International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Avinash Kamble1 , Pramod Survase2 , Vasimakram Mulla3 , Sana Mujawar4
Avinash Kamble; B-tech (Mechanical Engineering); Karad, Maharashtra, India Pramod Survase; B-tech (Mechanical Engineering); Karad, Maharashtra, India Vasimakram Mulla; B-tech (Mechanical Engineering); Karad, Maharashtra, India Sana Mujawar; B-tech (Mechanical Engineering); Karad, Maharashtra, India Prof. S. J. Mulani; Dept. of Mechanical Engineering; DACOE, Karad, Maharashtra, India ***
This research aims to make an efficient portable device which can be monitoring the quality of water and make aware the consumer or user about the water they are going to drink or use. The contamination in water supply is biggest problem right now in world. Rural area’s water supply system is not stronger as compare to urban locality. Rural area population is blindly depended on water filter system because they don’t have any testing module under their budget limit. In this, the main water parameters are going to be carried out like TDS, Turbidity, hardness, and conductivity and monitored with help of microcontroller and different sensors. Innovation Challenge to develop ‘portable devices’ for testing drinking water quality.
Key Words: Portable, TDS, Turbidity etc.
Pollution of water bodies affects the ability of the body of water to provide the ecosystem services. Water bodies consist of for example like lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirandgroundwater.Pollutioniscausedbypolluting water bodies in such a way that negatively affects its legitimateuses.
Inthisproject,themainparametersthatdefinewaterquality aremonitoredandmonitored.Tomonitorallparametersof waterallmeasuredparametersarecomparedwiththreshold valueswhichdefinesthehighestpurity Oncetheparameters aremeasured,theyaresenttothedisplaypanelintheform ofalertnewsforinformationalpurposes
Itaimstodevelop'portabledevicesthatcanbeusedatthe householdlevel totestthedrinkingwaterquality'. Several typesofportabledevicesmaybedeveloped.Wecanpropose todevelopportabledevicesforoneortwoorallthreetypes ofwatertestingkits.
A]adevicewithabilitytotestallparameters.
B] A device with ability to only detect the presence of bacterialcontamination.
C] a device which test one or more parameters with portability.
Md. Galal Uddin Stephen et al. [1] (2021). The water quality index (WQI) model is a popular implement for evaluating surface water quality. Globally, the WQI model has been applied to evaluate water (surface water and groundwater) based on local water quality criteria. This paper presents a comparative analysis of the most commonly used models as well as issues affecting model accuracy.
S. P. Gordel et al [2] (2011) Fortheassessmentofwater pollution status of the water bodies, the following water quality parameters were analysed: (1) pH (2) Specific Conductance (3) Temperature (4) Total dissolved solid (TDS)(5)TotalSolids(TS)(6)TotalAlkalinity(7)Dissolved oxygen (DO) (8) Chemical oxygen demand (COD) (9) Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) (10) Total Hardness. Parametersthatmaybetestedconsistoftemperature,pH, turbidity, salinity, nitrates and phosphates, etc. An assessment of the aquatic macro invertebrates can also provideanindicationofwaterquality.
Mr. Sensin Zhaho et al [3] (2011). Thispaperpresents the Water Quality Monitoring System for Inland Lakes (WQMSIL)thataimstomakeitconvenientfortheexpertsto make a further decision-making and the public to participation.Remotesensingdata,combinedwithgroundbasedobservationdataprovideavarietyofinformationto reflect the problems of water quality of inland lakes. The improvementofthesysteminthefutureisalsopresentedin thepaper.
Anna F Rusydi et al. [4] (2021) studiedtheCorrelation between conductivity and total dissolved solid in various type of water These two parameters are correlated and usuallyexpressedbyasimpleequation:TDS=kEC(in250 C).TheprocessofobtainingTDSfromwatersampleismore complexthanthatofEC.Earlierresearchresultshavefound thattheconnectionbetweenTDSandECarenotatalltimes linear.Theratioisnotonlystronglyprejudicedbysalinity inside, but also by materials contents. In addition, the examinationofTDSconcentrationfromECvaluecanbeused
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
togiveanimpressionofwaterquality.Formoreexactness, TDS concentrations need to be analyzed using the gravimetricmethodinthelaboratory.
