International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dept. of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Mahaguru Institute of Technology, Mavelikkara Asst. Professor, Dept. of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Mahaguru Institute of Technology, Mavelikkara ***
Abstract –A brain tumor refers to a cluster of aberrant brain cells in medical terms. The manual detection of brain tumor from brain MRI images is a difficult task, and sometimes it can cause misdiagnosis. Medical scanning has made it possible to detect brain tumors using imaging tools. They give clinicians a detailed image of the human brain. It is possible to detect early illnesses with sophisticated Artificial Intelligence and neural network classification models. In this paper, the brain tumor is detected from MRI brain images using a CNN model named EfficientNet. Four Efficient Net models i.e., EfficientNet B0, EfficientNet B1, EfficientNetB2, and EfficientNetB3 have been used for brain tumor classification. The performance of each model has been evaluated and the best model is found among the four models.
Key Words: ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork,EfficientNet, Magnetic Resonance Image, Feature Extraction, Classification, Grey level run length matrix (GLRLM), ParticleSwarmOptimization(PSO)
Abraintumorisanabnormalmassofcellsthatproliferates andreproducesuncontrollablyinthebrain.Toidentifythis disease and determine the type of brain tumor, doctors performseveraltests[1].Thebrainscanisusedtoanalyze the tumor. The medical field has recently given increased attention to AI as a result of its successful applications. Classifying magnetic resonance images with artificial intelligence has gained much interest in medical image analysis. There are two general types of brain tumor classification.Thefirstisthecategorizationofbrainimages intonormalorabnormalclasses,secondistheclassification ofdifferentstagesofbraintumor.
Thispaper reviews and examines the brain tumor classificationbasedonEfficientNetmodels.Here,basedon thefeaturesextractedfrom thebrainscan,anindividual's MRI brain scan is categorized into either "tumor" or "no tumor."Themethodologyofbraintumorrecognitionusing EfficientNethasbeenexplainedinareexplainedinChapter 3. Chapter 4 shows the experimental results and performance comparison. The conclusion of the study is presentedinChapter5.
AcombinationoftheSVMclassifierandFuzzyCmeanshas beenusedfordetectingbraintumorin[2].Toobtainbrain attributes,thegreylevelrunlengthmatrix(GLRLM)hasbeen employed in this method SVM classifiers are employed to determinewhetherabrainscancontainsatumorornot.The SVMclassifier was trained by utilizing 96ofthe 120 brain MRIscansandthentestedusing24remainingimages.This method obtained a maximum of 91.66% accuracy in the classificationtask.Thebraintumorwasidentifiedin[3]by utilizingtheNaiveBayesClassifier.Anevaluationof50brain scans found an overall accuracy of 94%, with an 81.25 percent tumor identification rate and a 100% non-tumor detection rate. Here, eight morphological traits and three intensity features have been derived from the segmented grayscale brain picture to categorizethe tumor The Naive Classifierisasupervisedmachinelearningalgorithmthatis basedonBayesProbabilitytheory.
In [4], two distinct deep learning-based methods for classifyinganddetectingbraintumorshavebeensuggested. BRATS2018datasethasbeenusedinthiswork.FastAiand YOLOv5classification models were both accurate to 94.98 percent and 84.95%, respectively. Here, the classification modelwasconstructedBasedonResNet34.Toidentifythe braintumor,[5]usedasimple8-layerconvolutionalneural network. Acomparison of network performance with pretrained CNNs like VGG16, ResNet50, and InceptionV3 has been done to evaluate the network effectiveness. The proposedmodelachieved96%trainingaccuracyand89% validation accuracy for brain tumor recognition. Here, the proposed system outperforms all other pretrained CNN modelstakenforcomparison.
