International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Abstract Globally, hundreds of natural disasters happen every year. Identifying high impact areas and conducting an accurate analysis of the post disaster landscape are critical for disaster relief and recovery efforts. It would enable damage assessment and the identification of routes for early response to affected areas. Currently, after natural disasters that cause humanitarian crises, the mapping to be done is carried out by volunteer initiatives all over the world using satellite imagery. However, because the volunteers are mostly inexperienced and follow different processes, the process takes time and is inconsistent across the various initiatives. Comparing the pixel values of satellite images before and after the disaster could help identify changed areas. The Change Detection method can be used to compare pixel values more effectively compared to the human initiatives. Change detection examines changes in a region's spectral characteristics over time to determine the processes that lead to changes in land use or land cover. The purpose of change detection is to analyse the variability in images captured over a specific time period related to a specific area. This change in the image is used to detect the occurrence and amount of damage. In this project, a change detection based model is implemented for identifying disaster occurrence and predicting the percent probability of occurrence based on an analysis of a change map generated with the VGG 19 pre trained model as a feature extractor. In addition, a pre trained InceptionV3 model is used to perform binary classification in order to predict the type of disaster between hurricane and earthquake.
Key Words: natural disasters, change detection, bi temporal satellite images, pixel values, buildings,change maps
Adisasterisaseriousissuethathappensoverashortorlong period of time and results in significant losses to people, property,the economy,and theenvironmentthatexceeds thecapacityoftheaffectedcommunitytomanagetheuseof itsresources.Disasterscanbecausedbynatural,man made, andtechnicaldangersaswellasseveralotherfactorsthat influence how exposed and vulnerable depending on the population.Developingnationsbearthebruntofthecosts associated with natural disasters, and these nations also accountforover95%ofalldeathsresultingfromhazards.A
quick and prompt response is necessary during natural catastrophestoreducedamageandpreservelives.Thescale andimpactofdisastersmustbeaddressedbyeffectiveand knowledgeabledisastermanagement.
Identification and application of diverse ways to reduce disaster related losses are part of the ongoing, integrated process known as disaster management. Standardizing, organizing, and managing the data and information about disaster management is mostly done with the benefit of currenttechnology.Quickdatacollectionduringorbeforeto adisaster,thecreationofmapsandstatisticaldata,andthe presentationofthedatainvariousmediumsformanyusers aswellasontheInternetarenecessarytoaccomplishthis.
Governments commonly employ traditional disaster managementtechniques,suchassearchandrescueteams, fieldsurveyteams,andlocalgoverningbodies,toanalyzethe damages and the disaster's nature. Damage assessment is usuallydoneconsiderablylaterthananticipated,whichcan hinder quick relief efforts and deprive rescuers and the peoplewithouttheknowledgenecessarytocomprehendthe severityofthedisasterandtakeprecautions.Thesesurvey methods are very risky. Information from social media platforms can be utilized in these situations because it is affordableandquick.Datacanbesharedusingsocialmedia inavarietyofways,includingtext,photos,andvideo.These mediacanbehelpfulfordeterminingtheextentofdamage afterdisasters;thecondensednatureofsocialmediaposts makesitsimpletoswiftlycompilecrucialinformation.
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning. It uses artificialneuralnetworks,whicharecreatedtomimichow humans think and learn, whereas machine learning uses simpler principles. Larger, more complicated neural networksarenowpossible thankstodevelopmentsin big dataanalytics,whichenablecomputerstolearnandrespond todifficultsituationsfasterthanpeople.Speechrecognition, language translation, and image categorization have all benefited from deep learning. The most common natural disasters are earthquakes, wildfires, floods, droughts, and landslidesthatcausedamagetoman madestructuressuch as buildings and roads. Identifying affected and degraded areas at an early stage isa crucial issue for mitigating the negativeimpactsofdestructiveeventsandmanagingthem.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
A vision based disaster detection system that uses deep learningalgorithmscanbeusedtoquicklyextractfeatures fromdamagedareasfromoutdoorsatelliteimagery.Theuse ofsatelliteimageryfordisastermonitoringandresponsehas grown in popularity. Monitoring of the environment and climate, particularly in the detection and management of naturaldisasters,dependsmoreandmoreontheanalysisof satellite imagery. Prioritizing rescue operations, humanitarian assistance, and coordinating relief activities are important after a disaster. Since resources are often scarceindisaster affectedareas,thesemustbecarriedout quicklyandeffectively,anditiscriticaltopinpointtheplaces thathavesustainedthemostdamage.However,themajority ofcurrentdisastermappingeffortsaremanual,whichtakes timeandfrequentlyproducesinaccurateresults.
Change detection (CD) is a technique for identifying differences in the state of an object or phenomenon by observingitatdifferenttimes.Tocompareandevaluatetwo ormoreremotesensingimagescapturedinthesameareaat variousintervalstolearnmoreaboutchangestotheground object,changedetection(CD)basedonremotesensingdata is an essential application of remote sensing image interpretation.Thistechniquehasbeenextensivelyapplied in a variety of sectors, including scene classification, ecological environment monitoring, disaster assessment, agricultural study, and land planning. Deep learning techniques are currently being extensively studied in the fieldofremotesensingpicturetargetextraction.
