International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
1Department of Civil Engineering, Civil and Environmental Engineering Faculty, Mersin10, Turkey, Nicosia99138
2Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering and Technology, Abrar University, km6 Hodan district, Mogadishu, Somalia.
3Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering and Technology, Abrar University, km6 Hodan district, Mogadishu, Somalia.
4Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering and Technology, Abrar University, km6 Hodan district, Mogadishu, Somalia.
5Department of Civil Engineering, Mogadishu University, Hodan district, Mogadishu, Somalia ***
Abstract trafficrulesandimplementingroadregulations. Roadtrafficaccidentsarerapidlybecomingadangertopublic health and to regional economic development in many developed countries. Road traffic accidents add to the misery bycausingdeath,sickness,disability,grief,lossofincome,and property damage. In this report, some of the main findings of the analysis were presented in order to evaluate the causes and economic impacts of road accidents in Mogadishu Somalia. The research methodology of this study includes a literaturereview,siteobservations,personalinterviewsaswell as questionnaire surveys, and survey analysis. The sampling method was used, in order to determine the most representativesize ofapopulation.Intheprocessofselecting the sample from the target population, Random sampling technique as a probability sampling was used. Purposive samplingwas usedasnon probabilitysamplingtocategorize the respondents intovarious categories. The studyfoundthat the level of accidents in Mogadishu is very high, while these accidents are causing great loss of lives and destruction of valuable properties. The key factors contributing to road accidents in Mogadishu are night driving, narrow roads, and poor construction and bad planning of roads. Vehicle repair costs as well as medical costs are listed as having the highest economic impact due to road traffic accidents in Mogadishu. In order to eradicate the issue of road traffic accidents in Mogadishu, Somalia, it is recommended that the government improve road conditions and maintain roads in Mogadishu, improveroaddesignssuchasroadsandintersections,improve vehicle designs, establish skilled and well trained drivers, Increase numbers of the traffic police to enforce
Key Words: Road Traffic Accidents, Impact, Economic Costs of Road Traffic Accidents, Mogadishu, Somalia.
Road traffic accidents are considered to be the highest reasonforinjury,death,disabilityandpropertylossesinall nationsoftheworld,especiallyinlow andmiddle income
countries,untilroadtrafficaccidentsbecomeoneofthemost fundamentalcausesofhumanandeconomiclossesinurban communitiesinthepresentsituation(Atubi&Gbadamosi, 2015).
The occurrence of traffic accidents usually causes a significant number of human and financial casualties. The casualties mainly arise from the cost of care and loss of incomeinbothcasesofdeathandpermanent impairment. In2013,theWorldHealthOrganization(WHO)reportedthat almost 1.24 million people worldwide die each year from road traffic accidents. Fatalities are expected to rise to around1.9million peryear in2020 ifadequatemeasures arenottaken.Morethan90%ofthoseglobalfatalitieswill occur in low and middle income countries like Somalia, particularlyMogadishu(Mohamed,2015).
The problem of accidents is not only limited to the occurrenceanddestructionofvaluableproperty,butalsothe most economically active and productive age groups , especiallythosebetweentheagesof15and45years,arethe mostheavilyinvolvedintrafficaccidents,whichimpliesthat accidents present a global challenge to the earning and activepopulation(Atubi&Gbadamosi,2015)Thiswillaffect monetary development, simultaneously with the lack of valuablestaffmembersandcreativeparticipantsfacingthe economicbuilders.Moreover,bodilydisabledpatientswith thelowestearningcapacityareseverelyaffectedastheyare most likely to rely on physical activity (WHO, 1996), and victimstendtostaylongerthanaverageinthehospital.The global fixtures and impacts of road accidents are as follows(AsianDevelopmentBank&ASEAN,2005):
1.Roadcrashesareestimatedtokill1.2millionpeopleand injure20 50millionpeopleperyear(dailyroadtollsofmore than3000,i.e.,nearly140deathsperhour)
2.Death rates ofdeaths in developing countriesare much higher(atleast50timeshigher)thanindevelopedcountries
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

3. About 88 per cent of deaths worldwide occur in developingcountries
4.Itisexpectedtokill2.4millionin2020.
5.Roadtrafficdeathsareexpectedtorisebynearly90%in low andmiddle incomecountriesandtodecreaseby30% inhigh incomecountries.
6.Sustaineddecliningtrendsinroadfatalitiesindeveloped countrieshavebeenattributedtoconcertedeffortsinmany sectors, including effective coordination, community involvement.
Road traffic incidents are multi factorial, grouping can be done into three major human, environmental, and vehicle variables(Daniel,2016).Human,environmental,andvehicle factorswerefoundtohavecausedmorethan92%ofroad trafficaccidentsindevelopingcountries.Although drivers aloneattributeapproximately80%ofroadaccidentsinthe world(Ramisetty Mikler&Almakadma,2016).However,it is defined that the human and environmental factors that affect road traffic accidents are the most common factors, whiletheuseofdrugs,theuseofcellphoneswhiledrivingor crossing roads, the lack of use of seats Chaudhry & Iqbal (2018) describe human risk factors that may lead to road trafficaccidents(Chaudhry&Iqbal).
Humanriskfactorsthatcontributetoroadtrafficaccidents maybedriving factorssuch asdrunken driving, excessive speed,non compliancewithtrafficlaws,imprudentdriving, drivingfatigue,sleepiness,youngeragedriving,inadequate use of helmets, safety belts, medical conditions (sudden illness, myocardial infarction, impaired vision), psychological factors (impulse danger), defects, Psychologicalfactors(riskofimpulse),defectivejudgment, slow decision making, aggression, poor vision, factional familydays,anddiversionwhendrivingoncellphonesare also responsible human factors leading to road traffic accidents(Y.Zhang,Jing,Sun,Fang,&Feng,2019).
Drivers' errorsaccountfor about80%oftheworld’s road incidents. The Traffic Related errors are more common in youngdrivers,whereasroadrage,overconfidence,failureto complywithroadsignals,overtaking,andover speedarethe factors most associated with road accidents (Syed, 2017). The following are the most common errors that drivers makeasaresultofroadtrafficaccidents.
There are several road and environmental factors which causeandcontribute to roadtrafficaccidents worldwide. The environmental risk factors are mostly related to the roads, like the narrow roads, defective roads, defective layoutofcrossroads,poorlighting,poorconstruction,and bad planning of roads. (Shantajit, T., Kumar, C. R., & Zahiruddin,Q.S.2018),Howevertrafficcontroldevicessuch as,signalcondition,streetlightingandweatherconditions are also considered as an environmental factors which
commonlycontributestheroadtrafficaccidents(Y.Zhanget al.,2019),
Thereareapproximately 1.25milliondeathsannuallydueto roadtrafficaccidentsworldwide,whiletherearealso20 50 millioncasesofnon fatalinjuriesannually.Thecycleusers, motorcyclistaswellthepedestriansarethemostvulnerable people of the accidents. The consequences of road traffic accidents cause financial burdens for the victims, their friends,familymembers,employers,insurancecompanies, and the government. It is difficult to measure the exact financial loss of human suffering and sacrifices. The compensationoffinanciallosscanbethepainsufferingfrom accident cost or of the future in the form of reduction in expectancyoflifeandfuturelostincome.Pastlostincomeon medical expenses, vehicle repair, vehicle hire, and travel expensescanalsobeincludedfortotalfinancialloss(Jamroz etal.,2018).
