International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[1] M.tech student, Institute of engineering and technology, Lucknow
[2] Asst. Professor, dept. of civil engineering, Institute of engineering and technology, Lucknow ***
Abstract – This study comprises state-of-art knowledge in the seismic response of vertically irregular building frame, During severe seismic shaking irregular building may suffer disproportionate damage or collapse that can be minimized by increasing robustness The prime objective of this study is to find out the how irregular buildingsshowstherebehaviorwhentheseismicloadsor effects with real time seismic data apply on the structure. Analysis is going to be done with finite element analysis using time history data in the E-TAB 2016 software, and inseismiczoneIV.
Key Words: Verticle irregularity, time history analysis.
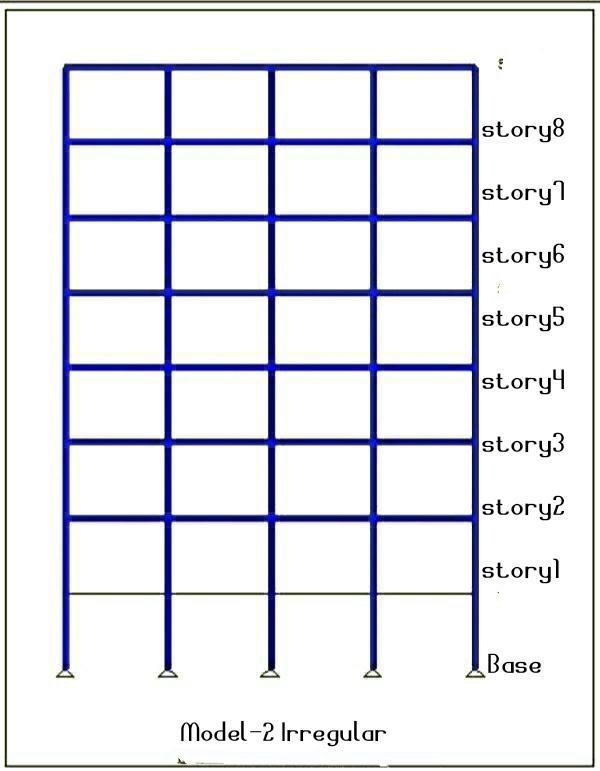
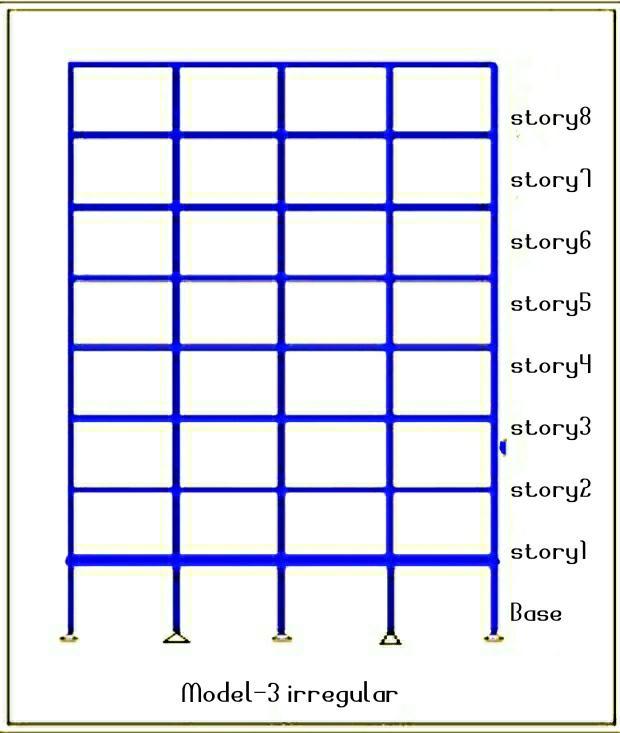
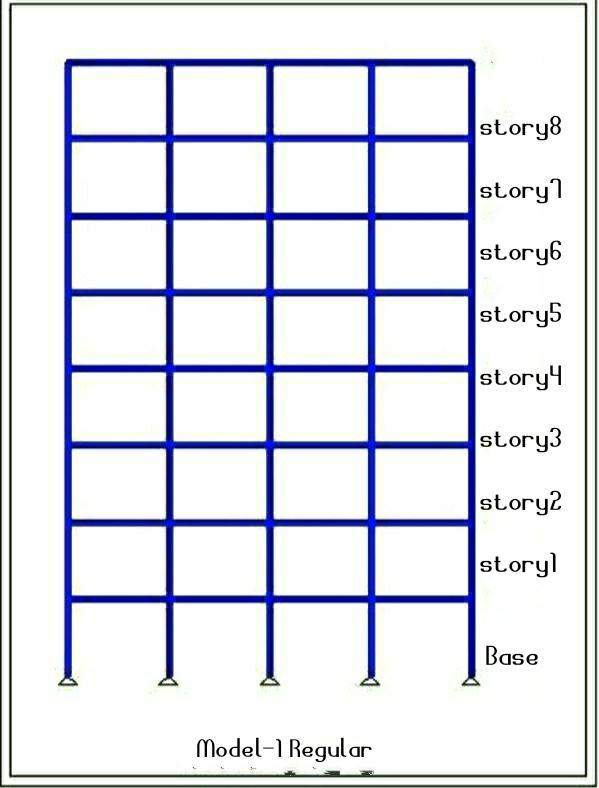
Presence of asymmertricity in the reinforced concrete increases seismic vulnerability; In areas in the word that experience a high frequency of the earthquake, considering irregularity is an integral part of the process of earthquake engineering or structural designing irregularitiesariseduringanearthquake.Weaknessinthe structure can be caused by discontinuities in the mass, stiffness, or geometry. Vertical irregularity of a structure becomes the primary cause of failure during an earthquake. Zones with vertical irregularity are carefully evaluated and developed with the appropriate treatment whensuchstructuresarebuiltinhighseismiczones,such as zone IV or zone V. Soil structure interaction's seismic consequencesmustbetakenintoaccount.Threemodels Model 1 (regular), Model 2 (story-1, without slab), and Model 3 (story-1, slab with double thickness) were taken intoconsiderationforanalysisinthecurrentstudy.
