International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
***
Abstract Irregularities in building during seismic suffer much higher than the regular shape building in high seismic zones. Indian standard code IS1893(Part 1) provided various guidelines to improve their performance during seismic activity and minimize their post earth quake damages. One such major irregularities is Re Entrant corners building. To study the behaviour of such building with re entrant corners and remedial mechanism to be applied so that it can perform better during seismic activity. This study will focus on the performance of such building with and without in plane horizontal bracing provided at re entrant conners.
Key Words: Planirregularity,Re EntrantCorners,InPlane horizontalbracings,dynamicseismic.
Irregularitiesinbuildingconfigurationleadstouncertainties in behaviour during transient loading condition such as seismicactivities.Irregularitiesleadstoabruptchangesin strength or stiffness of structural element which leads to poorbehaviourofoverallstructure.Pastseismicactivities haveprovedthatbuildingwithirregularitiessuffersevere damages than the regular configured building. To understandtheirbehaviourandtominimizetheeffectofre entrantcorners,asperIS1893(Part 1)“abuildingissaidto have re entrant corner in any plan direction, when its structural configuration in plan has a projection of size graterthan15percentofitsoverallplandimensioninthat direction”hencethisstudyhasfocusedonintroducing “in plane horizontal bracing” at corners and studied the differentparametersduringdynamicseismic.Forthestudya sixstoreyedbuilding(A/L=25%)hasbeenconsidered,one withoutanyinplanecornersbracingandotheronewithin plane corner bracing at every floor level, Parameters considered during modelling are such as seismic zone V, Importance factor 1.0, Response Reduction factor 5, Soil type Medium, Structure type Special Moment Resisting Framebuilding.
VaishnaviVishnuBattul1,MithunSawant2,TejashriGulve3 , Rohit Deshmukh4, studied “Seismic Effect on Re entrant CornerColumns”andtheyhaveobservedfromabovestudy
thatforre entrantcornercolumnsneedmoreattentionthan the other columns. These columns should be designed properly. After proper modifications the bending moment capacity of re entrant corner column is increased by 1.5 times.
NikhilDixit1,AbhishekJhanjhot2 studiedthe“Analysisand Design of Irregular Building with Re entrant Corner using PushoverAnalysis”.Theyconcludedthatthestorydriftsofa framedstructurewiththeshearwallasastiffelementatthe re entrantcornerislessthanstructureswithoutashearwall inbothzones.Thestorydisplacementoffourstructureswith and without a shear wall in both the zone indicate the displacementindirectionwithloadconditioni.e.,x direction forPXislessforstiffelement(shearwallatthere entrant corner).
GaneshGawande1,Dr.S.B.Borghate2,studiedthe“Seismic Performance of Re Entrant Corner Building Under the Different Earthquake Direction”, from the analysis result showsitisconcludedthatre entrantplanirregularbuilding is more vulnerable towards seismic impact compared to regularbuildingintermsoftopfloordisplacements. Result showsthatre entrantcornerplanirregularbuildingshows anincreaseupto42%inconsideredjointdisplacement.But incaseofnonlineardynamicanalysistheincidentanglethat produces increase up to 38 % in terms on relative displacements.
A.S.Dhanyashree1,R.Akash2,M.Ashok3,S.R.Premsai4,B.N. Bhavyashree5 “Studied the Effect of Re entrant Corner RC FramedBuildingunderSeismicLoad”andstrengtheningitby BracingtheyconcludedthatBuildingswithhigherpercentage ofre entrantcorneraresusceptibletomoreseismicdamages particularlyinhighseismiczones.Buildingwithre entrant corner shows more displacement at the notches than the regularbuilding.Structurestrengthenedbybracingatthere entrantcornershowedbetterperformancethanthebuilding withoutbracing.
