International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Student of M.tech in Electronics and communication department,Dr Rammanohar lohia Avadh University Ayodha Uttar Pradesh India
Assistant professor in Electronics and communication department Dr Rammanohar lohia Avadh University Ayodhya Uttar Pradesh India
Professor in Electronics and communication department Dr Rammanohar lohia Avadh University Ayodhya Uttar Pradesh India ***
Abstract - Duetorevolutionarydevelopmentsinelectronic and communication, mobile and handheld devices have becomeapartofourdailylife.Asaresult,thevolumeofdata trafficontheInternetisincreasingdaybyday.Toprovide unlimited,uninterruptedandcontent-richservicestothese devices, the 5th Generation (5G) of network technology emerged.A5GnetworkcanprovidebetterQualityofService (QoS) along with higher data rates than 4G network and havelesslatency.Thepaperappraisesvariousgenerationsof wireless networks. Furthermore, it explores various challenges in implementation of the 5G network and applicationareasofthe5Gnetwork.
Keywords: Internet of Things, Device-to-device communication, Smart Health, Smart farming.
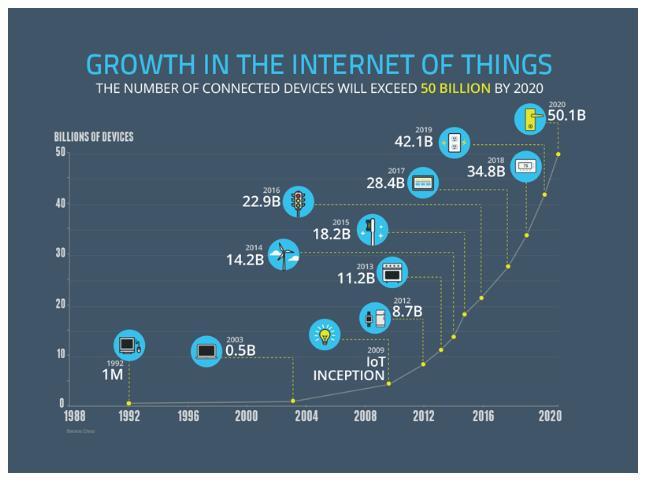
Toprovideubiquitousservicestomobiledevicesthecellular system came into existence. Now a-days, Industry and academiabotharetryingtodevelopbetteralternativesto provide high-speed bandwidth and real-time services to mobile devices. 5G enables next generation wireless networkstoprovidebetterEnd-to-End(E2E)connectivityin on-demand fashion. Analysis by Computer Information SystemCompany(CISCO)statethatmobiledatatrafficmay increaseup-to4.8Zettabyte (ZB)[1]peryear by2022, or 396Exabyte’s(EB)/month,whileitwasonly1.5ZB/yearor 122EB/monthin2017.Inanotheranalysis byCISCO,it is projected that in 2020, approximately 50 billion smart deviceswillbelinkedtotheInternet.Figure1showsgrowth ofInternetofThings(IoT)enableddevicesontheInternet. Inthelastdecade,IoThasreformedthepervasivecomputing duetonumerousapplicationareassuchassmartcity,smart agricultural, smart health etc. The IoT paradigm encompasses a group of smart devices and sensor nodes. Sensornodesmonitorthepredefinedparametersandshares viatheInternet.Inananalysis,itisfoundthattherewillbe billionsofdeviceswithonaveragesixtosevendevicesper personbytheyear2020[2].In2022,morethanonetrillion sensor nodes will be attached to the Internet. It is also
expectedthatinthenexttwentyyearsapproximatelyfortyfive trillion devices will be attached to the Internet. To provide uninterrupted services to these mobile devices is compelling to search for an alternative to 4G. It is an assumption that a new generation of cellular is proposed approximately every Ten years. The last generation of cellularnetwork,i.e.4Gnetworkwasintroducedin2011and itisexpectedthat5G[3]networkmaybestandardisedand deployedin2020.
The scope of the 5G is not limited to the radio technology; it can also provide services to fixed host communication, cloud infrastructure, etc. The extension servicesofthe5Gmobilenetworkimprovetheecosystemof thetelecommunicationnetworkandprovideservicestothe healthcare industry, agriculture industry, and smart city projects in an energy efficient manner. 5G builds the foundationofdigitalizationfrompersonalcommunicationto the interconnection of society. Digitalization builds incredibleprospectsformobilecommunicationbutsuffers from severe challenges towards mobile communication technologies.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
speed up to 144kbps. The most popular 2.5G-access technologieswereGPRS,CodeDivisionMultipleAccess-2000 (CDMA2000) and Enhanced Data Rate for GSM Evolution (EDGE).
F.Third Generation (3G) wireless networks were standardizedin2000.Thebasicobjectivetodesign2Gwas voice communication and high-speed data transfer up to 2Mbps. The most popular 3G-access technologies were Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA), CDMA2000 and Universal Mobile Telecommunications Systems(UMTS)technologies.Toutilizethebenefitsof3G
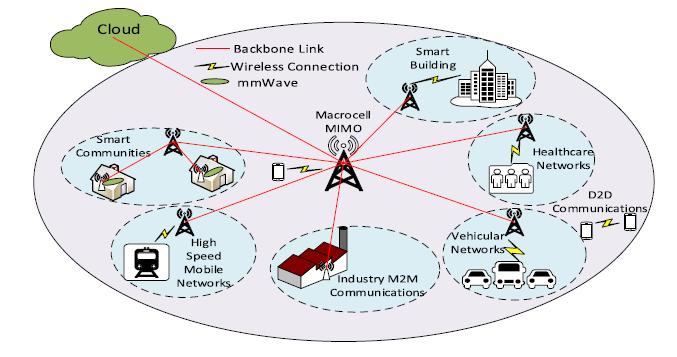
Fig. 2. Applicationareaandtechnologiesof5G
The First Generation (1G) wireless networks were standardizedinearly1981forvoicecommunication.Itwas able to handle data transfer speeds of up-to 2.4kbps. The mostpopular1G-accesstechnologieswereAdvancedMobile PhoneSystem(AMPS),NordicMobilePhoneSystem(NMTS), Total Access Communication System (TACS) etc. Analog signals were responsible for carrying out voice in 1G. It suffersfromvariousissuessuchaslowgradedsignalquality, lowcapacity,lesssecureandunreliablehandoff.
The Second Generation (2G) of wireless networks was standardized in 1990. It was primarily used for voice communicationandwasabletohandledatatransferspeeds up-to64kbps.Itwasalsoabletodatacommunicationwith limited speed. The most popular 2G-access technologies were Global Systems for Mobile communications (GSM), Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) and IS-95. 2G technology was also able to send text messages, picture messages,andMMSMultimediaMessagingServices(MMS). It is also able to provide secure point-to-point communication i.e. only the intended receiver can receive and read the message. 2G was suffering from some of the criticalissuessuchaslowdatarate,limitedcapacityofcells, higher handover latency, limited mobility etc. Also the 2G enabledphoneshavelimitedfacilities.
Itwasanextensionofsecond-generationwirelesssystems.It introduces a packet-based switching technique known as General Packet Radio Services (GPRS). Furthermore, it is able to provide better communication by use of packet switching and circuit switching techniques along with services provided by 2G. It is able to handle data transfer
It was an extension of 3G wireless networks and standardizedin2008.Itwasprimarilydesignedtoimprove thedatarateofpresent3Gnetworksandwasabletohandle datatransferspeedsofupto3.6Mbps.Themostpopular3Gaccess technologies were HSDPA (High Speed Downlink Packet Access) and HSUPA (High Speed Uplink Packet Access). The 3.75G system was proposed as an improved version of the 3G network. The technology used in it was High Speed Packet Access Plus (HSPA+). The technology used in it was known as Long-Term Evolution technology (LTE)andFixedWorldwideInteroperabilityforMicrowave Access (WIMAX). These technologies are able to provide high-speedservicessuchasondemandvideos,composite web services, social media services etc. to multiple users simultaneously. Although 3G technology brings a radical change in the field of communication it suffers from expensive implementation, compatibility issues with 2G systems, heavy radiation of magnetic waves affects our brainsetc.
Fourth Generation (4G) wireless networks were standardisedin2010.4Gisdesignedtohandledatatransfer speedupto300MbpsalongwithQualityofService(QoS).In 4G,theusercanwatchonlineHighDefinition(HD)videoand can play online games. The most popular 4G-access technologies are Voice over LTE network VoLTE (use IP packets for voice). 3G Partnership Project A. (3GPP) is presently standardising Long Term Evolution (LTE). It reduceslatencyforcriticalapplicationsandprovidessecure mobility.ItalsosupportsIoTenableddevicestointeractin anefficientmanner.Like3G,4Gisalsocostlierintermsof hardware and implementation. For communication, it requireshigh-endmultifunctionaldevices,whichshouldbe compatiblewith4Gtechnology.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
B. 3Gand4Gsystemsmainlyfocusondeliveryofcontents tomobiledevicesratherthanefficientdelivery.the5G wirelessnetworkisabletoprovideservicestobillions ofdeviceswithlatencyclosetozero.Itisexpectedthat 5Gwill bestandardisedin2020.5Gcanhandle data transfer speed up to 10Gbps along with QoS. Higher speed allows watching online Ultra High Definition (UHD)videoandplayingonlinegames
C. Smartphone-basedspecificapplicationsweredeveloped to handle video calling, online games, email service, socialmediaservicessuchasFacebookandOrkutetc.
Challengesareaninherentpartofthenewdevelopment.The primary objective of 5G is to provide high-speed mobile broadband and better throughput along with ultra-low latency,highreliabilityandsecurityincomparisonto3Gor 4Gnetworks
5G has a complex infrastructure. Within a smaller geographicalregion,itrequiresalargenumberofBase Stations (BS) to install. It will increase high data transfer rate and reduce the energy consumption, although it will increase the cost of the network. To achieve high-speed, Cognitive Radio Networks (CRN) and Massive Multiple Input and Multiple Output (m MIMO)[11]architecturewillbedeployed.Toincrease theefficiencymMIMOusesalargenumberofantennas incomparisontocommunicatingdevices.ThemMIMO usesfrequencyrange30-300GHzandwavelength1-10 mm.
4G network uses half-duplex [6] communication i.e. therearetwoseparatechannelsoneforuploadingand another for downloading. On the other hand, 5G is designed for full duplex communication i.e. it will access the same channel for access and backhaul. Although it will increase link capacity, save the frequency spectrum and be economically better, practical implementation is very difficult due to interference.Therefore,italsorequiresamechanismto canceltheimpactofinterference.
4G Radio Network (RN) consumes approximately 7080%oftotalpower.ThisleadstoemissionofCO2inalarge
amountandcreatesanegativeimpactontheenvironment. Various solutions are proposed in 5G for the same. It includes Cloud-Radio Network (CRN), Visual Light Communication (VLC), millimeter wave (mm Wave) communication, D2D communication, Massive Multiple InputandMultipleOutput(mMIMO)architecturestomake 5Genvironmentalfriendly
Theroundtriplatencyofthe4Gnetworkisaround15 milliseconds (ms). It is assumed that the 5G network will have extremely low latency and result in lower packetlossandimprovethereliabilityofthenetwork. To achieve this, efficient caching [12], mm Wave, m MIMOarchitecturecanbeincorporatedin5Gnetwork
The 5G network will have extremely low latency. It will directlyaffectthequalityofservice,end-to-enddelivery, ease of connectivity, reliability etc., To improve QoS [5], delayboundQoS,intelligentequipmentandloadbalancing schemesareincorporated.
5G network will be based on small cell network architecture rather than Base Station (BS) centric architecture or more precisely device centre architecture. The cell may be a microcell or picocell. These cells are connected through ideal or non-ideal backhaularchitecture[13].Duetosmallercells,there willbehighmobilityandhandover[14-17].
Thetraditionalmobilecommunicationnetworksfocus on communication services to individual customers whereas 5Gfocus on individual as well as industryoriented services. The mobile IoT devices need less security whereas high-speed mobile services require high security. The major security challenges in 5G networksareDenialofService(DoS)attack,hijacking attacks, signalling storms, Resource (slice) theft, security keys exposure, IMSI catching attacks, IP spoofing,scanningattacks,TCPlevelattacks,Man-inthe-middle attack, configuration attacks, penetration attacks,user-identitytheftattacketc.
The exponential growth in mobile users and IoT devicesincreasesthevolumeofdataontheInternet.4G networksmaynotbeablehandlesuchahugevolumeof data. The 5G network is capable of handling large amountsofdatabetweenenddeviceswiththehelpof optimizedarchitecture.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
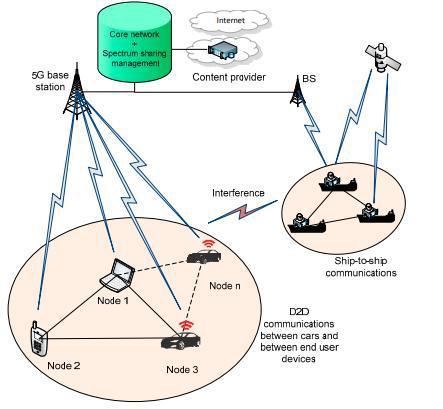
D2D [18] communications are mostly outside the territory of present cellular networks. These direct linksdirectlycommunicatewithoutinvolvingthebase station in communication. The walkie-talkie is an example of this but for communication a narrow spectrum is available and hence a bandwidth is available to communicate. The 5G system enables multi-RAT (Radio Access Technologies) systems for seamlesscommunication.TheD2Dcommunicationmay be single-hop or multi-hop. 5G allows D2D communication using LTE-Advanced, LTE Advanced Pro.Figure3showsahigh-speedD2Dcommunication modelin5G.
Fig.4. HeadmountedImmersiveEntertainmentdevice
Fig. 3 D2Dcommunicationmodelin5G
Itispresumedthat5Gwillbeupto100timesfasterthanthe presentcellularsystem withlowestlatencyand quality of services.Thefutureapplicationareamayinclude:

As the number of users on the Internet is increasing exponentially, it is difficult to provide live high definition videos to end users due to limited bandwidth capacity of 4G network and it is near to impossibletodeliverultra-highdefinitionvideos.The 5G network will be able to support the immersive entertainment[19]anywhereatanytimeduetolow latencyandbigbandwidthofferedbyit.5Gisableto project live virtual reality streams of sports, adventures,andrealworldimagesonaSmartphoneor headmounteddisplay(augmentedreality).Figure4, shows a head mounted Immersive Entertainment device.
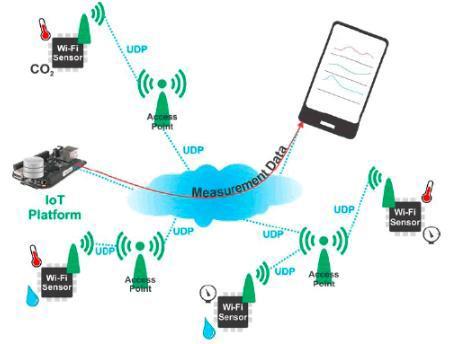
Monitoringthechangesintheenvironmentisoneof themostcriticalchallengestotheworld.Livingbeings suffer from sudden change in the climate due to unknown natural and environmental disasters, e.g., storm, flooding, drought, tsunami etc. Sensor nodes [20] are fixed at remote locations to monitor the environment [21] and the 5G network transmits the informationimmediately.Bydoing this,wecansave the lives of living beings. Recently, we have seen people lost due to the tsunami in Jakarta, Indonesia. Figure5showsmeasuringofenvironmentaldatawith thehelpofsensornodes.
The Indian agricultural system is based on traditional technique.SmartAgricultural[22]isamoderntechnique to monitor and automate the agricultural system to increasethequantityandqualityofagriculturalproducts. Smart agricultural systems gather real-time information
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
aboutcropswiththehelpofsensornodesinstalledinthe field. 5G is capable of sharing up-to-date information measured by sensor nodes. The information may be analyzed using Fog or Cloud computing and sent to the specificusertowhomitisvaluable.Smartfarminghasa numberofapplicationareassuchaswatermanagement, injectionoffertilizers,soilamendment,livestocksafetyand maturity monitoring, crop status, drilling, seeding and spraying,temperature,humidity,etc.Inassociationwith the Department of Telecommunications (DoT), Samsung hadannounceditsplanofcommencingtheFirstlarge-scale 5GtrialsinIndiaFigure6,showssmartagriculturesystem using5Gnetwork
Astudyin2016,fortheEuropeanCommissionestimated that in Europe, smart meters with 5G data capabilities couldprovideannualbenefitsof€6.47bnin2025,risingto €7.37bn in 2030 [24]. Figure 7 shows a smart metering systemusinga5Gnetwork.

Inexistingmeteringsystems,analogordigitalelectricity metersaremountedattheconsumerplace.Itmeasuresthe consumptionofelectricitybasedonpowerusedbyelectric equipment.Thesemeterscanbetamperedveryeasilyeven without a trace. It indirectly affects the economy of the country. Smart meter [23] is an advanced technique to measure the consumption of energy. It records the frequency and voltage in real time fashion and communicates the recorded information to the central systemusingwirelessmedia.Theinformationconsistsof timestamp,UniqueID(UID)of meter,currentreadingof meter, maximum power supplied by meter etc. Smart meters allow controlling and balancing of the load remotelyi.e.increaseordecreasetheloadondemand.5G iscapableenoughtoprovideserviceslikeasmartmetering systeminrealtimefashion.
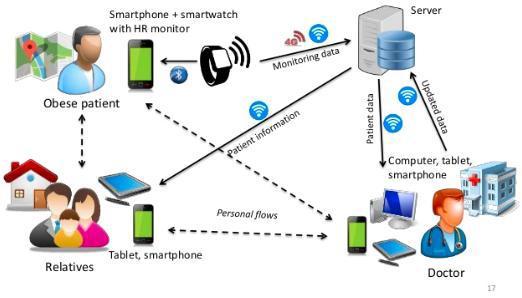
Therecentdevelopmentsandadvancementinthefield of medical technology significantly improves the living standard of people and makes them healthier. Still healthcare services [25] rural areas are worst due to unavailabilityofdoctors,medicalinformation,andmedical services.Asa result,healthcareisa criticalissueinboth urban and remote areas. 5G, robotics and artificial intelligence are able to provide healthcare services to patientsfromanywhere.Thepatienthealthcanmonitored with the help of virtual visits i.e. tiny sensor nodes may implantedorattachedtowearableclothsandthesenodes are able to monitor vital parameters such as blood pressure,sugarlevel,heartbeat,anxietyetc.onrealtime basis and sends the information to the hospitals and relativesonrealtimebasis.Theserecordswillbeavailable to physicians and medical professionals anytime and anywhere for investigation. 5G will not only be cost efficient but also provide convenience and better and timeliermedicaloutcomes.5Gcantransmitlargeimaging filesefficiently.Accordingtoresearch,itisestimatedthat the telemedicine market may increase at a compound annual growth-rate of 16.5% from 2017 to 2023 [26]. Telemedicine requires a high-speed data transmission network that may send real-time high-quality video wirelessly. 5G enables high-speed connectivity among a seriesofconnectedsensornodes,cloud-basedstorageand services. 5G will allow cloud-based storage of electronic medicalrecordsofindividualpatients.The5Gsystemwill allowcontinuousmonitoring,predictiveanalytics,remote diagnosis and imaging, efficient management of these records,whichmayhavemedicalimagesandvideo.Figure 8,showsasmarthealthsystemusinga5Gnetwork.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Remote object manipulation science [27] is in its childhood.Itallowsperformingsomeactions/operations byanobjectataremotelocation.Anon-livingobjectsuch as a robot performs the operation. This may include surgery, diffusion of bomb/mines, etc. According to the report,approximately48%ofpatientsarereadytoaccept remoteroboticsurgery,whereas61%peoplebelievethat robotic surgery is very risky as it depends on Internet services. The 5G network is capable of providing ubiquitous networks for remote services. Healthcare industry,IoTindustryandM
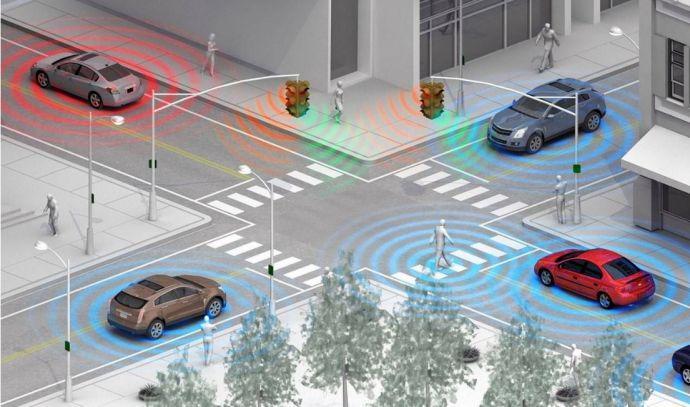
VehicularAd-hocNetwork(VANET)isasubclassofMobile Ad-hoc Network (MANET) [28] and Internet of Vehicles [29]. In VANET, the vehicles communicate with another vehicles, acknowledged as Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) communication or fixed infrastructure Road Side Units (RSUs), acknowledged as Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication, continually to gather information about roadconditions,traffic,congestionsetc.Alargenumberof vehicles are moving on the road and to exchange up-todateinformationthecommunicationdelaymustbeleast. 5Giscapableofexchangingreal-timeinformationamong vehicles connected through the Internet. 5G is capable enough to provide services to the Intelligent TransportationSystem(ITS).Figure9,showsITSenabled vehicles connected through the Internet via the 5G network.
make the Smartphone revolution seems like a miniscule advancement. In a technical report, it is found that wearable and artificial intelligence devices improve the performance of the healthcare sector by monitoring variousvitalparametersrelatedtohumanhealth.Figure 10,showsasmartwearablewristwatchwith5Gnetwork.

5Gmakeslifeeasierforthesegadgets,doingawaywithany requirementoftop-end,overtlycostlyprocessors.5Gwill lendthemtherequiredcomputingpowerandtherein,the superfastspeedandreliableconnectivitythattheyneedto do justice to the user. The combination of 5G and wearable’s[30]areexpectedtobesopowerfulthatitwill
Fig.10. SmartWearablewristwatchthrough5Gnetwork
Security is one of the critical issues of smart cities. The securitycanbemanagedbymobilevideosurveillance[31]. It may be part of trains, metros, buses, taxis, transport vehicles,policecars,dronesetc.5Gisabletoprovidereal timeupdatesforeachmovementoftheabove.
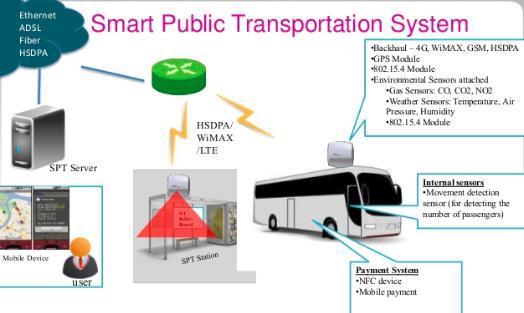
Trafficcongestionisoneofthemajorchallengestosociety nowadays. It indirectly affects the productivity of industries,createsenvironmentalpollutionanddegrades the quality of life in society. 5G technologies are able to collecthugeamountsofdatareal-timeinformationfrom vehicles,drivers,roadsensorsandcamerasinstalledatthe side.Itwillhelptomanagetrafficflow[32].Forexample,it canmanagethetrafficsignalsaccordingtodensityoftraffic androadusageandlimittrafficenteringacongestionzone. Figure 11, shows an example of a public transportation systemconnectedthrough5Gnetwork
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Initially the paper briefly introduced various wireless generations. Furthermore, the paper discusses various issuesandchallengesinimplementationof5Gnetworksand itssolutions.IoTdeviceshavenumerousapplicationareas. Hence,lateron,thepaperexploresthevariousapplication areasofthe5Gnetwork.
1. https://www.networkworld.com/article/3323063/inter net/cisco-predic ts-nearly-5-zettabytes-of-ip-traffic-peryear-by-2022.html.
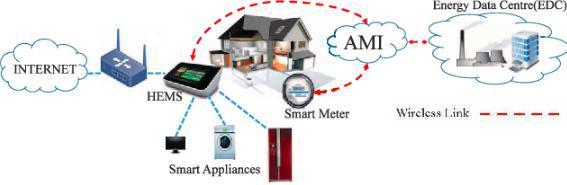
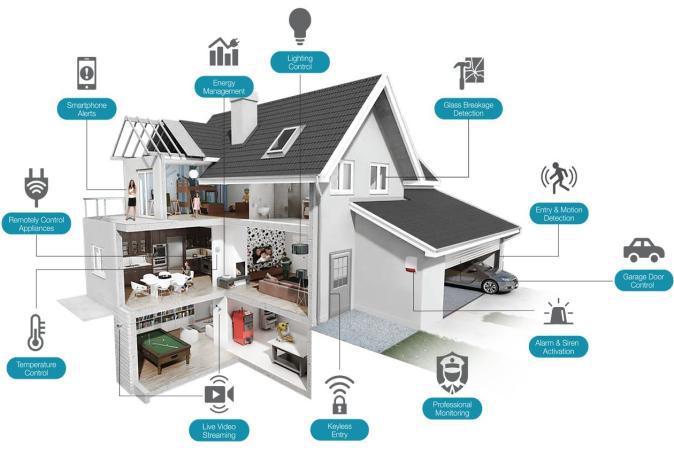
A smart home is a house in which most of the home appliances such as light, refrigerator, televisions, air conditioners, security system etc. are monitored and controlled through the Internet. A node in general is a SmartphoneconnectedtotheInternet. Theseappliances areequippedwithIoTsensornodes[33-34]andcontrolled using Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks (Lo WPAN)mobilecommunicationprotocol.Figure12,shows an example of a smart home connected through a 5G network.
2. https://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/ciscoenterprises-are-leading-t he-internet-ofthings_us_59a41fcee4b0a62d0987b0c6.
3 JessicaMoysen,LorenzaGiupponi,“From4Gto5G:Selforganizednetworkmanagementmeetsmachinelearning”, ComputerCommunications,vol.129,2018,pp.248–268.
4.G. Bacci, E. V. Belmega, P. Mertikopoulos, and L. Sanguinetti,“Energyawarecompetitivepowerallocationin heterogeneousnetworkswithQoSconstraints”,IEEETrans. WirelessCommun.,vol.14,no.9,2015,pp.4728–4742.
5.C. She, C. Yang, and L. Liu, “Energy-efficient resource allocationforMIMO-OFDMsystemsservingrandomsources withstatisticalQoSrequirement,”IEEETrans.Commun.,vol. 63,no.11,2015,pp.4125-4141.
6.InhyokCha,YogendraShah,AndreasU.Schmidt,Andreas Leicher, and Michael Victor (Mike) Meyerstein, “Trust in M2MCommunication,”IEEEVehicularTech.Mag.,vol.4,no. 3,2009,pp.69-75.
7.M.N.Tehrani,M.Uysal,andH.Yanikomeroglu,“Device-todevicecommunicationin5Gcellularnetworks:Challenges, solutions,andfuturedirections”,IEEECommunicationMag., vol.52,no.5,2014,pp.86–92.
8. Jeffrey G. Andrews, Stefano Buzzi, Wan Choi,Stephen V. Hanly, Angel Lozano, Anthony, C. K. Soong, and Jianzhong CharlieZhang,“WhatWill5GBe?”,IEEEJournalonSelected Areas in Communications, vol. 32, no. 6, 2014, pp. 10651082.
RapiddevelopmentinITandelectronicindustriesfocuseson development of hand-held and tiny sensor devices. These sensor nodes, especially IoT enabled devices, form a network. A high-speed data network is required for communicationamongthesedevices.4Gisunabletomeet thedemandofbandwidthandlatency.Asaresult,industries and researchers presented 5G as an alternative to 4G. 5G networks are capable of meeting industry requirements.
9 T.Rappaport, WirelessCommunications:Principlesand Practice,Prentice-Hall,EnglewoodCliffs,NJ,1996.
10.Changyang She, Chenyang Yang, and TonyQ.S. Quek, "Radio Resource Management for Ultra-reliable and LowlatencyCommunications,"IEEECommunicationsMagazine, Nol.55,No.6,2017,pp.72-78.
11. S. Buzzi, C. I, T. Klein, V. Poor, C. Yang, A. Zappone, "A SurveyofEnergy-EfficientTechniquesfor5GNetworksand
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

ChallengesAhead,"IEEEJSAC,vol.34,no.4,2016,pp.697709.
12. D. Liu and C. Yang, “Energy efficiency of downlink networkswithcaching atbasestations,”IEEE J.Sel.Areas Commun.,vol.34,no.4,2016,pp.907–922.
13. D. W. K. Ng, E. S. Lo, and R. Schober, “Energy-efficient resource allocation in multi-cell OFDMA systems with limitedbackhaulcapacity,”IEEETrans.WirelessCommun., vol.11,no.10,2012,pp.3618–3631.
14.ArunKumarTripathi,R.RadhakrishnanandJ.S.Lather, “Secure and Optimized Authentication Scheme in Proxy MobileIPv6(SOAS-PMIPv6)toreduceHandoverLatency”, InternationalJournalofComputerNetworkandInformation Security,vol.9,issue10,2017,pp.1-12.
15.Arun Kumar TripathiandSurendra Kumar Tripathi, “A Qualitative Analysis of Secured Handover Management SchemesforMobileIPv6enabledNetworks”,International Conference on Innovative Applications of Computational IntelligenceonPower,EnergyandControlswiththeirimpact onHumanity(CIPECH-18),2018,pp.1-8.
16.ShwetaSinghandArunKumarTripathi,“AComparative Study of Internet Protocols in MANET”, International ConferenceonAdvancesinComputerSciences(ICACDS-16), Ghaziabad-India,vol.721,2016,pp:221-231.
17. ArunKumarTripathiandShwetaSingh,“AComparative Analysis on Internet Protocols in Cloud-Mobile Environment”,InternationalJournalofControlTheoryand Applications(IJCTA),vol.9,issue17,2016,pp.9161-9169.
18. PimmyGandotra,RakeshKumarJhaandSanjeevJain,“A survey on device-to-device (D2D) communication: Architecture and security issues, Journal of Network and ComputerApplications,vol.78,2017,pp.9-29.
19. Muhanna A.Muhanna, “Virtual reality and the CAVE: Taxonomy,interactionchallengesandresearchdirections”, JournalofKingSaudUniversity,ComputerandInformation Sciences,vol.27,Issue3,2015,pp.344-361.
20.ArunKumarTripathiandAjayAgarwal,“AnApproach towards Time Synchronization Based Secure Protocol for Wireless Sensor Network”, International Conference on NetworkedDigitalTechnologies(NDT-2010),vol.88,issue2, 2010,pp.321-332.
21. Muhammad Saqib Jamil, Muhammad Atif Jamil, Anam Mazhar, Ahsan Ikram, Abdullah Ahmed, Usman Munawar, “Smart Environment Monitoring System by Employing Wireless Sensor Networks on Vehicles for Pollution Free SmartCities”,ProcediaEngineering,vol.107,2015,pp.480484.
22. GustavoSain, Ana María Loboguerrero, Caitlin CornerDolloff,MiguelLizarazo,AndreeaNowak,DeissyMartínezBarón,NadineAndrieu,“Costsandbenefitsofclimate-smart agriculture: The case of the Dry Corridor in Guatemala”, AgriculturalSystems,vol.151,2017,pp.163-173.
23. YasinKabalci, "A survey on smart metering and smart grid communication", Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,vol.57,2016,pp.302-318.
24.https://www.engerati.com/transmission-anddistribution/article/comm unications-networkstechnologies/5g-%E2%80%93-driver-next
25. A. Solanas, C. Patsakis,M. Conti et al., “Smart health: a context-aware health paradigm within smart cities,” IEEE CommunicationsMagazine,vol.52,no.8,2014,pp.74-81.
26.https://www.beckershospitalreview.com/telehealth/glo bal-telemedicin e-market-to-experience-16-5-annualgrowth-rate-through-2023.html
27.H.Ashrafian,O.Clancy,V.Grover,A.Darzi,"Theevolution ofroboticsurgery:surgicalandanaestheticaspects",British JournalofAnaesthesia,vol.119,Supplement1,2017,pp.i72i84.
28.ShwetaSinghandArunKumarTripathi,“AComparative Study of Internet Protocols in MANET”, International ConferenceonAdvancesinComputerSciences(ICACDS-16), vol.721,pp.221-231.
29.LuigiAtzori,AlessandroFloris,RobertoGirau,Michele Nitti, Giovanni Pau, "Towards the implementation of the Social Internet of Vehicles", Computer Networks, vol.147, 2018,pp.132-145.
30. J. Granjal, E. Monteiro, and J. S. Silva, “Security for the InternetofThings:Asurveyofexistingprotocolsandopen researchissues,”IEEECommun.SurveysTuts.,vol.17,no.3, 2015,pp.1294–1312.
31. Kun-chan Lan, Chien-Ming Chou, Han-YiWang, " An Incentive-Based Framework for Vehicle-Based Mobile Sensing", Procedia Computer Science, vol. 10, 2012, pp. 1152-1157.
32. Agachai Sumalee, Hung Wai Ho, "Smarter and more connected:Futureintelligenttransportationsystem",IATSS Research,vol.42,Issue2,2018,pp.67-71.
33 H. M. Raafat et al., “Fog intelligence for real-time IoT sensordataanalytics,”IEEEAccess,vol.5,2017,pp.24062–24069.