International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Arduino Based Bluetooth Controlled Robotic Car
Prashant Pal1, Shashank Kumar Singh2, Pawan Kumar Patel3 , Shaikh Mubeen Yaqub4 , Rushikesh Mugdal5 , Khan Shareque Khalid6
Prashant Pal, Scientist B, National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology ,Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India.
Shashank Kumar Singh, Scientist B, National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India
Pawan Kumar Patel, STA, National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India.
Shaikh Mubeen, B. Tech (ESE) National Institute of Electronics and I.T, Aurangabad (Maharashtra), India. Rushikesh Mugdal, B.tech (ESE) National Institute of Electronics and I.T, Aurangabad (Maharashtra), India. Khan Shareque, B.Tech (ESE)National Institute of Electronics and I.T, Aurangabad (Maharashtra), India. ***
Abstract - BLUETOOTH CONTROLLED ROBOTIC CAR(BCRC) is a mobile robot whose motions can be controlled by the user by giving a specific voice, or other commands using a Bluetooth device. In This Bluetooth Model,weareusingvoicecommandstocontroltheRobotic car.Thespeechisreceivedbyamicrophoneandprocessed by the voice module. When a command for the robot is recognized, then the voice module sends a command messagetotherobot’smicrocontroller.
Thisproject VControlledRobotic Vehicle helpsto control robots through voice commands received via an androidapplication.Theintegrationofthecontrolunitwith a Bluetooth device is done to capture and read the voice commands. The robotic vehicle then operates as per the commandreceivedtheviaandroidapplication.
ForthisAtmel AVRAtmega 328microcontroller is integratedinthesystemwhichmakesitpossibletooperate thevehicleviatheandroidapplication.
Key Words: Arduino Uno, Bluetooth Model (HC 05), Atmega328Microcontroller,PiezoElectricBuzzer,L293D MotordriverIC,etc
1. INTRODUCTION
TheBLUETOOTHCONTROLLEDROBOTICCARiscontrolled throughvoicecommandsgivenbytheuserwhoisoperating thesystem.Thesevoicecommandneedstobegiventhrough anandroidappthatisinstalledontheuser’sandroidmobile. Please note that users should have a good internet connection in order to have a smooth operation of the androidapplication.Speechrecognitionisdonewithinthe androidappandthenarespectivecommandissenttothe voice-controlledrobotvehicle.Themicrocontrollerfittedto the Robot decodes these commands and gives an appropriatecommandtothemotorsconnectedtotherobot.
In a Bluetooth voice-operated robot the robotic vehiclemovementiscontrolledviavoicecommand.Thisis an Arduino Uno base project. In this project, we use a Bluetooth device to receive commands from users. Users use the android application to give the command to the Bluetoothdevice.TheBluetoothdevicereceivesacommand fromtheapplicationandtransmitsthesametoAtmelAVR AT mega 328 microcontrollers then the microcontroller controls the robotic vehicle as per command. The microcontrolleristhemainunitofourproject.It’sacentral processing unit (CPU) of the Robot. It receives various commands from the Bluetooth decoder and gives the respective output motor driver ICs. This robotic vehicle operatedon5commandsforward,reverse,left,right,and stop. In this project, we use Atmel AVR AT mega 328 microcontrollers after receiving the above command microcontrollertomovethemotorsaspercommand.The communication between the android application and Bluetoothisserialcommunication.Therobotiscontrolled byanAndroidmobilephonethatconnectsto aBluetooth decoderattachedtotherobot.Thus,weneed1mobile&1 Bluetoothdecoder.ABluetoothdecoderisalwaysconnected totheRobotandanothermobilephoneisusedtocontrol the movements of the Robot. It consists of a Bluetooth decoder.ItgivesASCIIcodeoutput.Thisreceiverenables wirelesstransmission&receptionofserialdata.Ithas10 metersrange.DCmotorusedforroboticvehiclemovement.
1.1 OBJECTIVE
Themainobjectiveoftheprojectistocontrolthe roboticcarinthedesiredposition.
Theprojectistocontroltherobotbythevoiceor pushbutton.
