International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
2
1 MTech Scholar, Civil Engineering Department, Institute of Engineering and Technology, Lucknow, India
2Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Institute of Engineering and Technology, Lucknow, India ***
Abstract One of the main sources of drinking water in Gorakhpurcityisgroundwater(India.).10samplinglocations were chosen for this study's examinations into 10 physical chemical parameters. Between January 2022 and May 2022, during pre and post monsoon months, the work was completed. For assessing water quality, the datasets were subjected to the Hortons method analysis in order to look at seasonal variations in groundwater quality. According to drinkingwaterstandards,theaveragevaluesofpH,turbidity, TDS, total hardness, alkalinity, chloride, nitrate, arsenic, sulphate, and iron content are all within acceptable limits. Additionally, it was found that the parameter's mean values varied relatively little between samples, as opposed to the larger variance seen across.
Key Words: Seasonal Assessment, Ground water, Ph, TDS, Iron, Hardness.
Water is critical and mainly used natural resources. It is fundamental unit of the environment to sustain all reasonablylifeduringthisplanate.Elevatedwaterdemand inagriculturallikewiseasindustrialsectorhasbeenshown in developed country because of unpredicted population growth;urbanization,advancementoftechnologyandbetter standardsof living. From thefull availablewater on earth only 0.16% is suitable for individual consumption and therefore the remaining is polluted because of various ecologicalreasons.Withoutwater,lifewouldn'tbesustained on earth since all the plants and animals contained water around60%byvolume.(Tiwarietal.,2014)Dischargingthe domestic sewage and industrialized effluents into natural streamisoneineveryofthereasonthankstowhichwater resources has become polluted in India or in developing countries.(Saeedi et al., 2009) Groundwater pollution has become a major subject of public concern over the world since water quality performs important role for all living beings. Water quality is a term that is repeatedly defined amongmarinescientists,engineers,managers,andguiding principle.Assessmentofwaterqualityimpairmentpresents challenges to water resource planners. The sequence of changes in quality characteristics of water because of various reasons, in nowadays have become the topic of diverse investigations which played a substantial role in assessingwaterquality.(Vermaetal.,2013)Alsothepossible correlationsamongtheseparameters,significantonesfairly indicate the quality of drinking water in Gorakhpur city.
Groundwatersamplesweretakenatseverallocationsacross Gorakhpur.Physico chemicalpropertiesofthesampleswere examined using the established analytical techniques of IS:3025.(Krishna etal.,2014) Anumber ofvariables were measured, including pH, turbidity, iron, nitrate, chloride, total dissolved solids, sulphate, arsenic, and alkalinity. Results demonstrate that ground water samples, with the exception of total hardness and total dissolved solids, showed only modest seasonal variations in physical chemical constituent concentration.(Districts et al., 2021) WiththeexceptionofTDSandtotalhardness,groundwater had the highest concentration of maximal inorganic componentsduringthepostmonsoonseason.Effectiveuse oftheWaterQualityIndextoaccessgroundwaterqualityin spaceandtodepictseasonalchangesingroundwaterquality characteristics.(JHARIYAetal.,2018)
GorakhpurislocatedintheTarairegionoftheriversRapti andRohniat26°45'northlatitudeand83°22'eastlongitude. ItislocatedclosetotheNepaliborderintheeasternsection oftheIndianstateofUttarPradesh.thelargestsettlementon theTransghagarPlain.Thenameofthecitywaschosenin honors of Saint Guru Gorakhpur, who lived in the 12th century. Being situated close to the border between India andNepalandhavingexcellentrailconnectionsmakesthe city's location extremely advantageous. which has a populationofroughly6,71,048lakhsandisfamousforthe Gorakhnath temple and Gita Press, is the main town of easternUttarPradesh.
Water samples were taken from the shallow deep hand pump and India mark II placed in 2 litre sterile plastic containers.Inordertodeterminethephysicalandchemical characteristicsofthegroundwatersamples,suchaspH,TDS, turbidity,alkalinity,TH,chloride,arsenic,sulphate,nitrate, andiron,conventionalanalyticalproceduresdetailedin(IS 3025). Gorakhpur District were chosen. For physico chemical examination, the materials were collected in sterilizedone literplasticbottles.Thesamplesweretaken from India Mark II hand pumps placed by government organizationsaswellasshallowdepthhandpumpsinstalled bylocalsfordrinkingwater.Thesampleswereexaminedin accordancewiththeestablishedprotocols.Allsamplescame fromthoselocationswheredrinking qualitygroundwater wasbeingextracted.(Singh&Gupta,2022)Foreachseason,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
groundwatersamplequalityparametersareevaluated(pre &postmonsoon).Thegeneralproceduresfollowedforwater qualityanalysiswererepresentedusingflowchart.(JHARIYA etal.,2018)
Table1Parametersofwaterwiththeirpermissiblelimits ofdrinkingwater,recommendedagencyandunitweights. S.No. Parameters Standard Values Recommended Agency UnitWeight 1. pH 6.5 8.5 BIS:10500:2012 0.001135 2 Turbidity 5NTU BIS:10500:2012 0.001929 3 Iron 0.3mg/l BIS:10500:2012 0.032 4 Sulphate 200mg/l BIS:10500:2012 0.00004822 5 TDS 500mg/l BIS:10500:2012 0.00001929 6 TH 200mg/l BIS:10500:2012 0.00004822 7 Alkalinity 200mg/l BIS:10500:2012 0.00004822 8 Chloride 250mg/l BIS:10500:2012 0.00003858 9 Nitrate 45mg/l BIS:10500:2012 0.0002143 10 Arsenic 0.01mg/l BIS:10500:2012 0.964
Parameters Pre monsoon Post monsoon
pH 7.12 7.035
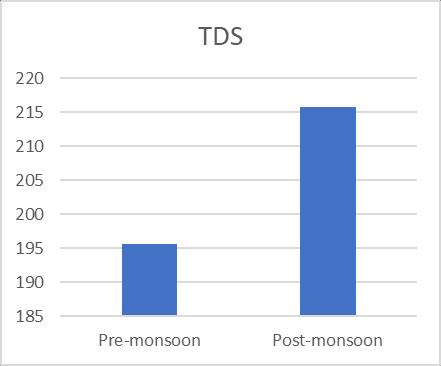
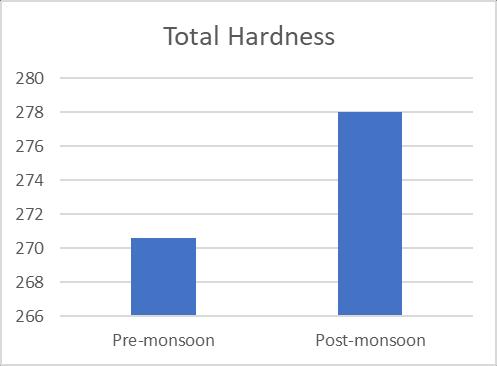
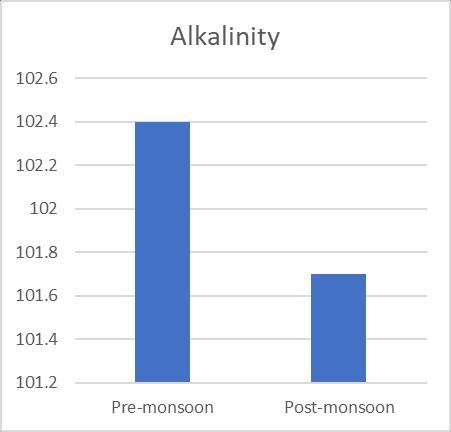
Turbidity 1.96 1.94 TDS 195.7 215.8 TH 270.63 278 Alkalinity 102.4 101.7 Chloride 86.66 81.66 Iron 1.77 1.474 Nitrate 8.12 9.377 Sulphate 46.975 46.75 Arsenic 0 0
Table 2 presents the results of the physicochemical parameter analyses, the means of the variables, and the special and temporal variation that they reflect. Visually. Results should be compressed. Considering the evaluated quality metrics and associated requirements for drinking waterprovided by(BIS:2012). The valueof hydrogenion concentrationdetermineswhetherwaterisacidicorbasic. ThecurrentinvestigationclearlyshowedthatthepHwithin theBIS2012limitrecordedrangesbetween6.65and7.45 before monsoon and 6.78 and 7.49 after monsoon season (Fig.1). pH values above 7.0 may result in incrustation, residuedeposits,andtroublechlorinatingwatertosterilize it, whereas pH values below 7 may result causetuberculationandrust.TheWorldHealthOrganization recommendsapHvalueof6.5orhigherfordrinkingwater topreventcorrosion,andinmostglobaldrainagebasins,a pHvaluebetween6.5and8.5generallyindicatesadequate water quality. Water turbidity, which is caused by substancesexistinginsuspendedform,representshowclear the water is. In the chosen location, average turbidity readings were 1.69 during premonsoon and 1.94 during postmonsoon.Premonsoon andpostmonsoonseasonsare whenturbiditychanges(Fig.2).Surfacewatercontamination canoccurinshalloworpoorlyconstructedwellsorsprings, especiallyduringspringrunofforperiodsofsevererainfall. Duetofloodingduringtherainyseason,copiousamountsof rain, and runoff from agricultural regions, turbidity levels were quite high. Groundwater turbidity is primarily inorganic and brought on by natural geological processes. Highturbiditylevelsorabruptfluctuationsinturbidityhave been seen in this region as a result of the area's water systems'relianceonshalloworpoorlyconstructedbodiesof water.TDSlevelsinwaterareagoodindicatorofsalinity.It includesalloftheothersolidsandmineralcomponentsthat aredissolvedinthe water. Thestudy's mean TDS values
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
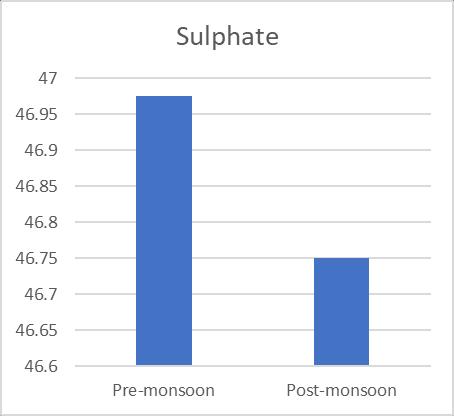
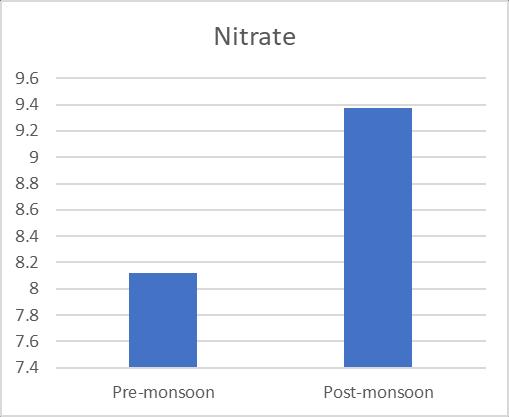
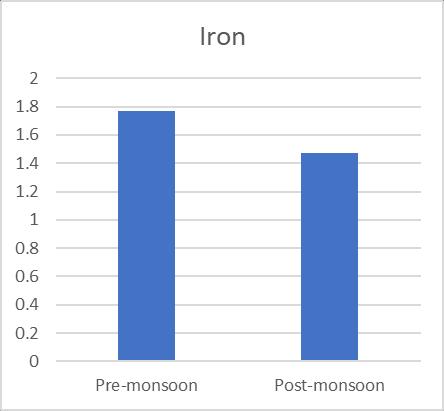
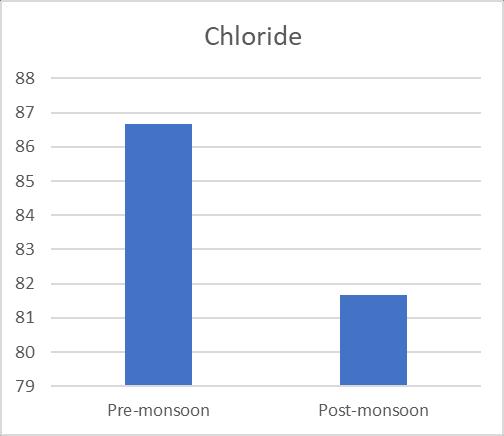
varied, and they were supported by a number of sources. 125 mg/L to 281 mg/L and 140 mg/L to 280 mg/L, respectively,concentrationsaccordingontheseasons(pre& postmonsoon).Additionally,Fig.3 shows the variationin TDSofgroundwatersamplesduringbothseasons.TheBIS recommendedguidelinesvalueof2000mg/L wasusedto classify the examined water samples as acceptable. The presence of sulphates and chlorides in the water which mayoriginatefromnaturalsources,sewageeffluents,urban runoff, etc. founded the somewhat higher TDS concentrationsingroundwater.TDSreadingsthatarehigh affectflavour.Although thealkalinitylevelintheresearch area's ground water is within normal limits, seasonal variationscanbeseen.128mg/Lofalkalinitywasfoundin thesummersample(pre monsoon),whichwasfollowedby 122mg/Linthewinter(postmonsoon).Themildalkalinity in groundwater samples may be the result of increased effluent,domesticsewage,etc.leaching.Whilehardwateris undesirableforwashingclothesandusinginthehomesince itusesalotofsoap.Inthisstudy,hardnessfluctuatesacross therangeof194mg/L to516mg/L and190mg/L to560 mg/L inthe pre andpost monsoonseasons, respectively, andisabovetheacceptablelimitinbothseasons. Chloride levelsinnatural water bodiesareinfluencedbyindustrial processes,agriculturalpractises,andthepresenceofrocks thathavebeenexposedtochloride.Accordingtoastudy,the content of chloride was 86.66 mg/L in the summer (premonsoon)and81.66mg/Linthewinter(postmonsoon). Figure6depictsthevariationinchloridelevelsduringthe two seasons. Since groundwater is a recipient of sewage effluent, farm drainage, and municipal garbage, it has a makeablechlorideconcentrationaddedtoit.Thechloride concentrationinthegroundwillinevitablyriseasaresultof sewageeffluentsbeingusedaswatersources,givingwater andotherliquidsanunpleasanttaste.Acrucialconsideration indeterminingnaturalwater'ssuitabilityforcommunitiesis itssulphatecontent.Inthepremonsoonandpostmonsoon seasons,theobservedvalueofsulphaterangesfrom41.57 mg/L to 46.97 mg/L, respectively. Sulfate16 is present becausetotheleachingofsaltsandotherminerals,aswellas theoutflowofhomesewageandmanufacturingwasteinthis area. High sulphate concentrations in water bodies have harmful effects on fish life and cause diarrhoea and other gastrointestinal problems in humans. The results of the Nitrate and Iron there are almost no unusual changes in nitrateofwatersamples.
Fig -1 pHofthePreandPostmonsoon
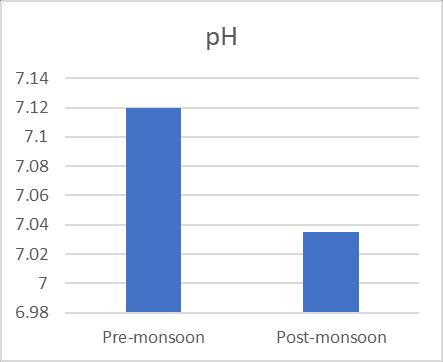
Fig 2 TurbidityofthePreandPostmonsoon
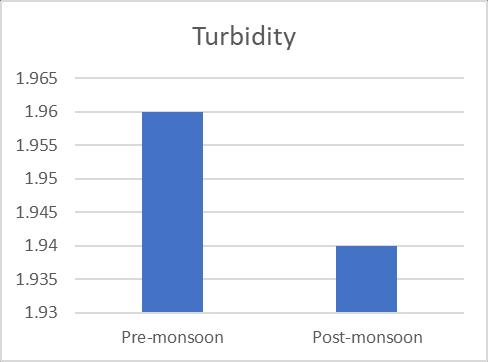
Fig-3 TDSofthePreandPostmonsoon
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Understandinggroundwaterqualityisessentialbecauseitis the primary factor determining whether it is suitable for intended best use. In the vicinity of the sewage treatment plant, the physicochemical properties of groundwater samplesfromrandomlychosendiversewatersources(India markII,shallowdeephandpump)wereexaminedtoassess thepotentialqualityofthegroundwater.Fortheresidentsin the study area, boreholes and hand pumps are the main sourcesofwater(fordrinkinganddomesticneeds).Thebulk ofthechosencharacteristics,withtheexceptionofturbidity, arewithintherangethatisacceptablefordrinkingwater. The research demonstrates that groundwater is safe for humanconsumptionandpublichealth
[1] Districts, G., Azam, A., & Sarma, B. K. (2021). Contamination of Groundwater by Arsenic in Ballia 9289(1),33 37.
[2] JHARIYA,G.,SINGH,R.M.,&MOHAN,D.(2018).Seasonal Assessment of Groundwater Quality in Bhagwanpur, Varanasi. Current World Environment, 13(3),481 489. https://doi.org/10.12944/cwe.13.3.21
[3] Krishna,S.,Logeshkumaran,•A,Magesh,•NS,Prince,•, Godson, S., & Chandrasekar, • N. (2014). Hydro geochemistry and application of water quality index (WQI)forgroundwaterqualityassessment,AnnaNagar, partofChennaiCity,TamilNadu,India. Applied Water Science 2014 5:4, 5(4), 335 343. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13201 014 0196 4
[4] Saeedi, M., Abessi, O., Sharifi, F., & Meraji, H. (2009). Development of groundwater quality index. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2009 163:1, 163(1),327 335.https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661 009 0837 5
[5] Singh, G. G., & Gupta, A. (2022). Assessment of Groundwater Quality in Gorakhpur City for Drinking Purpose July
[6] Tiwari, A., Singh, P., & Mahato, M. (2014). GIS Based Evaluation of Water Quality Index of Groundwater ResourcesinWestBokarocoalfield,India. CurrentWorld Environment, 9(3), 843 850. https://doi.org/10.12944/CWE.9.3.35
[7] Verma, A., Student, P. G., Pandey, G., & Professor, A. (2013).StudyofSomePhysico ChemicalParametersof Groundwater in Gorakhpur District. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology, 2(11). https://doi.org/10.17577/IJERTV2IS110998
[8] Saini,Y.,Bhardwaj,N.andGautam,R.Physico Chemical AnalysisofGroundwaterOfJhotwaraPanchayatSamiti, Jaipur(Rajasthan).TheEcoscan,(2010);4(1):137 139
[9] Khan, A. A., and Khan M. N.International Science Congress Association Physico Chemical Study of GroundwateratShahjahanpurcity,UttarPradesh,India, ResearchJournalofChemicalSciences,(2015);5(1),55 59
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
