International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
4 . 1, 2, 3, 4. SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING VELLORE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY VELLORE (TN.), INDIA.
ABSTRACT – Theadmissionsprocessisastruggleforuniversitiesnowadays,particularlythosethatfocusonSTEMfieldslike computer science and engineering.In ordertoidentify students who would be successful in their programmers,universities shoulduseobjectivecriteriaforadmissions.Thesuggestedtechniquewastestedusingadatasetconsistingof2,039students from2016through2019whowereenrolledintheInformationandComputerScienceCollegeoftheaSaudistateinstitution. The findings show that early academic success at university may be predicted prior to admission using certain criteria. The findings also suggest that a student's score on the Scholastic Proficiency Admission Test is the best predictive factor for admission.Thisscoreshouldthusbegivengreaterweightinselectionprocedures.
Index terms – Data Mining, SVM, ANN, Decision tree.
Inordertoidentifystudentswhowouldbesuccessfulintheir programmes, universities should use objective criteria for admissions. Additionally, each school should use the most advanced methods for estimating an individual student's potentialintheclassroombeforeenrollingthem.Thiswould help policymakers at universities establish effective admissions standards. Nonetheless, most universities have difficulty analysing their massive educational datasets to foretell students' success [1]. This is because they rely only on traditional statistical approaches, as opposed to more modern and effective prediction methods like Educational Data Mining (EDM), the most widely used method for assessing and predicting students' performance [2–6]. In ordertoanticipatestudents'performance,EDMfirstinvolves gatheringmeaningfulinformationandtrendsfromamassive educational database [2]. Better data allows for more plannedapproachestoboostingstudents'academicstanding.
This research aims to aid colleges in their admissions processes by providing more accurate predictions of applicants' future academic achievement using data mining methods.
In various areas, this research adds to the existing body of knowledge. At first, we use four data mining classification models to foretell candidates' early academic success based on their profiles before they enrol. Quiz and final exam scores, extracurricular involvement, student demographics, cumulativegradepointaverage,andsocialnetworkcontacts
areamongtheprofiledata mostoftenutilised forpredicting students' success in higher education (e.g. [7]–[10]). However, factors that may be used to predict student achievement, like as pre-admission test results, are seldom takenintoaccountintheadmissionsprocess(e.g.[11]–[13]). This research focuses on these underappreciated indicators. We also compare four categorization methods for making predictions about students' performance and determine which one is most effective in terms of accuracy, precision, recall,andF1-Measure.
Second, we use a correlation coefficient analysis to find out howtheselectioncriteriaforincomingfreshmenaffecttheir GPA after the first semester. We also determine the best predictive admissions criteria for student achievement so thatdecision-makersmaygivethatfactorgreaterweight.
Third, theinstitution where this research wasdoneadopted a new admissions policy that gave different weight to the qualities that were shown to be most important. By comparingthe cumulative grade point averages of freshmen accepted under the old and new systems, this research demonstrated the wisdom of the latter. The number of freshmen with outstanding or very good cumulative GPAs roseby31%,whilethenumberwithacceptableorbadGPAs fellby18%.
The huge sample size of 2,039 students from the Faculty of InformationandComputer Sciences(CCIS)ofPrinceNourah bint Abdulrahman University (PNU) in Riyadh, Kingdom of SaudiArabia,setsthisresearchapartfromothersinthearea
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
offorecastingstudentperformance(KSA).Ithasmorefemale students than any other institution in the world. Most previous research in this area validates the efficacy of their modelsusingsignificantlysmallersamples.
Attributes and prediction techniques are the two most important aspects in predicting student achievement. The cumulativegradepointaverage(CGPA)ofcollegestudentsis the single most important factor in determining their academic success. Many studies have benefited from its use (e.g. [7]–[10]). Assessments, quiz scores, lab work, & final examgradesareadditionalindicatorsemployedbyacademic performance studies (e.g. [8], [9],). Only a small number of studies have accounted for demographics, student activities, andsocialnetworksasindependentvariables.
However, in the admissions process, input factors such as pre-admissionexamsareseldomemployed(e.g.[11]-[13])to predict student success in university. This is what we'll be lookingatindetail.
Many different data mining categorization methods have beenusedtoattempttoforetellhowwellstudents woulddo intheircourses.Inoneresearch,forinstance,ANNisusedto predict how well 505 students would do in their eighthsemester classes. Using Decision Trees, a model was presentedtopredictstudentsuccessinspecificcourseswith little data (32 and 42 students). An analysis of 1,600 students' grades for a single class using Naive Bayes. The research uses SVM on a dataset of 1,074 individuals to forecasttheacademicsuccessofat-riskfreshmen.