A brain tumor classification system based on Fuzzy C meansalgorithmandSVMhavebeenproposedin[6].FuzzyC meansalgorithmisdoneforextractingbrainfeaturesfrom MRI brain scan and SVM is used for classification of brain scaninto‘tumoraffected’or‘tumornotaffected,class.The proposed detection system gives an accuracy of 97.89% accuracy.Abrainimageclassificationmodelthatcategorizes a person’s brain scan into either the ‘tumorous’ or ‘nontumorous’classhasbeenimplementedin[7]byutilizing ParticleSwarmOptimization(PSO)basedsegmentation,and SVM classifier. PSO is used to partition the precise cancer region.Adiscretewavelettransformation(DWT)isapplied
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Fig.1:Blockdiagramoftheproposedsystem
tothethirteenattributesthathavebeenextractedtoobtain brainfeatures.TwoSVMclassifiersareusedtoclassifybrain images:alinearSVMandaradialbasisfunctionSVM.Here linearSVMgivesanaccuracyof71%andradial basisSVM givesanaccuracyof85%.
Inthisworktransferlearning-basedapproachforclassifying brainscanshasbeenemployed.EfficientNetmodelsareused here for automatic feature extraction and classification of brainfeatures Thebraintumordetectionsystemconsistsof two phases.One isthetrainingphaseand the other isthe testingphase.Inthetrainingphase,featureextractionand classification on the training data set are done to create a predictionmodel.Inthetestingphase,testdataisfedtothe predictionmodeltodeterminewhetherthepersonhasthe tumorornot.Themainstepsinvolvedinbothphasesarei) inputtheMRIdataii)preprocessingiii)featureextraction andclassification.
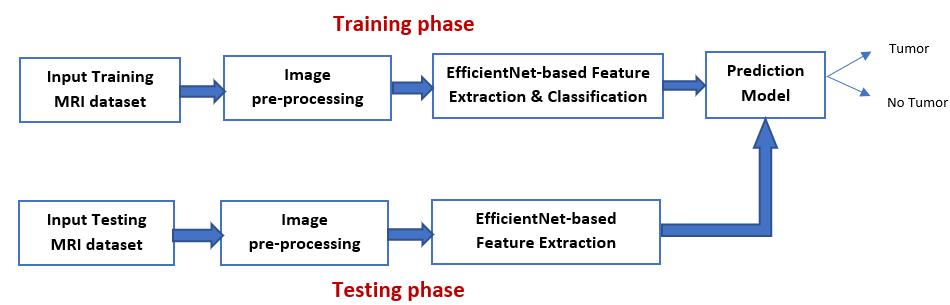
The two-dimensional Magnetic resonance image of an individual’s brain is fed as the input to the system. The datasetispartitioned:asatrainingandtestingset.Normally data is partitioned in 80:20 or 70:30 ratio. The dataset is collectedfromKaggle.
The two-dimensional MRI brain data are of non-uniform size.TheEfficientNetarchitecturerequiresinputdimensions of 224 × 224. Therefore, the 2D brain images have been resizedtoauniformdimensionof224×224×3.