Road traffic accidents are currently deteriorating the financial wealth of many nations. In this regard, (WHO 2004);urgesthat,ineconomicterms,thecostofroadcrash injuriesisestimatedatroughly1%ofGrossNationalProduct (GNP) in low income countries, 1.5% in middle income countries and 2% in high income countries. The direct economiccostsofglobalroadcrasheshavebeenestimated atUS$518 billion,withthe costs inlow incomecountries estimated at US$ 65 billion exceeding the total annual amountreceivedindevelopmentassistance.Inadditionto this, in terms of regional disparities of cost, the main considered Cost items of road traffic accidents could be differedfromonestudytoanother,thecostofroadtraffic accidentsusinghumancapitalapproachcanbecategorized into three major components and they are; human costs, propertydamagescostsandgeneralcrashcosts.HumanCost Fatalitylossofoutput,Disabilitylossofoutput,Injurylossof output(off workcost)Medicalcost,Familyandcommunity losscost,Funeralcost.PropertyDamageCost,Vehiclerepair cost, el time delay cost Police work cost, Insurance and Vehicledetentionperiodcost,on vehiclepropertydamage cost,GeneralCrashCost,(Ghadi,Török,&Tánczos,2018).
Themajorityofthevictimsfromroadtrafficaccidentsare mostly suffer from lack of income, as well as lack of employmentopportunities.Itiscommonlyincludetheeffect inabilitytopursuetohappinessandactivitieslikesportand evenentertainments(Chaudhry&Iqbal,2018).Additionthat thepainsufferingvictimsfromtheroadaccidentshavehuge financial lossesintheform ofreductionoflife expectancy andfuturelostincome(Gorea,2016).Additionallythefamily ofthevictimhasfinancialburden especiallywhenincome lossordecreasebythevictim(s)(Ghadietal.,2018).Indirect lossesduetoroadtrafficvictimsareexist.Whiletheperson sufferingfromPost traumaticstressdisorder(PTSD)havea problem to their works as compare to the other persons withoutPTDS.Joblossesduetolongleavesarealsocommon amonginthevictims(Gorea,2016).Howeversomestudies
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
trytoestimatethesecostbyconductingasurveyaccording totheirexperienceofthematter(Ghadietal.,2018).
ThisstudywasconductedintotoMogadishucity.Thisarea wasselectedpurposelymainlyduetothreereasons.Firstly, in the recent years Mogadishu City has been observed to haveahigherrateoftrafficaccidentsthananyothercityin Somalia.Secondly,business wiseMogadishuistheindustrial and commercial city which means that it attracts large numbers of people from other places in the country and thirdly,theresearcherknowsmoreaboutthecityroads.The following figure:2.1 Mogadishu Map, was shown at intersection of Dabka, roundabout of KM4, intersection of ZoobeandintersectionofHawl wadag.
Thesamplingframewasthepopulationlivingandworking in Mogadishu city, as it is recognized to be used with the samplingtechnique.
This is the overall population. The population lives in Mogadishu,whichhas245,000citizens. AsshowninEq.(1), Slovin's formula was used to select a sample from the targetpopulation (1) n = sample size, N = study population size, e = margin of errors,thatactsasanallowanceforpossibleerrorsthatmay arisefortherespondents,
Theconfidencelevelis93%.
Themarginoferroris7%. =205.
During the analysis, the researcher administered the questionnaires, and under his guidance, the respondents wereexpectedtofillthemout.Thereweretwomajorforms ofquestionnaires:closedandopenendedones.Therationale behindusingclosedendedquestionswastobedirect,brief, andstraight to the point.Aboveall,thismethodwassaidto beresearchefficientinthesensethatitisnotexpensive,is freefrominterviewerbias,andtherespondentswereina positiontoprovideaccurateandclearanswers.
Populationisthegroupofpotentialparticipants,objects,or eventstowhomortowhichresearcherswanttogeneralize theresultsofthestudyderivedfromasampledrawnfrom the population. The target population was drivers, pedestrians,roadaccidentsvictimsinMogadishu,aswellthe business owners and experts. Those categories were selectedforthereasonthatoftheirbeingrichinformation categoriesaccordingtheroadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishu city.
Dataanalysisreferstocalculatingsuremeasuresalongwith searchingforrelationshippatternsthatexistinsomeofthe groups of records. The field gathered data was used. The questionnaires were then entered into excel software for dataanalysisandthenpublishedinMS wordsoftware.As noted earlier, the analysis involved descriptive statistics. Thatinvolvedusingpercentagestopresenttherespondents' distribution.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Data presentation mostly shows the analyzed data by tables and graphs
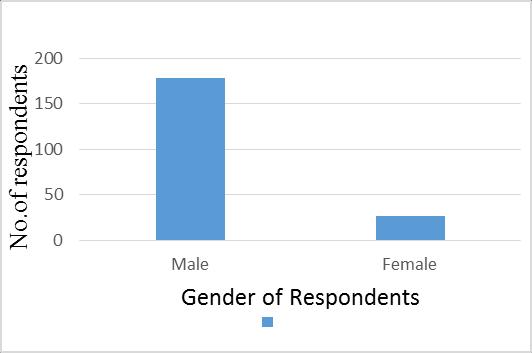
Thepurposeofthispartwastoincludeallgendercategories intherespondents.Accordingtotherespondents,outof205, 178(87%)maleswereinterviewed,while27(13,87%)ofthe totalsamplesizewasfemale.Figure3.1shows thevariation ingenderoftherespondents,inthestudy.
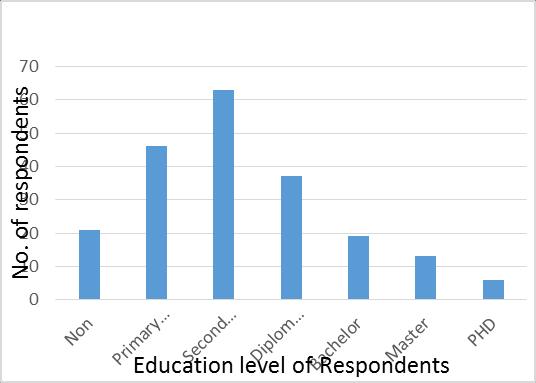
Knowledgeisanimportantfactorfordealingwithdailylife obstaclesand forfindingouttheexactreasonsbehindthe problem,whichcanhelptheresearcher gathermorefactual information about the field. In this study, the research findingsshowedthat 21(10.2%)ofrespondentswereNon meaning that there was no educational history, 41(20%) primary level of respondents, 68(33.1%) majority level of respondents,37(18%)diploma,16(8%)bachelor,13(6.3%) master,9(4.4%)ofrespondentswerePHDholders.Figure 3.3showsthedifferinglevelsofrespondents'education.
