International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
2
1PG Student, Dept. of Computer Science and engineering, Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering, Bengaluru, India
2Professor, Dept. of Computer Science and engineering, Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering, Bengaluru, India ***
Abstract - Plant diseases can lower the quality and output of agricultural products. For the sake of the health and wellness of the entire globe, it is crucial to identify plant illnesses as soon as possible. Automatic plant disease detection is a growing area of research. Identifying plant diseases that will minimize crop loss and hence boost production efficiency is the primary objective of this work. This paper suggests a method for identifying plant leaf diseases and taking preventative action in the agriculture sector utilizing image processing and well known convolutional neural network (CNN) models, AlexNet. First, this method is used to examine the signs of a sick leaf using images from Kaggle Plant Dataset. Following that, dataset images are subjected to feature extraction and classification using AlexNet to detect leaf diseases. In order to give a preventative measures strategy for the discovered leaf diseases and to develop a thorough understanding of plant health, a graphical interface provided. The suggested approach outperforms conventional and end to end CNN based approaches, demonstrating a considerable increase in processingspeedand discriminativepower.
OneofthemostsignificantareasoftheIndianeconomyis agriculture. It serves as the foundation for the nation's progress. Finding plant diseases is one of the biggest issues the agriculture industry has to deal with. In the past,knowledgeableindividualswouldidentifydiseases.It isexceedinglychallengingforfarmerstogetintouchwith professionalsinisolatedplaces.Oneofthemaincausesof plant diseases is climate change. In big farms, there is a significant loss in agricultural output if the illness is not identified at the appropriate time. Since they can't precisely view the farmer's issue at the service Centre, they occasionally advise farmers on plant diseases in the wrong way. The crop can be destroyed as a result of this. Any illness that occurs naturally can have detrimental impacts on grains and vegetables as well as eventually lowerproduction,productquality,andoutput.Inorderto reduce agricultural erosion, appropriate categorization anddiagnosisofleafdiseasemaybevital.Different grains and Vegetable leaves have various illnesses, including bacterial, fungal, and viral ones. A very effective method for identifying illness signs employing expertise and
scientific knowledge must be developed. If the image features are not picked carefully, even the most sophisticated machine learning classifier will deliver a poor classification performance. For real world applications,findingsignificantanddiscriminativetraitsis adifficultissue.Additionally,aspicturesarecollectedina variety of lighting situations, it is important for the extracted features to be resistant against noise and invariant to multiple transformations (such as scale, rotation, and illumination conditions). Recent deep learning algorithms are mostly utilized for pattern recognition since they have successfully been used to distinguish between various outlines. DL makes feature extractionautomated.TheDLdeliversahighaccuracyrate in the classification job and, when compared to other conventional machine learning methods, decreases error rateandcomputationaltime.
For this work, the initial collection of images of crop leaves is made using Kaggle datasets. A standard digital camera or a high resolution camera on a mobile phone mightbeusedtotakethepictures.Thegatheredleavesare subjected to image processing. On plant leaves, several image processing techniques are used, including acquisition, preprocessing, restoration, segmentation, augmentation,featureextraction,andclassification. These images may be transformed into aligned structures using image augmentation techniques like flipping, cropping, and rotation, and other features like portion, color information, or borders can be tracked in the image. In this study, convolutional neural network (CNN) models like AlexNet, which are various classification methodologiesbeingused.Imagesofhealthyandillleaves are categorized by AlexNet, and the numerous leaf diseases are identified. In addition, many of the technologies presently in use in agriculture fieldcan identify some plant leaf diseases but do not offer a strategyfortakingpreventativeaction.
Due to this, the system suggested in this research uses a graphical user interface to both detect disorders andofferapreventativeaction. Themajorsummaryofthe suggested framework is provided by the contributions below: In order to diagnose diseases, we first use image processingtechniquesonleafdatasets.Second,weusethe AlexNet architectures to categorize the processed leaf images. Thirdly, the accuracy of the categorization of all leaf diseases is examined in this work. We examine and
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
create the graphical layout for illness identification with preventative measures in the final step. Numerous computationaltechniqueshavebeencreatedinthefieldof modern agriculture to assist farmers in detecting plant illnessesandmonitoringthehealthydevelopmentoftheir crops. The identification of plants, leaves, and stems as well as the knowledge of diseases, their occurrence rate, and their symptoms are therefore essential for the effectivegrowthofplants.Thus,thereisspacetowork on the creation of cutting edge, effective, and quick interpretive algorithms that will aid in the detection of illnesses. The suggested technique uses software to automaticallyidentifyandcalculatetexturaldataforplant leafdiseases.
