International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
MAYANK PANDEY1 , Dr. ANJALI S. PATIL2
1PG Student, MUP, Dept. of Architecture, M.I.T.S, Gwalior (M.P)
2Associate Professor, Dept. of Architecture, M.I.T.S, Gwalior (M.P) ***
Abstract - Local differences in India has been a standout amongst the most basic advancement issue which has pulled in worries from all quarters, be it approach producers, strategy implementers, academicians or the general public on the loose. It has by and by touched off the discussion on the current disparities between the created and immature nations when all is said in done and between various areas inside these nations specifically. The bury and intra-territorial imbalances of the nation are being watched not just as far as their differential macroeconomic parameters like GDP, GNP and so on yet in addition in connection to different statistic and social advancement markers, for example, wellbeing, instruction, business and so on. India being a creating nation, it turns into even more critical to examine these inconsistencies as the new financial strategies have additionally augmented the hole between the rich and the poor states. The present investigation plans to break down the examples of the local variations in the dimensions of improvement in India. Thinking about this, four pointers have been chosen to recognize the spatial examples of regional disparities in India.
Key Words: RegionalDisparities,SocioEconomicDevelopment.
Todaywehaveenteredthe21stcentury.Onthisoccasion,whenwelooktowardsourpast,theinclusivereturnsofsuccessand failureareshownonournationaloverseasregionalandlocallevel.Thedevelopment-orientedsuccessesgivesatisfactionon onehand;theotherfailuresandotherfailuresmakeourpsychoanalystgrieve.Atthenationallevel,wehavealsomadesome progress which we certainly should not have done. This unwanted development has created many social and economic inequalities,apartfromthe actual structureofdevelopment,hasmadetheproblemofproviding employment,education, accommodationbalancedfoodalongwithbasicfacilitiestomaketheproblemmorecomplex.
Theimmaturezonesbecauseoftheconditionofunderminingoftheirconventionalfinancialandlossofconfidence,have anincredibletesttotheorganizers.Becauseoftheadministrationapproachesandprojectsofspatio-monetaryadvancementa noteworthypieceofventuregoestothoseregionwhichareasofnowcreatedorhavesomepotentialforimprovementregarding agribusiness,enterprisesorfoundation.Thisprocedureproducesawkwardnaturebetweentheareas.Theaccompanyingtheme isbeentaken,asitisasignificantremarkablesubjectandratherbeinganoteworthyissuethereisnolegitimatefeaturetothe point.Alongtheselines,fortheimprovementoftheentirenation,thereisanoteworthyworrytobecenteredaroundthelimit territorialaberrations.Developingtheurbanandlocalregionsparallelcanpromptaquickpaceintheimprovementoftheentire nation.Theidealutilizationofaccessibleassetsistheneedofgreatimportance.Consistentlyexpandingpopulacehaslimitedthe assets and their utilization. As the provincial region have somewhat unexpected necessities in comparison to the urban communities.
