International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1
, Manasa Jonnalagadda2
1Professor, Computer Science & Engineering, G Narayanamma Institute of Technology & Science, Telangana, India 2 M Tech Student, Computer Science & Engineering, G Narayanamma Institute of Technology & Science, Telangana, India ***
Abstract - Mental health is a stabilizing force of an individual’s emotional well-being, and any distress can cause imbalances in one’s conventional routine and plethora of mental disorders. Mental health concerns usually took a backseat during the pandemic and impacts seamless functioning for teachers and students in educational environment. Depression is a mental health condition manifesting constant elevation or lowering of person’s mood and little interest in everyday activities causing substantial impairment in everyday life. Depression in particular is influenced by complex array of factors including everyday stress, academic strain, compounded negative emotions and panic due to COVID-19 outbreak. Research conducted in healthcare domain in par with Artificial Intelligence provides various methods for detection and diagnosis of depression. However, minimal research is conducted predicting depression based on individual’s situation and their environment in early stages. The objective of this study is to propose a context aware model for teachers and students for predicting risk of depression in educational framework and pandemic. The datasets are created through structured self-reporting questionnaires and potential variables for depression risk are identified with Regression analysis. Related context information is extracted in relevance with each potential variable and Convolutional Neural Networks is applied for depression risk prediction. Subsequently, accuracy of the proposed model for teachers and students is evaluated with performance metrics and comparative analysis of Multiple Regression and Convolutional Neural Networks.
Key Words: Mental Health, Depression Risk, Convolutional Neural Networks, Multiple Regression, Machine Learning.
COVID-19isaglobalhumanitariancataclysmthathaslefttheworldinshamblesovertherecentyears.InIndia,ithasenforced rapidtransitionineducation,IT,healthcare,andothersectors,todigitizeandimplementvariousstrategiesfortheirseamless functioning[10].Specifically,schoolsandcollegeswereforcedtorunemergencyonlinelearning/classescausingprolonged socialisolationandincreasingacademicstressorsonbothteachersandstudents.Italsohadmajorimpactoneveryone’slife, disturbingindividual’sconventional activitiesalong withtheirphysical andmental health.Massfearanduncertaintyhas reflecteddisparagingeffectinholisticwell-beingofapersonsteeringstrongemotionslikestress,anxiety,anger,depression, andothercomplexarrayoffactors.Workstress,difficultfinancialsituation,familyissues,personalandprofessionalproblems, changesduetotheCOVID-19andotherpsychologicalandenvironmentalparametersoriginatingfromanindividual’swayof lifecontributetodistressandmentalhealthdisorders.
AccordingtoWorldHealthOrganization(WHO),depressionrankshighamongcommonmentaldebilities.Depressionisa mentalhealthconditionmanifestingconstantelevationorloweringofperson’sframeofmindandlossofinterest indaily activitiescausingsubstantialimpairmentineverydaylife.Giventhecurrentshiftsintheeducationallandscapeoverthepast years,depressionhasbecomeincreasinglycommoninteachersandstudentsinIndia.Itisanemotionaldichotomyfoundin various strata of the society and in different age groups. Parameters like complete burnout, extreme work strain due to academicandcurricularresponsibilitiesinteachers;andacademicstressors,peerandsocietalpressureinstudentscouldafflict the individual’s ecosystem. Thus, a souring need rises to support the emotional well-being of teachers and students by predictingdepressionriskinpreliminarystagestopotentiallyreducetheescalationoftheillnessandinturnimprovetheir qualityoflife.
MachineLearningandDeepLearningbasedmentalhealthexplorations[11]haveattractedlotofattentiontopredictmental disordersusingmultimodaldataliketext,images,andvideos.ApproacheslikeDeepNeuralNetworks(DNN)andRegression hasopenedanewfrontiertoaddressearlyscreening,detection,prediction,anddiagnosisofvariousdisordersbytracking compoundemotionalparametersassociatedwiththementalhealthchallenges.Thestatisticalandcomputationalmethods extendedbyMachineLearningassistinconstructingrobustautomatedpredictionanddetectionofdepressivesymptomswith theabilitytolearnandtrainfromdata.Multimodaldatarelyingonfrequentmeasurementsofdepressionstatusprocuredfrom various sources have been implemented with deep learning models for early recognition of depression symptoms in the individuals. However, minimal research exists for classifying and predicting individual’s emotional state based on their
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
situationandcircumstanceswhichiscontextaware.Theproposedsystememphasizesonpredictingriskofdepressionin teachersandstudentsbasedonpotentialvariablesaffectingthedepressionriskinpandemicandeducationalenvironment alongwiththeircontextinformation.Realtimedataiscollectedforteachersandstudentsviastructuredquestionnairesandis further synthesized with Conditional Tabular Generative Adversarial Networks (CTGAN) model. Regression analysis is employed to identify potential variables influencing depression risk/prone predictor (DPP) along with their context information.ConvolutionNeuralNetworks(CNN)isthendesignedtocomputethevaluesofthepotentialvariablesusingtheir relatedcontextinformationfollowedbycalculationofDPPtopredictriskofdepressionforbothteachersandstudents.The objectivesoftheproposedworkare:
Thestudyistoidentifydepressionriskbasedonworkforce,emotionalwell-being,academicstressors,professional growth,andotherfactorsaffectingduringthepandemicinteachersandstudents.