The comparative analysis of regular and irregular structure will be based on the base shear, story stiffness, Storydisplacement&driftanalysis
Earthquake is the greatest anticipated lateral force that resultsfromgroundaccelerationanddependsonthekind of soil. Story Stiffness, or the total stiffness of all permanentmembersparticipatinginacertainstory.
Here we are going to compare and analyze the different type of buildings with there stiffness, base shear, story
displacement and drift index values. In modeling we used the E-TAB 2016 for structural seismic analysis, we also used the Finite Element Method with the Time History input data When it comes to irregular structure design Timehistorymethodgivesthebestresultsforlateralforce distribution with actual ground acceleration data that has beenexperiencedinthepast
Mainobjectiveofthepaperistoknowthebehaviorofthe structureunderdifferentparameters
To know the behavior of the structure with differentgeometricconditions
To know the story stiffness of the structure for bothregularandirregular
To know the base shear conditions in the both thecases
To find out the Story Displacement difference betweensymmetric&asymmetricbuilding
To show the differences in Drift index for both cases
The present work is carried out to understand the behavior of structure, when we use the irregular buildinginsteadofregularbuilding.Therearestepby step procedures involved in the modeling and analysisofthestructure
Irregularities can be defined in two major parts, they are: 1- Planirregularity 2- Verticalirregularity
[1] Piyush Mishra [2] Er. Prince Yadav
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
In plan irregular buildings, five types irregularity present,theyare:
● Torsion Irregularity
● Re-entrantCorners.
● DiaphragmDiscontinuity.
● Out-of-Plane Offsets
● Non-parallel Systems
In vertical irregular buildings also five types rregularitypresenttheyare:
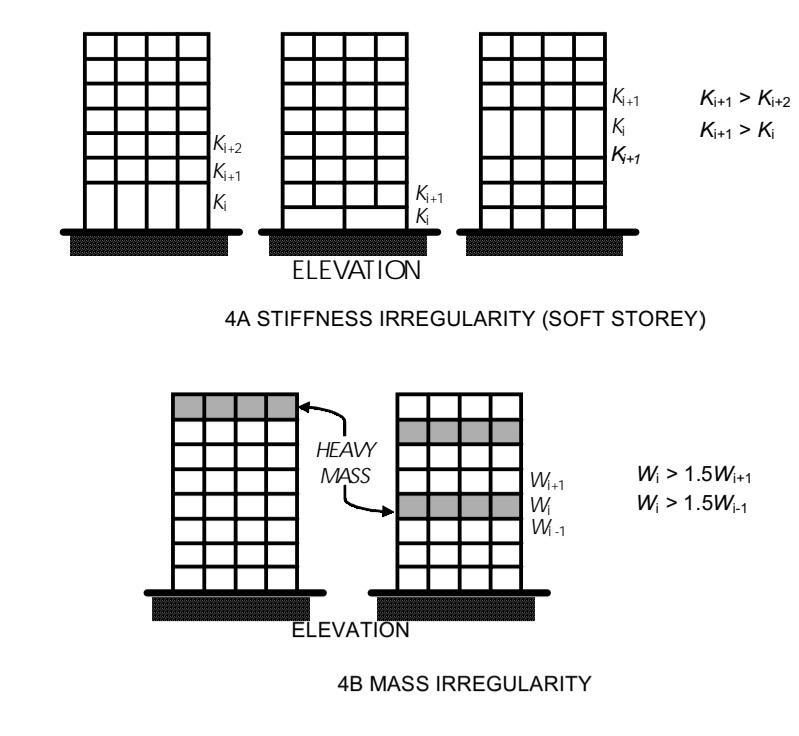


●Stiffness. Irregularity
●Soft Storey
●ExtremeSoftStorey.
