauds have increased year by year, causing tremendous concern in society. Typical frauds include falsifying information, concealing third-partyliability,falsifiedelectronicbills.
Therefore, this paper proposes a healthcare insurance anti-fraud system based on blockchain. Sharing the data such as inspection reports, prescriptions, and treatment records related to the medical procedures of the relevant medical institutions with the healthcare insurance agencies is an essential element for identifying violations of healthcare insurancepolicies.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
[5] Research of Medical Insurance Based on the Combination of Blockchain and Credit Technology.
Blockchain technology can effectively solve many problems in credit investigation technology. The combination of blockchain technology and credit investigation technology is more popular to apply in many fields. In the field of medical insurance, a medical insurance monitoring system can be established under the mode of blockchain and credit investigation, which can effectively solve the problems of medical insurance dishonesty.
[6] MI Store: a Blockchain-Based Medical Insurance Storage System
In this paper, they proposed a blockchain-based threshold medical insurance storage system, called MI Store. When combined with the blockchain, it brings some special benefits to the system., e.g. decentralisation, tamper resistance and registration nodes allow users to check publicly verifiable data. Firstly, the blockchain’s property of tamper-resistance gives users high-credibility. Moreover, due to decentralization,userscancommunicatewitheachother withoutthethird-parties.
III. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
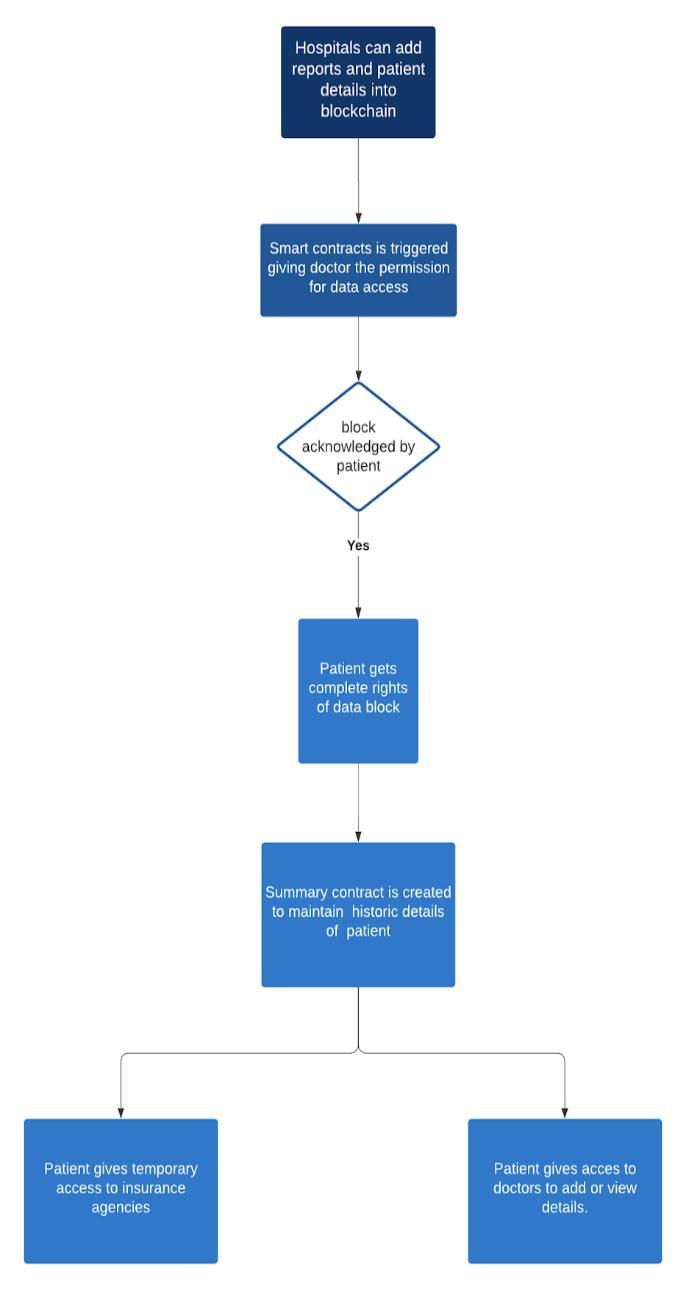
We implement a system wherein a patient would havethecontroltograntandrevoketheaccessrightsof his medical records but he won’t have the rights to create a new record. This functionality is desirable as a doctor is more accountable and this would ensure that the data generated into the system is authentic and credible.Thisdatawillberecordedinasmartcontracts. Since for a patient, the records can originate from different sources we need to keep a track of all such contracts related to a patient. This will be our summary contractwhichmapapatienttoallit’srelatedrecords.
Insurer will get access to the patients enrolled for a policyafterthepatientsclaimanypolicy.Oncetheclaims are processed the insurer will reimburse the patient accordingly.
The records are true account as in Blockchain, stored data isimmutableandpermanent,itcannot be modified or deleted, which makes the technology meet the main data integrity requirements. Since storing the images of billsormedicalrecords,onblockchainwillresultinhigh gas amount, the images are stored in ipfs which uses content-addressing to uniquely identify each file in a globalnamespaceconnectingallcomputingdevices.This content-address is stored in smart contracts. These files canbeeasilyretrievedfromtheaddress.
