International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Aman khajuria1, Sourabh Lalotra2
***
Abstract - The paper is concerned with study of behavior of irregular shaped multistory building structures and regular shaped multistory buildings with floating columns and flat slab as feature in them. The objective is to carry out seismic analysis of various models of RCC buildings using Staad Pro for response spectrum analysis, modal time history analysis, Time history analysis and also finding out variation in peak storey shear value, base shear value, storey drift, displacement values for each of these regular shaped model and irregular shaped model with flat slab and floating columns and comparing the result of irregular vertically ,irregular horizontally and regular story structures on these parameters in bar chart graphical manner for variation in the result for different types of structures with same height and reaching a conclusion for variation of result in these structures in a comparative study.
Key Words: Dynamic analysis (Response spectrum Analysis,Modaltimehistoryanalysis,Timehistoryanalysis) peak story shear, base shear, storey drift, displacement, memberstress,RCCStructureIS1893:2016part1,
1.INTRODUCTION
In recent times, trend of multi storey parking, shops and commercialspacesisonriseinurbanareas.Sometimes,such structureshasto be constructed invery limitedavailable space in cities so sometimes it is not possible to built the structureinregularbuildingdimensionssuchasrectangular orsquareshapebuildingandalternativetypeofbuildings arepossibletobeconstructed insuchareassuchasIshape U shape or L shape structure and sometimes vertically irregularstructuresarepreferredduetodesignaestheticsor structurewithlessareaatgroundlevelandareaincreasing decreasing as go upwards . So, with this use of floating columnconceptandflatslabcomeintouse.So,thisthesisis anattempttostudythebehavepatternofsuchstructures and their comparison with regular building on the parameters such as (seismic response by response spectrum method for 6 mode shapes, Peak storey shear ,base shear value, time period frequency values, storey drift , displacement, torsional irregularity etc). So,
different building shapes were put into analyses and comparisonoftheresultwasdonewithfloatingcolumnand flat slab as main feature in the buildings G+15 storey structures were analyse in three models of different horizontalandverticalgeometriesforstudyingbehaviorof floating columns in them and two models for studying behavior of flat slab buildings on above mentioned parameters. Also, comparison of economical value and stabilitybehaviorofG+20storeyhighrisebuildingwasdone for a normal beam column building and a building with floatingcolumnandflatslabbuilding wasdoneinStaadpro software as very less work done in this area in Staad pro software.
1.1. OBJECTIVES
ToCalculatetheDesignlateralforcesonfollowing structuresusingResponsespectrumAnalysis,Time history Analysis , and to compare the results of differentmodelsofRCCstructureshavingfloating column and flat slabs as feature in them using STAADproV8isoftware:
Vertically irregular model with floating column.G+15
Regularmodelwithsameheight.G+15
Horizontally irregular model with floating column.G+15
Horizontallyirregularmodelwithflatslab.G+15
Regularmodelwithflatslab.G+15
To study the variation in values of peak storey shear forfollowingmodels:
Verticallyirregularmodelwithfloatingcolumn.
Horizontallyirregularmodelwithfloatingcolumn.
Regularmodelwithsameheight.
Tostudythevariationinvaluesof baseshearfor followingmodels:
Verticallyirregularmodelwithfloatingcolumn.
Horizontallyirregularmodelwithfloatingcolumn.
Regularmodelwithsameheight.
Comparative Study on behavior of irregular & regular geometry multistory buildings with floating columns and flat slabs as feature under different parameters based on IS 1893:2016 Part 1 using STAAD Pro.1Aman khajuria Department of Civil Engineering M.TECH Structural Design. 2Sourabh Lalotra Assistant Professor Department of Civil engineering, 3Sri Sai College of Engineering & Technology, Badhani, Pathankot, Punjab
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Horizontallyirregularmodelwithflatslab
Regularmodelwithflatslab.
