Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Machine Learning Techniques
Sahoo1, Bijaya Kumar Ekka2
1Department of Electronics and Instrumentations Odisha University of Technology and Research Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
2Professor, Department of Electronics and Instrumentations Odisha University of Technology and Research Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India ***
Abstract:
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a fatal, degenerative brain ailment that gradually decreases people of their ability to think clearly and recall things. A common cause of dementia is Alzheimer's disease. Dementia is the term used to describe the loss of cognitive functioning, which includes thinking, recalling,andreasoning,aswellasbehaviouralskills to the point where it affects daily life. To identify diseases and aid doctors in making observations based decisions, image processing is frequently employed in the medical industry. The goal of the study is to identify Alzheimer's disease as early as possible so that patients can be treated before their brains experience irreversible alterations. A significant development in Machine Learning and Deep Learning technology leads to accurately classifying MRI based images. But a high benchmark is needed while classifying Medical related tasks. A small mistake may lead to serious health complexion over time or may lead to fatal. We proposed a method to uses the brain's magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) from the coronal, axial and sagittal planes using a Deep Learning based Image classifier to emphasise the detection of the damaged brain with an accuracy of 99.5 %. Trying to compare our suggested model to many state of the art models, it hasaccomplishedahigh levelbenchmark.
Keywords- Alzheimer’s disease, Mild cognitive impairment,Imageprocessing,Dementia.
1. INTRODUCTION
Thebrainisthemainorganofthehumanbody.Itisvital to treat brain illnesses since, in most situations, once alterationstakeplace,theycannotbereversedunlessin rare circumstances. The loss of cognitive and practical reasoning is known as dementia. The leading cause of dementia is Alzheimer's disease. Mid 60s is when Alzheimer's initially manifests. More than 6.5 million people are thought to have Alzheimer's disease. Memory loss, language difficulties, and behavioral modificationsaresomeofthesymptomsofAlzheimer's
disease. Word finding problems, visual problems, decreased reasoning, and poor judgments are the symptoms of the non memory aspect. The biological indications are blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and brain imaging. Mild Alzheimer's, moderate Alzheimer's, and severe Alzheimer's are the three stages of the disease. The hereditary component of early onset Alzheimer's disease and the complicated chain of brain changes that leadtolate onsetAlzheimer'sdiseasearethecauses.The capacity to detect Alzheimer's disease by studying changes in the brain, body fluids, and lifestyle are the otherreasons,alongwithgenetics,environment,lifestyle, and health. The aberrant protein or chemical aggregates (amyloidplaques),tangledfibrebundles(tautangle),and loss of connections between nerve cells in the brain are all symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. A decade after the beginning of the development of the disease, the symptoms of Alzheimer's start to show. When a healthy neuron stops functioning, the connection with the other neurons is lost, and the cell eventually dies. The accumulation of amyloid plaques and protein tau tangles in the brain is what generates this. The hippocampus, a crucial component in establishing memories, will be the firstbrainregiontobedamaged.Theaffectedareasofthe brain started to shrink as it spread to other regions gradually, and by the time it reached its ultimate stage, the entire brain had significantly shrunk in size. [1]. TherearemanytechniquesareavailablebutMRIandCT Scans are more effective in diagnosis. While MRI is more effectivetocapturelow levelfeaturesofthebrainsoMRI isveryusefulfortrainingadeepneuralnetwork.Wehave trained our proposed model with MRI datasets and compared it with different Machine Learning and Deep LearningbasedState of the artModels.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
MRI scans can be utilised in image processing to determine the likelihood of AD early detection. Intensity adjustment, K means clustering, and the region growing method for extracting white matter and grey matter are threeimageprocessingtechniquesutilisedinMRIs.Using the same approach, the brain's volume may be determined. The axial (top view), coronal (back view), and sagittal (side view) planes of a brain MRI are

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

