Quantum Computation: An Overview
Adithya Narayan*1, Aravind Harinarayanan*2, Sonus Vareed*3
3 School of Computer Science and Engineering (SCOPE), VIT Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India
ABSTRACT
Quantumtheoryisoneofthemostadvancedandprogressivefieldsofsciencetoday.Ithasgivenwaytonewhorizonsin moderntechnology.Ithasalsoopenedthepossibilityofexpressingandcommunicatinginformationindifferentways.Up until now the information was always expressed and communicated through physical or digital ways. In this paper we provideanin depthlookintothemajorconcernsofQuantumcomputingandQuantummachinelearning.
Keywords: QuantumComputing,QuantumMachineLearning,Qubits,ComputerEvolution
I. INTRODUCTION

Eversincetheintroduction ofthebasicComputerin1837 byCharlesBabbagecomputershaveundergoneextraordinary development from its 30 ton ancestor to the high speed modern Computer, we see today. Even though computers have undergone vast changes in these years, it is important to note that its fundamental principle remains the same, i.e., to interpretandmanipulateanencodingofbinarydigitsintoausefulcomputationalresult.
Thenumberofatomsrequiredtorepresenta bitofmemoryhasdecreasedexponentiallyascomputersevolvedfromthe early valves, gears and vacuum tubes to the integrated chips and microprocessors we see today. This is the basis of the Moore’sLaw,whichstatesthat computerprocessingpowerdoubleseveryeighteenmonths.
NowifweextrapolatethegraphofMoore’sLaw,wecaninferthatsoonerorlatereachbitofmemoryshouldbeencoded byparticlesofsubatomicsize.
ThispointisalsosupportedbythesurveymadebyKeyesin1988asshowninfigurebelow.

Fig:1.Showingthenumberofdopantimpuritiesinabipolartransistorlogicwithyear
1. Thisisaplotwhichshowsthenumberofelectronsrequiredtostoreasinglebitofinformation.
2. By extrapolating this plot, we can infer that we might be within the reach of an atomic scale of computations withinadecade.
3. Ananalysisoftheplotsuggeststhatwemightbewithinthereachofatomicscalecomputationswithinadecadeor soattheatomicscalehowever.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Subatomic particles are governed by quantum mechanics which are quite different from the classical logic, which determinethepropertiesofconventionallogicgates.
So,byMoore’slawifcomputersaretobecomesmallerinfuture,new,quantumtechnologymustreplacetheconventional classical technology. Quantum technology can not only decrease the size and multiply the clock seed of microprocessors butitcanalsosupportnewalgorithmswhicharequantitativelyandqualitativelybetter.
With the size of the components shrinking into subatomic sizes, scientists have begun to investigate the potential of quantum behaviors for computation. Astonishingly it seems that a computer which functions in a quantum way is more powerfulthananyclassicalcomputercaneverbe.Thephysicallimitationsofaclassicalcomputerandthepossibilityofa quantumcomputertoperformcertainuseful tasksmorequicklythananyclassicalcomputerdrivethestudyof quantum computing.
Quantumcomputingopensupnewrealmsinthefieldsofparallelismandmasscomputation,italsohasamemorywhichis exponentially larger than its apparent physical size. A few and simple concepts from quantum mechanics are needed to makequantumcomputersapossibility.Ifthequantumcomputerisaninevitabilityoranimpossibilityisthemillion dollar question.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
History of Quantum Computing
Theideaofusingquantummechanicsincomputationaldeviceswasfirstexploredinthe1970’sbyCharlesHBennet,Paul Benioff,DavidDeutschand RichardP.Feynman.Feynmanwasamongthefewwho triedtoprovidetheconcept ofa new kind of Computer which was based on the principles of quantum physics. He also constructed an abstract model which shows how a quantum system could be used to do computational calculations and also predict that it could be used to simulatephysicalproblemswhichpertainedtoquantumphysicswhichwasimpossibleuntilthen.Thatis,hecouldanalyze that this quantum mechanical computer could be used to solve the problems which a classical computer could not, especiallythosepertainingtoquantummechanicalbodyproblemsandthosewhichifwehadtriedtosolveona classical computerwouldrequireexponentiallygrowingtime.
Later, Deutsch realized that Feynman’s assertion could eventually lead to a general purpose quantum computer. He furtherprovedthatanyphysicalprocess,inprinciplecouldbemodelledperfectlybyaquantumcomputer.Thus,opening upunlimitedpossibilitiesincomparisonwithaclassicalcomputer.PeterShorIn1994showedthata quantumcomputer could be used to factor huge numbers immensely fast. Thus, transforming the field of quantum computing from just an academiccuriositytoasensationtheworldover.
Potency of Quantum Computing
Aquantumcomputerwith500qubits(referappendix)willhave2500superposition(referappendix)states,whereineach stateisequivalenttoasinglelistof500binarydigits(1’sand0’s)ina classicalcomputer.Theoreticallysuchacomputer couldoperateon2500 statessimultaneously.Also,bythelawsofquantummechanicsobservingsucha systemwillcauseit tocollapseintoasinglequantumstate,givingasingleansweri.e.,asinglelistof1'sand0's.HencethiskindofComputeris equivalentto10150 processorsinaclassicalcomputer.
Drawbacks of Classical Computing and Advent of Quantum Computers
In1970theconceptofpublickeyencryptionsystemwasintroduced.Itwasbasedontheprincipleofasafewithtwokeys, one public key to lock it and one private key to open it. Basically, it means that anyone can lock the safe but only one personcanopenit.Inrealitythesekeysarejustlargeintegers.Itisalsoeasytoderiveapublickeyfromaprivatekey but notviceversa.Thisisbecausethissystem isbased ontheprinciplethatmathematical operationscanbedone quickly in onedirectionbutnottheother.e.g.:multiplicationoverfactorization.
Inthecaseoffactorization,theuseofcomputationalresourcesisimmenseaswekeepincreasingthenumberofdigits.The public key cryptosystems are based on the assumption that the factorization of large integers is very difficult. Most encryption algorithms today like the RSA, DES are based on the assumption that using the technology today even the fastest computers would take millions of years to crack the encryption. But by quantifying the factorization of large numbersthistimecanbeexponentiallyreduced
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Quantum Factorization vs Classical Factorization
Thefactoringofbignumbersremainedbeyondthecapabilitiesofanyrealisticcomputingdevicesbecauseupuntilnowno one considered that quantum computation could be employed to perform such operations. According to the algorithm developed by Peter Shor factoring an integer using a quantum computer runs in O((lnN)2+є) steps where є is very small comparedtoO(exp((64/9)1/3(lnN)1/3(lnlnN)2/3))ofaclassicalcomputer.
Thatis,factorizinga1000 digitnumberwillrequireonlyafewmillionstepsforaquantumcomputercomparedtowhicha classicalfactorizationsystemwhichwouldtakemorethan12billionyearstofactorizea100 digitnumber.This,suggests thefutilityofpublickey basedcryptosystems.
Othermajorproblemsthataquantumcomputerhasagreatadvantageoveraclassicalcomputerare:
1. SearchingofanitemwithaspecificpropertyfromacollectionofNitems.
2. Simulation of a quantum system: By using a quantum computer we can solve the problem of polynomial slowdownwhichgenerallyoccursinaclassicalcomputer.
Quantum Computing and Parallelism
Parallelism is a concept in computation which refers to running multiple calculations or multiple processes simultaneously. Classical computers are inherently inefficient to carry out parallelism. This, is because in classical computers the microprocessors operate such thatthe primary test is first divided intosmalleror fundamental tasksand thesetasksarecarriedoutseriallyoneatatime.TheprogressofclassicalComputerinparallelismhasbeenveryslowand unsteady. This is mainly due to the fact that in classical computers the CPU is rapidly cycling from one task to the other thus creating the impression that it is running multiple tasks simultaneously. Hence this is not true parallelism. This can only be achieved by using a quantum computer, i.e., by implementing quantum parallelism. We can understand the quantum state as a superposition of many classical and classical like states. If this superposition can be protected from entanglementwithitsenvironment(decoherence)aparallelismcanbesetuponaserialmachinelikequantumparallelism.
Other Benefits of Quantum Computing
Artificial intelligence: Being much faster and able to do more calculations at a very short amount of time, quantum computers could learn faster even by using the simplest mistake bound model (refer appendix). It will also aid us in developing complex compression algorithms, voice and image recognition, molecular simulations, true randomness and quantum communication. It can also make communication become more secure because with the help of quantum communication both receiver and sender are alerted when a third party tries to catch the signal. It can alsoincrease the speedofcommunicationbyallowingmoreinformationtobecommunicatedperbit.
Quantum Entanglement and Decoherence
Bythebasicprincipleofquantummechanicsthatwhennoexternalsystemisinteractingwithouroriginalsystemthenour system will be a blend or superposition(ref)of all four quantum states. It also states that if we try to measure any of the featuresofthissystemthenwecausethesystemtocollapseintoanyoneofthestates.Ifsomethinginteractswithonepart ofoursystemthewholesystemwillbeaffected.i.e.,wecanjudgeorcalculatethespinofoneparticlebyjustdetermining the spin of the other entangled particle. This is the basis of quantum computing; it essentially means that to get the information in 2N bits we would only require N qubits or N qubits can contain the information in 2N bits. The qubits in quantum computer can exist in multiple states at the same time. i.e., it can be 0 and 1 at the same time. And by the principle of quantum entanglement to determine the value of 4 qubits we only need to the values of 2 qubits. Hence drasticallyeffectingthespeedandfunctioningoftheprocessor.
Drawbacks of quantum systems
Decoherence
Itreferstothelossofquantumcoherence.Quantumparticlesactaswavesandcanbedefinedbyusingwavefunctionsas longasthereisaphaserelationshipbetweendifferentstatesitissaidtobecoherent.Thiscoherenceisthebasicproperty of quantum mechanics and is an essential part of quantum computing. However, when a quantum system is not totally
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
isolated but is in contact with its surroundings it loses its coherence over time. This process is referred to as quantum decoherence.Asaresultofthisprocessthequantumbehaviorislost.Itcanleadtothelossofinformation.
Cost of Production
Thecost of production ofa quantum computerisalsoa major milestone.In 1997 GerstenfeldandChuang madethefirst quantum computer based on magnetic resonance technology. It was just a simple searching program using Grover’s algorithm.Thepriceofmakingthis2 qubitcomputerwasapproximately$1million.
Other Major Requirements
Scientists,engineersandphysicistswhoaretryingtoexecutequantumoperationsfacetwomajorproblems:
1. The qubits need to be shielded from the external environment, otherwise it could destroy the delicate quantum states required for computation. Moreover, longer we can maintain a qubit in its desired state greater will be the coherencetimeandhencemoreefficientthecomputation.
