International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1
, JUNIOR RESEARCH FELLOW, B.SAMPATH KUMAR2
, SC-‘F’,TECHNOLOGY DIRECTOR,DRDO-CAS,HYDERABAD,INDIA***
Abstract - In this work welding of two aluminum plates willbedonewitharootgapof0.25mmalongwithaspeedof 1400and1800rpm.Afterthiswehave changedrootgapto 0.5mm and 0.75 mm along with the same speeds. After weldingattheserootgaps,theworkpiecesareinvestigated for different weld parameters. Here we will be doing HardnesstestusingBrinellHardnessTestingMachineand Vickers Hardness Testing Machine . After that weld parameters are tested for tensile strength using universal testing machine. We will examine the Microstructure behavior of Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 6082 with differentrootgapsandtoolspeeds
Key Words: Friction Stir Welding, Al 6082, Vickers Hardness Test, Brinell Hardness Test, Micro Structure Analysis.
Frictionstirweldingisasolidstateweldingprocess,isthe newest addition to friction welding, a solid state welding process. Solid state welding, as the term implies, is the formation of joints n the solid state, without fusion. Solid state welding includes processes such as cold welding, explosion welding, ultrasonic welding, roll welding, forge welding.
Therearedifferenttypesoffrictionweldingsuchas Rotary Friction Welding, Inertia Friction Welding, spin welding, friction surfacing,Friction Stud Welding, , Linear Friction Welding
1.2
Chromium:0.25%max
Copper:0.1%max
Iron:0.5%max
Magnesium:0.6to1.2%
Manganese:0.4%to1.0%
Silicon:0.7to1.3%and Titanium:0.1%max
PhysicalProperties
Density : 2700kg/m^3
MeltingPoint : 555°C
ModulusOfElasticity : 70GPa
ElectricalResistivity : 0.038x10-6 Ω.m
ThermalConductivity : 180W/m.K
ThermalExpansion : 24x10-6 /K
1.1.
Thealloycompositionof6082aluminumis
Aluminum:95.2to98.3%
Fig 1.1. Aluminum 6082 Plates Ready For Friction Stir Welding.
Fig 1.2. Shoulder Shaped tool used For Friction Stir Welding.

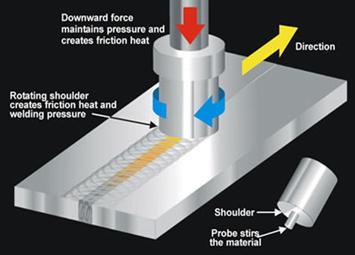
Friction stir welding is done on the 6 specimens of Aluminum 6082 by the following root gaps with different rpm’s.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Fig 2.1. Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 6082 With 0.25mm root gap at 1400 rpm


Fig.2.5. Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 6082 With 0.5mm root gap at 1800 rpm
Fig.2.2. Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 6082 With 0.5mm root gap at 1400 rpm

Fig 2.6. Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 6082 With 0.75mm root gap at 1800 rpm
ON FSW 6082
Inthisworkvariousweldparametersoffrictionstirwelded Aluminum6082areexaminedbyconductingthefollowing tests.



