International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1 T.Y. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Vishwakarma Institute
***
Abstract – Various manufacturing techniques are used by different industries in the productionofdifferent equipment or spare parts of complex machines and mechanicalassemblies. A place where metal is molten and allowed to solidify to give it a desired shape is called a foundry. Casting, being one of the most ancient and convenient techniques, is used inthe making of complex parts of various centrifugal pumps, motors, automobiles, etc. where the metal has to go through various physical phases throughout the manufacturing process. However, many supplementary steps need to be taken to ensure a good quality of casting in order to avoid failure ofthe entire mechanical system.
Keywords – industries, machinaries, foundry, casting, quality, failure
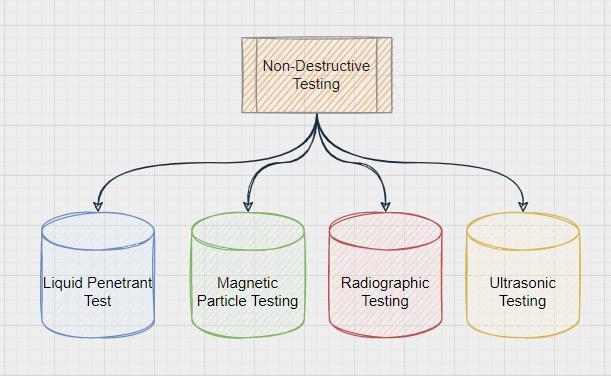
The following paper briefly mentions the different steps involvedinthemanufacturingofvarioussteelcomponents such as automotive spares, engine blocks, machine tool bases,cylinderheads,centrifugalpumps,etc.usingthesandcastingmethod.Sandcastingisthemostwidelyusedcasting method.Theadvantageofusingsandtomanufacturemetal products is that sand is very resistant to elevated temperatures.Almostallmetalcastingmaterialscanbesand cast and these castings range in size from very small to extremely large. It also explains the other necessary measures that need to be taken to prevent failure of the castingandenhanceitsstrengthanddurability.Thepaper clearlymentionsthevariousscientificprocessesalsocalled as foundry processes in a step-by-step manner such as pattern making, core making, molding, melting, pouring, decoring, knockout, various cutting processes, heat treatmentcycles,shotblasting,machining,fettling,grinding, dimensionalrework,acidpickling,non-destructivetesting, finishing,punching,etc.,eachbeingequallyimportantfrom thepointofviewofthequality,durabilityandidentityofthe casting.Also,themicrostructureofthematerial,alsocalled as grain structure, plays an important role in defining the properties of the entire casting. The following paper also focuses on the various heat treatment techniques used to obtain a definite microstructure to impart the desired propertiesinthecasting.
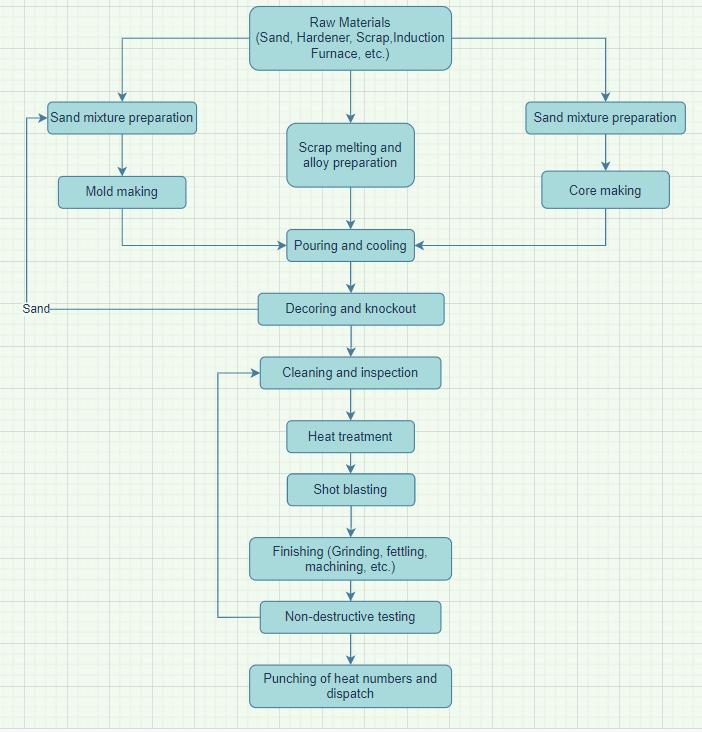
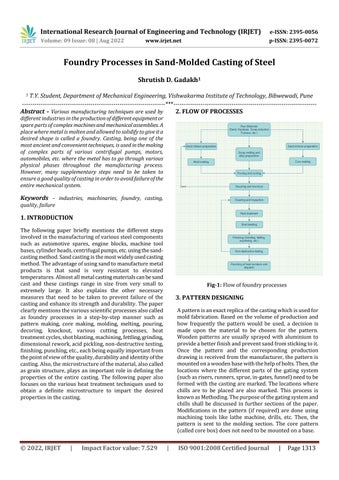
Fig-1: Flowoffoundryprocesses
