International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1M.Tech, Computer Science and Engineering, SR Institute of Management & Technology, Lucknow, India
2Associate Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, SR Institute of Management & Technology, Lucknow ***
Abstract - Non-control-flow Trojans present in embedded systems provide a risk to the data utilized in the decisionmaking process because of the risk they pose to that data. In order to adjust for the bias in the data, the output data is slanted in such a way that judgments are made either slightly earlier or slightly later than what was originally intended. This is done by keeping the system running continuously and limiting the amount of input data that the system adjusts to a certain geographic area. This approach eliminates the need for the customary testing carried out by a third party. The functional behavior of a binary may be extracted, shown in a waveform, and anomalies also known as localized behaviors can be found by using the Ghidra decompile in combination with the discrete wavelet transform. To do this, decode the data using Ghidra and then depict the functional behavior using discrete wavelet transform. This idea is made possible by the fact that the people who created the Ghidra decompile also created the discrete wavelet transform. With the help of Ghidra, one can do a Monte Carlo simulation of phase-shifted Bessel functions of the first type with a Gaussian Trojan that has random magnitude (also known as amplitude), location (also known as mean), and breadth (also known as variance). Ghidra may be used to better understand the behavior of a simple programmed in operation. Ghidra may also be used to finish out a Monte Carlo simulation of second-order phase-shifted Bessel functions using a Gaussian distribution. The discrete wavelet transform may identify anomalies that are situated in a very specific focal area on the map.
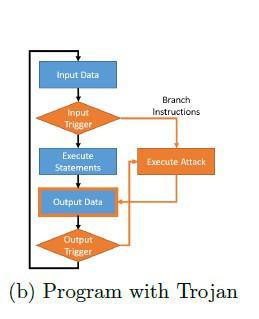
the form of a Gaussian function; we'll call this a Gaussian Trojan. The missile decision system incorporates this functionbyappendingittothereceivedcoordinatebefore sending it on. The value added is zero for almost all GPS coordinates outside of the targets because the function is Gaussian.TheGPSguidanceismanipulatedbythisaddition, andthepayloadisfiredinthewrongdirection.Onepossible outcomeisthattheTrojansimplydivertsthepayloadsothat itcannotharmanyoneelse.However,theTrojanmaychange the target, causing collateral damage. However, please explainthemeaningofaTrojanthatdoesnotinterferewith thecontrolflow.Muchofthediscussionaboutanti-malware measuresrevolvesaroundpreventinganinterruptioninthe normal execution of a programme. While a programme is beingexecuted,thestackpointerfollowsapathknownas thecontrolflow.Figure2showstheresult.Controlflowis theprocessofmodifyingdatathatisusedtodirectexecution ofanapplication.Trojansaltertheprogram'sexecutionby reroutingcontrol tomaliciousscriptsorunneededlibrary code[2].ViewFigure2.ThedynamicsofflowregulationThe system-agnostic nature of Trojans makes it possible for hackerstoexploitawiderangeofplatformswiththesame malicious code (i.e. granting the attacker equal or higher privilegesthanthevictim).
Due to the specialised nature of military avionics applications and missions, they are easy prey for Trojan assaultsthatbypasscontrolflows.Consideranunmanned aerialvehicle(UAV)equippedwithGPS-guidedmissilesand an autonomous weapon system. The vendor writes and supplies the guided missiles' decision-making software in binaryexecutableform.Inordertoensurethesafetyofthe mission,thisprocedureisactivatedwhentheUAVisabove theintendedtarget.
However,theorganisationwasbreachedbeforethebinary wasdelivered,anditcontainsanon-controlflowTrojanin
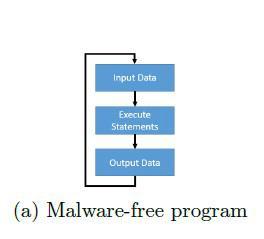
Figure-1: Program control flow diagram of Malware free Diagram.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
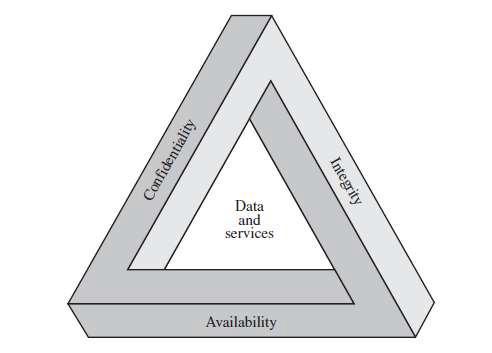
Theabovediagramshowstheinterdependenceofthreecore concepts:privacy,security,andaccessibility.Thisisknown astheCIAtriad,anditiswidelyacknowledgedasthethree most important tenets of information security. Any vulnerabilityinevenonepartofthesystemmightallowthe wholethingtobecompromised.
Thereissometerminologyusedinthemalware:
1.3.1. Attack Vector.
An attack vector is a technique for gaining unauthorized accessinsideacomputerornetworkforacriminalpurpose byexploitingthesystem'sweaknesses.
1.3.2. Risk.
Figure-2: Program control flow diagram of Program with Trojan
Below we discuss two statistical techniques to feature selection,principal component analysis(PCA)and logistic regression (LR), that were selected and used due to their goodperformanceinfeatureselectionworkforthedetection andidentificationofmalware.Throughtheuseofprincipal component analysis (PCA) and logistic regression techniques,themostemblematicfeaturesofnetworktraffic fromtheCICAndMal2017datasetwereselected.
Thenatureofsoftwareisestablishedbythekindandextent of the information it contains. One may forecast the input andoutputdata'ssequenceandtimethankstodeterminacy. System designers may benefit from three separate resources confidentiality, integrity, and availability as theyworktobuildasafeandreliableendresult.
Itisthepotentialforharmtocomeaboutasaresultofany dangerinthethreatlandscapeexploitingthesystemforits ownends,includingthedisclosureofsensitiveinformation likeusernamesandpasswords,thelossofproprietarydata, andthetarnishingofthecompany'sgoodname.Damageto or loss of data stored on computer systems is another definitionofrisk.
1.3.3. Threat.
Anything that can take advantage of vulnerability, either intentionallyorunintentionally,togainaccessto,harms,or destroyanasset.
1.3.4. Vulnerability.
Different threats can exploit weaknesses or holes in a systemssecurityprogramme,designpolicies,andexecution to obtain unauthorized access to a computer system or network.
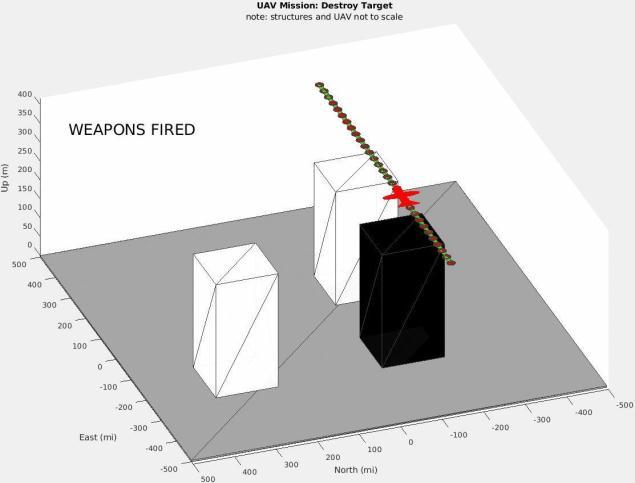
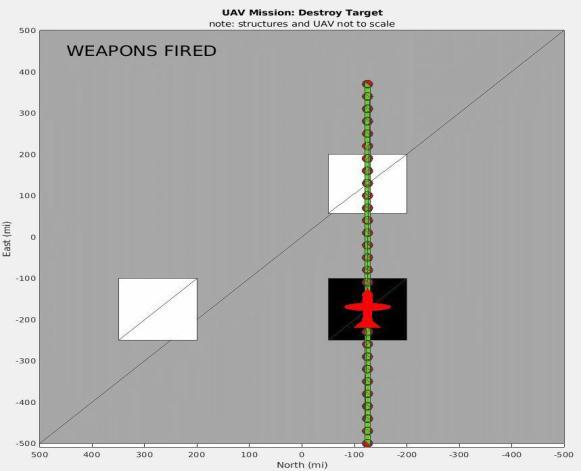
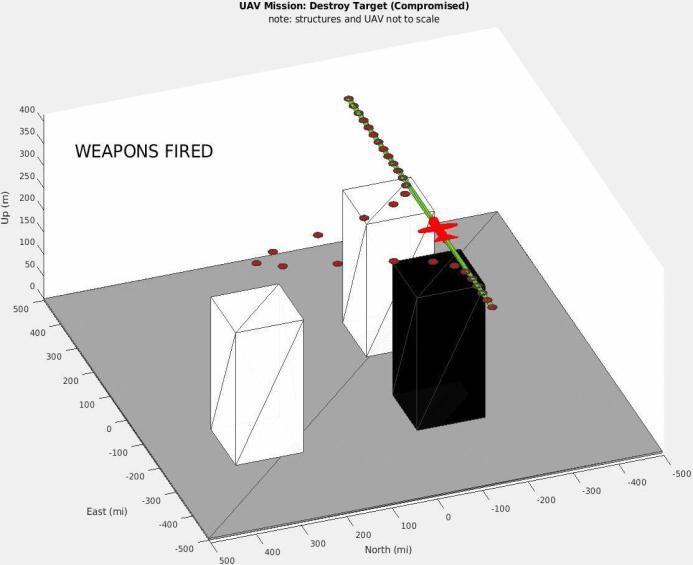
Matlab code is located that may be used to run the simulationoftheChapter-01scenario.InFigures4and5,we see the instant the UAV shoots against the target (the structure outlined in black) from a circling perspective in Figure-4 and a birds-eye perspective in Figure 5. The unmannedaerialvehicle(UAV)ishoveringrightabovethe target,andtheredGPScoordinatesestablishedbeforehand indicate that the payload will actually reach the target. Figures6and7depicttheinclusionofaGaussianTrojanasa supply-chainembeddedassaulttotheguidedmissiles'GPS readings from comparable perspectives. This allows the systemtofirethepayloadonafreshtargetlocated400miles distantaftertheUAV'sGPSreadinghasalreadytransmitted thefireinstruction.Byextendingthissituationbyanother degreeoflongitude,thedistancewouldincreaseto60miles (calculatedusing[7]).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
As discussed in Chapter I, localized behavior refers to the Gaussian Trojan's small, localized impact on the sensor output.However,notallregionaldeviationsinbehaviorare harmful(i.e.thepropercoordinatesforfiringthepayload). So, it's impossible to predict the total number of local behaviors detected after accounting for noise, typical behavior,andmaliciousbehavior.Morelocalactivitiesare likelytobeconsiderednormalorbenignthanmalevolent. This is discussed in more depth elsewhere, however the phrase "localized behavior" is introduced here and used throughoutinthetext.

Toappreciatetheoriginalityoftheapproach,itisnecessary to first comprehend the shortcomings of existing control flowTrojandetectiontechniques.CodingfromTrojansand other malicious programmes is often checked against signature databases of previously detected malware [8]. WhilecontrolflowTrojansignaturesaregenerallyregarded dangerous, non-control flow Trojansignaturesare not. As seen above, the output of GPS sensors may have been intentionally tampered with via the introduction of the GaussianTrojan.
Figure-6:
Figure-7:
Investigationandimprovementofdecompilersisongoing. Hex-Raysdecompilehasbeenthemostpopularcommercial solutionforalongtime.Universityresearcherscreatetheir owndecompilerslikePhoenixandFoxDecduetothehigh pricetagofcommerciallyavailableoptionsandthedesireto pushdecompileresearchahead.In2019,theNSAreleased Ghidra,itsdecompiler,providingreverseengineersaccessto acutting-edgeplatformwithouttheneedforexpensivehexraysorscholarlystudies.
Figure-5:
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Whenitcomestodecompilers,Hex-Raysisthegoldstandard [19,20].Namedafterthefirmthatcreatedandmaintainsit, Hex-Rays, the same people behind the gold standard in disassembly,IDAPro[20].Hex-Rayshasapricetag,butthe otherdecompilerswe'vecoveredhereareopen-sourceand sofreetouseandcontributeto.Becauseofthislimitation, Hex-Rayscouldnotbeusedinthisinvestigation.
Schwartzetal.[19]introducedthe Phoenix decompiler in 2013.WhencomparedtoHex-Rays[19],Phoenix'sstructural analysistechnique,whichmakesuseofiterativerefinement and semantics preservation, was shown to recover 28% more controlflow structure. Decompilations with more informationretrievedare betterat extracting the binary's functionalbehaviourandtheconsequencesoftheTrojanon the programme, but they won't be any better at detecting non-controlflowTrojans.
