International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Rakesh.M 1*, Narendra Babu B.R 2
1Assistant Professor, Department of Biomedical & Robotic Engineering, Mysore University School of Engineering, University of Mysore, Manasagangotri, Mysuru, Karnataka, India
2 Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Vidya Vikas Institute of Engineering & Technology, under Visvesvaraya Technological University Mysuru, Karnataka, India.***
Abstract – The Rochelle salt which is also familiarly known as Potassium Sodium Tartrate also commonly called as Seignette salt. This material has goodpiezoelectric properties and effects; it is obtained from natural crystal which is basically obtained inside the surface of barrels at the cellar. It is used inelectroplating inelectronics field. The present paper work describes the structure which is composed of Rochelle salt which is easily developed with polymer composite to obtain add on advantages of piezo effect also it is environmentally friendly, the product is biocompatible in nature. Inthe viewof a cleaner energy harvesting technology, active sensor response, this material is developed to study its properties
The major methods of processing such as polymerization, and other important material characteristics have been studied such as Morphological, microcrytallinity parameters of Rochelle salt have depicted that it consists of pure form of Rochelle salt through EDS analysis, itshowsthatitmoderately aligned peaks in X ray diffraction analysis. FTIR testing showed satisfactory absorption behavior which is illustrated. The Rochelle salt based PVDF polymer composite also exhibitedto Electrical goodconductivity behaviorisbriefedto uplift the potential of this green piezoelectric material.
Key words: Rochellesalt,PVDF,XRD,SEM,EDX,Dielectric.
Inpastfewdecades,alargefundinghasbeeninvestedinthe domain of biomedical sectors and related industries as a resultmanyinnovationinthelightofbiosensorsarebeen developed [1]. This innovations has lead to numerous currentprospectsfortheuseofbiosensorsinthedetection, monitoring,andmedicinaldiagnosisofbiologicalmolecules and diseases such as sugar (diabetes), dangerous death deceasessuchascancercelldetection,andsoon[2-5].The “electricalactivity”ofmanymaterialshasbeenknowntoa mankind for several decades. In 1880 Jacques and Pierre Curie discovered that the compression of single crystal samplestourmalinealongcertaindirectionsyieldedhavethe presenceofelectricalchargeonthesamplesurface[6].Inthe early years of research, the sonar systems two both
importantmaterialssuchasquartzandRochellesaltwere usedforelectricalinvestigationalstudy.Quartzhadbetter mechanical properties, which was advantageous in the fabricationprocess.
On the other hand, Rochelle salt had better piezoelectric response; also it is very sensitive acoustic and vibration mechanical application material. The sodium potassium tartratetetrahydrate (NaKC4H4O6•4H2O)which alsocalled Rochelle salt, is one of the ferroelectric and piezoelectric materialswhichincludenorareelementinitscomposition, veryusefullyinfoodindustries,preparationofsilvermirrors anditis goodenvironmentalcompatibility.Rochellesaltis the oldest and has been for a long time the only known ferroelectricandpiezoelectricmaterial[11,12].
PolyvinylidenefluorideormostfamiliarlyknownasPVDF whichishighlynotrespondingthermoplasticfluoropolymer material which is synthesized by the polymerization of diflouride. PVDF has four crystallinephasessuchasalpha (α),beta(β),gama(γ)anddelta(δ)whichstronglydepends onchainconfirmation[7][8].PVDFismostfavorablyusedin piezoelectric energy harvesting, sensors, transducers applicationsetc.ThePVDFpolymerhasseveralproperties suchasbiocompatible,itisresistancetowardsthechemicals, excellent thin films development quality, it is cost effectivenesscomparedtoothermaterials[9][10].Amongall four crystalline phases, it is observed that β spontaneous polarizationcapabilityandpiezoelectricsensitivity,dueto thischaracterizationitexhibitselectroactivephaseinPVDF polymers, where in this property can be utilized to form nanogenerator.
2.1 Materials and methods: TheRochellesaltisatypeof crystallinesolidmaterial,whichisalsoknownbyothername Potassiumsodiumtartratetetrahydrate.Thedoublesaltof Rochelle salt and mono potassium phosphate were the piezoelectricinitialmaterialswhichwerefoundout.David Brewsterwasthefirsttimedemonstratedthepiezoelectric propertiesfromRochellesalts[13].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
These material characteristics led to transducers development had an exceptionally high output rate with typical pick-up cartridge outputs as much as two volts or more.Rochellesaltisdeliquescentsoanytransducersbased onthe material deterioratedifstored in dampconditions. The important physical properties of Rochelle salt are tabulatedinthetable-1,asthisRochellesaltwaspurchased fromAldrichcompanyprivateltd.
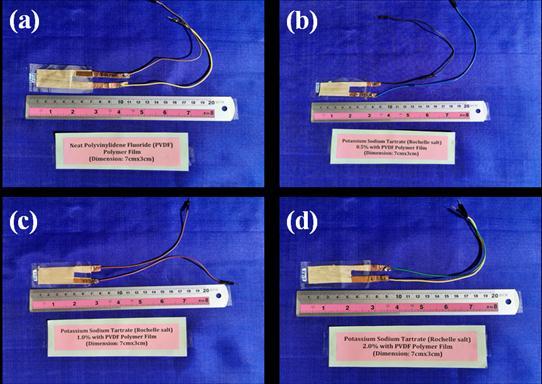
Table: -1:PhysicalpropertiesofRochellesalt
Sl. No. Properties Rochelle salt
1 Chemicalempirical formula KNaC4H4O6·4H2O
2 Molarmass 282.1g/mol
3 Outwardform Itiscolourlessin nature
4 Smell(Odor) Ithasnosmell
5 Density 1.78g/cm³
6 Meltingpoint Ithasthepropertyto meltat75˚C
7 Itssteamingpointor Boiling Itcanwithstandheat upto220˚C
8 Solubilityinwater 26g/100mL(0℃); 66g/100mL(26℃)
9 Solubilityinethanol Itisinsoluble.
The PVDF is a mixture of both crystalline and amorphous structurethathasbeenextensivelyconsideredforitsprime piezoelectricproperties,highchemicalresistanceinnature, strength,anditisalsothermalresistance[14].Amongthem, thebeta(β)phasehasthelargestspontaneouspolarization perunitcellandthereforepresentsthehighestelectroactive properties[15].ThecontentsinPVDFwasfoundtoincrease by about 8% with a silver nanoparticle ,AgNPs content of 0.4%, which is most vital and useful silver nano particle whichhasgoodpiezoelectriccharacteristicsforengineering applications [16]. This chemical is also purchased from Aldrichcompanyprivateltd.
The service temperature up to 150˚C exhibit good combinationofpropertiessuchas
•Goodchemicalresistance.
•Highmechanicaltoughness.
•GoodPiezoelectricandpyroelectricproperties.
•Aswellasgoodprocessability.
2.2.1
In detail, the polymerization process is carried out as follows.ForapolymerofPVDF,0.5%,1%and2%ofRochelle salt is mixed, for 1gram of PVDF,0.01gram, 0.02gram of Rochelle salt which gives rise to 0.5%,1% and 2% of polymers, is processed. Then the homogenous solution of polymer composites of Rochelle salt with PVDF polymer basedsolutionwaspouredintoacleanglassmouldandthe solventisdriedbyusinghotairovenat60˚Cintheabsence ofwaterfor3-4hours.After3hoursthepolymerfilmswere carefullypeeledfromtheglasstray.Inthispresentmethod, thecalculatedamountofPVDFwasconsideredanddiffused in suitable solvent amalgam i.e, dimethyl formamide and dimethylacetamideinthedefiniteproportionbykeepingit hot plate. The process also involves Laser ablation is a methodof breaking downone part of material to create a microfeatureusingalaserbeam.
Laterthechemicalprecipitationsolutionisheatedwithhigh temperature.Infurtherstage,magneticsteerprocedureis carriedoutandsetthetemperatureupto70˚-100˚Coreven above.HencethePVDFbasedRochellesaltcompositewith different percentages is carried out. To fabricate the electrode(silverpaste),theas-preparedRochellesaltbased PVDFcompositefilminitiallyitwascarefullycutinto7cmx 3 cm dimensions and the silver gel was uniformly coated usingthedoctorblademethod.Asmallpieceofconductive adhesive copper tape was attached over the composite, whichbehaveslikepositiveandnegativeterminalsasshown inthefig-1
2.2.2
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The Rochelle salt powder sample is weighed of 0.1 gram, individual samples are grinded the by using pestle and mortar.Transferthegrindedsampletothepalletsetup.The setupwasassembledtightlywithinstrument.Thepressure of 15 Kg/cm2 is applied to pallet equipment. The applied pressureismaintainedfor2-4minutes.Finallythepressure was released manually and circular pallets are collected frompalletsetasshownintheFig-2.ThepalletsofRochelle saltelementsispreparedinordertoperformmorphological studies,electricalbehaviorstudies.
TheScanningElectronMicroscopy(SEM)Make.,HITACHI, S3400N(Japan),ithasanvoltageaccelerationofabout515KV,basicallythistechniqueisusedinstudyingofsurface conducting.Thedevicewasfurtherdevelopedbyimproving thedesignofS3000N,whichwaswellacceptedintheglobal market.Ittake6minutesofdurationforcoldstart,andless than 100 seconds to exchange specimen, it requires only 2.0KVAofpowersupply[17][18].
ItisalsoknownasEDSorEDAX,whichisabasicallyanX-ray elemental technique used to identify the elemental compositionandallocatetogetherwithatomicnumberfor the materials such PZT, BZT, SiO2, Rochelle salt, Polymers etc. The device has typical product research application, reformulation, etc. The equipment maker, is thermo scientificNORON7,ithasthecapacitytoredefinex-raypulse processefficiently,suchasmorethan1,000,000countsper secondmorethandoublepreviouslyavailablecountrates.It can reduce amount of time required to process and also executetocollectthedatarequired[18].
2.2.3 Polymerization technique to obtain Rochelle salt based PVDF Polymer thin films.

TheweightratioofpolymerPVDFbasedRochellesaltisfirst takentocarryoutthepolymerizationprocess.Inthismethod calculatedamountPVDFwasweighedandisdissolvedwith suitable solvent mixture of Dimethyl formide (DMA) in a defineproportionbykeepingitinhotplatewithsteeringat 55˚C-60˚Cforonehourdurationinabeaker.Aftercomplete dissolutionofthePVDFthenaddthecalculatedamountof rochellesaltfillerandhomogenoussolutionwasobtainedby usingultrasonication[17][18].
TheXRDequipmentspecificationsasfollowsRigakusmart lab diffractometer with radiation Cuk α Consisting the wavelength 1.5406 Å spec. The equipment can scan the particleswiththerangespanof6°–80°withthescanspeed of5˚/mininstepsof0.02°.Thesystemexecutionofprocess voltageanditscurrentvaluesareasfollowswere30kVand 15mArespectively.Materialstructureperformancestudyof Rochelle salt/Quartz/PZT/BZT and other nanohybrid was performed by using X-ray Diffracto meter at room Temperature[18].
FTIRspectroscopyequipmentisutilizedusedtoensurethat rawmaterials,intermediatecompoundsandfinalproducts are within required specifications. The equipment specificationsareasfollows,Maker,PerkinElmerSpectrum Version ,model spectrum 2 series, NIOS2 Main software, which is of standard with high performance DTGS (DeuteratedTriglycineSulfate)MIRdetector.Whereinitis mostidealandmostsuitableforlow-light,highthroughput applications. The spectral range is from 8,300-350cm-1 through the data collection, which has the best data resolution of 0.5cm-1, optional Zn Se windows for exceptionallyhumidenvironmentconditions.
The impedanceanalyzermakeris Wayne Kerr,the6500B series which is the entry level model in the range. This deviceprovidespreciseandrapidtestingofmaterialsupto 120MHz.Ithasbestinclassthefrequencyrangeofabout ±0.05%. These specifications of the instrument make the process high accuracy, component design which is ideal tasks for many choice of experimentation. Some of the electricalbehavioranalysissuchasconductance,dielectric constant, dielectric loss, capacitance basic accuracy is an excellent ±0.05% can be executed. The instrument will calculatethenearestequivalentcircuitparametersforthe measurementtracksandrevisetheresults.Alternatively,the parameters of the component may be entered so that instrument will automatically plot the frequency characterization.[16-18].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
4.1 X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of Rochelle salt with PVDF based composites.
4.2 Fourier Transforms Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) study for Rochelle salt and PVDF composite with different percentages.
Transmittance (a.u.)
Fig-3. XRDpatternofaspreparedRochellesaltwith different%weightPVDFbasedcomposites.
The representative powder X-ray diffraction pattern of PotassiumsodiumtartratetetrahydrateisgiveninFig.3.The above plot of the diffraction pattern is represented in the range2θbetween10˚to50˚wherethediffractionpeaksat 2θ values of 16.41°, 19.72°, 20.96°, 23.81°, 24.42°, 27.60°, 28.12°, 29.71°, 32.83°, 35.62°, 39.63° and 44.92° which is indexedby(210),(220),(211),(031),(221),(231),(002), (321),(410),(132),(440),and(113),thereflectionplanesof Rochelle salt with Orthorhombic crystal with space group P21212 particle structure with lattice parameter ɑ = 11.7859Å,b=14.1972Å,andc=6.1875Å.
Due to the polymerization process of Rochelle salt with PVDF polymer, the X-ray diffraction of polymerized materials such as 0.5%RS-PVDF, 1%RS-PVDF and 2%RSPVDF are not well crystallized and slowly shifted in small range, but plain PVDF as depicted better peaks of crystallizedmaterials[19].
2RS-PVDF 1RS-PVDF
Fig.4. FT-IRspectrumsofRochellesaltandRochellesalt basedPVDFcompositefilms.
Thepeakswhicharerelatedtotheelongationandbendingof C–C bonds which is obtained in very low frequency band region(i.e.belowthevalue500cm-1).ThebroadrangeofC-C stretchingofthebondsis1200–800cm-1 intheregion.The peaksintheabovefig.4,withvaluesof1082,1118and890 cm-1canbeassignedvibrationsofC–Cstretching.Thedimers ,CarboxylicaciddepictsaverybroadintenseO–Hstretching absorptionintheregionof3300–2500cm-1[20].Thecrystal latticeconsistsofcarboxylicacidwhichshows withpeaksat 2978,2924and3271cm-1 whichhaswitness.
Theabsorption bands ofinfraredspectra hastherange of 511and840cm-1,thisrangeofvaluesdepictsthatthePVDF polymer material contains β-phase in the structure. The band range at 764, 795 cm-1 has clearly showed that it consistsofαphase,whileotherrangeofvalues778,795,and 834cm-1havebeenattributedtoγphase.The840cm-1,range ofvaluecorrespondstoPVDFwithβphase[21].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
4.4 Electrical conductivity behavior of Rochelle salt based PVDF Composite materials.
3.0x10-5
2.5x10-5
Conductivity ( ohm -1 m -1 )
2.0x10-5
1.5x10-5
1.0x10-5
5.0x10-6
0.0
0.5RS-PVDF 1RS-PVDF 2RS-PVDF PVDF
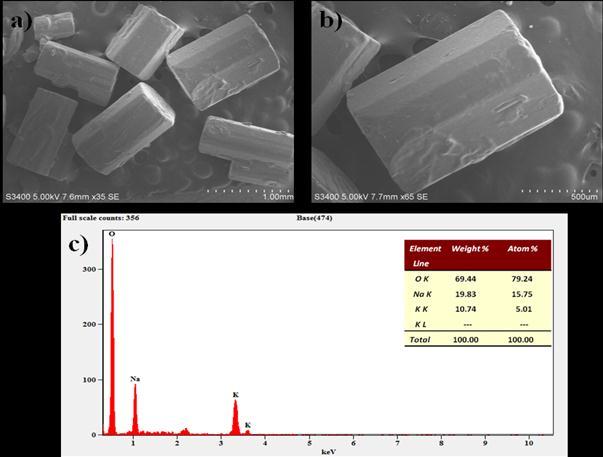
Fig.5 a)&b)aretheSEMimagesofRochellesaltmaterials andc)EDSofRochellesaltwithinsertedtableofdifferent weightandatomicpercentage.