●Mass Irregularity.
●Vertical GeometricIrregularity
FormodellingandanlysingE-TAB2016softwarehasbeen used , here I have been created three model having 9story building with model Type-1 Regular bulding, Model type-2 Irregular building have no slab at story 1, Model Type-3 irregular building with double depth of slab on story1
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Structural Properties :-
Plandimension 16X15m2
No.ofstories 9
Floortofloorheight 3000mm
Beamsize 250X500mm
Columnsize 450X450mm
Thicknessofslab 150mm
Zone IV
Zonefactor 0.24(IS1893:2016)
Importancefactor 1(IS1893:2016)
Responsereductionfactor 5(IS1893:2016)
Gradeofconcrete M30
Gradeofsteel Fe415 Densityofconcrete 25kN/m3
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Some of loading properties at building is describe below
There are various type of loading properties used in the structureareasfollows
Deadloadofslab 3.75kN/m2
Floorfinishload 1.0kN/m2
Rooffinishload 1.0kN/m2
Liveload 3.0kN/m2 (IS1893:2016)
There is one more fundamental to be added for valuable contribution i.e. Time History Data to be used for seismic valuation
Time history data is always taken from the past experience of the seismic wave and that help in analyzing thereal timevaluationofstructuredesigning
TIME HISTORY DATA
Depth(Km) 46.0 Magnitude 7.8 Region Iran-Pakistan-Border-Region
Alldetailstakenfrom IMD
StationCode DCE
StationLat. 28.795N
StationLong. 77.118E
StationHeight(m) 208.0
SiteClass CVs30between200m/secto375m/sec
RecordTime 16.04.201310:49:13.829
SamplingRate 200Hz
RecordDuration 169.970Sec. Direction E-W(E-positive)
Max.Acceleration 1.521cm/sec2
Asperobservationofgraphresultsshowsthatstiffnessin theirregularbuildingwith doubledepthofslabatstory1 is 16.74% is more than regular building (model 1) & 23.92% more than the irregular building with no slab on story1(model2)
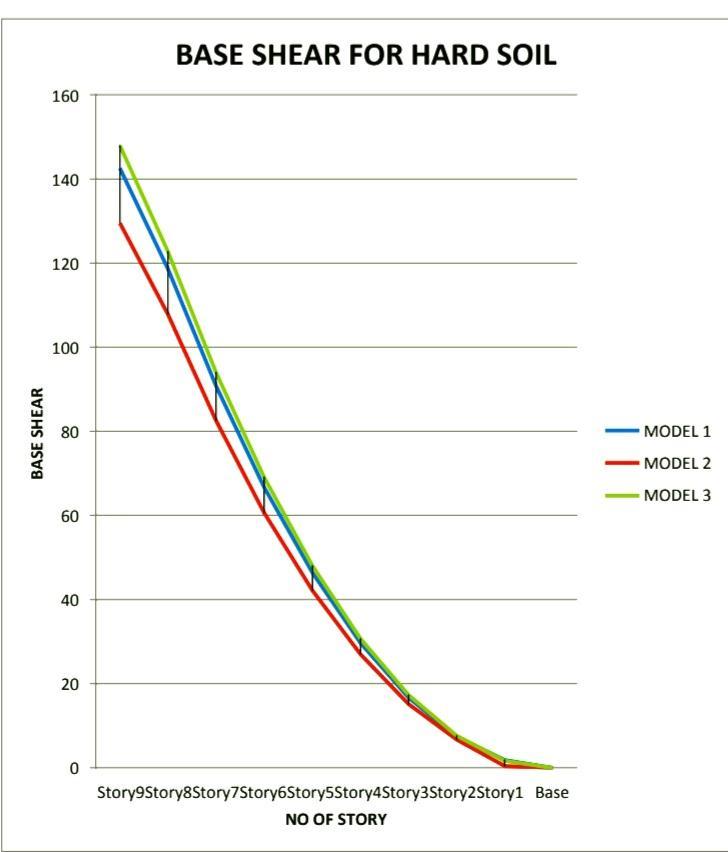
Asperobservationofgraphresultsshowsthatbaseshear intheirregularbuildingwithdoubledepthofslabatstory 1 is 3.80% is more than regular building (model 1) & 14.23% more than the irregular building with no slab on story1(model2)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
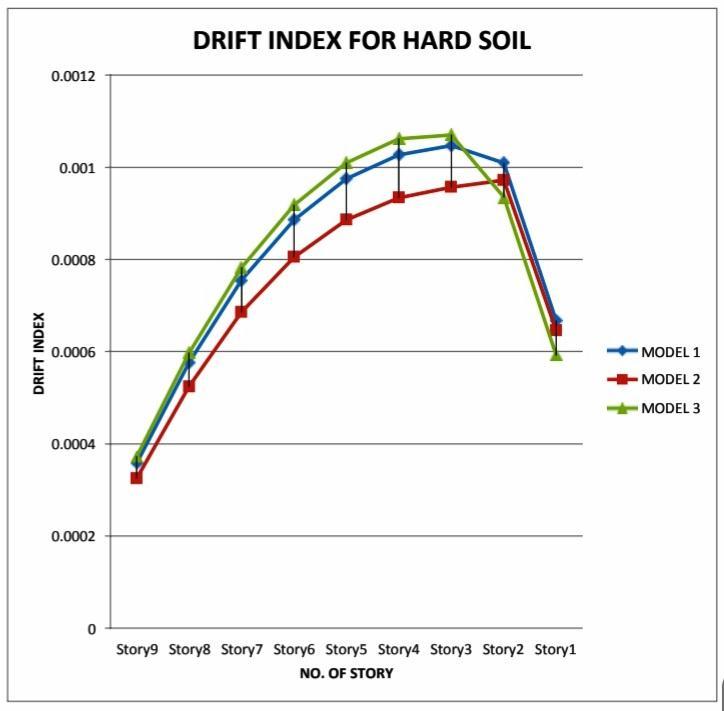
As per observation of graph results shows that base drift index in the irregular building with double depth of slab atstory1is12.66%islessthanregularbuilding(model1) & 9.12% less than the irregular building with no slab on story1(model2)
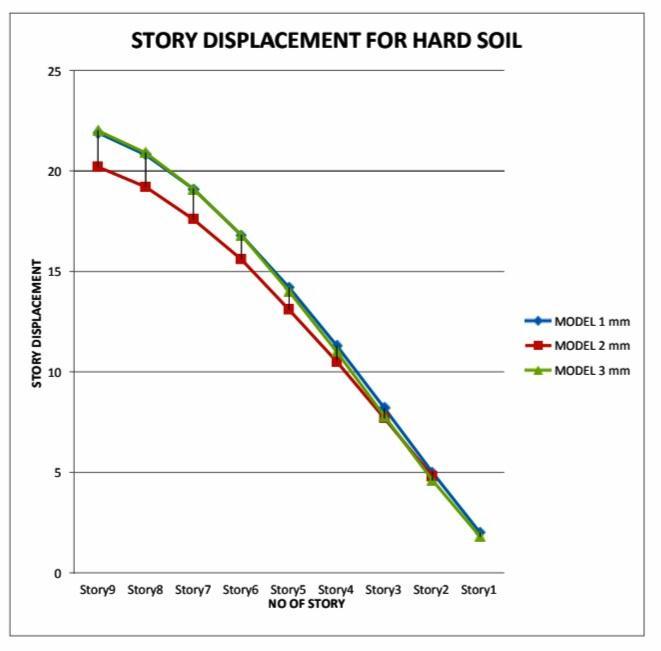
As per observation of graph results shows that story displacement in the irregular building with double depth of slab at story 1 is 7.76% is more than regular building (model1)&36.41% morethantheirregularbuildingwith noslabonstory1(model2)
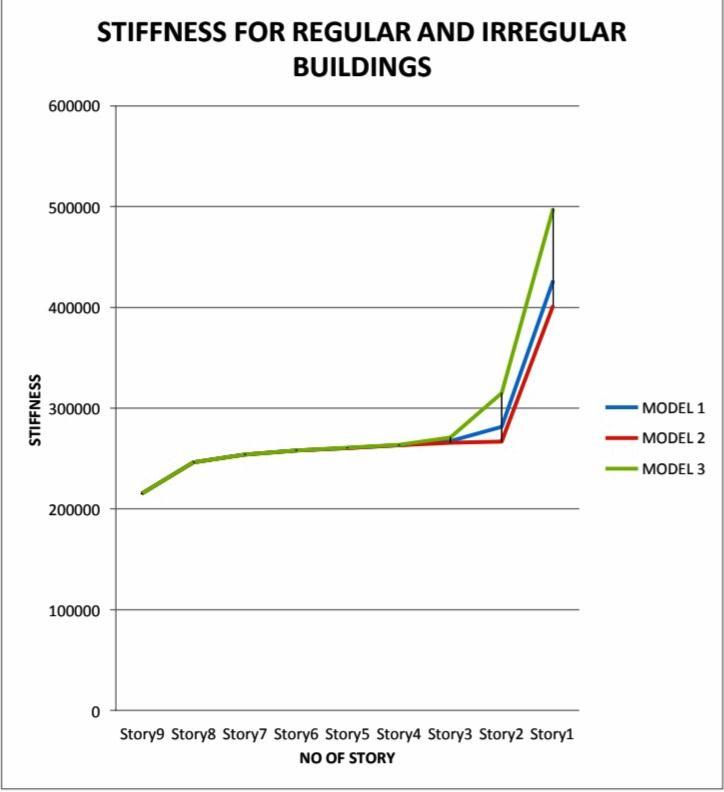
Asweallknowthatbaseshearonsuperstructure is all depend on the soil condition (stiffness of soil) as per observation maximum value of base shear gives in model -3 and model-2 shows lowest valuesthanthemodel-1&Model-3
Maximum value of base shear will be found at peak height of the structure , also base shear decreasesasthestiffnessofthesoildecreases
Asweknowstory stiffnessisthesumofstiffness of all permanent member present, as per observationmaximumvalueofbasesheargivesin model -3 and model-2 shows lowest values than themodel-1&Model-3
Maximum value of stiffness is observed at the baseofthestructure
As we know displacement of structure is observe with reference to base , as per observation maximum value of base shear gives in model -3 andmodel-2showslowestvaluesthanthemodel1&Model-3
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

As per observations drift index in the irregular building with double depth of slab shows lowest value for drift index and regular building shows lesser value than the irregular with no slab on story 1, here model 2 shows lowest value among allofthem
1- JinuMaryMathew,CinithaA,UmeshaPK,Nagesh R Iyer and EapenSakaria (2014), “Seismic response of RC building by considering soil structure interaction” International Journal of Structural & Civil Engineering, Res. ISSN 2319 –6009Vol.3,pp160-172
2- JiangXinliangandZhangYanan(2013),“Influence of Structure Plane Size on Seismic Response of Soil-Structure Interaction”, World Earthquake Engineering,Vol.19No.5.pp345-350
3- Cinitha.A,UmeshaP.KandNageshR.Iyer(2015), “Soil structure interaction analysis for seismic response of an asymmetric RC building”, International Conference on Computer Modeling andSimulation.,pp1-6
4- Shehata E. Abdel Raheem, Mohamed M. Ahmed and Tarek M. A. Alazrak (2015), “Evaluation of soil–foundation–structure interaction effects on seismic response demands of multi-story MRF buildingsonraftfoundations”,AdvanceStructural Engineering.,pp11-30
5- IS 1893(Part 1):2002, Criteria for Earthquake ResistantDesignofStructures-General provisions and Buildings, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
6- Shreya Thusoo,KaranModi,RajeshKumar,Hitesh Madahar, “Response of Buildings with Soil Structure Interaction with Varying Soil Types” , International Journal of Civil, Environmental, Structural, Construction and Architectural Engineering,Volume-09,No-4,2015
7- Kuladeepu M N, G Narayana, B K Narendra, “ssi effect on dynamic behavior of 3Dbuilding frames with raft footing”, IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN:2319-1163|pISSN:2321-7308.
8- RenuRaghuveeran,HashifaHassanP,“SeismicSoil Structure Interaction Effects on RC Bare Frames Resting on Pile-Grid Foundation”, International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications,
Volume5, Issue10, October 2015 1ISSN22503153.
9- Mr.RahulSawantand. M.N.Bajad(2016),“Effectof Soil-Structure Interaction on High Rise RC Building”. IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSRJMCE), Volume 13, Issue1,pp85-91
10- Nitish Kumar. S,Praveen J. V. “Study of Soil Structure Interaction Effect on Multi-Story RCFrameStructuresRestingOverRaftFoundation under Earthquake Caused Agitation”, InternationalJournal of Engineering Research & Technology(IJERT),ISSN:2278-0181,Vol.5Issue 06,June-2016