In the recent decades, because of the significant human casualties that follow disasters, disaster detection has emergedasoneofthemostintriguingscientifictopics.Using sensors and straightforward image processing methods, researchershaveexaminedtheeffectsofchangesbrought aboutbydisasters.Disasterdetectionsystems,accordingto apreviousstudy,haveseveralseriousflaws, includingthe inabilitytoobservedisastersbeyondacertaindistance.This is a result of the low accuracy and a limited number of catastrophedetectionsensorsthatonlyreceiveverbalinput. Duetotheenormousnumberofsatelliteimagesthatmustbe viewed in a short amount of time, operators also struggle with disaster detection. Therefore, this could result in a calamitybeingmissedormisjudged.Itisessentialtodevelop an automatic disaster detection system that monitors the occurrence of disasters over a greater area using satellite images,withtheuseofdeeplearningtechniques.
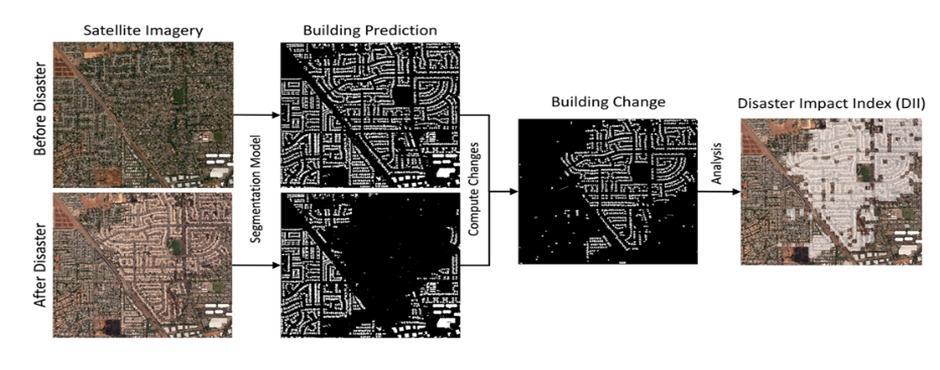
TrainedmodelsonCNNdetecthuman madefeatures,such asbuildings.Inordertotrainonexistingmethodologiesfor disaster impact assessments, new classes of structures damagedbyfiremustbemanuallyannotated,whichcanbe time consumingandexpensivetodevelop [1].Onlybuilding data sets are used in this new approach. Figure 1 depicts disasteridentificationusingbuildingpredictionsinsatellite images that are processed using a segmentation model to obtain an accurate disaster analysis. These are easily accessible and expandable to address other, comparable natural calamities. The models are initially trained to recognizethesehigh leveltraitsbecausevariationsowingto the seasons, the time of day, or other circumstances may result in inaccurate findings (i.e., buildings) and then produce prediction masks in disaster affected areas. The areasofmaximalchangecanbedeterminedbycalculating therelativechangebetweenfeaturestakenfromsnapshots ofdatacapturedbothbeforeandafteradisaster.
Automaticbuildingchangedetection(BCD)fromaerial imagesisanimportantresearchareainthefieldofremote sensing [7] becausetheresultsarerequiredforavarietyof applications such as monitoring urbanization, identifying unauthorizedorillegalstructures,detectingchangesinland use,updatingdigitalmaps,androuteplanning.BCDisused to evaluate the state of damaged structures following earthquakesandothernaturaldisasters,aidingwithrescue operations and rehabilitation plans. There are more and moredistantsensingimagesthatneedto be processed as remotesensingtechnologyadvance.Duetothelabor and time intensivenatureofmanual processing,whichmostly reliesonhumaninterpretation,unsupervisedalgorithmsare required to perform BCD in the absence of ground truth. NumerousBCDsystemsandtechniqueshavebeenbuiltfor organizing remote sensing data, and more current techniquesarealwaysbeingdeveloped.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The identification and monitoring of structures using remotely sensed photography is extremely valuable for tracking urbanization. Numerous techniques have been developedfortheautomaticdetectionofchangesbasedon bi temporalormulti temporalremotesensingimages.They rangefrompixel orientedtoobject oriented,fromspectral characteristics based to artificial intelligence based, and from pixel oriented to object oriented. BCD typically involves two main processes: building change generation (BCG) and segmentation of the building change map. The majorpartofBCD,BCG,whichseekstohighlightchangesin the buildings, has a direct impact on accuracy. In low or medium resolution photos, these approaches have been shown to be able to detect abrupt changes. In order to extract building areas, bi temporal aerial photos are first combined using semantic segmentation based on a deep convolutionalneuralnetworktocapturechangeinformation.
processingapproachtomeettheapplication'sactualneeds. In this study, changes in bi temporal satellite images are detectedusingafeaturechangedetectionmodelbasedon VGG 19,andtheresultsarethenanalyzedtodeterminethe percentage likelihood that a disaster would occur. Humanitarian groups need to act quickly and effectively whenanaturaldisasteroccurs.Accurateknowledgeofthe calamity will be essential to providing an efficient rescue. Rich and trustworthy information is provided by satellite imagestoaidprofessionaldecision making. Developadeep learning workflow to assist assistance workers in time limited emergencies in order to help identify disasters despite the lack of data. Assessing the applicability of learning based transfer convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in supporting building damage assessment in an emergencycontextitisveryimportanttoidentifythetypeof disaster that has occurred between earthquake and hurricanes.