Giventhisspecificsituation,theproposedtheorytriestoaddressthetopicofterritorialincongruitiesinstudyregion-how theseemerge,proceedtopersevereandwhatshouldbepossibletoresolvethem.Theexplicittargetsoftheexaminationthat willbetendedtothroughthispropositioninclude:
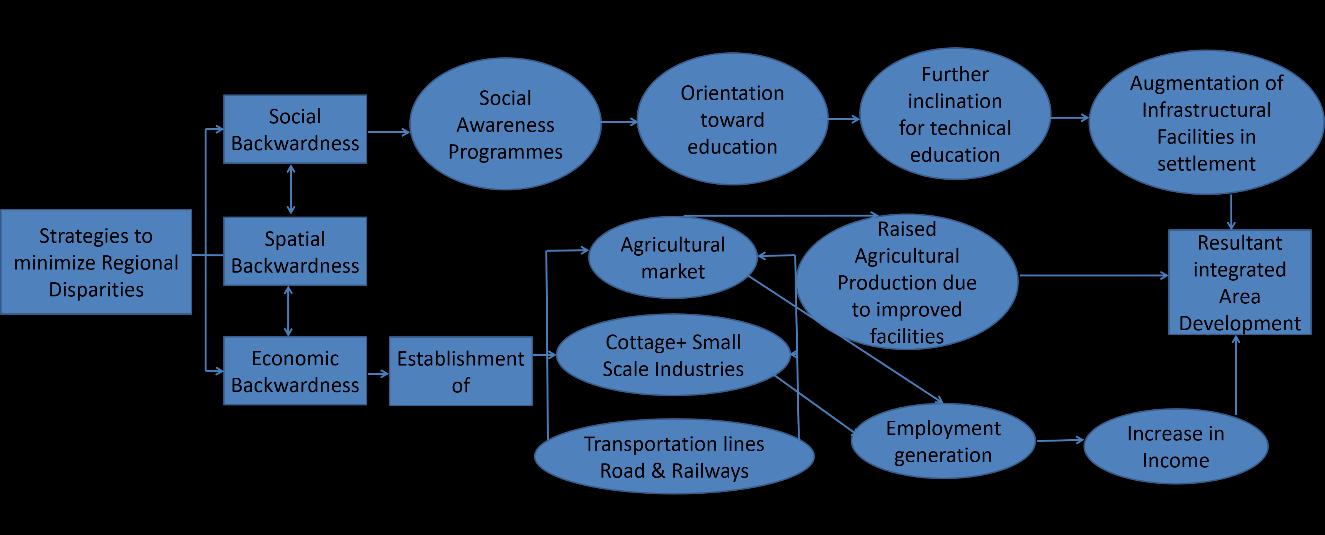
Todevelopstrategiestominimizeregionaldisparitiesthroughsocio-economicdevelopmentofthreeidentifieddistricts.
Tofindouttheindicatorsofregionaldisparitiesandsocio-economicdevelopment.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Toanalyzetheregionaldisparitiesinperformanceofkeysocio-economicindicators(Population,PopulationDensity, DecadalGrowthRate,SexRatio,SC/STSexRatio,RuralUrbanSexratio,LiteracyRate,GenderGapinLiteracy,Work ParticipationRatio,No.ofIndustries,No.ofElectrifiedvillages,No.ofPostOffices/OneLakhPopulation,No.ofBanks, No.ofPrimaryHealthCenters,andTotalRoadLength/100sq.kmoflandarea).
Todevelopstrategiestominimizetheregionaldisparitieswithrespecttosocio-economicdevelopment.
The present research is primarily based on the analysis of secondary data sources. Since regional development is a multivariateconcept,tracingitstrajectoryovertimerequiresanalysisoftimeseriesdataofcertainkeysocio-economicvariables thatareintegraltoanunderstandingofthedevelopmentdynamics. Atthesametime,ahistoricalevaluativeapproachhasalso been adopted to delve deep into the causes of the rise and perpetuation of inequalities given the varied districts specific historicallegacies,governmentpolicies,geographicalsettingandcontextualsocio-spatialrelations.GivenThepurposeofthe research,thefollowingIndicatorsmeasuresofRegionaldisparitiesinSocio-Economicdevelopmenthavebeentakenupfor comparison:(1)Population;(2)RuralUrbanPopulation;(3)PopulationDensity;(4)DecadalGrowthRate;(5)SexRatio;(6) SC/STSexRatio;(7)RuralUrbanSexRatio;(8)LiteracyRate;(9)GenderGapinLiteracy;(10)WorkParticipationRatio;(11)No. of Industries;(12)No.ofElectrified Villages;(13)No. ofPostOffices per 1LakhPopulation;(14) No. ofBanks per 1Lakh Population;(15)No.ofPrimaryHealthCentersper1LakhPopulation;(16)TotalRoadLengthper100sq.kmofLandarea.