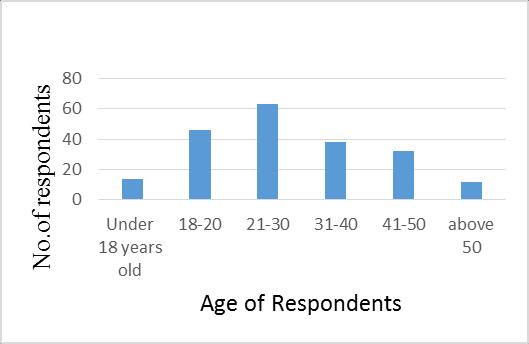
Driver age is one of the main contributing factors to road trafficaccidents,sointhisresearch,thisquestionwasadded totheexamtodeterminetherespondent'sage.Asshownin figure3.2,theageofrespondentsinthisstudywasclassified intosixgroups,betweenages18 20,21 30years,31 40,41 50years,andover50years.Theresearchfindingfromthis surveyshowsthat14(7%)oftherespondentsinthissample wereundertheageof18yearsold.46(22%)respondents were between the ages of 18 20years old. 61(31%) of respondentsaged21to30yearsoldandtheyisthemajority. Itisalsoseenthat38(19%)ofrespondentswerebetween31 and 40 years old, while 32(16%) of respondents were between 41 and 50 years old. However, 12(6%) of the respondentswereover50yearsold.Figure3.2indicatesthe agedifferencesofrespondentsinthisstudy.
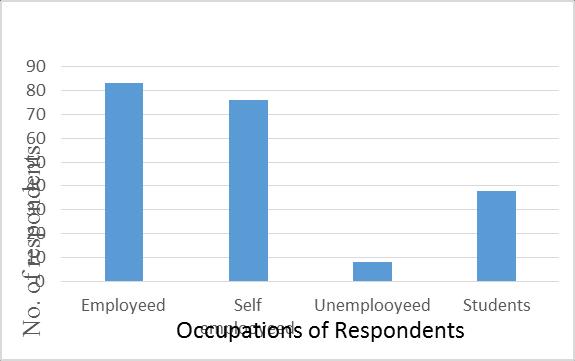
Accidents involve things in the smooth line of work that breakdown.Thiswillleadtoasignificantdownturninthe employmentofworkingpeopleandenterprises.Iaddedthe question to predict the economic consequences of road accidentsinurbanareas.areas.Theresearchfindingsofthe study showed that that 83(40%) of the respondents were employed,76(37%)oftherespondentswereself employed
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

were self employed, 8(4%) of the respondents were unemployed; and 38(19%) of the respondents were students.SFigure3.4showstheoccupationsofrespondents.
hadamonthlyincomeofbetweenUSD100 200,66(32%)of respondents had a monthly income of between USD 300 500. This is the majority, 55(27%) of respondents had a monthly income of between USD 600 800, 15(7%) of respondents had a monthly income of between USD 600 800. Figure 3.6 showed that the monthly income of the respondentsinthisstudy.
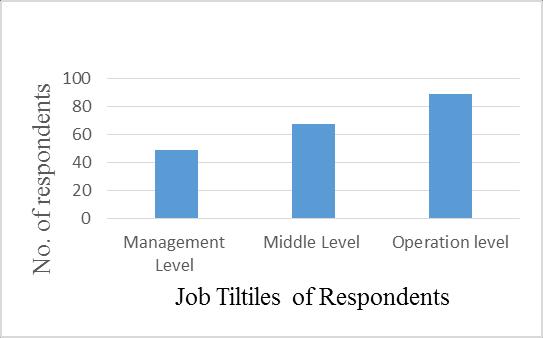
Every time a senior person is involved in an accident, it directlyaffectsthefinancesandlivesofmanypeopleinthe community. So this question was to add the job titles of respondents in the study. Research results indicate that 49(24%)ofrespondentsweremanagementlevel,67(33%) of respondents were middle level, and 89(43%) of respondentswereorganizationallevel,whichisthemajority of respondents. Figure 3.5 shows the job titles of the respondentsinthisstudy.
Theaimofthissectionwastodeterminethelevelandtypes of road traffic accidents in Mogadishu City, the kinds of vehiclesthatare alwaysinvolvedinroadtrafficaccidents, the responsible parties in road traffic accidents in Mogadishu, the periods when the most injuries occur in Mogadishu,aswellastheareasthatalwayshavethehighest incident rate and the major factors that contribute to the roadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishu.
A. The level of road traffic accidents in Mogadishu
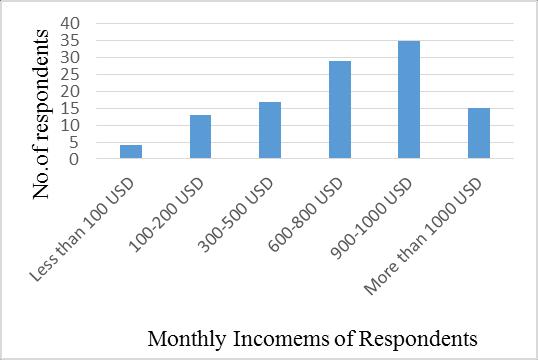
Therespondents'monthlyincomeshouldassessthedegree towhichroadtrafficaccidents'financialcrisisisimpacting thepopulationinthecity.Thequestionwasintroducedto analyzethemonthlyincomeoftherespondentsinthestudy. Research findings of this study showed that 4(2%) of respondentshadlessthanUSD100,43(21%)ofrespondents
ToknowThelevelofaccidentsinthecityshouldallowthe researchers and the relevant agencies in the city of Mogadishutoalertpeopleaboutthepossibilityofaccidents astheyrise.Sothisquestionwasintroducedtoassesstraffic accidentsatalevelinMogadishucity.Theresearchfindings showedthatoutof205,18(9%),oftheserespondentssaid thatthelevelof 57(28%),oftheserespondentssaidthatthe level of accidents is high, and 130(63%) of these respondents said that the level of road traffic accidents is veryhigh. Table 3.1and Figure 3.7showthelevel ofroad trafficaccidentsinMogadishucity.