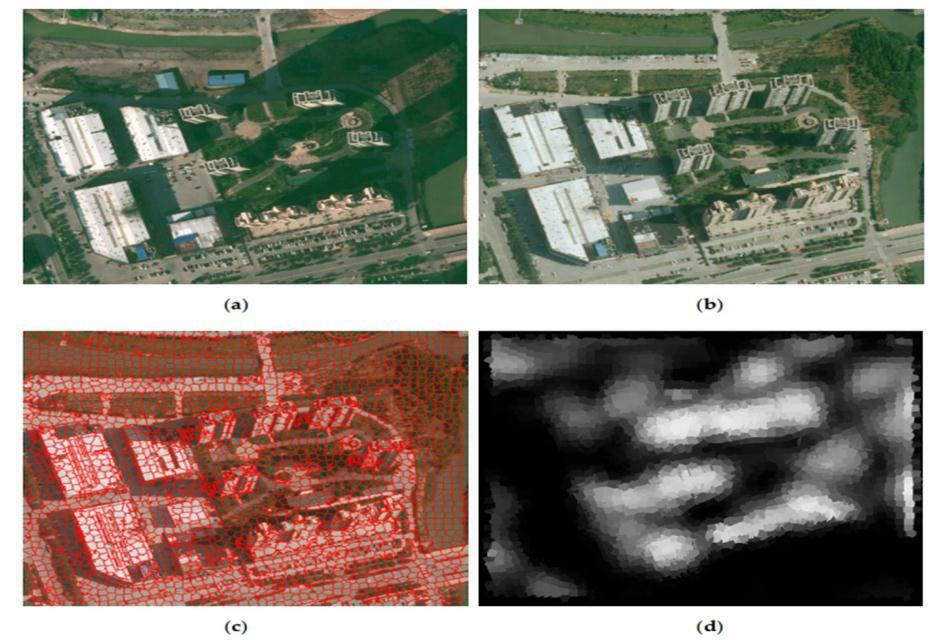

Fig 2: Bi temporalimages,thecorrespondingimage object,andchangeconfidencemap.(a)TheRGBaerial imageattimet1,(b)theRGBaerialimageattimet2,(c) superpositionofthebi temporalimage objectandthe RGBaerialimageattimet2,and(d)thechangemap.
Deep learning can be used to extract high level semantic featuresfrommulti temporalimages [2],suchasspectrum, space, and texture, to create a nonlinear relationship betweentheattributesofgroundobjectsinmulti temporal photos. Deep learning based distant change detection models are distinct from conventional remote change detectionalgorithms.Itcanrecognizedatacharacteristics, reducing the dependency on labor intensive human work during feature extraction in remote sensing photos. It not onlyincreasestheremoteimagechangedetection'saccuracy but also provides a brand new automatic and intelligent
Imagescapturedattwo timeintervalsmustbeoverlaid inorderforthecomparisonbetweencorrespondingplaces to make sense. The latter aims to eliminate atmospheric attenuationdistortioncausedbyabsorptionandscattering in the atmosphere as well as radiance or reflectance differences brought on by the digitalization process of sensors, which reduces false alarms brought on by these radiationerrorsinchangedetection [4].Asubstantial,top notchtrainingsetthatcanaidalgorithmsincomprehending particular patterns or series of outcomes is necessary in order to construct the AI model. Bi temporal images are labelledorannotatedincertainwaystohelptheAImodel quickly pick up on the traits of the altered objects. Below Figure 1, represents an annotated example for building changedetection,whichiscomposedoftworemotesensing images captured at two different time intervals and a correspondinggroundtruthlabelledwithbuildingchanges at the pixel level. The AI model can be trained in a supervised manner using the data from the real world. A trainingsetforAImodeltrainingandatestsetforaccuracy assessmentthroughoutthetrainingprocesscantypicallybe created from the training set after it has been generated. Iteratively and alternatively, the testing and training operations are carried out. Bi temporal pre and post disasterimagesconsistingofbuildingsissuppliedtochange detection algorithm. Change maps can be produced more intelligently and automatically for useful applications by utilizingatrainedAImodel.Additionally,thiscansupport the generalization potential and resilience of the model, whichisacrucialcomponentinassessingtheviabilityofthe change detection method based on AI and it predicts the percentprobabilityofoccurrenceofdisasterandidentifythe typeofdisaster.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Data acquisition is the first step in both the traditional change detection flow and the AI based change detection flow,withthegoalofobtainingthechangedetectionmapfor variousapplications [3]. WhileAI basedsystemsnormally requireanadditionaltrainingsetcreationprocessandanAI model training process for change detection, traditional approaches typically involve two phases after data preparation, including a homogenization process and a changedetectionprocess.AItechniquesarethemainstaysof AI based methodologies. Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, often known as machine intelligence, can improveperformanceinavarietyofdata processingjobs.It can be described as a system's capacity to accurately understandexternalinput,learnfromthatdata,andusethat learning to accomplish particular tasks and goals through adaptablechanges.
For an accurate understanding of land surface changesusingEarthobservationdata,changedetection(CD) is a crucial tool. It is also crucial for spotting linkages betweensocialandenvironmentaleventsingeoscience.To produceaprecisechangemap,asuperviseddeeplearning (DL) basedchangedetectionmethodwassuggested.Theuse ofDLtotackletheCDproblemwithmultitemporalremote sensing imageries is growing in popularity because of its excellentperformanceandtremendouspotentialinthefields ofpatternrecognitionandnonlinearproblemmodelling [5]. Convolutionalneuralnetworks(CNN)inparticularareused indeeplearning(DL)algorithmstomonitorenvironmental change and classify it into change and no change classes. There have been significant advancements in change detection,asshownbythesystematicanalysisandwidely deployed networks in DL, but there are still numerous obstacles in CD because of a lack of training data, prior knowledge, image complexity, etc. However, even if these difficultiesareovercome,therearestillmanyfundamental problemsinRSdatasetsthathavenotyetbeenaddressed, such as heterogeneous data, multiresolution images, and globalinformationofhigh resolutionandlarge scaleimages. Thisisbecauseofchangingrequirementsanddiversedata. Therefore, it is strongly advised that future research concentratemoreonthesedifficulties.
New applications for resolving geospatial problems in metropolitanareashavebeendevelopedasaresultofthe accessibilityofhigh resolutionsatelliteimagery.Duetoits wide range of applications, such as city modelling, map updating, and urban monitoring, building detection from remote sensing images has been an important area of
research.Animagemustbemanuallyprocessed,whichtakes a lot of time and effort. As a result, techniques have been created that need little or no human effort. Building detectionhasimprovedrecentlythankstoseveralautomatic andsemi automatedtechniques [6]
Ingeneral,therearetwoaspectstothebuildingdetection processusingsatelliteimages:objectandthreshold based. Segments are generated and given features by the object based approach (shape, spectral, and height). To identify buildings,thethreshold basedmethodcreatesanormalized differencevegetationindex(NDVI)anddigitalsurfacemodel (DSM).
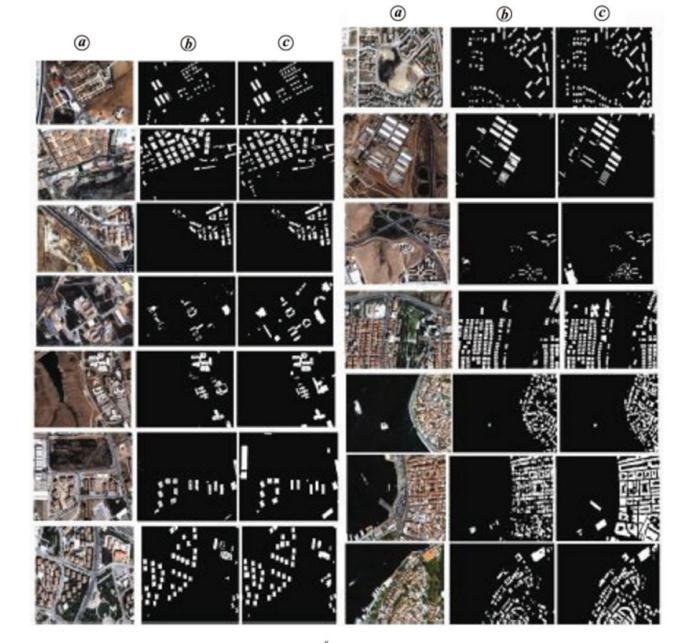
Fig 3: BuildingdetectionfromVHRmultispectralimages hasbeenmadepossibleviaacognitive basedautomated method.Resultsofcognitive basedmethodswhere(a) indicatesinputimages;(b)outputimagesand (c)referenceimages.
Disaster managers and responders rely on timely and accurate information about the disaster situations during sudden natural disasters in order to develop effective disaster management strategies and make swift response decisions.
InastudyperformedbyXiaoChen,etal. [8] automatesthe process of using satellite imagery to locate damaged structuresandtocategorizetheseverityofthedamage.The Unet model, which holds image data in the form of compresseddata,isusedtoextractfeaturesfromtheimages. Buildinglocationanddamageclassificationareautomated usinga learningtechnique builtontopofsatellitephotos.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
The difficulty in determining the boundaries of computationallyexpensiveobjectsisduetothesubstantial amountofdata.
Carlos Gonzalez, et al. [9], proposes the portability and accelerationoftheinferencesprocessonadeepconvolution neuralnetworkmodeltodetectrapidearthquakedamageon very high resolution (VHR) remotesensingdata using the Intel OpenVINOtoolkit.Experimental resultsdemonstrate thattheoptimisedmodeloffersgoodaccuracyfordamage identificationwithanotableincreaseinexecutionspeedon CPU+GPU. The network cannot be trained more quickly usingOpenVINO,anditisnotalwayssimpletoretrainthe modelsusingspecificdata.
Pei JunLee,etal. [10] presentsasystemofcombiningdeep learningandimagetransformalgorithmstodetectlandslide location in satellite images. To identify whether satellite photos of landslides are present, a convolution neural network is deployed. The Hue Bi dimensional Empirical ModeDecomposition(H BEMD)transformationalgorithmis suggested in order to accurately identify landslides under various illumination situations from classed landslide photos.Todeterminethealgorithmthatismostappropriate for real time implementation, the four networks' performances are assessed and contrasted in terms of accuracy and real time performance. A large dataset is needed for the classification strategy, which reduces the generalizabilityofthemodel.
Diyana Kinaneva, et al. [11], propose a platform that uses UnmannedAerialVehicles(UAVs),whichconstantlypatrol overpotentiallythreatenedbyfireareas.TheUAVshaveon board computing capabilities and make use of the capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI). Early forest fire detection is accomplished by using both fixed wing and rotary wingUAVs.It'spossiblethattheUAVscan'tefficiently covereveryarea.Disastersthatmightstrikeinunexpected placeswouldn'tbedetectedbythesystem.Alargedatasetis neededfortheclassificationstrategy.
ShaheenKhatoon,etal. [12],proposedadisastertaxonomy for emergency response and utilized the same taxonomy with an emergency response pipeline and deep learning basedimageclassificationtoautomatethedecision making process for emergency response. In order to evaluate disaster relatedimagesanddeterminethetypesofdisasters, algorithmslikeVGG 16andYouOnlyLookOnce(YOLO)are utilized. CNN based classification and object detection, modelsareusedtoclassifyincomingimagesintothedisaster or non disaster types. An information fusion module that combinesthetwo levellabelledimagesandmapsthemtoa specificresponsecategoryinferredbythetaxonomy.Images onsocialmediamightnotalwaysbereliable;theymightbe made up. It can be challenging to obtain pictures that adequately depict every aspect of a disaster affected country.
KrishnaKantSingha,etal. [13],proposedanovelneurofuzzy classifierHybridKohonenFuzzyC Means r(HKFCM r).The classifierisacombinationoftheFCM rclusteringmethod andtheKohonenClusteringNetwork(KCN).Theinputand outputlayersmakeupthesoletwolayersoftheHKFCM r network architecture, which is comparable to a straightforwardKCNnetwork.Thehybridizationresultsina more efficient, less complex and faster classifier for classifyingsatelliteimages.Toevaluatetheeffectivenessof themethod,theerrormatrixwascomputed.Oneofthetwo clustering methods, KCN, uses an artificial termination strategy and is sequential. The KCN may have a sluggish convergence rate and may not always be able to handle complexitywell.
SomaShiraishi,etal. [14],proposesanautomaticdisaster detectionsystembyimplementingoneoftheadvancedeep learningtechniques,convolutionalneuralnetwork(CNN),to analysis satellite images. By establishing an automatic disaster detection system, the data given here could help withadvancementsinefficientlydetectingnaturaldisasters. The training data set for each disaster consists of 30000 40000 patches, and each patch is automatically trained in CNNtoidentifytheimmediategeographicareaoftheevent. The proposed system needs a lot of data since optical picturesfromdisaster affectedareaswillhaveavarietyof features that are particularly challenging to cover in the trainingset.
Ying Liua, et al. [15], propose a deep learning based landslide recognition method for optical remote sensing images.Inordertocapturemoredistinctfeatureshiddenin landslide image. A specific wavelet transformation is proposedtobeutilizedasthepre processingtechniquein ordertocapturemoredifferentfeaturesburiedinlandslide images. Pre processing and classification model training landslidefeaturerepresentationcomprisingtwophasesof the suggested landslide recognition approach. Support vectormachine(SVM)andartificialneuralnetwork(ANN) areusedasthecounterpartstoshowhowwelloursuggested model performs. Wave transforms are quite sophisticated anddemandalotofcomputingpower.Alotofdataisneeded for the auto encoder used for denoising and feature extraction.
Keiller Nogueira, et al. [16], proposed a Relation network designed for takingintoaccounttherelationshipbetween pairsofobjectsduringtraining.Twoneuralnetworks,fand g, that have jointly learned parameters make up an RN. Neuralnetworksareemployedandtrainedforclassification in runs 1, 2, 3, and 4, with a flooding event serving as the positive class. In those runs, the test set was ranked from highest to lowest according to the classification score to producethefinalranking.Alargedatasetisrequiredforthe classificationmethod.Adataset,nomatterhowhuge,won't be able to effectively cover all the variables of a disaster impactedarea,whichdecreasesthegeneralizabilityofthe modelforusecaseslikedisasteridentification.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
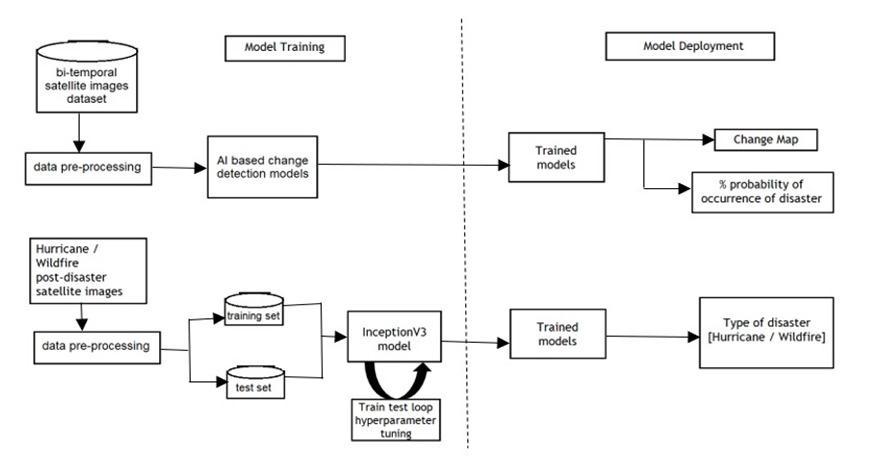
In this paper, we propose a 2phase network for disaster identificationandclassification.Thefirstnetworkisadeep learning based change detection [17] framework that analysesbi temporalsatelliteimagesofurbanareasmainly containingbuildingasthetopographicalfeaturestogenerate achangemap.Thegeneratedchangemapisfurtheranalyzed to compute the percentage probability of occurrence of disaster. If a disaster is predicted to have occurred by the firstnetwork,thesecondnetworkthentriestoidentifythe typeofdisasterbetweenhurricaneandwildfire.
Forchange mapgeneration, a featureextractor [18] is implemented using a pre trained VGG 19 model [19]. Bi temporal satellite images, i.e., images at two consecutive timeintervalsareusedasinputthisnetwork.Imageattime interval T1 and time interval T2 are given as input to the featureextractormodeloneaftertheothertogeneratetwo featuremaps.Thetwogeneratedfeaturemapsarecompared to generate a change map. For this comparison, a mathematical function termed Reduced Sum of Squares (RSS) [20] is used. This method is used to identify any discrepanciesinthetwogeneratedfeaturemaps.TheRSS method outputs a change map. We then use Otsu thresholding method [21] to analyze the change map to identifyanoptimalthresholdvalueofpixels.Ifapixelvalue inthechangemapisanabovetheidentifiedthreshold,the pixel isrepresentedin whiteinthedisplayedchange map and if the change map pixel value is below the identified threshold,itisrepresentedinblack.Theblackregioninthe changemaprepresentsunchangedareasinthebi temporal imagesandthewhitepixelsrepresentthechangedareasin thebi temporalimages.
Inthegeneratedchangemap,thenumberofblack pixelsi.e.,thepixelsrepresentingnochangeandthenumber ofwhitepixelsi.e.,pixelsrepresentingchangearecomputed. The percent probability of occurrence of disaster is then calculatedaspercentofwhitepixelsi.e.,pixelsrepresenting changepresentinthechangemap.
Percent probability of occurrence of disaster = (No. Of white pixels / Total no. of pixels) * 100
Transferlearning [22] ismachinelearningresearch problemwhereinamodelpreviouslytrainedisreusedona similar but different dataset. The previously learnt knowledgesuchasweightsandcommonfeaturesarereused in a similar use case. An Inception v3 [23] pre trained model is used for binary classification with its last layer frozen.Themodel isgivena single temporal postdisaster
image as input and predicts the type of disaster between hurricaneandwildfireasoutput.
ThedatasetselectedisthexBDlabeleddataset [24].The dataset is a collection of satellite images from before and afternaturaldisasters.Almostallimagescontainbuildings whicharedeterminedtobeinoneof4damagecategories afterthedisaster nodamage,minordamage,majordamage, or destroyed. The pre and post disaster images of each buildingareofvirtuallyidenticalresolutionandframedina similar area in the image Each building also comes "pre outlined"withinitsimage.Thecsvfilescontainingthelabels indicate polygons in which each building in an image is contained, helping to locate individual buildings in each image.DataPre processingisappliedtotheimagesusedfor training Inception V3 model for identifying the type of disaster between hurricane and earthquake. Post disaster imagesarecollectedfrompreandpostdisasterbi temporal satelliteimagesofhurricaneandearthquakehitareas.The images are converted from BGR color format to Keras compatibleRGBcolorformat.Theimagesareresizedto244 X 244 (input size of Inception V3 model). Class labels “hurricane and earthquake" are assigned to the corresponding images. Images are converted into Numpy arrayformatandare normalizedtotheinterval [0,1]. The datasetisbuiltintotrainandtestsetintheratio8:2.The categoricallabelsareencodedintobinarydigitsof0and1.
The dataset is a collection of bi temporal satellite imagestakenbeforeandafternaturaldisasters.Almostall imagescontainbuildingsthathavebeendeterminedtobe pre and post disaster images of the same building, with nearlyidentical resolutionandframedina similararea of the image. These images are pre processed before being usedtotraintheInceptionV3modeltodistinguishbetween
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
hurricanes and earthquake. Pre and post disaster bi temporal satellite images of hurricane and earthquake hit areasareusedtocreatepostdisasterimages.Theimagesare given the class labels "Hurricane and Earthquake." For feature extraction, the VGG 19 model based on transfer learningisused.
Themodelextractsfeaturesfromtwobi temporal satelliteimages.Thetwofeaturemapsarecomparedusing Reduced Sum of Squares (RSS) mathematical functions to generateachangemap,wherewhitepixelsrepresentchange and black pixels represent no change. A disaster's percentage occurrence is calculated as the percentage of whitepixelsinthechangemap.Thetransferlearning based Inception V3 model is trained to distinguish between hurricaneandearthquakedisastersbasedonsatelliteimages ofdisaster affectedareas.Foridentifyingdisasterbetween hurricane and earthquake, the VGG 19 based AI change detection model and the trained Inception V3 model are deployed. Figure 4 depicts pictorial representation of proposedsystemarchitecture.Afteruploadingbi temporal satellite images, the user receives a change map and a predictionofthepercentageofdisasteroccurrence,andifa disaster occurs, the type of disaster is predicted between hurricaneandearthquake.
TABLE 1: TestCasesforBi temporalSatelliteImages
TestCasesforBi temporalSatelliteImages Test# Testdata input Expected result Actual result Pass orfail
1. bi temporal satellite image without damage
2. bi temporal satellite imagewith mild damage
3. bi temporal satellite imagewith moderate damage
4. bi temporal satellite imagewith high damage
100%no damage 100%no damage pass
X% chancesof occurrence ofdisaster
Y% chancesof occurrence ofdisaster
X% chancesof occurrence ofdisaster
5. bi temporal satellite imagewith complete damage
100% disaster occurred
100% disaster occurred
pass
Z% chancesof occurrence ofdisaster
Y% chancesof occurrence ofdisaster
pass
Itispossibletodeterminewhetherornotthedisasterhas occurredusingthechangemapcreatedafteranalysisofthe uploadedimages.Thebi temporalimages'changedareasare representedbywhitepixelsonthechangemapwhiletheir unchangedareasarerepresentedbytheblackregioninthe change map. The number of black pixels, or pixels representingnochange,andthenumberofwhitepixels,or pixelsrepresentingchange,arecomputedforthegenerated change map. The percentage of white pixels, or pixels representingchangeinthechangemap,thatarepresentis thenusedtocalculatethepercentageofadisasteroccurring.

Z% chancesof occurrence ofdisaster
pass
TheaboveFigure5showsthechangemapcreatedforthebi temporal images used for testing. The percentage of disastersthatoccurred, estimatedto be97.397%,andthe type of disaster, estimated to be "Wildfire," are also determinedusingthesamechangemap.
pass
The goal of this project is to develop a system that successfullyrecognizesdisastersusingbi temporalsatellite photosandoffersrelevantinformationsuchasthetypeof disaster and an analysis report. The proposed system
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
intendstoapplymultiplechangedetectionframeworksfor disaster identification and to compare them in order to discoverthebestapproachfortheusecase.
Bytheendofthisproject,themodelwillbecapableof:
• Generatingchangemap
• Predict the percent probability of occurrence of disaster
• Predictthetypeofdisasterbetweenhurricaneand earthquake
Theresultsaredisplayedonthescreen.Itincludesachange map,percentprobabilityofoccurrenceofdisasterandthe typeofdisasterbetweenhurricaneandearthquake.
The change maps generated and percent probability of occurrenceofdisasterhaveoverninetypercentaccuracyas determinedthroughmanualevaluation.Theaccuracyofthe InceptionV3 pre trained model for predicting the type of disasterbetweenearthquakeandhurricaneis89%.
• Utilized for rapid, timely and efficient disaster response.
• Enablesoperatorsandplannerstoorganizebetter disasterresponse.
• Provides guidance to emergency responders to rescuevictims.
• Yields information that is used to help expedite clean upandrebuilding.
• Provides up to date information to emergency responders,governmentauthorities,andconcerned citizens, allowing them to effectively identify hazards.
Theproposedsystemmodelcanpredictthetypeof disasterbetweenearthquakeandhurricaneonly.
Extendingtheproject'scapabilitiestopredictmore typesofdisasterslikewildfire,tsunami,etc.Extendingthe project’scapabilitiestopredicttheextentofdamagecaused bydisaster.
We would like to express our gratitude to our guide, Prof. ManasaTP,AssistantProfessor,DepartmentofCSE,BIT,who gaveusthiswonderfulopportunitytoresearchon"AI based change detection for disaster identification utilizing bi temporalsatelliteimages"topic.Herhelpfulinsightsintothis topicmadethisa veryrichlearningexperience.Wewould alsoliketothankourprofessors,DepartmentofCSEandthe collegefortheirguidanceandsupport.
[1] Siti Nor Khuzaimah Binti Amit and Yoshimitsu Aoki. “Disaster detection from aerial imagery with convolutionalneuralnetwork.”InKnowledgeCreation andIntelligentComputing(IESKCIC),2017International ElectronicsSymposiumon.IEEE,2017.
[2] YingLiua,LinzhiWua,“GeologicalDisasterRecognition on Optical Remote Sensing Images Using Deep Learning”,2016PublishedbyElsevierBV
[3] Pan,F.;Wu,Z.;Jia,X.;Liu,Q.;Xu,Y.;Wei,Z.“ATemporal Reliable Method for Change Detection in High Resolution Bi Temporal Remote Sensing Images.” RemoteSens.2022,14,3100.
[4] WenzhongShi ,MinZhang ,RuiZhang,ShanxiongChen and Zhao Zhan, “Change Detection Based on Artificial Intelligence: State of the Art and Challenges”, Remote Sens,MDPI,2020
[5] Shafique,A.;Cao,G.;Khan,Z.;Asad,M.;Aslam,M.“Deep Learning Based Change Detection in Remote Sensing Images:AReview.”RemoteSens.2022
[6] Naveen Chandra, and Himadri Vaidya, “Building detection methods from remotely sensed images”, A Review.currentscience,vol.122,no.11,2022
[7] Jinqi Gong , Xiangyun Hu *, Shiyan Pang and Kun Li, “PatchMatchingandDenseCRF BasedCo Refinement forBuildingChangeDetectionfromBi TemporalAerial Images”,MDPI,2019
[8] Y. Yi and W. Zhang, "A New Deep Learning Based ApproachforEarthquake TriggeredLandslideDetection FromSingle TemporalRapidEyeSatelliteImagery",in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, vol. 13, pp. 6166 6176,2020,doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3028855.
[9] Xiao Chen, “Using Satellite Imagery to Automate BuildingDamageAssessment:AcasestudyofthexBD dataset”,inIEEE,2020.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

[10] SergioBernabe,CarlosGonzalezandAdrianFernandez, “Portability and Acceleration of Deep Learning Inferences to Detect Rapid Earthquake Damage from VHR Remote Sensing Images Using Intel OpenVINO Toolkit’’vol.10,2021.
[11] Trong An Bui, Pei Jun Lee, Kai Yew Lum, Clarissa Loh andKyoTan,“DeepLearningforLandslideRecognition inSatelliteArchitecture”,vol.14,pp.654781120,2020.
[12] Diyana Kinaneva, Georgi Hristov, Jordan Raychev and Plamen Zahariev, “Early Forest Fire Detection Using DronesandArtificialIntelligence”,2019.
[13] Amna Asif, Shaheen Khatoon, Md Maruf Hasan, “Automaticanalysisofsocialmediaimagestoidentify disaster type and infer appropriate emergency response”,vol.61618907,2021.
[14] KrishnaKantSinghaandAkanshaSingh,“Identificationof flooded area from satellite images using Hybrid KohonenFuzzyC Meanssigmaclassifier”,2017.
[15] Tetsuo Inoshita and Yoshimitsu Aoki, “Analysis of satellite images for disaster detection”, vol.61324567, pp:00987,2019.
[16] Ying Liua and Linzhi Wu, “Geological Disaster Recognition on Optical Remote Sensing Images Using DeepLearning”,2021.
[17] Khelifi,Lazhar&Mignotte,Max.(2020).“DeepLearning for Change Detection in Remote Sensing Images: Comprehensive Review and Meta Analysis”. IEEE Access.PP.1 1.10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3008036.
[18] Guyon, I., Elisseeff, A. (2006). “An Introduction to FeatureExtraction.”In:Guyon,I.,Nikravesh,M.,Gunn,S., Zadeh, L.A. (eds) Feature Extraction. Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing, vol 207. Springer, Berlin,Heidelberg.
Available:https://doi.org/10.1007/978 3 540 35488 8_1
[19] Simonyan,Karen&Zisserman,Andrew.(2014).“Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large Scale Image Recognition.”arXiv1409.1556.
[20] Zhang, Yashun & Peet, Matthew & Gu, Keqin. (2010). “Reducing the computational cost of the Sum of Squaresstabilitytestfortime delayedsystems.”5018 5023.10.1109/ACC.2010.5530749.
[21] Yousefi,Jamileh.(2015).“ImageBinarizationusingOtsu ThresholdingAlgorithm.”10.13140/RG.2.1.4758.9284.
[22] Weiss, K., Khoshgoftaar, T.M. & Wang, D. “A survey of transfer learning”. J Big Data 3, 9 (2016). Available: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537 016 0043 6
[23] Nguyen, Long & Lin, Dongyun & Lin, Zhiping & Cao, Jiuwen. (2018). “Deep CNNs for microscopic image classificationbyexploitingtransferlearningandfeature concatenation.”1 5.10.1109/ISCAS.2018.8351550.
[24] Gupta, Ritwik; Goodman, Bryce; Patel, Nirav; Hosfelt, Richard; Sajeev, Sandra; Heim, Eric; et al. (2019): “CreatingxBD:ADatasetforAssessingBuildingDamage from Satellite Imagery.” Carnegie Mellon University. Preprint.https://doi.org/10.1184/R1/8135576.v1
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal