International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Md.Shoaib Hussain.S 1 , Akash B.T 2 , Manoj M.J 3 , Lakshmi.N 4 , Rohan Gowda.L,5 Yashash Kotehal K.V 6
1 Faculty, 2,3,4,5,6 Students,Department of Civil Engineering APS POLYTECHNIC Somanahalli, Kanakapura main Road Bengaluru, Karnataka, India ***
Theemphasisofthispaperisonthefiltrationefficiencyof geotextiles. As we know treatment (operation) of wastewater has become an absolute prerequisite. An inventive, inexpensive and effective method of purifying andcleaningwastewaterbeforedischargingintoanyother water systems is to be compelled. Coagulation-flocculation is a chemical water treatment approach typically applied priortosedimentationandfiltrationtointensifytheability of a treatment process to remove particles. Filtration is considered the most important solid-liquid detachment / separation process in water treatment, as well as in wastewater treatment. As a matter of fact, Geotextiles in general are textiles in the traditional sense, but they containsyntheticfibersmoreoflessthannaturalfiberslike silk,cottonorwoolhence,biodegradationisnotaproblem. Thesesyntheticfibersaremadeintoflexible,porousfabrics bystandardweavingmachineryoraremattedtogetherina random non-woven manner [2]. Proper choice of geotextile filtersplaysacrucialroleinachievingsatisfactoryfiltration performance [2]. In this research non-woven geotextile fabrics of 100,150,200 & 300 GSM were used for the treatment of domestic wastewater. The laboratory portion ofthestudyincluded a column test withalternating layers of filter media consisting of sand, gravel, pebbles and charcoal. Non-woven geotextile were sandwiched within the filter media. Geotextiles were placed at the upper, middle and bottom layer. The various study parameters include pH, TSS, BOD, Hardness & Turbidity. The porosity of the geotextile material played an important role in filtration process, it was clearly observed that as the pore sizedecreasedthefiltrationefficiencyincreased.
Keywords: wastewater, coagulation-flocculation, geotextile,suspendedparticles,porous.
Wastewater emerges from both industrial and domestic activitiesand their Treatment,ManagementandReuse are one of the key subjects of the day that demands high technical know-how, energy and infrastructure to attain a better treatment goal. [4] Industrially rejected water is specific to the nature of industry and hence the nature of treatment adopted might be idiosyncratic (unique) but
domesticwastewater orsewerage isconsistent in identity. As known, there are a lot of known and unknown impuritiesinwastewaterthathastobeeffectivelyremoved to get preferably premium quality treated water. Contaminantremovaltechnologiestakeupacentralrolein the primary treatment process of any wastewater treatment [3]. With an efficient & effective contaminant removalsystem,mostoftheparametersinthewastewater could be cracked. Effective wastewater treatment is very much essential to protect both human and environmental health, regardless of the size of the community. Potential contaminants in domestic wastewater include diseasecausing bacteria, infectious viruses, household chemicals andexcessnutrientssuchasammonia,alongwiththemore traditional suspended solids and biochemical oxygen demand [1]. Utilization of geotextiles in the treatment of domestic wastewater shall be considered as an inventive, inexpensiveandeffectivemethodofpurifyingandcleaning wastewater before discharging into any other water systems. Geotextiles in general are textiles in the traditional sense, buttheycontain syntheticfibersmore of less than natural fibers like silk, cotton or wool hence, biodegradation and subsequent short lifetime is not a problem. These synthetic fibers are made into flexible, porous fabrics by standard weaving machinery or are mattedtogetherinarandomnon-wovenmanner [1].Proper choice of geotextile filters plays a crucial role in achieving satisfactoryfiltrationperformance.
The main objective of this project is treatment of domesticwastewaterbyusing geotextilesinthefilter media.
To characterize the various Physio-chemical characteristicsparameterforthedomesticwastetobe treated.
Reducing the pH, Alkalinity, Acidity, Turbidity, Hardness, BOD and TDS of the domestic waste water byusinggeotextileasafiltermedia
Finding out the percentage of effectiveness in the impurityremovalusinggeotextileasafiltermedia.
Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

Wastewater: domestic waste water is the waste water carrying human wastes including kitchen, bath & other wastes from residences, buildings, industrial establishments or other places. For this experimental programme, waste water samples were collected from a waste water treatment plant close to the college campus through grab sampling technique. The initially collected waste water was tested for its characteristics & the followingresultswereobtained.