Hardness Test with Vickers Hardness Testing MachineandBrinellHardnessTestingMachine MicroStructureAnalysis
Fig.2.3. Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 6082 With 0.75mm root gap at 1400 rpm
TheBrinell hardness test methodas used to determine Brinellhardness,isdefinedinASTME10.Mostcommonlyit is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarseorthathaveasurfacethatistooroughtobetested usinganothertestmethod,e.g.,castingsandforgings.Brinell testing often use a very high test load (3000 kgf) and a 10mm wide indenter so that the resulting indentation averagesoutmostsurfaceandsub-surfaceinconsistencies
Fig.2.4. Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 6082 With 0.25mm root gap at 1800 rpm
Anironball oftemperedsteel ora hardmetal ball witha knowndiameterispressedverticallywithatestforceFinan isolated testing surface. Test force is exerted during a definedtime(from2to8seconds);incidencetimemustbe from10to15seconds.Brinellhardnessiscalculatedbythe pressure diameter and the test force. The hardness measurement developed by Brinell is used for soft and mediumhardmetals,non-alloyedconstructiongradesteel, aluminium, wood and work materials with irregular structuressuchascastiron.Anironballoronemadeofa hardmetalisstruckwithadefinedforceformeasurement againstthesurfaceofthematerial.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Hardnesstestwillbecarriedoutonthefollowingsamples.
1. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.25mmattoolspeed1400
2. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.5mmattoolspeed1400
3. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.75mmattoolspeed1400
4. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.25mmattoolspeed1800
5. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.5mmattoolspeed1800
6. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.75mmattoolspeed1800
TheVickershardnesstestmethodconsistsofindentingthe testmaterialwithadiamondindenter,intheformofaright pyramid with a square base and an angle of 136 degrees betweenoppositefacessubjectedtoaloadof1to100kgf. Thefullloadisnormallyappliedfor10to15seconds.The two diagonals of the indentation left in the surface of the material after removal of the load are measured using a microscopeandtheiraveragecalculated.
The area of the sloping surface of the indentation is calculated.TheVickershardnessisthequotientobtainedby dividing the kgf load by the square mm area of indentation.TheVickershardnesstestmeasureshardwork materialsbutalsothehardnessofmaterialsandthinwallsor marginalareas.
Tensile Test is done with Universal Testing machine for examining the Variation of Ultimate Tensile Strength of Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 6082 with different root gaps and at different tool speeds. i.e., Tensile test will be carriedoutonthefollowingsamples.


1. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.25mmattoolspeed1400

2. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.5mmattoolspeed1400
3. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.75mmattoolspeed1400
4. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.25mmattoolspeed1800
5. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.5mmattoolspeed1800
6. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.75mmattoolspeed1800
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056


Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
TheMicrostructureanalysisisdonetofindthevariationin the microstructure of Aluminum 6082 with Friction Stir weldingwithdifferentrootgapsandatdifferenttoolspeeds. Analysiswillbeconductedonthefollowingsamples.

1. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.25mmattoolspeed1400
2. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.5mmattoolspeed1400
3. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.75mmattoolspeed1400
4. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.25mmattoolspeed1800
5. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.5mmattoolspeed1800
Fig.4.2. Tensile Test Specimens

Microstructureanalysisisthestructureofmaterialisstudied undermagnification.
Microstructure is the small scale structure of a material, definedasthestructureofapreparedsurfaceofmaterialas revealed by a microscope above 25× magnificationThe microstructureofamaterialcanstronglyinfluencephysical propertiessuchasstrength,toughness,ductility,hardness, corrosion resistance, high/low temperature behavior or wear resistance. These properties in turn govern the application of these materials in industrial practice. Microstructure at scales smaller than can be viewed withopticalmicroscope.
6. Friction Stir Welded aluminum 6082 with root gap of 0.75mmattoolspeed1800 Fig.5.2.
Fig.5.1. optical microscope

