International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1Under Graduate, School of Computer Science Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, Tamil Nadu, India
2Under Graduate, School of Computer Science Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, Tamil Nadu, India 3Associate Professor Senior, School of Computer Science Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, Tamil Nadu, India ***
Abstract - Attacks involving mobile malware have grown as cybercriminals work harder to mislead victims into downloading infected text messages and apps in order to steal their personal data, including passwords and bank account details. Most of mobile malware can not only steal usernames and passwords for bank and email accounts, but it can also record audio and video, trace your location, and even wipe your data and information. As mobile malware advances, more attacks are leveraging these abrasive features. To keep our information secure, an effective detecting technique is needed. The study examines several detection methods, from the most accurate to the least effective, and covers the most recent mobile malware detection approaches in Android and iOS, we have filtered 218 papers and have done extensive study on various malware detection techniques which are recent and innovative.
Table 1: ComparisonofAndroidandiOSoperating systems
Specificati on Mobile Operating system Android iOS
Developer Googleandopen handsetalliance AppleInc
Initial release September23,2008 July29,2007
Latest release Android12 iOS15.3.1andiPad OS15.3.1
Source model Opensource Closed,withopensourcecomponents
KeyWords: Mobile Malware, Detection, Analysis, Android,IOS
The development of mobile smart phone technology has enabled the public to download hundreds of different mobileapplicationsusingtheirmobiledevices.Thesehave leduserstoquicklyaccessinformationandresourcesfrom any place and at any time. The services offered by mobile smartphones have attributed to a rise in the number of mobilephonesubscriptionsglobally.AsperITU2021,4.9 billion people, or approximately 63 percent of the global population, are estimated to be online in 2021. This indicatesa nearly17percentgrowthrateover2019,with a projected 800 million individuals using the internet throughout that time. By the conclusion of the forecast period, with an expected 800 million people associated with the internet during that period. There are estimated to be 6.7 billion unique mobile consumers by the end of thereviewperiod,increasingover6.1billionattheendof 2021. Subscriptions for smartphones continue to go up. Theremightbe6.3billionbytheendof2021,accountsfor approximately77%ofallactivesubscribers. It’sprevalent that mobile malware is still affecting a bulk of devices world-wide. We have made a table (Table-1) which compare different components of Android and iOS OperatingSystems.
Third-party appstores
Inadditiontothe officialGooglePlay Store,thereare severalotherapp marketplaces
Third-partyapp shopsareblocked byApple.Youmust jailbreakthephone todownloadapps fromotherstores
Security securityupdates everymonth occasionally updatedsecurity
[7] The five levels that constitute the Android operating system are depicted in Fig-1, with the Linux kernel serve asthebottomlayerandcontrollinghardwareabstraction. The platform libraries level contains a collection of librariessuchasWebKit,Libc,SGL,SQLite,SSL,Mediaand Surface Manager. Android's Java-based libraries have included following. View and widget for Android The application framework level gives high level services to programs in form of Java classes. Apps are written for installation in the level above, known as the application level.
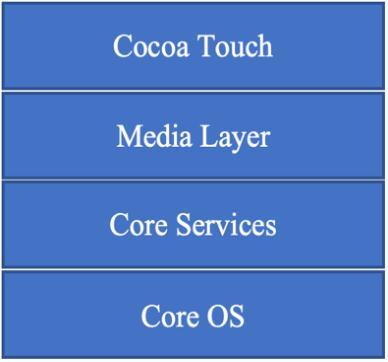
The iOS architecture is represented in Fig-2. The Cocoa Touch layer includes the frameworks for iOS apps. The media layer includes the graphics, video, and audio technologiesforiOSapps.Thecoreserviceslayercontains the important system services for iOS apps The core OS layer involves the basic features upon which most other technologiesarebuilt.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
are compromised by phishing via emails, Text messages, andfraudulentupdates.