Predicting first-year cumulative grade point averages in the computer engineering departments of Saudi public institutions was investigated here using a variety of admissions factors as input qualities. Few research conducted in KSA and published on the topic have focused outside of medical schools (e.g. [11]–[13], [15]). While EDM may help uncover hidden patterns in huge datasets, it has not been applied in these investigations. Study, which used oneoftheEDMapproaches(i.e.,J48decisiontree)tousually considered'finalGPAbasedongradesinallclasses,isoneof the few on the issue that has been limited to a computer science institution. Authors gathered information from the transcriptsof236ComputerScienceCollegestudentsatKing Saud University (KSU) from Saudi Arabia. They determined which classes had the most influence on the cumulative grade point average. However, they only used a single EDM methodology on a tiny dataset to make predictions about
studentperformance&didnotdouble-checktheirworkwith anyotherEDMmethods.
This study used the Linear Regression method, a common method for determining the connection between independent variables (i.e., predictors) or a predictor variables (i.e., future academic performance), to answer the firstquestion(Cantheadmissioncriterionthatbestpredicts future academic performance be identified?) (i.e., response). We used this model to analyse the correlation between the three entrance factors (HSGA, SAAT, and GAT) and the cumulative grade point average (CGPA) after the first two semesters of study. We utilised the correlation coefficient, a standard statistical measure of the strength and direction of linearcorrelationsbetweentwovariables,tocharacterisethe linear link between each admission criterion and the CGPA. In addition, we employed the determination coefficient to characterise the relative impact of each admission criterion onthestudents'first-yearCGPA.
Using four well-known data mining classification techniques Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Decision Tree (DT), Support Vector Machine (SVM), or Naive Bayes we createdfourpredictionmodelstoaddressthesecondissuein thisresearch.
Although there are many other methodsforclassifying DMs, the following four are the ones we settled on for this article duetothesalientqualitiestheyshare.
The artificial neural network (ANN) is a common tool in evolutionary computational modelling (EDM) because it attempts to replicate the way the human brain works to address difficult issues. It is made up of a collection of modules thattake in a set ofweighted inputsand producea correspondingoutput.Predictingstudentperformanceusing ANN has been the subject of several published publications (e.g.,[8]).Weutiliseditaswellsinceitcanlearnfromasmall sample and can discover all conceivable relationships between variables. The accuracy with which ANN models predicted which applicants would be approved and which would be rejected was also superior to that of traditional classificationmethods.Duetothelimitedsizeofthedatasets, the ANN model in this investigation used a simple topology calledMultilayerPerception(MLP).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Inadecisiontree,thenodesarerankedfrommostimportant to least important. Each node in the graph represents a propertyofaninstance,ortheedgesbetweenthemstandfor therangeofvaluesthepropertymaytake.Sincethismethod is so popular among scientists, we choose to employ it (e.g., [1], [6], [7], [9]). It makes uncomplicated and easy-tounderstand value predictions. In addition, it performs well withbothcategoryandnumericfeatures,requiresnothingin thewayofcomplicateddatapreparation,andexpressesrules that can be simply understood and comprehended by users [6].
Inorderto divideitemsintotheirrespectivecategories,this methodconstructsa hyperplane.The generalisationerrorof aSVMmethoddecreaseswithincreasingdistancefromofthe hyper - plane to the closest object. SVM is utilised in this work because it is well-suited for tiny datasets, and it has beenusedinonlyalimited numberofpreviousstudies(e.g., [7]).Additionally,itisquickerthantheothermethods.
Naive Bayes is a straightforward probabilistic method that uses independent assumptions across variables to apply Bayes' theorem. It calculates the chances of each item belonging to each category. Due to its computational efficiency, widespread usage in relevant literature, and generaleaseofimplementation,thismethodwasselectedfor thisinvestigation.
3)Weusedaccuracy,recall,precision,orF1-Measuremetrics toanalyseandcomparetheperformancesofthefourmodels in order to answer the third research question in this work (Which datamining prediction approach performs best in this study?). (For a detailed breakdown of evaluation metrics, please refer to Section A, Experimental Design below.)
4) We developed this same second stage of the research to make a comparison the first-year CGPAs of incoming freshmen admitted in 2018-2019 using the new admission weightsofcriteriatotheinauguralCGPAsofformerstudents admitted in 2016-2 using the old admission weight of each criterion, in order to answer the 4th question in this research.
