International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Tanirika R1,Dr Rekha PM2 ,Dr Anil BC3
1Senior at Delhi Public School South, Bangalore, India, tanirikar05@gmail.com
2Professor and Head of the Department Information Science and Engineering JSS Academy of Technical Education Bangalore, India
3Associate Professor and Head (AI and ML) Department of Computer Science and Engineering, JSS Academy of Technical Education, Bangalore, India***
Abstract Counterfeit Drugs in developing countries are increasing at an alarming rate. More than 10% of the Global Pharmaceutical supply chain is impacted by counterfeit drugs. In particular, poor countries are affected on a much larger scale. Data indicates that up to 25% of the medicines used in poor countries are not genuine [1]. The increased number of issues due to counterfeit drugs demands an innovative and scalable solution for the product traceability in the pharmaceutical supply chain. In this paper, we have leveraged NFC and blockchain technologies to track the movement of the drugs from manufacturer to the end consumer in order to prevent the counterfeiting of drugs. We propose an approach that publishes the NFC tag to the Blockchain and establishes the transit path for better tracking and traceability across the pharmaceutical supply chain. The proposed solution focuses on publishing the NFC signature along with product details into the blockchain using smart contracts. Manufacturers can define the exact transit path for the movement of drugs in the supply chain and all the participants in the supply chain can trace and track the product location and details at any moment. Our approach prevents counterfeiting and provides a high level of transparency into the pharmaceutical supply chain in a most reliable, scalable and efficient manner
Key words Blockchain, NFC, Counterfeit drugs, pharmaceuticalindustry,Tracking,supplychain
Counterfeit drugs may contain no active ingredient, incorrectingredients,ortoxins.Thesemedicinescompromise the treatment of chronic diseases, causing many health problems, even death. The United States Drug Enforcement Administration seized more than 9.5 million lethal fake pills in2021.Annuallymorethan$200billionofcounterfeitdrugs are supplied in the market [2]. Patients also lose trust in the drugthatissuppliedinthehealthcareindustry.
Alongandcomplexsupplychainfacilitatescounterfeits.Itis difficult totrack thecounterfeit drugs due to the intricacy of thesupplychain.
The current pharmaceutical supply chain involves many parties from the manufacturer to distributors, repackages andwholesalersbeforereachingtheconsumer.Thereisvery little visibility between the organizations involved in the supplychaininordertotracktheauthenticityofthedrug.
Traditional supply chains usually adopt centralized anticounterfeit solutions. That kind of arrangement is subject to therisksofdatamodification.
We propose a decentralized application framework that records transactions at every stage of the supply chain and provides an efficient method for tracking and tracing the medicines.
The main contribution of this paper can be summarized as follows:
We discuss the prevailing solutions in the market and the recent research work on preventing counterfeitingproducts.
We present an NFC and blockchain-based solution for traceability and visibility in the Pharma supply chainusingEOSIOsmartcontracts.
We have discussed the method of tracking NFC tags in the blockchain, featuring main interactions betweenalltheparticipantsinthesupplychain,with entityrelationsandsequencediagrams.
We use EOSIO testnet framework to simulate and test the smart contract algorithms that are used to detectandpreventthecounterfeitdrugs.

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thereminderofthepaperisorganizedasfollows.
Section 2 presents the Market and existing solutions in the pharmaceutical supply chain. In section 3, we discuss the current research and related work. Sec4 & 5 explains the importanceandcapabilitysetoftheBlockchain&NFC.Sec 6 describestheproposedsolution,sequencediagramandhighlevel overview. Sec 7listsout the featureset Sec 8describes all the algorithms implemented as part of the proposed solution. Sec 9 Describes the feasibility and market adaptability Sec 10 & 11 concludes the study and future developmentprospects.
This section describes the pharmaceutical supply chain challenges in detail, highlighting the existing solutions and its limitations. This segment will also explain as to why combining Blockchainand NFCcouldbea bettersolution to reducecounterfeitproducts.
Pharmaceutical supply chain as represented in Figure 1 involves many transit paths between manufacturer and the patient. The manufacturer ships the drugs to wholesale distributors. The wholesale distributor further ships to master retailers and then stocked at retail before it reaches the end consumers. This offers a great opportunity for fraudsterstointroducecounterfeitproducts
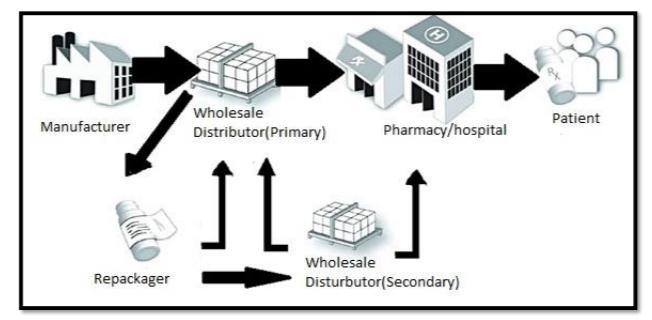
Secondary wholesalers do not directly purchase the medicines from the manufacturer. They usually buy it from different parties like the primary wholesaler. Primary wholesalers may also purchase the drugs from a secondary wholesaler if the demand is high. The products move between different wholesalers before being repackaged and soldtothepatients.Thismovementofdrugswithindifferent wholesalersprovidesanopportunityforcounterfeitdrugsto enterthesupplychain. Whilerepackagingcounterfeitdrugs may be given original labels, making the identification of counterfeitdrugsevenharder.
“When legitimate medication makes its way to distribution channels not authorized by drug manufacturers, this is considered the gray market. Largely, these medications are divertedoutofthelegitimatesupplychainduetopricepoint differentialsoravailabilitygapsindifferentgeographies.”[3] These diversions from the supply chain provide opportunitiesforcounterfeitdrugstoenterthesupplychain andthesedrugscannotbeeasilytracked.
Few solutions like Holographic Packaging, RFID, and Mass Encryptionarealreadyinthemarket.Inthecaseholographic packaging, each package will contain the hologram and it is visible to the end consumer. Holographic implementation is expensive. It can be easily cloned. Also, it is difficult to determinetheoriginoffraudulentactivity.

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Mass Encryption based solution involves adding an encrypted code and can be decoded at every stage of the supply chain. Mass Encryption techniques require high data storagewhichincreasesthecostofimplementation.
In RFID based solutions each package is allotted a unique identifier. RFID solutions are expensive to implement and it isnottamperedproof.
Most common counterfeit attacks in the existing solutions include (1) Modification of the Medical data in the tag. e.g., Expirydate(2)Cloning oftheexisting productdetailsintoa differenttag(3)Insiderattackduetotheleakedprivatekeys usedforsigningtheRFIDs.
Our solution uses both NFC and Blockchain technologies to track and trace the products from the manufacturer to patientsandalsoverifytheauthenticityofthedrug
Inthissection,wewillreviewsomeoftherecentresearch works on preventing counterfeit and improving traceability of products in the supply chain. Traceability is the ability to followthematerialsfromthebeginningofthesupplychainto thecustomerwhopurchasestheproduct.
Recently there is a lot of interest in the traceability of productsinthesupplychain.Themostcommonsolutionsare basedonIOTtechnologyemployingRFIDandusingacentral infrastructure to trace the product along the supply chain [11] - [13]. These kinds of centralized solutions lack data protection.Anyuserwhohasaccesstotheservercanmodify the data stored in the server. Further, centralized solutions arenotefficientandlacktransparency.
Problems like Data Protection and lack of transparency can be resolved using Blockchain technologies. Advantages and benefitsofblockchainareexplainedinSectionIV
Application of Blockchain for traceability of products in the supplychainareaddressedacrossindustrieslikeFoodChain, Banking,Finance,Pharmaceutical.
Food supply chain traceability is discussed by Tian using blockchain and Internet of Things [14]. Tse et al compared the blockchain based solutions with the traditional solutions forthefoodsupplychain[15].KumarandTripathicombined encryptedQRcodeswithblockchain[16].Saxenaetal.didan experimental study and created Pharmacrypt to reduce counterfeit drugs [17]. Peng Zhu al introduces a new blockchain consensus algorithm and access control to improvesecurityandprivacyprotection.
Asevidentfromtherelatedwork,thereisagrowingtrendin adaptingblockchainbasedsolutionsforinformationsecurity, traceability and to reduce counterfeit products. However, mostoftheBlockchainbasedsolutionslackpracticality.Most of the paper discusses the conceptual methods of using blockchain in the pharmaceutical industry falling short of specific implementation framework (or) approach. Our proposed solution combines NFC and blockchain and tracks theNFCtagacrossthesupplychain.NFCistamperproofand has programmable memory to provide more insights about the drugs and origin information. Benefits of NFC are discussedinSectionV.