Tostudyandidentifythecontextinformationrelatedtothepotentialfactorspromptingdepressionrisk.
Tostudythedepressionriskoccurringinbothteachersandstudentsduringpandemicbytakingreal-timedata.
Therestofthepaperisorganizedasfollows.Section2focusesonoutliningthepreviousstudiesconductedonmentalhealth problemsanddepressiondetectionwithusingvariousMachineLearningmodelsandDeepLearningmodels.Theproposed modelfordepressionriskpredictioninteachersandstudentsisaddressedinSection3byutilizingMultipleRegressionand CNN.Section4presentstheresultsandperformanceevaluationfollowedbyconclusionsandfutureextensionsinSection5.
Emotional well-being is one of the most vital concerns in health care sector with accentuated indication of its influence worldwide.WHOdefinedmentalhealthas“completecognitive,emotionalandsocialbehavioroftheindividual.”Depressionis concededbyWHOasthesinglelargestcontributortohealth-relatedconstrictionslikedisturbedqualityoflife,compounded negativeemotions,cognitiveandpsychologicalimbalances,andevensuicidaldeaths.Irrespectiveofage,peoplewithdepression tendtohidetheirinterwovenemotionsandsufferinsilenceduetosocialstigmainthesocietyleadingtoprolongeddelayin findingnecessaryhelpneeded.DrasticchangesoverthepastyearsduetoCOVID-19pandemic hasfueled intricatehealth, societal, economic, and educational changes around the world in teachersand students. [6], [17]. On a broader spectrum, identifyingmentalimbalancesmakeuseoftraditionalmethods(face-to-faceinterviewsandself-reportingquestionnaires)which areinterminableandlabour-intensive.Additionally,clinicaldiagnosisofdepressionisdifficultbecausetheillnessitselfmanifests in diverse ways and diagnosis is highly dependent on specialists’ expertise. Thus, integration of traditional methods and technology such as wearable sensors provide a way for periodic monitoring and treating the patients with mental health problems.Nonetheless,developmentofautomateddetectionandpredictionwithobjectiveevaluationwashighlydesirableto complementtraditionalmethodsandmedicaldiagnosis.
Incorporating health care and technology is beneficial in discovery and prediction of various physical and mental health conditionsmakingitpossibletoprovidepropertreatmentandcareneededfortheindividuals.TheadvancementofMachine LearningalgorithmsandDeepLearningtechniqueshavebeenboundtooffernewapplicationsforlearningandidentifying mentalhealthsymptoms,buildingmodelsforpredictionanddetectionfordiseaseprogressionandimprovingperformanceof the developed models. Various statistical, computational and reinforcement techniques have been effective in enabling automateddetectionandpredictionofdepression.Growthinavailabilityofdataalongsideenhancementstocomputingpower hasdirectedtoariseinresearchandapplicationsdeeplearningtechniques.
Machine Learning algorithms like Random Forest [9], Naive Bayes [13] and Support Vector Machine (SVM) [7], [28] are commonly used techniques in many previous studies to detect symptoms of major depressive disorder using datasets encompassingbehavioral patternsofpatients.Alongsideofthesetechniques,Logistic Regression,K-NearestNeighborand Neuralnetworksareusedforextractingpredictivefeaturesandidentifyinggeneralanxietyanddepressivedisorder.Instudy conductedinthementalhealthdomain,Nemesureetal[19]aimedtodetectMajorDepressiveDisorderandGeneralizedAnxiety Disorderbycollectingsamplesfromundergraduatestudentsthroughgeneralhealthscreeningandpsychiatricassessment.Use ofXBoostclassifierbecamethefirstknownproposedsystemforpredictingthetwodisordersbyenablingthemodeltolearnand trainfromelectronichealthrecordsdata.Althoughthesystemshowedpotentialitspredictivevaliditybydetectingunknown psychiatricdiagnosis,thegeneralhealthscreeningprocessmaynothavecoveredallcaseswithinthepopulation.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page320

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Similarly,largepartialdatasetsofhealthsurveydatathroughPhQ-9andSF-25scalesweretakenasinputtoanEnsemblebinary classifier[25]foridentifyingdepression.Theclassifierwastobestableandrobustwhilepredictingdepressedcasesbasedon correlationbetweenquality-of-lifescaleanddepressivesymptoms.However,reliabilityandsensitivityofthedevelopedsystems aretobeassessedonaddeddatasets.
Datadrivenapproacheswereintroducedformodelingasystemfordiagnosisofdepressivedisorderduringthepandemic. Supervisedandunsupervisedlearningalongsideofclinicaldatasavedtimeandcostindatacollectionwhichisessentialwhile designingadatadrivenmodel[4].Predictivemodelingforinferringdepressionbecamepopularwithmultimodaldata.Large datasetsofaudioandvideodataacquiredfromRedditpostswithDeeplearningmodelssuchasRecurrentNeuralNetworks (RNN)[1]ispresentedforpredictionanddiagnosisofsuiciderisks.Similarly,multimodal datacollectedthroughquestion answermechanismwasutilizedtomooddisordersandidentifytheindividual’smentalstateofmind.AutoencodersandLong Short Term Memory were employed for this purpose. First model extracted features from facial expressions and speech responsewhereasthelattermodelanalyzedthetemporalinformationofthestimulatedresponses.AutoencodersandLongShort Term Memory are also utilized to prevail over misdiagnosis of bipolar disorder as unipolar disorder [24]. Small datasets acquired through audio and video data are extracted from feature selection methods like Regression and Support Vector Machine was implemented for classifying depression [21]. Apart from this, Regression analysis and CNN are combined to automaticallyassessdepressionandforeseedepressionseverity[29]fromhumanbehavior.Themodelcreatedtwosequence descriptorswiththehelpofgazedirectionsandfacialactionprimitives.Theresultsofthismodelattainedfromtrainingthe system on AVEC 2016 DAIC-WOZ database, achieved significant progress compared to previous state-of-art in terms of estimatingdepressionseverity.