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

SPEED ROOT
GAP BRINELL HARDNESS
IMP 1 IMP 2 IMP3 IMP 4
1400 0.25 62.4 61.8 61.2 61.80
0.5 60.4 60.1 59.5 60.00
0.75 57.3 57.9 58.4 57.87
1800 0.25 63.0 63.6 64.2 63.60 0.5 62.4 61.8 61.2 61.80 0.75 59.5 60.1 60.6 60.07
Table:5.1 Brinell Hardness Test Values
5.2 Vickers Hardness Test Values
Hardness Testing Parameters
Type of Hardness test : VHN
Type of Material : AL6082 Dimensions : 100*60*5
Type of Intender : Diamond Load applied : 5Kgs
SPEED ROOT GAP VICKERS HARDNESS
IMP 1 IMP 2 IMP3 IMP 4
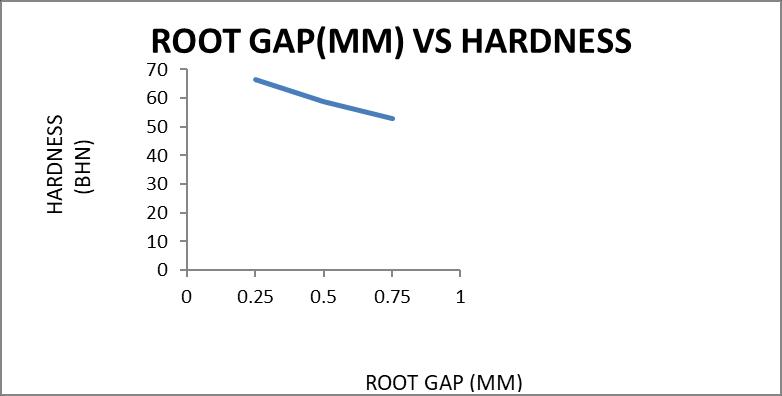
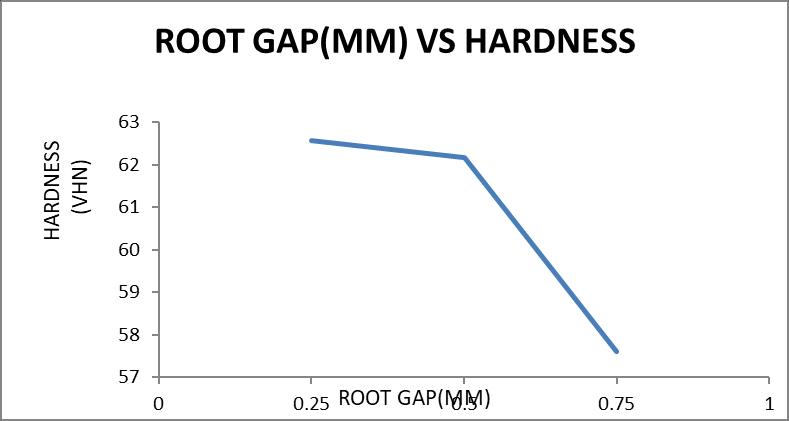
1400 0.25 67.0 66.6 66.3 66.63 0.5 58.0 60.0 58.3 58.77 0.75 52.1 53.3 52.8 52.73 1800 0.25 63.2 62.6 61.9 62.57 0.5 61.6 62.3 62.6 62.17 0.75 58.0 57.7 57.1 57.60
Table:5.2 Vickers Hardness Test Values
Graph 5.2 Variation of hardness with root gap at 1800 rpm 5.3.Tensile Test Values
SPEED ROOT GAP TENSILETESTREADINGS UTL UTS N/MM2 YIELD (%) YIELD LOAD Kn
YIELD STRENGT H N/MM2
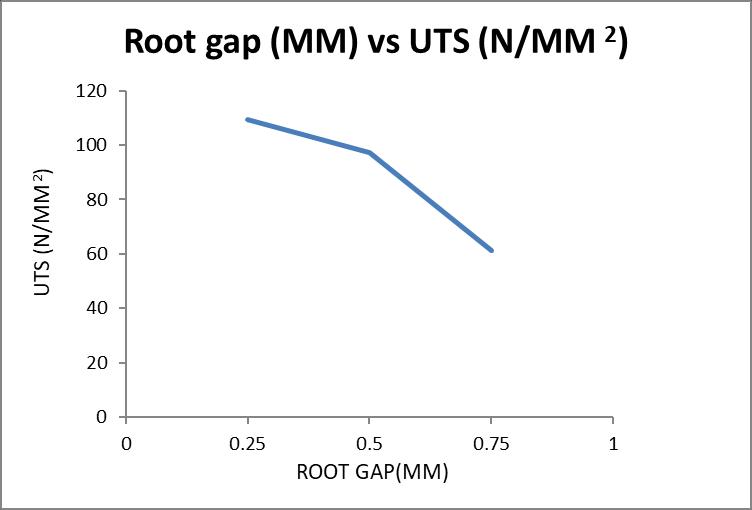
1400 0.25 8.240 109.18 2 3.540 4.960 65.721 0.5 7.080 97.346 2.500 5.680 78.097 0.75 4.120 61.028 1.160 3.120 46.215
1800 0.25 3.120 42.804 3.780 2.200 30.187 0.5 1.920 30.573 3.640 1.880 29.936 0.75 1.840 26.320 1.760 1.400 20.026
Table 5.3. Overall Tensile Test Readings with different root gaps at different speeds
Graph 5.1 Variation of hardness with root gap at 1400 rpm
Graph 5.3: variation of ultimate tensile strength values with root gap at 1400 rpm
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page383
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Fig.:5.5 Grain size of 0.5 root gap specimen at 1400 rpm