analysed quantitatively and clinically using MATLAB. [2]. Using various image segmentation techniques, imageprocessingistheprocessofremovingtheRegion of Interest from the image. The K means clustering approach, region expanding, watershed, thresholding, split and merge, and other techniques are used in picture segmentation. The segmentation of X rays of radiographic welds with abnormalities including porosityandthelack offusion,inadequatepenetration, and wormhole detected is done using these segmentation approaches. This technique is used to identify the defective regions. In processing medical computer vision, optical character recognition, and imaging a radiograph for industry, they are thus frequentlyimplemented.[3].Oneofthealgorithmsthat thepopularclusteringalgorithm.Thisarticlediscussion of k means algorithms that have been updated, such as Applying the initial partial stretching improvement to thepicture toincreaseimagequality.Individual cluster is generated the cluster's first centre using and Using subjective clustering, you can create. The means technique is used to segment pictures using the producedcentre[4].ForADdetection,thedeeplearning architecture is recommended in order to solve the limitations of the machine learning algorithm methodology . It can identify both instances of AD and mild cosgnitive impairment. In order to identify the prodromal stage of AD and MCI, it suggests a deep learning architecture that makes use of stacked autoencoder and softmax output layer. This architecture may conduct detection utilising domain specific prior knowledge while examining several training sample classes and less labelled training samples [5]. One of the most fatal diseases is a brain tumour. In the identification procedure, image processingcanbequitehelpful.
2.1 Related works
The state of the art for applying DL and ML algorithms to diagnose dementia and Alzheimer's disease is covered in this section. With the use of the pattern similarity score, the study proposes new metrics for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease. The conditional probabilities predicted by logistic regression are used by the authors to describe the metrics. Furthermore, they investigate the effectiveness of anatomical and cognitive impairment, which is utilised to produce the output of the classifiers from various forms of data. To diagnose Alzheimer's disease, the authors employ online databases of MRI scan pictures and other cognitive parameters, like RAVLT tests, MOCA and FDG scores, etc[6]. In particular, methods for grouping patients with Alzheimer's disease are created based on logistic regression and SVM. A system based on speech processingwasprovidedbyAmmaretal.[7]toidentify dementia. With verbal description and human
transcription of the speech data, the framework was utilised to extract characteristics from people with dementia and those without dementia. In order to train ML classifiers, The speech and textual characteristics were employed. Only 79 percent of the time did the authors get it right. The authors of [8] provided another intriguing piece of work in which they described a detectiontechniquebasedonbrainMRIimagesbasedon Eigenbrain.Intheirmethod,themodel wastrainedusing SVM and particle swarm optimization. In identifying the areas of the brain affected by Alzheimer's disease, their plan produced good results. In a similar vein, writers in [9]usedMRIdatatoidentifydementiaandotherfeatures usinggradientboostandArtificialNeuralNetwork(ANN) models. Based on cognitive and linguistic aspects, the authors [10] presented a hybrid multimodal approach. The model was trained by the authors using ANN to identify Alzheimer's disease and its severity. Currently, deep learning based technology is being used in most cases, which results in improvement of results. The imbalance of classes is the most common problem in these methods. Recently DNNs are replaced by CNNs for better training time, GPU utilisation, and accuracy. Existing models for classifications can be more complex foremployingMRIdatasets.[11]
3. METHODOLOGY
Wehaveproposedthefollowingmethodologytotrainthe model and compared the performance of the trained model using the test dataset. The entire methodology is divided into 2 parts. Part I is the Deep learning based modelwhereasinthesecondpartwehaveusedMachine Learning based models. As ML based models are more efficientand timefortrainingand processing isveryless it is preferable for low end devices. Deep Learning models are bulky but more precise so it is preferable insteadofMLmodels.[12]
Fig 1:Methodology
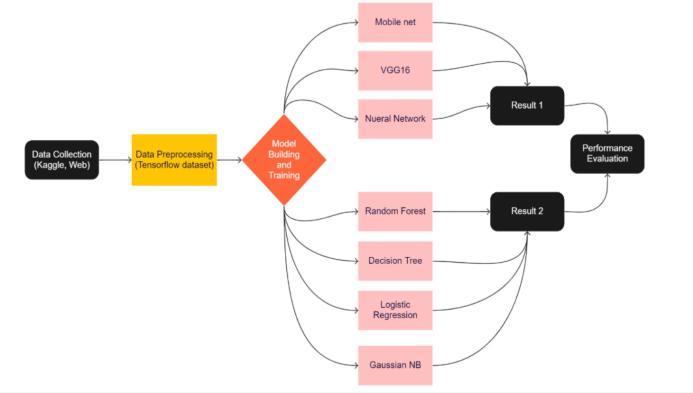
4. DATASET
The data is collected from Kaggle, which is an open source platform for data scientists and machine learning
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

engineers to compete and collaborate to enhance their skills.TheDataishandcollectedfromvariouswebsites witheachandeverylabelverified.Thedatasetisconsist of4filesforeachclass
isnotsousefulincaseoflackofdatasopre trainedCNN modelarchitecturelikeVGG16,andMobileNetisused.