Shreyasvi CB1,Shivakumaraswamy2 studied the “Seismic ResponseofBuildingswithRe EntrantCornersinDifferent SeismicZone”andtheyconcludedthatThecolumnslocated nearthere entrantcornersexperiencemoreseismicloads ascomparedtootherinteriorcolumns.Hence,theyrequire higher ductile detailing when compared to other columns. Buildingmodelwithhigherpercentageofre entrantcorner undergo larger joint displacement. Re entrant buildings
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
undergo larger displacements and drifts when compared with regular buildings. The modal time periods obtained fromresponsespectrumanalysisimplicatesthattheregular buildings have longer time periods than re entrant buildings. Asre entrantbuildingshavelessertimeperiods, they are more susceptible to ground motions and the probability of undergoing damage due to high frequency groundmotionsishigh.
Tarak Banerjee1, Arya Banerjee2 studied “A Study on OptimizingthePositioningofShearWallsforaPlusShaped IrregularBuilding”andtheyconcludedthatskilfullychoosing the positions of shear walls can make a difference in the performanceofstructures.Storeydisplacementsarefound lowformodel2,withshearwallsatthecoreandedges,as well as this structure exhibits extremely high values of stiffnessandlowflexibility.Itisperformedbetterinstorey drift showing almost equal drifts for all floors. Model 1 exhibits high flexibility in comparison with the other two models,showshighervaluesofperiods.Model2,whereshear wallsareplacedatthecoreandalongedges,performsbetter. The model with shear walls at edges and at re entrant corners showing lower values for torsional moments. Torsionalmomentsreduceconsiderablybyprovidingshear wallsatre entrantcorners.
Bethany Marie Brown, studied “Lateral Loads on Re entrantCornerStructures“heconcludedthathelengthofthe legsofastructurehasadirectcorrelationtothemagnitudeof the axial forces in the struts in the re entrantcorner. The longerthelegis perpendiculartothestrut,thehigherthe axialforcewillbeinthestrut. Thisisduetothediaphragm being idealized as a simple beam. The axial forces in the interiorandexteriorchordsfollowthetrendofthebending momentdiagramasthelengthofthevariablelegincreases. Sinceitwasfoundthatthevariablelegactsmoresimilarlyto aproppedcantileverthanasimplysupportedbeam,theaxial forcesintheinteriorandexteriorchordsfollowthetrendof the bending moment diagram for a propped cantilever insteadofasimplysupportedbeamasinitiallyassumed.
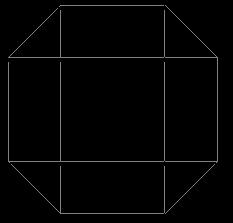
Two 9.0m x9.0m building has been taken for the Staad analysis with 2.250m projection al around the building in symmetricalmanner,onewithoutcornerbracingsandother one with corner bracings with the following seismic parameters, zone V, Importance factor 1.0, Response Reduction factor 5, Soil type Medium, Structure type SpecialMomentResistingFramebuilding.
Fig 1:Buildingwithoutcornerbracings(Plan)
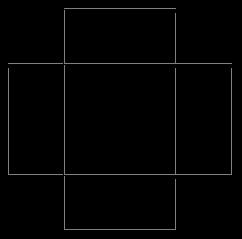
Fig 2:Buildingwithcornerbracings(Plan)
Fig 3:WithoutBracings Fig 4:WithBracings
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
RESPONSE OF STRUCTURE WITHOUT IN PLANE BRACING
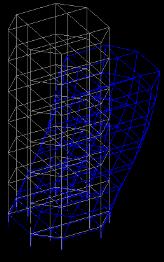
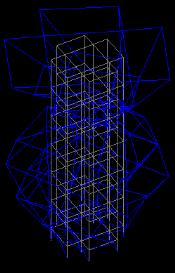
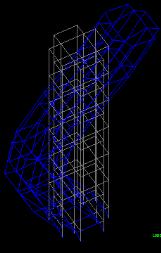
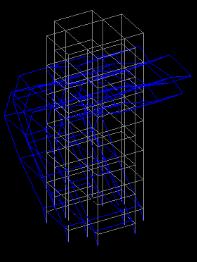
Fromthebelowdataithasfoundthatthestructurewithout the in plane horizontal 90% mass participate in mode 13 whileinstructurewithinplanehorizontalbracing90%mass participateinmode9alsomassparticipationincreasewith usingbracingintherangeof10%.Henceitperformsbetter duringseismicactivity.
