International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
(M.Tech. Structural Eng.), Civil Engineering Department, Institute of Engineering and Technology, Lucknow Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Institute of Engineering and Technology, Lucknow ***
Flatslabconstructionpracticefacesgreatriskduringsevereearthquakeshaking.Inthestudytwodifferenttypesofflat slab buildings are taken into account; flat slab with drops and flat slab with shear wall at periphery. This lateral force resisting mechanism strengthens structural stiffness of these flat slab structures. It is observed that the lateral force resistingcapacityofflatslabstructureincreasessignificantlywiththeuseofshearwall.
KEYWORDS: shear wall, flat slab with shear wall at periphery, flat slab with drop, pushover, ETABS software, seismic response.
Seismic activity is one of nature's most damaging phenomena, and their occurrence is often unforeseeable. The Traditional RC Frame structures are extensively utilized for construction in today's world. Flat slab construction has significant benefits over traditional RC Frame construction in terms of architectural freedom, space use, ease of form work,andconstructionspeed.Earthquakearemostlycausedbytectonicandvolcanoactivityso,itisourresponsibilityto fulfilltheprovisionofearthquakeresistantdesignIS1893andIS13920shouldbecompletelyadhered.Hereinthispaper two different types of flat slab buildings are taken into account. The behavior of flat slab building with 2 models was analyzed,andanonlinearstaticpushoveranalysistechniqueisusedinthestudy.
Klemencic et al. conductedaseveraltestsonpost-tensionedwallconnectionswithslab,andthefindingsrevealedthat thejointsfailatinternalstoreydrift5%.
Weidlinger and Ettouney studiedthetectoniclateraldisturbanceofhighrisebuildingofflatslabintheNewYorkCity.
Vinod Goud (2015):- The structural behaviour of shear wall – flat slab interaction is studied; among the important objectivessomeareresistancetovariousforcesofactionaswellastheadvantageofshearwallsontheperformanceof thesebuildingsstructuresunderseismicforces.
Robertson et al research concluded brittle punching failure caused by shear stresses and asymmetrical forces transferredbetweenslabsandcolumnsInconsistentmomentsalsocauselargeshearstressesintheslabwhensubjected toaflatslabwithadropandashearwallatdifferentlocationsduringearthquakehasbeeninvestigatedintensively.
Pushover analysis isusedto identify the nonlinear behaviourofstructuresunderdynamicloading,such asmaxstorey displacement,storeyshear,overturningmoment,storeydrift,andmaxstoreydrift.That'sasortofnon-linearstaticand dynamicanalysisinwhichthestructure'sstrengthisevaluatedbeyonditslimitofproportionality.
Due to their effective span/depth ratios and the savings generated by constraining storey heights, concrete flat slab systems are a common kind of reinforced concrete structures, primarily in medium-sized industries. These slabs are prone towards gradual failure than slab-beam-column complexes because the pressure formerly absorbed by the removed columns cannot be shifted in the absence of beams. It is consequently critical to evaluate the resistance to progressive collapse of RC flat slab constructions. As a result, it was advised that in seismically prone areas, flat-slab constructionshouldonlybeimplementedastheverticalstructuralmemberssysteminstructuresbracedbyframework or shear walls responsible for the structure's transverse capacity. To withstand gravity loads, slab–column interfaces
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1171
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
must absorb the lateral elastic deformation of the primary lateral load-resisting structural parts resulting punching failure.
Tocomparetheresultsofdisplacement,baseshearandstoreydriftparametersasspecifiedinIS-1893:2016forvarious flat slab also to maximize the performance of various flat slab building models in relation to various types of force resistingsystemsfurthertoinvestigatethenonlinearbehaviourofflatslabbuildingssubjectedtoseismicstresses.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
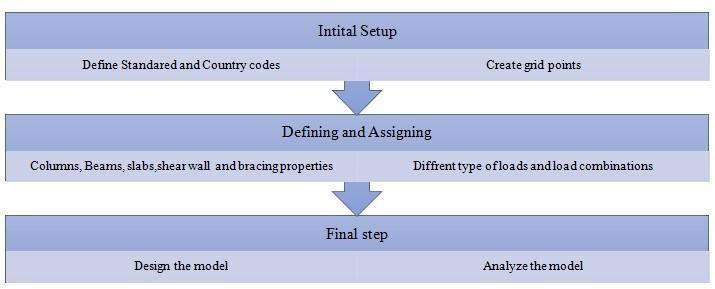
In this paper we model a G+9 BUILDING with plan layout of 25x15m. After this we assign material properties, section propertiesandloadconditionusingcode IS1893(Part1)inETABSv16software.Thenweperformpushoveranalysis to analyzenon-linearbehaviourinboththemodelsandcomparemoreefficientandsustainablebuildingofthetwo.
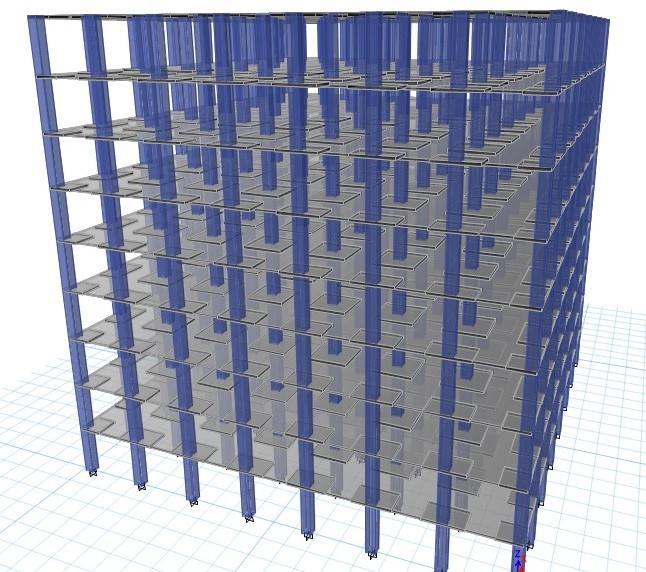
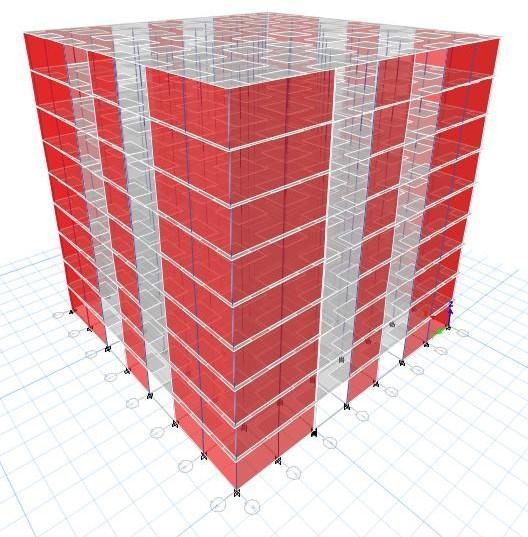
Thecomparativeinvestigationwascarriedoutundercertaincondition
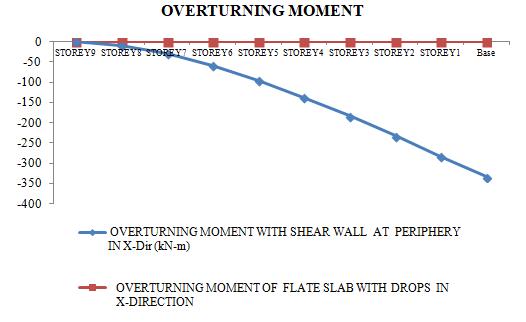
The graph demonstrates the overturning moment in horizontal plane is on the structure as a whole resulting from the dynamic earthquake forces. The overturning moment with negative value depicts the counter balancing the seismic disturbanceresultsinmorestabilityforshearwallatperipheryascomparedtoflatslabwithdrop,thusmodel1ismuch stableascomparedtomodel2.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The restraining moment for building with shear wall at periphery is more as compared to building for flat slab with drops. According to IS 456:20000, Cl. 20.1, structurestability in the event of resisting moment must be larger than 6/5 timesthemaximummomentduetothenormaldeadloadandgreaterthan7/5timesthetypicalappliedloads.
Asshownbelowthetablewhenshearwallplacedatperipheryandflatslabarecomparedtothestoreydisplacementas parameter. IS 1893:2016 defines the permissible value of storey displacement as 0.004 of storey height (H).The shear wall acting as a resisting system limits the excessive lateral displacement at different location comparison between the twoareasfollows;
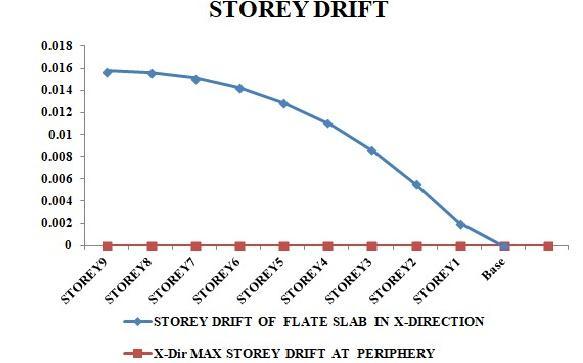
Accordingtothefollowingcharts,thestoreydisplacementanddriftwillbelessatthebottomandhigheratthetop.The averagestoreydisplacementofflatslabasperIS456:2000,Cl.20.5,shallnotexceedH/500forlateralswayattop,where H is the building's entire height. According to IS 1893(Part -I) Cl. 7. 11.1, the minimum storey drift shall not be greater than0.004timesthestoreyheight.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1174

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The building with flat slab with drop has storey drift is 0.015752 m whereas in building with shear wall at periphery storey is 1.31E-07 m both are in max permissible limit is 0.192 m. Hence our building is safe, in y as a well as in x direction,driftvaluesareunderpermissiblelimitaccordingtoIS1893.
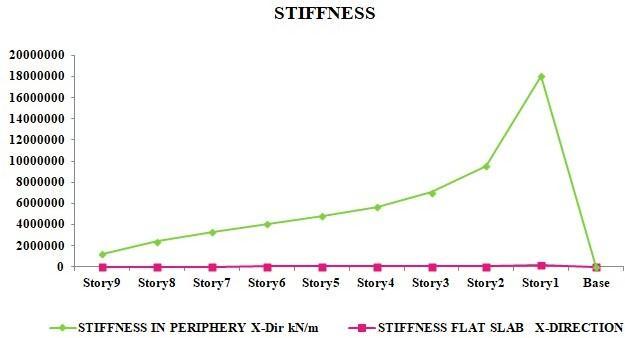
The relative storey drift ratio is the most vital displacement-related characteristic that must be regulated to reduce the damage to structures subjected to earthquake-induced ground accelerations. The demand for tale drifts changes with temporal variation of ground motion. The stiffness and storey drift relation is inversely proportional to each other, the stifferthestructureislesserwillbethedriftinrespectivedirectioneitherX-directionorY-direction.
Theshearatperipherycanbeusedwhereeconomyisconsidered,todecreasestheflexibilityofconcretetheframewith flat slab is recommended with the use of shear walls results in an increase in wall stiffness. As the stiffness grows, the leveldriftlowerssignificantly.
ThestiffnessofmodelwithshearwallatFlatslabshowslowerstabilityascomparedtomodelwithatperiphery.ThusAt peripheryprovidesmorestabilitytobuildingunderlateralloads.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
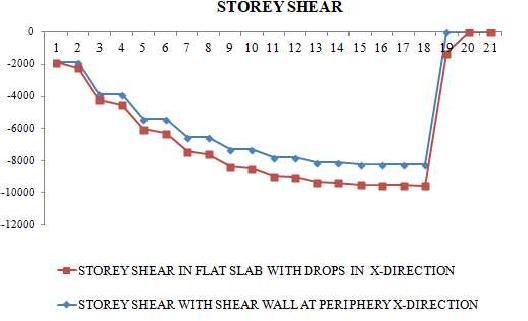
Thestoreyshearinxdirectionwithshearwallatperipheryhasmoreresistancetostoreyshearthanflatslabwithdrop. Thus;thebuildingismuchstableunderlateralseismicloadingwithperipheryrespecttoflatslabwithdrop.
Thelateralforceactingperstoreyissignificantlyhigherincaseofshearwall atperipherybut thelateralforcedecreases fromtopstoreytobaseincaseofflatslabwithdrops.
Shearwallatperipheryoffersbetterresistancetolateralforces andserviceabilityandstabilityofthestructureresulting inincreasingthestiffnessofbuildingandprovidingseismicstabilityunderlateralforces.
Flat slab building with drops offers greater flexibility than building with shear wall at periphery In order to decrease deformationdemandsduringmajorearthquakes,strongerstructuralsystemssuchasshearwallswithsteelbracing and shearwallatcorecanbeusedasreplacement.
Thevalueofdisplacementobtainedunderactionoflateralforcesforshearwallat peripheryisbetterwhencomparedto flatslabwithdrops.
1. Ahmad J. Durrani, S.T.Mau and Yi-Li,(1994). “Earthquake Response of Flat Slab Buildings, Journal of Structural Engineering”,Vol.120.
2. Chopra,A.K.“DynamicsofStructures:Theoryandapplicationstoearthquakeengineering”,3rdEd.,Prentice-Hall, NewDelhi,(1998).
3. H.-S.Kim,D. G.Lee,(2004)“Efficientanalysisofflatslabstructures.
4. IS456:2000,“PlainandReinforcedconcrete–Codeofpractice”,BureauofIndianStandards,NewDelhi
5. KavitaGolghate,VijayBaradiyaandAmitSharma,“PushoverAnalysisof4Storey’sReinforcedConcreteBuilding”, InternationalJournalofLatestTrendsinEngineeringandTechnology.
6. Kokot S, Anthoine A, Negro P, Solomos G. Static and dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete flat slab frame buildingforprogressivecollapse.EngStruct2012;40:205–17.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.02.026.
7. Liu M. Progressive collapse design of seismic steel frames using structural optimization. J Constr SteelRes2011; 67(3):322–32.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2010.10.009.
8. UFC4-023-03.Designofbuildingstoresistprogressivecollapse.UnifiedFacilitiesCriteria,DepartmentofDefense, USA;2009.
9. Klemencic R, Fry JA, Hurtado G, Moehle JP. Performance of post-tensioned slab-X-Bracing wall connection. PTI Journal2006;4(2):7–23
10. VamvatsikosD,CornellCA.Incrementaldynamicanalysis.EarthqEngStructDyn2002;31:491–51
11. Seismosoft. SeismoStruct – A computer program for static and dynamic nonlinear analysis of framed structures; 2018-availablefromhttp://www.seismosoft.com.
12. X.I.E. Junju , W.E.N. Zenping , 2008 , A measure of drift demand for earthquake ground motions based on Timoshenkobeammodel.In14thWorldConferenceonEarthquakeEngineering
13. Tuken,N.Siddiqui,Assessmentofshearwallquantityinseismic-resistantdesignofreinforcedconcretebuildings, Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (AJSE) Springe 38 (10) (2013) 2639–2648. Tuken, N. Siddiqui, SBC-based assessment of shear wallquantityinmomentresistingframebuildings,KSCEJ.Civ.Eng.Springe19(1)(2015)188–199.