International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Virender Kumar Mehla1, Seema Mehla2 , Mohit Mathur3
1Associate Professor, ECE Deptt., Geetanjali Institute of Technical Studies, Udaipur, Rajasthan
2Assistant Professor, Computer Engineering Deptt.,, NIT Kurukshetra
3Assistant Professor, Deptt. of Electrical Engineering, Geetanjali Institute of Technical Studies, Udaipur, Rajasthan ***
Abstract - An EEG signal is a brief recording of the brain's spontaneous electrical activity. EEG measures and evaluates signals generated by the bombardment of neurons within the brain. EEG signals possess small amplitude of the order of micro volts that are contaminated by a variety of noises known as artifacts. These artifacts include ocular artifacts, power-line interference, breathing, and muscle activities. These signals are employed to diagnose various types of brain disorders such as epilepsy, stroke, tumors, sleep apnea, and parasomnia; therefore, these signals must be free from artifacts for proper analysis and detection of these diseases. To eliminate these artifacts from the recorded EEG signals, numerous EEG denoising methods such as regression, blind source separation (BSS), wavelet transform (WT), empirical mode decomposition (EMD) have been presented by the researchers in the literature. In this paper, detailed reviews of these techniques have been presented.
Key Words: Artifacts,Blindsourceseparation,Braindisorder,Electroencephalogram,EMD.
Electroencephalography(EEG)signalisthetermforthemeasurementofspontaneousbrainimpulsesinthehumanbrain[1], [2]. The nervous system communicates in an electric language. The nerve cells inside the human brain perform tasksby adaptingthetransmissionofelectricalcurrentsacrossthemembranes.Theseelectricalcurrentsgenerateelectricandmagnetic fieldscanbecapturedfromthescalp'ssurfaceusingelectrodes[3].TheElectroencephalogram(EEG),whichisarecordingof the electrical activity of the brain, is made by amplifying the potential differences between several electrodes. In EEG, electrodesareoftenpositionedonaperson'sscalpinordertorecordtheelectricalactivityofthecerebralcortex'snervecells. EEGoftenidentifiesthesignalsproducedwhenbillionsofneuronsareactiveatonceratherthanrecordingtheactivityofa single neuron. It primarily captures the signal coming from the tiny portion of the brain that surrounds each electrode. Neurotransmitters binding to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane cause changes in membrane potential, which are typicallymeasuredbyEEG.EEGrecordingsshowthebrainsignalsaswaveswithdifferentamplitudes,frequencies,andshapes. It can be used to track brain activity that takes place during an event, such as finishing a task without the presence of a particularevent. TheEEGis employedinseveral clinical applicationssuchasepilepticseizuredetection,sleep disorders, tumors, stroke, and other brain dysfunction. The brain, the central part of the nervous system, controls the coordination betweenhumanmusclesandnerves.EEGisapopularnon-invasivetoolforinterpretingthecomplexitiesofthehumanbrain duetoitslowcost,easytouse,andhightemporalresolution.BraindeathisalsointerpretedanddetectedusinganEEGsignal. AsEEGmonitorstheelectricalactivityofthebraininlargegroupsofneurons,itisdifficulttopinpointtheactivityseenusing EEGtoapreciselocationinthebrain.
Theanalysisoflong-termEEGrecordingisachallengingtask.TheEEGsignalpossessesalowamplitudeoftheorderofafew micro volts to 100 micro volts and a frequency range from a few Hz to 100 Hz [4]. Depending upon amplitude level and frequencyrange[5],[6],theEEGsignalcanbecategorisedintofivefrequencybands,whosedescriptionisshowninTable1. Thesebrainwavesrepresentvariousmentalconditionsofthepatient.AsEEGsignalishavingalowamplitudeoftheorderof microvoltthatcanbeeasilycontaminatedbyvariousartefacts.Theseartefactscanbeofintrinsictypesorextrinsictypes.
Frequencyband Frequency(Hz) Amplitude(µV) BrainActivity
Delta 0.5-4 20-200 DeepSleeping
Theta 4-7 Lessthan20
Dreaming:Meditation
Alpha 8-13 30-50 Relaxed,Eyeclosed
Beta 13-30 5-30 thinking,cognition,highalert
Gamma Greaterthan30 Greaterthan50 Consciousness
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Variousartefactshavebeeneliminatedbymaintaininganappropriaterecordingenvironmentandconductingexperiments underthesupervisionofclinicalexperts[7].Avarietyofapproachescanbeemployedtoeliminateartefactsfromtherecorded EEGsignalsandenhancethesignal-to-noise(SNR)ratiooftheinputsignal.Oneofthemostfundamentalapproachesissimple signalaveraging.Theunderlyingassumptionofsignalaveragingisthatwhilethesignalofinterestisprovidedandsteady,the artefactscontainedintherecordedsignalarerandom[8].Thedrawbackofsignalaveragingisthatitcannotbeapplicableto non-stationarysignalslikeEEGsignals,whichareofinterest.AnotheroptionistosimplydiscardcontaminatedEEGepochs. However,inthismethod,therecordeddataismanuallyreviewed,analysedandinterpretedthecontaminatedsegments,and thenfinallyrejectedthosesegmentsfromtherecordedEEGsignals[9],[10].Whenthereisahighlevelofcontamination,this processistime-consumingandresultsinthelossofsignificantinformationhiddenintheoriginalsignal.Theprimarygoalof anydenoisingapproachistoeliminatethelevelofartefactswhilepreservingtheoriginalinformationoftherecordedsignal.
Itisoneofthecommonlyusedapproachesforeliminatingocularartefactsforinstanceeyeblinksandmovements.Boththe timedomainandthefrequencydomainareusedwiththistechnique[11],[12].Theperformanceofthismethoddependson simultaneousmonitoringofEEGandEOGrecordingstodeterminethoseparametersthatcharacterizetheexistenceofEOG artefactsintheEEGrecordings.Thiscanbeachievedusingaregressionparameter, whichcomputesanestimationofthe proportionofartefactsinthespecificEEGchannel.Thecorrectproceduremustinvolvesubtractionoftheestimatedvalueof EOGartefactsfromtherecordedEEGsignals[13],[14].
Where representstherecordedEEGsignalattimet,and denotesEOGinformationat time. denotesthe regressioncoefficientsand representstheuncorruptedEEGdataattimet.Themajordrawbackofthistechniqueisthatit caneliminateocularartifactseffectivelybutfailstoremoveotherartefactssuchasEMGartefacts,power-lineinterference,and baselinewandernoise.Thismethoddoesnotpossessanyreferencechannels.
BSSreferstoagroupofalgorithmsthathaverecentlygainedprominenceintheeliminationofartefactsfromrecordedEEG signals.Thismethodinvolvesrecoveringsourcedatafromalinearmixtureofrecordingchannelswithnopriorknowledgeof thesourcesignal.TheabilitytoidentifysourcesignaleitherastrueEEGsignaloranycorruptedsignalallowsfortheremovalof artefactswithoutlosinganysignificantinformationfromtherecordedEEGsignals[15].TheBSSalgorithmconsistsofthree mainsteps:separatingthesourcesignalfromalinearmixture,recognisingofartefactualsignal,andfinallyeliminatingthe artefactsfromtheoriginalsignalsbypreservingtherelevantinformation.AnumberofBSSalgorithmshavebeendistincton thebasisofdegreeofsignalseparation. AlthoughnumerousalgorithmshavebeendiscussedintheliteraturetoperformBSS, out of these, principal component analysis and independent component analysis are commonly used techniques for the separationofsourcesignals.Thealgorithmisselectedbasedonthethreeparameters:artefacttype,taintlevel,andtarget signal[16].TwocommonlyusedBSStechniquesinsignalprocessingare:
2.2.1 PrincipalComponentAnalysis(PCA):OneofthemostefficienttechniquesfortheseparationofcorrelatedmixturesisPCA ifthesourcesarestatisticallyuncorrelated[17].PCAretrievestheuncorrelatedsignalfromalinearmixtureusingsecond-order statistics.ThismethodemploysSingularValueDecomposition(SVD)tofindthefirstprincipalcomponentsP1,P2,……..,PKthat revealagreateramountofvariancepossessedbyKnumberoflinearlytransformedcomponents.Thedirectioninwhichthe inputvariableshavemaximumvarianceisselectedasthefirstprincipalcomponent.Thesecondprincipalcomponentsare orthogonaltothefirstcomponent.PCAisadimensionalreductiontechniquethatretainedthemaininformationoftheoriginal signals[18].PCAisemployedtocreatespatialfiltersfortheremovalofartifactsfromtherecordedEEGsignals[19].PCA-based filtersshowbetterperformanceincomparisontotheregressionmethodwhileremovingartifactsfromoriginalEEGsignals,but thistechniquefailstodistincttheocularartifactsfromtheEEGsignalsifbothhavesameamplitudes.
2.2.2 IndependentComponent Analysis(ICA):In1986, HaraultandJuttenintroduceda newtechniqueknown asICA,an advancedversionofPCA,whichuncorrelatedthesourcesignalsusinghigherorderstatistics.Ittransformsasetofvectorsinto maximallyindependentcomponents.ICA,basedontwoassumptionsnamely,independentcomponentsarenon-Gaussianand
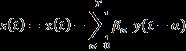
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
minimizationofmutualinformation[20],isemployedtorecovertheoriginalinformationthatisstatisticallyindependent. NumerousalgorithmsbasedonICAhavebeendiscussedintheliterature,outofwhichonlyafewICAmodelsareemployedfor processingnon-stationarysignalssuchasEEG,andECGsignals[21],[22].Thedisadvantageofthismethodisthatitneedsa manualselectionofartefactualcomponentsfromestimatedvariablesforcorrectivemeasures.
A wavelet is a basic function that acts as a window function. The wavelet transform utilizes a set of functions, known as decompositionofawaveletfunction,toexpressasignal.Thesignaldecompositioniscarriedoutusingasetofcoefficients knownaswaveletcoefficients.Thecoefficientsarecalleddetailedandapproximatecoefficients.Awavelettransform(WT)isa time-frequencyapproachinwhichthesignalisanalyzedintodifferentfrequenciesatdifferentresolutions,whichisknownas multiresolutionanalysis[23].Forhighfrequencycomponents,theWTprovidesstrongtimeresolutionbutweakfrequency resolution.Forlow-frequencycomponents,itprovidesdescentfrequencyresolutionbutsubparpoortimeresolution.
Intheaboveequation,thesymbol,τ,representstheshiftingparameterinthetimedomainwhilethesymbol,s,representsthe scalinginthefrequencydomain.TheWTprovidesbettertime-frequencylocalizationfeaturesincomparisontotheshort-time Fouriertransform(STFT)thataremoresuitablefortransientanalysisaswellastime-varyingbehaviorofnon-stationary signalssuchasECG,andEEGsignals[24].
Ingeneral,awavelet-basedapproachinvolvesthefollowingstepsfordenoisingoranalyzinganon-stationarysignal:
i) Signaldecompositionusingasuitablemotherwaveletanddecompositionlevel.
ii) Selectingthresholdvalueforwaveletcoefficients
iii) Takeinversewavelettransformtoreconstructtheoriginalsignal.
AdiscretewavelettransformduringdenoisingofEEGsignalsutilizestwoparametersnamelyscaling, andtranslation, of themotherwavelet, (t).
The main limitation of WT is that it is difficult to select the type of mother wavelet, thresholding value, and number of decompositionlevels.
EMDisanadaptivesignaldecompositionmethodemployedfortheanalysisofnon-stationarysignalssuchasEEGsignals.In 1998,N.E.HuangintroducedthismethodwhichemploystheconceptofinstantaneousfrequencyexplainedbytheHilbert HuangTransform(HHT)[25].HHTiscomposedoftwosections:empiricalmodedecompositionfollowedbyHilberttransform. TheEMDtechniquedecomposedthenon-stationaryEEGsignalsintoasetofnarrow-bandcomponentswhichascommonly knownasintrinsicbandfunctions(IMFs).ThistechniqueemploysasiftingprocesstoextracttheIMFsfromtheEEGsignal. EachIMFhastosatisfythefollowingtwocriteria:
i) Fortheentiredataset,thedifferencebetweenanumberofextremaandnumberofzerocrossingsshouldbe eitherequaltozeroortheyshoulddifferatthemostby1.
ii) At any instant of time, the average value of the upper and lower envelope defined by local maxima and minimashouldbezero.
UsingHilberttransform,eachIMFprovidesinstantaneousfrequencyasafunctionoftimethatrepresentsacuterecognitionof embeddedstructures.IthasbeennoticedintheliteraturethatthosenoisecomponentsnormallyfoundinthefirstfewIMFs when a signal is analyzed using the EMD technique [26]. Although EMD is an efficient and adaptive method for signal decomposition,itsuffersfrommanylimitationsthatincludemodemixing,endeffectartifacts,scalealignmentproblems,and non-orthogonalitywhileextractingIMFsfromthenon-stationarysignals.Theorthogonalityproblemhasbeensolvedusingan orthogonalandenergy-preservingEMDalgorithm[27].ScalealignmentissueisresolvedusingtheMultivariateEMDapproach [28]stillthismethodpossessesalackofmathematicalcompletenessandiscompletelybasedontheexpedientprocedure.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
TheanalysisofthehumanbrainhasbeengreatlyimpactedbytheuseofEEGintherealmofclinicalresearch.TheEEGsignalis taintedwithavarietyofartifacts,aswasalreadymentioned.EEGsignaldenoisingtechniquescomeinavarietywithvarious benefitsanddrawbacks.Thesetechniquesworkwellinacertaindomainandwithspecificartifacts.Forexample,theocularrelatedartifactscanbeeliminatedeffectivelyusingtheregressionmethod.IftheEEGsignaliscontaminatedwithothertypesof artifacts, this method fails to eliminate these artifacts. Besides this, this method utilizes one or more EOG channels. As a consequenceofthis,thismethodalsocancelsouttheneuralpotentialavailableintheEOGchannelwhileeliminatingocularbasedartifacts.Theproblemsencounteredintheregressionmethodareeliminatedusingtheprincipalcomponentanalysis approach(PCA).ThelimitationofthismethodisthatiftheartifactspresentinEEGsignalspossessapproximateamplitudes,it failstoeliminatetheartifacts.Torecoveruncorrelatedsignals,PCAusessecondorderstatistics;higherorderstatisticsare ineffective.
Thiscanbeavoidedbyusingtheindependentcomponentanalysis(ICA)approach,whichisbasedonblindsourceseparation. TheideaofdistinguishingdistinctcomponentsunderliestheICAapproach.Thistechniquecanbeusedtoisolateandgetridof manydifferentformsofEEGartifacts.ThemodifiedextensionofPCAisknownasICA.TheICAapproachcanbeusedtoremove EEGartifactsinavarietyofsituations.Itisoneofthemostusedtechniques.Complicatedcomputationsandmanualselectionof unrelatedindependentcomponentsaretwoofthismethod'sdrawbacks.Inaddition,whileEEGartifactsvaryinthefrequency domain,ICAoperatesinthetimedomain.Afterthis,Wavelettransformcameintoexistencethatcanrepresentasignalintime aswellasfrequencydomain.Thismethodpossessesbettertime-frequencylocalizationascomparedtotheshort-timeFourier transform method. This method decomposes the EEG signal into low and high-frequency components. Low-frequency components are called approximate wavelet coefficients and high-frequency components are referred to as detailed coefficients.Byapplyingthresholding,variousartifactscanbeeliminatedfromtherecordedsignalsandthefilteredsignalis reconstructed.Theselectionofpropermotherwaveletandlevelofdecompositionlevelsisstilldifficulttoapply,whichisthe primelimitationofthewaveletmethod.Inliterature,manyauthorsemployedacombinationoftwomethodstoeffectively eliminate the artifacts. In 2005, Berg et al. [29] employed a wavelet-ICA based approach for filtering the noise from the recordedsignal.In2007,Inusoetal.[30]proposedthesametechniqueforthefilteringofelectromyogram(EMG)signals. Theempiricalmodedecompositionmethod,anefficientmethodforanalysisofnon-stationaryEEGsignal,isemployedto recovertheoriginalsignalfromtherecordedsignalintermingledwithnoiseandartifacts.Theartifactsareeliminatedfromthe recordedsignalusingtheEMDmethodwhilepreservingtheoriginalcontentshiddeninthesignal.
Inthisstudy,varioustechniquesforeliminatingartifactsfromEEGsignalsaredescribed. Thesecomewithbenefitsanddrawbacks.Combiningthealgorithmsoftwoormorecurrentapproacheshelpsaddressthese constraints.Thesealgorithmscangetovereachother'slimitationsandprovidemoresuperiorandusefuloutcomesthanthey wouldasstandalonealgorithms.ThisisbecauseEEGartifactsvaryinthefrequencydomainwhereasICAoperatesinthetime domain.
[1]YongjianChen,NeuralNetworkBasedEEGDenoising,30thAnnualInternationalIEEEEMBSConferenceVancouver,British Columbia,Canada,August20-24,2008.
[2]GiuseppinaInuso,FabioLaForesta,NadiaMammone,FrancescoCarloMorabito,Wavelet-ICAmethodologyforefficient artefactremovalfromElectroencephalographicrecordings,ProceedingsofInternationalJointConferenceonNeuralNetworks, Orlando,Florida,USA,August12-17,2007.
[3]MrsVBabyDeepa,DrPThangaraj,DrSChitra, InvestigatingtheperformanceimprovementbysamplingtechniquesinEEG data,InternationalJournalonComputerScienceandEngineering,Vol.2,pp.2025-2028,2010.
[4]Teplan,M.‘FundamentalsofEEGmeasurement’,MeasurementScienceReview,Vol.2,No.2,pp.1–11,2002.
[5]Blanco,S.,Quiroga, R.Q., Rosso,O.A.andKochen,S. ‘Time-frequencyanalysisof electroencephalogramseries’, Physics ReviewE,Vol.51,No.3,pp.2624–2631,1995.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[6] De-Xiang, Z., Xiao-Pei, W. and Xiao-Jing, G. ‘The EEG signal preprocessing based on empirical mode decomposition’, InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsandBiomedicalEngineering,Shanghai,pp.2131–2134,2008.
[7]GuruvaReddy,A.andNarava,S.‘ArtefactremovalfromEEGsignals’,InternationalJournalofComputerApplications,Vol. 77,No.13,pp.17–19,2013.
[8]Repovš,G.‘DealingwithnoiseinEEGrecordinganddataanalysis’,InformaticaMedicaSlovenica,Vol.15,No.1,pp.18–25, 2010.
[9]Fitzgibbon,S.P.,Powers,D.M.W.,Pope,K.J.andClark,C.R.‘RemovalofEEGnoiseandartifactusingblindsourceseparation’, JournalofClinicalNeurophysiology,Vol.24,No.3,pp.1–12,2007.
[10] Scott, M., Bell, A.J., Jung, T.P. and Sejnowski, T. J. ‘Independent component analysis of electroencephalographic data’, AdvancesinNeuralInformationProcessingSystems,Vol.8,No.1,pp.145–151,1996.
[11] Jung, T. P., Makeig, S., Humphries, C., Lee, T. W., Mckeown, M. J., Iragui, V. and Sejnowski, T. J. ‘Removing electroencephalographicartifactsbyblindsourceseparation’,Psycho-physiology,Vol.37,No.1,pp.163–178,2000.
[12]Wang,Y.L.,Liu,J.H.andLiu,Y.C.‘AutomaticremovalofocularartifactsfromElectroencephalogramusingHilbert-Huang transform’,InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsandBiomedicalEngineering,Shanghai,pp.2138–2141,2008.
[13]Croft,R.J.andBarry,R.J.‘RemovalofocularartifactfromtheEEG:areview’,ClinicalNeurophysiology,Vol.30,No.1,pp.5–19,2000.
[14]Krishnaveni,V.,Jayaraman,S.,Aravind,S.,Hariharasudhan,V.andRamadoss,K.‘Automaticidentificationandremovalof ocularartifactsfromEEGusingwavelettransform’,MeasurementScienceReview,Vol.6,No.4,pp.45–57,2006.
[15]Fitzgibbon,S.P.,Powers,D.M.W.,Pope,K.J.andClark,C.R.‘RemovalofEEGnoiseandartifactusingblindsourceseparation’, JournalofClinicalNeurophysiology,Vol.24,No.3,pp. 1-12,2007.
[16]Berg,M.,Bondesson,E.,Low,S.Y.,Nordholm,S.andClaesson,I.‘Acombinedon-linePCA-ICAalgorithmforblindsource separation’,Asia-PacificConferenceonCommunications,Perth,WesternAustralia,pp.969–972,2005.
[17] Jung, T.P., Humphries, C., Lee, T-W., Makeig, S., Mckeown, M.J., Iragui, V. and Sejnowski, T. J. ‘Removing electroencephalographicartifacts:comparisonbetweenICAandPCA’,Proceedingsofthe1998IEEESignalProcessingSociety Workshop,Cambridge,pp.63–72,1998.
[18]Kang,D.andZhizeng,L.‘Amethodofdenoisingmulti-channelEEGsignalsfastbasedonPCAandDEBSS’,International ConferenceonComputerScienceandElectronicsEngineering,pp.322–326,2012.
[19]Lagerlund,T.D.,Sharbrough,F.W.andBusacker,N.E.‘Spatialfilteringofmultichannelelectroencephalographicrecordings throughprincipalcomponentanalysisbysingularvaluedecomposition’,ClinicalNeurophysiology,Vol.14,No.1,pp.73–82, 1997.
[20]Hyvärinen,A.andOja,E.‘Independentcomponentanalysis:algorithmsandapplications’,NeuralNetworks,Vol.13,Nos. 4/5,pp.411–430,2000.
[21]Albera,L., Kachenoura, A.,Comon,P., Karfoul,A., Wending,F., Senhadji,L.andMerlet,I. ‘ICA-based EEGdenoising: a comparativeanalysisoffifteenmethods’,BulletinofthePolishAcademyofScience-TechnicalSciences,Vol.60,No.3,pp.407–418,2012.
[22]Paulchamy,B.,Ilavennila,Jaya,J.andSaravanakumar,R.‘Comparativeevaluationofvariousindependentcomponents analysis(ICA)TechfortheremovalofartifactsofEEGsignals’,InternationalJournalofComputerScienceandNetworkSecurity, Vol.10,No.3,pp.226–234,2010.
[23]Li,Y.,Zhang,T.,Deng,L.,Wang,B.andNakamura,M.‘DenoisingandrhythmsextractionofEEGunder+Gzacceleration basedonwaveletpackettransform’,InternationalConferenceonComplexMedicalEngineering,Beijing,pp.642–647,2011.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[24]Zhou,W.andGotman,J.‘RemovalofEMGandECGartifactsfromEEGbasedonwavelettransformandICA’,Proceedingsof the26thAnnualInternationalConferenceoftheIEEEEMBS,SanFrancisco,CA,USA,pp.392–395,2004.
[25]Huang,N.E.,Shen,Z.,Long,S.R.,Wu,M.C.,Shih,H.H.,Zheng,Q.,Yen,N-C.,Tung,C.C.andLiu,H.H.‘Theempiricalmode decompositionandtheHilbertspectrumfornonlinearandnon-stationarytimeseriesanalysis’,ProceedingsofRoyalSocietyof LondonA,Vol.454,No.1971,pp.903–995.1998.
[26] De-Xiang, Z., Xiao-Pei, W. and Xiao-Jing, G. ‘The EEG signal pre-processing based on empirical mode decomposition’, InternationalConferenceonBioinformaticsandBiomedicalEngineering,Shanghai,pp.2131–2134,2008.
[27]SinghP,JoshiSD,PatneyRK,SahaK.TheHilbertspectrumandtheenergypreservingempiricalmodedecomposition,arXiv preprintarXiv:1504.04104,2015.
[28]RehmanN,MandicD.P.Multivariateempiricalmodedecomposition.ProceedingsofRoyalSocietyA466:1291–1302,2010.
[29]Berg,M.,Bondesson,E.,Low,S.Y.,Nordholm,S.andClaesson,I.‘Acombinedon-linePCA-ICAalgorithmforblindsource separation’,Asia-PacificConferenceonCommunications,Perth,WesternAustralia,pp.969–972,2005
[30] Inuso, G. and La Foresta, F. ‘Wavelet-ICA methodology for efficient artefact removal from electroencephalographic recordings’,ProceedingsofInternationalJointConferenceonNeuralNetworks,Orlando,Florida,USA,pp.12–17,2007.