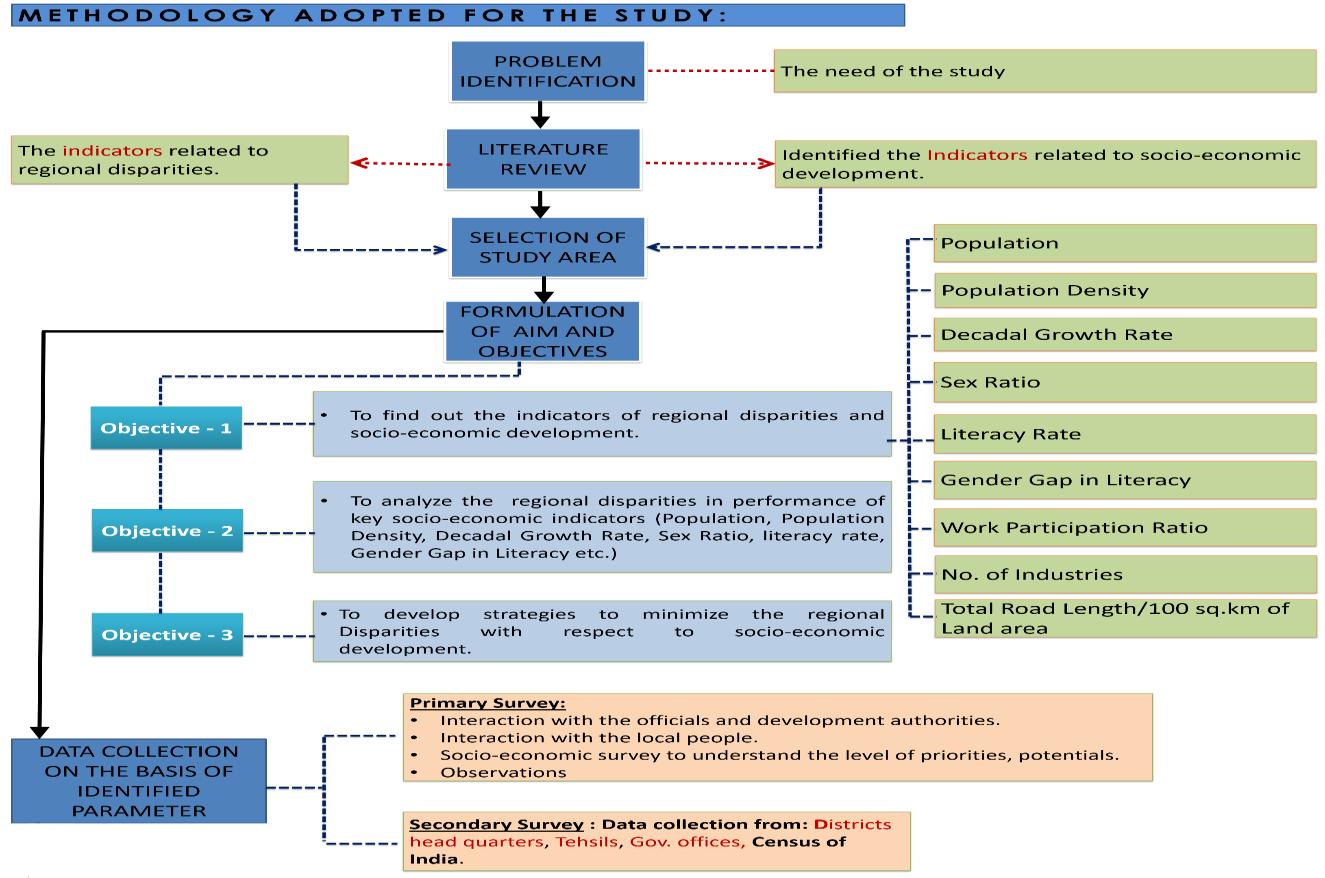
Themethodologyfollowedforpreparinga‘MinimizeStrategyforaRegionaldisparitiesisgiven.itconsistofthefollowing broadstages.
