International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1 PG Student Department Of Mechanical Engineering, 2Head Of The Department, Mechanical Engineering, 3Associate Professor, Department Of Mechanical Engineering, Thanthai Periyar Government Institute Of Technology, Vellore, India. ***
Abstract - Aluminum matrix composite is a new generation of metal matrix composite which have the tendency to meet the emerging for advanced engineering application. The performanceofthesematerialsmostlydependsuponselecting right combinations of reinforcing materials. In the current work an effort as been made for the fabrication of Aluminum metalmatrixcompositefortheinvestigationofitsmechanical properties. The preparation of aluminum metal matrix composite is made by choosing AA6082 as matrix and by keeping weight % of reinforcements ZrO2 and the Ti are varied by 2%, 4% and 6%. The wear properties of metal matrixcompositeswerestudiedbyconductingweartestusing pin on disc machine as per ASTM G-99 standard. The experiment were conducting by adopting the taquchi technique with an L9 orthogonal array and analysis of variance approach was employed to evaluate the effect wear parameters load, percentage reinforcement and duration on wear rate of composites. These samples were fabricated by means of stir casting technique and the micro structural characteristics of composites are studied by using optical microscope. Mechanical properties such as impact strength, hardness, compression are studied and compared the results with base Aluminum 6082 results.
Key Words: Zirconiumoxide,Titanium,aluminumalloy,L9 orthogonalarray
Compositesaretheengineeringmaterialswhicharegaining importance because these composite models are desired propertiesbyconnectintwoormorenano,micro,ormacro constituentswithaninterfaceseparatingthemthatdifferin formandchemicalcompositionandareessentiallyinsoluble in each other based on the various applications . Every automotiveindustryintherecenttimekeentomanufacture thepartswhicharelightinweightwithexcellenttribological propertiesespeciallyinthemanufacturingareaswherewear resistance is given as the most important consideration. Aluminum,whichislightinweight,can beusedasamain matrixelementinthefabricationofcompositematerialsand these manufactured composite are termed as aluminum
value:
matrix composites (AMCs). Aluminum is mostly used industrialandfunctionalmetaloralloybecauseofitsunique combinationofpropertieslikelowdensity, highcorrosion resistanceandexcellentmechanicalproperties.Aluminum basedMetalMatrixCompositeshavebeendevelopedhasthe advanced materials for several applications in aerospace, automobile,transportation,marine,mineralprocessingand electrical packaging industries because they exhibit high specificstrengthandstiffness.Inthispaper,theprocessing, microstructural features, and mechanical behavior of an Al6082matrixcompositewhicharereinforcedwithvaried weightratiosofZrO2andTiarereported.Properselection ofreinforcingmaterialforAlmatrixcompositematerialand techniquesprocessareveryimportantfactorsinensuring thatdesiredpropertycombinationsareachieved.
Aluminum 6082 is a medium strengthalloy with excellent corrosionresistanceandmanganesepresentinitcontrolsthe grain structure, which results into a stronger alloy and its applicationareinthefieldofhighstressapplication Al6082 alloy possess high strength to density ratio and improved strengthtowards6000seriesalloys,wherelightweightand strengthpropertiesarecritical.Thesepropertiesleaditsuse inbicyclecomponents,rockclimbingequipment,hangglider airframes,chasisplatesofsportgrade.Al6082alloypossess thecapacityofhighlypolished,theyareworninmold tool manufacturing Thesematerialsexhibitedbettermechanical and tribological properties required for some automotive components for application basis Al6082 alloy used as a matrix material. Chemical composition Al6082 alloys is showninTable1.
Zirconiumdioxideisalsoknownaszirconiaandzirconium oxide, isacrystallinemetaloxidethathasfounditswayinto theceramicsindustry. Itischaracterizedbyitshighthermal resistivity,mechanicalresistance,andabrasiveproperties. Zirconium is as strong as tungsten & titanium. It is also corrosion- resistant and is harder than stainless steel or
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
silver.ZirconiaOxidehasthehigheststrengthandtoughness atroomtemperatureofalltheadvancedceramicmaterials.
Element Amount wt%
Al 87.7-91.1
Cr 0.0–0.25
Cu 0.0–0.10
Fe 0.0–0.50
Mg 0.60–1.20
Mn 0.40–1.00
Si 0.70–1.30
Ti 0.0-0.10
Zn 0.0–0.20
other Max0.20
Table -1: ChemicalCompositionofAA6082
Zirconiumdioxideishighlyresistanttocracking(including furtherdevelopmentofcracks)andmechanicalstress With a melting point of 2700ºC and a thermal expansion coefficient of 1.08×10-5 K-1 , zirconium dioxide is widely knownforitshighresistancetoheat.Thisisthereasonwhy the compound has found a wide variety of uses in refractoriesandhightemperatureindustries
Titanium in its pure form is a silvery metal known for its strengthandlowdensitycomparedtoothersimilarlyhard metals.Inmostindustries,however,titaniumalloyismuch more commonly used. It as the very tight substance to mixturethroughreinforcementalignforfurtherproperties depends.Attherequiredconsiderationthestrengthandwith samelightweighttheoryisaccomplished.Itiscruciallyused inindustriessuchasmilitarybasisandchemicalindustries.
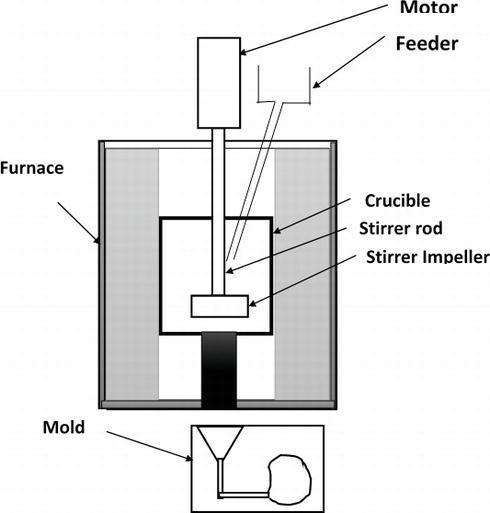
Initially 750 g of commerciallyavailable pure Al6082 was meltedinaresistanceheatedfurnaceupto973Kandcasted in a cast graphite crucible. Then Al6082 and zro2 and Ti reinforcementswerepreparedbyreinforcingthealuminum (averagesizeof30mm)with2%,4%and6%wtofzro2and Tibystircasting.Forthiswetookthreesplitupof250gmof commerciallypureAl6082andthen2%,4%and6%wtof zro2&Tiwereaddedtothealuminummeltforproduction of three different composites. Before doing this the reinforcements zro2 & Ti were preheated up to 473 K to remove moisture. Al6082 was melted by increasing the temperature to 973 K and the preheated reinforcement particles were combined to the melt at the time of development of vortex in the melt due to stirring.
Factor value:
Magnesiumwasaddedinordertoenhancethewettability between the reinforcements and the matrix. The melt temperaturewascontinuedat943–973Kduringincreaseof theparticlesandthestirrerspeedismaintainedat250–300 rpm. Thenthemeltwascastedinagraphitecrucible. And then poured in the die for solid shape. And we undergo throughTest
1.Wear
2.Hardness
3.Opticalmicroscope
4.Compression
5.Impact
Fig. 1 describestheexperimentalsetupofthestircasting
Fig -1 stircasting
Weartestspecimensofdimensiondiameter8mmandlength 32 mm were prepared. The end surfaces of the wear test specimens were properly cleaned and then polished with abrasivepaperofgrade400,600and1000,respectively.The weartesthasbeenperformedonpinondiscapparatus.The discofthepinondiscismadeofEN31steelhavingsurface roughness0.1.Thepinsanddiscwerecleanedproperlywith thehelpofacetonebeforeandafterweartest.Thewearwas measuredbycomputerizedpinondiscweartestingmachine asalossoftareinmicronlevels.