Thesoftwarerequirementsofoursystemare
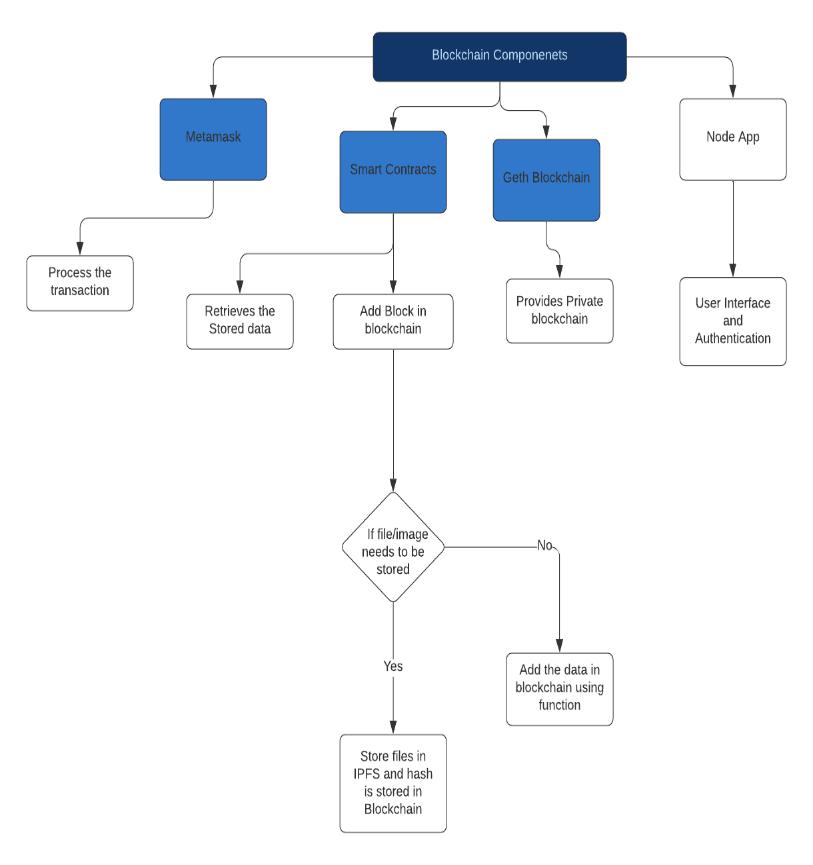
Ethereumnetwork:whereinthesmartcontractsare writteninsoliditylanguage.
Ganache : for mining blocks and testing our system. It provides 10 accounts and 100 ethers with each account.
Metamask : A browser extension which is used to connectourapptotheblockchain.Itisusedtomake thetransactionsthroughUI.
IPFS : Since our system demands storing of large files and data which can be in image and other format, We use Interplanetary File System(IPFS) which stores large files in a decentralized network and generates the hash of the stored address which is used for retrieving of the files and storing of the addressinblockchainnetwork.
Fig.
1. Blockchain Components
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
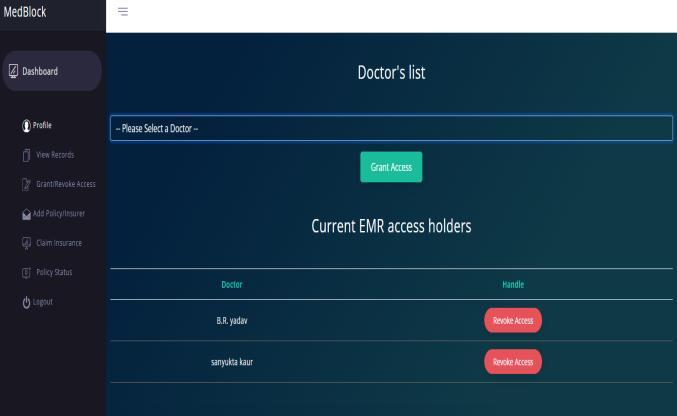
revoke the access from that doctor. Granting/revokingaccessrequiresethers.
Fig. 3. Grant access to doctor
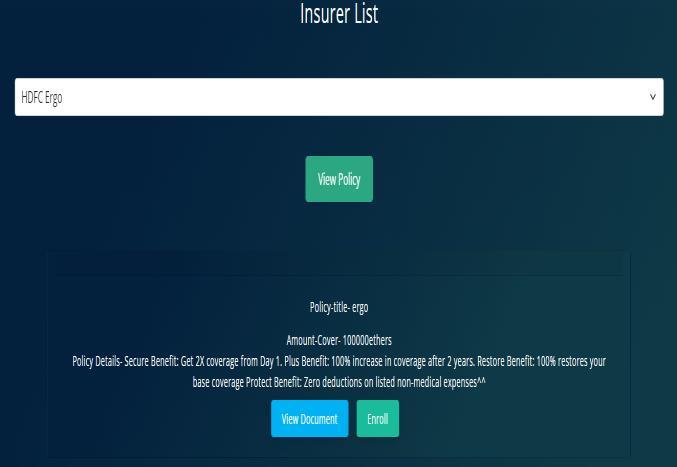
2. A patient can enroll into any medical insurance policy and then also claim for any policy if applicable.
Fig. 4. Enroll to policy
Fig. 2. Project Flow
A. Registeration of new user to blockchain:
The user first needs to register himself into the network. The system stores the public key of the user through metamask. When a patient registers himself, an ipfs hash key is generated for that user. This is used to store all the medical records and billsrelatedtothatuser.