Reviewofliteratureandconceptualization
Formulationofaimandobjectives.
Dataidentification,collection.
Chart -1:methodology.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Forestimatingtheextentandnatureofregionaldisparitiesworksofresearchershavebeenexamined.Thischapterreviews importantandrecentstudieswhichhighlighttheproblemofregionaldisparitiesinSocioeconomicdevelopment.Theissueof convergencehasalsobeenexaminedinsomeoftheresearchworksthatwerereviewedforthestudy.Thereviewofthese studiesalsohelpedinframingsuitablemethodologyforthepresentstudy.
Socio-economic development: Socio-economic development is the relationship among monetary pastime and social existence.Socio-monetaryimprovementisthecontinuousimprovementinsidethewell-beingandinsidethegeneralofresiding ofthehumanbeings.SociofinancialimprovementismeasuredwithsignsincludingGDP,lifeexpectancy,literacyandtiersof employment(Nayyar,2008).
Disparity: Theconditionorfactofbeingunequal,asinage,rank,ordegree;difference:"narrowtheeconomicdisparities amongregionsandindustries"(Slater,1995).
Regional disparities –differencesbetweeneconomicperformanceandwelfarebetweencountriesorregions(Development, 2002).
“Economic Backwardness” ofaregionindicatedbysymptomslikehighpopulationpressureonland,excessivedependenceon agriculture,absenceoflarge-scaleurbanization,lowproductivityinagricultureandcottageindustries,etc.(Kumar,2005).
Regional disparity means the difference between the rural areas and urban areas. For example, in urban areas roads are developedwhileinruralareasroadsarenotdevelopedthusitwillbetreatedasadifferencebetweentheregions.(Shafeeq, 2017).
Instandard,localdisparitiesorimbalances,wesupposedwidevariationsinlinewithcapitaprofits,literacyrates,availabilityof healthandtrainingservices,levelsofindustrialization,infrastructuralcentresetc.amongdistinctareas.Asalreadymentioned, thoseareascanbeeitherstatesorregionswithinaState(Bhatnagar,2004).
OtherdefinitionsarethosegivenbyOECD,accordingtowhichregional(spatial)disparitiesexpressthescopeofdifferenceof intensitymanifestationofeconomicphenomenaunderinvestigationobservedwithinregionsofgivencountry(OECD,2002).
Regionaldisparitymeansunbalancedspatialstructuresinsomeregionorindifferentregions.thesearemanifestedindifferent conditionsoflifeaswellasinunequaleconomicanddevelopmentpotential.Agoodexampleofspatialdisparityisthecontrast betweenurbanandruralareas(Ostrava,2010).
Disparitiesbetweenurbanandruralareasandbetweenregionsaretheresultoffivesetsoffactors:
Natural factors: MostvitalmotivefornearbydisparityisthatIndia’sdifferentareasareendowedwithspecificnaturaland human-primarilybasedsources.SomestatesincludingWestBengal,Jharkhand,Odisha,Chhattisgarhetc,areendowedwith bettermineralsourceswhilstotherssuchasPunjabandHaryanahavehigherirrigationcenters.Thevariationsinagro-climatic conditions,endowmentsofherbalassetsorgeographicplacetogetherwithdistancetoaseaportorcentersoftradedecidethe capacityfortheeconomicdevelopmentofanareaoranarea(Kumar,2005).
Socio-economic-cultural factors:valuesandtraditionseitherencourageordiscourageinnovation,entrepreneurship,and socialandeconomicmobility(Anon.,2010).
