A WEB BASED APPLICATION FOR RESUME PARSER USING NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES
1Assistant Professor, Computer Science & Engineering, Bangalore Institute of Technology, Karnataka, India 2,3,4,5 B.E Student, Computer Science & Engineering, Bangalore Institute of Technology, Karnataka, India ***

Abstract - Resume is a powerful tool in a job search which outlines one’s knowledge, skills, experience, expertise and accomplishments. An excellent resume attracts potential companies. It is very hard to find the right talent for a particular job. In order to make recruiters job easy, we have proposed a model which extracts details like education, projects, experience, phone no., email ID etc. and ranks the resumes based on company’s specifications using Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques. We have built a job portal where employees and applicants can upload resumes for a particular job, the required information will be parsed, structured resumes will be generated and the resumes of the employees will be ranked based on the company's skill set and employees skills mentioned in the resume.
Key Words: Parsing, Ranking, Natural Language Processing, K Nearest Neighbor, Vectorization, Cosine Similarity
1.INTRODUCTION
Earlier recruiters used to spend most of their time in manuallyscreeningresumes.Inthisprocess,organizations wouldloseouton qualitycandidatesandrecruiterswaste their time and effort. To avoid this, recruiters use automated Resume Parsing Systems in order to cut down onmonotonoustasksandmakerecruitmenteasy.Resume Parsing System, lets recruiters find highly qualified candidates for a certain position. We have designed a modelinwhichaparserwillextractcertainkeywordslike education,skills,experience,name,phoneno.,emailIDetc. from the resume that is fed to it and ranks it accordingly for making the job of HR manager easier to select candidatesforrecruitmentprocess.
Asetofresumesfromemployeesin.pdfformatistakenas input and the employer gets a list of candidates that has been rankedaccordingtoparserandclassifier.Applicants receivemailregardingstatusidentifiedwiththeirresumes.
In this proposed methodology, we are using Natural Language Processing technique for parsing the resume according to the particular companies. We use Named Entityrecognizer(NER)whichlabelsthedataaccordingto the type of their attribute and displays the text with the label.OneoftheplatformsofNERisspaCy,anopensource
named entity visualizer that is used for information extraction.KNNalgorithmisusedforclassification.
2. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
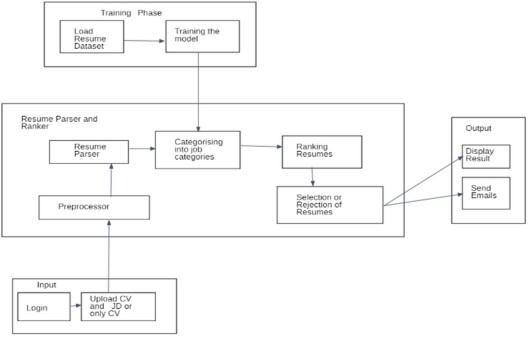
Fig 1: Architectureoftheproposedsystem
● Trainingmodule:Loadingdatasetisapartofthe training phase where we load our dataset to the model to test its accuracy. Trainingofthemodel isthe next partof this phase where we trainthe modelagainstthegivendataset.
● Input: The candidate and recruiter upload the resumesintherequiredformat.
● Processing: Each resume is parsed and the resumesarerankedaccordingtotheircategory.
● Output: The resumes along with their ranks are displayed and an option to send an email is given.
2.1 MODULE DESCRIPTION
● Login: In this component job seekers should register with our application and then they can login. Also in this component the recruiter can registerorlogintoourapplication.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
● InputJobAvailabilityandResumeUploader:The candidates upload their resume in pdf format. The recruiters can upload single or multiple resumes and can add the vacancy details and requiredskills.
● Resume Preprocessor: In this component, we remove any unnecessary information from resumes like stop words, hashtags, and specialcharacters.
● Resume Parser: We are extracting the resume contents like name, email, education, skills, etc usingthespacyparserfunction.
● Loadingthedataset:Inthiscomponentweloadthe labeled dataset into the system for testing against theuntraineddata.
