Seismic Response Study and Evaluation of Vibration Control of HighRise Structures: Viscous Fluid Damper, Viscoelastic Damper, Friction Dampers, Mass-Tuned Dampers(Vibration
I. ABSTRACT
The large engineering building structures are very expensive and too much intricated to maintain due to their chances of failure under various hazardous conditions. These buildings are needed to be protected against the damage due to the hazards conditions viz. earthquakeandseismicwaves.Dampingactsavitalrole in earthquake resistant structural design which decreases the response of the building when they are subjected to the lateral forces. In order to have these structure earthquakes resistant fluid viscous damper, viscoelastic dampers, friction damper, MR damper, pendulum mass tuned dampers are used. This paper studyalsodealswithassessingtheperformanceoffluid viscous damper, viscoelastic dampers, friction damper, MR damper, pendulum mass tuned dampers to reduce theseismicresponseofhigh-riseirregularstructures My main aim is to study a high-rise composite structural modeltoanalysedifferenttypesofanalysisandshowmy modelasanearthquakeproofstructure.
Keywords: Seismic response, fluid viscous damper, viscoelastic dampers, friction damper, MR damper, pendulum mass tuned damper, time history analysis, vibrationmechanism.
II. INTRODUCTION

In earthquake engineering vibration control devices are used to mitigate the seismic impact in different structural member. The main goal of earthquake resistant design to attain a structure with sufficient strength and ductility to assure life safety. Nowadays, three basic technologies are used to protect buildings from earthquakes effects. These are base isolation, passive energy dissipation devices and active control devices. A variety of passive energy dissipation devices (such as viscous dampers, viscoelastic dampers and friction dampers) have been developed. Including these MR dampers and Pendulum tuned mass damper (TMD) will also be implemented.
Damper) and MR Dampers
III. DETAIL DESCRIPTION OF DIFFERENT DAMPERS
a. Viscous Damper (VD)
Viscous dampers of varieties of materials & damping parameters were proposed and developed for seismic protection. Viscous fluid dampers commonly used as passiveenergydissipationdevicesforseismicprotection ofstructuresareprincipallycomposedofa pistonrod, a piston head and a cylinder filled with a viscous fluid. Fluidviscousdamperswhichoperateontheprincipleof fluid flow through orifices are installed in a number of structural applications. Example of construction of viscousfluidviscousdamperisshowninFig:1.
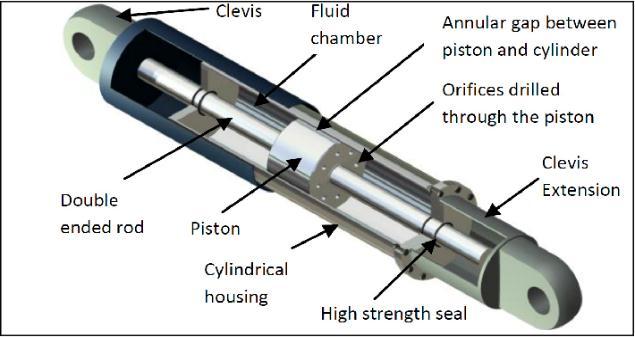
Figure 1.Viscous FluidDamper
b. Viscoelastic Dampers(VED)
Viscoelasticdampers have beencojoinedin a numberof high structures as an effective power or energy dissipating system to restrain wind and earthquake induced motion of heavy high structural system Viscoelastic Damper spatters the tall structure system'smechanicalenergybyconvertingitintoheat.
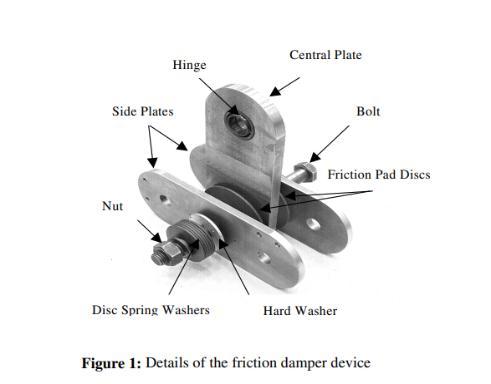
c. Frictiondamper
A friction damper device was designed to diminish and absorb the input energy in order to increase the building’s safety from natural disaster. It can be used in retrofittingorindesigningofnewbuildings.Thefriction
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume:09Issue: 08|Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
damper was tested intensively in order to verify its characteristics and performance. This device consists of
several steel plates that rotate against each other in oppositedirections,producingfrictionbetweenitsparts.