B. Patient:
1. Afterregisteringapatientneedstogiveaccessto selected doctors for adding new records to his account. A patient cannot himself add any new records,thisistoensurethatonlytrustedparties adddataintothechainandanyillicitdatacanbe traced back to the responsible user. After the data is uploaded by the doctor the patient can
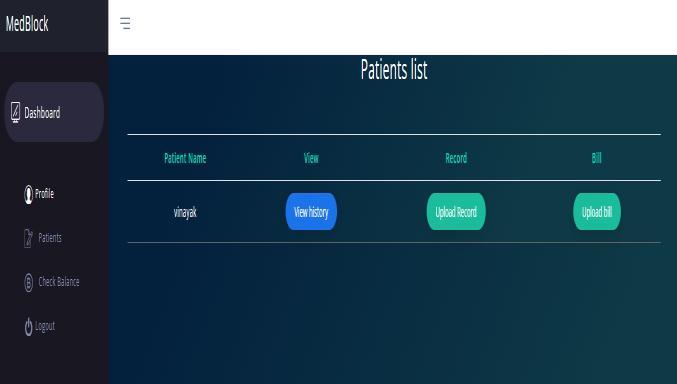
C. Doctor:
After registration, a doctor can see list of patientsthathehasaccesstoandthenproceedonto uploadanydocumentsrelatedtothatpatient.These documentsarestoredinIpfs,whichisapeer-to-peer network, and the hash address generated is stored intoblockchaintoreducetheamountofgasusedfor thetransaction
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
block. Nodes are the governing body of the blockchain and verify the legitimacy of transactions in each block. Onceablockoftransactionshasbeenverified,thedatais writtenintotheblockchain.
V. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Fig. 5. Upload files
D. Insurer:
Insurer can add policies to his account, patients can enrollforthesepoliciesandclaimthem.
Insurer can be given access to patients medical records when a patient claims any policy, this is to check which allexpensesarecoveredunderthepolicy.
We wish to extend our special gratitude to our guide Dr. Shalu Chopra and Prof Rohini Sawant who gave us the opportunity and guidance to work on the project Medblock. I am deeply indebted to them for their guidanceandconstantoversight.aswellasforproviding necessary information regarding the project & also for their support in completing the project. We would also like to express gratitude to all those who directly or indirectlycontributedtowardsthisproject.
VI. REFERENCES
[1]A.Dridi,A.TissaouiandS.Sassi,"Themedicalproject management (MPM) system," 2015 Global Summit on Computer & Information Technology (GSCIT), 2015, pp. 1-6,doi:10.1109/GSCIT.2015.7353336.
[2] M. Azhagiri, R. Amrita, R. Aparna and B. Jashmitha, "SecuredElectronicHealthRecordManagementSystem," 2018 3rd International Conference on Communication andElectronicsSystems(ICCES),2018,pp.915-919,doi: 10.1109/CESYS.2018.8724010.
[3] A. Azaria, A. Ekblaw, T. Vieira and A. Lippman, "MedRec: Using Blockchain for Medical Data Access and Permission Management," 2016 2nd International Conference on Open and Big Data (OBD), 2016, pp. 2530,doi:10.1109/OBD.2016.11.
Fig. 6. Approve Claim
IV. RESULT AND ANALYSIS
Weobservedthatcomparingtothecurrentsystemin themarket,ourproposedsystemismoreconvenientand reducestheresponsetimeininsuranceclaimingprocess by more than 60% and the Customer satisfaction is thereby received. The traditional method is also not secure and does not guarantee untampered and unforged reports, which may lead to loss of company’s revenue. Also due to public and private key system our method enables accountability in the system each peer acts as trustworthy node , even if some ill people enter the system they won’t be able to access the system and view or edit other people’s records unless he is given accessbyotheruser.
The proof of work concept in our system which is consensus algorithm requires each node in the blockchain network to solve a problem. The first node that solves the problem gets permission to add new a
[4] W. Liu, Q. Yu, Z. Li, Z. Li, Y. Su and J. Zhou, "A Blockchain-Based System for Anti-Fraud of Healthcare Insurance," 2019 IEEE 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), 2019, pp. 12641268,doi:10.1109/ICCC47050.2019.9064274.
[5] Z. Chang, "Research of Medical Insurance Based on the Combination of Blockchain and Credit Technology," 2020 Asia-Pacific Conference on Image Processing,Electronicsand Computers(IPEC),2020, pp. 428-430,
[6] Zhou, L., Wang, L. & Sun, Y. MIStore: a Blockchain-Based Medical Insurance Storage System. J Med Syst 42, 149 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-0996-4