We are proposing a pharmaceutical supplychain framework thatreadsthedatafromNFC,definestheexacttransitpathof the medicines and provides a method for improved transparency. Our solution is using the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPOS) framework that is highly scalable and can be implementedwithoutmuchcomplication
“Blockchainisanimmutable,distributed,decentralized,peerto-peerledger replicatedacross multiple nodesconnected in anetwork”,makingitpossibletorecorddataaboutanyevent or transaction as it happens. It consists of blocks in a chain usedtorecordasdigitalassetsusingasecurealgorithm”[4]
Data in every block is encrypted using the SHA-256 algorithm that makes modification to data very difficult.Any change in the data renders the modified block invalid. This abilityofblockchainspreventsalterationoftransitdataofthe drugswithinthesupplychain.
Data once created in the blockchain cannot be altered. Everytransactionisrecordedasauniqueentryandhistorical recordscannotbemodifiedorremoved.
This enables patients to view the entire history of the drugs from the manufacturer to the patients and eliminates anyopportunityfortheintroductionofCounterfeitdrugsinto thesupplychain.
The transparent features ofblockchain helps in detecting fraudateverystageofthetransit.
Recordscanbeaccessedusinga privatekeybytheownerof that record (manufacturer, wholesaler, distributor and the pharmacy) and with public keys by participants with whom they want to share information (Patients). The system is intended to enable the user to have full control of the data
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
whileallowingpatientstogaincompleteaccesstothetransit dataoftheproduct(medicines).
itemandvalidatetheauthenticityoftheproductinthesupply chain.
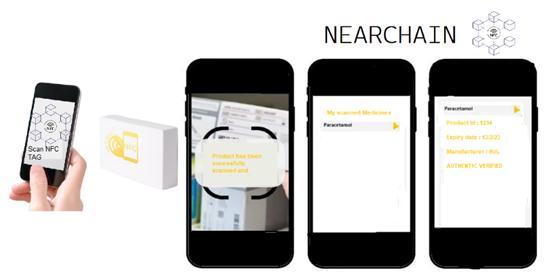
Each NFC tag has a unique signature, the expiry date of the drug and origin details stored within its memory. These detailscanbeobtainedbysimplyscanningtheNFCtagusing anNFCreaderonamobilephone.
These details are converted using a hashing algorithm for extrasecurityandthenstoredontheblockchainwhichcanbe accessedusingtheNEARCHAINapplication.

1. NFCistamperproofandcanonlybeappliedonce.Its antennabreakswhenattemptingtoremoveit.
2. An NFC Tag can hold essential information like product-ID, unique-ID, Date of Expiry and the status oftheproduct.
3. The data stored in the tag can be protected using a passwordwhichoffersmoresecurity
In this section, we will explain the solution that utilizes the EOSIO based smart contracts to publish the NFC details. Wewilldescribeindetailourapproachtotraceandtrackthe pharmaceuticaldrugs.
Our solution addresses most common counterfeit attacks including(1)ModificationoftheMedical data inthetag.e.g., Expiry date (2) Cloning of the existing product details into a differenttag(3)Insiderattackduetotheleakedprivatekeys usedforsigningtheNFC.
In addition to the above, our solution enables traceability of the Product and fetching the product details from the blockchainbyanyentity.Atahighlevel,oursolutionincludes threebuildingblocks:Registration,TransitandTracking.
Our proposed framework will focus on writing the data to NFC, reading the data from NFC, creating workflow, publishingthemedicaldatatotheblockchainandtracking.
In our solution we are using NFC to store details of the medicineandEOSIOblockchaintotrackthemovementofthe
The manufacturer can attach an NFC tag to their electronic goods before shipping,and the end consumer will be able to verify that the NFC tag is original and not tampered with, usingNEARCHAIN.
EOSIO is a leading open-source platform for blockchain innovationandperformance.[5]TheEOSIOplatformusesthe Delegated Proof of Stake (DPOS) algorithm. In DPOS block producersareselectedthroughavotingsystem.Anyonewho holdsatokencanbeinvolvedinthevotingprocess.[6]
Our proposed framework describes the creation and executionofsmartcontractsinEOSIObasedblockchain.
We have defined smart contracts for Registration Block, Transit Block and Tracking Block. Each smart contract is triggered by various entities like Manufacturer, Distributor, Pharmacy/Retailer and end consumer. Upon execution of smartcontracttransactionsaregeneratedandbroadcastedas partoftheproducedblockchaintoothernodes.
In EOSIO, all the state and application data are stored in the multi-Index table. Multi-Index tables provide quick access to the datastore. The blockchain records the transactions while theMultiindextablesareusedtostoredata
In our proposed framework for the pharmaceutical supplychainthefollowingentitiesareinvolvedininteracting withthesmartcontracts.
Manufacturer - The responsibility of the Manufacturer is to injects the data into the NFC tag and publishes the NFC tag informationtotheblockchain
Distributor/Retailer - Upon receiving the product, the distributorvariesthecontentoftheNFCtagandcrosscheck andupdatethestatusintheblockchain.
All entities - At any moment, one or more entities can be involvedintrackingthelocationoftheproductandvalidityof theproduct.

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
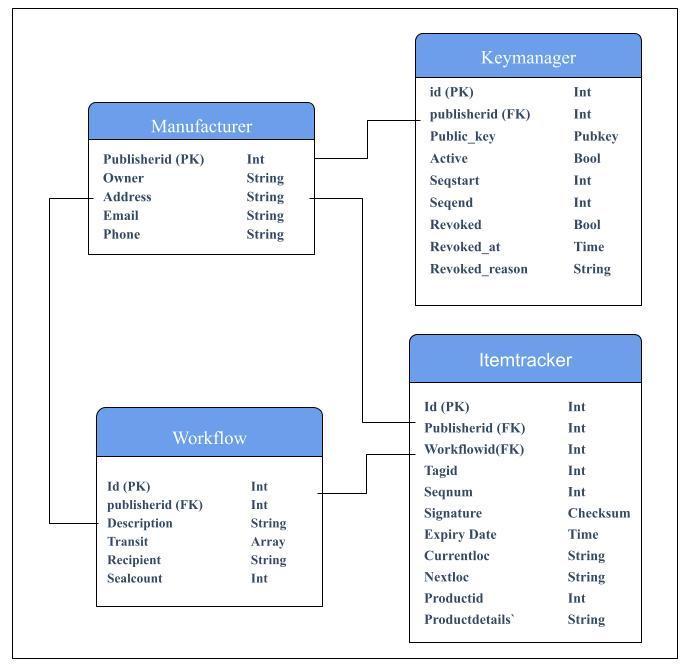
Figure 3 is a representative entity-relationship diagram that defines the table structure of the multi-index table and the relationshipbetweentheparticipatingentities.
In EOSIO Blockchain all the entities Manufacturer, WholesaleDistributor,RetailerandConsumerarecreatedan account. Each product itemthat is shipped in the blockchain has a unique product id. As represented in the Figure 5 Sequence Diagram, there are three major functional blocks: Registration,TransitandTransfer.
Foreachblockthereisalistofactionsthataredefinedand triggeredonthesmartcontractasmentionedinthesequence diagram.
In our proposed framework, the Manufacturer has to identify itself in the Blockchain by adding its details like Publisher ID, Owner, address, Email (Action: addManufactureID).
Manufacturer has to identify the total number of NFC tags required for a given product and pushes the total NFC tag (sealCount) along with the public Key into the blockchain. (Action:addSealCount)
Manufacturer writes all the necessary information like ProductID,SequenceNumberofNFCTag(seqNum),Product Details,ExpiryDateintotheNFCusingNFCWritersoftware. ItalsosignstheNFCLabelusingaprivatekey.
ManufacturerregistersthecontentoftheNFCtagalongwith thelabelsignaturetotheblockchain,thuspreventinginsider attack. (Action: addNFCTag). Now, it is not possible for someonetoproduceasealknowingtheprivatekeysincethe sequence number is already registered in the blockchain. seqNumpreventstheinsiderattackproblem.
Manufacturerdefinesthetransitflowfortheproduct.Transit flowisthepathinthesupplychainfromproductorigintillit reachestheendconsumer.(Action:createTransitFlow).Upon completion of the above steps, the product is ready for the nexttransitpath.
Now the product is received at the Transit Point. Transit nodereadsthecontentoftheNFCtagusingthepublickeyof theManufacturer.
Transit node reads the data in the NFC tag and matches the product details with that of the data available in the multi-
Indextable.Anymismatchinthedataindicatesthatthedata ismodifiedintheNFCtag.TransitNodealsoreadstheLabel Signature in the NFC and matches with the Signature in the blockchain.Any mismatch in the signature indicates that the productiscloned.
The last step is to verify the transit flow. If there is no mismatch in the transit path, then the Transit node updates thetransitstatus(Action:updateTransitStatus)
The above steps are repeated by all the transit nodes till it reachestheendcustomer.
Figure3EntityRelationshipDiagram
Our proposed framework provides a high level of transparency and security by providing traceability and productdetailsfunctionality.
Any entity can trigger the following action to track the locationoftheproductandtounderstandtheproductdetails. Once the product is received by the customer, they can scan theNFCtagandunderstandtheproductdetails.Theycanalso send the request to the blockchain to understand the transit path(Action:getTransitStatus)

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Belowlistedarethefeaturesoftheprototypedeveloped:
AssetCreation: NEARCHAIN creates a new asset for every unique product in the supply chain. The product’sinformationisuploadedtotheBlockchain onscanningtheNFCtag.
Tracking the asset: When a product is moved on to the next party in the supply chain, the application recordsthetransitandalsoupdatesthestatus.
1. A common wallet for account creation with
an automated password which needs to be stored.
2. An account is created for the contract creation
3. Every supplier in the supply chain has a private key while the user can use the public chain to view the information of the product.
View Details: User is able to verify if the drug is authenticandalsotracetheoriginofthedrug.
4. NFC can be password protected for more safety Figure4Sequencediagramrepresentingendtoendworkflow

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
This section we discuss the algorithms that define the workingprinciplesofourproposedapproach.
We have simulated the smart contract environment using EOSIOmulti-nodetestnet.
Ubuntu18.04Machine EOSIOframework NFCpcscNodeJSlibrary NFCReader/NFCTags
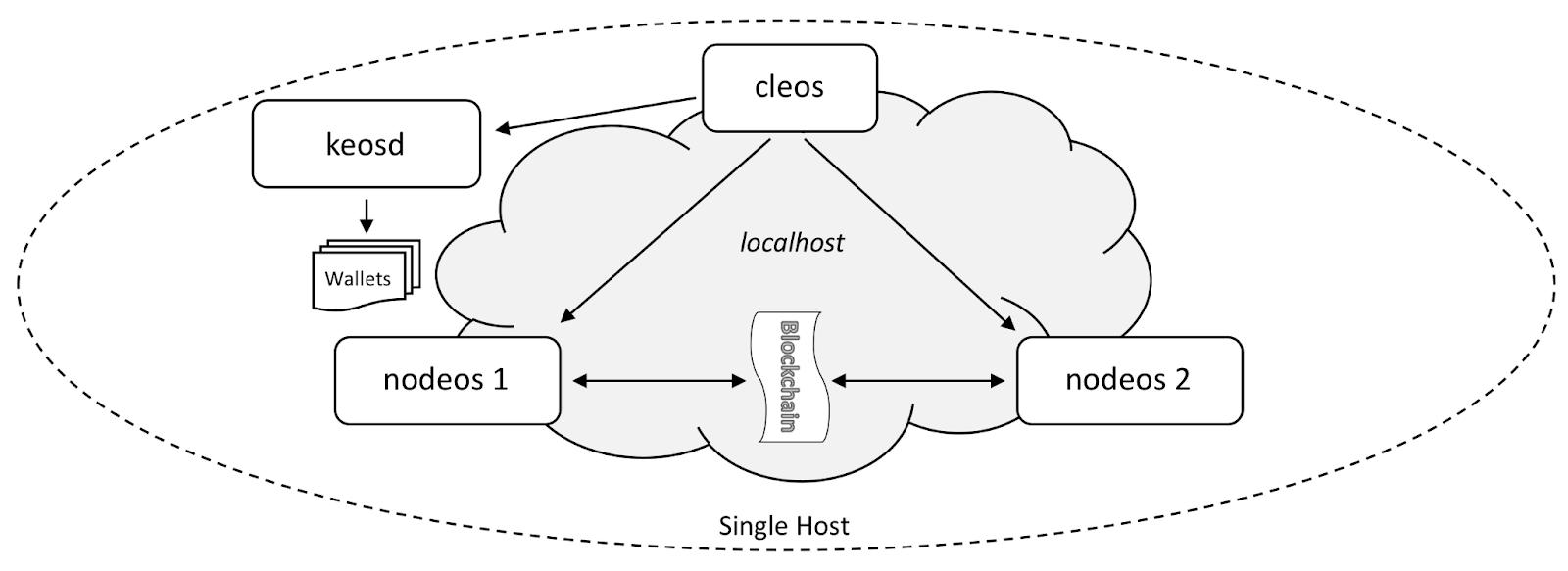
Below figure 6 depicts the multi-node setup environment usingopensourceEOSIOsoftware.Wehavesetuptwonodes onthesamecomputer.