Automatic feature extraction and classification of brain featuresfortumordetectionisdonebyEfficientNetmodels. Four efficient models have been used here. They are EfficientNetB0,EfficientNetB1,EfficientNetB2,EfficientNet B3. The EfficientNet is a CNN architecture where every depth, width, and resolution parameter are scaled continuouslybyapplyingacompoundcoefficient.Hereeach dimensionisconsistentlyscaledwithapredeterminedsetof scaling coefficients. This type of scaling increases model accuracyandefficiency[8].Thereare8EfficientNetmodels i.e,EfficientNetB0-B7.Outofthe8modelsEfficientNetB0-B3 hasbeenusedinthiswork.EveryEfficientNetmodelshave5 modules.Thenumberofsub-modulesvariesdependingon the model. Mobile inverted bottleneck convolution layer, squeeze layer, and excitation layer makes up the core of EfficientNet. EfficientNet B0 consists of 18 convolution layers.Sincetheyoutperformednumerousothernetworks (including DenseNet, Inception, and ResNet) on the ImageNet test,EfficientNets are advised for classification jobs.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
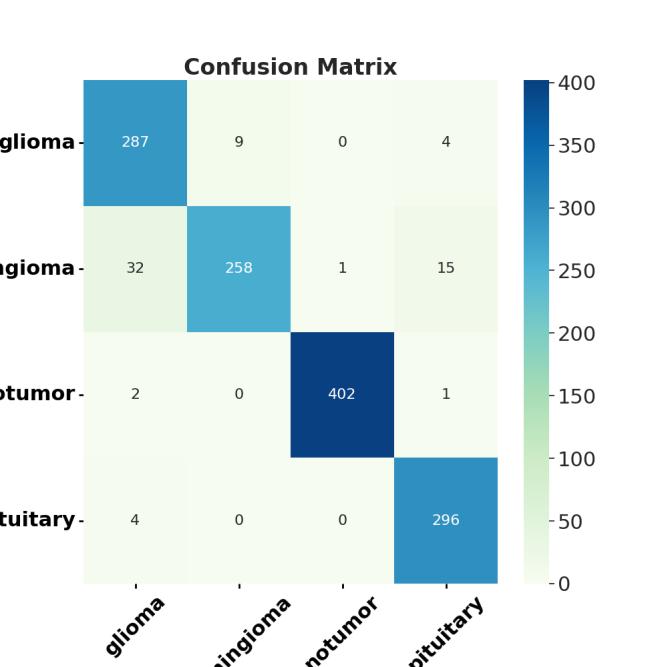