Graph 5.4: variation of ultimate tensile strength values with root gap at 1800 rpm

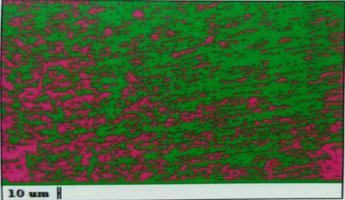
Fig.:5.6 Heat affected zone of 0.5 root gap specimen at 1400 rpm
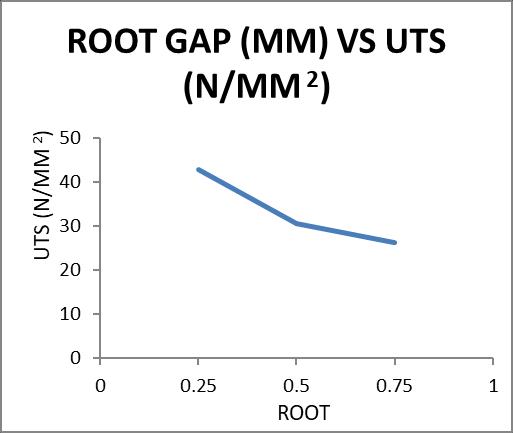
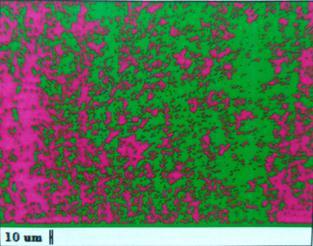
Fig.:5.3 Grain Size of 0.25 root gap specimen at 1400 rpm


Fig.:5.7 Grain Size of 0.75 root gap specimen at 1400 rpm
Fig.:5.4 Heat affected zone of 0.25 root gap specimen at 1400 rpm
Fig.:5.8 Heat affected zone of 0.75 root gap specimen at 1400 rpm
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Fig.:5.9 Grain Size of 0.25 root gap specimen at 1800 rpm

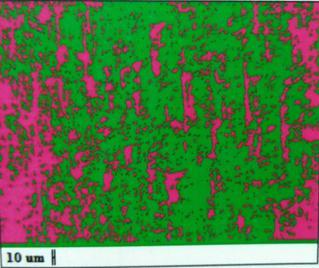

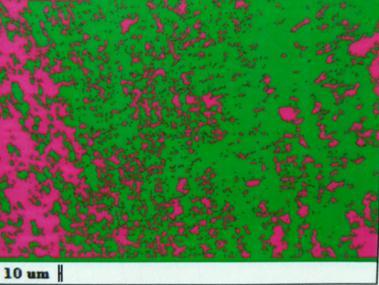
Fig.:5.12 Heat affected zone of 0.5 root gap specimen at 1800 rpm
Fig.:5.10 Heat affected zone of 0.25 root gap specimen at 1800 rpm
Fig.:5.13 Grain Size of 0.75 root gap specimen at 1800 rpm

Fig.:5.11 Grain Size of 0.5 root gap specimen at 1800 rpm
Fig.:5.14 Heat affected zone of 0.75 root gap specimen at 1800 rpm
Fromthepreviouschapterresultsfollowingconclusionscan bemadeforFSWAL6082.