Therearetwomajortypesofmethodologiesusuallyused
• Continuous method in this method the sensor is always submergedunderthewatertotransferthereadingstouser.
• Intermittent method in this method the sensor is programmedtogivereadingatspecifictimeinterval.
Astheprojectistomakedeviceportable,wehavechosen Intermittent Monitoring Approach. The benefits of this approacharethatlesspowerconsumptionwhichleadsto thelongerbatterylife,lessthermalissueslikeoverheating, no need for extra cooling fans which continuous method uses.Lowcostofmanufacturing.
Followingarethesteps
1.Sensing:TosensetheparameterslikeHardness,Turbidity, andTotalDissolvedSalt(TDS)weareusingTDSsensorand TurbiditySensorModulebothareanaloginnature.
2.ComputingandControlling:tocomputeandcontrolthe input data from the sensor we use ATmega328 the highperformance Microchip 8-bit AVR® RISC-based microcontroller combines 32 KB ISP Flash memory in the companyofread while-writeability,1KBEEPROM,2 KB SRAM, 23 general purpose I/O lines, 32 general purpose workingregisters,threeflexibletimer/countersbymeansof compare modes, internal and external interrupts, serial programmable UART, a byte-oriented Two-Wire serial interface,SPIserialport,6-channel10-bitA/Dconverter
3. Displaying or communicating: for display of computed data,weareusing1.8InchSPI128x160TFTLCDDisplay1.8 display has 128160 color pixels. Not like the low-priced Nokia6110andsimilarLCDdisplays,whichareCSTNtype andthushavedeprivedcolorandslowrefresh,thisdisplay, isatrueTFT.TheTFTdriver(ST7735R) isabletodisplay full 18-bit color (262,144 shades). And the 1.8 Inch SPI 128160TFTLCDDisplayModulewhichcomeuptowiththe similardriverchipsotherearenodoubtsthatourcodewill not work. It features a micro-SD card holder so we can simply fill the full color bitmaps from a FAT16/FAT32 formattedmicro-SDcard
Figure -1:FlowchartofMethodology
3.1. Arduino UNO: Arduino Microcontroller is an open sourcehardwareandsoftwarecompany,project,anduser community that designs and manufactures single-board microcontrollersandmicrocontrollerkitsforbuildingdigital devices
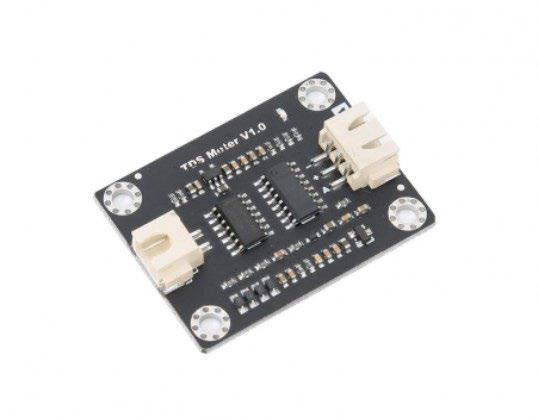



3.2. TDS sensor: TDSsensorthecommonlyusedTDStesting equipmentisaTDSpen.Althoughitisinexpensiveandeasy touse,itcannottransmitdatatothecontrolsystem,dolongterm online monitoring, and analyse the water quality. by means of a special instrument, although the data can be transmitted,theaccuracyishigh,butthepriceisverycostly To this end, we have particularly introduced the Arduinocompatible TDSsensor, whichcan beusedto measure the TDSvalueofwaterafterconnectingtotheArduinocontroller.
Fig -3: TDSmeter
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

3.3. Turbidity sensor: The Arduino turbidity sensor can detectandcheckthewaterqualitybyperformingaturbidity measurement. Turbidity measurements can be confirmed usingdigitaloranalogsignalsnexttothecorrespondingpins on the associated electronic module. The turbidity sensor emits infrared rays at its edges. It is imperceptible to the human eye and can detect particles floating in water and measurelighttransmissionanddispersionthatchangewith theamountofTSS(totalsuspendedsolid)change.
