International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1Student,Department of Environmental engineering,MCET,Desamangalam 679532,Kerala,India
2Professor, Department of Environmental engineering,MCET,Desamangalam 679532,Kerala,India ***
Abstract Desalination is an artificial process by which saline water is converted to fresh water. The most common desalination processes are distillation and reverse osmosis. Saltwater is desalinated to produce water suitable for human consumption or irrigation. Due to its energy consumption, desalinating sea water is more costlier than water recycling and water conservation. However, these alternatives are not always available and depletion of reserves is a critical problem worldwide. Desalination processes are usually driven by either thermal or mechanical energy In this project desalination of seawater is done using activated carbon prepared from water hyacinth, an aqua plant. Water hyacinth, an invasive species, can be converted into value added products. It has great effect on the reduction of salt and mineral content in the seawater. Seawater is treated with different dosages of water hyacinth activated carbon in several time intervals. The results showed good adsorption capacity of water hyacinth activated carbon and the sample with high percentage reduction of minerals is analysed for check to meet the irrigation water quality requirement. Total salt concentration, sodium adsorption ratio, residual sodium carbonate and boron content are checked to analyse the irrigation water quality of seawater after treating with water hyacinth activated carbon. Activated carbon produced from water hyacinth has been shown to be capable of reducing salinity by absorbing the mineral contents.
Key Words: DESALINATION,REVERSEOSMOSIS,WATER HYACINTH,ACTIVATEDCARBON,ADSORPTIONDesalinationis a process that takes away mineral componentsfromsalinewater.Moregenerally,desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a salt solution.Seawaterisdesalinatedtoproducewatersuitable forhumanconsumptionorirrigation.Desalinationisusedon many seagoingshipsandsubmarines. Most of the modern interestindesalinationisfocusedoncost effectiveprovision offresh waterfor human use. Along with recycledwastewater, it is one of the few rainfall independentwaterresources.
Waterofgoodqualityisessentialtohumanlifeandwaterof acceptable quality is essential for agricultural, industrial, domestic and commercial uses. Industries produces large
amountofwastewaterwhichisneedstobetreatedbefore disposal. Adsorption is the process of accumulating substances that are in solution on a suitable surface. The carbon is used to remove a portion of the remaining dissolved organic matter, residual amounts of inorganic compoundssuchasnitrogen,sulfidesandheavymetals.
Waterhyacinth(Eichhornia crassipes)isatypeofinvasive floatingplantfoundinwaterbodiesacrosstheworld.These invasivespeciesblockthesunlightreachingandoxygenlevel inwatersystems,whichresultsindamagingwaterquality and serious affecting various life forms in the ecosystem. Waterhyacinthhaslargegrowthrateinwastewaterdueto nutrients present in it causes its extremely rapid proliferation and congest growth, presenting serious challengesinnavigation,irrigation,andpowergeneration. However, the same plant having ability to absorb and concentrate many toxic metals and minerals from aquatic environments.
This project works on activated carbon is prepared from waterhyacinthandappliedforthedesalinationofseawater. Activatedcarbonisamaterialpreparedhavinghighdegree of porosity and an extended surface area. During water filtrationoragitationwithactivatedcarbon,contaminants adhere to the surface of these carbon granules or become trappedinthesmallporesoftheactivatedcarbon.
Themainobjectivesofthisprojectareasfollows:
To generate a cost effective and energy efficient methodof desalination
to meet rapidly increasing demand for water supplyincoastalandotherregionswithaccessto salinewaters.
Toobtainapollutionfreedesalinationapproach
Tomeettheirrigationwaterrequirements
Seawater sample is collected and tests for finding the concentrationofsodium,chloride,hardnessandsulfurare
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072



conducted.Waterhyacinthisatypeofinvasivefloatingplant foundinwaterbodies.Itiscollectedfromanearbypond.Itis thensundriedforoneweek.Removethedirt,mud,mosses, etc. by wash the plant several times with clean water. Subsequentwashingwithdistilledanddoubledistilledwater arealsodonetoremovethetediousmaterial.Itisthendried. About 25 grams of this material is treated with 20ml of concentratedsulphuricacid andthecharredmaterial was keptovernight.Thecharredmaterialisheatedinanovenat 100C about 4 6 hours. This is cooled and washed with distilledwatertoremoveanytraceofacid.Thenitisground and impregnated with a saturated solution of calcium chlorideanddried.Theactivatedsamplewasthenwashed withcopiousamountofdistilledwater.Thenitisovendried at90Candgroundtogetpowderedactivatedcarbon.
Clean 5 one liter beakers and fill them with sample of seawater.Keep eachbeaker below eachpaddleandlower thepaddlessuchthateachoneisabout1 cmabove thebottom.Add1,2,3,4,and5gofwaterhyacinthactivated carbonofintotheseawater samples. Immediatelyrunthe paddles at 100 rpm for 30 min, 60min, 90min,and 120min.Thenstopthemachine,liftoutthepaddlesandallow tosettlefor30minutes.Siphonouttheclarifiersamplesinto beakersandtestthecontents.
Thesamplewithmaximumpercentagereductionofminerals wascollectedandtestsareconductedtochecktheirrigation waterquality.Totalsaltconcentration,sodiumadsorption ratio, residual sodium carbonate and boron content are testedtofindingthesuitabilityofwaterforirrigation.
Seawater is tested to find the quantities of different parameters in seawater. The concentration of Sodium, chloride,hardnessandsulfurareanalysed.

TheobtainedvalueofDifferentconstituentsinseawaterare giveninthetable1
Table -1: Seawaterconstituents
PARAMETER SEAWATER CONTENT(ppm) sodium 15600 chloride 19400 hardness 6630 sulfur 884
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Table 1: parametersaftertreatmentfor30minutes
parameter 1gram WHAC 2gram WHAC 3gram WHAC 4gram GRAM 5gram GRAM
Sodium 15300 14992 14601 13982 13358 Chloride 18221 17122 16985 16112 15548 Hardness 6588 6125 5068 4589 3196 sulfur 758 695 658 622 599
Table 2: parametersaftertreatmentfor60minutes
parameter 1gram WHAC 2gram WHAC 3gram WHAC 4gram GRAM 5gram GRAM
Sodium 13110 12984 12214 11589 10521 Chloride 15401 14322 13958 13211 12895 Hardness 2195 2101 1085 986 912 sulfur 485 456 421 395 356
Table 3: parametersaftertreatmentfor90minutes
parameter 1gram WHAC 2gram WHAC 3gram WHAC 4gram GRAM 5gram GRAM
Sodium 10112 9851 9144 8873 8350 Chloride 12210 11985 11021 10811 9987 Hardness 859 812 796 763 705 sulfur 325 304 278 245 232
Table -4: parametersaftertreatmentfor120minutes
parameter 1gram WHAC 2gram WHAC 3gram WHAC 4gram GRAM 5gram GRAM
Sodium 7984 7325 7114 6857 6421 Chloride 9776 9258 8541 7824 7107 Hardness 685 625 556 496 445 sulfur 219 189 154 121 101
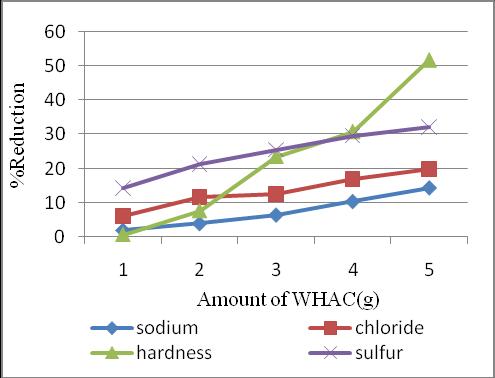
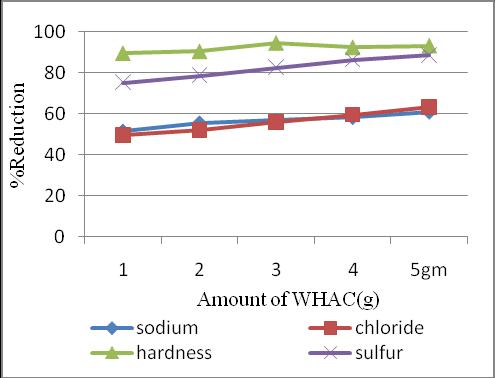
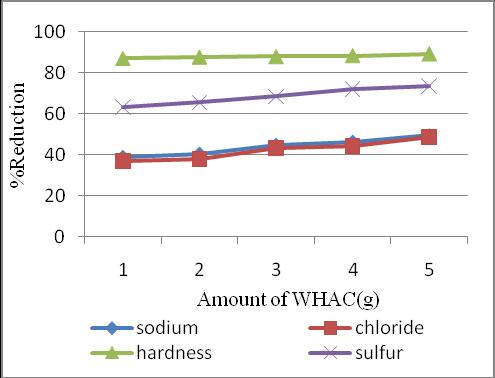
Percentage reduction of seawater constituents with the additionofWHACinspecificintervelsarefindout.
%Reduction
80
60
40
Chart 1:Graphshowing %reductionvsquantityof WHAC after30minutetreatment 0
100 1 2 3 4 5
20
Amount of WHAC(g) sodium chloride hardness sulfur
Chart -2:Graphshowing %reductionvsquantityof WHAC after60minutetreatment
This projectdealswiththeminimizationandreductioninthe amountsofthedissolvedimpuritiesinseawaterbytreating the seawater. The treatmentinvolved use of WHAC, which showedasignificantreductionintheamountofthedissolved impuritiesandsalts.Amongthetechnologiesofdesalination ofseawater,reverseosmosishasbeenrecognizedtobethe most cost efficient technology in comparison to thermal processes.However,thedesalinationindustryencountersa majorchallengethatconsistsinreverseosmosismembrane fouling, which implies a higher treatment cost due to the important frequency of membrane cleaning or/and replacement. Seawater contain different types of contaminantssuchasheavymetals,micropollutants,salinity andmicroorganisms,whichneedtoberemovedtomakeit suitable for potable uses. Reducing the volume of waste streams is an attractive option for minimizing the environmentalimpactandproducingbetterqualityproduct water.
The present study shows that the activated carbon preparedfromwaterhyacinthisaneffectiveadsorbentfor the removal of salt from seawater. During agitation contaminants adhere to the surface of activate carbon. Activatedcarbonabsorbersareefficienttoremoveunwanted tasteandodours,sodium,chlorineetcfromsalinewater, wastewaterand drinkingwater.Themaximumpercentage reductionisobtainedfromthesamplewith5gmWHAC.This sample is collected to check the irrigation water requirements.Theobtainedvaluesoftotalsaltconcentration, sodiumadsorptionratio,residualsodiumcarbonate,boron are1200micromhos/cm,9.6,1.64,1.4ppmrespectively.As perIS11624 1986thevaluesofallthefourparametersare withinthelimitanditcanbeconcludedthat thesampleof seawaterafteradsorptionusingWHACcanbesafelyusedfor irrigation purpose.Alsothistechniquecan appliedfor the removal of micro pollutants both in drinking water production and for the purification of treated wastewater beforedisposal.

[1] L. N. Nguyen, F. I. Hai, J. Kang, W. E. Price and L. D. Nghiem,”RemovalofTraceOrganicContaminantsbya Membrane Bioreactor Granular Activated Carbon (MBR GAC) System”, Bioresource Technology, 113, 169 173(2012).
[2] K.G.Babi,K.M.Koumenides,A.D.Nikolaou,C.A.Makri, F.K.Tzoumerkasand T.D. Lekkas,”PilotStudyofthe RemovalofTHMs,HAAsandDOCfromDrinkingWater by GAC Adsorption”, Desalination, 210(1,3), 215 224 (2007).
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[3] William T. Haller and D. L. Sutton graduate research assistant and assistant professor univ. Of florida. Agr. res.CenterfortLauderdale,florida33314“EffectofpH andhighphosphorusconcentrationongrowthofwater hyacinth” .
[4] E. Subha, S.Sasikala, G.Muthuraman,”Removal of Phosphatefromwastewaterusingnaturaladsorbents”, Departmentofchemistry,Presidencycollege,Chennai 600005,India
[5] IS11624 1986
[6] J.Margot,C.Kienle,A.Magnet,M.Weil,L.Rossi,L.F.de Alencastro, C. Abegglen, D. Thonney, N. Chèvre, M. SchärerandD.A.Barry,“TreatmentofMicroPollutants inMunicipalWastewater:OzoneorPowderedActivated Carbon“,Sci.TotalEnviron.,461 462,480 498(2013).
[7] L.N.Nguyen,F.I.Hai,J.Kang,W.E.Price,L.D.Nghiem, “CouplingGranularActivatedCarbonAdsorptionwith Membrane Bioreactor Treatment for Trace Organic Contaminant Removal: Breakthrough Behaviour of Persistent and Hydrophilic Compounds”, J. Environ. Manag.,119,173 181(2013).