Apatternisanexactreplicaofthecastingwhichisusedfor moldfabrication.Based on thevolumeofproduction and how frequently the pattern would be used, a decision is made upon the material to be chosen for the pattern. Wooden patterns are usually sprayed with aluminium to provideabetterfinishandpreventsandfromstickingtoit. Once the pattern and the corresponding production drawingisreceivedfromthemanufacturer,thepatternis mountedonawoodenbasewiththehelpofbolts.Then,the locations where the different parts of the gating system (suchasrisers,runners,sprue,in-gates,funnel)needtobe formedwiththecastingaremarked.Thelocationswhere chills are to be placed are also marked. This process is knownasMethoding.Thepurposeofthegatingsystemand chills shall be discussed in further sections of the paper. Modifications in the pattern (if required) are done using machining tools like lathe machine, drills, etc. Then, the pattern is sent to the molding section. The core pattern (calledcorebox)doesnotneedtobemountedonabase.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
It is the process of forming a solid sand core so that the actualcastinghasthedesiredshapedcavity.
A suitable composition for the sand-hardener mixture is chosenandpreparedandthebottomhalfofthecoreboxis filled with this mixture. Properly shaped metal rods are placedinthecoreboxforprovidingadditionalstrengthto the core if required, depending on the size of the core. Thermocolorwaxstripsarethenplacedinthesandcoreat appropriate locations which melt during the oven preheatingprocessthus,allowingthegastoescapefromthe core formed. This is very important to avoid crack formationandweakeningofthecore.Anumberofchillsare placed in the core at appropriate locations so that they absorbsomeoftheheatduringthesolidificationprocessof moltenmetalandimprovethecoolingrateofthecasting. Thenthetophalfofthecoreboxisplacedandclampedto the bottom half to prevent core expansion during preheating.Thesandmixtureisalsoaddedinthetophalfto completethecore.Risersareplacedwhereverrequiredin thecore.Severalvoidsarealsocreatedinthecoretoallow air to escape during preheating. Removal of excess sand takesplaceandthecoreisleftundisturbedforaspecified timetoharden.Thehardeningtimedependsuponthetype ofhardenerused.Thecoreissentfordressingandpainting whereitisspraypaintedwithaninflammablemixtureof paintandthinnerwhichissetonfiresothatthemoisturein the core gets removed. The core is then placed in the preheating oven for 5-6 hours for further hardening and moistureremoval.Thenthecoreissenttothecoresetting section where it is placed between the two halves of the moldbeforesendingittothepouringsection.Thisisdone byplacingthecoreinthedrag(bottomhalfofthemold)and thenplacingandgluingthecope(tophalfofthemold)over it.
Itistheprocessofformingamoldofthedesiredshapethat is further filled with molten metal to form the desired shapedcasting.
Themoldisfirstdividedintotwohalvesviz.cope(tophalf) and drag (bottom half) and the two halves are formed separately. The mold pattern is placed into the mold box andaccessorieslikethefunnel,sleeves,L-blends,firebricks, etc. are placed at appropriate locations for forming the gatingsystemalongwiththecasting.Thesand-hardenerresinmixtureispreparedwithsuitablecompositionandthe moldboxisfilledwiththissandmixture.Thesandisthen pressedtightlyinthemoldboxandthenallowedtosolidify. Theaboveprocessescanbedonemanuallyorwiththehelp
of machinaries depending upon the size of the mold. The hardenedmoldisthenspraypaintedwithpaintandthinner mixturewhichissetonfiretoremovethemoisturefromthe mold. Both the mold halves are passed through the preheating oven for further hardening and moisture removal.Thenthecorrespondingcoreisplacedinthedrag andthecopeistheninvertedandplacedoverthedragand gluedtoittoformthecompletemoldwhichisthentakento thepouringsection.
Fig-2: Arrangementofcompletemold
Scrapcollectedfromvarioussourcesisfirstsegregatedas perthematerialgrade.Thescrapisfirstheatedinanoven beforesendingittothefurnacesothatitmeltsquicker.The furnace used is an induction furnace where a number of copper coils are present around the furnace and carry a huge current that creates an electric field and induces a current(Eddycurrent)inthescrap.Thisresultsinheating of the scrap and melts it. These furnaces are lined inside withrefractorymaterialtopreventmeltingofthefurnace walls.Temperatureofthefurnaceismaintainedabovethe meltingpointofthematerialgradeandthetemperatureof the molten metal is checked frequently using a thermocouple. Supply of Argon gas is provided through pipes at the bottom of the furnace. This gas, being inert, doesnotreactwiththemetalbutliftstheimpuritiespresent in it. These impurities are adsorbed by the slack powder sprinkledoverthefurnace.SpecificamountsofAluminium (ingot and shots) and Calcium Silicide are added to the moltenmetalfordeoxidationofsteel.Otherwise,reactionof themetalwithoxygenmayalteritsproperties.
Themoltenmetalispouredintocertainladlesthatarelined inside with refractory material. The lining is done to preventtheladlesfrommeltingasthetemperatureofthe
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
moltenmetalisveryhigh.Also,theladleisfirstheatedtoa certaintemperaturebeforepouringmoltenmetalintoitto reducethecoolingrateofthemetal.Otherwise,themolten metalmaysolidifyevenbeforereachingtheentiremould thus, resulting in undesirable casting. Ladles are of two types viz., lip pouring and bottom pouring and have a steeringtocontroltheorientationoftheladle.Lippouring ladlesneedtobetiltedtopourthemetalwhereasbottom pouring ladles have an opening at the base that can the openedorclosedbyliftingorreleasingaheavyrodcalled bottompouringrod.Slackpowderisthensprinkledontop of the ladle to remove impurities. The lid of the ladle is covered with an insulating material like glass wool to preventheatlossestothesurrounding.Moltenmetalisthen poured in the pouring basin and is further carried to the entiremoldbythegatingsystem(sprue,runners,in-gates, risers). Also, the gas in the mold is allowed to burn to preventitfromgettingtrappedinthemold.Ariser(feeder) isusedtopreventcavitiesinthecastingthatcanformdue toshrinkageofthemetalonsolidification.Thisisdoneby providingexcessmetaltothemoldsothatthecavityforms in the riser and not the casting. Anti-piping Compound (APC) powder is then added on top of the riser opening. Thishasthefollowingadvantages.Firstly,itprevents the sparks of the molten metal from reaching the workmen. Also, the metal in the riser is exposed to atmosphere because of which the cooling and solidification may start fromtheriseritselfwhichisundesirable.AdditionofAPC breaks this exposure and the use of sleeves (made of exothermicmaterial)keepsthemetalintherisermoltenfor a longer duration than the casting. The casting cools at a comparatively faster rate due to the presence of chills. A smallamountofmetalispouredinasample/testmoldthat isfurtherusedforinspectingthequalityandpropertiesof thecasting
Boththetestsampleandthecastingareallowedtosolidify andthentakentothecastingdecoringareawherethemold isbrokendownandthecastingisremoved.Thepiecesof sand mold are sent to the knockdown section by a motorizedtrolleywhereheavyvibrationsofthecontainer resultin breakdown ofthe moldpieces to finesand.This sand, being a mixture of various sands, is sent for purificationandreuse.Thecastingcanalsoberemovedin theknockoutsectionitself.Thecastingisthenallowedto coolusingairquenchingorwaterquenching.