Theprojectisdesignedtocontrolaroboticvehicle byvoiceandmanualcontrolorremoteoperation
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1866
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1.2 NEED OF PROJECT
The main objective of developing this Bluetooth vehicle microcontroller project is to control Vehicles according to human voice commands sent through Bluetooth.ProjectArchitecturefollowswithhumaninput voiceandamplifiers,when a humansends a voicethen it automatically converts the voice from Analog to digital signalsviaconverters,herebandpassfiltersareconnected to fingerprint templates to generate fingerprints, this module works with comparing and controlling digital signalsandfinally,thissignalgoestothevehicle.
Ifthevehiclereceived thecorrectsignal whichis sent to be used then it can respond as per user project development. Now a day all robotics are working with signals and voice to control their functionality. Microcontrollers, Mat lab, and Micro semiconductors are usedtodevelopthiselectronicssystem.Thisapplicationis mainly useful for speech-enabled vehicle design and development. The advantages of this Voice recognition vehiclefollowswecontrolanyelectricalorelectronicdevice withvoicesignals
signalgoestothevehicle.Ifthevehiclereceivedthecorrect signalwhichissentbytheuser,thenitcanrespondasper userprojectdevelopment.Nowadayallroboticsareworking with signals and voice to control their functionality. Microcontrollers, Mat lab, and Micro semiconductors are usedtodevelopthiselectronicssystem.Thisapplicationis mainly useful for speech-enabled vehicle design and development. Advantages of this Voice recognition vehicle follow we control any electrical or electronic device with voicesignals
Fig 1.2: PROPOSED SYSTEM
The Bluetooth-controlled car moves according to the buttontouchedintheandroidBluetoothmobileapp.Torun this project first we need to download the Bluetooth app fromtheGoogleplaystore.WecanuseanyBluetoothapp thatsupportsorcansenddata.Herearesomeapps'names thatmightworkcorrectly.
BluetoothSPPProtocol
Bluetoothcontroller
2. METHODOLOGY
The main objective of developing this Bluetooth Voice recognition vehicle microcontroller project is to control Vehicles according to human voice commands Project Architecturefollowswithhumaninputvoice,whenhuman sends voice then it automatically converts the voice from Analogtodigitalsignalsviaconverters,thismoduleworks withcomparingandcontrollingdigitalsignalsandfinally,this
FIG 2.1: DATA FLOW DIAGRAM
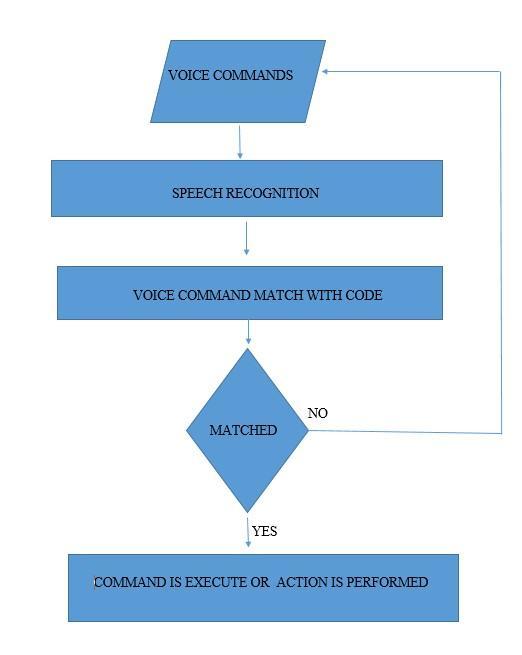
3. SYSTEM DEVOLOPMENT
3.1: BLOCK DIAGRAM OF SYSTEM
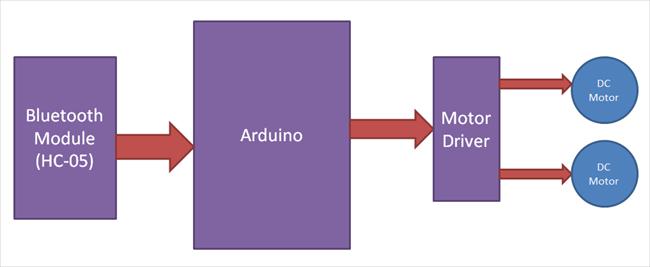
Fig 3.1 is the block diagram Bluetooth control robotic car. The car is controlled by voice command. The human voice is recognized, and the voice command is converted into a text command. This text command is comparedwithcodewritteninArduinoUnoprogramming, ifthecommandmatchesthecarmovingforward,back,left,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

or right this process is worked through by the Bluetooth module. This robotic car has another sensor like L293d motordrivingIC, LDR,LED,SR-04ULTRASONICSENSORETC.
theArduinocircuitforAnalogsignalinputandoutput.Two remaining two pins of Led connect to GND using a 10K register.