Infrastructure: India’stier one townsi.e.Mumbai,Bangalore,Delhi,Chennaiand Hyderabad areat breaking pointareas bootlicksinfundamentalinfrastructurewhichincludeselectricity,water,roadsandairportexist.Thefocusedmushroomingof outsourcingcompaniesinthesetownsleadinadditionhighergrowth,atthesametimeasdifferentregionsdonolongerposes thesamesituationwinninginthosemetropolitancities(Singha,2011).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Political factor: Becausethepoliticsofdefections,thedebaclesorfallsofgovernmentsandvotepoliticsthe(centralandstate) governmentsbecamepoliticallyweak.Therefore,thepriorityofthegovernmentbecametopleasetherichminoritysothatit mayrun.Tomitigateresentmentanddissatisfactionamongthegeneralmassithadtoplaypseudoroleofandontoremedythe poormassthroughvariousunsuccessfulemploymentandpoorwelfareprogrammes.Therefore,therichminorityandtheareas orregionsrelatingtotherichminoritybecameratherdevelopedbygettinglargerportionofthetotalfruitsofdevelopment moveofthecountry.Moreover,theregionsorcommunitiesrelatingtoeducatedandpoliticallyawarepeoplealsogotgreater shareineconomicdevelopmentbecausetheirgreaterpoliticalpressureonthegovernment.differencesinpoliticalpower betweenregionscanresultinintendedorunintendedbiasesingovernmentpolicies(Dholakia,2003).
Predominance of Agriculture:TheoccupationalshapeofIndiafromthestartisagriculture.In1921,itchangedinto76.0% andround72%in2001census.Thisindicateddegenerationfinancialconditions,deindustrializationandconsciousnessofthe financialsystem.Accordingtocensus2011,yet58.02%populaceisengagedwithagricultureandstaysterriblecomparedto industrializedcivilization(Bhatia,1999).
Global Disparity: Thetimeperiodglobaldisparitydescribesthedisparitiesthatexistamongthenations.Eachusofa isataexceptionallevelofimprovement,whichreasonsdisparitybetweennations.Somecountieshavebeenendowed withresourcesinabundance,whiletherearenationswhichareextraordinarilypoorinassets(K.Rajlakshmi,2013).
Natural –geographical(Climate,Topography,Terrain,LocationEtc.)
Man-Made (Social,Political,Economic)
Inter - State Disparity (Disparity between States): Inter–statedisparitiestherearealsoexistdisparitiesamongthe statesinIndia.Inter–kingdomdisparitiesornearbydisparitiesorlocalimbalancesreferstoastateofaffairswherean accordingtocapitaincome,preferredofliving,consumptionscenario,businessandagricultureimprovementarenot uniform in exceptional parts of a given area. Backwardness of kingdom might be the result of either the nearby diversityordisparity(Chaubey,1998).
Intra-State Disparity (Disparity within States): Intrastateinequalityreferstoinequalityinthecountry.Intra-local disparitiesindevelopmentisthoughtviamacroindicatorsofdevelopment,allocationofassets,bestofgovernance, farmingshape,financialadvantageandconsumptionpatternsandestimatesofmonetarycircumstance.(K.Rajlakshmi, 2013).
Rural-Urban disparity: Rural-city disparity has been generic in India for a while. Rural regions are taken into considerationbackwardareasinphrasesofavailabilityofbasicinfrastructure-roads,electricity,waterandsanitation centers,schoolsandhospitals,andsoforth.Inassessment,thosefacilitiesareprimarilytobehadinurbanareas.Itis duetotheabsenceofsuchfacilitiesthatruralareaslagbehindurbanregionsintermsoftheprimaryindicatorsof development-poverty,illiteracy,unemployment,etc.(K.Rajlakshmi,2013).
ToestimatetherangeandnatureofregionalinequalityfunctionsResearchershavebeeninvestigated.Thischaptermakes importantandrecentreviewsStudiesthathighlighttheproblemofregionalinequalitiesfinanciallytheissueofdevelopment convergencehasalsobeenexaminedinIndiaSomeresearchworksreviewedforthestudy.reviewofThesestudiesalsohelped inpreparingthepropermethodforthecurrentstudy.
Thestudyareaselectedbasedonthefactthatthedevelopmenteffortshouldbecarriedoutbasedonprioritytotheregional disparitieswhichhasgotresourcebaseandpotentialforthesame.Comparingthecertaincriticalindicatorsofdevelopmentof theGwalior,ShivpuriandGunadistricts.Theseindicatorsare:Population,PopulationDensity,PerCapitaGDP,LiteracyRate, UrbanRuralPopulationetc.
DemographicIndicators PopulationDensity
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
LiteracyRate
RuralUrbanpopulation
Socio-Economic overview
Population
DecadalGrowthRate
SexRatio
LiteracyRate
GenderGapinLiteracy
RuralurbanPopulation
Infrastructure
Infrastructureservicesarebasicservicewithoutwhichprimary,secondary,andtertiaryactivitiesmaynotbeimproved.
Banking
Electricity
HealthCentres
Postoffices
Economy
GrossDomesticProduct
PerCapitaIncome
PerCapitaIncome growth
Primarysectorissubdividedintofivemajorsectorsasmentionedbelow: i. Crops ii. Livestock iii. ForestryandLogging iv. Fishingandaquaculture
Miningandquarrying
Secondarysectorissubdividedintothreemainsub-sectorsasmentionedbelow: i. Manufacturing ii. Electricity,Gas,Watersupplyandotherutilities iii. Construction
Tertiarysectorissubdividedintosevenmajorsectorsasmentionedbelow: i. Trade,repair,hotels,andrestaurants ii. Transportbyothermeansandstorage
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

iii. Railways iv. Communication&servicesrelatedtobroadcasting v. FinancialServices vi. RealEstateownershipofdwellingandprofessionalservices vii. PublicAdministration
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a summary measure of average achievement in key dimensions of human development:alongandhealthylife,beingknowledgeableandhaveadecentstandardofliving.TheHDIisthegeometricmean ofnormalizedindicesforeachofthethreedimensions. 11.
Themainobjectiveorpurposeofthisstudyhasbeentoinvestigatethe disparitiesintheSocio-economicdevelopmentbyaset ofindicatorssuchasPopulation,PopulationDensity,Sexratio,RuralUrbanSexratio,LiteracyRate,GenderGapinLiteracy, WorkParticipationRatio,RuralUrbanPopulation,sectorwiseGDDP,GDDPgrowthrate,percapitaincome,PostOfficesaccess, No.ofBanksperonelakhPopulation,No.ofPrimaryHealthCentersperonelakhPopulation,No.ofElectrifiedVillages,Total RoadLength/100squarekilometerofLandarea.
1. Ahluwalia,M.S.,2013.RegionalBalanceinIndianplanning.
2. Anon., 2010. webpage/ social Issues/ Economic/ Socioeconomic development. [Online] Available at: http://www.personal.psu.edu[Accessed2018].
3. Bhatia,M.,1999.RuralInfrastructureandGrowthinAgriculture.EconomicandPoliticalWeekly,pp.43-48.
4. Bhat,L.,1994.GeographicalPerspectivesandtheProblemof.IASSIQuarterly,p.4.
5. CensusofIndia,2011.
6. Chaubey,V.,1998.InterstateVariationinIndia,Rural-UrbanDisparity.IndianJournalofRegionalScience.
7. CMIE,C.f.M.I.E.,1991.DevelopmentStatusofInfrastructureinIndia.
8. Dholakia,R.,2003.RegionalDisparityinEconomicandHuman.EconomicandPoliticalWeekly.
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1008
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
9. India,G.o.,2015.NitiAayog.[Online] Availableat: https://data.gov.in/catalog/major-socio-economic-indicatorsstates-india[AccessedApril2018].
10. K.Rajlakshmi, 2013. Growing Regional Disparities in India’s Development. International Journal of Educational ResearchandTechnology,Volume4.
11. Kumar,D.S.V.,2016.RegionalImbalancesinIndia.september.
12. Kumar,S.,2005.RegionalImbalance.
13. Kumar,S.V.,2016.RegionalImbalanceinIndia.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1009