● Building KNN classifier: In this component we use sklearn class to train a model to predict the suitable job title for their skills which is extracted fromtheseekersresume.
● Categorizing into jobs categories: Uses the trained model from the previous component to categorize eachresumeintocorrespondingjobcategory.
● Resume Ranker: In this component system will compare the cosine similarity between the job seekersskillsandrecruiter’srequirementskills for the corresponding job using NLP. Based on the similarityscoreresumesareranked.
● Resume selection and rejection: Depending on the number of vacancies the resumes will get selected orrejected.
● Resultsaredisplayed:Thelistofrankedresumesis displayedtotherecruiter.
● Emails are sent: Status emails regarding selection orrejectionoftheirapplicationaresent.
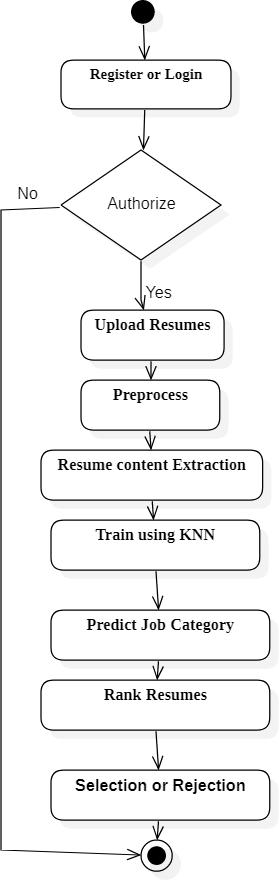
The user registers or login to the system and uploads the resume.The system preprocesses , categorizes and ranks the resume and displays the output. The stepsperformed bythesystemareexplainedinthefurther sections.
Fig 2: Activitydiagramoftheresumeranker application
3.1 PREPROCESSING
The natural language expressed in the resumes are not suitableforapplicationofanymachinelearningorNatural language processing techniques. Hence the primary purpose of this preprocessing step is data cleaning. We have used spacy, an open source natural language processing library to perform preprocessing of the resumes.
Thefirststepinpreprocessingissentencedetection.Each sentence is identified and isolated. The next step in preprocessing is tokenization. Tokenization is extracting the words and reducing them into their basic form. Example: extracting “organization” and reducing it into “organize”. The reduced form of the word is called as a token.
In the next step, the punctuations and stop words are removed. Stop words are frequently used words that do
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
not increase the meaning of the sentence but make the sentence grammatically legible. Examples of stop words are:are,to,for,is,asetc.
In the next step, each token is reduced to a lemma. Lemma is the shortest form of a word that makes complete sense. It is the simplest form of the word that hasameaning.Exampleofreducingatokentoalemmais reducing“was”to“be”.
Patternmatchingisthenextstepinpreprocessing.Itisa natural language processing technique that matches phrase and tokens with a text corpus. Regular expressions are used to perform this task. Example of pattern matching is : for matching phone number the followingregularexpression is used: (r'[\+\(]?[1-9][0-9 .\-\(\)]{8,}[0-9]').Similarlytheskillsandrequireddetails areextractedfromtheresume.
3.2 TRAINING USING KNN ALGORITHM
K nearest neighbors is a lazy learner algorithm. The symboliccharacteristicfeatureofalazylearneralgorithm is that it is trained during test time. KNN is a supervised learningalgorithm.Theinputtothelearningisalabelset ofinput. Wehave used the KNN algorithm toclassifythe resumesintosuitablejobcategories.Oncethecategoryis defined for each of the resumes, the resumes can be ranked.
In the KNN algorithm implementation, the Euclidean distanceiscalculatedbetweentheinstance,whichhasto beclassified,andeachoftheinstanceinthetrainingsetis calculated. “k” is a predefined integer that is considered to identify the classification of the instance. Once the distances are computed, the “k” shortest distances are considered for computing the output of the instance. “k” is usually an odd integer to avoid conflicts. The label in majorityofthe“k”labelsisassignedtotheinstanceasthe output.