•ElectrodeInterface:XH2.54-2P
NumberofNeedles:2
TotalLength:83cm ConnectionInterface:XH2.54-2P
Color:Black Other:WaterproofProbe
•Hardware
•DFRduinoUNOR3(oralike)x1
•AnalogTDSSensorx1
•TDSProbex1
•JumperWiresx3
Fig -4: Turbiditysensor
3.4. LCD display: Waveshare2inchLCDdisplaymodule.A general purpose LCD display module with IPS screen, 2 inchesdiagonal,240x320resolutions,embeddedcontroller, andcommunicationviaSPIinterface.ItsupportsRaspberry Pi,STM32,Arduino,etc.

•testedliquidx1
•Software:ArduinoIDEversion:V1.0.xorV1.8.x
4.2 For Turbidity module
Workingvoltage DC5V Workingcurrent 30Ma(max) Responsetime <500msec InsulationResistance 100MΩ(Min) Operatingtemperature(0C) -30~+80 Length(mm) 33 Width(mm) 20 Height(mm) 12 Weight(gm) 55
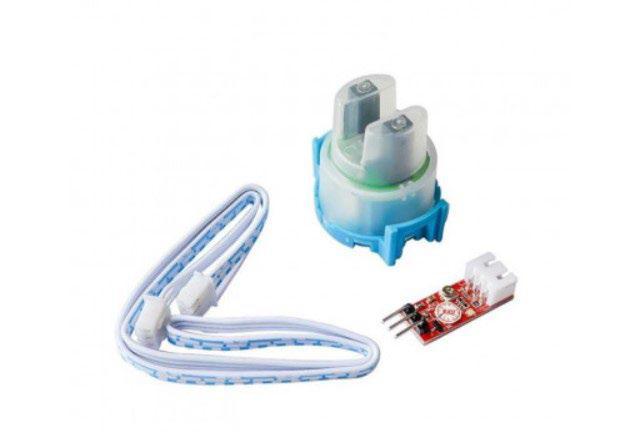

Fig -5: LCDscreen
4.1. For TDS module
Gravity:AnalogTDSSensorTECHSPECS
SignalTransmitterBoard
•InputVoltage:3.3~5.5V
•OutputVoltage:0~2.3V
•WorkingCurrent:3~6mA
•TDSMeasurementRange:0~1000ppm
•TDSMeasurementAccuracy:±10%F.S.(25℃)
•ModuleSize:42*32mm
•ModuleInterface:PH2.0-3P
Shipmentweight 0059kg ShipmentDimensions 8×5×5cm
4.3 For Arduino UNO
•Microcontroller:MicrochipATmega328P
•OperatingVoltage:5Volts
•InputVoltage:7to20Volts
•DigitalI/OPins:14(ofwhich6canprovidePWMoutput)
•PWMPins:6pins
•UART:1
•I2C:1
•SPI:1
•AnalogInputPins:6
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page128
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

•DCCurrentperI/OPin:20mA
•DCCurrentforsupply3.3VPin:50mA
•FlashMemory:32KBofwhich0.5KB
•SRAM:2KB
•EEPROM:1KB
•ClockSpeed:16MHz
•Length:68.6mm
•Width:53.4mm
•Weight:25g
•ICSPHeader:Yes
•Powersource:DCPowerJack&USBPort
General2inchIPSLCDDisplayModule240×320resolution, Brand:Waveshare
• Operating voltage: 3.3V/5V (Please make sure that the voltage of power supply and logic voltage are consistent, otherwiseitwillnotworkproperly)
•Interface:SPI
•LCDtype:IPS
•Controller:ST7789V
•Resolution:240(V)x320(H)RGB
•Displaysize:30.60(H)x40.80(V)mm
•Pixelsize:0.0975(H)x0.0975(V)mm
•Dimension:58x35(mm)
-6:pinconfiguration
•LED:Built-inLEDdrivenbydigitalpin13.Ifthepinishigh, theLEDwillbeon,andifthepinislow,itwillbeoff.
• VIN: The input voltage to theArduino or originalboard when using anexternal powersupply. Powercanbe suppliedthroughthispinor,ifpoweredthroughadpower jack,accessitthroughthispin.