2. For the execution of the algorithm the qubits have to be entangled and also controllable on demand. Hence the perfectbalancebetweenisolationandinteractioniscrucial
Quantum Interference and Quantum Superposition - Theoretical visualization of quantum computer
Justlikethefundamentalunitoflightisknownasphoton,inaquantumcomputerthefundamentalunitofinformationis calleda“qubit”.Thequbitisanalogoustothebitwhichisthefundamentalunitofordinarycomputers,butunlikethebit which is binary qubit is more quaternary in nature. This unique property of a qubit is actually a consequence of its adherencetofollowthelawsofquantummotions.Abitcanexistas1or0(classicalstates)howeveraqubitexistsnotonly as1and0butalsoinstatesthatareablendofsuperpositionofthegivenclassicalstates.Insimplewordsaqubitcanexist as 0,1 or simultaneously as both 0 and 1, along with a coefficient that represents the probability of each state. Such a conceptisdifferentfromthelawsofclassicalphysicsandobeys lawsofquantum mechanicswhichbecomesignificantat theatomiclevel.Aqubit canbevisualizedhaving a spinofhalfof an electronsystem, the two states being the +/ ofthe basicspinthatis+1/2, 1/2.ThesetwostatesindeedrepresentthetwoEigenstates(referappendix)ofthezcomponent of an external magnetic field of same magnitude of spin. The existence of qubit seems strange but in reality, a beam of singlephotoncanbeusedtorepresentaqubit.Thedifferentstateswillbethestatesofpolarization(horizontalorvertical) with respect to a chosen axis. Thus, the qubit takes 0,1 as the value which are then associated with two eigenstates of a spinofanelectron.
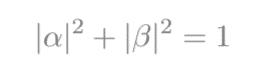
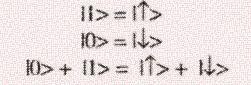
Qubitcanexistnotonlyinthesestatesbutalsoinstatesthatareasuperpositionof thegivenstateswhichhave complex coefficients and this property distinguishes a qubit from the normal bit. A state of a qubit can be described by the given equation: Hereα,βarecomplexnumberwhichsatisfytheequation: Inmathematicaltermssincethegeneralstateofaqubitisthesuperpositionoftwopurestateswithcomplexcoefficients, the state is described as a vector in the complex two dimensional space and the pure states form the basis of this representation. One of the most famous experiments that demonstrate quantum superposition is the beam splitting of light.
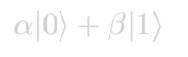
Figure1:BeamSplitting

Asseenintheabovefigurethelightsourceemitsaphotonontothehalf silveredmirror.Themirrorsplitsthelightinsuch awaythathalfofthelightistransmittedtowardsdetectorBandotherhalfisreflectedtowardsdetectorA.Sincea single photoncannotbesplitasithasasinglequantizedenergystate(hν),soitisdetectedwithhalfprobabilityatbothAand B. ThisprobabilityvalueisderivedfromthefactthatwhenAhasdetectedsomethingthenBdoesnotandviceversa.Hence theprobabilityisequallydistributedbetweenthetwodetectors.Accordingtoclassicalmechanicsonemaythinkthatthe given photon travels either vertically or horizontally randomly choosing between the two paths. However according to quantummechanics,thephotonactuallytravelsboththepathssimultaneously,collapsingtoagivenpaththatishorizontal orverticaluponmeasurement.Thiseffectisknownasthesingle particleinterference(referappendix)resultingfromthe linear superposition of the possible states of the given two paths. The phenomenon is better explained with another experimentasshowninfigure2.Inthisexperimenttwobeamsplitters(referappendix)andtwofullysilveredmirrorsare used. A beam splitter is basically a half polished mirror (half silvered mirror). As the first experiment shows the beam splitter splits the beam into two parts the transmitted part and the reflected part. In the second experiment the photon falls on a beam splitter. The two beams then recombine with the help of the fully silvered mirrors. Finally, the beam is againsplitwiththehelpofabeamsplitterbeforereachingthedetectors.Eachbeamsplitterintroducesa50%chancethat thebeammaygoeitherway.Oncethephotonstrikesthemirrorineitherwayafterthefirstsplitterthelaterarrangement is similar to that of the first experiment. Thus, the photon travelling vertically when strikes the mirror should produce a 50%chanceofgettingdetectedateitherAorB.Thesamehappensforthe photonmovingalongthehorizontaldirection. However,theactualresultsaredrasticallydifferent.Itisfoundthatifthetwopossiblepathsareofthesamelength,then thereisa100%probabilityofphotonreachingdetectorAand0%probabilityofphotonreachingdetectorB.Itseemsthat itisinescapableforthephotontostrikedetectorA,insomesensewecansaythatthephotonhastravelledbothpaths.
Figure2:Wave ParticleNatureofLight


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Thisphenomenoncanbedemonstratedbyplacinganabsorbingscreeninthewayofeitheroftheroutes,thenthephoton becomesequallyprobableatdetectorAandB. WhenoneofthepathsareactuallyblockedthephotonreachesdetectorB. WithboththeroutesopenthephotonmusthaveknownthatitcannotreachBsoitmusthavetravelledbothpaths.Hence itisjustifiedtosaythatbetweenthetwobeamsplittersthephotonexists inboththetransmittedandreflectedpaths,or wecansaythatthephotonisinacoherentsuperpositionofbeingpresentinthetransmittedbeamandinreflectedbeam. Thisinferenceisduetolinearsuperpositionprinciple.Thisistheconceptthatmaketheresearchinquantumcomputinga rather new branch of thought. It is because quantum computers possess these unique characteristics that it gives them potentialtobeincrediblypowerfulcomputationaldevice.

Quantum Entanglement
Classical physics help us to well describe the correlations existing in our day to day life. One of the basic examples of a day to daycorrelationcanbepresentedwithasimpleexample.Supposewehaveacattrappedinaboxwithfoodthathas beenpoisoned. Weknowthecorrelationbetweentheeventofcateatingthefoodandtheeventofthecat’sdeath.Hence thereexistsacorrelationbetweentheexistenceofthecatandwhetherthecatatethefood.