Geotextiles: Geotextile is a produced fabric made out of various polymer mixes and it has a permeable or penetrable character that grips or holds the suspended solids. Geotextile has a capacity to extended life time of intermediate sand filter by inability the accumulation of surface of it and also reliability and performance of traditional graded soil filter and easy to construct. These fabrics are broadly defined as sheet or web structure bonded together by entanglingfiberorfilaments(andby perforating films) mechanically, thermally or chemically. Four non-woven geotextiles (100GSM 120GSM, 200GSM and 300GSM) of varying properties were used in the study. Different combinations of these geotextiles were employed in the research work for filtration analysis to evaluatetheefficiencyofgeotextilefilters.Theyareflator tuftedporoussheetsthataremadedirectlyfromseparate fibers,moltenplasticorplasticfilm. [2]
GRAVEL:Gravelisalooseaggregationofrockfragments. Gravelarisesnaturallythroughouttheworldasaresultof sedimentary and erosive geologic approaches; it is also produced in abundant quantities commercially as crushed stone. It should be – hard, durable, free from impurities,properlyroundedandhaveadensityofabout 1600kg.Itgripsthesandandpermitsthefilteredwaterto move freely through the underdrains. It also permits the wash water to move upward uniformly on sand. The gravel is placed in5 to6 layers having finest sizeon top. Surface texture plays a vital role in developing the bond betweenanaggregateparticleandacementingmaterial.
SAND: Crushed rock is the best type of filtration sand since it has less chance of being contaminated with pathogens or organic material. Grains of sand are rounded and uniform in size. It is a loose granular substance, typically pale yellowish brown, resulting from the erosion silica and other rocks and forming major constituents of beaches riverbeds, seabed, deserts. Obtainedfromhardrocksuchas –Quartzite,Basalt,etcit free from –clay and organic matter uniform size and nature hard and resistant. If placed in HCL for 24 hr, it shouldnotlosemorethan5%ofitsweight.
PEBBLES: A pebble is a small, hard and smooth, round stone which is found on beaches and at the bottom of rivers. Pebbles are generally considered larger than
granules, less than 20 millimeters diameter. Pebble tools areamongtheearliestknownman-madeartifacts,dating fromthePaleolithicperiodofhumanhistory.