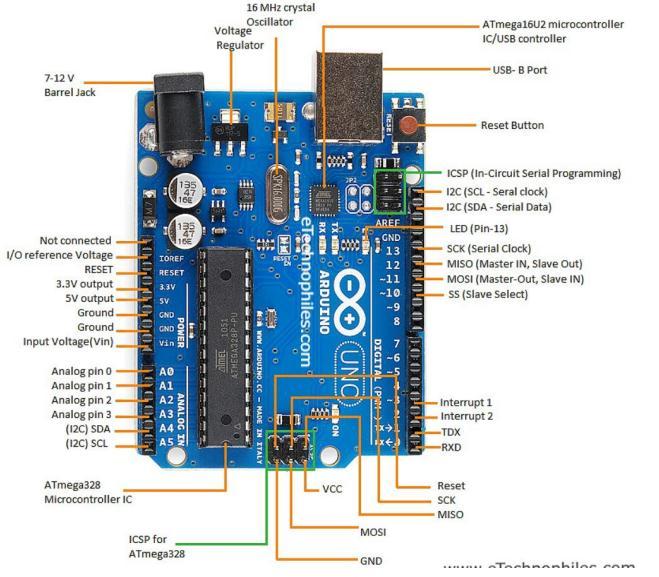
• 5V: This pin outputs a regulated 5V fromaregulator on board.TheboardcanbepoweredfromeithertheDCjack(720V), the USB connector (5V), or theboard'sVIN pin (720V).Applying a voltagethroughthe 5V or 3.3V pins bypassestheregulatorandcandamagetheboard.
• 3V3: The 3.3 volt of powersupply is generated by onboardregulator.The maximumcurrentconsumption is50mA.
•GND:Groundpins.
•IOREF:ThispinontheArduino/Genuinoboardprovides the voltage referenceused bythe microcontrollerto operate.Awell-configuredshieldreads the IOREF pin voltageandselectstheappropriatecurrentsourceorallows theoutputvoltageconvertertooperateat5Vor3.3V.
•Reset:Usuallyused to add a reset button toa shieldthatblockstheshieldontheboard.
Somepinshavespecializedfunctions:
•Serial/UART:pins0(RX)and1(TX).Employstoreceive (RX)andtransmit(TX)TTLserialdata.Thesepinsarelinked to the corresponding pins of the ATmega8U2 USB-to-TTL serialchip.
• External interrupts: pins 2 and 3. These pins can be configuredforgenerateaninterruptonalowvalue,anedge whichisrisingorfalling,orachangeinvalues
•PulseWidthModulation(PWM):pins3,5,6,9,10,and11. Canoffer8-bitPWMoutputalongwiththeanalogWrite() function.
•SerialPeripheralInterface(SPI):pins10(SS),11(MOSI), 12(MISO),13(SCK).
•Two-WireInterface(TWI)/I2C:PinsareSDA(A4)andSCL (A5). Hold up TWI communication by means of the Wire library.
•AREF(analogreference):itisreferencevoltageinsupport oftheanaloginputs.
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The purpose of this study is to analyze the actual functionalityofthedeviceanditseffectiveness.Inorderto reachthegoal,adetailedinvestigationofwaterparameters andtheirmeasurementswill becarriedout inall possible aspects.
It concludes that device successfully delivering expected results without any lag in reading varying. It is easy to handle and as it is portable so any external connections need.
1. JamieBartram(1996):WaterQualityMonitoring:-A practicalguidetothedesignandimplementationof freshwater quality studies and monitoring programmes
2. “PCBDESIGN”,AndreLA‘Mouth,Udemy
3. “WaterQualityMonitoringforRuralAreas”,Nikhil Kedia, 1st International Conference on Next GenerationComputingTechnologies(NGCT-2015) Dehradun,2015
4. Demetillo, A.T., Japitana, M.V. & Taboada, E.(April 2019):-Asystemformonitoringwaterqualityina large aquatic area using wireless sensor network technology.
5. “WaterQualityMonitoringSystem-IoTBased”,Jayti Bhatt,JigneshPatoliyaIRFIC,2016.
6. “Correlation Between Conductivity And Total Dissolved Solid In Various Type Of Water: A Review”, Anna.F.Rusydi, Global Colloquium on GeoscienceandEngineering,2017.
7. Sathish Pasika, Sai Teja Gandla,:- Smart Water Quality Monitoring System With Cost-Effective UsingIot,Heliyon,Volume6,Issue72020.
8. S.A. Abbasi (1998) Water Quality: Sampling and Analysis
9. “Texas Instruments”, Datasheets, LMV3244, CD460BM
10. DIGIKEY.in
11. MOUSER.in
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