TheL293DmoduleisusedtorunDCmotors.TwoDC motorsareconnectedtotheL293Dmodule.Eachmotorhas twoconnectionsthispinisconnectedto thedigitalpinof theArduinoUnoboard.OneisVccpinL293DICrequiredan s+5Vpowersupplytorun.ThispinanotherVccpinisused to give power supply to run DC motors. Motor required +12VpowersupplyandlastisgroundinisconnecttoGND pinofArduinoUnocircuitboard.
4. PROGRAMMING CODES
Fig 3.2 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
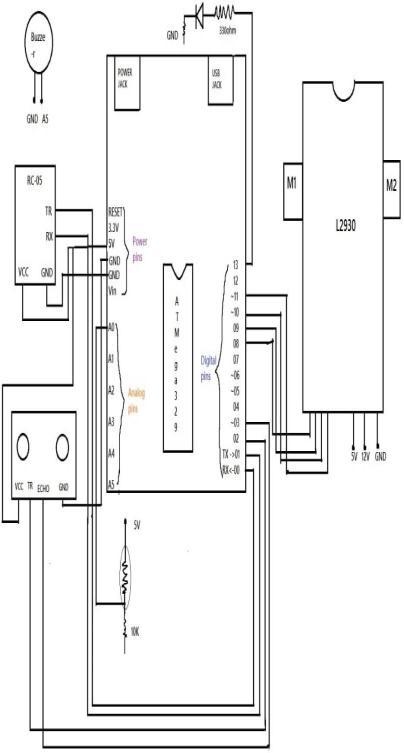
Fig3.2ShownBluetoothcontrollingroboticscarusing ArduinosystemArchitecture.Inthisdifferentcircuitboard Connected to the Arduino circuit for making voicecontrolled.+5VpowersupplygiventotheArduinocircuit toActiveArduinoboard.6AnalogpinsareusedforAnalog signals and 13 digital pins are used for receiving and transmittingsignals.
HC SR 05 is a Bluetooth module connected to an ArduinoUnoboardforestablishingserialcommunication between mobile and robot. HC SR 05 module has 4 pins VCC,ground,RDX,andTxd.TheVCCisconnectedto+5volt pinofArduinoboard,GndpinHc05isconnectedtoground pinofArduinoboard,RDXpini.e.,receiveisconnectedtoTX pin of Arduino board, Txd pin i.e. Transmit Pin (TX) ConnectedtotheReceiverPin(Rx)ofArduinoCircuit.The receiver pin of HR SC 05 Connects to the TX pin of the ArduinoCircuit.
UltrasonicsensorHCSRhas4pins.Vccpinconnectsto the Power Supply pin (Vcc) and GND pin connects to the GND of the Arduino Circuit. Trigger input signal pin connected to the Pin 2 Digital pin and echo output signal pinsconnectedtothePin3ofArduinoCircuitboard.