Identifying plant diseases has largely been conducted in the early stages using various machine learning techniques. The following steps are generally followed by all systems. Digital cameras are first used to capture the photographs. The photos are then preprocessed using severalpreprocessingmethods.Then,theexpertstakethe crucial elements out of those images, and the classifier uses those features as inputs. Here, the method of image processing and feature extraction is what determines the classification accuracy. It takes a long time and is really difficult.
There is discussion of current trends in the use of CNN and deep learning architectures in agricultural applications.[1]Focusestoidentifyandcategorizevarious plant diseases, the authors present the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model.This CNN combines with Machine Learning SVM for feature extraction and classification. So it requires more time for processing and exhibit less accuracy. In [2] this research, we explore image processing techniques for the identification and classification of leaf plant diseases that benefit agriculturalistsworkinginthesectorofagriculture.There are several phases included in it, including image acquisition, image processing, segmentation, feature extraction, and classification. The specific researchers made incorrect diagnoses and classifications of plant illnesses using various computations and frameworks. In [3] identifying plants, leaves, and stems as well as learning about illnesses, their prevalence, and their symptoms is essential for successful plant cultivation. Therefore,thereisroomtoconcentrateoncreatingnovel, effective,andquickinterpretivealgorithmsthatwillaidin illness detection. A software system for the automatic identification and computation of textural statistics for plant leaf diseases is the proposed system. In [6] using image processing and two well known convolutional neural network (CNN) models as AlexNet and ResNet 50, the article suggests plants leaf disease diagnosis and preventive measures technique in the agricultural field. First, this method is used to examine the signs of sick
leaves forKaggle datasets of potato and tomato leaves. Then, using AlexNet and ResNet50 models together with imageprocessing,thefeatureextractionandclassification process is carried out on dataset images to identify leaf illnesses. The testing findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the suggested strategy, which achieves an overall accuracyof97and 96.1percent. In Paper[7]uses EfficientNetandDenseNet,twoDeepConvolutionalNeural Network models, to detect apple plant diseases from photos of apple plant leaves and correctly classify them into four categories. Included in the categories are "healthy," "scab," "rust," and "many illnesses." In this study, the dataset for apple leaf disease is enhanced utilizing image annotation and data augmentation techniques, specifically Canny Edge Detection, Blurring, andFlipping.Basedonanexpandeddataset,modelsusing EfficientNetB7 and Dense Net are suggested, providing accuracy of 99.8% and 99.75%, respectively, and addressing convolutional neural network drawbacks. To create even more precise and reliable models, stacking, ensembling, and strong validation procedures might be used.
The suggested CNN model in [8] aims to distinguish between fruit and leaf types that are healthy and those that have common citrus illnesses like black spot, canker, scab, greening, and Melanose. By combining multiple layers, the proposed CNN model captures complementing discriminative characteristics. On the Citrus and Plant Village datasets, the CNN model was compared to other cutting edge deep learning methods. The CNN Model performs better than the rivals in a number of measuring measures, according to the testing data. With a test accuracy of 94.55 percent, the CNN Model is a useful tool for farmers who want to characterize citrus fruit/leaf illnesses. With a single dataset in a single domain, isperformedoncitrusfruit/leafdiseaseidentification,but formoredomainsrequiresresearch.
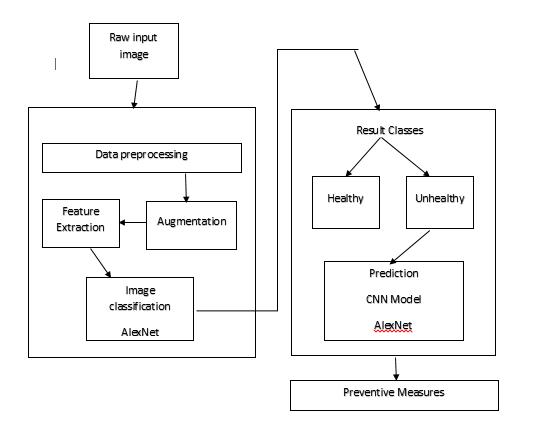
Thesuggestedframeworkfordetectingleafdiseaseand taking preventive action. The fundamentals of the suggested technique with leaf image gathering are illustratedinthisframework.
1. Images of leaves were extracted from the Kaggle dataset.Ona datasetof leaf images, imageprocessing methods such as image preprocessing, image augmentation, feature extraction, conversion to an array format, feature selection, and classification are used.
2. A training set and a testing set are created from the dataset.
3. The dataset image is trained, and data is then extracted using a deep learning approach. Using CNN topologies like AlexNet, this research proposes a methodfordetectingleafillnesses.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
4. Additionally, a plan for leaf disease prevention has beendevised.
The following steps are controlled step by step by the suggested approach to detect leaf diseases indicated in Fig 1
on 80% of the dataset, with the remaining 20% used for testing.
Fig 1: OverviewoftheProposedSystem
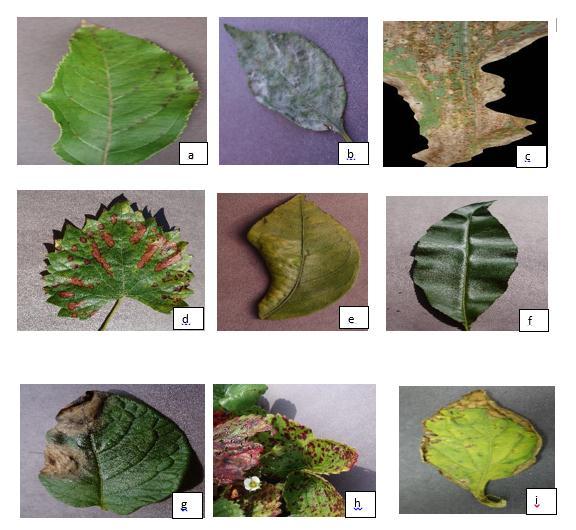
The importance of using quantitative or qualitative datasets to support field study performance, data preference, or research integrity cannot be overstated. However, a high resolution digital camera or a smart camera can be used to capture leaf photos for databases. For our investigation of the effectiveness of our research, we have taken leaf photos from samples in the Kaggle dataset shown in the below fig 2, which includes both healthy and diseased leaf images. This dataset includes pictures of common plant illnesses among its 54323 images of leaves from 38 distinct kinds of plants. Since colored photos provide more accuracy than grayscale photographs, all of the images utilized in this work are coloredimages.

The training and testing sets are created by randomly dividing the total dataset. The model is trained using the training set. These sets are typically divided into portions of 60 % to 40 %, 80% to 20 %, etc. The training dataset can be expanded to include more images to produce the most accurate results. In this study, the model is trained
Toimprovethequalityoftheleafimagesandremoveany undesirable elements, the pre processing technique is required. Where itconverts raw input leaf image datasets into suitable process datasets format. Phases of these procedures include data cleansing, integration, reduction, and transformation. It controls the missing data, corrects the inconsistent data, and removes the unwanted distortion during the data cleaning step. In leaf image datasets, diverse and heterogeneous data, as well as data redundancy, are typical situations of data retrieval procedures that must be resolved in order to organize an uniformrepresentationofthedata.Toimprovethespeed and effectiveness of image processing, a significant amount of data is removed during the data reduction process.
To reduce the dependability of the attributes in the data assessment structures and units for data image conversion,theoperationsofdatatransformationexecute
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
the data smoothing, aggregation, feature construction, normalization, and discretization. For training datasets andtestingdatasetsanalysis,theseleafimagedatasetsare scaled and transformed into 256*256 dimension. Pre processingtechniquescanbeusedtopreparedatasetsfor identifying leaf diseases using databases of leaf images. Converting a NumPy array with a range of 0 to 255 to a float tensor with a range of 0 to 1 is what it means to "transformthedatasetinto tensordata type."Thedataset is normalized in order to do a mean and standard deviation calculation. This is doneto each image in the collection
To accurately diagnose leaf disease, augmentation is required to modify and facilitate the display of the leaf image. To reduce the risk of over fitting and to improve the model's simplicity, the training and testing leaf image datasetsare expanded. The original leafpicturecollection is resized using flipping, cropping, and rotating procedures, and the leaf images are converted into RGB using color transformation technology, all as part of the augmentation process. However, in order to preserve the balancedqualityandamountofimagesinthehealthyand unhealthy leaf datasets, augmented leaf images were developed.
Inthisstudy,featureextractionandclassificationareboth carried out using a pre trained AlexNet. The big dataset named ImageNet, which comprises 14 million photos, has alreadybeenusedtotraintheAlexNetinthiscase.
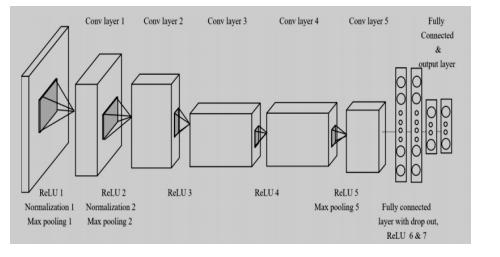
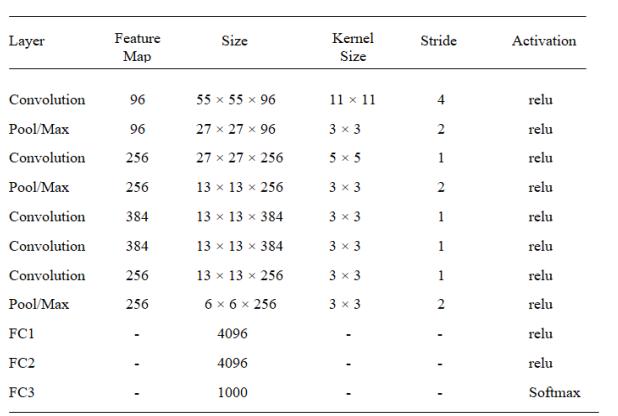
TheCNNArchitectureisacollectionofuniquelayersthat, with the aid of a differentiable function, convert input volume into output volume. The first convolutional network to employ a GPU to improve performance was AlexNet. Five convolutional layers, three max pooling layers, two normalization layers, two fully connected layers, and one softmax layer make up the AlexNet architecture shown in the fig 3 . Nonlinear activation function ReLU and convolutional filters make up each convolutional layer. Max pooling is carried out using the pooling layers.Because completely connected layers are present, input size is fixed. The input size is typically stated as 224x224x3, however because of padding, it actually comes out to be 227x227x3.There are 60 million parametersinAlexNet.
• TheactivationfunctionReLUisbeingused.
• Made use of no longer common normalization layers
• 128 piecebatchsize
• SGDMomentumasanalgorithmforlearning
• Extensive data augmentation, including jittering, cropping,flipping,colorcorrection,etc.
• Assemblingmodelsforthebestoutcomes.
Convolution,numerouspoolinglayers,theRectifiedLinear Unit (ReLu), normalization layers, and a dense layer for prediction will be used to develop a Convolution Neural Network (CNN) model that has already been trained on AlexNet.Theimageisinitiallyresizedto227*227.Next,the first convolution layer receives the image.96 kernels of 11x11 pixels are applied in the first layer. These kernels identifyvariousimageedges.Theimageisthenpassedon tothesecondconvolutionlayer,where256kernelsofsize 5*5areused.Themaxpoolinglayerthenuses3*3pooling witheachkernelfunctiontominimizetheimagesize.Until the input size is 3*3 with 256 kernels, this will be repeated. Finally, 4096 neurons were used to build the twofullyconnectedlayers.Theconnectionsbetweeneach neuron are extensive. According to the classes in our dataset, the final layer's 1000 classes are broken down into38classes.
After all convolution layer and the final two fully connected layers, a non linear, non saturating activation function called ReLu is used. The speed is increased. To address the over fitting, the dropout is added to the network. The dropout will enhance network performance during the testing phase. This model makes advantage of batch normalization to boost speed, performance, and neuralnetworkstabilityshowninthefig 4.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The user's graphical layout shown in fig 5 is created in suchawayapplicationoftheleafdiseaseclassificationcan displaythemessageofleafdiseaseandprovidepreventive measures for a rich knowledge of plant health to farmer. This graphical interface is created using JavaScript which provides interface for the Deep learning model AlexNet. Forthefarmers,therearetwointerfaces.Fortheuploaded photos, one is utilized to display the disease and the precautions. Other interfaces show the disease detection accuracy for the given image, interpreting the percentage ofdiseaseclassificationaccuracy.
Fig 4: ParametersofAlexNetArchitecture
Each of the network's convolutional layers serves as a featureextractor.TheTensoflow,AlexNetmodelisdivided into a stage for feature extraction and another for classification. The classifier is made up of fully connected layers, while the feature extractor is made up of convolutional layers. The crucial features are extracted fromtheinputbytheconvolutionallayer.Edges,lines,and corners are low level features that are extracted by the firstconvolutionlayer.Higher levellayersgethigher level features out of the data. The base learning rate, momentum, and batch size are the hyper parameters that are utilized in the AlexNet architecture. This hyper parameter describes the network's hierarchical structure andtrainingprocess.
To categorize the class of leaf illnesses, the classification based CNN model in the image processing system uses trained data and test data of leaf pictures. The model is prepared to classify any unlabeled plant photos once the training procedure is complete. The model receives an image as input, compares it to images used for training and testing, and outputs both the plant name and the diseasename.Iftheplantspeciesisincludedinthedataset and the model has been successfully trained, the model can detect the illness. The test image and trained model arecomparedaftereffectivetrainingandpreprocessingin ordertoidentifythedisease.
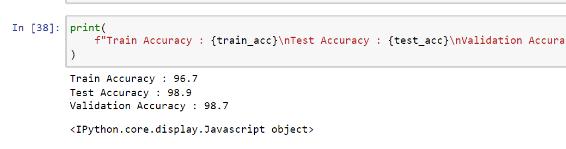
A set of experiments was conducted on a dataset that included two categories of healthy and unhealthy leaf images to represent the performance of the experiments. 60%oftheleafimageswereusedforthetrainingdataset, and the remaining 40%were used for the testing dataset. Forthepurposeofclassifyingandidentifyingleafdiseases, gathered image datasets are subjected to deep learning architectures such as AlexNet. 25 epochs were used, and the batch size was set to 64. To gauge the model's precision,40%ofthephotosfromthePlantVillagedataset wereused.40%oftheimagesineachclasswerechosenat randomtobetested.Thecorrectnessofthetestingdataset is greater than 98.9% as shown in the fig 6. In other words, 97 out of 100 input photos were correctly classified. Accuracy increases along with increasing the training dataset and epoch. The model's accuracy is at its highest,98.9%,atthe10thepoch.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
internet.Thephotographsshouldbeinthe.jpgformatand should be in color. The following page, which shows the predictions for the uploaded image, will be redirected afterthephotographshavebeenuploadedasshowninthe fig 8
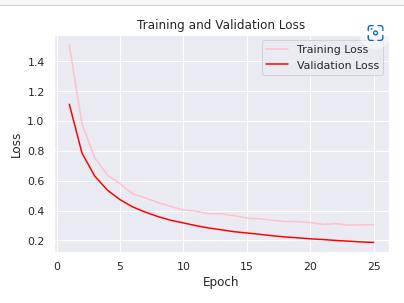
The loss for the model's generated by training and Validation graphs is displayed in the fig 7 below. As the epochgets bigger, the loss gradually decreases. When opposed to training loss, validation loss is less. The model'slossisatitslowest,20%,atthe25thepoch.
Along with the disease term, an image is displayed. Here, you have the option of simultaneously uploading one or more photographs. The user's graphical layout is created in such a way after the application of the leaf disease classificationsystemthatitcandisplaythemessageofleaf disease and provide preventive measures for a rich knowledgeofplanthealthtofarmer
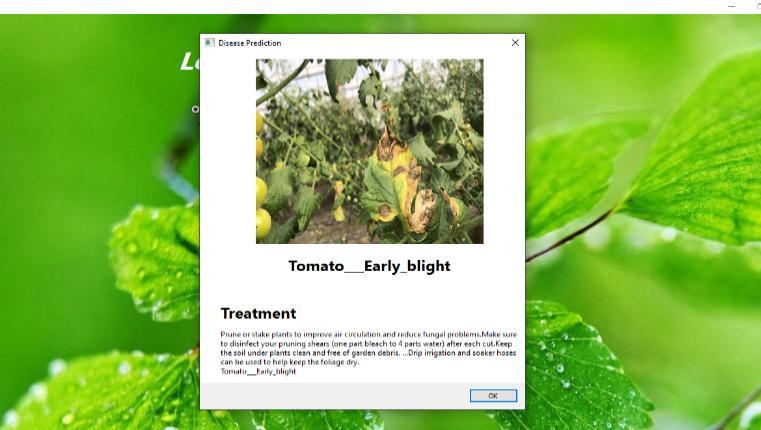
Asdepictedinthefig 9,whentheimageisprovidedbythe user, it haspredictedtomato early blight as diseaseand offerscontrolstrategiesforthatdisease.
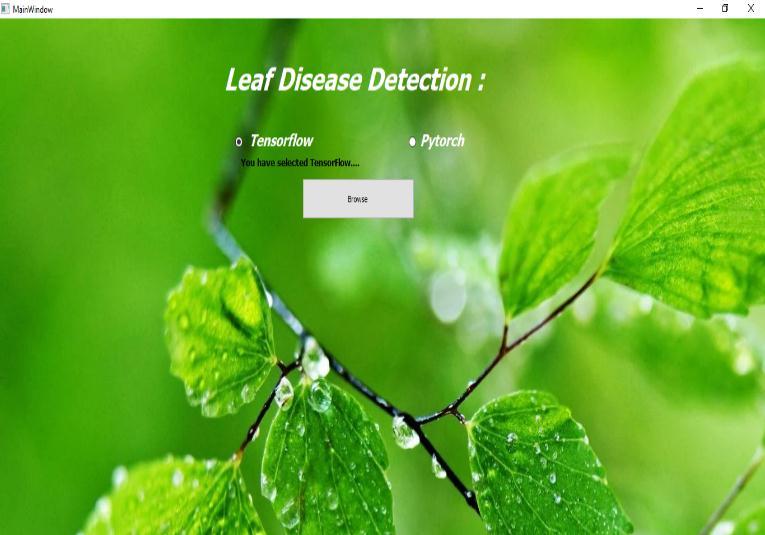
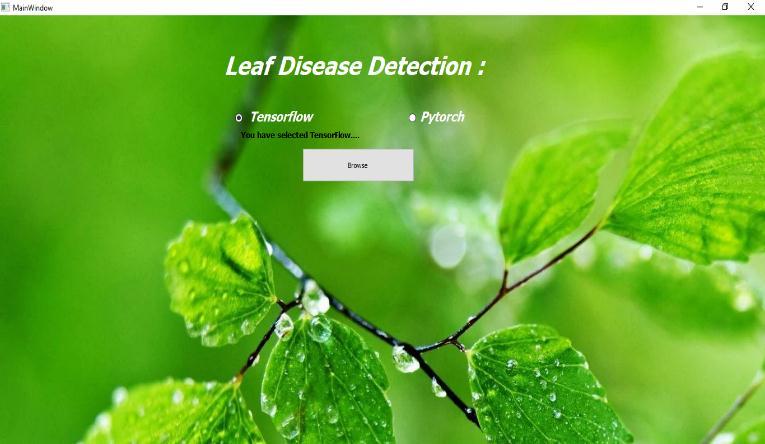
TheJavaScriptwebapplicationframeworkoffersavariety oftoolsforbuildingjavawebapplications.Withthehelpof the JavaScript displayedweb application is developed showninfig 8
On this webpage, there are two radio buttons that are denotedbytensorflow,andthePyTorchusermustchoose one of them. One utilizes PyTorch to forecast while another uses Tensor Flow in the backend. There are two buttons on this website, upload and choose files buttons. The pictures are taken with a phone camera or a regular camera, and they may be downloaded and posted via the
Theotherinterface,denotedbythePyTorchradiobutton, is in charge of understanding the percentage of illness classification accuracy and displaying the disease detectionaccuracyfortheprovidedimage.
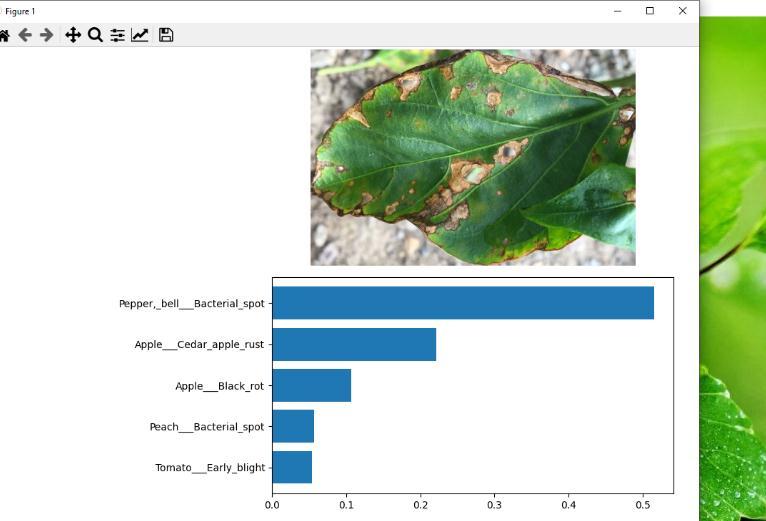
When an image is uploaded, accuracy is displayed as a graphwiththenameofthedisease,asshowninthefig 10
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

OneofthemostsignificantareasoftheIndianeconomyis agriculture. The ability to predict agricultural diseases is crucial for any nation's economy to grow. The suggested method classifies the various plant diseases included in the Plant Village dataset using a CNN model. The AlexNet architecturewillclassifythenumerousplantdiseasesinto 38 different distinct classes. Data pre processing, augmentation,anddata extractionoperationsareusedon leaf datasets from Kaggle to look at the signs of diseased leaves. Additionally, this system uses the AlexNet architectures to classify the processed leaf images. The overall categorization accuracy of leaf diseases is also examined in this work. For which this approach has a better accuracy estimatedfrom the AlexNet model of 98.9%. The graphical structure for leaf disease diagnosis with preventative measures can therefore be demonstrated. On thissuggested system, alternative learning rates could be explored in the future. The suggested system can be further improved by including newfeatureslike thelocation ofstoresnearthe user, a list of pesticides and fertilizers, real time communication with agricultural specialists through chat orvideoconference,etc.
[1] Stefania Barburiceanu , Serban Meza, (Member, Ieee), Bogdan Orza , Raul Malutan, and Romulus Terebes, (Member,Ieee),” ConvolutionalNeuralNetworksfor Texture Feature Extraction. Applications to Leaf Disease Classification in Precision Agriculture”, VOLUME 9, Dec. 2021, pp. 160085 160103 , doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3131002
[2] Mobeen Ahmad,Muhammad Abdullah, Hyeonjoon Moon, Dongil Han,” Plant Disease Detection in Imbalanced Datasets Using Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks With Stepwise Transfer Learning”, Volume 9, Oct 2021, pp. 140565 140580, DOI:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3119655
[3] Abirami Devaraj , Karunya Rathan , Sarvepalli Jaahnavi, K Indira, “Identification of Plant Disease using Image Processing Technique” April. 2019, DOI: 10.1109/ICCSP.2019.8698056
[4] Md. Arifur Rahman, Md. Mukitul Islam, G M Shahir Mahdee, Md. Wasi Ul Kabir ,“mproved Segmentation ApproachforPlantDiseaseDetection”,Dec.2019,DOI: 10.1109/ICASERT.2019.8934895
[5] Xinda Liu ,Weiqing Min , Shuhuan Mei , Lili Wang, Shuqiang Jiang,” Plant Disease Recognition: A Large Scale Benchmark Dataset and a Visual Region and Loss Reweighting Approach”, volume 30, Jan. 2021, pp.2003 2015,DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3049334
[6] Husnul Ajra, Mst. Khairun Nahar, Lipika Sarkar, Md. Shohidul Islam,”DiseaseDetectionofPlantLeafusing Image Processing and CNN with Preventive Measures”, Dec. 2020 DOI: 10.1109/ETCCE51779.2020.9350890
[7] V V Srinidhi, Apoorva Sahay, K. Deeba ,” Plant Pathology Disease Detection in Apple Leaves Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks : Apple Leaves Disease Detection using Efficient Net and Dense Net” ,May. 2021, DOI: 10.1109/ICCMC51019.2021.9418268
[8] Asad Khattak , Muhammad Usama Asghar , Ulfat Batool , Muhammad Zubair Asghar , Hayat Ullah , Mabrook Al Rakhami , (Member, Ieee), and Abdu Gumaei ,” Automatic Detection of Citrus Fruit and Leaves Diseases Using Deep Neural Network Model” , Vol. 9, July. 2021, pp. 112942 112954, DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3096895
[9] S. Santhana Hari, M. Sivakumar , P. Renuga , S. karthikeyan ,S. Suriya,” Detection of Plant Disease by Leaf Image Using Convolutional Neural Network”, Nov.2019,DOI:10.1109/ViTECoN.2019.8899748
[10] G. Madhulatha, O. Ramadevi ,” Recognition of Plant Diseases using Convolutional Neural Network”, Dec. 2021, pp. 738 743, DOI: 10.1109/I SMAC49090.2020.9243422
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page 2826