International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1,2
Abstract - Face Recognition is a computer program that can find, follow, recognize, or confirm human faces in a photograph or video taken by a camera. A method for encoding a picture via a contraction transformation, on a picture space where a hard and fast point is close to the original image, is known as image compression. Finding the methods that are most useful and appropriate for the project being done is the aim. It is a computer application that automatically recognize or verifies someone using a digital image or video frame from a video source. Automatic face recognition systems are often used to verify users via ID verification services. They function by recognizing and quantifyingfacialexpressions inanimageandcancompare a person's face from a digital picture or video to a database of faces. People may be recognized using facial recognition technology inrealtime,oncamera,orinmovies.Onesubsetof biometric security may be biometric authentication. Voice, fingerprint, retinal, and iris recognition are examples of further types of biometric software. The major objectives are to construct a full face recognition project as a Face recognition and data gathering, Educate the Detector, Face identification.Thelastphaseofprojectfindingsandsummary is now complete. Here, we use our camera to take a replacement face, and if its face has already been taken and trained, our recognizer produces a "prediction" and provides its ID and index, indicating how certain it is about this match.
Key Words: Face Identification, Image recognition, BULDP, SVM, Data gathering ….
In several domains and disciplines, FACE recognition is a significant research issue .this is due to the fact that biometricidentificationisafundamentalhumanbehaviour thatisnecessaryforsuccessfulhumancommunicationand interaction, in addition to a variety of useful applications including mugshot tracing, access control, credit card recognition,andsecuritymonitoring.Themainfunctionof imageanalysisistoexaminevisualdatainordertosolvea visionissue.
The second analysis covers two additional topics: pattern classification, which uses this higher-level information to identifyitemsinaphotograph,andfeatureextraction,which is the process of obtaining lower-level image information likeshapeorcolorinformation.
Since identity verification has been introduced as an identification method to be used in passports, it has
***
repeatedly demonstrated its significance. As a result, it is nownotonlyathoroughlyresearchedareaofimageanalysis, patternrecognition,andadditionalaccuratebiometrics,but ithasalsobecomeaveryimportantpartofourdailylives.
The human recognition method in our image processing projectmaybeareal-timerobot.
We make use of a face-detection method for image processing.
Itaccuratelyrecognizesandtrackshumanfaces[6].
It is a system that recognizes human faces, supports its conclusionoroutcome,andthenhandstheballoff.
Softwarethatidentifiestheexternalbodypartutilizingthe various algorithms is created simultaneously with the hardware.
Theprogramcomparesvariouspicturestolearntorpreset imagestoactualvideoimages.
Theultimateobjectiveistospurimprovementinthepresent biometricauthenticationsystem,makingitmorereliableand effective.
Sparse representation-based techniques have recently shown to perform well in image classification and face recognition.
Gao et al. [35] presented SRC-FDC, a wholly original dimensionality reduction approach supported by sparse representation, which takes into consideration both the spatialEuclideandistributionandthelocalreconstruction relation,whichencodeboththelocalinternalgeometryand theglobalstructure.Toovercomethedisadvantagesofthe informationrepresentation,modifytheprocedureinsidethe sparse representation. A novel transfer subspace learning strategywasproposed,whichcombinesaclassifierdesign method with a changing data representation. Following additionalinvestigationofgroupsparsity,datalocality,and thekerneltrick,acombinedsparserepresentationapproach termed kernelized locality-sensitive group sparsity representation(KLS-GSRC)isdeveloped.
Toimprovetherobustnessoffacerecognitionforcomplex occlusionandseverecorruption,aniterativere-constrained groupsparserepresentationclassification(IRGSC)approach
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
wasproposed,inwhichweightedfeaturesandgroupsare usedtogethertoencodemorestructuralanddiscriminative informationthanotherregression-basedmethods.
Technicalimagecomparisonidentificationrequiresthemost timeandiscumbersome.
Weplannedabio-mimeticuncorrelatedlocaldifferentiate projection(BU-LDP)methodtoaddresstheaforementioned issuealongwithaspectsofhumancognition.
BU-LDP is based on U-DP but uses a different method of calculatingtheneighborhoodcoefficientthatisintendedto bemoreinlinewiththetraitsofimagethinking.
Theproposedadjacencycoefficienttakesintoaccountboth thesimilaritybetweendifferentsamplesaswellasthelaw between identical samples in adding to the group informationbetweensamples.
Furthermore,BU-LDPintroducestheideaofun-correlated spaces,whicheliminatescorrelationinthefinalvectorand lessensthedismissaloftheextractvectors.
Additionally,anexpandedvariantoftheBU-LDPinkernel spaceknownasKernel BiomimeticUn-correlatedLocality distinguishProjection(KBU-LDP)ispresented.
The tentative results are encouraging because we use our suggested BU-LDP methods for face recognition to demonstratetheirefficacy.
1.Facerecognitioniseasytouseand,inanycase,prevents thesubjectfrombeingawareofit. 2.Thisapproachispractical. 3.Facerecognitioniseasiertouse. 4.Itusesinexpensiveidentificationmethods. 5.Acceptabilityinsociety. 6. Biometric authentication is a sincere defence against diseasetransmission. 7.Thedevicewillbeforcedtounlock. 8.Moredifficulttohidefromcriminals. 9.Itiscapableofstoppingallfraud.
Theliteraturereviewacknowledgestheworkcarriedoutby previous researches. Omaima NA Al-Allaf proposed a Face recognitionsystembasedonrecentmethodwhichconcerned with both representation and recognition using artificial neuralnetworksispresented.Thispaperinitiallyprovides theoverviewoftheproposedfacerecognitionsystem,and explains the methodology used. It then evaluates the performanceofthesystembyapplyingtwo(2)photometric normalization techniques: histogram equalization and homomorphic filtering, and comparing with euclidean distance,andnormalizedcorrelationclassifiers.Thesystem produces promising results for face verification and face recognition[16]. I.Kotsia and I. Pitas proposed two novel methods for facial expression recognition in facial image sequences.TheuserhastomanuallyplacesomeofCandide gridnodestofacelandmarksdepictedatthefirstframeofthe image sequence under examination. The grid-trackingand deformation system used, based on deformable models, tracksthegridinconsecutivevideoframesovertime,asthe facialexpressionevolves,untiltheframethatcorrespondsto the greatest facial expression intensity. The geometrical displacement ofcertain selected Candidenodes, defined as thedifferenceofthenodecoordinatesbetweenthefirstand thegreatestfacialexpressionintensityframe,isusedasan input to a novel multiclass Support Vector Machine(SVM) systemofclassifiersthatareusedtorecognizeeitherthesix basicfacialexpressionsorasetofchosenFacialActionUnits (FAUs). The results on the Cohn-Kanade database show a recognition accuracy of 99.7% for facial expression recognitionusingtheproposedmulticlassSVMsand95.1% forfacialexpressionrecognitionbasedonFAUdetection[21].
Wecreatethesysteminthefirstmodulesuchthattheuser indexesthepicturedatafolderfirst.
The number of photos in the folder we indexed will be presentedwhentheindexhasbeencreated.
Theuserthenchoosesthesearchpicture.
LHandMLHareemployedthroughoutthefacerecognition technique.
The goal is to compare the encoded feature vector of one candidatetothefeaturevectorsofallothercandidatesusing thechi-squaredissimilaritymeasure.
Thiscomparisonisconductedbetweentwofeaturevectors ofNlength,F1andF2.
The match is shown by the matching area of the feature vectorwiththeabsolutelowestmeasuredvalue.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Inthismodule,aquerypicturechosenfromacollectionof photographsisusedtobuildahistogram.
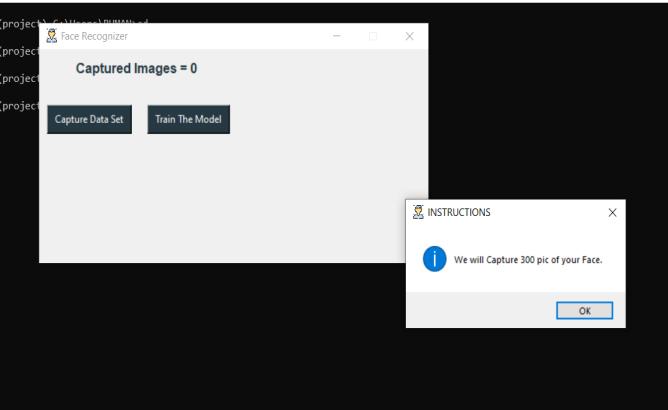
Thegraph'suprightaxisshowsthenumeralofpixelsinthis specifictone,whilethegraph'shorizontalaxisreflectstonal fluctuation.
Themiddleofthehorizontalaxissymbolisesmid-gray,the right side consequently represents bright and pure white parts,andtheleftsiderepresentsblackanddarkareas.
The world's dimensions that are shown in each of those zonesarerepresentedbytheverticalaxis.
Therefore, the majority of the information points in a histogramforanextremelydarkpicturewillbeontheleft sideandinthemiddleofthegraph.
In contrast, a histo -gram for a very bright picture with minimalshadowsorblackregionswouldhavethepopularof the data points in the center and on the right side of the graph.
In order to assess the performance of the proposed technique, we employ Support Vector Machine (S-VM) to recognise facial emotions. S-VM, a supervised machine learning method, may automatically convert data to a higher-dimensionalfeaturespace.
Asaresult,itidentifiesalinearhyperplanewithamaximum margin in this higher dimensional space to partition the informationintovariousclasses.Afterthehistogramfound in the module before, we automatically remove all the componentsandstorethemindividually.
Thephraseissupportedbytheretrievedcharacters.
We search for related photos that support the phrase identifiedinthemodulebeforeinthisone.
The descriptor's ability to be represented and easily extractedfromthefaceiswhatdetermineshowsuccessfulit is.
Largevariancesbetweenclasses(betweenvariouspeopleor expressions) and few to no differences within classes are idealcharacteristicsofanhonestdescriptor.
Thesedescriptorsareusedinavarietyofdomains,including biometricidentificationandfacecharacteristics.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ExperimentalresultsatLF-W,YALE,FERET,O-RLandCMU PIE show that BU-LDP and KBU-LDP outperform state-ofthe-arttechniquesbyasignificantmargin.
Despite having good results, BU-LDP is primarily a supervisedlearningapproach.
In reality, it may be challenging to get a large enough quantityoflabelledsamples,thereforeourfuturestudywill focusonhowtoswitchtousingun-labeledsamplesandhow toincludethemintoasemi-controlledtechnique.
Additionally,ND-LPP,BU-LDP,andKBU-LDPwillfailwhen everyonehasasingletrainingsample,asituationknownas the"onesampleissue,"whenthelocal variance matrix SL andthetotalvarianceatmosphereStarebothzeromatrix.
work.
FutureresearchandthedevelopmentofBU-LDPwillfocus onfindingasolutiontoonesampleproblemforND-LPP,BULDP,andKBU-LDPinordertotacklethisissue.
1.L.Zhi-fang,Y.Zhi-sheng,A.K.JainandW.Yun-qiong,2003, “Face Detection and Facial Feature Extraction in Color Image”, Proc. The Fifth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Applications (ICCIMA’03),pp.126-130,Xi’an,China.
Here,weutilizeourcameratocollectafreshface,andifit's previouslybeentakenandtrained,ourrecognizerreturnsits IDandaconfidenceindex.Facialrecognitionispopularfor entertainment,smartcards,security,lawenforcement,and surveillance.

Image processing, pattern recognition, computer vision is involved.ThisarticlecomparesU-DPwithLPPextensions.
The BU-LDP approach supports several strategies. First, a novelapproachtobuildingtheneighborhoodcoefficientin linewiththefeaturesofhumanperceptionisputforth.
Second, in order to guarantee that the final discriminant vectorsareuncorrelated,theideaofanuncorrelatedspaceis introduced. and as a result, we offer a particular BU-LDP solution.
The KBU-LDP is a proposed extension of the nuclear biomimeticuncorrelatedlocationdiscriminantprojection.
2. C. Lin, 2005, ―Face Detection by Color and Multilayer Feedforward Neural Network‖, Proc. 2005 IEEE InternationalConferenceonInformationRetrieval,pp.518523,cityandMacao,China.
3.S.KherchaouiandA.Houacine,2010,“Skincolormodel based face detection with constraints and template matching”,Proc.2010InternationalConferenceonMachine andWebIntelligence,pp.469-472,Algiers,Algeria.
4. P. Peer, J. Kovac, and F. Solina, 2003, “Robustexternal body partDetection in Complicated Color Images,” Proc. 2010The2ndIEEEInternationalConferenceonInformation Management and Engineering (ICIME), pp. 218 – 221, Chengdu,China.
5. M. Ş. Bayhan and M. Gökmen, 2008, ―Scale And Pose Invariant Face Detection And Tracking‖, Proc. 23rd International Symposium on Computerand dataSciences ISCIS'08,pp.1-6,Istanbul,Turkey.
6.C.C.Tsai,W.C.Cheng,J.S.TaurandC.W.Tao,2006,―Face DetectionUsingEigenfaceAndNeuralNetwork‖,Proc.2006 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics,pp.4343-4347,Taipei,Taiwan.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
7. X. Liu, G. Geng, and X. Wang, 2010, “Automatic Face DetectionsupportedBP Neural Network and Bayesian Decision,” Proc. 2010 Sixth International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC 2010), pp. 1590-1594, Shandong, China.
8.M.TayyabandM.F.Zafar,2009,“FaceDetectionUsing2DDiscrete Cosine Transform and Backpropagation Neural Network”,Proc.2009InternationalConferenceonEmerging Technologies, pp. 35-39, Islamabad, Pakistan. 15th International Conference on Machine Design and ManufacturingJune19-22,2012,Pamukkale,Denizli,Turkey
12.
9.W.Wang,Y.Gao,S.C.Hui,andM.K.Leung,2002,“AFast andRobustAlgorithmforFaceDetectionandLocalization,” Proc.9thInternationalConferenceonNeuralIP(ICONIP'O2), pp.2118-2121,Orchidorder,Singapore.
10.Y. Song, Y. Kim,U.Chang,and H.B. Kwon,2006, “Face RecognitionRobusttoLeft-RightFacialSymmetryShadows,” Pattern Recognition Vol. 39 (2006), pp. 1542–1545.
11.C.LiuandH.Wechsler,2003,―IndependentComponent AnalysisofGaborFeaturesforFaceRecognition‖,Proc.IEEE Transactions On Neural Networks, vol. 14, pp. 919-928.
12.K. Youssef and P. Woo, 2007,“A NewMethodforFace RecognitionsupportedColor Information and Neural Network”,Proc.ThirdInternationalConferenceonNatural Computing (ICNC 2007), pp. 585 – 589 , Hainan, China.
13. A. Rida and Dr.BoukelifAoued, 2004, "Neural Network BasedArtificialFaceRecognition",Proc.FirstInternational Symposium on Control, Communications and Signal Processing,pp.439–442,Hammamet,Tunisia.
14.Z.Mu-chun,2008,“FacerecognitionsupportedFastICA and RBF neural networks”, Proc. 2008 International SymposiumonIPandEngineering,pp.588-592,Shanghai, China.
15.D.NPritha,L.SavithaandS.S.Shylaja,2010,"Feedback NeuralNetworkFaceRecognitionUsingLaplacianGaussian FilterandSingularValueDecomposition",Proc.2010First International Conference on Embedded Intelligent Computing,pp.56-61,Bangalore,India.
16 Omaima NA Al-Allaf, - A Review of Face Detection SystemssupportedArtificial Neural Network Algorithms, arXivpreprintarXiv:1404.1292,2014.
17. Masi, Y. Wu, T. Hassner, and P. Natarajan, "Deep Face Recognition:ASurvey",201831stSIBGRAPIConferenceon Graphics,Patternsandpictures(SIBGRAPI),2018,pp.471478,doi:10.11./SIBGRAPI.2018.00067.
18. KHTeoh2,RCIsmail1,2,SZMNaziri2,RHussin2,MNM Isa2 and MSSM Basir3 ,- Face recognition and identificationemploying adeep learning approach Published under license by IOP Publishing Ltd Journal of Physics:ConferenceSeries,Volume1755,5thInternational Conference on Electronic Design (ICED) 2020 19 August 2020,Perlis,MalaysiaCitationKHTeohetal2021J.Phys.: Conf.Ser.1755012006
19. KH Teoh, RC Ismail, SZM Naziri, R Hussin, MNM Isa, MSSMBasir,-Facerecognitionandidentificationemploying adeep learning approach, Journal of Physics: Conference Series1755(1),012006,2021.
20.HaiHong,H.Neven,andC.vonderMalsburg,"Onlineface expressionrecognitionsupportedpersonalized galleries," Proceedings Third IEEE International Conference on AutomaticFaceandGestureRecognition,1998,pp.354-359, doi:10.1109/AFGR.1998.670974.
21.“FacialExpressionRecognitioninImageSequencesUsing Geometric Deformation Elements and Support Vector Machines” I. Kotsiaand that i. Pitas. IEEE Transactions on ImageProcessingVolume16Issue1January2007pp172–187
22. “Skin-Based Face Detection-Extraction andface expressionRecognition”byN.G.BourbakisandP.Kakumanu
23. “Extracting and matching meta-features for understandinghumanemotionalbehavior:Faceandspeech” N. Bourbakis, A. Esposito and D. Kavraki DOI:10.1007/s12559-010-9072-1 Published September 1, 2011
24. “A Local-Global Graph Approach forcountenanceRecognition” by P. Kakumanu and N. Bourbakis.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