The micro-hardness of composites was measured using Vickers hardness tester at a load of 500g applied for a durationof15sat20sdifferentlocationsonallspecimens.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Theaimofcompressiontestistofindoutthebehaviorofa material when perceiving compressive load by the measurement of fundamental variables, such as, strain, stress,anddeformation.Bytestingthespecimenwecanfind outthecompressivestrength,ultimatestrength,elasticlimit, yield strength among more parameters may all be determined.
Thefabricatedcompositewerecharacterizedusingoptical microscope.Thesamplesweregenerallypolishedemploying the normal metallographic procedure and the polished specimenswereetchedwithkeller’sagent.
Theimpacttestisusefultodesignerstoanalysetherelative impact resistance of specimen. The specimens were preparedforizodimpacttestofdimensions10*10mm2area and 55mm length to check impact strength by using universal impact testing machine. And also V slot 2*45 degreewascreatedbysawingthenfiledit.
The experiments were conduct as per the standard orthogonal array. The selection of the orthogonal array is basedontheconditionthatthedegreesoffreedomforthe orthogonalarrayshouldbegreaterthanoratleastequals sum of those of wear parameters. In the present investigationanL9orthogonalarraywaschosenasshownin Table2.Thewearparameterschosenfortheexperimentare (i) applied load (ii) reinforcement percentage (iii) sliding duration.Theexperimentconsistsof9tests(eachrowinthe L9orthogonalarray)andthecolumnswereassignedwith parameters.
Thefirstcolumnwasassignedtotheappliedload(L),second columnwasassignedtotheslidingspeed(S),thirdcolumn was assigned to the sliding distance (D). The experiments were conducted as per the orthogonal array with level of parameters given in each array row. The output to be studied is wear rate and coefficients of friction of the test samplesarerepeatedthreetimescorrespondingto27tests. Theexperimentalobservationsarefurthertransformedinto Signaltonoiseratio.
Theresponsetobestudiedwasthewearrateandcoefficient of friction with the objective as smaller the best, which is calculatedaslogarithmictransformationoflossfunctionas shownbelow,
3.1.1
Reinforcement (Zro2+Ti)
Load Duration Wearratio (micron)
2 10 5 214.42
2 20 10 489.32
2 30 15 764.27
4 10 10 536.37
4 20 15 809.44
4 30 5 373.44
6 10 15 856.86
6 20 5 456.93
6 30 10 731.63
Table – 2 weartestreadinginmicron
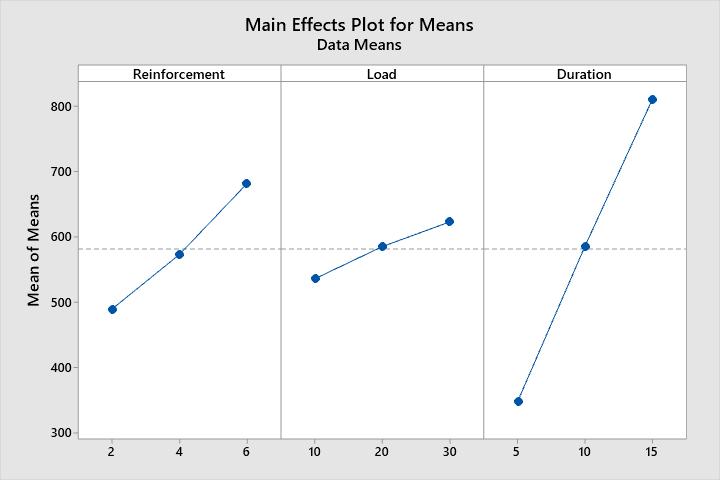
Analysisofvariance(ANOVA)wasintroducedbySirRonald Fisher. This analysis was carried out for a level of significance of 5%, i.e., for 95% level of confidence The purpose of ANOVA is to investigate the percentage of contributionofvarianceovertheresponseparameterandto find the influence of wear parameters. The ANOVA is also neededforestimatingtheerrorofvarianceandvarianceof thepredictionerror.Itcanbeobservedthattheload,sliding distance and wt% of reinforcement have the influence on wear of composite material. It can be observed from the ANOVA table that the wt% of Ti was the most significant parameter on the sliding wear of composites followed by applied load and sliding distance. This approach gives the variation of means and variance to absolute values consideredintheexperimentandnottheunitvalueofthe variable.