Tuned mass dampers stabilize against violent motion caused by harmonic absorber These types of dampers are used as a lightweight component to reduce the vibration of a system so that, in worst-case condition vibrationswillbeveryless.Thenaturalfrequencyofthe tuned mass damper is basically defined by its spring constant and the damping ratio determined by the dashpotsystemselements.
IV. LITERATURE REVIEW
d. Magnetorheological Damper (MR Damper)
Magneto-rheological dampers more commonly called as MR dampers. MR damper is also called as an intelligent damper. It is used for controlling the vibration of automobilesuspension.
The advantages of MR dampers arethat, (i) this type of dampers required very less control power, (ii) whose construction mechanism is very simple, (iii) Due tothissimpleconstructionmechanismithasalsoa very quick responsemechanism tocontrol thesignal and (iv) ithaslessnumbersofmovingparts.MRdampershavea lot of potential technology to deal with semi-active control power system. It is very much important to understandthedynamicbehaviourofsuchdevices.
Magnetorheological (MR) fluids, are different type of materials that, respond to an applied magnetic fieldwithaglitteringchangeinrheologicalbehaviouri.e; the branch of physics that deals with the deformation andtheflowofmatter,speciallythenon-Newtonianflow of fluid and the plastic flow of solids In the absence of magnetic field MR fluid act in a state of free-flowing liquid state But under the strong magnetic field it’ s viscosity can be increased by more than two orders of magnitudeinveryveryshorttimeanditexhibitsasolidlike characteristics. The strength of an MR fluid can be describedbyshearyieldstress.
e. Pendulum Tuned Mass Damper or Vibrationdamper
A mass tuned damper is called seismic damper. It is alsocalledharmonicabsorber.ItisSpecialtypeofdevice whichisusedinthestructurestominimizethevibration. TMD is used to prevent the discomfort, damage of the structures These types of dampers are used in power transmission, automobiles and high-rise buildings.
Analytical computations which were conducted by Shaik Khadervali et. al. [1] highlighted about the displacement, shear and moment which were compared for two models i.e., w/o dampers & with dampersattopstoreyofahighrisebuildinginzoneIII & zone -V in each soil and it was observed that 50% (approx.) displacement, shear and moment were reduced when the dampers were provided at eachelevation.
Mitsuo Asano et. al. [2] concluded based on their studyaresummarizedasfollows: Basedondynamic loadingexperiment,themechanicalpropertiesofthe damperswereroughlydividedintotwogroups.The first group showed non-linearity and reaction force degradation with small dependency on frequency. Thesecondgroupshowednoticeabledependencyon frequency, but non-linearity and reaction force degradationwassmall.Themechanicalmodelofthe dampers, which had dependency on frequency, was modelled by using ARX method. As the results of earthquakeresponseanalysisofabuildingequipped with VE dampers, the inter-story displacement as wellastheaccelerationresponseofthebuildingwas reduced.
Sang-Hyun Lee et. al. [3] presented a procedure for the optimum design of the VED by assigning eigenvalues required to achieve the desired structural response. Their optimization method providesinformationontheoptimallocationaswell as the magnitude of the damper parameters to achieve a given target by thorough study of the numerical analyses of a 10-story shear building and a plan-wise asymmetric structure. Their proposed methodcanprovidea reasonabledistributionofthe VED in structures with a symmetric or an asymmetric plan to meet a given target displacement.
Waseem SARWAR [4] describes that, DMA is a hypersensitive approach for investigating the dynamic scope of VEM. Dynamic properties of VE material are investigated, the DMA (Q800) apparatus reported fair differences in properties at
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume:09Issue: 08|Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
various frequencies and temperatures. Storage modulus, loss modulus, and loss factor increases with the increase in excitation frequency and decrease as the temperature increases.
Majd Armali et. al. [5] describes the results presented in this study for the nonlinear modal timehistoryanalysiswerecarriedoutonahigh rise reinforced concrete building formed by 40 storeys. They were represented by storey responses and time history plots for various parameters. They illustrate that the incorporation of friction dampers into the structure reduces considerably the building responsecomparedtoaconventionalshearwall system for the same building. The results analysis of structural period, roof displacement, storey displacements, roof acceleration and storey accelerations show a considerable reduction by using dampers against the conventional building without damping by optimizingtheirnumbersandlocations.
S. Lakshmi Shireen Banu et. al. [6] describes about the storey responses from the time history analysis in terms of PSA, PSV and SD have been reduced with the use of friction dampers.TheresponsespectrumcurvesofPSA, PSV and SD shows the reduction over time periodwiththeuseofdamperscomparedtothe buildings without dampers. The base shear in case of building with damper can be attributed to the increased mass by addition of damper bracesystemateachstoreylevel.Theresponses can be further reduced by the selection of damper,positionofdamper andshapeandtype ofconstructionofthebuildinginvolved.
Claude PASQUIN et. al. [7] providetheanalytical studies have shown that the friction-damped structure should perform well in the event of a majorearthquake.Astheseismic forces exerted on the structure are significantly reduced, the systemofferedsavingsinupgradecosts.Theuse of friction dampers has shown to provide a practicalandeconomicalsolutionfortheseismic upgradeofthebuilding.
Hongyan Gu et. al. [8] describesintheirarticle,a reliable earthquake protection system is developed using ACO optimization and decentralization mechanism in order to provide the protective scheme for tall building survivability as well as to safeguard the occupants. A dynamically decentralized approachisproposedinthisworkusingthePID controller for the self-regulation during the faulty condition in case, any of the sub-system goes down. The combination of optimization, decentralization and self-regulation provides betteroutcomesforthenumerical simulationof tracking and control mechanism during the earthquakescenario.
S K Mangal et. al. [9] describe in this paper, the optimization of geometric and response parameters of an MR damper using statistical tools coupled with FEM is presented. The geometric parameters are searched between lower and upper bounds having two/three levelsforeachoftheseparameters.Theprocess illustratedintheirpaperwillbeusefulforfuture automotive design engineers for predicting an optimizeddampingforceofanMRdamper.
Bhagyashree et. al. [10] describe about the placementofdamperindifferentpositionshows variation in the response of the structure and the force produced by the MR damper. When damper placed in any of the floor shows reductionintheresponsebutdamperpredicted forceandresponsecontrolvary.Therefore,from the result it can be inferred that MR damper placement in first floor is better situated to mitigate response of the structure because the force required to reduce the response is small when compared to other positioning of MR damper.
M. Setareh et. al. [11] describe this paper presentedastudyofPTMDstocontrolexcessive vibrations of floors. From the results presented here it can be concluded that PTMDs can provideapracticalmethodofvibrationcontrol.
V. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
1.) To model the “High-Rise Composite Structure”RCC and steel framed structure located in seismiczone-VregionofIndia.
2.) Structural modelling will consist of both: composite structure with and without incorporationofdampersatfoundationlevel.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume:09Issue: 08|Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
3.) Conduct “Response Spectra Analysis” for earthquakeinaccordancewithIS1893:2016.
4.) “Seismic Performance Evaluation” with and without various types of dampers: viscous dampers, viscoelastic dampers, friction dampers,MRdampers,MassTuneddampers.
5.) Conduct comparative study on all structural models based on following parameters: Lateral Force Distribution (Q), Base Shear (Vb), InterStorey Drift (∆interstorey), Load vs Rooftop DisplacementGraph(Pvs∆rooftop).
6.) Recommendincorporationofdampersidealfor thebuildingmodel(amongalldampers)
7.) CostAnalysis.
VI. CONCLUSION
Thefundamentalideasofdifferentdampersand seismiccontroldevicesarecoveredinthisstudy along with recent advancement and applications. The observation suggests that a varietyof technologies canbeutilizedto reduce seismicresponse.
Accepted: 16th November 2019, RESEARCH ARTICLE,WILEY.
2. S. Lakshmi Shireen Banu et. al. (2017), “Seismic Response Study and Evaluation of Vibration ControlofElevatedRCCStructureusingFriction Damper”, International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE) ISSN:2278-3075,Volume-8Issue-7,May,2019.
3. Adithya G. S et.al. (2016), "Performance evaluation of friction dampers under seismic loads”, IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 23191163|pISSN:2321-7308
4. Claude PASQUIN et. al. “Friction dampers for seismic rehabilitation of Eaton's building” , MONTREAL, 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vancouver, B.C., Canada,August1-6,2004PaperNo.1949
5. N. Priyanka1 et. al. “Seismic study of multistorey structure with fluid viscous dampers using Etabs”, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), e-ISSN: 2395-0056,Volume:06Issue:04|Apr2019
Generally, when an earthquake strikes a building or other structure, seismic waves penetratethebuildingandinducevibration.The seismic dampers then come into play and thus minimize the damaging effect and enhance the seismic performance of the structure. These are extensively used in buildings and bridge construction.Seismicdampersareusedinplace of structural elements such as a diagonal brace. These dampers are used- to protect the structure against earthquakes, to reduce the structural damages andincrease the strength of the structure, to decrease the effects of the seismicforcesandtoreducethedeformationsof thestructure.
6. Puneeth Sajjan et. al., “Study on the effect of viscous damper for RCC frame structure” , InternationalJournalofResearchinEngineering and Technology EISSN: 2319-1163 | PISSN: 2321-7308
7. SHAIKKHADERVALI et.al.,“SeismicAnalysisof a High-Rise Building with Viscous Dampers Using Etabs”, International journal of scientific engineering and technology research, ISSN 2319-8885, Vol.05, Issue.41, November-2016, Pages:8590-8596
Viscous dampers arevery efficient in absorbing minor as well as strong earthquakesas well as wind. Due to this reason, such dampers are extensivelyused in high-rise buildings. Viscous dampers can function at ambient temperatures rangingfrom40degreesto70degreesCelsius
VII. REFERENCES
1. Majd Armali et. al. “Effectiveness of friction dampers on the seismic behaviour of high rise building VS shear wall system”, Received: 28 October 2019 Revised: 15 November 2019
8. SU MYAT AYE et. al., “Comparative Study on Seismic Responseof RCStructureUsingViscous Dampers and Viscoelastic Dampers” , International journal of scientific engineering and technology research, ISSN 2319-8885, Vol.03,Issue.08,May-2014,Pages:1468-1478
9. Waseem SARWAR, “Viscoelastic material as energy dissipater viscoelastic damper for building structures to mitigate the seismic vibration”, CIVIL AND ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING REPORTS, CEER 2019; 29 (2): 041-049,DOI:10.2478/ceer-2019-0015
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume:09Issue: 08|Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
10. Sang-Hyun Lee et. al., “Optimal design of viscoelastic dampers using eigenvalue assignment”,EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERINGAND STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS, Earthquake Engng Struct. Dyn. 2004; 33:521–542 (DOI: 10.1002/eqe.364)
11. M.H.Mehrabi et.al.,“Modellingofaviscoelastic damper and its application in structural control” , PLoS ONE 12(6): e0176480. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176480, Editor: Jun Xu, Beihang University, CHINA, received: January 12, 2017, accepted: April 11, 2017,Published:June1,2017.
12. P.C.Chenet.al.,“Timedelaystudyonthesemiactive control with a magnetorheological damper”, The 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, October 12-17, 2008, Beijing,China.
13. Bhagyashree, Kavyashree, “Effectiveness of Magneto-Rheological Damper Placement in SeismicVibrationControl”,InternationalJournal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE) ISSN: 2278-3075, Volume8Issue-10,August2019.
14. Hongyan Gu et. al., “Research on vibration mechanism and control technology of building structure under earthquake action”, JOURNAL OF VIBROENGINEERING. SEPTEMBER 2021, VOLUME23,ISSUE6.
15. S K Mangal et. al., “Geometric parameter optimization of magneto-rheological damper using design of experiment technique” , Mangal and Kumar International Journal of Mechanical and Materials Engineering (2015) 10:4, DOI 10.1186/s40712-015-0031-1.
16. Dr. Mohan M. Murudi et. al., “Seismic effectiveness of tuned mass damper (TMD) for different ground motion parameters” , 13thWorld Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vancouver, B.C., Canada, August 16,2004,PaperNo.2325.
17. WenshuoMaet.al.,“OptimizationandTuningof Passive Tuned Mass Damper Embedded in Milling Tool for Chatter Mitigation” , J. Manuf. Mater.Process.2021,5,2.
18. NamHoangaet.al.,“Optimaltunedmassdamper for seismic applications and practical design formulas” , Engineering Structures 30 (2008) 707–715.
19. M. Setareh et. al., “A study of the application of the pendulum tuned mass dampers in building floor vibration controls”, High Performance Structures and Materials II, C.A. Brebbia & W.P. De Wilde (Editors) © 2004 WIT Press, www.witpress.com,ISBN1-85312-717-5
20. Mohammad Reza Arefi, “an analysis of viscous dampers impact on controlling the vibrations imposed on seismic vibrations”, journal of critical reviews, issn- 2394-5125 vol 7, issue 1, 2020