1. TheHardnessoftheFrictionstirweldedAL6082 willdecreasewiththe incrementinrootgapfrom0.25mmto0.75mm.
2. TheHardnessoftheFrictionstirweldedAL6082 willdecreasewiththe incrementinspinningtoolspeedfrom1400rpmto 1800rpm.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Sowecanconcludethatitcanbesuggestedtoopt frictionstirweldingofAL6082withlessrootgaps and welding should be done at low spinning tool speedtogetrequiredweldqualitywithimproved weld properties like Hardness, Ultimate tensile strength,Microstructureetc.
3. The Ultimate tensile strength of the Friction stir welded AL6082 will decrease with the incrementinrootgapfrom0.25mmto0.75mm.
4. The Ultimate tensile strength of the Friction stir weldedAL6082willdecreasewiththeincrementin spinningtoolspeedfrom1400rpmto1800rpm.
5. The Microstructure variation is more with more heat affected zones(HAZs) of the Friction stir weldedAL6082withtheincrementrootgapfrom 0.25to0.75mm.
6. The Microstructure variation is more with more heat affected zones(HAZs) of the Friction stir weldedAL6082withtheincrementinspinningtool speedfrom1400rpmto1800rpm.
So,wecanconcludethatitcanbesuggestedtoopt frictionstirweldingofAL6082withlessrootgaps and welding should be done at low spinning tool speedtogetrequiredweldqualitywithimproved weld properties like Hardness, Ultimate tensile strength,Microstructureetc.
Futureworkon Frictionstirweldingcanbecarriedoutand weld parameters can be investigated for similar (or) dissimilar metals by considering the influence of various other parameters like Deformation characteristics of the metal,Angleoftool,Pressureappliedbythespintooletc.
[1]W.S.Miller,L.Zhuang,J.Bottema,A.J.Wittebrood,P.De Smet, A. Haszler, A. Vieregge. “Recent development in aluminum alloys for the automotive industry”. Materials ScienceandEngineering(2000);A280:37–49.
[2]T.Watanabe,H.Takayama,K.Kimapong,N.Hotta,"Joining ofSteeltoAluminumAlloybyInterface-ActivatedAdhesion Welding".MaterialsScienceForum(2003);426-432:41294134.
[3] Takehiko Watanabe, Hirofumi Takayama, Atsushi Yanagisawa.“Joiningofaluminumalloytosteelbyfriction stir welding”. Journal of Materials Processing Technology (2006);178:342–349.
[4]C.M.Chen,R.Kovacevic.“JoiningofAl6061alloytoAISI 1018 steel by combined effects of fusion and solid state welding”.International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture(2004);44:1205–1214.
[
5]WHJiangandRKovacevic.“Feasibilitystudyoffriction stir welding of 6061-T6 aluminium alloy with AISI 1018 steel”.Proc.InstnMech.Engrs(2004);218:1323-1331.
[6] Aleš FRANC. “Heterogeneous joints between steel and aluminummadebymodifiedMIGprocess”.Metal2010.
[7]TsutomuTanaka,TaikiMorishigeandTomotakeHirata. “Comprehensive analysis of joint strength for dissimilar frictionstirweldsofmildsteeltoaluminumalloys”.Scripta Materialia(2009);61:756–759.
[8]EmelTaban,JerryE.Gould,JohnC.Lippold.“Dissimilar frictionweldingof6061-T6aluminumandAISI1018steel: Propertiesandmicrostructuralcharacterization”.Materials andDesign(2010);31:2305–2311.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

SREERAMSAI,B.Tech,M.Tech J.R.F,CAS-DRDO,HYDERABAD.