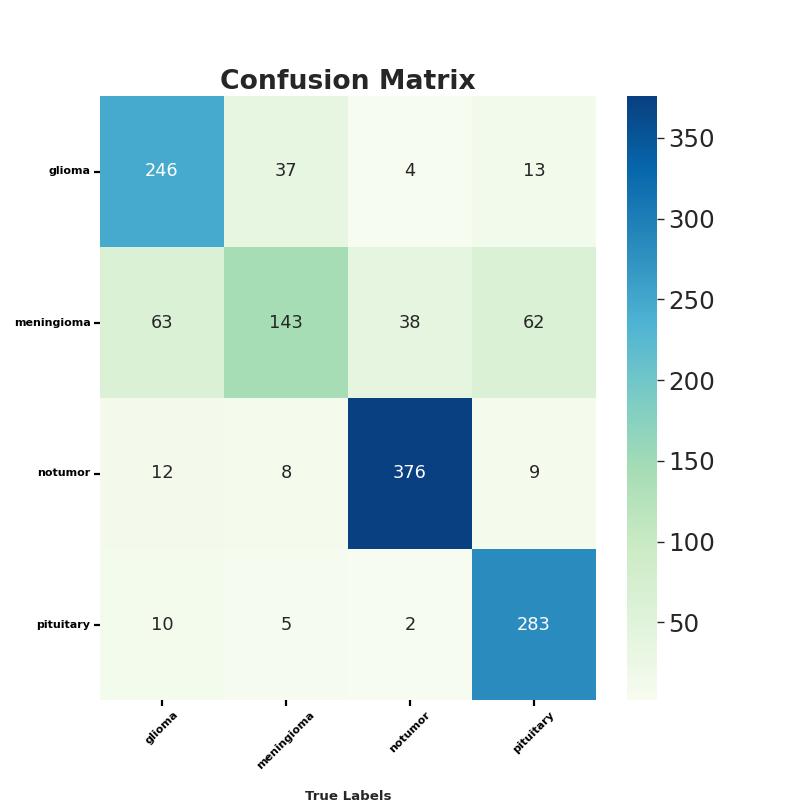
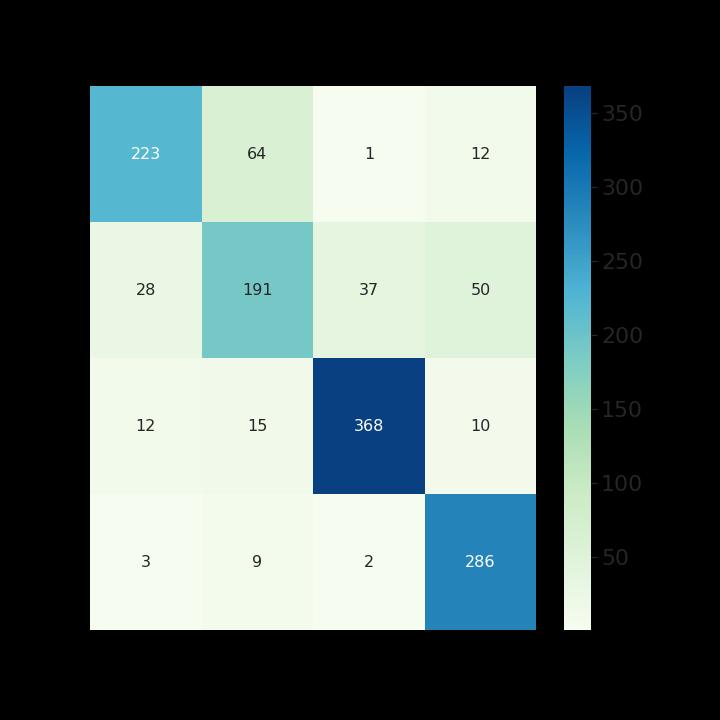
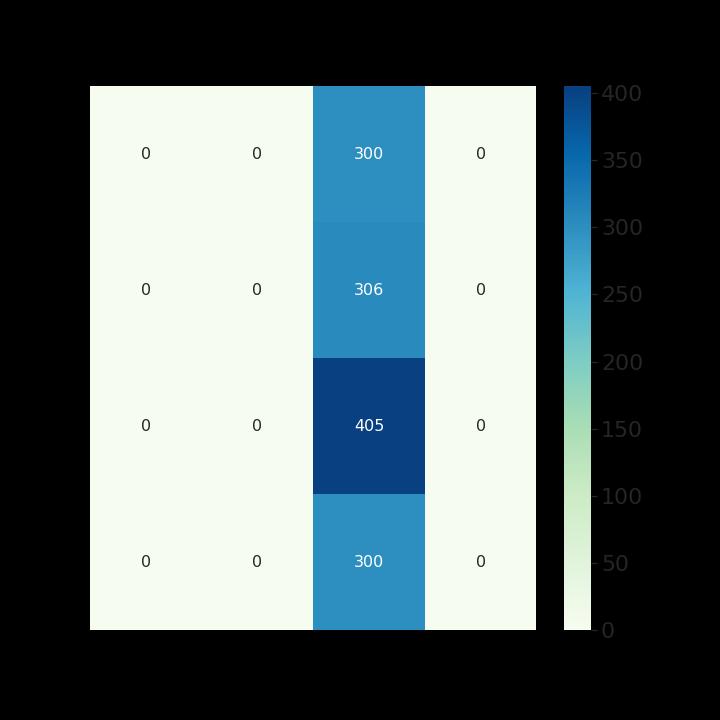
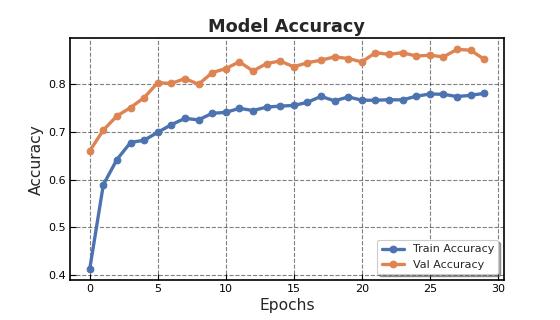
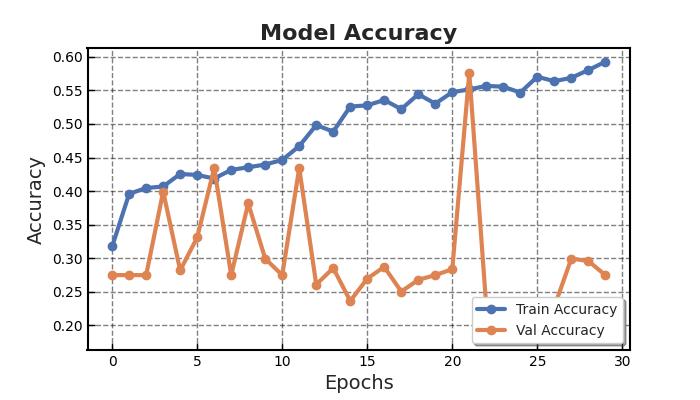
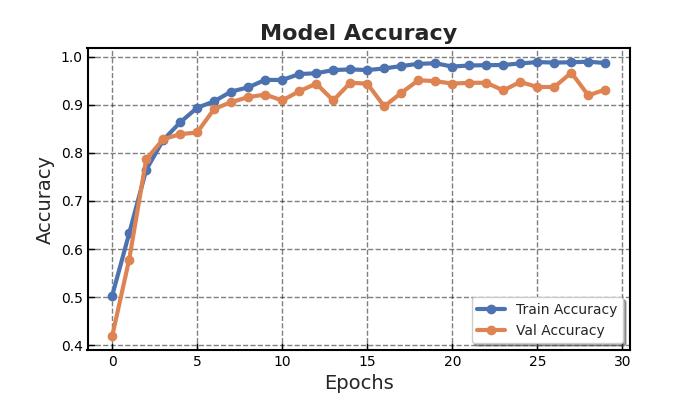
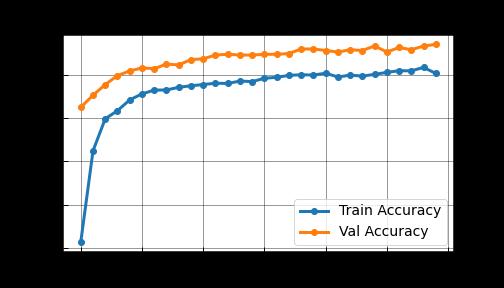
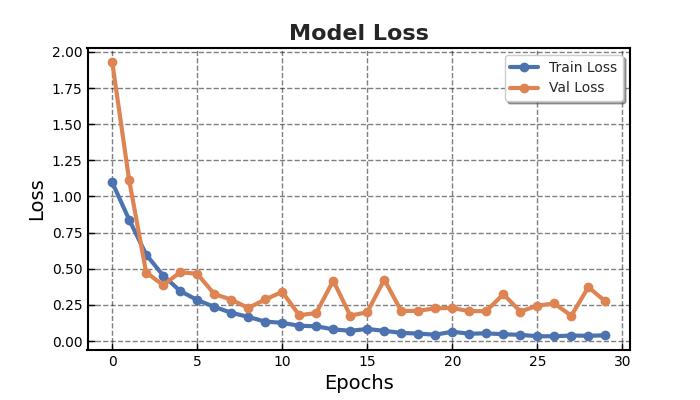
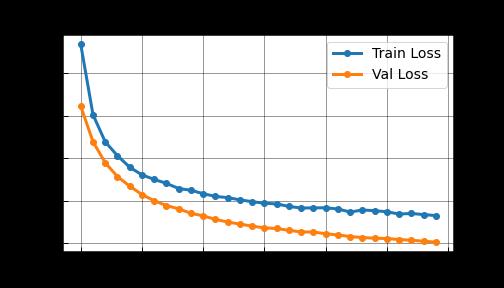
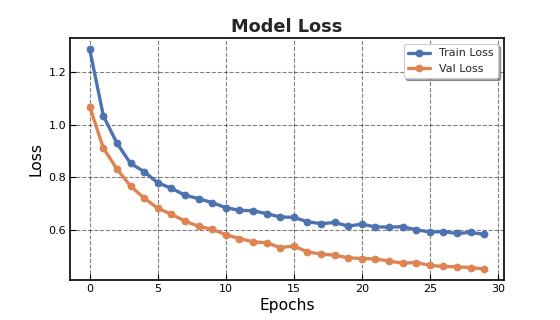
Two-dimensionalMRIimagesfromKagglewhichareresized toauniformdimensionof224×224×3arefedasinputtothe system. 5712 images were used for training and 1311 images were used for testing. Out of the four EfficientNet models, EfficientNet B3 provides higher accuracy in brain tumor classification task. EfficientNet B3 gives 98.8% training accuracy and 93.1% testing accuracy and outperforms all the other EfficientNet models. The least accurate was EfficientNet B0. This network model gives a low training accuracy score of 58.7% and a validation accuracy score of 27.5%. The accuracy and performance comparisonofvariousmodelsaregiveninTable1andTable 2.
Anabnormalproliferationofbraincellscanaffectthebrain's functionality.Detectinga braintumorearlycanresultina fasterresponsetotreatment,increasingsurvivalchances[8]. BraintumorsareoftendetectedusingMRIbrainscans.With the development of AI methods, CNN, a deep learning approach,canbeusedtocategorizeMRIimagesfortumor determination In this work, automatic brain tumor detectionusingfourCNNEfficientNetmodels(EfficientNet B0-B7)hasbeendoneandfoundthebestone.Incomparison toEfficientNetB0-B2models,EfficientNetB3showsthebest performance for brain tumor classification. In the future, EfficientNetB4-B7canalsobeusedtoclassifybraintumors andcheckiftheaccuracyofdetectionhasincreased.
[1] https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseasesconditions/brain-tumor/symptoms-causes/syc20350084
[2] ParveenandA.Singh,"DetectionofabraintumorinMRI images,usingacombinationoffuzzyc-meansandSVM," 20152ndInternationalConferenceonSignalProcessing andIntegratedNetworks(SPIN),2015,pp.98-102,DOI: 10.1109/SPIN.2015.7095308.
[3] H. T. Zaw, N. Maneerat and K. Y. Win, "Brain tumor detectionbasedonNaïveBayesClassification,"20195th International Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences and Technology (EAST), 2019, pp. 1-4, DOI: 10.1109/ICEAST.2019.8802562.
[4] N. M. Dipu, S. A. Shohan and K. M. A. Salam, "Deep Learning Based Brain Tumor Detection and Classification," 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Technologies (CONIT), 2021, pp. 1-6, DOI: 10.1109/CONIT51480.2021.9498384.
[5] Khan, H. A., Jue, W., Mushtaq, M., & Mushtaq, M. U. (2020).Brain tumorclassificationinMRIimageusing convolutionalneuralnetwork. Math. Biosci. Eng, 17(5), 6203-6216.
[6] A.HalderandO.Dobe,"DetectionoftumorinbrainMRI using fuzzy feature selection and support vector machine,"2016InternationalConferenceonAdvances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), 2016, pp. 1919-1923, DOI: 10.1109/ICACCI.2016.7732331.
[7] A.DixitandA.Nanda,"BrainMRImageClassificationvia PSObasedSegmentation,"2019TwelfthInternational Conference on Contemporary Computing (IC3), 2019, pp.1-5,DOI:10.1109/IC3.2019.8844883.
[8] T.ManthaandB.EswaraReddy,"ATransferLearning method for Brain Tumor Classification using EfficientNet-B3 model," 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computation System and Information TechnologyforSustainableSolutions(CSITSS),2021,pp. 1-6,DOI:10.1109/CSITSS54238.2021.9683036.
[9] K.Duvvuri,H.KanisettypalliandS.Jayan,"Detectionof Brain Tumor Using CNN and CNN-SVM," 2022 3rd International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), 2022, pp. 1-7, doi: 10.1109/INCET54531.2022.9824725.
[10] M. Gurbină, M. Lascu and D. Lascu, "Tumor Detection and Classification of MRI Brain Image using Different Wavelet Transforms and Support Vector Machines," 2019 42nd International Conference on TelecommunicationsandSignalProcessing(TSP),2019, pp.505-508,doi:10.1109/TSP.2019.8769040.
[11] MMonicaSubashiniandSaratKumarSahoo,BrainMR Image Segmentation for Tumour Detection using ArtificialNeuralNetworks,vol.5,no.2,Apr-May2013.
[12] G. Karayeğen and M. F. Akşahin, "Brain Tumor Prediction with Deep Learning and Tumor Volume Calculation," 2021 Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), 2021, pp. 1-4, doi: 10.1109/TIPTEKNO53239.2021.9632861.
[13] V.Zeljkovicetal.,"Automaticbraintumordetectionand segmentationinMRimages,"2014PanAmericanHealth Care Exchanges (PAHCE), 2014, pp. 1-1, doi: 10.1109/PAHCE.2014.6849645.
[14] K. T.K. and S. Xavier, "An Intelligent System for Early Assessment and Classification of Brain Tumor," 2018 Second International Conference on Inventive Communication and Computational Technologies (ICICCT), 2018, pp. 1265-1268, doi: 10.1109/ICICCT.2018.8473297.
[15] G Rajesh Chandra, Kolasani Ramchand and H Rao, "Tumordetectioninbrainusinggeneticalgorithm", 7th International Conference on Communication Computing and Virtualization Elsevier,2016.