[7] Backdoors exploit root privileges to mask malware againstantivirussoftware.Rageagainstthecage(RATC)is among the most well-known Android root vulnerabilities which grants complete control of the device. If the root exploitsucceedstogetrootaccesswithouttheindividual's consent, the virus can operate directly on the device, including software installation. The iOS Trojan Xagent facilitates the access to the back door of the infected deviceandobtainsdatafromit.
[7] Ransomware restricts users from gaining access their files by isolating the device or encrypting the file system until an amount is paid. FakeDefender.B is a virus that mimics to be Avast antivirus. It encrypts the victim's device in order to gain money. There were instances in 2017ofaniOSmalwarethatattackersexploitedtopop-up windowinBrowsers
Malware attacks on smart phones are developing as more mobileappsaresubmittedontheAppandPlaystoresday after day. [1] Although there are many types of mobile malware, such asTrojans, worms, botnets, spyware, and ransomware, the most notable iterations appear to establish a common inspiration: monetary gain. In this section,wewillbelookingforsomeofthemostprominent andrecentmobilemalwares.
ATrojanisasoftwareapplication thatappearstotheuser to be a safe application but executes dangerous actions in the background. Trojans are deployed to facilitate in the attack on a computer by executing operations that may break the system's security, allows for remote hacking. TrojanscompriseFakeNetflix,whichgathersusers'Netflix accountdetailsinAppsettings.TheTrojanKeyRaiderwas usedtoattainAppleIDsandpasswords.

Trojans steal sensitive data from users without their knowing. They can steal emails, chats, web history, and even financial details. According to the McAfee Mobile Threat Review, the frequency of mobile banking Trojans suchasBankBotsurgedby60%in2018.End-userdevices
[1] This application of mobile malware is prevalent these days. Android/LokiBot, for example, combines the features of cryptocurrency ransomware and a finance malware. It can encrypt data and send misleading email alertsinanordertodeceivevictimsintologgingintotheir bank accounts. Android/LokiBot has raised up to $2 million in profit by targeting over 100 financial firms and offeringkitsonthedarknet.
[7]A"botnet"isawebofinfectedsystemscomprisedofall users'smartphonesacrosstheworld.A"bot"isapieceof malware that allow attackers to take complete control of an unprotected smart phone; it is also referred as "Web robots." Geinimi is the codename of one of the Android botnets.
[7] Spyware is more like an eavesdropping software. It worksinthebackground,collectinginformationorgaining unauthorized connection to its maker. Nickspy and GPSSpy are two examples of Android spyware that monitortheperson'sconfidentialdetailsandtransferitto the owner. Passrobber is an example of an iOS spyware software. It can snoop in on SSL outbound connections, search for Apple IDs and passwords, and transmit the informationtoacommand-and-controlserver.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[1] Malware attacks for Cryptocurrency mining risen by 80 percent in 2018, despite being less effective than desktop counterparts. According to Kaspersky Security Network, the bulk of this type of virus is disguised within well-known applications that were discreetly mining bitcoinswhilewatchingcatvideos.
The current malware is treated by sophisticated techniques for identifying android malware. Nevertheless, theeffectivenessofeachapproachvariesdependingonthe variables that contribute to its focus. Based on the detection techniques the researchers have presented, the various research that are now available in this field are categorized, and their usability and effectiveness are evaluated. On mobile devices, various criteria are used to detectmaliciousactivity.Theresearchestablishmentisstill polarized about a defined as a standard. The contrast among static and dynamic analysis methods for malicious programs is made in an assertion. While signature- and anomaly-basedapproachesincorporatestaticanddynamic detection as subclasses, other experts use a different approachtoclassifymalware.
Thiskindchecksentitieswhichareeithercontainedinthe phone's SD storage or Memory for fitting characteristics usingadatabasethatincludesrecordsofmalwaresample signatures. A security service named Kirin was suggested by Enck et al. [15] for the Android system's operating system (OS). To use a collection of security protocols that are templates made to match questionable characteristics in an app's security settings, Kirin verifies an application at installation time. Further precisely, Kirin evaluates the securityconfigurationagainstwithasetofpredetermined security rules after the installer extracts security configurationfromthepackagemanifests.
The collection of signatures happens during in the deconstructionandanalysisofthemalwaresourcecodein a static signature-based technique. On the contrary, dynamic behavior-based methods obtain signatures just after malicious code has indeed been performed. In order to assess an app's malicious behavior, data is specifically gathered while the app is running. To accomplish this, a signature database or pattern collection is built using preconfigured and prearranged attack patterns that are giveninadvancebyspecialists.
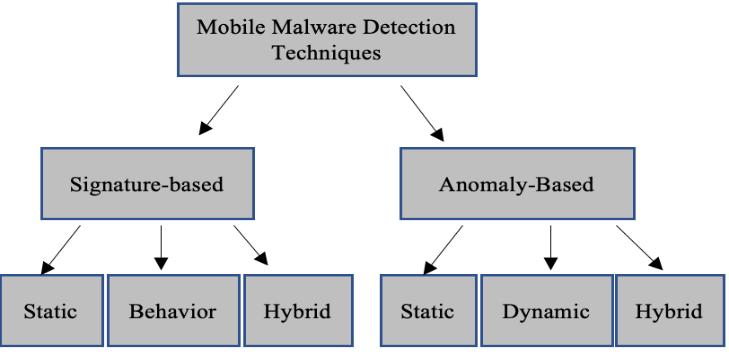
By eliminating the conceptual characteristics, this technique creates a recognizable signature. Malware is characterizedasanyapplicationthatsignaturematchesthe ones that previously existing. Methods for detecting malicioushaveaselectedclassificationvectorconnectedto a type of detection. Anomaly-based and signature-based are indeed the mainly two detection techniques. Using signature-based detection, the possible hazard or innocuous nature of suspicious code sections is identified by comparing them to trends and signatures from known malware. Behavior-based and static signature-based detection methods belong to the category of signaturebased detection. Static signature-based techniques are utilized by the bulk of commercial antivirus
solutions.
Static and behavior signature- based detection both are componentsofhybridsignature-baseddetection.Tousea crowdsourcinglogic,Papamartzivanosetal.[17]designed a host and cloud-based approach. Their platform offers three essential services, encompassing crowdsourcing, privacy-flow tracking, and the detection and remedy of privacy breaches. To prevent tasks requiring a significant number of resources, the user interacts the with cloud storageviaaTLSconnection.Theuserismadeupofthree components in total: a privacy inspection module, a response module, and an event sensor module. Crowdsourcing, detection, and hook up-date are indeed thethreecomponentsthatmakeupthecloudaspect.
The strategy employed by anomaly-based methods is much less rigorous. This is performed by recording a device's typical function more than a predetermined time period and utilizing the metrics of that model as both a baseline vector for erratic behavior. The static and dynamic strategies are applied to the analytical portion. While a dynamic approach does the evaluation while the application runs by collecting data including program execution and activities, the static method compares a program before installation by analyzing it. Anomalybased detection methods involve two stages: the training phase and the detection phase, based on whether the
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
anomaly is dynamic or static. In the initial instance, a healthy device is being utilized and this action is monitoredandlogged.On thecontraryside,thedetection step acts as a testing period, however during period variations from the paradigm employed in the training phasearerecognizedasanomalies.[1]
Theviralcontentisnotrequiredtobeprocessedforstatic anomaly-baseddetectionsystemstooperate.Theirtaskis to analyze the malicious sites application's code for only certainsoftwarecomponents,suspectbehavior,andsome other behavioral characteristics. It can not only discover unidentifiedviruses,butitisalsoabletoidentifypossible securityvulnerabilitiesinthesourcecode.Thistechnique, nevertheless, even has problems. Misdiagnosis rates are all still substantial and carrying out a code examination canindeedbetimeandsourceofenergy.
In this technique, the training and detection processes start happening as even the application is being utilized. This characteristic not only enables the detection of unknown malware, yet it also allows it possible to spot zero-day attacks. Nevertheless, as has been previously stated,there are a fewsevere misdiagnosis rateconcerns, notably using dynamic anomaly-based detection techniques. Reliable typical behavioral models must alwaysbecreatedduringthepracticesessionsinorderto decreasethisoccurrence.