Such correlations that occur in the macroscopic world are easy to identify, but when it comes down to the microscopic world governed by the laws of quantum mechanics here, we see that such correlations are not easy to predict. A similar casetothecatexampleaboveistheconditionofanatomthatcanundergodecay.So,wemaypredictitiseitherdecayed state or not decayed state, but this is not the only two states it is found that the atom can also exist in a state that is in betweenthesetwostatesthatisbetweendecayedandnotdecayed.Justasdiscussedbeforethisisduetothephenomenon oflinearsuperpositionoftwoquantummechanical statesofanatom.Thisisthesituationwhenitcomestooneatom,in thecaseoftwoatomsitisseenthatifone oftheatoms isdecayed thentheotheris alsodecayed. Thiscorrelation exists evenforthesuperpositionstate.Hencethisisproofof100%correlationbetweenthestateofthetwoatoms.Thiskindof supercorrelationiscalled Quantum Entanglement (referappendix).
ItwasEdwardSchrodingerwhodiscoveredthisconcept,hewasthefirsttorealizeitsweirdcharacteristics.SupposeInthe above given example the event of the cat eating the food was triggered by whether or not the nucleus has decayed. This means that if the decay happens the cat eats the food and dies, if the decay doesn’t happen then the cat lives, else if the nucleusisinasuperpositionstate,thenthecatcanbeconsideredinasituationwhereitisbothdeadandalive.Thisiswas indeed the very concept of ‘The Schrodinger Cat’. The only difference is that instead of poisoned food there was a lethal chemicalthatwouldbereleaseduponthenucleusdecay.Suchproblemsdon’tariseineverydaylifeandhenceonlywhenit comestoquantummechanicswegettoknowofsuchphenomena.
Figure 1:EPR Paradox Experiment
The topic of quantum entanglement was briefly discussed in the paper published by Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen who believedthatquantummechanicsisincompleteandnotwrong.Thepapertheypublishedbroughtintoconsiderationthe EPR paradox (refer appendix). The EPR paradox can be explained easily by the given experiment. Consider a He atom with just 2 electrons with quantum numbers n=1, l=0, s=1/2 and opposite spins. These two electrons in He are antiparallel (refer appendix) to each other and hence form an entangled pair. When the atom is provided sufficient energy, it disintegrates at rest and the two electrons fly away in opposite directions. The two electrons are taken apart. The real effect of the paradox is observed when a magnetic field is applied on one of the electrons causing its spin to be
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
flipped.Whenthishappens,itisobservedthatsimultaneouslythespinoftheotherelectronisalsoflipped.ThisistheEPR paradoxanditsuggestsawayofcommunicationwiththespeedfasterthanthatoflight.Themechanismofthiscannotbe explainedwithsurety,itisasimpletheorythatwemustbelievein.
This EPR paradox hence provides us with the idea of communication across space like events. Quantum Entanglement allowsqubitsseparatedbylargedistancestoinstantlyinteractwitheachotherataspeednotevenlimitedbythespeedof light. The distance between the electrons doesn’t matter as long as they are isolated. Hence together the concepts of quantum entanglement and quantum superposition does propose the creation of an enhanced computer with enormous computationalpower.
Bertlemann’s Socks
ThereisanotherconceptthatintroducesanewideatotheconceptofquantumentanglementandthisistheBertlemann’s socks.Allsuchconceptsarebetterexplainedthroughstories.Mr.Bertlemannalwaysusedtoweardifferentpairsofsocks and also, he used to wear only specific colour pair that is yellow blue, red green so on. He never breaks this order. So, if one can observe one of his socks then it is evident what colour the other is. This seems to be similar to a quantum entanglementsituationbutitisnot.Inquantumentanglementthechoiceofmeasurementplaysanimportantrole.There are many ways to measure the spin of an electron, the other particle arranges its spin accordingly. In the case of Bertlemanns Socks the onlooker plays this role of measurement selection. It is the onlooker that decides to see the one sockandpredicttheother.
EPR Situation, Bell Theorem and Hidden Variables:
John Bells analysis of the paper by Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen lead to contradictory conclusions. In his paper ‘On the Einstein Podolsky Rosen Paradox' he introduces the Bells theorem that proves that quantum mechanics is incompatible with the local hidden variable's theories. According to the local hidden variable's theory the interpretation of quantum mechanicsisahiddenvariabletheorythathastheaddedrequirementofconsistencywith local realism (referappendix). According to Bells examination of ‘Is Quantum Mechanics Complete?’ by Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen he concluded that theEPRcorrelationsalsoknownasquantumentanglementhavetobepredictedbysomesupplementaryparametersalso called hidden variables. The above results demonstrated that the hidden variables description in fact contradicts some predictionsofquantummechanics.Becauseofthesetwocontradictorytheoriestherewasnowaytofindoutthetruth.
An EPR Situation:
Theexperimentshownbelowusesasourcethatemitsapairofelectronsv1andv2travellinginoppositedirections.Each photon then falls onto a polarizer, which measures the linear polarization (refer appendix) along both the directions determinedbyorientationofthecorrespondingpolarizer.
Figure 2: Graph Description of The EPR Situation
Once the two photons come out of the polarizer there are two possible values for each measurement that is +1 or 1. Quantum mechanics allows the existence of a state of superposition (an EPR state) for which the measurements taken separatelyappearrandombutactuallyarestronglycorrelated.ItisfoundthatProbability(a,+1)andProbability(a, 1)for v1 is predicted to be 0.5 each, similar is the case for Probability (b, +1) and Probability (b, 1) independent of the orientationofb.