Afterthecastingiscooledbyquenching,itistakento the cuttingandgougingsectiontoremovetheunwantedparts that are not required in the casting i.e., funnel, risers, runners,gates,sprue,etc.
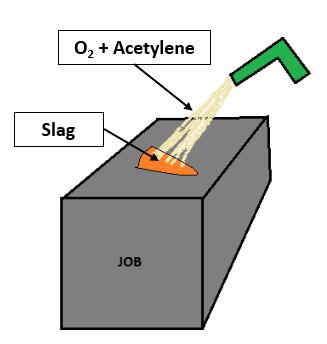
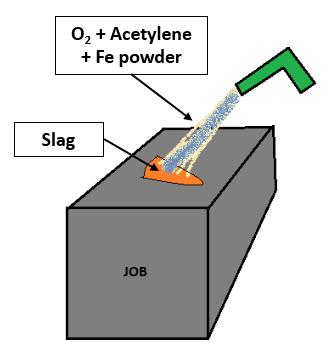
Gas cutting: Mixture of oxygen and Acetylene is used to preheatthemetaltoitsignitiontemperature(forsteel,700900 degree Celsius) but below its melting point. A jet of oxygen is directed into the preheated area initiating a vigorousexothermicchemicalreactionbetweenthemetal and oxygen to form a metal oxide or slag. The oxygen jet blowsawaytheslagenablingthejettopiercethroughthe material and continue to cut through it. Ignition temperatureofthematerialmustbelowerthanitsmelting point otherwise, the material would melt and flow away before cutting. Oxide melting point should be lower than that of the surrounding material so that it can be mechanically blown away by the oxygen jet. Oxidation reaction between the oxygen jet and metal must be sufficienttomaintaintheignitiontemperature.Minimum gaseous reaction products should be formed so as not to dilutethecuttingoxygen.
Powdercutting: Itissimilartogascuttingwithanaddition ofironpowdertotheoxygenjet.Stainlesssteel,castiron, nonferrous metals form refractory oxides (Oxides whose meltingpointishigherthanthematerial).Hence,powderis injectedintotheflametoformafluidslagwithlowmelting point. Acetylene, propane, MAPP (Methylacetylenepropadiene),propylene,naturalgasarethecommonlyused fuel gases among which acetylene produces the highest flametemperature.
Fig-3: Gascutting
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
tomaintainauniformtemperaturethroughoutthecasting. The temperature at different locations within the casting aremeasuredusingthermocouples.
Rodgouging(Aircarbonarc gouging):Itistheprocessof removingmaterialbymeansofheatgeneratedbycarbon arc.Itremovesexcessmaterialfromcastingandrequiresa carbon/graphiteelectrode,compressedair,standardpower source (like welding rectifier). An intense electric arc producedbetweentipofrodandworkpiececutsandmelts theworkpiece.Compressedairisusedforblowingawaythe molten metal thoroughly from the casting surface. The metalisgouged(cut)intheairflowdirection.Itisusedto remove excess weld beads also. The power source must haveaconstantcurrentoutputcharacteristicotherwise,the highvoltagecurrentcancausetheelectrodetiptoexplode whentouchedtotheworkpiece.Coppercoatingisgivento the graphite rod to reduce electrode erosion. Sometimes, waterispouredsimultaneouslyonthesurroundingareato preventitfromcrackingduetoexcessheat.
Process of heating the casting below its melting point to relieveinternalstressesdevelopedbyforging,weldingor duringsolidificationitself.Itisusedtoincrease/decrease hardness of the material by achieving the desired grain structure.
Processesinvolved:
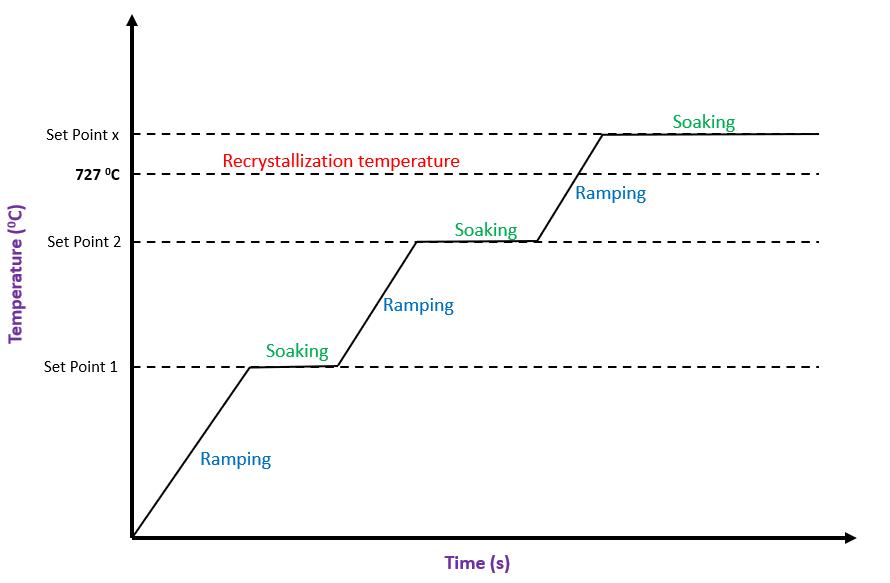
Theheattreatmentfurnacesarefirstlinedwithinsulating material(glasswool)ontheinsidetopreventheatlosses. Heat treatment process is controlled by heat treatment furnacecontrolpanel.Thefurnacetemperatureisincreased to a specific set point in multiple cycles. This process is calledasRamping.Thestartingtimeoftheprocessisnoted. Oncethetemperatureofthefurnacesreachesthedesired maximum,itisheldforaspecifictime.Thisprocessiscalled asSoaking.Thecoolingmethodtobeusedispredefined.For air quenching, the number of running fans is already specified.Multipleburnersareprovidedinsidethefurnace
It involves heating the casting above recrystallization temperature (727 degrees for steel), then soaking for a specific time till the desired microstructure has been achievedandthencoolingbyairquenching.
This process involves heating the casting above recrystallizationtemperature(727degrees),soakingforthe specified time and then cooling by controlled furnace cooling.
Airquenchingcoolsatafasterratethancontrolledfurnace cooling. Faster the rate of cooling, finer is the grain structurehence,greateristhehardness.Normalizedcasting isharderascomparedtoannealedcasting.Therefore,itis brittleanddifficulttomachine.Normalizingtemperatures areusuallyhigherthanannealingtemperatures.
Bothnormalizingandannealingtakeplacein3stagesviz. recovery stage, recrystallization stage and grain-growth stage.
Recoverystage:In thisstage,thefurnaceor otherheating device is used to raise the temperature of the material so thattheinternalstressesarerelieved.
Recrystallization stage: It involves heating the material aboveitsrecrystallizationtemperaturebutbelowitsmelting point so that new grains are formed without any residual stresses.
Grain-growthstage:Thematerialiscooledataspecificrate causingnewgrainstodevelopafterwhichthematerialwill bemoreworkable.Afterannealingandnormalizing,various subsequentoperationscanbecarriedouttoaltermechanical properties.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
This process is done by heating the casting above recrystallizationtemperature(727degrees),thensoaking foraspecifictimeandthencoolingbydippinginwater.
Water cools the casting immediately and this results in a veryfinegrainstructure.Hence,thecastingbecomesvery hardandbrittleandthus,difficulttomachine.
Water, brine, oil, etc. are used for solution treatment or solutionquenching.
Normalizedorwaterquenched(solutiontreated)castings are usually very hard. Hence, to reduce hardness and increasemachinability,temperingisdone.