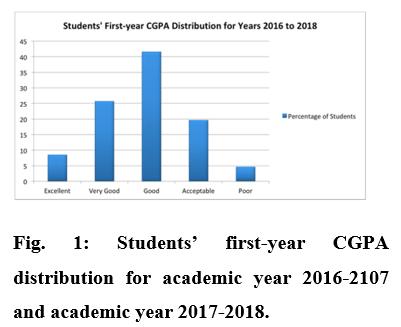
Data from PNU's CCIS student database was used for this analysis. However, the approaches used are universal and maybeimplementedinanyuniversitysetting.Thesefigures are from the Admitted & Registration Deanship's computerised academic database. The Institution Review Panel at PNU provided the necessary ethical clearance (Number 19-0152). In the first phase of our research, we gathered data on 1,569 students across all three departments and two cohorts: 902 students from the 2016–2017 school year and 667 students from the 2017–2018 schoolyear.
Second, we gathered 470 student records across the three departments from the 2018-2019 school year, when admissions were madeusingthe revised weightings.Similar situations like those described in the first section of the research occurred in other student bodies. We utilised this information to evaluate how newly accepted students' firstyear GPAs stacked up against those of incoming students underthepreviousweightingsystem.
Based on the initial numeric parameter CGPA, we built a category target variable (class). The PNU grading system uses a five-point scale, broken down as follows: exceptional (4.5), extremely good (3.75 to 4.5), great (2.75 to 3.75), ordinary (2.0 to 2.75), and bad (2.0). An illustration of the gradingscaleusedbystudentsinthe2016–17and2017–18 academicyears.
Just like we did with the data sets spanning 2016–2018 academicyears,weperformedwhichwasbeforetothesetof data spanning 2018–2019. There were 437 student files left overfromthe2018-2019schoolyear.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
We used Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), Decision Trees, Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and Naive Bayes to build fourdifferentpredictionmodels.Eachmodel wasdeveloped usingaten-foldcrossvalidation,with9datasetsusedduring training and 1 set employed while testing. This procedure wascarriedoutatotaloftentimes,onceforeveryoneofthe distinctsets.
The following ideas may be used to evaluate the efficacy of dataminingmodels:
Number of occasions for which a positive prediction was made(TruePositiveRate,orTP).
Number of times a negative result was wrongly labelled as positive;sometimescalledthe"FalsePositiveRate"(FP).
Number of occurrences when a negative prediction was madeaccurately;sometimescalledthe "TrueNegative Rate" (TN).
One measure of accuracy is the False Negative Rate (FN), whichisthepercentageofpositiveeventsthatwerewrongly labellednegative.
Predictive accuracy is quantified as the proportion of times anoutcomeisaccuratelyanticipated.
Preciseness equals (Total Probability) divided by (Total Probability) plus (First Probability) plus (Final Probability) (1)
Measured by (2), recall is the proportion of true positives thatwereaccuratelyanticipated.
CalculatingRecall:TP/(TP+FN)(2)
Accuracy is quantified as the proportion of true positives, anditmaybecalculatedas(3):
TP/(TP+FP)=Accuracy(3)
TheF1-Measurehighlightsaclassifier'sperformanceonboth commonandunusualcategories,anditrepresentsthetradeoff between recall and accuracy. There are four units of measurementforit:
Formula for F1 Measurement = 2 * Recall * Precision * (Recall+Precision)(4)
To improve first-year student performance, the PNU Admitted & Registration Deanship has chosen to implement changes to the present admissions procedure based on the
study's findings and suggestions. For the 2018-2019 school year, the dean's office decided to increase the weight of the SAAT criterion and adjust the weights of the other two criteria(HSGAandGAT)to30%and40%,respectively.Prior tothischange,thepercentageswere60%,20%,and20%.
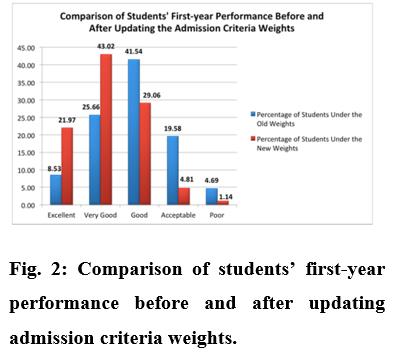
Figure2displaysacomparisonoffirst-yearCGPAsfromnew studentstothosefromprioryears.
This research was conducted with the aim of assisting universitiesinmakinginformedadmissionschoicesbasedon accurate predictions of prospective students' academic success after they are admitted. Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), Decision Trees, Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and Naive Bayes were used to propose and create four differentmodelsformakingpredictions.Theresearchuseda database including 2,039 student records from PNU, the biggestuniversityinKSA.However,theapproachesusedare universalandmaybeimplementedinanyuniversitysetting.
Theresultsoftheresearchlendcredencetotheemployment ofpredictionmodelsinhighereducation,wheretheymaybe put to good use in the allocation of scarce resources. Moreover,thefindingsdemonstratethat,withsufficientpreadmission data, a high-performance model to predict students'earlyperformancemaybecreated.Inthisresearch, for instance, the ANN model achieved an accuracy rate of roughly 79.22% in terms of its performance. The research also found that the ANN method achieved the highest levels of accuracy and precision, while the Decision Tree method achieved the highest levels of recall and F1-Measure. Out of allthemethods,NaiveBayesperformedthepoorest.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Students' personalities, demographics, families, and communication abilities are just a few of the pre-admission characteristics that have been shown to influence future academic success; further research is required. It's possible to employ other data mining methods, such as clustering, in subsequentresearch.
[1] H. Guruler, A. Istanbullu, and M. Karahasan, ‘‘A new student performance analysing system using knowledge discovery in higher educational databases,’’ Comput. Edu., vol.55,no.1,pp.247–254,Aug.2010.
[2] S. K. Mohamad and Z. Tasir, ‘‘Educational data mining: A review,’’ Procedia Social Behav. Sci., vol. 97, pp. 320–324, Nov.2013.
[3] A. Peña-Ayala, ‘‘Educational data mining: A survey and a data miningbased analysis of recent works,’’ Expert Syst. Appl.,vol.41,no.4,pp.1432–1462,Mar.2014.
[4] C. Romero and S. Ventura, ‘‘Educational data mining: A reviewofthestateoftheart,’’IEEETrans.Syst.,Man,Cybern. C,Appl.Rev.,vol.40,no.6,pp.601–618,Nov.2010.
[5] H. Aldowah, H. Al-Samarraie, and W. M. Fauzy, ‘‘Educational data mining and learning analytics for 21st century higher education: A review and synthesis,’’ TelematicsInformat.,vol.37,pp.13–49,Apr.2019.
[6]C.AnuradhaandT.Velmurugan,‘‘Acomparativeanalysis on the evaluation of classification algorithms in the prediction of students performance,’’ Indian J. Sci. Technol., vol.8,no.15,pp.974–6846,Jan.2015.
[7]V.L.Miguéis,A.Freitas,P.J.V.Garcia,andA.Silva,‘‘Early segmentation of students according to their academic performance: A predictive modelling approach,’’ Decis. SupportSyst.,vol.115,pp.36–51,Nov.2018.
[8] M. Mayilvaganan and D. Kalpanadevi, ‘‘Comparison of classification techniques for predicting the performance of studentsacademicenvironment,’’inProc.Int.Conf.Commun. Netw.Technol.,Sivakasi,India,Dec.2014,pp.113–118.
[9] S. Natek and M. Zwilling, ‘‘Student data mining solution–knowledge management system related to higher education institutions,’’ Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 41, no. 14, pp. 6400–6407,Oct.2014.
[10] T. M. Christian and M. Ayub, ‘‘Exploration of classification using NB tree for predicting students’ performance,’’ in Proc. Int. Conf. Data Softw. Eng. (ICODSE), Bandung,ID,USA,Nov.2014,pp.1–6.
[11]J.Albishri,S.Aly,andY.Alnemary,‘‘Admissioncriteriato Saudi medical schools. Which is the best predictor for successful achievement?’’ Saudi Med. J., vol. 33, pp. 1222–1228,2012.
[12]M. O. Al-Rukban,F.M. Munshi,H. Abdulghani,and I.AlHoqail, ‘‘The ability of the pre-admission criteria to predict performanceinaSaudimedicalschool,’’SaudiMed.J.,vol.31, pp.560–564,2010.
[13] A. M. Alhadlaq, O. F. Alshammari, S. M. Alsager, K. A. F. Neel, and A. G. Mohamed, ‘‘Ability of admissions criteria to predict early academic performance among students of health science colleges at King Saud University, Saudi Arabia,’’J.DentalEduc.,vol.79,pp.665–670,Jan.2015.
[14]S.M.HassanandM.S.Al-Razgan,‘‘Pre-universityexams effect on students GPA: A case study in IT department,’’ ProcediaComput.Sci.,vol.82,pp.127–131,2016.
[15] M. F. Al-Qahtani and T. M. Alanzi, ‘‘Comparisons of the predictive values of admission criteria for academic achievement among undergraduate students of health and non-healthscienceprofessions:Alongitudinalcohortstudy,’’ Psychol.Res.Behav.Manage.,vol.12,pp.1–6,Dec.2018.