Duetothelack ofinformation,itisassumedthatthesofttrigger Trojan is an addition to the standard functioning code.TheGaussianTrojantakesitsnamefromthefactthata GaussianfunctionwithanamplitudeofA,ameanof,anda standarddeviationof2isquitecloseto0everywhereexcept fortherangebetween32and+32.So,toachievethealwaysonstatewithminimalalterationstootheroutputs,itisjust to add 0 to the standard signal output. This extension creates,bydefinition,aregionalizedpatterninthesystem output.
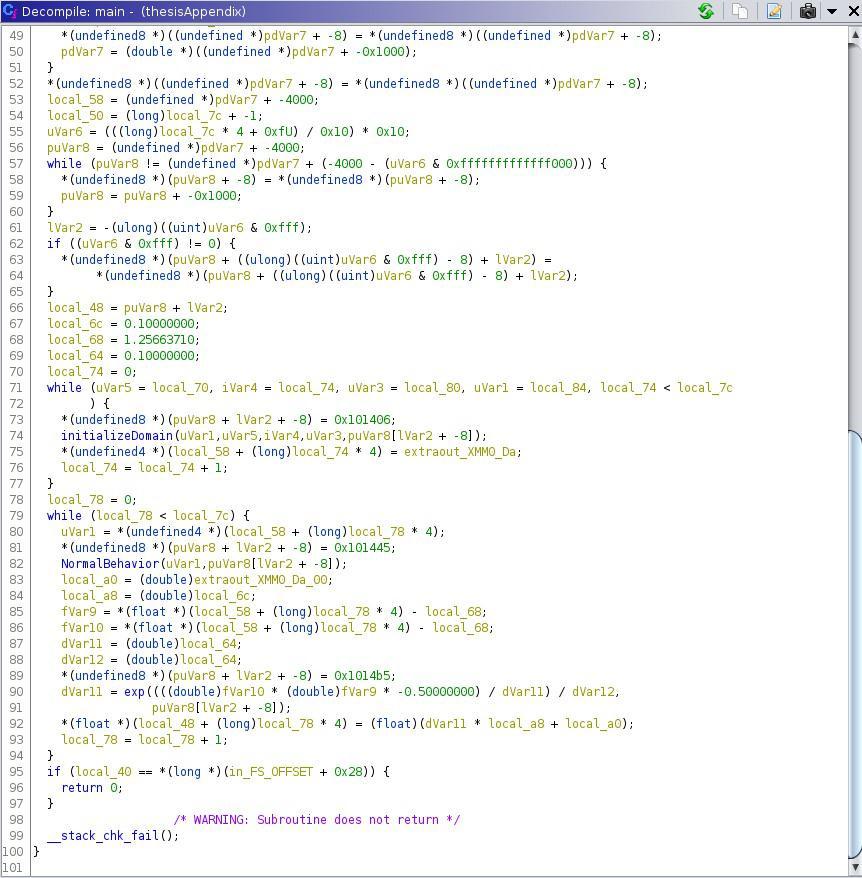
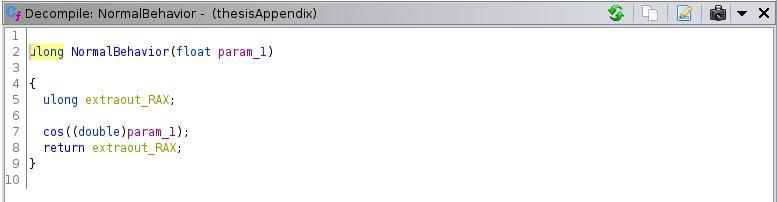
Interestingenough,whileinitialiseDomainiscalledwithfive parameters in main, the function signature only contains fourinputarguments.Anunsignedlongvariableisinitialised and returned unmodified by the function. The recompiled codeisapoorrepresentationoftheoriginalalgorithm.This isclearlynottheintendedfunctionalbehaviourofinitialise Domain, since the primary purpose of a function should neverbetoinitialiseanunusedvariableandreturnit.
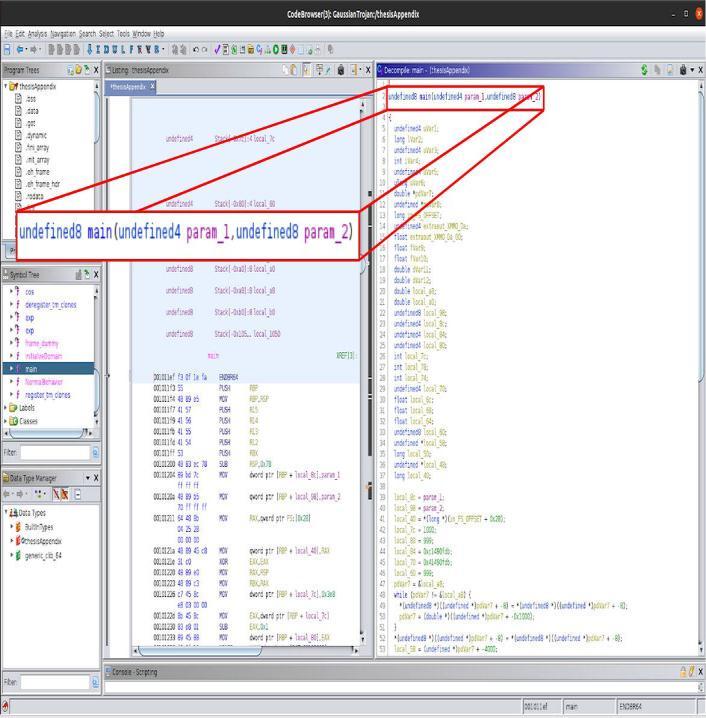
In order to do some last arithmetical manipulations on NormalBehaviorbeforetheprogrammeexits,itloopsback throughmainasshownbefore.There'salotofclutterinthe code,andithastobeorganised.Fromthestandpointofthe attacker,theTrojanwillbeconcealed(obfuscation,evolved, etc).Theanalystwillassumethattherearenofunctionswith names like Normal Behavior since all of the program's functionalityisconsiderednormal.Asaresult,youshouldn't assumethattheanalysiswillbeaseasyasthisone.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
3.“Cert-eulatestsecurityadvisories,”
4. https://cert.europa.eu/cert/newsletter/en/latest SecurityBulletins.html
5. “Multiple vulnerabilities in citrix,” https://media.cert.europa.eu/static/ SecurityAdvisories/2021/CERT-EU-SA2021-027.pdf.
6. “Critical vulnerability in vmware vcenter server,” https://media.cert.europa.eu/static/ SecurityAdvisories/2021/CERT-EU-SA2021-025.pdf.
Soft-trigger, always-on, non-control-flow Trojans may be detectedintheirearlystagesbyrecompilationandwavelet analysis.Ghidraismoreofareverseengineeringtoolthana generatorofsafe,recompilablesourcecode,sokeepthatin mindifyouplanonusingitforthelatterpurpose.Wecan infersufficientfunctionalityfromthetestedbasicbinary.On the other hand, the static Ghidra decompile may not be enough for a more complicated and, thus, more realistic binary. Cleaning up the code might be difficult and timeconsumingifyoudon'thaveafirmgraspofthealgorithms includedinthedecompiledbinaries.
The DWT is a powerful tool for finding small-scale aberrationsinwaveletanalysis.Inallthreeoftheseextreme examples, the Trojan created a strong pulse in high frequencychannelsthatwerenormallyquiteflat(orzero) (i.e.Levels1&2).Sincepulsesdonotappearineitherthe high-orlow-frequencychannels,itmaybeconcludedthat wavelet analysis does not function for more diffuse abnormalities.Becauseofthis,findingthembeforetheypass thethird-partytestsuitebecomesmorechallenging.
Last but not least, it is abundantly clear that non-controlflow Trojans that directly target decisionmaking data in embedded systems pose a significant risk to avionics and other embedded technology. These Trojans might infect everythingfromaweaponsystem'snavigationalgorithmto an autonomous vehicle's proximity sensor, causing fire alarmstogooff,unmannedaerialaircrafttostrayoffcourse, andthepublictobeplacedindanger.Astheworldcontinues topushtheboundariesofautonomoussystems,non-controlflow Trojans become a greater threat to the safety of innocentpeople.
1.S.Chen,J.Xu,E.C.Sezer,P.Gauriar,andR.K.Iyer,“Noncontrol-dataattacksarerealisticthreats,”Proceedingsofthe USENIXSecuritySymposium,pp.177–192,2005.
2. C. Cifuentes and K. J. Gough, “Decompilation of binary programs.”Software-Practice&Experience,vol.25,no.7,pp. 811–829,1995.
7.M.TehranipoorandF.Koushanfar,“Asurveyofhardware trojan taxonomy and detection.” IEEE Design & Test of Computers, Design & Test of Computers, IEEE, IEEE Des. Test.Comput,vol.27,no.1,2010.
8. “Latitude/longitude distance calculator,” https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/gccalc.shtml.
9. M. Sikorski and A. Honig, Practical Malware Analysis. WilliamPollock,2012.
10.“Virustotal,”https://www.virustotal.com/gui/.
11.M.Abadi,M.Budiu,U.Erlingsson,andJ.Ligatti,“Controlflowintegrityprinciples,implementations,andapplications,” 12thACMConference onComputerand Commu- nications Security,2009.
12.A.Seshadri,M.Luk,N.Qu,andA.Perrig,“Secvisor:Atiny hypervisor to provide lifetime kernel code integrity for commodityoses,”12thACM ConferenceonComputerand CommunicationsSecurity,2007.
13. W. Xu, D. C. DuVarney, and R. Sekar, “An efficient and backwards-compatible transformation to ensure memory safetyofcprograms.”ACMSIGSOFTSoftwareEngineering Notes (ACM Digital Library), vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 117 – 126, 2004.
14. D. Dhurjati and V. Adve, “Backwards-compatible array bounds checking for c with very low overhead.” ICSE: InternationalConferenceonSoftwareEngineering,pp.162–171,2006.
15.S.Nagarakatte,J.Zhao,M.M.K.Martin,andS.Zdancewic, “Softbound:Highlycompatibleandcompletespatialmemory safetyforc.”ACMSIGPLANNOTICES,vol.44,no.6,pp.245–258,2009.
16. ets: Compiler-enforced temporal safety for c.” ACM SIGPLANNOTICES,vol.45,no.8,pp.31–40,2010.
17. C. Cifuentes, “Reverse compilation techniques,” Ph.D. dissertation,QueenslandUniversityofTechnology,1994.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
18. M. H. Halstead, Machine-independent computer programming.SpartanBooks,1962.
19. Data Based Advisor. [electronic resource]., ser. LexisNexisAcademic,n.d.
20.E.J.Schwartz,J.Lee,M.Woo,andD.Burnley,“Nativex86 decompilation using semantics-preserving structural analysisanditerativecontrol-flowstructuring.”Proceedings ofthe22ndUSENIXSecuritySymposium,2013.
21. “Hex rays–state-of-the-art binary code analysis tools,” https://hex-rays.com/.
22.F.Verbeek,P.Olivier,andB.Ravindran,“Soundccode decompilationforasubsetofx86-64binaries,”Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Software EngineeringandFormalMethods,2020.
23.“Ghidrawebpage,”https://ghidra-sre.org/.
24.“Ghidrablog,”https://ghidra.re/
25.R.MessierandM.Berninger,GettingStartedwithGhidra. [electronicresource].O’ReillyMedia,Inc.,2019.
26. C. Eagle and K. Nance, The Ghidra Book. [electronic resource].NoStarchPress,2020.
27. D. Sundararajan, Discrete wavelet transform : a signal processingapproach.JohnWiley&Sons,2015.
28.M.GolgowskiandS.Osowski,“Anomalydetectioninecg usingwavelettransformation.”2020IEEE21stInternational Conference on Computational Problems of Elec- trical Engineering(CPEE),pp.1–4,2020.
29. O. Aydin and M. Kurnaz, “Wavelet-based anomaly detection on digital signals.” 2017 25th Signal Processing andCommunicationsApplicationsConference(SIU),Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU),201725th,pp.1–3,2017.
30. H. V. Poor, An Introduction to Signal Detection and Estimation.Dowden&Culver,1994.
31.“Avidabydevosoft,”https://avida.devosoft.org/.
32.S.Dolan,“movisturing-complete,”ComputerLaboratory, UniversityofCambridge,pp.1–4,2013.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