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2627
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Table 3.1 theLevelofRoadTrafficAccidentsin Mogadishu
No levelofaccidents inMogadishu No. of respondents Percentages
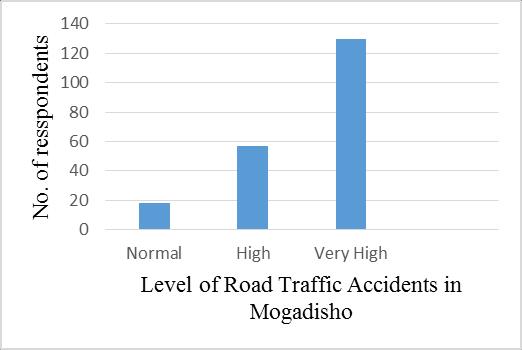
1 Normal 18 9% 2 High 57 28% 3 veryhigh 130 63% 4 Total 205 100%
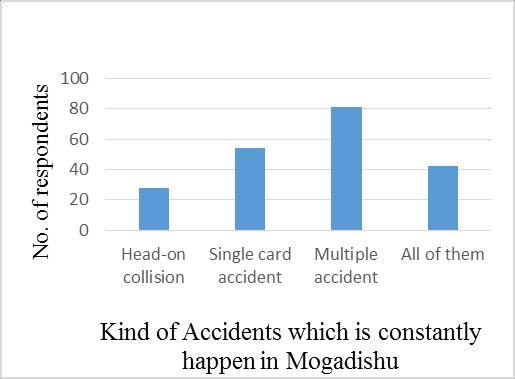
Table 3.2 KindofAccidentswhichisconstantlyhappenin Mogadishu
No kindofaccident. No. of respondents Percentages
1 1.Head on collision 28 14%
2 2.Single card accident 54 26%
3 3.Multiple accident 81 40%
4 4.Allofthem 42 20%
5 Total 205 100%
Figure 3.7 theLevelofRoadTrafficAccidentsin Mogadishu
Knowingthekindsofroadtrafficaccidentsthatalwaysoccur inthecitywouldprovidethegovernmentwithasolutionto thisproblem.Andthisquestionhasbeenaskedinorderto figureoutwhatkindofroadtrafficaccidents alwayshappen in Mogadishu. Research findings showed that out of 205, 18(9percent)oftheserespondentssaidtheroadaccident levelisnormal,57(28percent)ofthoserespondentssaidthe accidentlevelishigh,and130(63%)ofthoserespondents said the road accident level is very high. Table 3. 2 and Figure3.8belowshowthatthekindofRoadtrafficaccidents alwayshappeninMogadishucity.
C. Type of vehicle which is usually involved in road traffic accidents
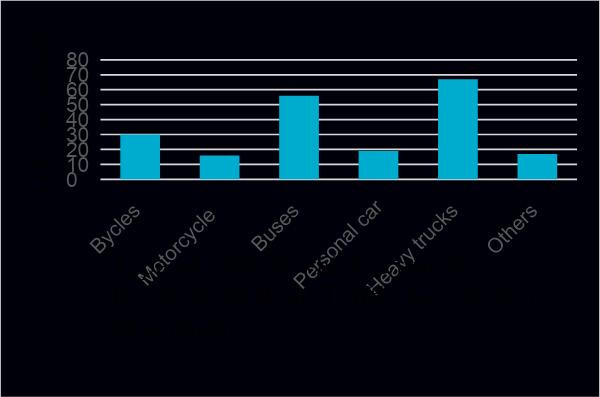
Ifthetypeofvehiclethatusuallycausescrashesisaccepted, itwillhelpthegovernmentcopewiththetypeinaspecific mannertoshielditfromthepopulation.Thisquestionwas addedtoevaluatethetypeofvehiclethatisusuallyinvolved inaccidentsinMogadishu.Researchfindingsfoundthatout of205,24(12%)ofthoserespondentssaidthatthetypeof vehicle that often causes injuries is a bicycle, 16(8%) of those respondents said that the type of vehicle is a motorcycle, 56(27%) of those respondents said that The type of vehicle that is always involved is a truck, and the remainderismadeupof19(9%)ofthoserespondents.Table 3.3andFigure3.9indicatethetypeofvehiclethatisalways involvedinroadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishu.

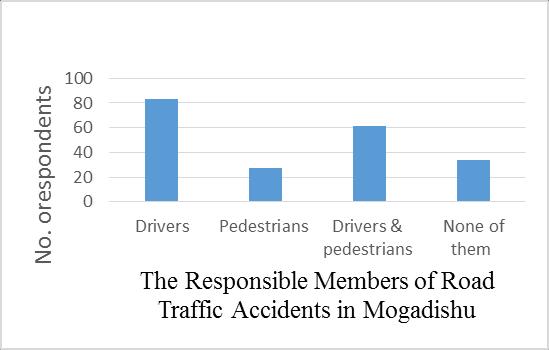
Recognizing the responsible members of road traffic accidents in the city will help the government to pay Pay special attention to these members. This question was introduced to evaluate the responsible members of road trafficaccidentsinMogadishu.Theresearchfindingsshowed thatoutof205,83(40%)oftheserespondentssaidthatthey said that the drivers are responsible for the road traffic accidentsinMogadishu.Thatisthemajority,27(13%),said that the pedestrians are responsible for the road traffic accidents in Mogadishu. In Somalia, 61(30%) of these respondents said that the drivers and pedestrians are responsible for the road traffic. Table 3.4 and Figure 3.10 showedthattheresponsiblepartiesinroadtrafficaccidents inMogadishu.
No The responsible members for road trafficaccidentsin Mogadishu
of respondents percentages 1 Drivers 83 40% 2 Pedestrians 27 13% 3 Drivers & pedestrians 61 30% 4 Noneofthem 34 17% 5 Total 205 100%
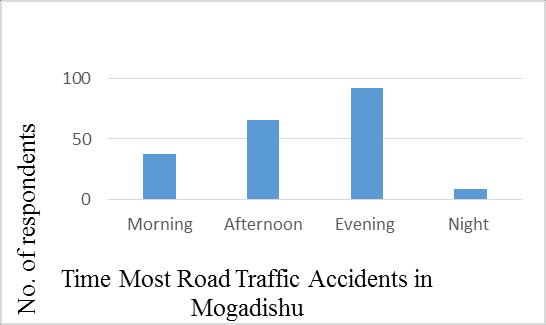
It'scrucialtoknowtheperiodwhenmosttrafficaccidents occurinthecityandwillgiveaccidentinformationtoboth roadusersandthepolice.Thisquestionwasaddedtolearn themomentthemostaccidentshappeninMogadishuCity. Research findings showed that out of 205, 38(19 %t), of those respondents said that the time that most accidents occur in Mogadishu is the morning, 66(32% of those respondents said that it is the afternoon, and that is the majority, 9(4%) of those respondents said that it is the evening.Table3.5andfigure3.11indicatethatthetimethat mostaccidentsoccurinMogadishucity.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Table 3.5 Time MostRoadAccidentsHappenin Mogadishu
No Time of accidents No. of respondents Percentages
1 Morning 38 19% 2 Afternoon 66 32% 3 Evening 92 45% 4 Night 9 4% 5 Total 205 100%
No The day that most accidentstakeplace
No. of respondents Percentages
1 Monday 11 5% 2 Tuesday 16 8% 3 Wednesday 36 18% 4 Thursday 49 24% 5 Friday 16 8% 6 Saturday 54 26% 7 Sunday 23 11% 8 Total 205 100%
F. The day on which most accidents take place in Mogadishu
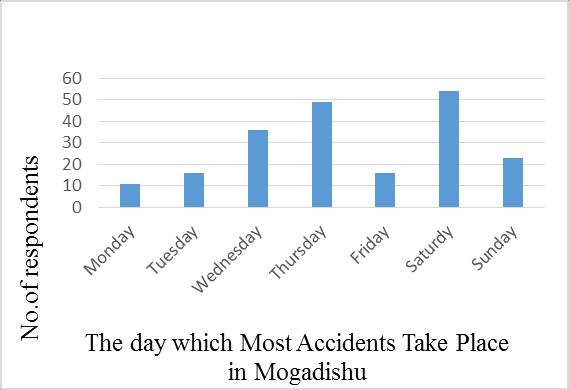
It's crucial to know the day of the week that most traffic accidents occur in the city and knowing this will give accidentinformationtobothroadusersandthepolice.This questionwasaddedtolearnthedayoftheweekthatmost accidentshappeninMogadishuCity.Theresearchfindings showedthat,outof205,11(5oftheserespondentssaidthat thedayofthe weekonwhichmostaccidentstakeplaceis Monday, 16(8%) of these respondents said it is Tuesday, 36(18%) of these respondents said that it is Wednesday, 49(24%) of these respondents said that it is Thursday, 16(8%)oftheserespondentssaidthatitisFriday,54(26%) oftheserespondentssaidthatitisSaturday. Table3.6and Figure 3.12 show that the day of the week that most accidentstakeplaceinMogadishucity.
G. The locations in Mogadishu where road accidents occur are high
Understanding the areas where the majority of traffic incidentsoccurinMogadishuwillmakethegovernmenttake extraresponsibilityforthoseareas.
And send more police to minimize accident risk. In the research questionnaire, this question was instructed to identify the locations where most injuries occur in Mogadishu.AccordingtotheResearchfindings,outof205, 31(15.1%) ofthese respondentssaidthatDabka &Taleex junctionsarelocationswhereroadtrafficaccidentsarehigh based on their experience, 39(19%) of these respondents said Dabka & Zoobe junctions are locations where road trafficaccidentsarehighbasedontheirexperience,15(7.3) of these respondents said Dabka & Zoobe junctions are locationswhereroadtrafficaccidentsarehighbasedontheir
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
experience, 33(16.1%), said K4 roundabout and Taleex intersections are the locations where the accisdebnts are high,45(22%) oftherespondentssaidDabka,Taleexand Zoobejunctionare the most common placeswhere traffic accidentsarehigh,17(8.3%),oftherespondentssaidHawl wadag and Zoobe junction are the places where accidents arehigh,whileonly4(2%),oftherespondentssaidBlackSea andBar Ubaharetheplaceswhereroadaccidentsarehigh based on their experience. The following Table 3.7 and Figure 3.13 show the locations in Mogadishu where road accidentsoccurfrequently
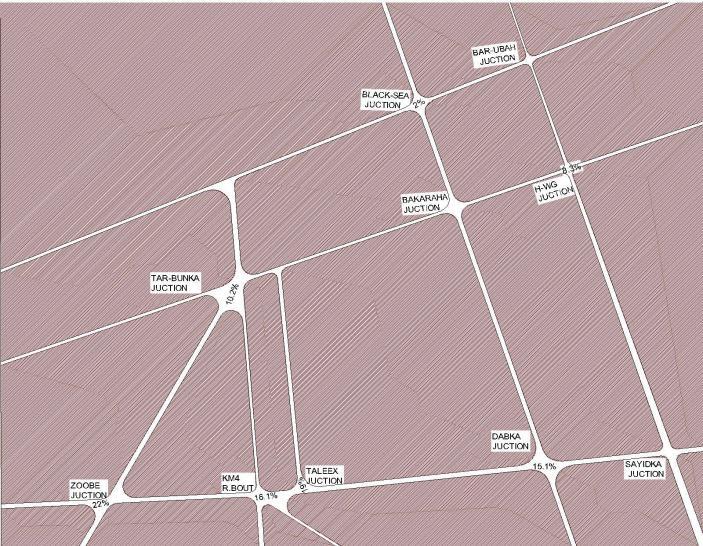
Table 3.7 LocationsinMogadishuwheretheRoad AccidentsoccurhighlyinMogadishu
No Location The number of respondents
Percentages
1 Dabka and Taleexjuctions 31 15.1%
2 Taleex & Zoobe juntions 39 19%
3 Dabka & Zoobe Juctions 15 7.3%
4 Km4 ronad bout &Taleexjuction 33 16.1%
5 Dabka, Taleex & ZobeJuctionsions 45 22%
6 Hawl Wadagand Zoobejuctions 17 8.3% 7 Tar Buunka,Taleex juctions
Figure 3.13: Locations in Mogadishu where road accidents occur frequently (GoogleMapofMogadishu).
H. The major contributory factors to road accidents in Mogadishu Somalia
Definingthemajorfactorsthatcontributetotheroadtraffic accidents in Mogadishu City can be of great benefit in determininghowtominimizethisproblemaswellasbeing extra vigilant in these circumstances, particularly where major factors are found in these areas. This may play a significantpartineliminatingseriousinjuriesfromaccidents aswellastheirimpactsoneconomicgrowth.Thistopicwas introducedtoanalyzethethoughtsoftherespondentsabout themajorfactorsthatcontributetotheroadtrafficaccidents inMogadishucity.
4 2%
21 10.2% 8 Blacksea,Taleex & Bar Ubax juctions
Total 205 100%
ThefigurebelowwastakenfromGooglemapofMogadishu. ToshowtheintersectionsinMogadishuCityandtherateof accidents at each intersection in Mogadishu City, in particulartheintersectionsshownintable3.7above.
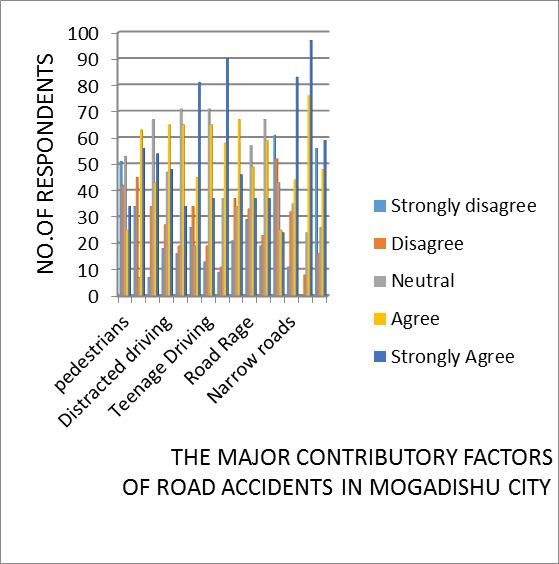
InTable3.8and Figure3.14.Wehavesurveydata on five point scale from strongly disagree to strongly disagree, neutral to strongly agree. in 14 different variables in this datasample.Inordertomeasuretheweightofeachelement inthetablesatisfactionsurveydatatablefunctionmethodto find out how many people responded to each of these categories.TheseCriteriaarealsousedtodeterminewhich factorhasthehighestpriorityandwhichonehastheleast priority.
Accordingtotheresearchfindings,theresultsshowedthe following:
I strongly disagree.
Accedingtothestronglydisagreetheresultindicatedthat pedestrians factor have 25% of strongly disagree. Over speedingfactorhas17%ofstronglydisagree.Drunkdriving factorhas3%ofstronglydisagree.Distracteddrivingfactor has9%ofstronglydisagree.Recklessdrivingfactorhas8% ofstronglydisagree.Nightdrivingfactorhas13%ofstrongly disagree.TeenageDrivingfactorhas6%ofstronglydisagree. Jumbling red Traffic lights factor has 4% of strongly
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2631
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
disagree. Overtaking & Wrong Driving factor has10% of strongly disagree. Road Rage factor has14% of strongly disagree.Lackofmarkingsignalsfactorhas9%ofstrongly disagree. Huge number of vehicles factor has 30% of stronglydisagree.Narrowroadsfactorhas 5%ofstrongly disagree Poorconstruction&badplanningofroadsfactor has 0%of stronglydisagree.All ofthem factor has27% of stronglydisagree.
Acceding to the Disagree the result indicated that Pedestriansfactorhave20%disagree.Over speedingfactor has22% disagree. Drunk driving factor has17% disagree. Distracteddrivingfactorhas13%disagree.Recklessdriving factor has 9% disagree. Night driving factor has 17% disagree.TeenageDrivingfactorhas9%disagree.Jumbling red Traffic lights factor has 5% disagree. Overtaking & Wrong Driving factor has18% disagree. Road Rage factor has16% disagree. Lack of marking signals factor has 11% disagree.Hugenumberofvehiclesfactorhas25%disagree. Narrowroadsfactorhas16%disagree Poorconstruction& bad planning of roads factor has 4% disagree. All of them factor8%disagree.
According to the Neutral, the result indicated that the pedestrianfactorhasa26%Neutral.Over speedingfactor has 3% Neural. Drunk driving factor has 33% Neural. Distracteddrivingfactorhas23%Neural.Recklessdriving factorhas35%Neural.Nightdrivingfactorhas9%Neural. TeenageDrivingfactorhas35%Neural.JumblingredTraffic lightsfactorhas18%Neural.Overtaking&WrongDriving factorhas17% Neural.RoadRage factorhas28%Neural. Lackofmarkingsignalsfactorhas33%Neural.Hugenumber ofvehiclesfactorhas21%Neural.Narrowroadsfactorhas 17%Neural. Poor construction & bad planning of roads factorhas12%Neural.Allofthemfactor13%Neural.
Acceptingtheagreement,theresultindicatedthat Pedestrian’sfactorhas12%agree.Over speedingfactorhas 31%agree.Drunkdrivingfactorhas21%agree.Distracted driving factor has 32% agree. Reckless driving factor has32%agree.Nightdrivingfactorhas22%agree. Teenage driversagreewith32%. JumblingredTrafficlightsfactor has28%agree. Overtaking&WrongDrivingfactorhas33% agree. Road Rage factor has24% agree. Lack of marking signalsfactorhas29%agree.Hugenumberofvehiclesfactor has12%agree. Narrowroadsfactorhas 21%agree Poor construction&badplanningofroadsfactorhas37%agree Allofthemagreewith23%.
I strongly agree.
Acceptingtheresult,theresultindicatedthatthepedestrian factor has 17% strongly agreed. Over speeding factor has 27%stronglyagree.Drunkdrivingfactorhas26%strongly agree. Distracted driving factor has 23% strongly agree. Recklessdrivingfactorhas17%stronglyagree.Nightdriving factorhas40%stronglyagree.TeenageDrivingfactorhas 18% strongly agree. Jumbling red Traffic lights factor has 44%stronglyagree.Overtaking&WrongDrivingfactorhas 22% strongly agree. Rage factor has 18% strongly agree. Lackofmarkingsignalsfactorhas18%stronglyagree.Huge numberofvehiclesfactorhas12%stronglyagree.Narrow roads factor has 40% strongly agree. Poor construction & badplanningofroadsfactorhas47%stronglyagree.Allof themfactorhas29%stronglyagree.
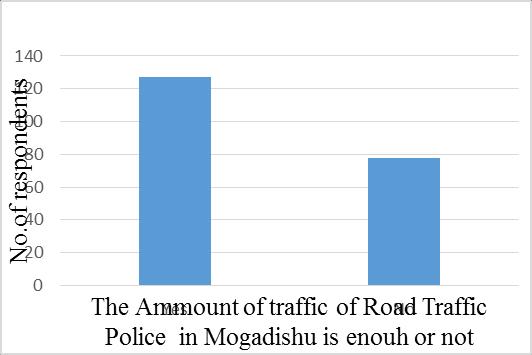
The fewer traffic police on the city's roads could possibly improve the rising number of accidents. The respondents wereaskedwhethertherewereenoughtrafficpoliceonthe city'sroads.Accordingtotheresearchfindingsshowedthat outofthese205, 127(62%),oftheserespondentssaidthat thereisenoughamountoftrafficpoliceinMogadishuroads andthatisthemajority,while78(38%)oftheserespondents saidthere isNo enoughtrafficpolice In Mogadishu, roads Figure3.15belowindicatedthatiftheamountofpoliceon thecityroadsisenoughornot.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
K. Difficulties which the traffic police department faces when enforcing road safety programs in Mogadishu City.
J. The Developmentsin the Police Department H ave Been Made in Relation to Road Traffic Accidents in Mogadishu
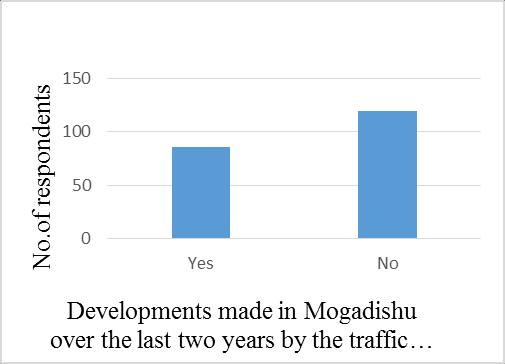
This question was added to assess developments made in Mogadishu over the last two years by the traffic police department.Theresearchfindingsshowedthat86(42%)of theserespondentsoutof205said"Yes," whichmeanspolice made tangible developments towards traffic accidents in Mogadishucity,while119(58%)ofthoserespondentssaid "No," which means police did not make any tangible developments towards road accidents in Mogadishu, Somalia.Figure4.16belowshowsthatifanydevelopments weremadebythetrafficpolicetoimplementtheroadsafety programs.
Departmentsoftrafficcontrolmayhavesomedifficultiesin dealing with the implementing the traffic safety related programs.Thisquestionwasintroducedinordertoassess thedifficultiesfacedbythetrafficpoliceinimplementingthe safetyprograms.Researchfindingsshowedthatoutof205, 26(13%) of those respondents stated that lack of traffic familiaritywiththefollowingrulesandrelegations,47(23%) statedthatindisciplineonroadsandviolationoftrafficrules, 39(19%)statedthatthelayoutofcityroads,48(23%)stated thatlackofwell trainedpoliceofferedtoenforcelows,and 28(14%) stated that lalows, and lack of provision traffic signs. 17 (8%) said that I don’t know. Table 3.9 below illustrates what the traffic police department faces when enforcingroadsafetymeasuresinthecityofMogadishu
Table 3.8 DifficultieswhichtheTrafficPolice Departmentfaceswhenenforcingroadsafetyprogramsin Mogadishucity.
No Respondent’sOpinion Responden tNumber Percenta ge
Figure 3.16 DevelopmentsmadeinMogadishuoverthe lasttwoyearsbythetrafficpolicedepartment.
1 Lack of familiarity with trafficwiththefollowing rulesandrelegations
26 13% 2 IndisciplineontheRoads and Violation of Traffic Rules
47 23% 3 The layout of the city's roads 39 19% 4 The lack of well trained policeofficerstoenforce thelaws
48 23% 5 Lack of provision for trafficsigns 28 14% 6 Idon’tknow 17 8%
Total 205 100%
ResearchresultsfromFigure3.7revealedthatabout63%of respondentsagreedthatthelevelofroadtrafficaccidentsin Mogadishu is very high. Several crashes are the most frequent form of road accident, happening mainly in Mogadishu,asseeninfigure4.8.Heavytrucksarethemain typesofcars,mostofwhichhaveroadcrashesinMogadishu,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

asseeninfigure3.9.Approximately40%oftherespondents in the survey also accepted that the drivers are the most liableparticipantsinroadtrafficincidentsinMogadishu,as shown in Figure 3.10. Research results from this analysis alsorevealedthatapproximately44%ofthoserespondents agreedthattheeveningwasthemostcommonaccidenttime in Mogadishu, as shown in Figure 3.11. Thursday and Saturday,asseeninfigure3.12,arethetwodaysonwhich themajorityoftheaccidentsoccurinMogadishu.Asshown in figure 3.13, Dabka, Taleex, and Zoobe junction are the places where most road traffic accidents take place. as shown in figure 3.14. Pedestrians, over speeding, Drunk driving,Distracteddriving,Recklessdriving,NightDriving TeenageDriving,Overtaking &Wrong Driving,RoadRage, Hugenumberofvehicles,Narrowroads,Poorconstruction& Badplanning ofroadsarethemostcontributoryfactorsof roadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishucity.
The result shows that road traffic accidents have more detrimental consequences on the life of the population causesthewidespread economicdecline,inparticularthe resultshowedtheroadtrafficaccidentscausealotoflossof time and money.The result showed that almost 41% of people wounded as a result of road traffic accidents in Mogadishu took at least 2 3 months following road traffic injuries to return to their place of work. This reflects the stress of the crash as well as the injuries suffered by the injured,whichistakingtoomuchtimetogetbacktotheir placesofwork.Theresultsshowedthatmostofthevictims donotreceivesalariesorhelpfromthegovernmentorthe company they work for during their absence from work, whichcanhaveasignificanteconomicimpactonvictimsin additiontotheirinjuries.Theresearchalsorevealedthatthe majority of victims did not seek compensation or support fromthegovernmentandtheorganizationwithwhichthey work during their absence from work and, in addition to their injury, may have a substantial economic effect on victims.Theresultshowedthat approximately30%ofthe victimsrequired600 800USDtorepairtheirvehiclesafter thecrash,whileapproximately13%ofthevictimsrequired morethan1000USDinordertorepairtheirvehicles,which isanexcessive amountofmoneythatcanbeneededafteran accident.Theresultshowedthatapproximately26%ofthe victimsrequired600 800USDtorepairtheirvehiclesafter the accidents, while approximately 13% of the victims requiredmorethan1000USDtorepairtheirvehicles,which makes excessive the amount of money that should be expectedaftertheaccidents.Nonetheless,theresultshowed that 34% of the population residing in Mogadishu acknowledged that the effects of road traffic accidents on economic growth are very high, while the majority of the people living in Mogadishu spend most of their money on medicalcosts,vehiclerepaircosts,police&administration costs,lossofproductivepopulation,lossofmanpowerHours
Finally,theresultrevealedthatapproximately81.0%ofthe populationlivinginMogadishuhavenoinsurancecoverfor legal expenses, which makes them more vulnerable to accidents,especiallyontheeconomicside.
According to the qualified drivers factor, the research findingsshowedthatstronglydisagree17%,disagree19%, andneutral2%,agree22%,andstronglyagree20%,which representsthisfactorhasthelowestdegreeofstrongagree, which gives less priority to eliminating road accidents in MogadishuCitycomparedtotheotherfactorsinthesame table.Accordingly,thedrivingfactorregulationsshouldbe strictly applied. Research findings show that factor is stronglydisagreedwithat12%,disagreedwithat12%,and neutral at 2%, agreeing with 22%, and strongly agreeing with27%,whichmeansthisfactorhasthehigher gradeof strongly agreeing with the previous factor, which gives it greater importance than the previous factor. Research findingsshowthatthisfactorhasanincreasing numberof trafficpolicemen.Researchfindingsshowthatthisfactorhas astrongdisagree17%,adisagree17%,apositive22%,an agree 16 %, and a strongly agree 28 %, which means this factor has the higher grade of strongly agree with the previousfactor,whichgivesmoreimportancethantotake comparedtotheotherThetwopreviousfactorsAccordingto thefactorofimprovingroadconditionandmaintenance,the research findings show that this factor strongly disagreed with3%,disagreedwith7%, neutrallyagreedwith25%, andstronglyagreedwith47%,whichreflectsthatthisfactor has a high degree of strong agreement and less degree of strongdisagreementwiththepreviousfactor,whichmakes thisfactorstronglydisagreewiththepreviousfactor,which makes this factor have more priority to take in order to eliminate the road traffic accidents in Mogadishu city. According to the factor of all of them, the findings of the researchshowedthatthefactorhadStronglyDisagree0%, Disagree 4 % and Neutral 11 %, 34 %, and 51% strongly agreed.Thisfactorhasthehighestgradeofstronglyagreed and no one selected strongly disagreed, which means this factor has the most time to take in order to eliminate the roadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishucity.
Based on the findings of the research, it is found that the accidentlevelinMogadishuisveryhigh,seefigure3.7.While the accidents cause great loss of life and other socio economic properties to be destroyed. For multi vehicle collision accidents that usually occur in Mogadishu See figure 3.8. Heavy trucks are the vehicle category most frequently included due to road traffic accidents on Mogadishu roads, see Figure 3.9. Dabka, Taleex, and Zobe junctions are places where road traffic accidents are
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2634
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
common in Mogadishu. Because they are located in the centerofthecity,thelargestnumberofvehiclesinthecity pass through these junctions, which makes the level of accidents higher than any other junction in the city. The governmentisthereforeexpectedtopaycarefulattentionto these junctions. Based on the research findings, 39.5% of theserespondents stronglyagreedthatnightdrivingisone ofthemainfactorscontributingtoroadtrafficaccidentsin Mogadishu. 40.5% of these strongly agreed that narrow roadsaresafer,while47%,whichisthemajority,strongly agreedthatpoorconstructionandbadplanningofroadsare one of the main factors which contribute to road traffic accidents in Mogadishu. See Figure 3. 14. Based on the researchresults,thestudyshowedthatoverthe lastyear, approximately 70 % of people living in Mogadishu were involvedinroadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishu.84%ofthose involvedinroadtrafficcollisions,take offtimefromwork. Around41.1% oftherespondentswerebetweenoneand twomonthsoffwork.Nevertheless,90%ofthosewhoquit their jobs did not receive any government assistance or worked for companies. However 90% who take off their worksdidnotanysupportfromeithergovernmentortheir workedforcompanies.93%ofthosewhodidnotreceiveany pay from either the government or their employers will continuetolosepaymentuntiltheyreturntotheirjobs.This showshowthesituationofaccidentsistroublingandhow thevictimscannotgetanysupportaftertheaccidentexcept from their families and friends, and this will increase the negativesocio economicimpactsofroadtrafficaccidentson humanlivesinMogadishu.Onceaskingtherespondentshow the harm caused by the accidents affects the economic growthinMogadishu,about50%ofthoserespondentssaid thatroadtrafficaccidentshaveveryhigheffectsasaresultof Mogadishu's economic growth and that is the majority, whichindicatesthattheaccidentsareverychallengingfor Mogadishu's economic growth Although any associated roadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishuhavetheirownspecial effectsandrequirebothcostandtime, thelossofvaluable property,damagedvehiclerepaircosts,aswellasmedical costshavethehighesteconomicimpactduetoroadtraffic accidents in Mogadishu . On the other hand, the cost of repairing vehicles and damage to property is limited to victims,whilethegovernmentdoesnotprovideanysupport to those people who have suffered from road traffic accidents.However,81%ofpeoplelivinginMogadishuhave nolegalexpenseinsurancecover,whichmakespeoplevery vulnerabletoroadtrafficaccidents,as roadtrafficaccidents result in significant economic losses. Since the victims cannotseekanyfinancialassistancefromthegovernmentor theinsuranceindustrytorecoverthedamagecausedbythe accident, Based on the research findings to eliminate the problemof roadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishu,Somalia,itis recommended to the government to improve the road conditionsandmaintaintheroadsinMogadishu,toimprove road designs such as road bouts and intersections, to improvevehicledesigns,togetqualifiedandwell trained drivers,toincreasethenumberoftraffic policetoenforce
thetrafficlaws,andtostrictlyapplythetrafficregulations while implementingalltheseabovepointscansignificantly reduceoreliminatetheroadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishu.
Road traffic accidents in several developing countries are increasinglybecomingathreattopublichealthandnational progress.Roadaccidentscontributingtosufferingbycausing death,injury,disability,sorrow,lossofincomeandmaterial damage. Based on the results of the research in Chapter 4(Result&Discussion),theresultsshowedthat:
✔ TheleveloftrafficaccidentsinMogadishuisvery high, and these accidents result in human lives being lost andvaluablesocio economicresourcesbeingdestroyed.
✔ Multiple accidents are the most common type of accident that always occurs in Mogadishu, whereas heavy trucks are the most common cause of road accidents in Mogadishu.
✔ Teleex &ZoobeJunctionsarethelocationswhere mostaccidentshappeninMogadishu.While the economic impactofincidentsinMogadishuisextremelyhigh.
✔ Lack of familiarity with traffic laws; disobedience to the traffic rules, lack of investment according to the trafficpolicedepartmentarethedifficultiesthatthetraffic departmentisfacingwhenimplementingthetrafficsafety programs.
✔ 70%oftherespondentsselectedwereinvolvedin roadtrafficaccidentsinMogadishuoverthelastyear.
✔ Asa resultoftrafficcollisionsinMogadishu,84% of these respondents took time off from their place of workinMogadishu.
✔ 90%ofthesewhoweretakingofftimeofworkas aresultoftrafficaccidentsdidnotgetdidnotreceiveany paymentintheperiodofabsencefromthework
✔ 93% of these who were not receive the payment will continue their loss of payment in period of absence fromthework
✔ 55% of those respondents who were involved in roadaccidentscauseddamagetotheirvehiclesasaresult ofroadaccidentsinMogadishu.
✔ Yet 81% of Mogadishu residents don't have legal expense compensation cover to help them cope with accidents, leaving them very vulnerable to the impacts of theincidents.
✔ ThemajorityoftrafficaccidentsinMogadishuare not related to the number of vehicles. The main culprit is
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

traffic. Accidents in Mogadishu are due to poor driving behavior.
✔ Lack of traffic management due to poorly trained trafficpolice
✔ Lackofroadtrafficsigns
✔ Poorly maintained vehicles break down in the streets.
✔ Overloadedtrucksoverturn orbreak downinthe street.
Atubi,A.O.,&Gbadamosi,K(2015).GlobalPositioningand Socio EconomicImpactofRoadTrafficAccidentsinNigeria : Matters Arising. American International Journal of Contemporary Research, 5(5),136 146.
Mohamed,H.A.(2015).EstimationofSocio EconomicCost of Road Accidents in Saudi Arabia: Willingness To Pay Approach (WTP). Advances in Management & Applied Economics, 5(3), 19. Retrieved from http://www.scienpress.com/Upload/AMAE/Vol5_3_5.pdf
Asian Development Bank, A., & ASEAN. (2005). the cost of road traffic accidents in Malaysia.
Daniel,O.C.(2016). Exploringthemajorcausesofroadtraffic accidents in Nairobi County
Ramisetty Mikler,S.,&Almakadma,A.(2016).Attitudesand behaviorstowardsriskydrivingamongadolescentsinSaudi Arabia. International Journal of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, 3(2), 55 63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpam.2016.03.003
Chaudhry, K., & Iqbal, M. J. (2018). The Economic Cost of Road Traffic Accidents in Twin Cities, Pakistan. European Scientific Journal, ESJ, 14(25), 142. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2018.v14n25p142
Zhang,Y.,Jing,L.,Sun,C.,Fang,J.,&Feng,Y.(2019).Human factors related to major road traffic accidents in China. Traffic Injury Prevention, 20(8), 796 800. https://doi.org/10.1080/15389588.2019.1670817
Syed,K.B.(2017).MaxillofacialInjuriesDuetoRoadTraffic Accidents in Saudi Arabia: A Review of Incidence, Demographic Factors, and Prevention Strategies. International Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences, 6(1), 1386. https://doi.org/10.19056/ijmdsjssmes/2017/v6i1/125560
Shantajit,T.,Kumar,C.R.,&Zahiruddin,Q.S.(2018).Road TrafficAccidentsinIndia:anOverview. InternationalJournal
of Clinical and Biomedical Research, 4(4), 36 38. https://doi.org/10.31878/ijcbr.2018.44.08
Jamroz, K., Romanowska, A., & Budzyński, M. (2018). An analysis of the impact of socio economic development on road safety is based on the example of Baltic Sea Region countries. 18th RS5C Conference, 1(12),1 12
Ghadi, M., Török, Á, & Tánczos, K. (2018). Study of the economic cost of road accidents in Jordan. Periodica Polytechnica Transportation Engineering, 46(3), 129 134. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPtr.10392
Gorea, D. R. K. (2016). Financial impact of road traffic accidents on the society. International Journal of Ethics, Trauma & Victimology, 2(1). https://doi.org/10.18099/ijetv.v2i1.11129
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2636