Here,castingisheatedbelowrecrystallizationtemperature, soakedforaspecifictimeandthencooledataspecificrate togetthedesiredpropertieslikehardness,grainstructure, machinability,etc.(eitherbycontrolledfurnacecoolingor airquenching).Aftertheheattreatment,thecastingissent forshotblastingandfurtherprocesses.
Intheaboveprocesses,thecastingisnotheatedtothefinal temperature in one step but rather in multiple steps by holdingthecastingatseveralintermediatetemperatures.
for 5-6 minutes. After the process, the casting becomes cleanandgreyishincolour. Also,any sandpresentinthe casting gets removed and the voids on the surface get openedAfterthis,thecastingissentforprimaryinspection. Ifthedefectsareworkable,onlythenthecastingissentfor furtherprocessingorelseitisrejected.
Theexcessmaterialremainedonthecastingafterpowder cuttingandrodgougingisremovedbymachiningorfettling. Thecastingismachinedtodesireddimensionswiththehelp of various machining tools. The feet and flanges of the involute casing are machined to desired dimensions and finish. This is usually done for the castings that are to be exported.Thecastingisgivenasmooth,shinysurfacefinish bygrindingoperations.
Then,thedimensionsofthecastingobtainedarecompared withtheexpecteddimensions.Anydimensiongreaterthan thedesiredoneisreducedbyrodgouginganddimensions smaller than the desired ones are increased by welding. Then, the affected area is again given a smooth finish by grinding.
Itisasurfacetreatmentusedtoremoveimpuritiessuchas stains, inorganic contaminants, rust or scale (oxide layer formed during hot working processes), etc. These are removedbyreactionswithmineralacids.Asthedamaged metallayergetsremoved,aproperlyalloyedsteelsurface gets exposed providing a good corrosion resistant performance. Commonly used acids for pickling are sulphuricacid,hydrochloric acid,nitricacid,hydrofluoric acid, phosphoric acid. Hydrochloric acid is used in steel castings.Eventhoughitismoreexpensivethansulphuric acid,itpicklesatafasterratewhileminimizingbasemetal loss.
Here, the casting goes through a number of quality tests without actually damaging or wasting the casting unlike tensiletest,Brienellhardnesstest,etc.
Fig-6: Rampingandsoaking
Theundesirableblackrustylayerdevelopedonthecasting after heat treatment gets removed by shot blasting. Very fineshots(madeofaluminium,steel,etc.)areblastedwith high velocity upon the casting with the help of multiple motorsandcorrespondingimpellers.Themachineworksin acyclicmanneri.e.,theshotsfallingdownarecollectedand reused. The castings are taken to and removed from the machine with the help of hangers provided around the machine.Thecastingsarekeptintheshotblastingmachine
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1317

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thecastingisfirstcleanedwithredfluorescentpaint.The paintisthenallowedtosettleandenterthesurfacepores andcracksforabout15minutes.Thentheentirecastingis washed using water and solvent based cleaner and dried using air blower. A developer solution is sprayed on the castingwhichturnstheentirecastingwhiteaftersometime andexposesthefluorescentpaintatlocationswherethere aredefects.Basedontheseverityofthedefects,adecisionis madeuponwhichdefectstoignoreandwhichonestofix. Then the entire casting is washed and the defective locations are marked. The paint penetrated in the cracks andholesisremovedbyawaterwashablepenetrant.
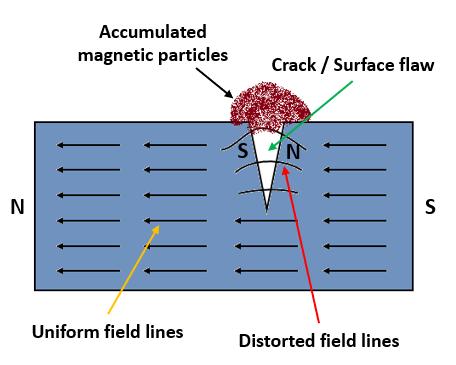
Itisusedfordetectionofsurfaceandnear-surfaceflawsin ferromagnetic materials and is primarily used for crack detection.Theworkpieceismagnetizedandthemagnetic fluxispresentpredominantlyinsidethematerial.Ifthereis anysurfacebreakingflaw,themagneticfieldisdistorted, causing local magnetic flux leakage around the flaw. This leakagefluxisdisplayedbycoveringthesurfacewithvery fine iron particles suspended in diesel. The particles accumulateattheregionsoffluxleakage,producingabuildupwhichcanbeseenvisuallyevenifthecrackisverysmall and narrow. Thus, a crack is indicated as a visible line of ironpowderormagneticparticlesonthesurface.