Static and dynamic anomaly-based detection are both usedinhybridanomaly-baseddetection.
The Authors [1] have tested with mobile malwares like Mobile Banking Trojans, Cryptocurrency Mining, Ransomware, Hybrid and did a Comprehensive comparison of the 22 mobile malware detection approaches during years 2009 and 2018. Both Android andIOSplatformsaretested
Methods tested in Detection techniques are APK Analysis, Behavior patterns, Native code analysis, Information flow analysis, iOS Software analyzer, SMS profiler, Network traffic, Op-code frequency, permission analysis, sandbox, Systemcalls
The authors [2] noticed that some researchers used machinelearningtodetect malware, whereasothersused deep learning to detect malware. Furthermore,others employed hybridanalysis, a combination of static and dynamicanalysiswasusedtodiscoverandclassifyknown malware. Several researchers developed Demonstrated Mobile Guard as a malware detection solution to protect
users from malware threats. Other researchers tested alternative methodologies, such as evolutionary computation,naïvebayes,andcomplexflows.
The authors [3] conducted an extensivesurvey on MLpowered approaches for screening Mobile malware. Several of the techniques used a unique set of core characteristics, such as the datasets, analysis (feature collection), and identification assessment measures. To complete this, they classified and carefully examined bestpublicationspublishedintheliteraturebetween2014 and 2021. This was conducted based on the type of analysis, feature extraction method, dataset, ML classification approaches, and measures used to evaluate their performance. They proposed a four-step resolution strategytoaidinthecontrolofthisproblemandserveasa baseline for future mobile ML-based Android malware detection methods. VirusShare, AndroZoo, MalGenome, ContagioMobile,Drebin,andDroidBenchwereamongthe malwaredatasetsused.
[4]A thorough analysis of ML-based Android malware detection methods is presented in this research. It analyses 106 carefully chosen articles and identifies their advantages and disadvantages as well as suggestions for development. Since it could be more challenging to improvesecurityaftertheprogrammehasbeendeployed, the ML-based methods for detecting source code vulnerabilities are explored in the final section. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) approach was used to perform this study. They discovered that DL techniques have been shown to be more accurate than conventional Machine Learningmodels.
Theauthorsintheresearch[5]helpstoexaminethemost popularandeffectiveapproachesandprovidesuggestions onwhichisoptimal.Ithasbeenrevealedthatusingastatic technique is less efficient at identifying dangerous materials that are gradually loaded from remote servers. While the dynamic approach is suitable because it continuously checks the script and is ready to identify suspicious content whenever it is performed, any type of malicious software that is not executed remains undetected.
Theauthorsofstudy[6]providedadetaileddescriptionof how well machine learning (ML) algorithms operate to detect malware on Smartphones without needing special access. ML-classifiers discover the ten types of Mobile Trojans on the Android Platform by studying device informationsuchasCPU,battery,andmemoryutilization. Over the course of a year, they used a statistical methodology comprised of 47 customers' device and malware data. They examine which device characteristics should be monitored the most in order to detect Mobile Trojans. The focus of this paper is on dynamic hardware
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
features.ModernmachinelearningclassifierslikeRandom Forest,K-NearestNeighbor,andThesedynamicproperties were used by AdaBoost. They portray the classification resultsforvariousfeaturesets,distinguishingbasicdevice features from app-specific features. Neither of the feature setsanalyzedrequirespecialaccess.Theirresultsindicate that the Random Forest classifier surpasses existing malwareclassifiersingeneral:itscoresanF1scoreof0.73 across10subtypesofMobileTrojans. TheRandomForest, K-Nearest Neighbors, and AdaBoost classifiers give F1 scores greater than 0.72and FNR less than 0.33 when trained separately to identify each subtype of Mobile Trojan.