To study the variation in local displacement, memberstressvalues,storeydriftvalues
FordifferentsetofmodelsoftheseRCCstructures withfloatingcolumnandflatslabsasfeaturealso regularstructuresforreachingaconclusionofeffect ofshapeandirregularities(mass,stiffness,vertical geometryirregularities,torsionalirregularities)of different structures in results as per Is1893:2016 part1.
Step6:-Analysing the Result of Different Models of Multistorey structures on Different parameters.:Analysisofvaluesoftherunnedanalysisofdifferentmodels separately.
Step7:- Collecting the Result and discussion of the results. :-Noting down the result of analysis of different models and representing it in graphical method for comparingthevaluesforvariationondifferentparameters.
Step8:-Future scope of the project andconclusion.:-After reachingconclusionsfromtheanalysisofresultsofdifferent models looking for future scopeof development in design andanalysisofmultistorystructures.
Tocarryoutseismicdesignoffollowingmodelsfor studyofsafetyandeconomicalvalue
G+20floatingcolumnflatslabbuilding.
SameheightG+20normalbeamcolumnbuilding.
2. METHODOLOGY
Thestepsundertakeninthepresentstudytoaccomplishthe abovementionedobjectivesareasfollows:-
Step1:- Planning and plotting the models:-Different modelswereplannedandplottedafter reviewingexisting literatures/paperbydifferentresearchersandusingautocad forplotting.
Step2:-Modeling the Project in Staad pro software.Three modelsof27mx27mwith45mtrheight(G+15)foranalysis ofresultsoffloatingcolumnmultistoreystructuresonewith verticalirregularGeometry,onewithhorizontallyirregularL shape geometry and one with regular geometry vertically and horizontally. One model of flat slab horizontally irregularflatslabstructureandonewithregulargeometry flatslabstructureof27mx27mbasedimensionwithsame height( G+15).Two models of G+21 one with vertically irregular geometry and one with regular geometry were modeledinstaadprofortheanalysis.
Step3:-Defining the Project properties and Loads.:- Sizes ofcolumnsandbeamweredefinedwithdeadloadandlive loadsandsupports.
Step4:-Response spectrum and static analysis of the Models.:-Response spectrum for analysis of dynamic behaviorbymeasuringpseudospectralacceleration,velocity or displacement as function of structural period for given timehistoryandlevelofdamping.
Static analysis for flat slab system with constant loads applied and system being simulated does not depend on time.
Step5:-Running the Analysis of the Models. Analysing withfactorslikelocaldisplacement,peakstoreydrift,max absolutestressesetc
Table -1: GeneralLoadings:S.N O DESCRIPTION LOAD CODEUSED
Dead loads
1 Slab=180mm thickness floatingcolumnmodels 4.5kn/sqm IS875 Part1:1987
2 finishing 2kn/sq.m IS875 Part1:1987 3 Slab=275mmthickness Flatslabmodels. 6.875kn/sqm IS875 Part1:1987 4 finishing 2kn/sq.m IS875 Part1:1987
3.06kn/sq.m Avg. IS875 Part1:1987 6 230mmbrickwall3mht. 13.8kn/m IS875 Part1:1987 7 115mmbrickwall3mht. 7.5kn/m IS875 Part1:1987 8 Parapetwall 3kn/m IS875 Part1:1987 Live load
9. Loadonfloorcorridor 4kn/m IS875 Part1:1987 10. Liveloadterrace 2kn/m IS
Part1:1987 11 Zone5 0.36 IS1893:Part1 12 Importancefactor 1 13 Response reduction factor 1.5SMRF
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2.1 BRIEF DESCRIPTION :
Various models of the multistory structures with flat slab and floating column as feature were analysed in staad pro for variation in seismic response with respect to shape using response spectrum method as per IS1893:2016 part1 and alsoforotherparametersofirregularitycheckingof thesemodelssuchaspeakstoreyshear,baseshear, memberstresses,lateraldisplacementperstorey of structureandvariationofscalefactorvalueforeach modelaccordingtoshapeandatlastinmodel6and model 7 analysis for earthquake design and comparisonforeconomicalvalueofconstructionof floatingcolumnflatslabbuildingandnormalbeam column building was studied through design of boththemodelsandnoticingthevalueofsteeland concreteused.
MODEL 1: Verticallyirregularmodelwithfloating column G+15 studied for seismic response using responsespectrummethod.
MODEL1:
MODEL2: Regular model with same height G+15 studied for seismic response using response spectrummethod.
MODEL3: Horizontally irregular model with floatingcolumn.G+15studiedforseismicresponse usingresponsespectrummethod.
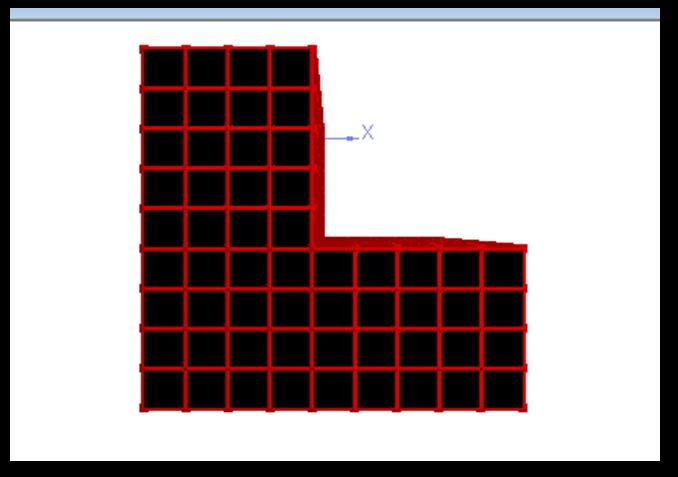
MODEL 2:
MODEL4: Horizontally irregular model with flat slab G+15 studied for seismic response using responsespectrummethod
MODEL5: Regular model with flat slab G+15 studied for seismic response using response spectrummethod.
MODEL3:
MODEL6: Flat slab floating column combination structureG+20studiedforearthquakedesignand winddesignanddesignedforeconomicalvalue.
MODEL7: Normal beam column structure G+20 studiedforearthquakedesignandwinddesignand designedeconomicalvalue.
CODES USED:
1 IS456:Codeofpracticeforplainandreinforcedconcrete.
2. IS875:Endsofpracticefordesignloadspart2imposed loads.
3. IS1893:2016:-Criteriaforearthquakeresistantdesign.
MODEL 4:
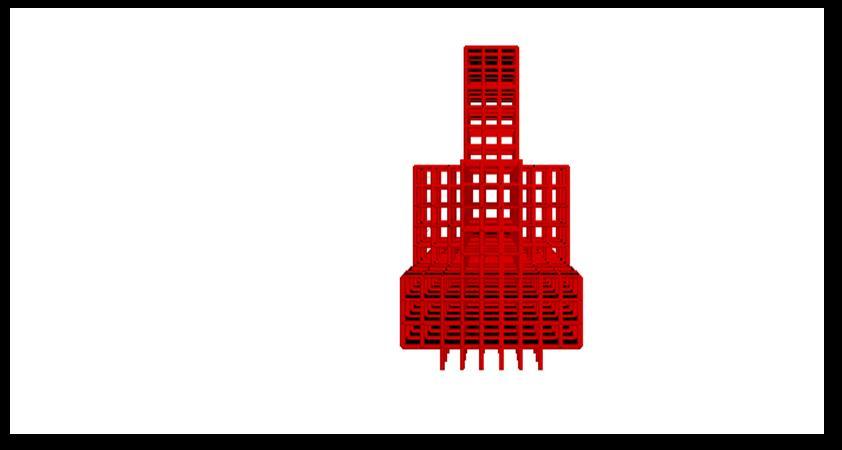
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

MODE1 MODE2 MODE3 MODE4 MODE5 MODE6

3. CONCLUSIONS
Various types of irregularities according to IS 1893:2016 Part1 were studied in different models of RCC multistory structureswithfloatingcolumnandflatslabasmainfeature inthemwithResponsespectrumanalysisinfirst5models andearthquakeanalysisandstudyofeconomicalvalues in model6and7bydesigningandresultswerecompared.Our resultscanbesummarizedasfollows:-

1.Modeshapesdeterminethedeformationintheshapesof the structure under earthquake conditions and results showsthatmodeshapeshashighestvalueforahorizontally regular G+15 structure as compared to other structures suchasaG+15verticallyirregularstructureandhorizontally irregularstructurewithsameheight withfloatingcolumn andforflatslabstructureirregular®ularshapedflatslab structure has almost same value for all mode shapes in dynamic analysis from response spectrum method thus, showingmassinregularshapedstructureisalmost twice as compared to vertically irregular and horizontal irregular structurethusshowingmass regularityismoreinthistype of structure for high rise building . Thus, concluding that heavystructuresvibratesslowly.