Magnetizationcanbeproducedbyanyofthefollowing ways:
By applying a permanent/electromagnet to the surface whichistermedasmagneticflow
Bypassingalargecurrentthroughtheoverallspecimenor itcanbedonelocallybymeansofcurrentprods
By putting the component/specimen inside a current carryingloop
By threading a current carrying bar through a hollow specimen
The method of magnetization should produce a magnetic fieldsuchthatthelinesofforceareatlargeanglestothe expected direction of cracks to be detected. So, magnetization is done more than once in different directions.Thiscanalsobedoneusingacombinationoftwo magneticfieldssothataswingingorrotatingmagneticfield can be produced which will detect a crack in any direction/orientation
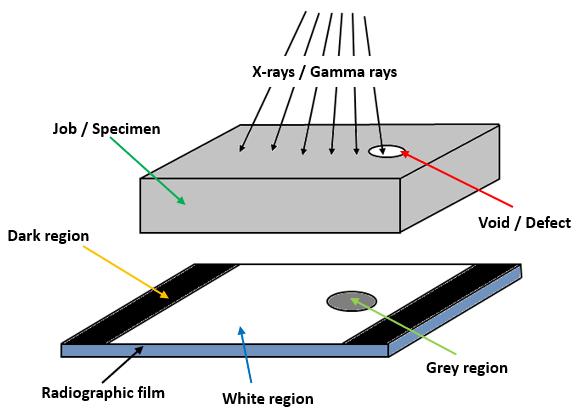
Ionizingradiationsareusedtopenetratethecross-sectional areaofacastingandapieceofradiographicfilmisexposed. Whendiscontinuitieslikecracks,gas,shrinkageorunfused chills or chaplets are present in a casting, the casting absorbslessradiationandmoreradiationreachesthefilm. This increased film exposure of the radiation ultimately producesanimageofthediscontinuityonthefilm.X-raysor Gamma rays areusedtopassionizing radiationsthrough thecasting.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Oncethedefectivelocationsaremarked,theyareentirely removed by rod gouging and then welded. The excess of weldbeadisremovedbygrindingandthenthecastingis sent for post weld heat treatment to relieve the stresses developedintheweld.Afterthepostweldheattreatment (PWHT), the casting is again sent for shot blasting (for carbon steels) or grit blasting (for stainless steels). The materialusedforgritblastingisaluminium.TheNDTsare performedagaintoensurewhetherthedefectshavebeen fixedornot.Finalfinishingandacidpicklingisdoneonce againafterallthedefectshavebeenremoved.
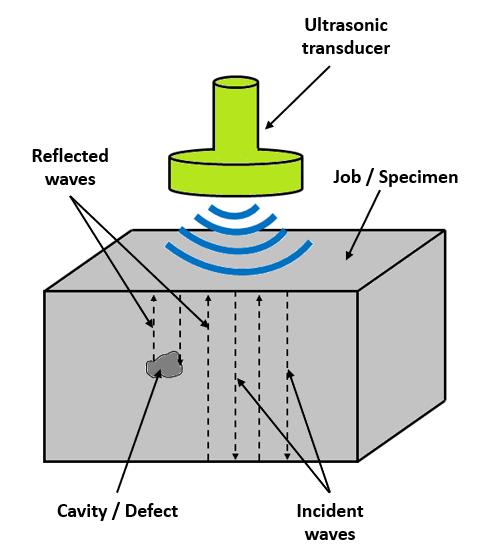
This method uses high frequency sound waves to detect surface and subsurface discontinuities in castings. It can alsomeasurethethicknessofthecastingatlocationswhere thehumanhandormechanicaldevicescannotreach.Here, anultrasonictransducertransformselectricalenergyinto mechanicalenergyintheformofsoundpressurewavesand thesoundpulsethus,generatedinitiatesatthetransducer, travelsthroughthecastingandisreflectedbyboththeback wall of the casting and any discontinuities that may be present. The transducer senses the reflected sound wave andconvertsittoanelectricalsignal.Thepropertiesofthe soundwaveliketransittime,amplitudeandshapegivean ideaaboutanydefectspresent.
Largecastingsusuallyhaveheatnumbers,patternnumbers andmaterialgradesembossed/extrudedonthemalongwith thecastingitself.However,somesmallcastingsneedtobe punchedusingmetalstampingtechnique.Thestamphasa specific dimension and has a letter or number embossed/extrudedatitstip.Thestampofthecorrectsize andlettermustbechosenforpunching.Holdingthestamp verticallyandhammeringit2-3timescreatesapunchofthe desiredletterornumberonthecastingAfteralltheabove processes,thecastingisfinallyreadyfordispatch.
Thispaperexplainsmostoftheprocessesinvolvedinsand casting of steels. It takes into account not only the basic foundryprocessesofmolding,scrapmeltingandpouringbut alsotheadditionalstepstakentoensureagoodqualityof the overall casting. The properties of the casting highly dependonthequalityofthemoldandhence,anumberof stepsaretakentostrengthenthemoldandremoveanyvoids or moisture contained within it. Moreover, the process of scrapmeltingneedstobedonecarefullywhereinadditional alloying elements need to be added to obtain the desired compositionofthematerial.
Thisstudyalsoexplainsthebasicsofheattreatmentofsteel castings.However,moreresearchneedstobedoneinorder to obtain detailed information about the various physical phases and the corresponding microstructures of steel obtained during heat treatment. A number of transformations take place during heat treatment (martensite, austenite, bainite, pearlite, etc.) resulting in differentmechanicalpropertiesofthecomponent.
Anumberofmachiningandfinishingprocesseshavebeen mentionedinthepaper.However,theimportanceofeachof themhighlydependsonthetypeofthecomponentandthe desiredfinish.Also,theavailabilityofresourcescanaffect the application of any process in a foundry. Many organizations,duetounavailabilityofspaceandresources, havetooutsourceinordertocompleteagivenprocess.Also, the materials, tools and equipment used for different processes vary from company to company leading to
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
differentqualityoffinishedproducts.Moreover,thequality and volume of production also depend upon the extent to whichmanuallabourandautomationareimplemented.
[1] Design and Manufacture of Casting Pattern Plates by RapidTooling,A.Pereira,J.A.Pérez,J.L.Diéguez,G.Peláez,J. E.Are
[2]GatingandRiseringinVerticalGreenSandMoulds,N.W. Rasmussen,R.AagaardandP.N.Hansen
[3]AStudyofCoreandit’stypesforCastingProcess,Dhairya S.Deore,GunjanB.Chaudhari,AmanG.Chaturvedi,Shrikant UttamGunjal
[4]Optimalfeederdesigninsandcastingprocessbygrowth method,R.TavakoliandP.Davami
[5]Foundryqualitycontrolaspectsandprospectstoreduce scrapreworkandrejectioninmetalcastingmanufacturing industries, T.R. Vijayaram, S. Sulaiman, A.M.S. Hamouda, M.H.M.Ahmad
[6]ComparativeStudyofAirCarbonArcGougingProcesson Sae316StainlessSteel,AnoopGDas,R.Abarna
[7] Kinetics of Oxyfuel Gas Cutting of Steels, Adedayo, AdelekeVictor
[8] Evaluation of Material Quality for Liquid-Penetrant InspectionBasedontheVisibilityoftheIndicatorPatternsof Flaws,Yu.A.Glazkov
[9] Reliability and sensitivity of magnetic particle nondestructivetestingindetectingthesurfacecracksofwelded components
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified
