International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
TERM DEPOSIT SUBSCRIPTION PREDICTION
Ram Teja Inturi1, Gurazada D V S Sriram Chandra2[1]Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Lovely Professional University, Phagwara [2] Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, KL Education Foundation, Guntur *** --
Abstract - In this paper, we are applying some of the most popular classification models) for classifying the term deposit dataset. J48 is another name for C4.5, which is the extension of the ID3 algorithm. We have collected 20 datasets from the UCI repository [1] containing many instances varying from 150 to 20000. We have compared the results obtained from both classification methods Random Forest and Decision Tree (J48). The classification parameters consist of correctly classified, incorrectly classified instances, F-measures, Precision, and recall parameters. We have discussed the advantages and disadvantages of using these two models on small datasets and large datasets. The results of classification are better when we use Random Forest on the same number of attributes and large datasets i.e. with a large number of instances, while J48 or C4.5 is good with small data sets (less number of instances). When we use Random Forest on the term deposit dataset shows that when the number of instances increased from 285 to 698, the percentage of correctly classified samples increased from 69% to 96% for the dataset with the same number of attributes, which means the accuracy of Random Forest increased. Logistic regression is a statistical modelthat in its basic form uses a logistic function to modela binary dependent variable, although many more complex extensions exist. Inregression analysis, logistic regression (or logit regression) is estimating the parameters of a logistic model(a form of binary regression).
Keywords - Classification, Random Forest, Decision Trees,LogisticRegression,Dataset,Algorithms.
1.INTRODUCTION
The application of the Decision Tree algorithm [2] is widely observed in various fields. Classification of text, comparison of text, and classification of data are the fieldswheretheyareused.Alongwiththese,inlibraries books are classified into different categories based on theirtypewiththeimplementationoftheDecisionTree. In hospitals, it is used for the diagnosis of diseases i.e. tumors,Cancer,heartdiseases,Hepatitis,etc.Companies, hospitals,colleges,anduniversitiesuseitformaintaining their records, timetables, etc. In the Stock market, it is alsousedforstatistics.
Decision Tree algorithms are highly effective in that the rules of classification are provided such that they are
human-readable.Alongwithalltheadvantages,thereare some drawbacks, one of the advantages is the sorting of all numerical attributes when a node is decided to be split by the tree. Such split on sorting numerical attributesbecomessomewhatcostly i.e.,runtime,sizeof memory, and efficiency especially if Decision Trees are applied on datasets with large size i.e., it has a large number of instances. In 2001, Bierman [4] proposed the idea of Random Forests which performed better when compared with other classifiers such as Support Vector Machines, Neural Networks, and Discriminant Analysis,anditalsoovercomestheoverfittingproblem.
These methods such as Bagging or Random subspaces [5][6] which are made by combining various classifiers and those methods produce diverse data by using randomization are proven to be efficient. The classifiersuserandomizationintheinductionprocessto build classifiers and introduce diversity. Random Forestshavegainedwidepopularityinmachinelearning due to their efficiency and accuracy in discriminant classification[7][8].
In computer vision, Random Forests are introducedbyLepitet[9][10].Inthisfield,his workhas provided foundations for papers such as class recognition [11][12], two-layer video segmentation [13] image classification, and person identification [14][15], as they use random forests. Wide ranges of visual clues are enabled naturally by Random Forests such as text, color, height, depth, width, etc. Random Forests are considered vision tools and they are efficient in this purpose.
Random Forest as defined in [4] is the genericprincipleofacombinationofclassifiersthatuses base classifiers that are L- tree-structured {h (X, Ѳn), N=1,2,3,...L}, where X represents the input data and {Ѳn}isafamilyofidenticalandnotindependentandalso distributed random vectors. In Random Forest the classifiers use random data to construct a decision tree from the available data. For example, in Random Forest each decision tree (as Random Subspaces) is built by randomly sampling a subset, and for each decision tree, random sampling of the training dataset is done to producediversedecisiontrees(ConceptofBagging).
Logistic regressionis a statisticalmodelthat in its basic form uses alogisticfunction tomodela binary
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
dependent variable, although many more complex extensions exist. Inregressionanalysis,logistic regression(orlogit regression) is estimating the parameters of alogistic model(a form of binaryregression).
In a Random Forest, the features are selected randomlyfordecisiontreesplit.Thecorrelationbetween each tree in random forest decreases by randomly selecting features from a dataset which increases the predictivepoweroftherandomforestandalsoincreases efficiency.SomeoftheadvantagesofRandomForestare [16]:
Random forest also overcomes the problem of overfitting.
Randomforestsarealsolesssensitivetooutliers intrainingdata.
Pair-wise proximity between the samples is measuredbythetrainedmodel.
In this article, we discuss the accuracy and other parameters when decision trees, Random Forests, and Logistic Regression are applied to the term deposit dataset. The main objective of this comparison is to create a line between these classification methods. This also helps in the selection of a suitable model. The rest of the paper is as follows: Section 2 is about Literature Review and Decision Tree related classification algorithm which also includes the Random Forest and Logistic Regression and the datasets used are described in Section 3. Section 4 deals with the results and conclusion.
2. DATASET
Setting parameters is easy which therefore eliminatesthepruningofthedata.
Variableimportanceisgeneratedautomatically.
Accuracyisgeneratedautomatically.
Random Forest not only uses the advantages of decision trees but also uses the bagging concepts,itsvotingscheme[17]throughwhichdecisions aremadeandrandomsamplesofsubsetsaregenerated. Random Forests most of the time achieve better results thandecisiontrees.
The Random Forest is appropriate for datamodelingwhichishighdimensionalasitcanhandle missing values and also can handle numerical and categorical and continuous data and also binary data. The bootstrapping process and ensembling make RandomForeststrongtoovercometheproblemssuchas overfittingandmakessurethatthereisnoneedtoprune the trees. Besides some advantages such as high accuracy, Random Forest is also efficient, interpretable, and not parametric for some types of datasets [2]. The modelinterpretabilityandpredictionaccuracyaresome of the very unique features among some of the machine learning methods provided by Random Forest. By utilizing random sampling and ensembling techniques betteraccuracyandgeneralizationofdata.
Bagging provides generalization, which improves with the decrease in variance and improves the overall generalization error. As same as a decrease in bias is achievedbyusingboostingprocess[19]. RandomForest has some main features which have gained some focus are:
Accurate prediction results for different processes.
Byusingmodel training, the importanceofeach featureismeasured.
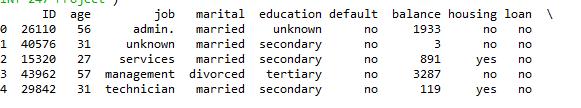
You are provided with the following files: 1. train.csv: Use this dataset to train the model. This file contains all the client and calls details as well as the target variable “subscribed”.Youhavetotrainyourmodelusingthisfile. 2. test.csv: Use the trained model to predict whether a newsetofclientswillsubscribetothetermdeposit.The sampleofthedatasetisshowninfig-1.
2.1 Variable Definition
IDUniqueclientID age-Ageoftheclient job-Typeofjob marital-Maritalstatusoftheclient education-Educationlevel
default-Creditindefault housing-Housingloan loan-Personalloan contact-Typeofcommunication month-Contactmonth day_of_week-Dayoftheweekofcontact duration-Contactduration campaignnumber-numberofcontactsperformedduring thiscampaigntotheclient
pdays -number of days that passed by after the client was last contacted the previous number of contacts performedbeforethiscampaign poutcome -the outcome of the previous marketing campaign Subscribed (target) has the client subscribed to a term deposit?
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Here in this problem, we will fit train.csv in the term deposit dataset in this model, predict the test.csv data, andsavetheresult.
3.2 Decision Tree
Fig1:Sampleviewof Dataset
We have applied data pre-processing to the dataset to check if any null values are present. we will apply Dataframe.isnull(). sum() to check the number of null values in each column. If no null values are present we are clear to go. If null values are present apply simple imputer on numerical values and categorical values on categorical variables. Now we will visualize data and as weknowthetargetwewillmake acorrelationmatrixof all variables with the target variable. If the target is independent of any variables we can use variable reduction by dropping some columns. Then we will applythreeclassificationmethodstotrainthedataset.
3. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
We have used three classification algorithms on this term deposit dataset. They are Logistic Regression, DecisionTrees,andRandomForests.
3.1 Logistic Regression
LogisticRegressionwasusedinthebiologicalsciencesin the early twentieth century. It was then used in many social science applications.Logistic Regression is used when the dependent variable (target) is categorical. You canunderstanditbylookingattheFig-2
Forexample,
Topredictwhetheranemailisaspam(1)or(0) Whetherthetumorismalignant(1)ornot(0)
Decision Trees follow a supervised classification approach.Theideacamefromanordinarytreestructure that was made up of a root and nodes branches and leaves. In a similar manner, the Decision Tree is constructed from nodes that represent circles and the branches are represented by segments that connect nodes. A Decision Tree starts from the root, moves downward,andgenerallyisdrawnfromlefttoright.The nodefromwhere thetreestartsiscalled theroot node. The node where the chain ends is known as the leaf node.Twoormorebranchescanbeextendedfromeach internalnodethatisthenodethatisnottheleafnode.A node represents certain characteristics while branches represent a range of values. These ranges act as partitionsforthesetofvaluesofgivencharacteristics.
Apply the Decision Tree model on train.csvandpredicttest.csvdataandsavetheresults.
3.3 Random Forest
Random Forest developed by Breiman [4] is a group ofnon-pruned classification or regression trees made byrandomly selecting samples from training data.The inductionprocessselects randomfeatures.Predictionis done by aggregating (majority voting) the votes of eachtree and the majority output will be given. Each tree isshownasdescribedin[4]:
Fig2-LogisticRegressionChart
ForMnumberofinputvariables,thevariablem isselectedsothatm<Missatisfiedateachnode, m variables are selected randomly from M and the best split on this m is used for splitting. During the forest building, the value of m is madeconstant.
BySamplingNrandomly,Ifthenoofcasesinthe training set is N but with replacement process, from original data. This sample will be used as thetrainingsetformakingthetree.
Eachtreeismadetothehighestpossibleextent. Pruningisnotused.
Apply Random Forest on train.csv and predict test.csv andsavetheresults.
Now we have applied all three models to get the model with the highest accuracy and apply hyperparameter tuningtoincreaseaccuracy.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
We have applied all three models to the dataset and we aregoingtocomparetheresults.Ofallthreemodels,the random forest gives the highest accuracy as shown in Fig-3
5. CONCLUSION
Fig3-Results
RandomForest givesthehighest accuracysoI am going toincreasetheaccuracybyusinghyperparametertuning asinFig-4.Wearetryingtoincreasemax_estimatorsand seewhethertheaccuracyincreasesornot
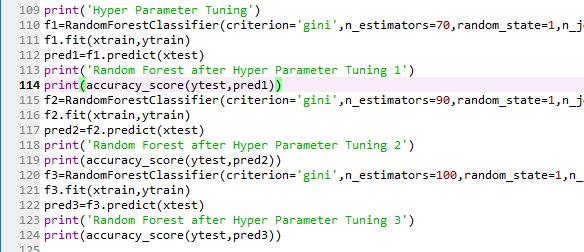
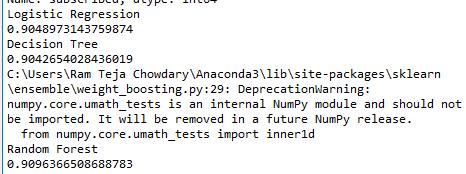
Fig4-Hyperparametertuning
Inthefigure-5wecanseetheincreaseinaccuracyafter hyperparametertuning.
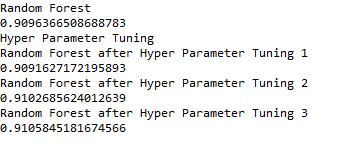
Fig5-Results
Fromtheresults,wecansaythattheRandomForesthas increased classification performance and yields results thataremoreaccurateandpreciseinthecasesofalarge number of instances in datasets. These scenarios also include the missing values problem in the datasets and besides accuracy, it also removes the problem of the over-fitting generated by the missing values in the datasets.Therefore,fortheclassificationproblems,ifone hastodo classificationby choosing oneamong the treebased classifiers set, we suggest using the Random Forestwithgreatconfidenceforthemajorityanddiverse classificationproblems.
6. REFERENCES
[1] A. Asuncion and D. Newman, "The UCI machine learningrepository",2008.
[2] Yanjun Qi, “Random Forest for Bioinformatics”. (2010)
[3] Yael Ben, “A Decision Tree Algorithm in Artificial Intelligence”,2010.
[4] Breiman L, Random Forests classifier, Machine Learning,2001.
[5]“Baggingpredictors,"MachineLearning,vol.24,1996.
[6]THo,"constructingdecisiontreeforests,",1998.
[7]AmitY,GemanD:Shapequantizationandrecognition withrandomizedtrees,1997.
[8]“Comparison of Decision Tree methods for finding activeobjects”YonghengZhaoinclassification(2012).
[9] Lepetit V, Fua P: Keypoint recognition using randomizedtrees.(2006)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 08 | Aug 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

[10] Ozuysal M, Fua P, Lepetit, V.: Fast keypoint recognitionintenlinesofcode.(2007)
[11] Winn J, Criminisi A: Object class recognition at a glance.(2006)
[12] Shotton J, Johnson R.: Semantic texton forests for imagecategorizationandsegmentation.(2008)
[13] Yin P, Criminisi A, Essa, I.A.: Tree-based classifiers forbilayervideosegmentation.(2007)
[14] Bosh, X.: Imageclassification using Random Forests andferns.(2007)
[15]Apostolof,N,Zisserman,A:Whoareyou?-real-time personidentification.(2007)
[16]IntroductiontoDecisionTreesandRandomForests inclassification,NedHorning.
[17] Breiman, L: Random Forests. Machine. Learning. (2001)