2.Frequencycycle/secandfrequencyperiodvaluesshowsa inverserelationshipintheanalysisoffirst5models.Thus, showingthatcycle/secwerelowerforheavystructures.
3.Peak storey shear values in the analysis of first three models shows that model with regular shaped G+15 structurehashighervaluethanothertwomodelsi.emodel1 andmodel3andstorey2showshighestvalueandstory14 showslowestvalueinallthestructuresrespectively.Thus, showing that lateral force acting due to seismic pressure weremaximumforregularshapedbuilding.
4.Base shear value is the total lateral force acting on buildingatitsbasewhichisequaltostoreyshearinbottom storey and was highest in model 2 and was highest for modes 1&2 .Thus,concludingthatshearwalls need to be employedshearforcesinregularbuildingmodel2andmodel 5incaseofflatslab.
5.Responsespectrumvaluesforgeneralizedweightshows thatregularflatslabG+15storystructureshowedhighest valueforthemodesandspeciallymode6.Thus,concluding thatvibrations werefasterinthisstructureasstiffnesswas high.
6.NaturalfundamentalTimeperiod valueswashighestfor flat slab building thus showing greater mass and stiffness andSa/gspectralacceleration valuewashighestforfloating columnstructuresshowinggreaterspectralaccelerationor displacement.
7.Local displacement value was highest for model 2 G+15 regularhorizontal structure. Thus,showing thatstructure withlongerperiodshowsgreaterdisplacement.
8.Intheanalysisofmemberstress(momentsperunitwidth) values model 1 showed highest value for 3 members compared to model 2.Thus, concluding that a regular planned structure is under lesser member stresses as comparedtoverticalgeometricallyirregularstructure.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
9IntheanalysisofstoreydriftforaG+15floatingcolumn structure and a flat slab structure Dmax/Dv i.e (0.8 for model3and0.3formodel4)valuesforboththestructures werelessthan1.2or1.4. Thus,rulingoutanypossibilityof torsionalirregularityforbothtypesofstructures.
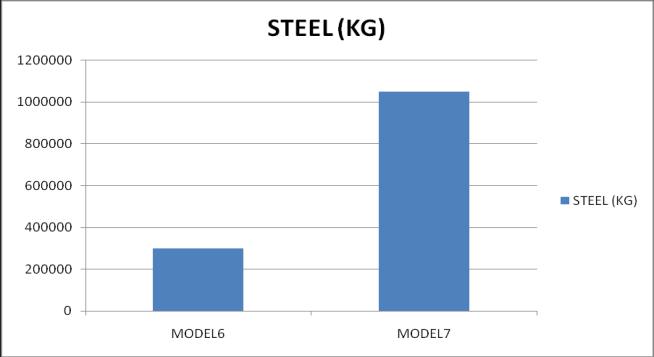
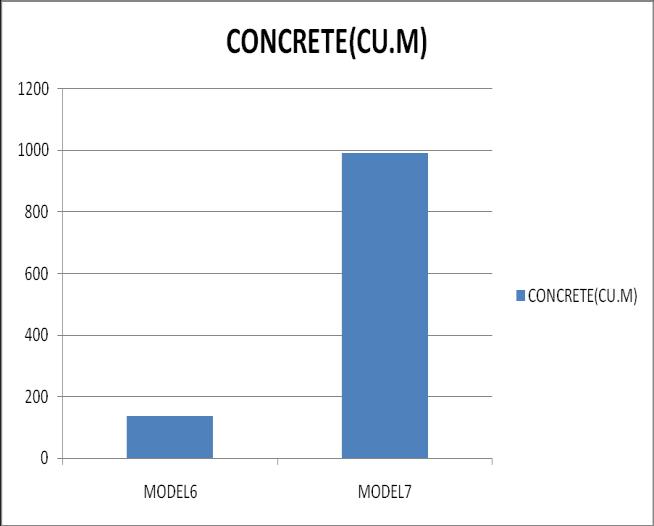
10. A floating column flat slab G+20 irregular structure utilized a much less quantity of steel and concrete etc as comparedtosameheightnormalbeamcolumnstructurebut withlowerstabilityas seismicweight wasalsogreaterbut stiffness was almost same in both structure but natural fundamentaltimewasslightlesserinmodel6.
11.Vbvaluewaslowestingeometricallyirregularstructure infloatingcolumnstructureandhorizontallyirregularflat slabstructureandnormalbeamcolumnstructureinanalysis of types of structures as compared to other geometry structures. Thus, showing that these structures have less seismicweightascomparedtoothers.
REFERENCES
“Influence of combine vertical irregularity in the response of the earthquake resistance RC structure”inIRJET.
Bureau of Indian Standards: IS-875,Part 1, Live loadsonbuildingsandstructures,NewDelhi,India, 1987
Susanta Banerjee and Dr. Sanjaya K Patro, "Structural Economics of Seismic Resistant RC Building with Floating Column", 55th Annual Technical,JournalofOrissaStateCentre,Institute ofEngineers(India),2014,pp.211-217.,
Onkar V. Sapate, “Interrelationship between moment values of columns in a building with different architectural complexities and different seismiczones”,InternationalJournalofEngineering Research and Development, Volume 5, Issue 2 (December2012),Pp.55-59..

RavikumarCM,BabuNarayan KS,SujithB,Venkat Reddy, “Effect Of Irregular Configurations On Seismic Vulnerability Of RC Buildings” , Architecture Research 2012, 2(3): 20-26 DOI: 10.5923/J.Arch.20120203.01
BIOGRAPHIES
Karthik.K.N,VidyashreeD(2015),“Effectsofthe steel bracing on vertically irregular RCC building framesundertheseismicloading”.
IS 1893(Part1)-2002 code, “Earthquake resistant designofstructures”.
Dr.VinodHosur,Atextbook“Earthquakeresistant design of building structures”. [6] Bryan Stafford Smith, Alex Coull, A text book “tall Building structures”
A.D’Ambrisi, M. De Stefano, S. Viti(2008)“Seismic performance of irregular 3D RC frames”.The 14 World Conference on EarthquakeEngineering.
IS456:2000,”Plainandreinforcedconcrete-Codeof practice” Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi, 1995.
IS:875(part–3)-1987codeofpracticefordesign loads for building and structures-Dead loads.
IS:875(part–3)-1987codeofpracticefordesign loadsforbuildingandstructures-Imposedloads.
Bureau of Indian Standards: IS-875,Part 1, Dead loadsonbuildingsandstructures,NewDelhi,India, 1987
Er.Amankhajuria Diploma in buiding design softwares. Building construction consultant Engineer.