FromallthesepreviousstudiesitcanbeobservedthatMachineLearningandDeepLearningtechniquesareintegrated,ora singletechniqueisemployedforpredictionanddiagnosis.Often, detectionanddiagnosisweredeterminedbyconsidering symptomsofmentalhealthdisorders.Thedatastreamlinedfordepressivedisorderpredictionwasclinicaldata,patients’voice orvisualdata.Acquiringclinicaldataforanalysisisachallengingtaskashospitalsandclinicsdonotdisclosepatients’records duetoprivacyanddatasensitivity.Availabilityofresources,specificallyequipmentneededforattainingaudioandvideodata becomesdifficultiftheyarenotwithintheaffordablerange.Assuch,itisnecessarytoconsiderthediversesituationsalongwith depressivesymptomsforpredictiondepressionriskinpilotstagesandprovidethehelpneededfortheindividualstocope.
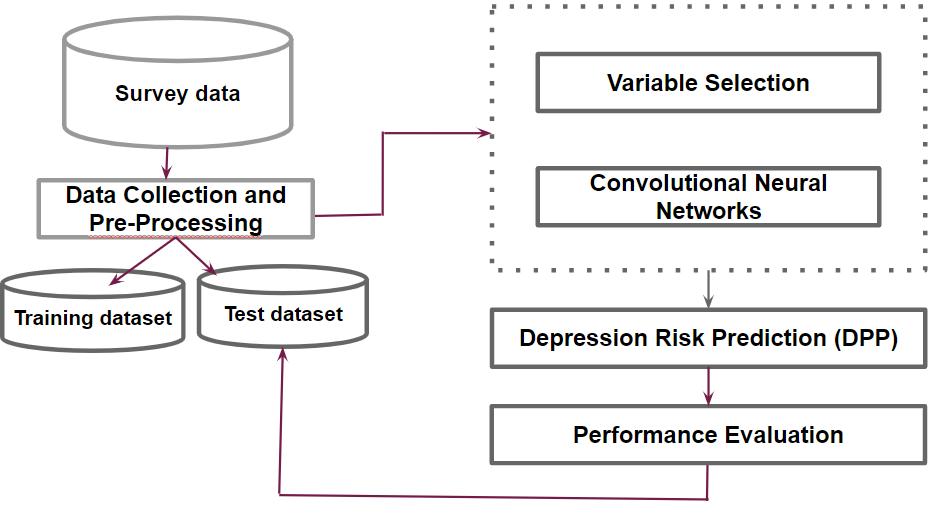
Depressionisanongoingproblem,anditcanlastforweeks,months,oryears.Theproposedsolutiondetermineddepression riskorDPPinteachersandstudentsduringCOVID-19ineducationalenvironmentusingMachineLearningalgorithmandDeep Learningmodels.Itisimportanttorecognizeandaddresstheharmfuleffectsofdejectedemotionalstateoftheindividualto avoidlongtermcomplicationsinacademicandpersonallife.TheproposedDepressionProne/RiskPredictorisdevelopedin fourstepsasshowninFig-1.
Fig-1: ArchitectureforDepressionRiskPredictor
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Clinicaldatasetsordatacollectedthroughhealthsurveysaregenerallyusedasdepressiondatasets.However,duetothescarcity ofopensourceddatasetsfordepressioninteachersandstudents,datasetsonbasisofglobalpandemicandacademicfactors havebeencreated.Inthefirstofproposedsystem,primarydataiscollectedthroughstructuredquestionnairesforbothteachers andstudents. Theself-reporting questionnairearedesigned separatelyforteachersandstudentsin referencetostandard depressionscalessuchasPatientsHealthQuestionnaire(PHQ-9),Beck’sDepressionInventory(BDI),CanadaMentalHealth surveyduringthepandemictoassessgeneralmentalhealthforteachers[26]andUSAMentalHealthSurveyduringpandemicto analyzedepressionofstudents[2].Thequestionnairescontain50questionscategorizedinto8sectionsonthebasisoffactors influencingthedepressionrisk.BoththequestionnairesarevalidatedbythePsychiatristandrealtimedataiscollectedby conductingasurveythroughgoogleformsinvariouseducationalinstitutesacrossHyderabadcity.Thesurveyisconducted duringthetimeofstringentlockdownsbykeepinviewemotionalstateoftheindividualforpastonemonth.Thesampleddatais furthersynthesizedusingCTGAN.Themodeliswelldefinedforformulatingdataforcategoricaldataintabularformatbasedon frequencyofvaluesineachtabularcolumn.TeachersandstudentsDatasetsarepreprocessedandaresplitinto80%training dataand20%testingdata.