The writers of paper [7] reviewed numerous attack methods against the leading two competitor smartphone operating systems, iOS and Android. They also presented up-to-datemalware threatfigures for the last3yearsand explained the techniques used to deploy mobile malware. Following that, the most frequent malware detection technologies for mobile applications were reviewed. They then recognized and analyzed the weaknesses in each malwaredetectiontechnique.
They proposed using APIs and permissions to discover malware on Android in their article [8]. They created two types of feature vectors: common feature vectors and mixed feature vectors. They had focused their study on static analysis approaches. The stages of their project are asfollows:reverseengineering,featureextraction,feature vector development, and classification. They were able to attain 97.25 percent accuracy for shared data and 96.56 percent accuracy for combined features using logistic regression. They increased the feature count by removing low variance features, with which researchers achieved 95.87percentaccuracy,inordertominimizetrainingand testingtimesforclassification.
A major examination on Android malware analysis and detectionmethods wasdone between 2010 and 2015 [9]. A total of 58 ultimate publications among 1514 total publications were filtered and identified for the analysis after the studies that didn't reflect the following criteria were excluded. People who readthe summary gained a deeper understanding of the state of Android malware detection today, which included the most commonly used techniques, malware analysis techniques, functionalities for malware analysis, algorithms for making distinctions among both malware and non-malware, and likelihood of success for all efficient implementations. Information retrieved from selected papers: Approaches for detecting malware,Methodologiesforanalyzingmalware,Algorithm employed, Characteristics used, Scale of examination, success probability of detection, Distributor, paper type, andmalwaretypes.
Thissurveystudy[10]containsadescriptionoftheinitial phases of development of mobile malware, exploit
pathways,detectingapproaches,andsecuritymeasures.It also discusses the differences between mobile malware andPCsecurity, aswell asresearchactivities tominimize them. The focus of this research is on the safeguards employed by iPhone and Android handsets to prevent invasions. They have highlighted several detection strategies, such as cloud-based systems, dynamic or behavioral analysis, and static analysis. The detection system's method includes both signature-based and anomaly-based technologies. They highlighted the researchconducted priorto definingdata-centricsecurity systems, or even the defense mechanisms examined in variousplatforms.
In all these papers Authors have used various methods to accurately detect mobile malware in the devices. A wide range of methods were employed, and machine learning techniquesremaineddominantandmostfutureworksare mostly done on machine learning and deep learning algorithms. As They are suitable for dynamic and hybrid malwaredetection.
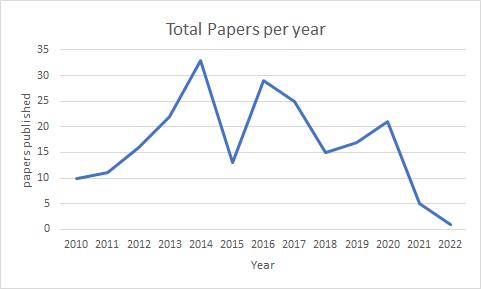
Wehavereviewedaround500+papersandtookthemost relevant of them and cut the number down to 218. The papersinclude fromvarious sourceslikejournals,articles and research papers. Different malware detection techniques were introduced and reviewed by various authors we have represented them pictographically according to the methods, types and accuracy of the techniques.First,wehaveplottedalinechartrepresenting numberofpapers published(in Fig-4) onMobilemalware detectiondividedbyeachyearrangingfrom2010to2022.
In x-axis we have years from 2010 to 2022 and in y-axis number of papers published. From the chart we can observe that in year 2014 there were more papers published from the papers we collected. Even though there’s a minor dip in 2015 Increase in mobile malware detectionpapersareincreasedin2016.Andlatestresearch papersmostlyincludedetectiontechniquesusingMachine
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
learning and deep learning algorithms. As Malwares are becoming more intelligent as time grows one need to combat these malwares using Artificial intelligent detection mechanisms more specifically using machine learning and deep learning techniques. Past detection algorithms were mostly static, or anomaly based which render useless in detecting latest malware which also use machine learning to get past the security systems. Attackers are becoming more sophisticated. Research in Mobilemalwareissuretoincreaseinthefuture.