The SEM is very versatile and powerful tool for material characterization study. It basically uses electrons for imaging; it shrinks the material dimensions for obtaining goodmorphologicalstudies.
The micrographs depicts the 0.5-1.5 mm size of freely distributedcrystalsareobservedinRochellesaltmaterials and it is dried at required temperature about 60˚C. Each crystal of Rochelle salt materials is well crystallized in orthorhombicphase.
TheEDSprocessisstudiedofindividual crystals,herethe resultsofthetestingistabulatedintheabovefig-5(c).The elementsclearlyshowsthatallarepresentintherequired stoichimetricamount,thereisnoimpuritiesdetectedinthe EDS spectra of the sample at the suggested temperature, whichshowsthematerialisofpureformlatticestructure.
0 1x106 2x106 3x106 4x106 5x106
Frequency(Hz)
Fig.6 DielectricalconductivityofPVDFnano-composites withdifferentconcentrationsofRochellesalt nanoparticles.
ThedielectricconductivitybehavioroftheneatPVDFfilm whichhascomparedwiththepolymersofRochellesaltwith the PVDF with 0.5, 1 and 2 wt % with respect to the frequencyalongthexaxisplotinthefig.6 TheRochellesalt exhibits good dielectric constant and high piezoelectric properties[22].Itwasobservedthat,neatPVDFexhibited gooddielectricalconductivitypropertywhencomparedwith thedifferentconcentrationofRSwithPVDF.
Fromthegraph,itisobservedthat1wt%ofRochellesaltPVDF polymer exhibited maximum dielectric conductivity comparedwiththe0.5%and2.0wt%ofRochellesalt.The dielectric conductivity of 0.5%RS-PVDF and 2%Rochelle Salt-PVDFshowsminimumperformance.
Thefuturescopeofthematerialdevelopedcanbeenormous used in various fields of engineering such as Energy harvesting,sensorapplicationscanbeappliedonfloortiles asthevehicleispassedonthefloortiles,weightsensors,and automotiveenginecontrolsystem.Voltagesensorssuchas applicationsinwirelesssensors.
In this chapter, the study explains the ferroelectric phase transition,inRochellesaltatmacroscopiclevel,microscopic level.TheXRDstudyhasconfirmedthatthecrystalsystem shows the diffraction pattern which is represented in the range2θbetween10˚to50˚whereitclearlydemonstrates thediffractionpeaks.TheAppearanceofsharpwellisnotso definedpeaksinXRDconfirmsthecrystallinityofthesample is slightly shifted towards sideward. In infrared spectra,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
absorptionbandsat511and840cm 1whichbasicallyshows thepresenceofβ-phaseofthePVDF.Thebandsat764,795 cm-1havebeenattributedtotheαphasewhile778,795and 834cm-1 havebeenassignedtoγphaseand840cm-1 which correlate tothe βphaseof PVDF filmswhichshowsgood performanceandmaterialcharacteristics ofpolymer.
The elements clearly shows that all are present in the required stoichimetric amount, there is no impurities detected in the EDS spectra of the sample. It is observed from the graph, that1 weightpercentageofRochellesaltPVDF based polymer exhibited maximum dielectric conductivity with value slightly more than 5.0x10-6 at a frequency of 3x106Hz, when compared with other two compositionofRochellesaltdopedwithPVDFpolymer.
I,wouldliketorecordtheappreciationtoallthepeoplein providing inputs for writing this paper. First of all, the appreciation goes to Dr. B.R. Narendra Babu, Research supervisor, Professor and COE, Department of Mechanical Engineering,VVIET,Mysore,Karnataka,Indiaforcontinuous guidanceandsupportforentirework.
In addition, special thanks to University of Mysore and VisvesvarayaTechnologicalUniversityforaccommodating research facilities required for work. Besides, I am also grateful to all my family members and friends for encouragingtheirloveandsupport.
1.E.H.YooandS.Y.Lee,Sensors,10(2010)4558
2.J.S.Schultz,S.MansouriandI.J.Goldstein,DiabetesCare,5 (1982)245
3. D. Zhang, Y. Peng, H. Qi, Q. Gao and C. Zhang, Biosens. Bioelectron.,25(2010)1088
4.B.Pan,D.Cui,Y.Sheng,C.Ozkan,F.Gao,R.He,Q.Li,P.Xu andT.Huang,CancerRes.,67(2007)8156.
5.X.Jia,L.Tan,Q.Xie,Y.ZhangandS.Yao,Sensor.Actuator. B-Chem.,134(2008)273.
6. J. Curie and P. Curie. D´eveloppement, par pression, de l’´electricit´epolairedanslescristauxh´emi`edres`afaces inclin´ees.Comptesrendus,91:294–295,1880.
7. Binoy Bera.,Madhumita das Sarkhar, Piezoelectricity in PVDF and Piezoelectric based a Nanogenerator: A concept,IOSR Journal of Applied Physics,e-ISSN:22744861,Volume9,Issue3,June2017.
8.ShuaibingGuo.,XuexinDuan.,MengyingXie.,KeanChinAw and Qiannan Xue ; Composites, Fabrication and
Application of Polyvinylidene Fluoride for Flexible Electromechanical Devices: A Review, Micromachines,MPDI,Published:3December2020.
9.N.Murayama.,K.Nakamura.,H.Obara.,M.Segawa,Thestrong piezoelectricity in polyvinylidene fluroide (PVDF), Elsevier,Volume14,Issue1,2002.
10. Shivaji H.,Wankhade.,ShivamTiwari., Anupama Gaur.,PralayMaiti, PVDF–PZT nanohybrid based nanogenerator for energy harvesting applications, Elsevier,Volume6,November2020.
11.BuschG.EarlyHistoryofFerroelectricity.Ferroelectrics 1987;74;267-284
12. Kanzig W. History of Ferroelectricity 1938-1955. Ferroelectrics1987:74;285-291.
13. S. D. Brewster, Observations on the pyro-electricity of minerals:WilliamBlackwood,1824.
14.Mokhtari,F.;Shamshirsaz,M.;Latifi,M.Investigationof_ phase formation in piezoelectric response of electrospun polyvinylidenefluoridenanofibers:LiCl additiveandincreasingfiberstension.Polym.Eng.Sci. 2016,56,61–70.
15. Mokhtari, F.; Latifi, M.; Shamshirsaz, M. Electrospinning/electrosprayofpolyvinylidenefluoride (PVDF): Piezoelectric nanofibers. J. Text. Inst. 2016, 107,1037–1055.
16. Issa, A.A.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.; Luyt, A.S.; Ponnamma, D.; Hassan, M.K. Physico-Mechanical, Dielectric, and Piezoelectric Properties of PVDF Electrospun Mats ContainingSilverNanoparticles.J.CarbonRes.2017,3, 30.
17. Ricardo Luiz Barros de Freitas., Walter Katsumi Sakamoto., Luciana Paro Scarin Freitas., Fabian Castro,Antonio P. Lima Filho., Claudio Kitano., and Aparecido Augusto de Carvalho, Characterization of PZT/PVDFCompositeFilmasFunctionalMaterial,IEEE SENSORSJournal,Vol.18,No.12,June15,2018.
18. Shivaji H.,Wankhade.,ShivamTiwari., Anupama Gaur.,PralayMaiti, PVDF–PZT nanohybrid based nanogenerator for energy harvesting applications, Elsevier,Volume6,November2020.
19. C. H. Görbitz and E. Sagstuen, "Potassium sodium (2R, 3R)-tartrate tetrahydrate: the paraelectric phase of Rochellesaltat105K,"ActaCrystallographicaSection E:StructureReportsOnline, vol.64,pp.m507-m508, 2008.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
20.R.Silverstein,F.Webster,andD.Kiemle,"ProtonNMR spectrometry,"SpectrometricIdentificationofOrganic Compounds,7thed.;JohnWiley&SonsInc.:NewYork, NY,USA,p.142,2005.
21. Y. Bormashenko, R. Pogreb, O. Stanevsky, and E. Bormashenko,"Vibrational spectrumofPVDF andits interpretation,"Polymertesting,vol.23,pp.791-796, 2004.
22.C.B.SawyerandC.Tower,"Rochellesaltasadielectric," Physicalreview,vol.35,p.269,1930.