VGG16 One of the famous model architectures which won ILSVR 2013 and outperformed GoogleLeNet[14]. It has achieved remarkable accuracy of 92.7 % on 1000 classimagesof14millioninsize.
The dataset also contains a train set for training and a test setforvalidation.Itcontainsaround5000images.
Fig 2:Imagesfromeachclass.

Tensorflow dataset API: Using the tf.data API, you can create intricate input pipelines from straightforward, reusableparts[13].Thepipelineforanimagemodel,for instance, may combine information from files in a distributed file system, make random alterations to every image, and combine a batch of randomly chosen photos for training. Extracting symbols from raw text input, transforming them to embedding IDs using a lookup table, and batching together sequences of variouslengthsmayallbeincludedinthepipelinefora textmodel.Itispossibleto managesignificantvolumes of data, read from many data formats, and carry out intricate changes thanks to the tf.data API. DeepLearning model is trained using tf.data API with a batchsizeof32images.
5. ALGORITHM USED
5.1 Deep Learning Based Algorithm
Thehumanvisualbrainservedastheinspirationforthe CNNdesignthatweemployedforthisinvestigation.The input stream of information is received by the human eye in its receptive field, which is comparable to how the input is convolved during the convolution procedureandusesitsinputtooperateontheimageto create the feature map. Which inspires the Convolutional operation. A CNN consists of several maximum layers with ReLU activation functions completely linked layers as well as layer pooling. all inputs are gone through various processes to arrive at the finished product in the design of a multi or binary classifier. the morphing operation is shared by several neuronsandconnectedthroughthem. shift invariance, local connectivity, and hyper parameters enhance the network'sstrength.SometimesCNNmodelfromscratch
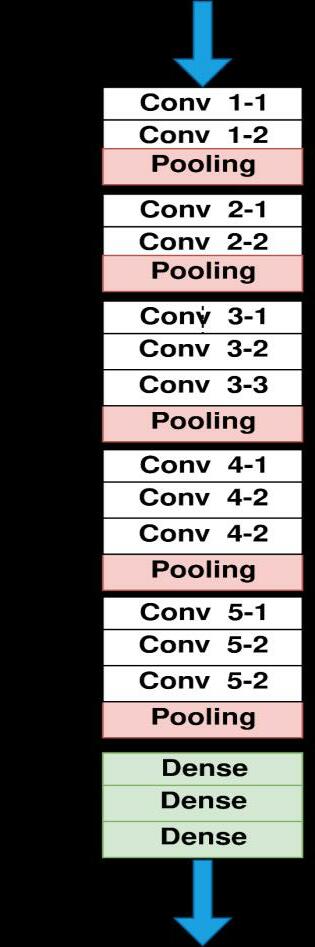
Fig -3: ThearchitectureoftheVGG 16Model
It has two or three convolution layers, then one pooling layer. The same is repeated over 5 6 times and finally, some dense layer has been added. This Dense layer is trainable whereas the convolutions layers are non trainable.Trainabledenselayersareusedasafinetuning layer. The input layer consists of the size of images and theoutput layeris a Softmaxlayer whoseunitis decided basedonthenumberofclasses.
5.1.1 MobileNet
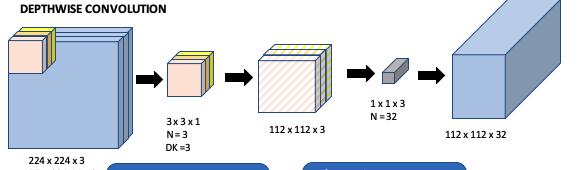
It is a very lightweight computer vision model intended for very low end devices[15]. It uses the method of depthwise separable convolution methodology and significantly reduces the parameters as compared to the normal CNN model but it achieves remarkable performances.
Fig 4:ArchitectureofMobilenet
Fig 5: DepthwiseConvolutionLayer(B)
Depthwise convolution contains less no. of parameters ascomparedtonormalconvolutions.
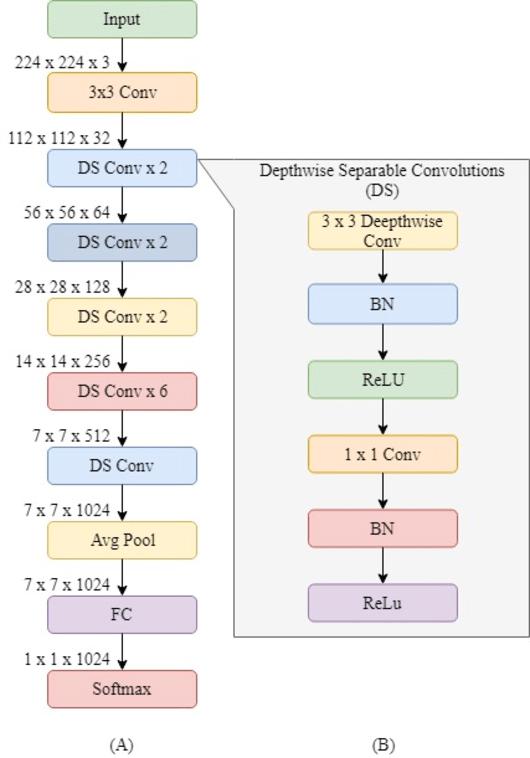
The model is followed by multiple layers of depthwise convolution and a softmax layer at the final output layer.
5.1.2 CNN model
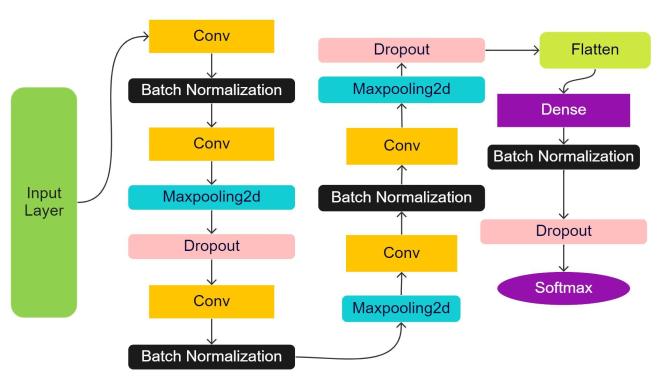
Convolutional neural networksmodel isvery useful for a large dataset [16]. Our proposed CNN consists of convolution layers, Batch Normalization layers, Maxpooling layer, Dropout layers, and a softmax layer whichisusedasOutputaccordingtono.ofclasses.The inputlayerconsistsofthesizeoftheimage.
Fig -6: ProposedarchitectureofNeuralNetworkModel
There is 5 Convolution layers followed by a batchNormalization and a maxpooling layer. After 2 Convolution layers, one dropout layer is used for fasteningthetrainingprocess.Theinput layerconsists of thesizeoftheimagewhichis(176,208,3),Asthedataset consistsof4classes.
LossFunctions:
Thecategoricalcrossentropylossfunction[17]computes thefollowingsumtodeterminethelossofanexample:
Loss= ∑ ̂ ̂
is the goal value that corresponds to the i th scalar valueinthemodeloutput,outputsizeisthetotalnumber ofscalarvaluesinthemodeloutput,andsoon.

How easily two discrete probability distributions may be distinguished from one another is extremely well measuredbythisloss.Inthissituation,thelikelihoodthat eventihappensisdenotedby ̂ ,andthetotalofall ̂ is 1,indicatingthatpreciselyoneeventmighthappen.
The negative sign makes sure that the loss decreases as thedistributionsapproachoneanother.
5.2 Machine Learning Model
5.2.1 Gaussian Naive Bayes
Using the Bayes theorem, the Naive Bayes classification method was created [18]. When applying supervised learning approaches, it is a straightforward but efficient method for predictive modeling. The Naive Bayes approach is simple to grasp. For incomplete or unbalanced datasets, it offers better outcomes. The machine learning classifier NaiveBayes uses the Bayes Theorem.GivenP(C),P(X),andP(X|C),onemayapplythe Bayes theorem to calculate the posterior probability of P(C|X).
P(X|C). Therefore,
P(C|X)=(P(X|C)P(C) /P(X)12]
P(C|X)=posteriorprobabilityoftargetclass
P(X|C)=probabilityofpredictorclass
P(C)=probabilityofclassC(whichisbeingtrue)
P(X)=priorprobabilityofpredictorclass
5.2.2
Decision Tree Classifier:
A classification focused supervised machine learning algorithm is a decision tree classifier. Nodes and internodes are used for classification. Instances are categorizedbyrootnodesaccordingtotheirproperties. Additionally, these nodes represent classification while these leafnodesare made upoftwo or more branches. [19]Usingthemostdataacquiredacrossallcriteria,the decisiontreeselectseachnodeateachlevel.
5.2.3 Logistic Regression
It is a supervised learning method that utilises a predetermined set of independent factors for categorical dependent variables [20]. It explains the relationship between independent and dependent variables and is utilised for predictive analysis. Classifying an input into groups is the outcome of minimising the cost function. The cost function can be writtenas: = ∑ log +(1 )log(1 )]
Where (x)=
5.2.4
Random Forest
During training, random forests (RF) build several distinct decision trees. The average prediction for regressionorthemedianoftheclassesforclassification is created by combining the predictions from all trees[21].Theyarereferredtoasensembleapproaches sincetheycombineresultsintoafinaljudgement.
6. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
6.1 Precision
Precision is the ratio of correctly predicted observations to all expected positive observations in termsofpositiveobservations.
Precision=TP/TP+FP
6.2 Recall
Recallisthepercentageofaccuratelyanticipatedpositive observations to all of the actual class observations. The formulaforthefollowingis TP/TP+FN
6.3 Accuracy
The easiest performance metric to understand is accuracy, which is just the proportion of properly predicted observations to all observations. The formula forthefollowingis
Accuracy=
6.4
F1 Score
The weighted average of Precision and Recall is the F1 Score. Therefore, both false positives and false negatives are included while calculating this score. Although it is true that F1 is often more advantageous than accuracy, especially if you have an uneven class distribution, it is not as intuitively easy to grasp as accuracy. When false positives and false negatives cost about the same, accuracyperformsbest.Ifthereisasignificantdifference in the costs of false positives and false negatives, it is preferabletoincludebothPrecisionandRecall.
F1Score=
7. Evaluation Matrix
Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1Score
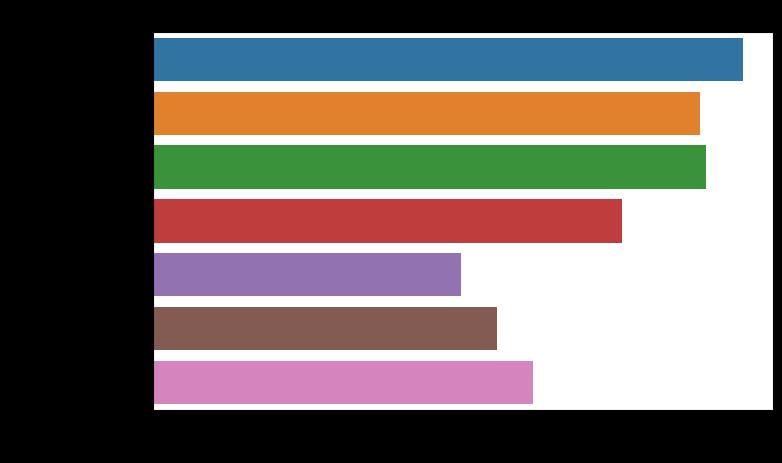
CNN Model 99.47 98.22 99.01 98.61
Mobilenet 92.24 91.11 90.89 90.50
VGG 16 93.24 89.33 87.22 88.32
Logistic Regressio n
79.00 81.00 81.00 81.00
Gaussian NB 52.00 57.00 55.00 55.00
Decision Tree 58.00 67.00 67.01 67.00
Random Forest 64.00 69.00 64.00 59.00
Table 1:Evaluationmatrix
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2723

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

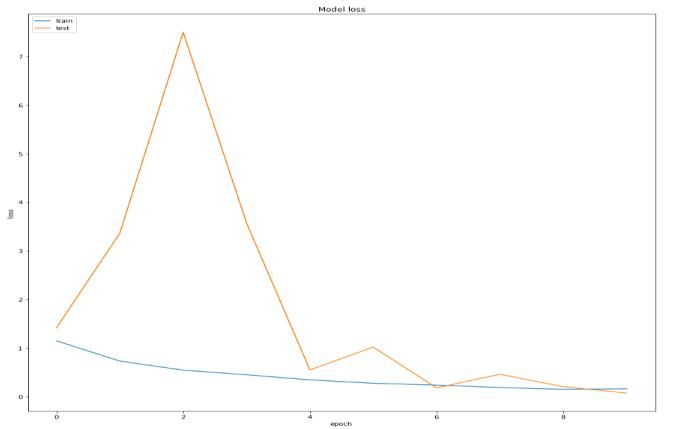
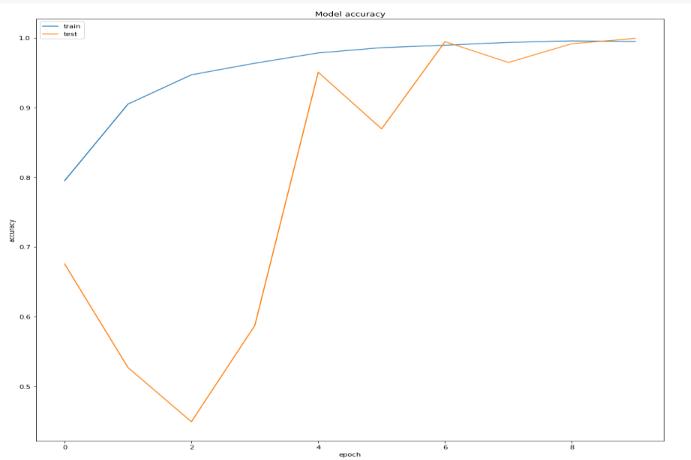
The dataset consists of 4 classes (Mention the four classes). Our proposed model has achieved remarkable accuracyontestdatawhichis99.47%.
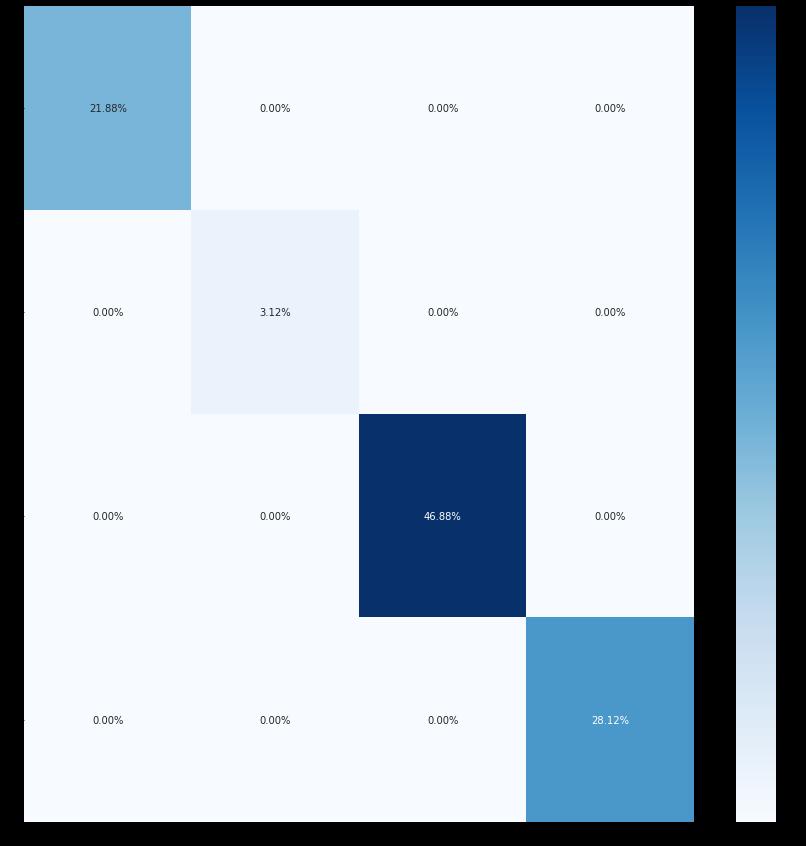
7.1 Confusion Matrix
A confusion matrix of dimension n x n connected to a classifier,wherenis the numberof distinctclasses,the predicted and actual classification are displayed[22]. The elements of a confusion matrix include the percentages of accurate negative forecasts, wrong positivepredictions,incorrectnegativepredictions,and correctpositivepredictionsareasfollows:a,b,c,andd. This matrix may be used to determine the prediction accuracyandclassificationerrorasfollows:
8. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE REFERENCES
Since there is currently no known treatment for Alzheimer's,itismorecrucialtoloweringrisk,giveearly intervention,andpreciselyevaluatesymptoms.Ascanbe seen from the literature review, numerous efforts have
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

been made to identify Alzheimer's Disease using various machine learning algorithms and micro simulation techniques; however, it is still difficult to identify pertinent characteristics that can Kavitha et al. Early Stage Alzheimer's Disease Prediction detect Alzheimer's very early. In order to increase the accuracy of detection approaches, future studies will concentrate on the extraction and analysis of novel featuresthataremorelikelytohelpintheidentification of Alzheimer's disease as well as on the removal of redundant and unnecessary characteristics from currentfeaturessets.
Using more precise data with features of age, gender and previous record of the disease may boost the accuracy to a greater extent in practical real time scenarios. More models can be trained to segment the affectedpartisalsouseful.
REFERENCES
[1] Bhushan I, Kour M, Kour G, et al. Alzheimer’s disease: Causes and treatment A review. Ann Biotechnol.2018;1(1):1002.
[2] S. Padmanaban, K. Thiruvenkadam, P. T., M. Thirumalaiselvi, και R. Kumar, ‘A Role of Medical Imaging Techniques in Human Brain Tumour Treatment’,τ.8,pp.565 568,012020.
[3]A.Hosny,C.Parmar,J.Quackenbush,L.H.Schwartz, και H.J. W.L.Aerts, ‘Artificial intelligence in radiology’, Nat Rev Cancer, τ. 18, τχ. 8, pp. 500 510, Αυγούστου 2018.
[4] C. Kalyani, R. Kama, και G. Reddy, ‘A review on optimised K means and FCM clustering techniques for biomedical image segmentation using level set formulation’, BiomedicalResearch,τ.29,012018.
[5]D.JhaκαιG. R.Kwon,‘Alzheimer’sDiseaseDetection Using Sparse Autoencoder, Scale Conjugate Gradient and Softmax Output Layer with Fine Tuning’, τ. 7, pp. 13 17,022017.
[6] P. Lodha, A. Talele, και K. Degaonkar, ‘Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Machine Learning’, 08 2018, pp.1 4.
[7] R. Ammar και Y. Benayed, ‘Speech Processing for Early Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis: Machine Learning BasedApproach’,102018,pp.1 8.
[8]D.R.SarvamangalaκαιR.V.Kulkarni,‘Convolutional neural networks in medical image understanding: a survey’, EvolutionaryIntelligence, τ. 15, τχ. 1, pp. 1 22, Μαρτίου2022.
[9]R. Rawat, M. Akram, Mithil, και S. Pradeep, Dementia Detection Using Machine Learning by Stacking Models 2020.
[10] K. Dashtipour κ.ά., ‘Detecting Alzheimer’s Disease UsingMachineLearningMethods’,2022,pp.89 100.
[11]Shikalgar,Arifa&Sonavane,Shefali.κ.ά.,HybridDeep Learning Approach for Classifying Alzheimer Disease BasedonMultimodal2020
[12]F.Emmert Streib,Z.Yang,H.Feng,S.Tripathi,καιM. Dehmer, ‘An Introductory Review of Deep Learning for Prediction Models With Big Data’, Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence,τ.3,2020.
[13]D. G. Murray, J. Šimša, A. Klimovic, και I. Indyk, ‘Tf.Data: A Machine Learning Data Processing Framework’, Proc. VLDB Endow., τ. 14, τχ. 12, pp. 2945 2958,Ιουλίου2021.
[14]C. Szegedy κ.ά.,‘Going deeper with convolutions’, 06 2015,pp.1 9.
[15] A. G. Howard et al., “MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications.”2017.
[16] R. Yamashita, M. Nishio, R. K. G. Do, και K. Togashi, ‘Convolutional neural networks: an overview and applicationin radiology’, InsightsintoImaging,τ.9,τχ. 4, pp.611 629,Αυγούστου2018.
[17] Rusiecki, Andrzej. ‘Trimmed categorical cross entropy for deep learning with label noise. Electronics Letters’.55.10.1049/el.2018.7980.2019
[18] Y. Huang και L. Li, ‘Naive Bayes classification algorithm based on small sample set’, στο 2011 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and IntelligenceSystems,2011,pp.34 39.
[19]A.Navada,A.N.Ansari,S.Patil andB.A.Sonkamble, "Overview of use of decision tree algorithms in machine learning," 2011 IEEE Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium, 2011, pp. 37 42, doi: 10.1109/ICSGRC.2011.5991826.
[20] J. J. DeStefano, "Logistic regression and the Boltzmann machine," 1990 IJCNN International Joint ConferenceonNeuralNetworks, 1990, pp. 199 204 vol.3, doi:10.1109/IJCNN.1990.137845.
[21] L. Monno, R. Bellotti, P. Calvini, R. Monge, G. B. Frisoni and M. Pievani, "Hippocampal segmentation by Random Forest classification," 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications, 2011,pp.536 539,doi:10.1109/MeMeA.2011.5966763.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[22] T. C. W. Landgrebe and R. P. W. Duin, "Efficient Multiclass ROC Approximation by Decomposition via Confusion Matrix Perturbation Analysis," in IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 810 822, May 2008, doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70740.