Theprobabilityforobservingboth+forbothphotonsisgivenby0.5Cos^2(a.b). Ifthepolarizersareparallelthena.b=0, thenwehaveprobability0.5.Forcrosspolarizersa.b=pi/2,theprobabilityis0.Thefinalresultsforthetwophotonsofthe

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
same pair are hence, always identical which means there is complete correlation. Such correlations among events which appear random occur not only in physics but also in other fields. The basic conclusion derived by John Bell is that the natural generalizationoftheEPRreasoningleadstotheassumptionthatquantum mechanicsisnota final descriptionof physicalreality.Thecompletedescriptionofapairmustincludeasomethinginadditiontothestatevector,thissomething isthehiddenvariables.
Bell Inequalities
Bell tried to predict the correlation between the two polarized states of a photon. Bell's inequalities basically concern about the measurements made by observers on pairs of particles that have interacted and then separated. In the above experiment the particle pair is photon and they have emerged from the same source meaning they have interacted and then they separated. The measurement made in the above experiment is the measurement of polarized states of the photons. According to Bell certain constraints must apply to the relationship between the correlation of the given two photon pairs. The polarized states of photon hence cannot take any set of value as some constraints apply to the correlation.Ifweconsiderthepossibleorientationsas[(a.b),(a'.b),(a.b'),(a'.b')],thecorrespondingcorrelationcoefficients arerestrictedbyBell inequalitiesaccordingtowhichagivecombinationofthesecoefficients's'isbetween 2and+2for anyvalidhiddenvariabletheory. Thevalueofsaspredictedbyquantummechanics doesnotmatchthesvaluegiven by Bells inequalities. Bell inequalities basically describe a test for the validity of the hidden variable theory hence as the s valuedoesnotmatch,wecanconcludethatthehiddenvariabletheorydoesnotaccountoftheEPRcorrelationpredicted byQuantumMechanics.
Bell inequality has the assumption of local hidden variable models as its foundation. According to the assumption of localitytheresultofameasurementbyapolarisercannotbemanipulatedorinfluencedbythechoiceoftheorientationof otherremotelylocatedpolariser.Thisisanoutcomeof Einstein’s rulethatnosignal canmovewitha speedgreaterthan thatoflight.Bellinequalitiesalsoapplytoothertheories. Finally,anytheoryinwhicheachphotonhasarealitylocalised inspacetime,determininganymeasurementwillcauseinequalitiesthatwillconflictwithquantummechanics.Thus,Bells Theoremcanbefinallyphrasedas'Somequantummechanicalpredictionscannotbecopiedbyanylocalrealisticmodelin Einstein'sideasoftheoryofhiddenvariables.
Requirement
Here,inthissection,weconsideronhowtobuildaQuantumComputer.SimilartoaclassiccomputeraQuantumcomputer also require Universal Gates, which implement any legitimate quantum computation. There are five experimental requirementsforbuildingaquantumcomputer.
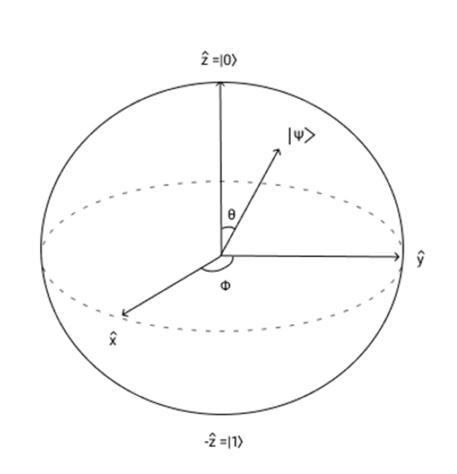
The Bloch sphere is a representation of a qubit, the fundamental building block of quantum computers.
Source: Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quantum_computing

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Thefirstrequirementistheabilitytocomputequantuminformationefficiently.Second,aquantumcomputerrequires the ability to set an initial state. This appears to be a main problem for most quantum systems because of the imperfect isolationfrom the environment and thedifficultyofproducing desired input states. Third, a quantum computer requires the need of a long decoherence time which should be much longer than the operation of gates. Decoherence is the coupling betweenqubit (two level system)andits environmentand thisresultsin theloss of quantum phasecoherence. After decoherence, quantum mechanical properties associated with coherence such as superposition and entanglement cannot be observed. The fourth requirement is the ability to measure output results from certain qubits. Generally, the output of a quantum algorithm is quantum superposition. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain result from quantum state using classical systems of very high fidelity. The fifth requirement is the ability to construct a universal set of quantum gates.
There have been several implementations of quantum computers. One of these include the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance(NMR).ThisComputerusesavialofliquid filledwithsamplemoleculesasqubits.Anion trapbasedquantum computerusesastringofionsconfinedinalineartrap.Eachionrepresentsaqubitandismanipulatedbylaserbeams.A Cavity Quantum Electrodynamics (QED) based computer is schemed to use photons as qubits. A Quantum dot based quantum computer uses spins or energy levels of electrons that are confined in quantum dots as qubits that are further fabricated by semiconductor materials. Since we can control the states of qubits electrically, like we do in classical computers, this method has its advantage as the current semiconductor technology can be applied for the fabrication of the quantum computer. A Superconducting quantum computer uses the Josephson junctions (refer appendix) in superconductingcircuitsasqubits.
Since it is extremely difficult to isolate quantum registers efficiently from their environments, a real quantum computerneedstobedesignedwithbyconsideringtheeffectsoferrorsonthestateofquantumregisters.Toprotectthe quantum states against the effects of noise several Quantum Error Correcting (QEC) schemes have been proposed. QEC codesaredevelopedbasedonprinciplessimilartoclassicerror correctingcode.
Applications
Most algorithms need a larger number of high quality qubits in order to be useful, most likely requiring quantum error correction far beyond the available quantum resources. Also, the current inability to load large quantities of input data efficiently suggests that many of these applications would be difficult to implement in practice. Also, algorithms are not themselvesapplications;buttheyarebasicelementsthatmustbecombinedtoperformaparticulartask.
The best example for an application of quantum algorithm is in the field of cryptography, an application which is based on mathematics. The potential near term usage of a quantum computer is currently an area of active researchastheseareapplicationsthatrequirefewer qubitsandcanbeimplementedwitha comparativelyshallowcode. The electronicstructure problem, owing to the fieldsof chemistry and materialsscience,requiressolvingfor theground state energies and wave functions of electrons. Electronic structure defines chemical properties as well as the rates and productsofchemicalreactions.Whileclassicalcomputingapproachestothisproblemmaybequiteeffective,theymostly failtoreachthegivenamountofaccuracy.Quantumcomputerwillprovideefficientsolutionstotheaboveproblem.
Anotherimportantaspectinthepathofuseful quantumcomputersis Quantum Supremacy (a demonstration of any quantum computation that is hard for a classical computer i.e., whether or not a computation is useful)(referappendix).Quantumsupremacywouldaddresstheviabilityofquantumcomputersaswellasprovideatest ofquantumtheory.
Challenges
Aclassicalcomputerusesbitstorepresentthevaluesduringitsoperation,whileaquantumcomputeruseswhatiscalled as Quantum bits(qubits). Abitcanbeeither0or1butaqubitcanrepresentvalues0or1,orsomecombinationofboth simultaneously which is known as superposition. But a quantum computer can work in an exponentially larger problem space.Manyinnovationsoverthelast25yearshaveenabledresearcherstobuildphysicalsystemsthatprovidetheneeded isolationandcontrolforquantumcomputing.Evenitispossibletomakeveryhigh qualityqubits,creatingandmakinguse of these quantum computers is indeed challenging. These computers use a different set of operations than those of classicalcomputers,requiringnewalgorithms,software,hardwareandcontroltechnologies.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1) Rejectionofnoisebyqubitsisnotpossibleintrinsically
One of the main differences between a classical and quantum computer is how these handle unwanted small variations,ornoiseinthesystem.Sinceaqubitisacombinationofoneandzero,qubitsandquantumgatescannot readily reject small errors or noise that occur in the physical circuits. So, one of the most significant design parametersforthosesystemswhichoperateonphysicalqubitsistheirerrorrates.
2) LoadingofLargeDataInputs
Whileaquantumcomputercanuseasmallnumberofqubitstorepresentanexponentiallylargerquantityofdata, presently there is not a method to rapidly convert large amount of classical data to a quantum state. As a consequence, the amount of time needed to create the quantum input state would typically dominate the computationtime,reducingthequantumadvantage.
3) QuantumErrorCorrectionrequiredforError Freequantumcomputer
Although, the physical qubit operations are much sensitive to noise, it is possible to carry out a Quantum error correction(QEC)algorithminaphysicalcomputertoemulateanoise freequantumcomputer.WhileQEC'smight beessentialtocreateerror freequantumcomputer,theyaretooresourceintensivetobeusedinshort term.
4) QuantumAlgorithmdesignisChallenging
One can extract exactly the same amount of data from a quantum computer that one can do from a physical computer of the same magnitude. To receive the benefits of a quantum computer, quantum algorithm must leverage uniquely quantum features to arrive the final classical result. So, achieving quantum speeding up requiresfullynewkindsofalgorithmsandverycleveralgorithmdesigns
5) IntermediateStateofaquantumcomputerisdifficulttobemeasured
The debugging methods for classical Computer rely on memory, and reading of intermediate machine states; whichisbothnotpossibleinaquantumcomputer.Aquantumstatecannotbecopiedsimplyforlaterevaluation. Newapproachestodebuggingarecrucialforthedevelopmentoflarge scalequantumcomputers.
6) NecessityofaSoftwareStackforQuantumComputers
Asquantumprogramsaredifferentfromprogramsforclassical computers,developmentandresearchisneeded forfurtherdevelopmentofthesoftwaretool stack.Asthesesoftwaretoolsdrivethe hardware,the development ofbothhardwareandsoftwaretoolswilldefinitelyshortenthetimeforthesequantumcomputers.
Thermodynamics
Basedonthelawsofthermodynamics,computersarealsosubjecttothermodynamicconstraint.Computersaremachines so,likeallmachinestheyareallsubjecttothermodynamicconstraints.Similartoanyphysicalsystem,moderncomputers based on digital devices, also produce heat in operation. It is important of an ideal computer capable of shaping, maintaining and moving around digital signals, without any heat generation. But there is one place where heat is produced, when information is erased, the phase space associated with the system that stores the information shrinks. Removingasinglebitofinformationreducesentropyofthesystemthatstoredtheinformation.Thisreductionofentropy causestheheatreleasetotheenvironment.Thus,ifacomputercanbeconstructedthatdoesnotremoveanyinformation, such a computer could work without generating any heat at. This is the situation in quantum computers. Quantum Computation is a reversible process. It is therefore possible in principle, to carry out quantum computation without generating heat. But, in reality the computer would definitely generate a lot of heat because of electric pulses moving across copper wires and their emission of heat due to resistance. The reversibility capability of quantum computers is realized byconceivingspecial gates.Fortheconstructionofdigital computers,NOR, AND,NANDandXOR gates areused whichareirreversiblegatesandthesegenerateheat.
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

Here the amount of information on the right hand side of the equation is less than the amount on left hand side. Using Toffoli Gates, it can be demonstrated that quantum computers are capable of carrying out computation using reversible stepsalone.
Realization of Quantum Computers experimentally
Thearchitecturalsimplicitymakesquantumcomputerfaster,cheaperandsmaller,butitsconceptualcomplexityis severe problems for its experimental realization. Moreover, some attempts have been made in this direction by encouraging success.ItisrealizedthatitmaynotbetoolongwhenthequantumcomputercouldreplacethedigitalComputerwithits fullrealization.Someoftheattributesfortheexperimentalrealizationofaquantumcomputeraresummarizedasfollows:
Ion Traps:
AniontrapquantumcomputerwasimplementedfirstbyMonroeandcollaboratorsin1995followedbySchwarzschildin theyear1996.Theiontrapcomputerusesencodingsofdatainenergystatesofionsaswellasvibrationalmodesbetween theions.Theoretically,eachionisoperatedbya laser.AfundamentalanalysisdemonstratedthatFouriertransformscan beexaminedwiththeiontraptypeofComputer.ThisleadstoShor'sfactoringalgorithm,whichismainlybasedonFourier transforms.
Quantum Electrodynamics Cavity:
Quantum electrodynamics (QED) cavity computer was first demonstrated by Hette and collaborators in 1995. The computer contains of a QED cavity filled with some cesium atoms and an arrangement of lasers, phase shift detectors, polarizer and mirrors. The setup is an actual quantum computer because it can create, manipulate and preserve superpositionandentanglements.
Quantum Dots:
Quantumcomputerswhich arebasedon quantumdottechnologyuse muchsimplerarchitectureand moresophisticated experimental,mathematicalandtheoreticalskillsincomparisontothequantumcomputerimplementationsdiscussedso far. An array of quantum dots, where the dots are connected with the nearest neighbors by means of gated tunnelling barriers are used for fabricating quantum gates using the split gate technique. This scheme has one of the primary advantages:thequbitsaremainlycontrolledelectrically.Themaindisadvantageofthisarchitectureisthatquantumdots cancommunicatewiththeirnearestneighborsonlyresultingdatareadoutisquitetricky.
Josephson Junctions

TheJosephsonjunctionquantumcomputerwasdemonstratedin 1999byNakamuraandco workers.InthisComputer,a Cooper pair box, which is a small superconducting island electrode is weakly coupled to a bulk superconductor. Weak coupling between the superconductors creates a Josephson junction between them which behaves as a capacitor. If the Cooperboxisassmallasaquantumdot,thechargingcurrentbreaksintoadiscretetransferofseparateCooperpairs,so thatultimatelyitispossibletotransferasingleCooperpairacrossthejunction.Likequantumdot,computersinJosephson junction computers also, qubits are controlled mainly electrically. Josephson junction's quantum computers are among muchneededcandidatesforfuturedevelopments.
Future Directions of Quantum Computing
Thebasesforthesubjectofquantumcomputationhavebecomewelldeveloped,buttheremainingtechnologyrequiredfor itsfuturegrowth isstill underdevelopment.Thisincludesquantumalgorithms,understanding the dynamicsandcontrol of decoherence. Reversibility of quantum computation may assist in solving problems which are simple in one direction anddifficultintheothersense.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Quantum Field Theory (refer appendix) can extend quantum computation to allow the creation and destruction of quanta.Theverynaturalsettingforsuchanoperationisquantumoptics.The Double slit experiment (referappendix)is permittedinquantumoperationbecausetheintensityoftwocopiesishalfthepreviousvalue.Thoughitsdynamicsisnot well understood Decoherence (refer appendix) can described as an effective process. In order to control decoherence, oneshouldbeabletofigureouttheeigenstatesfavoredbytheenvironmentinthesetup.Thedynamicsofmeasurement processisalsonotunderstoodeither.Measurementisdescribedasanon unitaryprojectoroperator.Ultimately,boththe systemandtheobserveraremadeofquantumbuildingblocks,andaunifiedquantumdescriptionofbothmeasurements needtobedeveloped.Itisimportanttostudythetransitionfromclassicaltoquantumsystems.Enlargementofthesystem from microscopic to mesoscopic levels and its reduction from macroscopic to mesoscopic levels can take us there to the target.
Theoreticaldevelopmentsalonewillbenousewithoutacorrespondingtechnology.Inthepresentday,theminiaturization of electronic circuits is not much away from quantum reality of nature. To devise new instruments, we must change our view pointfromscientifictotechnological quantumeffects.Itistruethatthefutureworldseesa morepracticalusageof quantumcomputers.
Quantum Machine Learning
The field of quantum computing has a lot to contribute to several domains like optimization, quantum simulation, cryptography,machinelearning.Oneofthemostimportantone’sbeingthefieldofQuantumMachineLearning.Quantum MachineLearningistheintegrationofquantumalgorithmswithmachinelearningprograms.Thereare2importantterms in focus, quantum algorithms and machine learning. Quantum algorithm are algorithms that run on a realistic model of quantum computation, which is the quantum circuit model of computation. The latter term machine learning is basically usingdatatopredictdataandforecastdata.
Quantum computing can help scale down the amount of time taken to train a machinelearning model by an exponential factor.ThesamehasbeenprovedbyGoogle’squantumbeyond classicalexperimentwhichused53qubitstodemonstrate it could perform a calculation in 200s on a quantum computer which otherwise would have taken 10000 years on the largestclassicalcomputerswepossess.
As discussed above Quantum Computing relies on the abilities of qubits to be put into superposition and share entanglement with one another. Classical computers perform deterministic operations, but by harnessing the ability of superposition and entanglement quantum computers can perform quantum operations that are difficult to emulate at scalewithclassicalcomputers.
Just like any machine learning model, even quantum machine learning requires data and a model, algo to build on the provideddata.Thisinthecaseofquantummachinelearningisquantumdataandhybridquantumclassicalmodels.
Quantum Data
Quantum data is the data source that occurs in a natural or artificial quantum system, data generated by a quantum computerisanexampleofsuchdata.Quantumdataexhibitsthepropertiesofsuperpositionandentanglementleadingto joint probability distributions that could require exponential amount of classical computational resources to store. The Noisy Intermediate Scale Quantum generates data that are noisy and typically entangles just before the measurements occurs, thus making them a little more interpretable. Heuristic machine learning models can be developed on this noisy entanglesdatatoextractusefulclassicaldata.Tooursurprisethereareseveralprojectsthataimattransformingquantum data received from NSIQ, one such being the TensorFlow Quantum library (TFQ) which provides methods to develop modelsthatdisentangleandgeneralizecorrelationsinquantumdata.
Hybrid Quantum Classical Models
A quantum model can represent and generalize, correlate data from a quantum mechanical origin. The current quantum processors we possess are still small and noisy thus making us depend on the need for NISQ processors to work with classical co processors to become effective. TensorFlow being a platform that supports heterogenous computing across CPUs,GPUs,TPUs,itisusedasabaseplatformtoexperimentwithhybridquantum classicalalgorithm.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
III. CONCLUSION
Inthispaper,wehaveprovidedanintroductiontotheworldofQuantumcomputingandthefutureimportanceofthefield. Wehaveanalyzedthefieldofquantumcomputingbyprovidingdetailsfromthebeginningofthefielduntilnowwhere we are overlooking into the field for more reasonable applications. The field has its own benefits in terms of accuracy and precisionbutalsohasitsownlimitationsconsideringthepresentcircumstancesofthetechnology.Butthedevelopmentof thisfieldwillindeedbeofimmenseimportancetotheworldofComputerandthoseworkinginit!
IV. REFERENCES
Mainsource:
● A Study on the basics of Quantum Computing, Department d’Informatique et de recherché operationnelle, UniversitedeMontreal.Thegivenresearchpaperisareinterpretationofthegivenresearchpaper.Thediagrams takenhavebeenmodified.
OtherSources:
● Wikipedia BellsTheorem,EPRParadox
● ResearchGate
● Scholarpedia
● link.springer.com
● hackaday.com
● https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parallel_computing
● Archil Avaliani,International University,December 1, 2002,Quantum Computers
{Daniel, G. (1999). Quantum Error Correcting Codes. Retrieved on November 31st, 2002 from: http://qso.lanl.gov/~gottesma/QECC.html
Manay, K. (1998). Quantum computers could be a billion times faster than Pentium
III. USA Today. Retrieved on December 1st, 2002 from: http://www.amd1.com/quantum_computers.html
Quantum Computers. Retrieved on December 1st, 2002 from: http://www.ewh.ieee.org/r10/bombay/news4/Quantum_Computers.htm
Quantum Computers & Moore's Law. Retrieved on December 1st, 2002 from: http://www.qubyte.com
Quantum Computers: What are They and What Do They Mean to Us? Retrieved on December 1st, 2002 from: http://www.carolla.com/quantum/QuantumComputers.htm
West, J (2000). Quantum Computers. Retrieved December 1, 2002 from California Institute of Technology, educational website:
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

http://www.cs.caltech.edu/~westside/quantum intro.html#qc}
● Frontiers of Engineering: Reports on Leading Edge Engineering from the 2018 Symposium.
● 8803 Machine Learning Theory
● Maria Florina Balcan Lecture 4: September 1st, 2011
V. APPENDIX
● Mistake bound model: AnalgorithmAissaidtolearnCinthemistakeboundmodelifforanyconceptc∈C,and fororderingofexamplesconsistentwithc,thetotalnumberofmistakesevermadebyAisboundedbyp(n, size(c)),wherepisanypolynomial.
● Qubit: Aqubitisthebasicunitofquantuminformation.
● Superposition: Itisaprinciplethatstatesthattheresultantresponsecausedbytwoormorestimuliisthetotal sumoftheresponsesthatmighthavebeencausedbyeachstimulusindividually.
● Eigenstates: Aquantummechanicalstatecorrespondingtoaneigenvalue.
● Polarization: Apropertythatclarifiesthegeometricalorientationoftheoscillation.
● Interference:Intermsofwaves,itisthecombinationoftwoormoreelectromagneticwavestoformaresultant displacement.
● Beam Splitter:Opticaldevicethatsplitsbeamoflightintotwo.Extensivelyusedintelecommunication.
● Entanglement:Acomplicatedorcomprisingrelationshiporsituation.
● Antiparallel: Parallelbutmovingororientedinoppositedirections
● Paradox: A seemingly contradictory statement or proposition which when investigated may prove to be well foundedortrue.
● Local Realism: It is basically a premise (or accurately a combination of two premises) introduced by Einstein, Podolsky,Rosen.
● Quantum Supremacy:Intermsofquantumcomputing,quantumsupremacyisthetargetofdemonstratingthata programmablequantumdevicecansolveaproblemwhichnoclassicalcomputercanfeasiblysolve.
● The Schrödinger Cat: It is a thought experiment sometimes also considered as a paradox, devised by Erwin Schrodingerin1935.
● Josephson junctions: TheJosephsoneffectisthephenomenonofsupercurrent,a currentthatflowsindefinitely without any voltage applied, across a device which is known as a Josephson junction, which consists of two or moresuperconductorswhichiscoupledbyaweaklink.
● Decoherence: Itcanbeviewedasthelossofinformationfromasystemintotheenvironment,sinceeverysystem islooselycoupledwithitssurroundings.
● Quantum Field Theory: In theoretical physics, quantum field theory can be defined as a theoretical framework that combines classical field theory, quantum mechanics and special relativity but not general relativity's descriptionofgravity.
● Double slit experiment: The double slit experiment is a demonstration that light as well as matter can display characteristicsofbothclassicallydefinedwavesaswellasparticles.
● Universal Gates: A universal gate is a gate which can implement any Boolean function without using any other gatetype.
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2754