Table 1: MassParticipationwithoutcornerbracings
Mode X Y Z Summ X Summ Y Summ Z
1 0 0 75.72 0 0 75.724
2 75.72 0 0 75.724 0 75.724 3 0 0 0 75.724 0 75.724 4 0 0 10.51 75.724 0 86.237 5 10.51 0 0 86.237 0 86.237 6 0 0 0 86.237 0 86.237 7 0 0 0 86.237 0 86.237 8 0 0 3.69 86.237 0 89.928 9 3.69 0 0 89.928 0 89.928 10 0 0 0 89.928 0 89.928 11 0 0 0 89.928 0 89.928 12 0 0 0 89.928 0 89.928 13 0 0 1.81 89.928 0 91.736
Table -2: MassParticipationwithcornerbracings
Mode X Y Z Summ X Summ Y Summ Z
1 0 0 76.0 5 0 0 76.053
2 76.05 0 0 76.053 0 76.053 3 0 0 0 76.053 0 76.053 4 0.01 0 10.6 76.059 0 86.654 5 10.6 0 0.01 86.66 0 86.66 6 0 0 0 86.66 0 86.66 7 0 0 0 86.66 0 86.66 8 0.04 0 3.5 86.704 0 90.164 9 3.5 0 0.04 90.208 0 90.208 10 0 0 0 90.208 0 90.208 11 0 0 0 90.208 0 90.208 12 0 0 0 90.208 0 90.208 13 1.47 0 0.23 91.681 0 90.435
MODE-1 MODE-2 MODE-3
MODE-4 MODE-5 MODE-6
Fig 4:DynamicResponseofsixmodes
RESPONSE OF STRUCTURE WITH IN PLANE BRACING
MODE-1 MODE-2 MODE-3
MODE-4 MODE-5 MODE-6
Fig 5:DynamicResponseofsixmodes
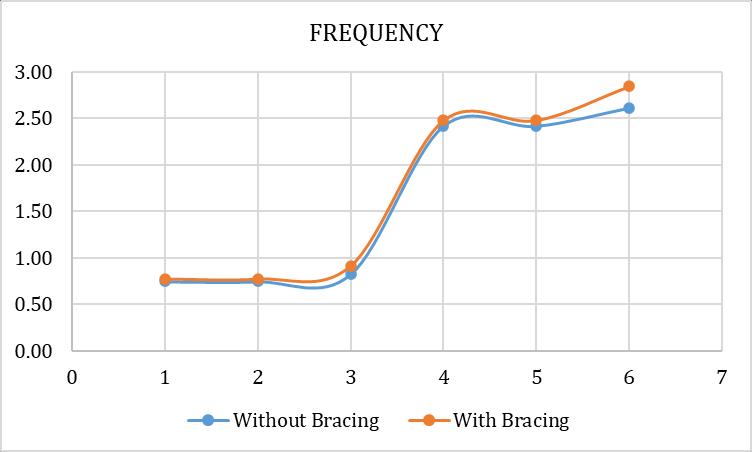
2.2 FREQUENCY
Fromthebelowdataithasfoundthatthefrequencyofthe structurewiththein planehorizontalbracingincreaseinthe range of 10%. Hence it performs better during seismic activity
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Table 3: Frequencywithoutcornerbracings
Mode Frequency (Cycles/Sec) Period(Sec)
1 0.75 1.34 2 0.75 1.34 3 0.82 1.21 4 2.42 0.41 5 2.42 0.41 6 2.62 0.38
Table 4: Frequencywithcornerbracings
Mode Frequency (Cycles/Sec) Period(Sec) 1 0.77 1.30 2 0.77 1.30 3 0.91 1.10 4 2.48 0.40 5 2.48 0.40 6 2.85 0.35