Teachers’datasetcontainsvariablesimpellingdepressionrisksuchasdailyworkload,challengesfacedinadaptingtonew teachingstyles,professionalgrowth,balanceofpersonalandprofessionallife,effectsofstressonhealth,sleepandeatinghabits andeffectsofpandemicimposedontheindividual.Forexample,forthevariable‘Balancingpersonalandprofessionallife’values areorderedas:notatallexhausting,mildlyexhausting,moderatelyexhausting,andseverelyexhausting.Thisself-reporting questionnairecontainscategoricaldataandislabeledbasedonCES-D.Thislabeleddataisusedtogenerateadatasetof10,000 samplesusingCTGANwhicharestoredinaCommaSeparatedValues(CSV)file.Thegenerateddataisevaluatedagainstthereal timedatatoattainasimilaritymeasureandtoevaluatethemodel.Anevaluationof0.73187wasachievedindicatingthatthe synthesizeddatawas73.18%liketherealsampledata.ThesampledatasetforteachersinCSVfileisshowninTable-1.
Table-1: Teachers’Dataset
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Students’datasetcontainsvariablesinfluencingdepressionrisksuchasacademicworkload,challengesfacedinadaptingto onlinelearning,careerplanning,balanceofpersonalandprofessionallife,effectsofstressonhealth,sleepandeatinghabits, socialinteractionsandeffectsofpandemicforcedontheindividual.Forexample,forthevariable‘Careerplanningduring pandemic’valuesareorderedas:notatallsatisfying,mildlysatisfying,moderatelysatisfying,andseverelysatisfying.
Thisself-reportingquestionnairecontainscategoricaldataandislabeledbasedonCES-D.Thislabeleddataisusedtogenerate adatasetof10,000samplesusingCTGANwhicharestoredinaCSVfile.Thegenerateddataisevaluatedagainsttherealtime datatoattainasimilaritymeasureandtoevaluatethemodel.Anevaluationindicatingthatthesynthesizeddatawas76.89% liketherealtimedatasetwasachieved.Table-2showssampledatasetforstudentsinCSVfile.
Table-2: Students’Dataset
S.No Attribute/Variable Name Value
1 x1
Helplessness
1:Notatall
Overburdenedwith Workload 1:Nil 2:Low 3:Moderate 4:High 2 x2 Noofsittinghours 1:Nil 2:Low 3:Moderate 4:High 3 x3 Effectivenessof OnlineLearning 1:High 2:Moderate 3:Low 4:Nil 49 x49
2:Severaldays
3:Morethanhalfthedays 4:Nearlyeveryday 50 x50 Lonelinessdueto SocialIsolation
1:Notatall 2:Severaldays
3:Morethanhalfthedays 4:Nearlyeveryday
In the second step, Multiple Regression with Backward Elimination is implemented for identifying potential variables significantlyaffectingdepressionriskinteachersandstudents.Inthisapproach,asignificancelevelαisfixedseparatelyfor teachersandstudents.Itindicatedtheprobabilityofrejectingthetruenullhypothesis.MultipleRegressionmodelisfitwithall thefeaturesandinputfeatureswithhighestp-valueareidentified.Ifthefeaturewithhighestp-valuesisgreaterthanα,the featureiseliminatedfromthedataset.Themodelisfitagainwiththisnewdatasetandtheprocessisrepeateduntilhighestpvalue from all the remaining features in the dataset is less than the significance level thus eliminating less important or noteworthyfeatures.
Forteacher’sdataset,asignificancelevelis0.1ischosenandoutof50inputfeaturestenpotentialvariablesofdepressionrisk havebeenidentified.Table-3demonstratestheresultofregressionanalysiswithp-value<=0.1.‘StdError’representsthe standarderror,and‘t-value’isat-teststatisticalvalueindicatingthestatisticsoftheinfluenceofvariables.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Table-3 PotentialVariablesforTeachers’Dataset
Variable Description Coeff (estimate) Std Error t-value P > |t|
x4 Academic & other curricular responsibilities -0.012423 0.008 -1.500 0.134
x5 MethodofInstructionsforteaching 0.020720 0.008 2.663 0.008
x10 Managingstudents’behavior 0.017433 0.008 2.155 0.031
x14 ProfessionalgrowthduringPandemic 0.013284 0.008 1.698 0.090
x17 Adaptingtoonlineteachingplatform 0.015574 0.008 1.880 0.060
x27 Managing time toachieve personal & professionalgoals 0.014560 0.009 1.631 0.103
x33 Nutrition:OvereatingorpoorAppetite 0.011402 0.008 1.406 0.130 x38 Concernaboutone’shealth&safety protocols 0.018196 0.009 1.996 0.046
x41 Restlessness -0.012795 0.009 -1.352 0.127 x48 Losinginterestinwork 0.015779 0.008 1.943 0.052
Inadditiontothisregressionequationisformed.Theprobabilityofdataondepressionriskisgeneratedasoutputwhichis they-intercept.Eachoftheselectedpotentialvariablesforteachersismultipliedbytheestimatedvalue,andthenthe multipliedresultsarealladdeduptoobtaintheprobabilityinformationondepressionriskinteachers.
DPP=(2.4697)+(0.0124*x4)+(0.0207*x5)+(0.0174*x10)+(0.0132*x14)+(0.0155*x17)+(0.0145*x27)+(0.0114*x33) +(0.0181*x38)+(-0.0127*x41)+(0.0157*x48) (1)
Forstudent’sdataset,asignificancelevel=0.01isselectedandoutof50inputfeaturessevenpotentialvariablesofdepression riskhavebeenidentified.Table-4displaystheresultofMultipleRegressionwithp-value<=0.01.‘StdError’representsthe standarderror,and‘t-value’isthet-teststatisticalvalueindicatingthestatisticsoftheinfluenceofvariables.
Table-4 PotentialVariablesforStudents’Dataset
Variable Description Coeff (estimate) Std Error tvalue P > |t|
x6 Preparednessofthetopic 0.027871 0.011 2.566 0.010
x15 Supportfromfriends/classmates 0.027745 0.012 2.869 0.018
x20 Joboffersduringpandemic 0.034288 0.012 2.375 0.004
x30 Effectsofstressonphysicaland mentalhealth 0.038418 0.012 3.144 0.002
x37 NervousnessandAnxiety 0.031912 0.012 2.685 0.007
x40 Worryaboutfinancialhealth 0.023554 0.010 2.354 0.019
x33 Nutrition:OvereatingorpoorAppetite 0.011402 0.008 1.406 0.130
x41 Restlessness 0.032338 0.012 2.649 0.008
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page324

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Regressionequationisalsoattainedforpredictingdepressionriskforstudentsinthelaststepoftheproposedsystem. DPP=(0.5209)+(0.0278*x6)+(0.0277*x15)+(0.0342*x20)+(0.0384*x30)+(0.0319*x37)+(0.0235*x40)+(0.0323*x41) (2)
Inthepenultimatestepoftheproposedsolution,relatedcontextinformationforeachofthepotentialvariableisidentifiedby implementingMultipleRegressionwithBackwardEliminationdescribedinthepreviousstep.Thepotentialvariablesobtained inthepreviousstepareusedasthedependentvariableandtherelevantcontextinformationisobtainedinhighrelationwith thepotentialdepressionvariables.
Asignificancelevelof0.1andrelevantcontextisidentifiedforeachofthe10potentialvariables.Forexample,thepotential variablex48:‘Losinginterestinwork’isassociatedwithcontextinformationvariables:x2:Classpreparationandteachingtime, x7:Meetingclassroomexpectations,x31:Effectsofstressonphysicalandmentalhealthandx38:Concernaboutone’shealth andsafetyprotocols.TheresultsofthissteparepresentedinTable-5.
Potential Variable Related Context Information
x4 x2,x16,x19,x23,x28,x32,x39,x47 x5 x7,x11,x21,x22,x43,x49 x10 x1,x26,x40 x14 x31,x37 x17 x25,x28,x36 x27 x21,x26,x37 x33 x29,x40,x47 x38 x7,x16,x23,x24,x26,x43 x41 x8,x19,x25,x44,x50 x48 x2,x7,x31,x38
Asignificancelevelof0.01andrelevantcontextisidentifiedforeachofthe7potentialvariables.Forexample,thepotential variable x20: ‘Job offers during Pandemic’ is associated with 3 context information variables: x17: Career planning, x38: Concernaboutone’shealthandsafetyprotocolsandx43:Feelingdownandhopeless.Table-6projectsresultsofthisstep.
Potential Variable Related Context Information
x6 x12,x21,x22,x23,x42,x44,x45,x46,x48 x15 x5,x16,x19,x28,x39,x44,x48 x20 x17,x38,x43 x30 x2,x25,x39,x44,x48 x37 x2,x9,x12,x23,x25,x32,x38,x39,x42,x45,x46,x48 x40 x2,x5,x12,x13,x16,x17,x19,x22,x25,x27,x38,x39,x43, x44,x45,x46,x49 x41 x1,x9,x22,x42,x46,x48
value:
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

CNNmodelsareprimarilydevelopedfordealingwithimageclassificationproblemsinwhichthemodellearnstorepresent two-dimensionaldatareferredtoasfeaturelearning.Thesameprocedurecanbeharnessedonone-dimensionalcategorical datainwhichthemodelextractsfeaturesfromsequenceofobservations.Inthelaststepoftheproposedalternative,CNN modelisimplementedoncategoricaldatawithTheRectifiedLinearUnit(ReLu)astheactivationfunctionandAdamoptimizer. OncetheCNNmodelisconstructed,themodelistrainedandcompiledtobetterfitthesystemandthenevaluatedagainstthe testdatatopredicttheoutputvalues.FlattenandDropoutarealsoaddedtothemodeltoimproveitsperformance.
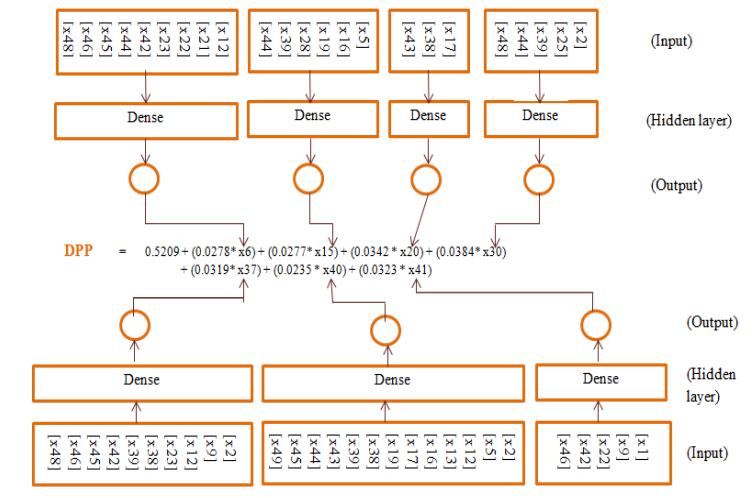
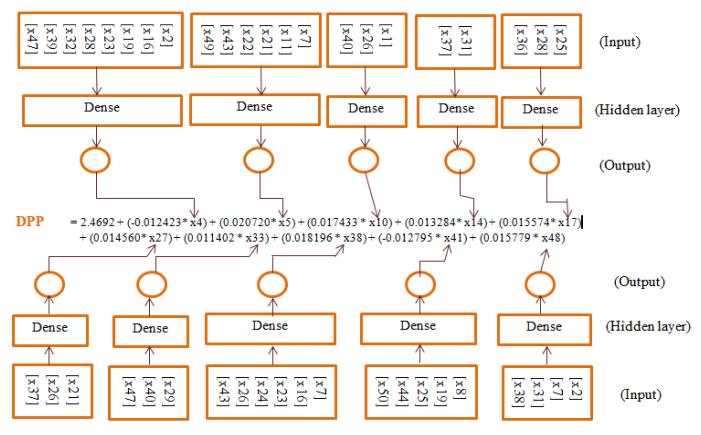
CNNmodelisdesignedwithcontextvariablesasinputandthevalueofpotentialvariableastheoutput.10potentialvariables areidentifiedfordepressionriskandeachoneisusedforaCNN.10CNNsarelearnedseparatelytorestrictthenumberof hiddenlayersandreducethetimeforlearning.TheoutputofeachCNNissubstitutedintheregressionequation(1)presented topredictthedegreeofdepression.Fig-2showsthecontextpredictionprocessfortheDPP.
Fig-2: ProposedCNNprocessforDepressionRiskPredictioninTeachers
Eachofthe7potentialvariablesidentifiedfordepressionriskareusedwithCNNmodel.7CNNsintotalarelearnedseparately to restrict the number of hidden layers and cut back the time for learning. For the connection of the learned CNNs, the regressionequationisapplied.TheoutputofeachCNNissubstitutedintheregressionequation(2)topredictthedegreeof depressionandFig-3showsthecontextpredictionprocessfortheDPP.
Fig.-3: ProposedCNNprocessforDepressionRiskPredictioninTeachers
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page326
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
MachineLearningalgorithmsandDeepLearningtechniqueshavebeenformulatedforthepredictionofdepressionriskin teachers and students. The proposed CNN model uses dynamic context information for depression risk prediction and individual learning promoteslearning in a brief time. Thevariablesidentified throughCNN are substitutedin regression equationforpredictingdepressionrisk.Thepredicteddepressionriskforstudentsandteachershasbeencategorizedinto4 stages:norisk,mildrisk,moderaterisk,andsevereriskonthebasisofCES-D[20]ofNationalMentalHealthCenter.The performance of teachers’ and students’ module is evaluated in terms of goodness-of-fit, accuracy and residual error. A comparative analysis with General CNN, Multiple Regression and the proposed CNN model are executed to predict the depressionriskindependentlyforbothteachersandstudents.
Fromtheavailableperformancemetrics,forMultipleregressionRSEandMultipleR^2scoreisusedforevaluatingtheresults obtained.ResidualStandardError,RSEisdefinedas“thedifferencebetweenpredictedvalueintheregressionmodelandthe actualdata.”MultipleR^2isthe“variancerateofdependentvariables”whichcanbeexplainedbytheregressionmodel.Inthe GeneralCNN,theperformancemeasureschosenareLossfunctionandAccuracy.Lossfunctionisusedtoassessthe“difference betweenthedataobtainedbylearningandrealdata.Largerthevalueis,themorethelearneddataisinconsistentwiththereal data.”MeanAbsolutePercentageError(MAPE)andAccuracyarethemetricsforevaluatingtheperformanceofproposedCNN model.MAPEcanbeconsideredasalossfunctiontodefinetheerrortermedbythemodelevaluation.UsingMAPEaccuracyof themodelcanbeestimatedintermsofthedifferencesbetweentheactualandestimatedvalues.
Teachers’modulewasimplementedwithdatasetcontaining10,000samplesand50inputvariables.Thetargetvariable,DPP waspredictedbyvariableselectionreducingtheinputfeaturesfrom50to10.Relatedcontextinformationforeachofthese10 potentialvariablesisidentifiedusingregressionanalysis.CNNismodeledforeachpotentialvariabletofinditsvaluewith related context information as input to the deep learning model. The DPP was predicted by computing its value in the regressionequation(1)alongwiththese10potentialvariablesandtheircontextinformation.
Table-7 ComparativeAnalysisandPerformanceEvaluationforTeachers
Depression Risk Prediction for Teachers
Multiple Regression
RSE 0.7305
Multiple R^2 0.0094
CNN Loss 1.4742 Accuracy 0.3890
Proposed CNN Model
MAPE 0.3047
Accuracy 0.6952
FromTable-7,itisobservedthattheproposedCNNmoduledisplayedabestperformance.Inregressionanalysistopredict teachers’depressionrisk,aRSEwasmeasuredtobeabout0.7indicatingalargerdifferencebetweenpredictedvaluesand actualvalues.Inaddition,proposedmodelisobservedtohavealesservalueoflossandhigheraccuracythangeneralCNN.This comparative analysis shows that the proposed CNN model has better performance with accuracy of 0.69 than multiple regressionanalysisandgeneralCNNintermsofdepressionriskforteachers.
Students’modulewasimplementedwithdatasetcontaining10,000samplesand50inputvariables.Thetargetvariable,DPP waspredictedbyvariableselectionreducingtheinputfeaturesfrom50to7variables.These7potentialfeaturesalongwith theirrelatedcontextinformationarefittotheproposedCNNandthevalueofDPPwaspredictedusingtheregressionequation (2).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Depression Risk Prediction for Students
Multiple Regression
RSE 1.0476 Multiple R^2 0.0408
CNN Loss 1.2519 Accuracy 0.3751
Proposed CNN Model
MAPE 0.4386 Accuracy 0.6113
FromTable-8,itisobservedthattheproposedCNNmodeldisplayedabestperformance.Inregressionanalysistopredict students’depressionrisk,RSEwasmeasuredtobeabout1.04indicatingalargerdiscrepancybetweenpredictedvalueand actual value. The proposed model is observed to have a lesser value of loss and higher accuracy than general CNN. This comparative analysis shows that the proposed CNN model has better performance with accuracy of 0.61 than multiple regressionanalysisandgeneralCNNintermsofdepressionriskforstudents.
TheproposedsystemforpredictingdepressionriskinteachersandstudentswasdevelopedusingMultipleRegressionfor feature selection and CNN for prediction. A questionnaire based data was collected independently for both teachers and students.Forteacher’smodule10potentialvariablesandforstudents’module7potentialvariablesareselectedandrelated contextinformationisidentifiedfollowedbydepressionriskprediction.Anaccuracyof69.52%forteachersand61.13%for studentsisachievedfordepressionriskprediction.Itisobservedthatdepressionriskpredictionforteachers’modulehas better performance and results in comparison with depression risk prediction for students’ module. The real time data collectionischallengingasperceptionandideologyaboutmentalhealthdiffersinindividuals.Timeisalimitingfactorfor conductingsurveyforwiderangeofrespondents.Inaddition,synthesizeddatawasusedalongwithrealtimedatatomeasure depression risk accuracy. The proposed system can be extended further significantly increasing the model accuracy by accumulatingmorerealtimedataandimplementingdifferentMachineLearningtechniques.Themodelcanbeenhancedto predictstresslevels,anxiety,andothermentalhealthconditions.Lastly,themodelcanbeenhancedbydesigningafrontend systemwithendtoendintegrationtofocusonindividualpredictions.
[1] Alambo,Amanuel&Gaur,Manas&Lokala,Usha&Kursuncu,Ugur&Thirunarayan,Krishnaprasad&Gyrard,Amelie& Sheth,Amit&Welton,Randon&Pathak,JyotishmanQuestionAnsweringforSuicideRiskAssessmentUsingReddit, 2019
[2] Basheti IA, Mhaidat QN, Mhaidat HN Prevalence of anxiety and depression during COVID-19 pandemic among healthcarestudentsinJordananditseffectontheirlearningprocess:Anationalsurvey.PLoSOne,2019
[3] Chintalapudi N, Battineni G, Amenta F. Sentimental Analysis of COVID-19 Tweets Using Deep Learning Models. InfectiousDiseaseReports,2021.
[4] Choi,B.,Shim,G.,Jeong,B.etal. Data-drivenanalysisusingmultipleself-reportquestionnairestoidentifycollege studentsathighriskofdepressivedisorder.SciRep10,7867,2020
[5] Coppersmith,Glen&Leary,Ryan&Crutchley,Patrick&Fine,Alex.NaturalLanguageProcessingofSocialMediaas ScreeningforSuicideRisk.BiomedicalInformaticsInsights,2018
[6] DiCarloD.T.,MontemurroN.,PetrellaG.,SicilianoG.,CeravoloR.,PerriniP.Exploringtheclinicalassociationbetween neurologicalsymptomsandCOVID-19pandemicoutbreak:Asystematicreviewofcurrentliterature.J.2021,Neurol.; 268:1561–1569.
[7] DeChoudhuryM,CountsS,HorvitzEsocialmediaasameasurementtoolofdepressioninpopulations,2013.
[8] Du,J.etal.Extractingpsychiatricstressorsforsuicidefromsocialmediausingdeeplearning.BMCMed.Inform.Decis. Mak.2018,18,43.
[9] FatimaI,MukhtarH,AhmadHF,RajpootKAnalysisofuser-generatedcontentfromonlinesocialcommunitiesto characteriseandpredictdepressiondegree.2018,JInformSci44(5):683–695.
[10] Geraci,J.etal.Applyingdeepneuralnetworkstounstructuredtextnotesinelectronicmedicalrecordsforphenotyping youthdepression.Evid.BasedMent.Health20,83–87,2017
[11] Gkotsis,G.etal.CharacterisationofmentalhealthconditionsinsocialmediausingInformedDeepLearning.2017.Sci. Rep.7,45141.
[12] HarapanH,ItohN,YufikaA,WinardiW,KeamS,TeH,MegawatiD,HayatiZ,WagnerAL,MudatsirM.Coronavirus disease2019(COVID-19):Aliteraturereview.JInfectPublicHealth.2020(5):667-673.
[13] Hassan AU, Hussain J, Hussain M, Sadiq M, Lee S Sentiment analysis of social networking sites (SNS) data using machinelearningapproachforthemeasurementofdepression.2017,IEEE,NewYork.
[14] J.GaunArtificialintelligenceinhealthcareandmedicine:Promises,ethicalchallengesandgovernance, 2019,Chin. Med.Sci.J.,vol34,no.2,pp.76-83.
[15] Kuo ES, Vander Stoep A, Herting JR, Grupp K, McCauley E How to identify students for school-based depression intervention:canschoolrecordreviewbesubstitutedforuniversaldepressionscreening?.JChildAdolescPsychiatric Nurs.;2013,26(1):42-52
[16] Lin,E.etal.Adeeplearningapproachforpredictingantidepressantresponseinmajordepressionusingclinicaland geneticbiomarkers.2018,Front.Psychiatry9,290.
[17] Lin,H.etal.Detectingstressbasedonsocialinteractionsinsocialnetworks.2017.IEEETrans.Knowl.DataEn.29, 1820–1833.
[18] Minkos M.L., Gelbar N.W. Considerations for educators in supporting student learning in the midst of COVID-19. Psychol.2021.Sch;58:416–426.
[19] Nemesure,M.D.,Heinz,M.V.,Huang,R.etal.Predictivemodelingofdepressionandanxietyusingelectronichealth recordsandanovelmachinelearningapproachwithartificialintelligence.SciRep11,1980,yr2021
[20] RadloffLSTheCES-DScale:ASelf-ReportDepressionScaleforResearchintheGeneralPopulation. 1977Applied PsychologicalMeasurement;1(3):385-401.
[21] S.M.Alghowinem,T.Gedeon,R.Goecke,J.CohnandG.Parker,InterpretationofDepressionDetectionModelsvia FeatureSelectionMethods,in2020,IEEETransactionsonAffectiveComputing.
[22] S.Song,L.ShenandM.Valstar,HumanBehaviour-BasedAutomaticDepressionAnalysisUsingHand-CraftedStatistics andDeepLearnedSpectralFeatures,13thIEEEInternationalConferenceonAutomaticFace&GestureRecognition, 2018.
[23] Stough,Laura &Baker, Lynn.IdentifyingDepression:InStudents withMental Retardation. TeachingExceptional Children,1991
[24] Su,M.H.,Wu,C.H.,Huang,K.Y.&Yang,T.HCell-coupledlongshort-termmemorywithl-skipfusionmechanismfor mooddisorderdetectionthroughelicitedaudiovisualfeatures.2019,IEEETrans.NeuralNetw.Learn.
[25] Tao,X.,Chi,O.,Delaney,P.J.etal.DetectingdepressionusinganensembleclassifierbasedonQualityofLifescales. BrainInf.2021.
[26] TeachersMentalHealthSurvey,CanadianTeachersFederation,Canada,2020.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page329

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[27] Tran,T.&Kavuluru,RPredictingmentalconditionsbasedonhistoryofpresentillnessinpsychiatricnoteswithdeep neuralnetworks.J.Biomed.Inform.75,S138–S14,2017.
[28] TsugawaS,KikuchiY,KishinoF,NakajimaK,ItohY,OhsakiHRecognizingdepressionfromtwitteractivity.pp.3187–3196,2015
[29] WangHui,TianXuemei,WangXianrui,WangYun,EvolutionandEmergingTrendsinDepressionResearchFrom2004 to2019:ALiteratureVisualizationAnalysis,FrontiersinPsychiatry,volume12,2021
Dr.A.sharada,ProfessorinCSEdept,obtainedPh.DfromJNTUHintheareaofSpeechRecognitionhasbeen workinginG.NarayanammaInstituteofTechnology&Scienceforlast20years.Sheisworkingonvarious R&DprojectsintheareasofVoiceAssistantsforElderlyandPatientcare,MentalHealthAnalysis,Assistive Technology. She published around 25 papers in International Journals like Springer and ACM and in Internationalconferences.ShehasdevelopedcontentforGradianceportalofStanforduniversity.Toher credit,shehasa license fortheresearchworkdoneinfinalizing Telugu Phone set and Phoneme chart applicable to Speech Recognition research underCreativeCommonsUnportedLicense.Received Best Teacher Award from Institute for Exploring Advances in Engineeringin Mar, 2018. Dr.Sharada has adoptedmanybooksforvariousuniversitiesandreviewedbooksonUML,C,DataStructures,C++and JAVAforpopularpublisherslikeTataMcGrawHill,Pearson,OxfordUniversityPressetc.

ManasaJonnalagaddareceivedB.Techdegreein2018fromG NarayanammaInstituteofTechnology& Science and worked at Infosys, India for 2 years She is currently a final year M.Tech student of G NarayanammaInstituteofTechnology&Scienceandworkingasa softwareprogrammeratThomson Reuters HerprimaryresearchinterestisMachineLearningandDeepLearningApplicationsinHealthcare domain