Epoch is the number of times the instance is input to the training algorithm. Higher epoch results in output with highaccuracy.Wehavedefinedtheepochtobe20and the “k”valuetobe5.
3.3 VECTORIZATION AND COSINE SIMILARITY
Vectorizationisjargonforaclassicapproachofconverting acomputerfilefromitsrawformat(i.e.text)intovectors of real numbers which is the format that ML models support. This approach has been there ever since computerswerefirstbuilt,it'sworkedwonderfullyacross various domains, and it’s now utilized in NLP. In Machine Learning,vectorizationmaybeastepinfeatureextraction. The thought is to induce some distinct features out of the
text for the model to coach on, by converting text to numerical vectors. There are many ways to perform vectorization,aswe’ll seeshortly.Wearegoing tosee the one that's utilized in this particular project more closely which is TF-IDF. TF-IDF or Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequency, may be a numerical statistic that’s intendedtoreflecthowimportantawordistoadocument. In Bag of Words, the vectorization is simply concerned withthefrequencyof vocabularywords inan exceedingly given document. As a result, articles, prepositions, and conjunctions whichdon'tcontributemuch tothe meaning getthemaximumamountofimportanceas,say,adjectives. TF-IDFhelpsustobeatthisissue.Wordsthatgetrepeated too often don’t overpower less frequent but important words.Ithastwoparts:
i)TF
TFstandsforTermFrequency.Soonecanimaginethatthis number will always stay ≤ 1, thus we now judge how frequentawordiswithinthecontextofallofthewordsin adocument.Wecalculatethisusingthefollowingformula: ii)IDF
It stands for Inverse Document Frequency, but before we get into IDF, we must be aware of DF Document Frequency.DF tellsus aboutthe proportionof documents thatcontain a particular word.IDF isthe reciprocal of the Document Frequency. The intuition behind it's that the more common a word is across all documents, the lesser itsimportanceisforthisdocument.Alogarithmistakento dampen the effect of IDF within the final calculation. We usethefollowingformulatocalculateDF:
WeusethefollowingformulatocalculateIDF:
This can be how TF-IDF manages to include the importance of a word. The higher the score, the more importantthatwordis.Despitebeingsosimple,TF-IDFis understood to be extensively utilized in tasks like InformationRetrievaltogaugewhichresponseisthebest for a question , especially useful during a chatbot or in Keyword Extraction to work out which word is the most relevantinadocument.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Cosinesimilaritymaybeametricaccustomedtomeasure how similar the documents are no matter their size. Mathematically, it measures the cosine of the angle between two vectors projected in a very multidimensional space. The cosine similarity is advantageous because whether or not the 2 similar documentsarefarapartbytheEuclideandistance(dueto thedimensionsofthedocument),likelihoodisthatthey'll still be oriented closer together. The smaller the angle, higherthecosinesimilarity.Itdoesthisbycalculatingthe similarityscorebetweenthevectors,whichisfinishedby finding the angles between them. The range of similarities is between 0 and 1. If the worth of the similarity score between two vectors is 1, it means there'sagreatersimilaritybetweenthe2vectors.
On the opposite hand, if the worth of the similarity score between two vectors is 0, it means there's no similarity between the 2 vectors. When the similarity score is one, theanglebetweentwovectorsis0andwhenthesimilarity score is 0, the angle between two vectors is 90 degrees. Cosine Similarity is one in all the methods to seek out similaritiesbetweenthe2documents.