ThephotoelectricbuzzerhasTwoPinsOnepinconnectedto theDigitalofArduinoandonepinconnectedtothe GNDpinofArduinoCircuitboard.Inthissystem,twoLEDs areused.TwopinsofLedareconnectedtotheAnalogpinof
chardata; intm1_c=8; intm1_a=9; intm2_c=10; intm2_a=11; constinttrigPin1=6; constintechoPin1=7; intbuz=A5; intled1=A4; intled2=A3; voidsetup()
Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(m1_c,OUTPUT); pinMode(m1_a,OUTPUT); pinMode(m2_c,OUTPUT); pinMode(m2_a,OUTPUT); pinMode(buz,OUTPUT); pinMode(led1,OUTPUT); pinMode(led2,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(m1_c,HIGH); digitalWrite(m1_a,HIGH); digitalWrite(m2_c,HIGH); digitalWrite(m2_a,HIGH); digitalWrite(buz,LOW); digitalWrite(led1,LOW); digitalWrite(led2,LOW);
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
delay(1000); } voidloop() { data=Serial.read(); longduration1,inches1,cm1; pinMode(trigPin1,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(trigPin1,LOW); delayMicroseconds(2); digitalWrite(trigPin1,HIGH); delayMicroseconds(10); digitalWrite(trigPin1,LOW); pinMode(echoPin1,INPUT); duration1=pulseIn(echoPin1,HIGH); inches1=microsecondsToInches(duration1); cm1=microsecondsToCentimeters(duration1); if(analogRead(A0)<=500) { digitalWrite(led1,HIGH); digitalWrite(led2,HIGH); } else { digitalWrite(led1,LOW); digitalWrite(led2,LOW); } if(cm1>=20) { digitalWrite(buz,LOW); if(data=='a') { digitalWrite(m1_c,HIGH); digitalWrite(m1_a,LOW); digitalWrite(m2_c,HIGH); digitalWrite(m2_a,LOW); delay(10);
} if(data=='b') {
digitalWrite(m1_c,LOW); digitalWrite(m1_a,HIGH); digitalWrite(m2_c,LOW); digitalWrite(m2_a,HIGH); delay(10); } if(data=='c') {
digitalWrite(m1_c,HIGH); digitalWrite(m1_a,LOW); digitalWrite(m2_c,HIGH); digitalWrite(m2_a,HIGH); delay(10); } if(data=='d') { digitalWrite(m1_c,HIGH); digitalWrite(m1_a,HIGH); digitalWrite(m2_c,HIGH); digitalWrite(m2_a,LOW); delay(10); } if(data=='e') {
5. CONCLUSIONS
Theintegrationofvoicereorganizationsystemintorobotics vehiclehelpdisabledpeople.
Thespeechcontrolsystem,thoughquitesimple,showsthe abilitytoapplyspeechreorganizationtechniquestocontrol theapplication.
The method provides real-time operation, in this system androidapplicationisusedtorecognizehumanvoiceandis convertedtotext,thetextisfurtherprocessedandusedto controlroboticsmovements
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
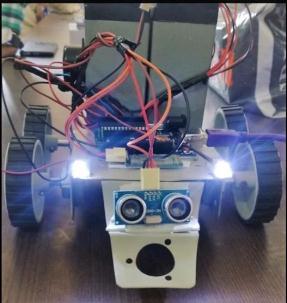
PROJECT OUTPUT



BIOGRAPHIES
PrashantPal,ScientistB,National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology, Aurangabad,Maharashtra,India. prashantpal@nielit.gov.in
ShashankKumarSingh,ScientistB, NationalInstituteofElectronics& Information Technology, Aurangabad,Maharashtra,India shashank@nielit.gov.in
PawanKumarPatel,STA,National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology, Aurangabad,Maharashtra,India
pawankumar@nielit.gov.in
7. RESULTS
DCmotorrotatingproperly.
Wirelessconnectionpasswordworkingproperly.
Obstacledetectionisworkinggood. Carworkingonallcommands. Allthedevicesworkingproperly.
8. REFERENCES
[1] Aniket R. Yeole, Sapana M. Bramhankar, Monali D. Wani, "Smart Phone Controlled Robot Using ATMEGA328 Microcontroller", ISO 3297: 2007 Pg:352-356
[2] R.M.Narayana,HarshaChapala,"VoiceControlRobot using Android Application “, Volume :4, ISSN: 2277 5668Pg:332-337


[3] Ritika Pahuja, Narender Kumar, "Android Mobile Phone Controlled Bluetooth Robot Using 8051 Microcontroller”,ISSN(Online):Pg:2347–3878
[4] K. Kannan, Dr. J. Selvakumar, “Arduino Based BLUETOOTH CONTROLLED ROBOTIC CAR“, Volume:02issue:01,Mar-2015ISSN:2395-0072



[5] Mrumal.K. Pathak, Javed Khan, “ROBOT CONTROL DESIGNUSINGANDROIDSMARTPHONE",2Feb2015, ISSN:2347-5471
Shaikh Mubeen, B Tech (ESE) National Institute of Electronics and I.T, Aurangabad (Maharashtra),India Skalfeen1187@gmail.com

Rushikesh Mugdal, B.tech (ESE) National Institute of Electronics and I.T, Aurangabad (Maharashtra),India rushimugdal86@gmail.com


KhanShareque,B.Tech(ESE) National Institute of Electronics and I.T, Aurangabad (Maharashtra),India Sharequekhan866@gmail.com