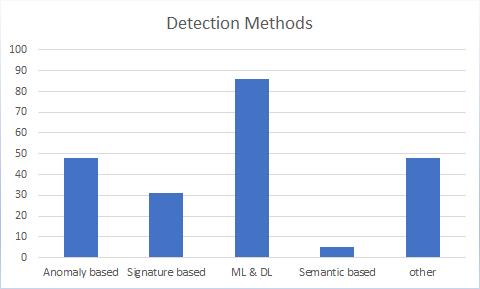
In Fig-7, The bar chart shows the diversity of detection methods reviewed, from the chart we can see machine learning and deep learning methods are popular for implementing detection techniques and in second place we have anomaly-based detection which is also quite researched method among authors. And there are other techniqueswhicharequitenewanduncommon.
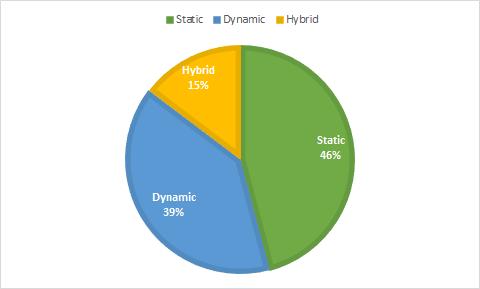
In Fig-5, The pie chart gives a pictorial representation of typesofmalwaredetectiontechniquesstatic,dynamicand hybrid were shown, there were more static techniques reviewedcomparedtodynamicandhybrid.fromthisdata we can say that static malware detection technique is morepopularandnextisdynamicdetectiontechnique.
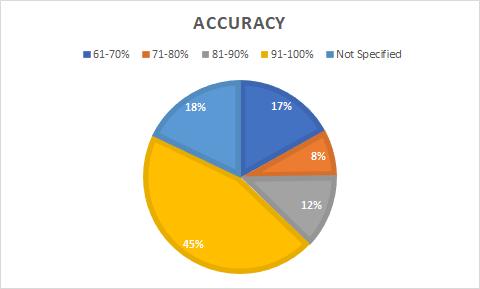
In Fig-6, The accuracy of algorithms we have shown in a pie chart, the algorithms we reviewed are mostly of 91100% accuracy and 18% of authors haven’t specified the accuracy or have given some other metrics which are difficulttoapproximate.17%paperswereviewedhave6170% accuracy these are from the early years of paper publication. and a total of 20% with accuracy between 71%-90%. The data shows us that mobile malware detection techniques are doing pretty good in recent years.
Wehavelookedatvariousdetectiontechniqueswhichare modern and recent. we can interpret from results that mostauthorsarefocusingonMachinelearningalgorithms to detect the malware. They used various datasets and algorithmsimprovetheaccuracyindetectingthemalware. we also observed that most malwares are prevalent in android platforms and many papers are exclusively written for detection in android operating system. As malwares continue to increase new techniques are developed. The authors have looked for malware from kernel level to application level. they employed methods like signature-based, anomaly-based, permission-based etc. [5] It has been established that utilizing a static technique is less reliable at discovering the dangerous threats that are constantly loaded from cloud computers. The dynamic approach is suitable because it regularly monitors the application and is capable to identify the threateningcomponentonceitisemployed.
[2] Numerous researchers have developed The Mobile Guard as a malware detection software to protect consumers from malware attacks. Other authors additionally experimented with different methodologies, such as evolutionary computation, Nave Bayes, and Complex-Flow. [3] Ensemble models first appeared in the published papers after 2015. These algorithms are included in moststudiespublished between 2015 and 2020 that employs a frequently updated malware database,suchasVirusShareorAndroZoo.
[6] High-performance RF, KNN, and AdaBoost have been used to classify a single piece of malware. When various
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
typesweretrainedforeachformofmalwareattackinthis research,RFandKNN executedwell.AdaBoost'sexcellent performanceisasignificantdiscoveryinthisfield.[8]The authors of this paper identified a feature vector using several classifiers and discovered that logistic regression produced97.25percentaccuracyforcommontraits.They were able to reduce the number of permissionsand gained95.87 percent accuracy by omitting low variance parameters.[9]Malwarecomesinawidevarietyofforms, including Trojan horses, spyware, virus, trap doors, and others. Not every report highlighted the precise type of malware detected. It was hard to generalize, but the detection methods made it easier to identify the various malware strains. The Common types of malwares discovered were Trojan horses, Geinimi, DoridDream, Awide,andPlankton.
This study offers a cutting-edge survey on the current subject of mobile virus detection methods. In order to achieve this, we classified and briefly assessed the many detection strategies that were put out in the literature during the course of the previous 12 years, from 2010 to 2022, depending on their detection approach. The review gavereadersabetterunderstandingofthecurrentstateof Android malware detection, including the most popular techniques,malwareanalysistechniques,featuresusedfor malwareanalysis,algorithmsusedtodistinguish between malware and non-malware, and the success rates of all suggested methods. In an effort to provide a thorough review of this difficult and rapidly developing subject, we also highlight the advantages and drawbacks for each category of techniques and each analyzed scheme, as appropriate. According to the review, there may be chances in this subject in the future. Therefore, it will assist in supplying the deserving researchers working in this sector with suggestions and requirements for future development of such systems with improved approaches tocombattheemergenceofnewAndroidmalwares.
We appreciate Professor Manikandan K for viewing theabstract and giving comments which enabled us to decide to convert the abstract into a comprehensive research survey. The analysis had been done in2022 research project that has been carried out particularly to raise the awareness of the situation of Android malware detection methodologies and technologies between the yearsof 2010and2022.Thecontributors'viewpointsare those that have been conveyed in reference to any topics inthispublication.
[1] KOULIARIDIS, V., BARMPATSALOU, K., KAMBOURAKIS, G., & CHEN, S. (2020). A Survey on Mobile Malware Detection Techniques. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, E103.D(2), 204–211.doi:10.1587/transinf.2019ini0003
[2] Sallow, Amira & M.Sadeeq, Mohammed & Zebari, Rizgar & Abdulrazzaq, Maiwan & Mahmood, Mayyadah&Shukur,Hanan &Haji,Lailan.(2020). An Investigation for Mobile Malware Behavioral and Detection Techniques Based on Android Platform. IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering. 22. 14-20. 10.9790/0661-2204021420
[3] Kouliaridis V, Kambourakis G. A Comprehensive Survey on Machine Learning Techniques for Android Malware Detection. Information. 2021; 12(5):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12050185.
[4] Senanayake J, Kalutarage H, Al-Kadri MO. Android Mobile Malware Detection Using MachineLearning: A Systematic Review. Electronics. 2021; 10(13):1606. doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131606
[5] Gyamfi, N. K., & Owusu, E. (2018). Survey of Mobile Malware Analysis, Detection Techniques and Tool. 2018 IEEE 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON).doi:10.1109/iemcon.2018.8614895.
[6] J. S. Panman de Wit, D. Bucur, and J. van der Ham. 2022. Dynamic Detection of Mobile Malware Using Smartphone Data and Machine Learning. Digital Threats 3, 2, Article 9 (June 2022), 24 pages. doi.org/10.1145/3484246.
[7] Amro, B. (2018). Malware detection techniques for mobiledevices.arXivpreprintarXiv:1801.02837.
[8] Tiwari, S. R., & Shukla, R. U. (2018, July). An android malware detection technique based on optimized permissions and API. In 2018 International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications(ICIRCA)(pp.258-263).IEEE
[9] Dema,K.,&Jamtsho,T.(2019).Asystematicreviewon android malware detection. Asian Journal For Convergence In Technology (AJCT) ISSN-2350-1146, 5(3),83-86
[10] Ramu,S.(2012).Mobilemalware evolution, detection anddefense.EECE571B,termsurveypaper.