In Taguchi method, the term “signal” represents the desirablevalue(mean)fortheoutputcharacteristicsandthe term“noise”representstheundesirablevaluefortheoutput characteristics. Taguchi uses S/N ratio to measure the qualitycharacteristicsdeviatingfromthedesiredvalue.The influence of control parameters such as wt% of reinforcement,loadappliedandslidingdistancecontenthas beenanalysedandtherankofinvolvedfactorslikewearrate ofcompositematerialswhichsupportsS/Nratioresponseis givenintheTable2.4.Itisevidentfromthetablethatamong these process parameters, normal pressure is a dominant factoronthewearrate.Theinfluenceofcontrolledprocess parameters on wear rate. It also determines the most influentialparameterforintheexperiment.wearistakenas the objective function and Taguchi’s “smaller is Better”
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
quality characteristic is chosen to maximum the objective function
Wear ratio (micron) = -160.2 + 48.12 Reinforcement +4.361Load+46.19Duration
Level Reinforcement Load Duration
1 489.3 535.9 348.3
2 573.1 585.2 585.8
3 681.8 623.1 810.2
Delta 192.5 87.2 461.9
Rank 2 3 1
Table-3 ResponseTableforMeans
Level Reinforcement Load Duration
1 52.69 53.29 50.42
2 54.73 55.05 55.22
3 56.38 55.47 58.16
Delta 3.69 2.17 7.74
Rank 2 3 1
Table-4 ResponseTableforS/NRatios
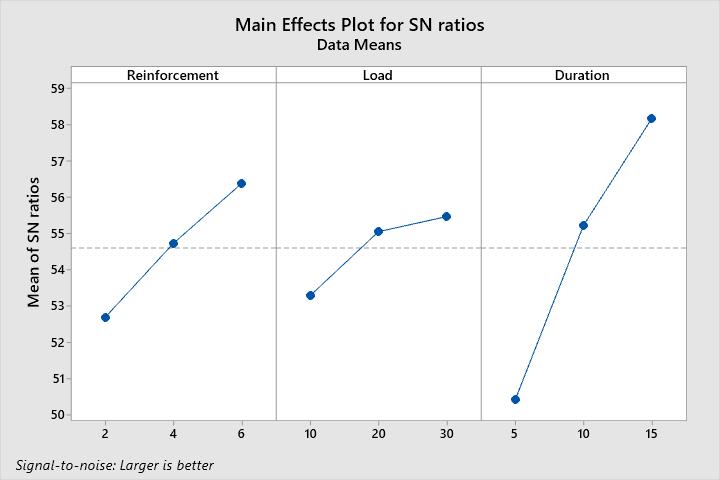
Wearratioisdecreaseswithincreasesinwt%ofzirconium oxide & titanium reinforcement particles. Moreover, the increasesinwt%ofreinforcementismainlyattributedto grain refined of the matrix. Wear rate of the composites reducedwiththeincreaseintheloadwhereaswithhigher content of zirconium oxide & titanium reinforcement particles,thecompositesexhibitedhigherwearresistance. Therefore, increasing wt % of reinforcement is refine the matrixgrainandincreasestheproperty
Factor value:
Fig-4 Residualplotsforawearratio(micron)
Generally hardness of the composites increases as the ceramicparticlereinforcementincreasesincomposites.But inAl6082-zro2 & Ti composites due to the presence of chemical reinforcement which is hard in nature we can observe significant increases in the hardness of reinforcementcomposites.FromFig.5wecanobservethat thehardnessofthereinforcedcompositesisgreaterthanthe hardnessoftheunreinforcedalloy.Maximumhardnessvalue 63.79HVwasobservedforsample4.Hardnessofalloyand compositesobservedthatmicrovickershardnessvaluesare increaseswhenincreasingofreinforcementvolumefraction comparedtobasealloyAl6082.Becauseoftworeasonsthey are mainly zro2 and Ti with alumina. And values are indicatedingivenbelowgraph.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Compressive strength is the capacity of a material or structuretowithstandloadsLeaningtoscaledownsize,as disputed to tensile strength, which withstands loads are disposed to elongate. Compressive strength abide compression where as tensile strength resists tension. In presentinvestigationofstrengthofmaterials,compressive strengthcanbeevaluated.Somematerialsfractureattheir compressivestrengthlimit;othersdeformirreversibly,soa givenamountofdeformationmaybeconsideredasthelimit forcompressiveload.Compressivestrengthisakeyvaluefor design of structures. Fig-6 describes the individual Compression test results of each sample and we can conclude that the maximum compression strength is 394.82MPaforsample3whichisincreased12.5%compared to the sample 1. As the reinforcement content increases compressionstrengthvalueincreases.
The impact test is useful to find the notch sensitivity and toughnessofengineeringmaterials.Thistestisconvenientto analysesthetoughnessofmetalsandtheidenticaltestsare usedforceramics,polymersandcomposites.IzodV-notch test is useful to find percentage of energy consumed by a material.Itisgenerallyappliedinindustry,becauseitisvery accessibletoprepareandtoconducttestandtheresultswill beobtainedveryquickly,accurately.Fromtheresults,itis noticed that the percentage of energy consumed by the manufacturedcompositeremindsame.Theimpactstrength observedfromresultsenergyabsorbedbythealloyislower than composites. When reinforcement volume fraction increasesthenimpactspecificpowerwouldincreases.
Fig-7 describes the individual Impact test results of each sample and we can conclude that the maximum Impact strengthisobtainedatsample4.
390
380
STRESS STRAIN
370
360
350
400 0 0.2 0.4 0.6
394.82 381.82 351.31 340
Impact (joules)
20
15
10
Fig-6 compressionstrength 13.8 14.2 15.7 17.9 0
5
SAMPLE 1 SAMPLE 2 SAMPLE 3 SAMPLE 4
IMPACT(JOULES)
Fig-7 Impactstrengthresult
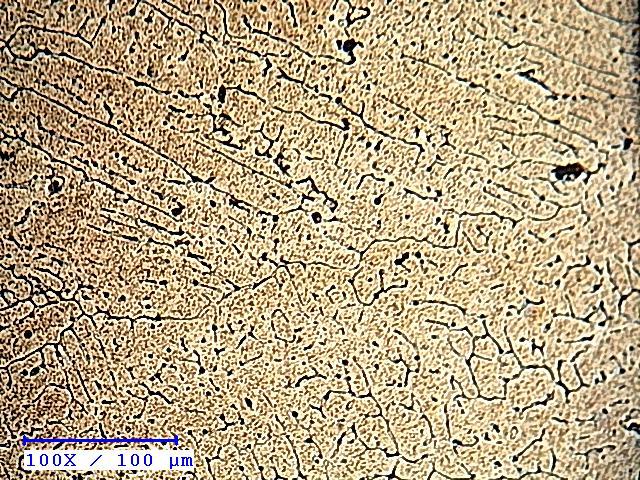
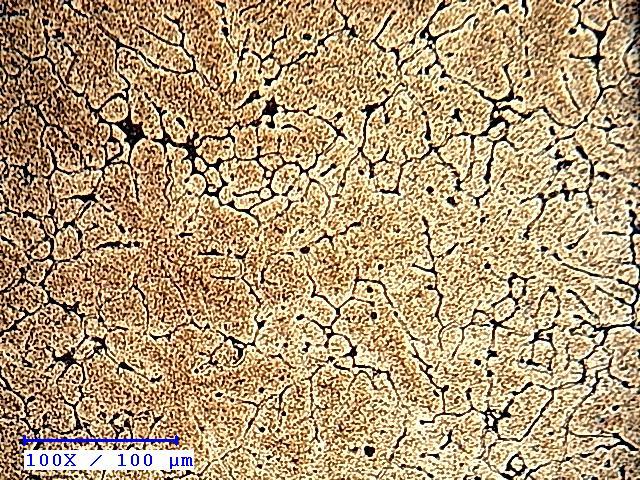
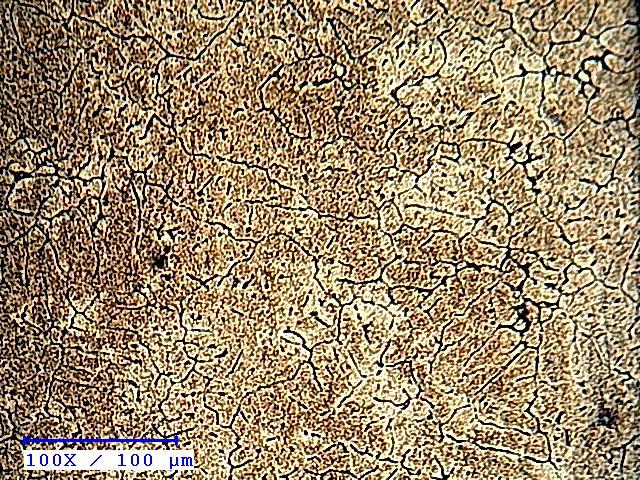
Zro2&Tiusedincompositeswascharacterisedbyoptical microscope. It can be seen that the reinsed are coarse comparedtoFigures(a),(b)and(c)withfinergrainswhen reinforcementof100μmwasusedasthefiler.Zro2&Tiof smaller particle size with higher surface area refined the grainsofthealloy.Itwasalsoobservedthatreinforcement dispersedinAl6082alloyasseenfromthehomogeneityof the microstructures. Figures (b), (c) and (a) respectively showthemicrographsofthecompositesreinforcedwith 2,4 and6wt%reinforcement(Zro2&Ti)of100μmparticlesize This observations showed that there was uniform distributionofparticlesthroughoutthematrix
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[2] B. Ramgopal Reddy et al.[2017] “Fabrication and Characterization of Silicon Carbide and Fly Ash Reinforced”
[3] Ch.Hima Gireesh et.al [2017] “Mechanical Characterization of Aluminum Metal Matrix CompositeReinforcedwithAloeverapowder”
[4] K.RaviKumaret.al[2018]“Mechanicalproperties andcharacterizationofzirconiumoxide(ZrO2)and coconut shell ash(CSA) reinforced aluminum (Al 6082)matrixhybridcomposite”
[5] C.U. Atuanya et.al[2014] “Evaluation of Al–Cu–Mg alloy/bean pod ash nanoparticles synthesis by doublelayerfeeding–stircastingmethod”
[6] HimanshuKala,K.K.SMer,SandeepKumar[2014] “A Review on Mechanical and Tribological BehaviorsofStirCast MatrixComposites.”
[7] G. Vijaybabu , K. PrasadRaju, V.V.M.K. Raju, K. Sunilkumar [2014] “Studies on effect of ash in aluminumhybridmetalmatrixcomposites”
[8] RamBabuMatta,Prof.RavindraBabuP,Associate Prof. JARanga Babu[2019] “EffectofMechanical Properties on Palm Sprout Shell Ash Reinforced WithAl-6061AlloyMetalMatrixComposites”
[9] Oluyemi Ojo DARAMOLA1, Adeolu Adesoji ADEDIRAN, Ayodele Tolu FADUMIYE [2015] “Evaluation of the mechanical properties and corrosionbehaviourofcoconutshellashreinforced aluminum(6063)alloycomposites.”
[10] Kenneth Kanayo Alaneme, Olusola Joseph Ajayi [2015]“Microstructureand mechanicalbehavior of stir-cast Zn–27Al based composites reinforced withricehuskash,siliconcarbide,andgraphite”
[1] Ajay Kumar Yadav et al.[2018] “Aluminum Metal MatrixCompositewithRiceHuskasReinforcement”