Inthefigure6,keosdisthewalletmanagementapplication.
“Nodeos is the demon that processes smart contracts, validates transactions, produces blocks containing valid transactions, and confirms blocks to record them in the blockchain”.
cleos is the command line interface that helps to communicate with the REST API interface of the Nodeos process.
Technically we can have any number of distributors and consumersaspartofthesupplychain
1. Manufacturer(Issuer) 2. WholesaleDistributor(Transit_1) 3. Pharmacy(or)Hospital(Transit_2) 4. Patient(Recipient)
CreateAccountsandWalletinBlockchain:
Create 4 User Accounts corresponding to Manufacturer,Wholesaledistributor,Pharmacistthe recipientforwalletcreation.
Create Wallet in Blockchain Network using account Pharmawallet
Import private keys of Manufacturer, Transit_1, Transit_2, RecipientinPharmawallet.
Manufacturer creates a smart contract that has defined actions for adding NFC tags, publishing the Product details, creating the transit path in the supply chain, updating the status by all transit points and fetching the transit status fromtheblockchain.
Uponcreationofsmartcontract,Manufacturerpublishesthe total seal required for a given project, sequence number of the NFC tags and the publicKey of the Manufacturer as definedinAlgorithm1.
Figure5 SimulatedEnvironmenthttps://developers.eos.io/manuals/eos/v2.0/nodeos/usage/developmentenvironment/local-multi-node-testnet
In this simulated environment we have assumed 4 majors partiesaspartofthepharmasupplychainasbelow.
Manufacturerisresponsibleforcreatingthecompletetransit path.AsindicatedinAlgorithm2,
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 1603

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Manufacturer defines the complete transit path using the action: createTransitflow. Manufacturer defines the necessary and required routes in the supply chain. In this case transit path is defined as Manufacturer, Distributor, PharmacyandRecipient.
Now all the initial setup is ready for the product to be shipped.Manufacturerwritestherequiredproductdatainto theNFC
tag. Data includes drug information, expiry date, sequence number of the tag, and signature Hash of the NFC tag. Once thewritingiscompletedin thenfcTag,thedatafromthetag is pushed to the blockchain as explained in algorithm 3. Manufacturer defines the nextLoc using the transit flow informationdefinedintheblockchain.
Atthispoint,theitemcanbeshippedtothenexttransitpath. Upon receiving the item in the next transit location, the informationintheNFCtagisreadandcrossverifiedwiththe blockchain. If the drug details in the NFC match with the drug details in the blockchain and if the product has not expired, the transit status is updated in the blockchain as mentionedintheAlgorithm4.
Algorithm 5 and Algorithm 6 explains the transit status and product status details. Any entities can check the current locationoftheproductintheblockchainandunderstandthe productdetailsatanypointintimebasedonthedatastored intheblockchain.
Algorithm1Addseqstart,seqendandpublicKey
Input: ManufacturerID,publicKey,maxSeals
1 ManufacturerID is same as the publisherID corresponding to the Manufacturer as represented inFig3. 2 publicKeyissharedbythemanufacturerin theblockchain,whichprovidesownershipfor ManufacturertoupdatesealCount,seqnumber. 3 if ManufacturerIDexistsinblockchain then 4 if maxSeals>0 then 5 seqStart=0,seqEnd=0 6 fetchseqEndfromtheblockchain 7 seqStart= seqEnd+1 8 seqEnd=seqStart+maxSeals-1
9 Updatearecordinthetable “Keymanager”thefollowingfields seqStart,seqEnd,publicKey. 10 else 11
Notifyerrortotheclientsideforinvalid maxSeals 12 end 14 else 15 Notifyerrortotheclientsidefor “InvalidmanufacturerId 16 end 17 end
Algorithm2createTransitFlow
Input: publisherId,workflowId,transitArray,recipient, description 1 if publisherhasownership, then 2 if workflowIdisuniqueandnotexistsinthe blockchain then 3 if transitaccountsandrecipientaccount existsintheblockchain then 4 Updaterecordintheworkflowtablewith thefollowing:workflowId,description, transitArray,recipient 5 else 6 Notifytotheclient“transitorrecipient accountdoesnotexist” 7 end 8 else 9 Notifytotheclient“workflowIdalready existsintheblockchain” 10 end 11 else 12 Notifytotheclient“publisherdoesnot exists”

13 end
Algorithm3 AddnfcTag
Input: publisherId,tagId,seqNum,sighash,expiryDate, ProductID,ProductDetails,workflowId,Manufacturer 1 if publisherIDexistsinblockchain then 2 if workflowexistsinblockchain then 3 if seqNumORsighashdoesexists inblockchain then 4 fetchnexttransitIdfromworkflowTable currentLoc=publisherID nextLoc=transitId Update tagId,seqNum,sighash, expiryDate,currentLoc,nextLocProductID,Pr oductDetailsintheblockchain 5 else 6 Notifytoclient “seqNum ORsighashalreadyexistsinblockchain” 7 end 8 else 9 Notifytoclient “Workflowdoes notexists” 10 else 11 Notifytoclient“publisherIddoes notexists” 12 end
Algorithm4 UpdateTransitStatus
Input: transitId,seqNum,tagId,status,notes,transit 1 if transitIdhasownership then 2 if transitId==nextLocthen 3 if seqNumexists then 4 if workflowexistsforcorrespondingseqNum then
e-ISSN: 2395-0056
5 currentLoc=transit 6 nextloc = nexttransitlocationfrom workflow 7 Updaterecordintheitemtrackertable withthestatus,notes 8 else 9 NotifyClient“workflowdoesnotexists forthegivennfcTag” 10 end 11 else 12 NotifyClient“seqNumdoesnotexists” 13 end 14 else Notifyclient“Invalidtransitpath” 15 end 16 else 17 Notifyclient“transtIddoesnothave Permissiontoupdaterecords” 18 end
Algorithm5 GetTransitStatus
Input: seqNum 1 if seqNumexistsinItemTracker then 2 Notifyclient“currentlocation” 3 else 4 Notifyclient“Notabletotrack” 5 end
Algorithm6 GetProductStatus
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 1605
Input: seqNum 1 if seqNumexistsinItemTracker then 2 if todayDate<= expiryDateinItemTrackerthen
e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

The Blockchain Technology in Healthcare market is estimatedtosurpass6.17billionUSDin2027,withprojected growth of 52.1 Compound annual growth rate. Primary growthdriversinclude
1. Riseincounterfeitdrugs
2. IOTinhealthcare
3. Risingneedtostoreandsecuremedicalapplication
4. Increaseinthenumberofmedicaldatabreaches
The Near Field Communication Market in Healthcare is estimatedtosurpass$278.80Millionby2025growingatan estimatedrateofmorethan11.36%during2020to2025[7].
As the numbers above suggest an increase in the market of both NFC and blockchain in the healthcare industry, our solution is viable and can be deployed to manage a pharmaceuticalsupplychain.
Counterfeit medicine or fake medicines as discussed earlier can be fatal when taken and even life-threatening as they contain small or no traces of the active ingredient that is requiredtokeepyouhealthy.Ithasbeenestimatedthatfake antimalarialdrugscontributetonearly450,000preventable deathseveryyear[8].
Figure6CounterfeitPharmaceuticalgraph https://www.raconteur.net/counterfeit-medicines-killingpeople-and-brands/
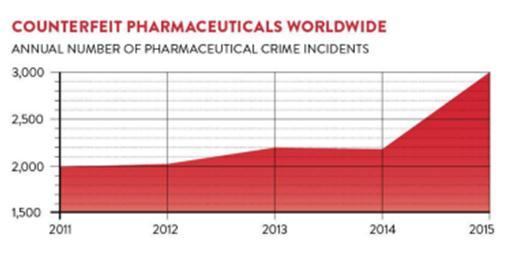
The number of cases of medicines reported falsified or substandardincreaseseveryday asrepresentedinFigure7. While the impact of counterfeit drugs on public health is huge, manufacturers also suffer. The current global market forcounterfeitdrugsalesaccountsfor$75billion,according to the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy [9]. Counterfeit Drug Market Grows by 20% Per Year [10]. The productionofcounterfeitdrugscontinuestoincreasedueto high profit margin and low detectability especially in the low-andmedium-incomecountries.
Effective supply chain management is a challenge in every industry. However, there is an additional challenge in healthcare as a compromised supply chain can be life –threatening. The involvement of multiple parties in the transportation of the medicines makes the detection of counterfeitdrugs verydifficult.Thereislittleornovisibility between the organizations involved in the supply chain and thepatientscannotverifyifadrugisauthenticornot.
The increase in the number of users of online pharmacies has widened the global market for counterfeit drugs. Unlicensed, substandard and falsified medicines are sold illegally in online pharmacies and patients buy them due to thehighdemandandlowsupplyofcertainmedicines.
We have combined NFC and Blockchain technology to providea secure,transparentandviablesolutiontoprevent counterfeiting of drugs. Utilizing blockchain and NFC technology can provide a secure, transparent, and distributednetworkwhichenablessupplychainverification, detectpotentialcounterfeitproducts,andimprovethesafety of the public’s health. The patients can trace the movement of the medicinal drugs along the supply chain and also read essential information like the product ID, unique item-ID,

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
expiry date, product information and customer support contactdetailsbyreadingtheNFCtag,usingtheNFCreader apponthemobilephone.
As there are new discoveries made in the pharmaceutical industry and new medicines created that require more complex manufacturing and supply chains compared to smallmoleculedrugs,blockchainmaybeusedasstandardin the manufacturing industry to track the drugs through the complexsupplychains.
On reflection, we believe that NEARCHAIN has the potential to be developed and used in the healthcare industry as representedinfigure8
[1] https://www.pharma-mkting.com/articles/pmn46article02/
[2] https://www.forbes.com/sites/sap/2019/10/03/counterfei t-drugs-a-bitter-pill-to-swallow/
[3] https://www.st.com/content/st_com/en/premiumcontent/premium-content-smarter-end-to-end-supplychains-combining-blockchain-and-nfc-rfid-technologies.html
[4] https://medium.com/swlh/a-simple-guide-tounderstanding-blockchain-8dd09356b153
[5] https://eos.io/about/
[6]https://developers.eos.io/welcome/v2.1/introductionto-eosio/core_concepts
[7]https://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/333938 9/near-field-communication-in-healthcare-market
[8] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4064812/
[9] https://www.lifescienceleader.com/doc/governmentand-industry-come-together-to-stop-billion-drug-0001
[10]
https://www.packworld.com/issues/ecommerce/article/21102806/200-billion-pharmacounterfeit-drug-market-growing-by-20-per-year
[11] T. Inaba, ‘‘Inference of product quality by using RFIDenabled trace-ability information a study on the US pharmaceutical supply chain,’’in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. RFID, Apr.2009,pp.298–305,doi:10.1109/RFID.2009.4911170.
[12] B. A. Alzahrani, K. Mahmood, and S. Kumari, ‘‘Lightweight authenti-cation protocol for NFC based anticounterfeiting system in IoT infrastructure,’’ IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 76357–76367, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989305.
[13] M. Wazid, A. K. Das, M. K. Khan, A. A.-D. Al-Ghaiheb, N. Kumar, and A. V. Vasilakos, ‘‘Secure authentication scheme formedicineanti-counterfeitingsysteminIoTenvironment,’’ IEEE Internet Things J., vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 1634–1646, Oct. 2017,doi:10.1109/JIOT.2017.2706752.
[14]Tian,F.(2017,June).Asupplychaintraceabilitysystem for food safety based on HACCP, blockchain &Internet of things. In Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM),2017InternationalConferenceon,1-6.IEEE.
[15] Tse, D., Zhang, B., Yang, Y., Cheng, C., and Mu,H. (2017, December). Blockchain application in food supply information security. In Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), 2017 IEEE International Conferenceon,1357-1361.IEEE.
[16] R. Kumar and R. Tripathi, ‘‘Traceability of counterfeit medicinesupplychainthroughblockchain,’’inProc.11thInt. Conf. Commun. Syst.Netw. (COMSNETS), Jan. 2019, pp. 568–570,doi:10.1109/COMSNETS.2019.8711418.
[17]N.Saxena,I.Thomas,P.Gope,P.Burnap,andN.Kumar, ‘‘PharmaCrypt: Blockchain for critical pharmaceutical industry to counterfeit drugs,’’ Computer, vol. 53, no. 7, pp. 29–44,Jul.2020,doi:10.1109/mc.2020.2989238.