3.4 RESULTS
Fig -3: Jobcategorydistributionpiechart
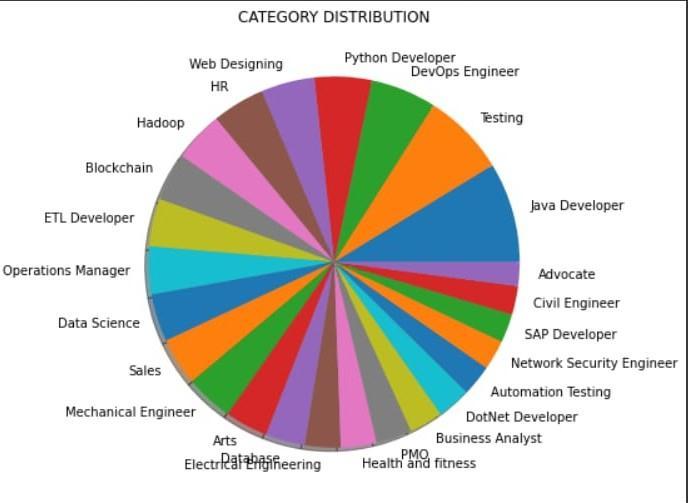
WearetrainingthemodelusingKNNclassificationmodel. We calculate the accuracy by dividing the amount of correct predictions by the entire number of samples. Amongthe24classesavailablewecalculatetheprecision, recall, f1 score and support to know whether the training set is being classified properly. Precision is defined because the ratio of correctly classified positive samples (TruePositive)toacompletenumberofclassifiedpositive samples.Therecalliscalculatedbecausetheratiobetween the numbers of Positive samples correctly classified as Positivetothefull number ofPositivesamples. Support is
the total entries of every class within the actual dataset. The ultimate accuracy recorded at the top of the report is 0.99.
4. CONCLUSIONS
Our approach is to make the work of companies and candidates easier and effective. The aim of the proposed model is to ease the recruitment process. The process ensures to provide quality applicants to the companies. Unfair and discriminatory practises will be dampened. Resumes are ranked on the basis of information provided in the form of technical skills. However, the proposed modelhasafewlimitations.Thisprocessrequiresresumes to be in a particular format. The recruiter can add the requirementsofonlyonejobcategoryatatimeafter which a list of ranked resumes for the set of resumes that were uploaded can be viewed. If there is missing data within a resume, the respective candidate is not notified and the resumegetsrejected.
REFERENCES
[1]. Ayishathahira and Sreejith, “Combination of neural networks and conditional random fields for efficient resume parsing”, International CET ConferenceonControl, CommunicationandComputing(IC4),2018.
[2]. Dr.Parkavi A,Pooja Pandey,Poornima J,Vaibhavi G S,Kaveri BW, “E Recruitment system through resume parsing, psychometric test and social media analysis”, IJARBEST,2019.
[3]. Papiya Das, Manjusha Pandey, Siddharth Swarup Rautaray, “A CV parser model using entity extraction processandbigdatatools”,IJITCS,2018.
4]. Nirali Bhaliya, Jay Gandhi, Dheeraj Kumar Singh, “NLP basedextractionofrelevantresumeusingmachinelearning ”, IJITEE,2020.
[5].Fahad,SKAhammad,andAbdulsamadEbrahimYahya, “Inflectional review of deep learning on natural language processing”, International Conference on Smart ComputingandElectronicEnterprise(ICSCEE),2018.
[6]. Shicheng Zu and Xiulai Wang, “Resume information extractionwithanoveltextblocksegmentationalgorithm”, International Journal on Natural Language Computing (IJNLC)Vol.8,No.5,October2019.
[7]. Y. Deng, H. Lei, X. Li and Y. Lin, “An improved deep neural network model for job matching”, International ConferenceonArtificialIntelligenceandBigData(ICAIBD) 2018.
[8]. S. Sawleshwarkar, N.Rangnani, V. Mariwalla and A.Halbe, “Simplified recruitment model using Text Mining on psychometric and aptitude test”, Second International ConferenceonElectronics, Communication andAerospace Technology(ICECA)2018.
[9]. H. Suen and H. Chen, “Screening passive job seekers on facebook”, International Cognitive Cities Conference (IC3)2018.
[10]. Mujtaba, Dena F., and Nihar R. Mahapatra, “Ethical considerations in AI based recruitment”, IEEE International Symposium on Technology and Society (ISTAS)2019.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2607