COAL: coal is agreeable product for carbon filtration becauseitisreadilyactivatedandhasinflatedavailability. There are three different types of coal that can be employed for filtration: anthracite, bituminous or lignite. Of these, bituminous coal is the ideal/best choice due to its higher microporosity, its resistance to impact, its strength and the ease with which it is regenerated. It is commonly referred to as “black coal” and contains the same substance as of asphalt. Adsorption is the most importantpartforfiltrationinactivatedcarbon.Aswater spreads out over the surface area of the rigid block, the dissolved solids within it are captivated to the surface of thecarbonandremainwhilethewatercontinuesonward. Additional filtration comes from the size and volume of theporesthemselves.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
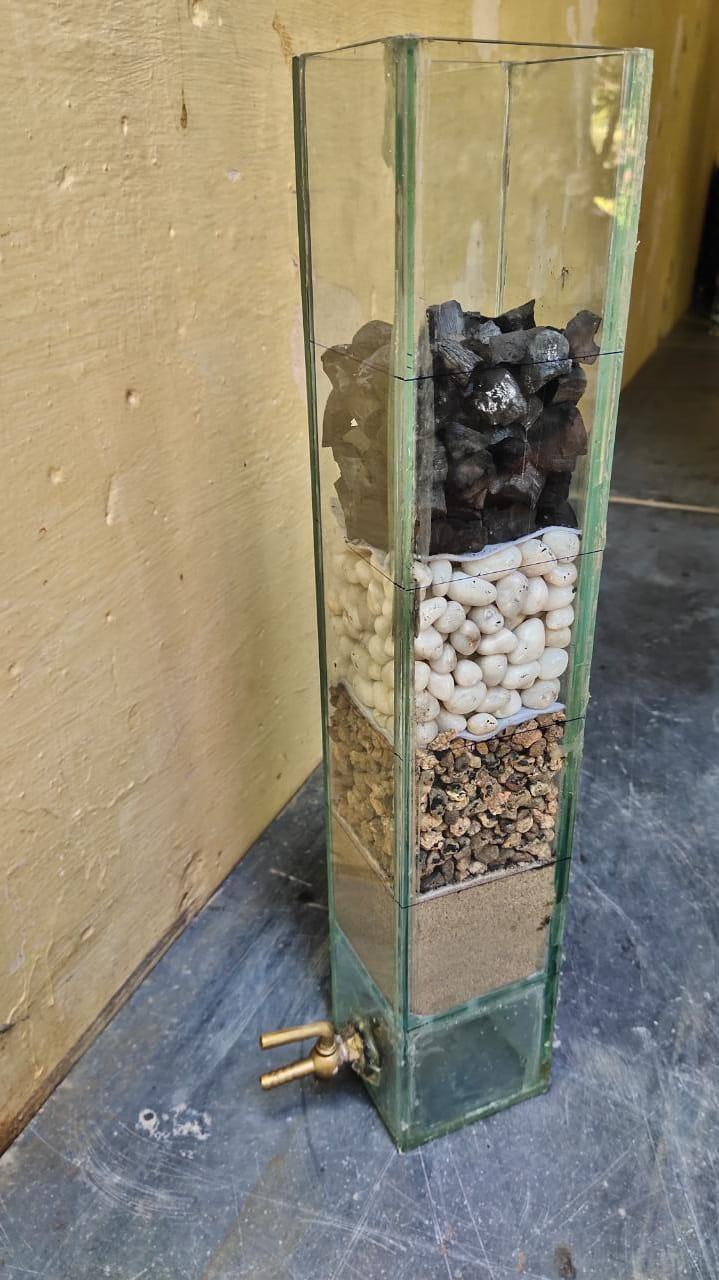

A square column was fabricated using flexi glass with an internal diameter of 8cm and 50cm length. The column was provided with 1 outlet port made out of brass at a distance of 3cm from the bottom in order to collect the effluentsample.Aglassplatewith6mmperforationswas providedatadistanceof8cmfromthebottomsothatthe water trickles down with uniform distribution. Pebbles, Gravel,Coal,Riversand&geotextiles(100,120,200&300 GSM) were used in the filter media. Each layer of filter mediawas8cmthick.Thearrangementofthefiltermedia was done based on the size of the particles, (coarser particles on the bottom) the figure below shows the fabrication details of the column setup. The wastewater was allowed to flow through the column by gravity with uniformdistributionoverthefilterbedlayers&laterthe samples were collected & analyzed for various parametersaslistedabove
Parameters Valueobtained pH 7.94 Alkalinityinmg/l 305.63 Acidityinmg/l 100.10 TurbidityinNTU 653 Hardnessinmg/l 464 Solidsinmg/l 593 BODinmg/l 89.12
Table 01- initial characteristics of waste water sample
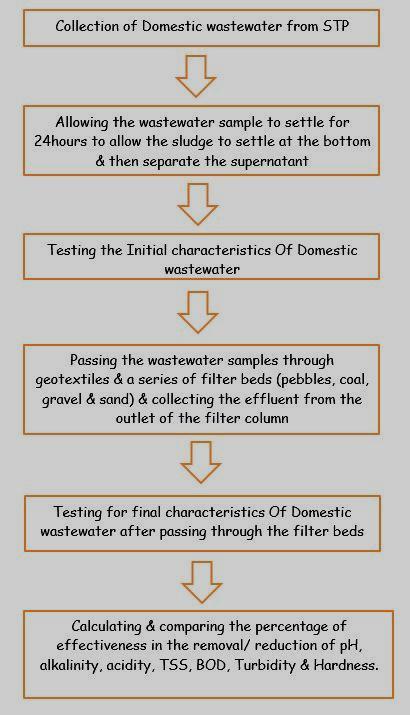
Variation in pH
FabricsizeinGSM pH 120 7.41 150 7.35 200 7.22 300 7.20
Table 02- results for variation in pH
Figure 01- filter column setup
The water sample immediately was tested for its initial characterizationand the following results were obtained
Figure 02- Variation in pH
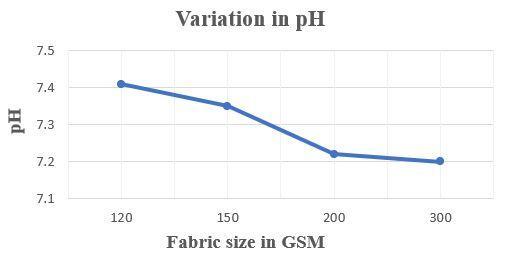
Variation in Alkalinity
FabricsizeinGSM Alkalinityinmg/L 120 209 150 206.19 200 200.93 300 182
Table 03- results for variation in Alkalinity
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Figure 03- variation in Alkalinity Variation in Acidity
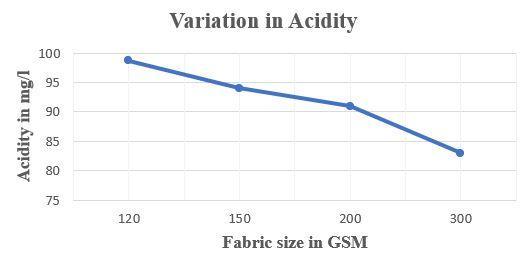
FabricsizeinGSM Acidityinmg/L 120 98.74 150 94.00 200 91.00 300 83.00
Table 04- results for variation in Acidity
Figure 04- variation in Acidity
Variation in Hardness
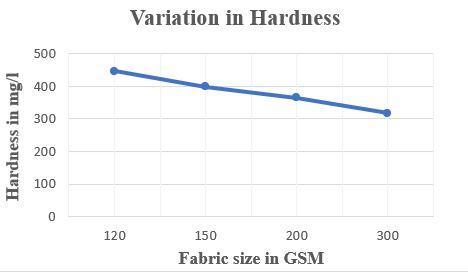
FabricsizeinGSM Hardnessinmg/L 120 445 150 398 200 364.12 300 317.69
Table 05- results for variation in Hardness
Figure 05 – variation in Hardness Variation in Turbidity
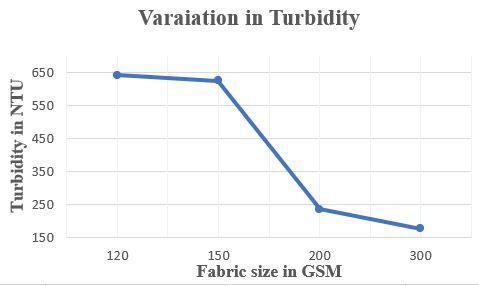
FabricsizeinGSM TurbidityinNTU 120 641 150 624 200 235 300 175
Table 06- results for variation in Turbidity
Figure 06 – variation in Turbidity Variation in BOD
FabricsizeinGSM BODinmg/L 120 78.4 150 76.7 200 75.4 300 70.16
Table 07- results for variation in BOD
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
geotextile, as compared to their natural soil counterparts,isan advantageinso far aslight weight on the subgrade, less airspace used, and avoidance of quarriedsand,gravel,andclaysoilmaterials.Theease of geotextiles installation is significant in comparison tothicksoillayers(sands,gravels,orclays)
[1]“Coirgeotextilebaffleasbiofilmattachmentmedia for grey water treatment” Ammena.F. A, Anju.KC2018
Figure 07 – variation in BOD
Variation in Solids
FabricsizeinGSM Solidsinmg/L 120 523 150 220 200 163 300 159
Table 08- results for variation in solids
[2] “Treatment of domestic waste water using chemicalcoagulationfollowedbygeotextilefiltration” Revathi,SadashivaMurthy.B.M-2016
[3] “Capacity of textile filters for waste water treatment at changeable waste water level hydraulic model”MarcinSpychała,MaciejPawlak-2016
[4] “Treatment of Combined Sewer Overflows Using Geotextile Baffle Contact Method” Eyup Korkut, Cevat Yaman,RogerMarino-2014
[5]“Performanceofcoirgeotextilesasattachedmedia in biofilters for nutrient removal” Gopan Mukkulath, Santhoh.G.Thampi-2012
[6] “Effects of waste water filtration on permeability” C.Yaman,JPMartin,&E.Korkut-2006
[7] Emin. M Kutay and Ahmet H. Aydilek, 2005, Filtration Performance of Two-layer Geotextile Systems, GeotechnicalTestingJournal,Vol.28,No1
[8] Aydilek. A. H. and Edil. T. B, 2002, Filtration Performance of Woven Geotextile with Wastewater Treatment Sludge, Geosynthetics International, IFAI, Vol.9,No.1,pp.41-69.
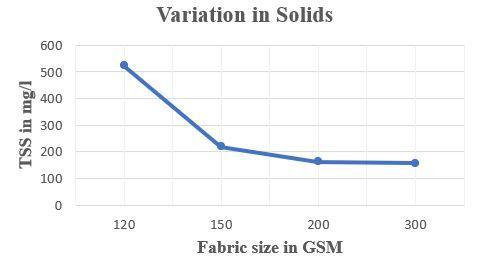
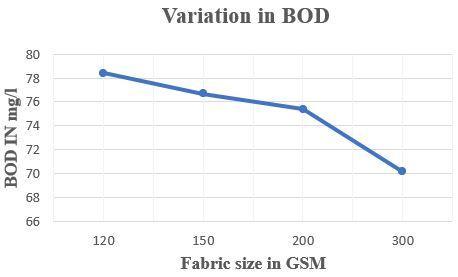
Figure 08- variation in solids
From the literature as discussed above, it is observed that less work is carried out on filtration of domestic wastewater using geotextile filter. Use of geotextiles has been found very effective solution in the treatment of wastewater. Geotextiles provide more strength, flexibility, durability and controlled degradation compared to sand filters. As geotextiles consist of synthetic fibers, bio degradation is not a problem. Geotextile filters improve the reliability and performance of traditional graded soil filters and are easiertoconstruct.Thelowthicknessof
[9] Edil. T. B And A. H. Aydilek, 2003, Long Term Filtration Performance of Nonwoven GeotextileSludgeSystems,GeosyntheticsInternational,10,No.4, 110-123
[10] Kwangyeol Lee and Hanyong Jeon, 2008, Evaluation of Clogging Effects on Nonwoven Geotextile Filters by Negative-ion Treatment, Fibers andPolymers,Vol.9,No.3,Pp.365-373.