Table 6: Floordisplacementwithbracings
Floor Displacement(cm)
X Z
1 0.1629 0.0003 2 1.3567 0.0006 3 2.7674 0.0004 4 4.0742 0.0004 5 5.1745 0.0004 6 6.0079 0.0003 7 6.5509 0.0009
Fig 7:Frequencywith&withoutbracings
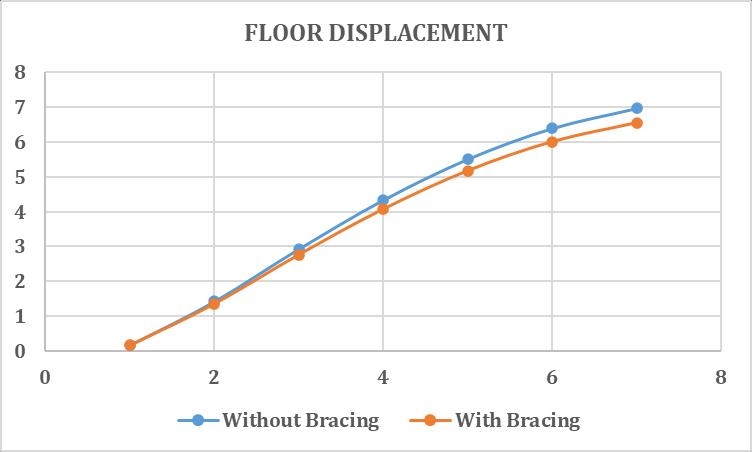
2.3 FLOOR DISPLACEMENT
Fromthebelowdataithasfoundthatthefloordisplacement ofthestructurewiththein planehorizontalbracingdecrease intherangeof10%becauseitprovidedmorelateralstiffness inthedirectionofseismicforces.Henceitperformsbetter duringseismicactivity.
Table 5: Floordisplacementwithoutbracings
Floor Displacement(cm)
X Z
1 0.1709 0 2 1.4226 0.0002 3 2.9315 0.0001 4 4.3342 0.0002 5 5.5103 0.0001 6 6.3958 0.0003 7 6.9717 0.0007
Fig 8:FloorDisplacementwith&withoutbracings
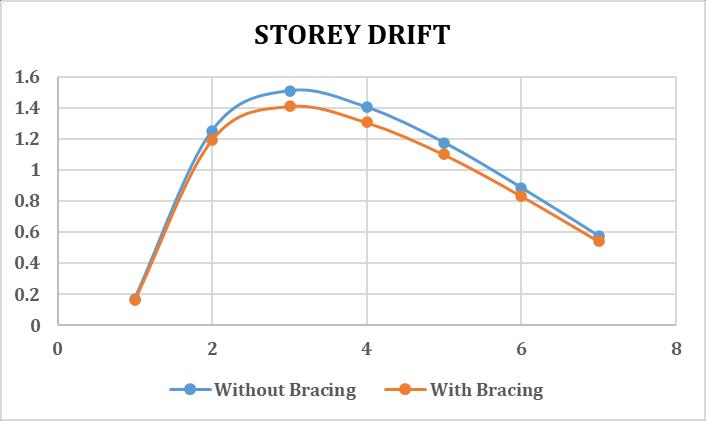
2.4 STOREY DRIFT
Fromthebelowdataithasfoundthatthestoreydriftofthe structurewiththein planehorizontalbracingdecreaseinthe range of 10% as bracing provide lateral stiffness to floors. Henceitperformsbetterduringseismicactivity.
Table 7: Storeydriftwithoutcornerbracings
Floor StoreyDrift(cm) X Z 1 0.1709 0 2 1.2517 0.0001 3 1.5089 0 4 1.4027 0 5 1.1761 0 6 0.8856 0.0002 7 0.5759 0.0004
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Table -8: Storeydriftwithcornerbracings
Fig 9:StoreyDriftwith&withoutbracings
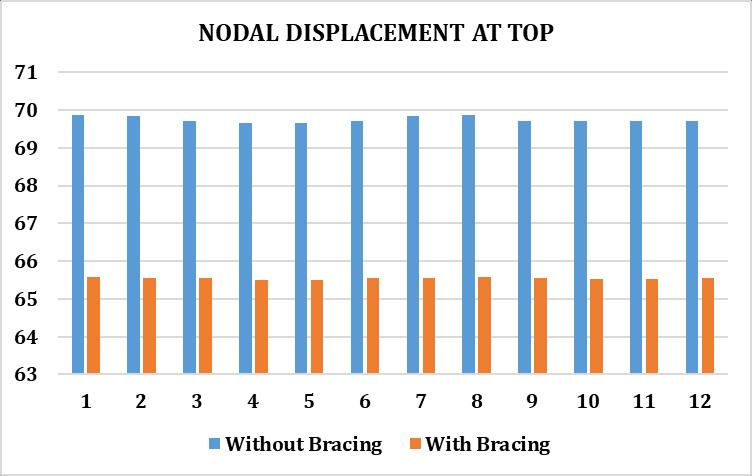
2.5 NODAL DISPLACEMENT AT TOP
FromthebelowdataithasfoundthattheNodaldisplacement ofthestructurewiththein planehorizontalbracingdecrease in the range of 10% as bracing provide lateral stiffness to floors.Henceitperformsbetterduringseismicactivity.
Table 9: NodalDisplacementwithwithoutcornerbracings
Floor StoreyDrift(cm) X Z 1 0.1629 0.0003 2 1.1938 0.0003 3 1.4107 0.0002 4 1.3068 0 5 1.1002 0 6 0.8335 0.0001 7 0.543 0.0006 Nodes WithoutBracing WithBracing 85 69.856 65.575 86 69.828 65.548 87 69.696 65.539 88 69.666 65.5 89 69.666 65.5 90 69.696 65.539 91 69.828 65.548 92 69.856 65.575 93 69.714 65.557 94 69.696 65.529 95 69.696 65.529 96 69.714 65.557
Fig 10:NodalDisplacementattopwith&withoutbracings
Resultshowsthatre entrantirregularbuildingis morevulnerabletowardsseismiccomparedtore entrantirregularbuildingwithcornerbracingsin termsofmassparticipation,withoutbracing90% mass participate in mode 13 while with bracing 90% mass participate in mode 9 which is a great improveinitsperformanceinseismiccondition.
Resultshowsthatre entrantirregularbuildingwith corner bracing improves it frequency, floor displacement,storeydriftandnodaldisplacementis decreases almost 10% compare to the re entrant irregularbuildingwithoutcornerbracing.
[1] Vaishnavi Vishnu Battul1, Mithun Sawant2, Tejashri Gulve3,RohitDeshmukh4,“StudyofSeismicEffecton Re entrant Corner Column” Journal of Advances and ScholarlyResearchesinAlliedEducationVol.XV,Issue No.2,(SpecialIssue)April 2018,ISSN2230 7540.
[2] NikhilDixit1,AbhishekJhanjhot2“Analysis and Design of Irregular Building with Re entrant Corner using Pushover Analysis”. International Journal of EngineeringResearchandApplicationswww.ijera.com, ISSN:2248 9622,Vol.11,Issue10,(Series III)October 2021,pp.01 12.
[3] Ganesh Gawande1 , Dr. S. B. Borghate 2, “Seismic Performance of Re Entrant Corner Building Under the Different Earthquake Direction”AsianJournalof Convergence in Technology, Volume 4 Issue III, ISSN No.:2350 1146,I.F 5.11.
[4] A. S. Dhanyashree1, R. Akash2, M. Ashok3, S. R. Premsai4,B.N.Bhavyashree5“StudiedtheEffectofRe entrantCornerRCFramedBuildingunderSeismicLoad
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

and StrengtheningitbyBracing“InternationalJournal of Research in Engineering, Science and Management
Volume 2,Issue 6,June 2019,www.ijresm.com|ISSN (Online):2581 5792.
[5] Shreyasvi CB1, Shivakumaraswamy2 “Seismic Response of Buildings with Re Entrant Corners in DifferentSeismicZones” IJRET:InternationalJournal ofResearchinEngineeringandTechnologyeISSN:2319 1163|pISSN:2321 7308.
[6] TarakBanerjee1,AryaBanerjee2studied“A Study on Optimizing the Positioning of Shear Walls for a Plus Shaped Irregular Building” International Research JournalofEngineeringandTechnology(IRJET)e ISSN: 2395 0056 Volume: 08 Issue: 10 | Oct 2021 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072.
[7] BethanyMarieBrown,studied“Lateral Loads on Reentrant Corner Structures”A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for degree of MasterOfScienceinCivilEngineeringWashingtonState University, Department of Civil and Environmental EngineeringMay2014.
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |