International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

2
1M.Tech Department of Civil Engineering, Gogte Institute of Technology Belagavi. 2Assistant Professor Department of Civil Engineering, Gogte Institute of Technology Belagavi. ***
Abstract - In India, exorbitant land prices and a lack of available land might lead to the construction of multi story buildings. Phenomena called anearthquakemightprovidethe most damaging forces for structures. Buildings need to be designed properly to keep people safe. The main goal is to create an earthquake resistant construction by conducting a seismic study of the building using a static equivalent technique of research and using E TABS software for both static and dynamic analysis. A G+10 Non Braced and Braced (X, V andInvertedV) building plan is takeninto consideration for this. For seismic zone II, III, IV, and V, calculations are made. By calculating all acting loads on the structure, including the lateral loads brought on by Time history data. The Seismic response i.e. Displacement, Storey Drift, Base Shear and Modal mass participating ratio are obtained.
Key Words: Linear Time History Analysis, Storey Displacement, Storey Drift, Base Shear, Bracing, Seismic Intensities.
Constructions constructed to withstand earthquakes are known as earthquake resistant structures. The aim of earthquakeresistantconstructionistoerectstructuresthat perform better during seismic activity than their conventionalcounterparts,eventhoughnostructurecanbe completelyimpervioustoearthquakedamage.
Thespecificationofgroundmotionfrompriorearthquake data is the foundation for the earthquake design of the structure. Therefore, it is crucial to create any significant constructionwithearthquakeresistanceinaccordancewith seismic frequency to prevent damage. However, because earthquakeforcesvaryandareunpredictable,itisnecessary toanalysestructuresunderallseismicforcesusingsoftware tools.
Forbuildingsthatdon'tresistearthquakeforces,aseismic studyshouldbeperformed.Sincedynamicinfluencesmight be included in seismic analysis, the accurate analysis will usuallybecomechallenging.However,analogouslinearstatic
analysisissufficientforsimpleregularstructures;thiskind of analysis is done for regular and low rise buildings. The multi story building will undergo seismic analysis in accordancewiththerequirementsoftheIS1893 2016code (part 1). Either a time history analysis approach or a responsespectrummethodisusedfordynamicanalysis.
Insteadoftheprevious version'sfiveorsixseismiczones, the earthquake zoning map of India now splits the nation into four seismic zones (Zones II, III, IV, and V). This partitioning map predicts that Zone V will experience the highestdegreeofseismicity,whileZone0willexperiencethe lowestlevelofseismicity.Eachzonedemonstrateshowan earthquake'seffectsataparticularlocationcorroboratedthe observationsoftheaffectedareasandmayevenbedepicted using a descriptive scale like the Medvedev Sponheuer Karnikscale,whichisamacrounstableintensityscaleused togaugetheseverityofgroundshakingbasedoneffectsthat have been observed in a specific area of the earthquake's occurrence.
These are the truss braced structural frames, which primarily use components in tension or compression to withstand lateral forces. Braced frames can withstand stressesbetterthanarectangularmoment resistingframe becausetheyaremorefrequentlysubjectedtoaxialloads. Thebracedframestructureisintendedtoperformbetter. Braces can be arranged in an X shaped, V shaped, or invertedV shapedconfiguration.
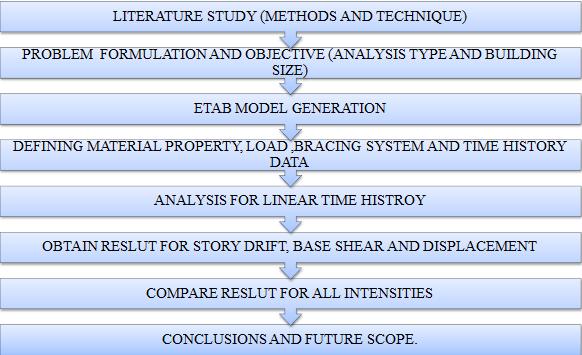
Thecurrentstudyaimstoinvestigatetheseismicanalysisof a multi storey building (G+10) with braced (X, V, and InvertedV)andwithoutbracedsymmetricalinplan,under earthquakeload,byadoptingalineartimehistoryanalysis methodtoevaluatestoreydriftanddisplacementsandother comparisons at zone II, III, IV and V Analysis of structure usingdynamicmethodandfindingoutdrift,displacement, andbasesheartounderstandthefundamentalprinciplesof structures.Creatinga3DmodelofthestructureusingtheE TABS software to conduct a thorough analysis, to analyse
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2595
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
8. TopStoreyHeight 3.5m 9. BottomStoreyHeight 4m 10. WallThickness 0.230m 11. SlabThickness 0.150m 12. Beamsize 0.23mX0.45m 13. Columnsize 0.45mX0.45m 14. LiveLoad 3.5kN/m2 15. FloorFinish 1.5kN/m2 16. ParapetWall 1.25m 17. DensityofConcrete 24kN/m3 18. DensityOfBrickwall 19kN/m3 19. Bracings X,VandInvV
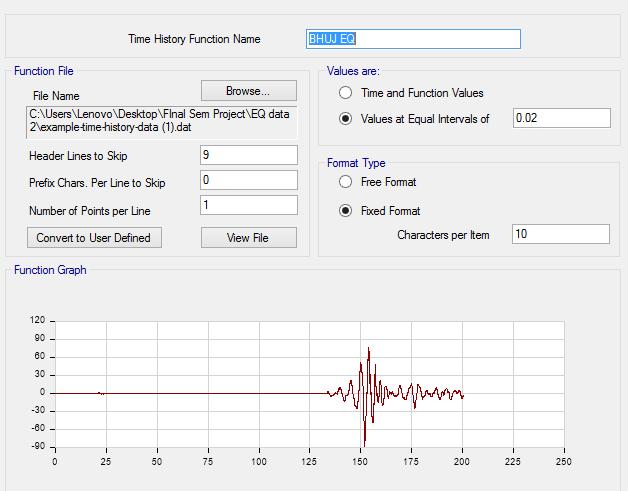
TheETABSanalysisusesavarietyoftimehistoriesasreal timeseismicdata.Itisuptoustochoosethedatatoutilize astheinputparametersforthesoftwareanalysis.Thetime historyoftheBhujEarthquake,whichhappenedonJanuary 26, 2001 in Gujarat, India, will be taken into account as a lineartimehistoryanalysisiscarriedoutona multi story RCCbuildingframeinthisstudy.
S.N O EQ Date Scale P.G.A g 1. BHUJ,INDIA Jan26 2001 6.9 0.110
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
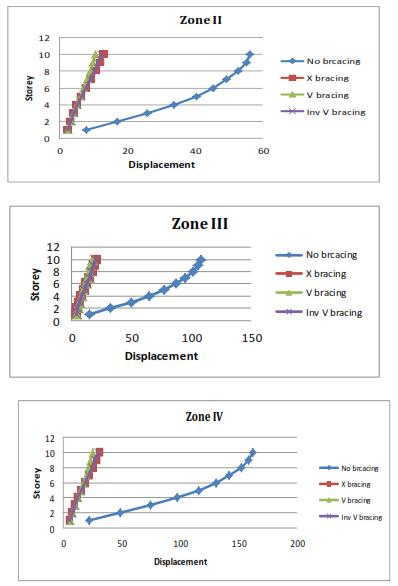
8. RESULTS Y axis is obtained for all results.
Displacement (mm) Zone II
Storey Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing
10 56.385 13.125 10.53 12.233 9 55.192 11.995 9.754 11.298
8 52.923 10.708 8.971 10.204 7 49.402 9.322 8.109 8.984 6 45.392 7.886 7.182 7.688
5 40.348 6.463 6.208 6.373 4 33.838 5.186 5.216 5.103 3 25.91 4.061 4.236 4.05 2 16.931 3.111 3.324 3.174 1 7.724 2.329 2.376 2.317
Displacement (mm) Zone III
Storey Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing
10 108.266 20.989 16.877 19.627 9 105.976 19.182 15.632 18.126 8 101.619 17.124 14.377 16.371 7 94.858 14.907 12.997 14.414
7 213.443 33.57 29.228 30.091
6 196.117 28.399 25.886 25.6
5 174.326 23.274 22.378 21.076
4 146.198 18.678 18.8 17.299
3 111.946 14.624 15.267 13.788
2 73.153 11.205 11.98 10.759
1 33.373 8.387 8.566 7.832
Displacement (mm) Zone IV
Storey Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing
10 162.398 31.483 25.297 29.428 9 158.963 28.773 23.432 27.178 8 152.429 25.686 21.55 24.546 7 142.287 22.36 19.481 21.612 6 130.737 18.916 17.253 18.495 5 116.21 15.502 14.915 15.332 4 97.46 12.441 12.53 12.276 3 74.626 9.74 10.175 9.742 2 48.766 7.463 7.985 7.635 1 22.247 5.587 5.709 5.573
Displacement (mm) Zone V
Storey Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing
6 87.158 12.61 11.51 12.335 5 77.474 10.335 9.95 10.225 4 64.973 8.294 8.359 8.188 3 49.751 6.494 6.788 6.497 2 32.51 4.975 5.327 5.092 1 14.832 3.724 3.809 3.717 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0
10 243.612 47.267 37.955 41.432 9 238.459 43.198 35.157 38.187 8 228.656 38.564 32.333 34.344
No brcacing X bracing V bracing Inv V bracing
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e ISSN: 2395 0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
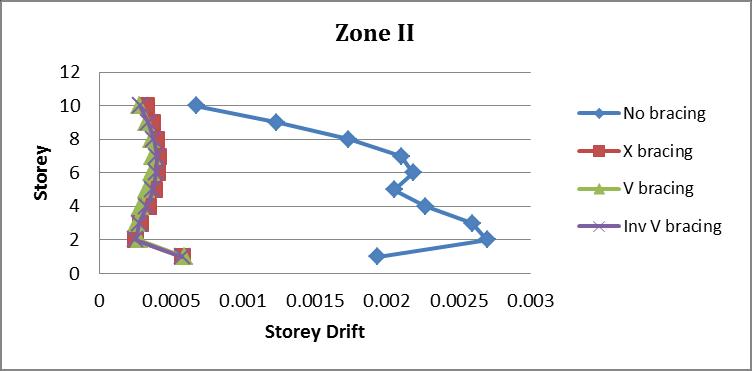
Storey Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing
10 0.001938 0.000782 0.00067 0.000689
9 0.003539 0.000882 0.00079 0.000822
Storey Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing
10 0.000673 0.000326 0.000279 0.000286
9 0.001229 0.000368 0.000329 0.000342
8 0.001736 0.000396 0.000361 0.00038
7 0.0021 0.00041 0.000373 0.0004
6 0.002184 0.000407 0.000363 0.000398
5 0.002049 0.000384 0.000331 0.000374
4 0.002265 0.000345 0.000289 0.000332
3 0.002592 0.000285 0.000261 0.000277 2 0.002698 0.000251 0.00028 0.000255
1 0.001931 0.000582 0.000593 0.000579
Storey Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing
10 0.001292 0.000521 0.000447 0.00046 9 0.002359 0.000588 0.000527 0.000548
8 0.003333 0.000634 0.000579 0.00061 7 0.004032 0.000656 0.000598 0.000641
6 0.004194 0.00065 0.000581 0.000638
5 0.003934 0.000615 0.00053 0.0006 4 0.004349 0.000551 0.000464 0.000532
3 0.004978 0.000456 0.000419 0.000445
2 0.00518 0.000402 0.000449 0.000409 1 0.003708 0.000931 0.000951 0.000929
8 0.005 0.00095 0.000867 0.000915 7 0.006047 0.000984 0.000896 0.000962 6 0.006291 0.000975 0.000871 0.000957 5 0.005901 0.000922 0.000795 0.000899 4 0.006524 0.000827 0.000695 0.000798 3 0.007467 0.000684 0.000627 0.000667 2 0.00777 0.000602 0.000673 0.000614 1 0.005562 0.001397 0.001425 0.001393
Zone IV
bracing
Storey Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing 10 0.002908 0.001174 0.001006 0.00099 9 0.005309 0.001324 0.001185 0.001173 8 0.0075 0.001427 0.001301 0.001296 7 0.009072 0.001477 0.001344 0.001351 6 0.009437 0.001464 0.001307 0.001332 5 0.008852 0.001384 0.001192 0.001239 4 0.009786 0.001242 0.001043 0.001121 3 0.011201 0.001027 0.000941 0.000927 2 0.011656 0.000904 0.001009 0.000866 1 0.008343 0.002097 0.002139 0.001958
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
Zone X Bracing V Bracing InvV Bracing 2 491.570 489.760 489.190 3 786.090 784.940 784.860 4 1179.140 1176.580 1176.800 5 1770.310 1765.920 1757.550
Modal mass participating ratio.
Mode Nobracing Xbracing Vbracing InvVbracing Time % Time % Time % Time %
1 2.695 82.11(UY) 1.526 84.93(UY) 1.646 84.46(UY) 1.583 85.41(UY)
2 2.539 82.19(UX) 1.432 87.31(UX) 1.528 86.43(UX) 1.467 87.59(UX)
3 2.252 82.84(RZ) 1.055 93.54(RZ) 1.125 92.2(RZ) 1.095 93.22(RZ)
4 0.87 9.97(UY) 0.497 13.84(UY) 0.527 13.59(UY) 0.525 12.78(UY)
5 0.822 10.21(UX) 0.474 11.79(UX) 0.496 12.26(UX) 0.492 11.17(UX)
6 0.733 9.6(RZ) 0.343 6.14(RZ) 0.365 7.2(RZ) 0.358 6.2(RZ)
7 0.492 3.6(UY) 0.223 0.97(UY) 0.254 1.42(UY) 0.252 1.2(UY)
8 0.465 3.5(UX) 0.207 0.69(UX) 0.23 0.97(UX) 0.228 0.89(UX)
9 0.421 3.5(RZ) 0.143 0.25(RZ) 0.166 0.44(RZ) 0.165 0.41(RZ)
10 0.33 1.88(UY) 0.138 0.16(UY) 0.165 0.3(UY) 0.164 0.28(UY)
11 0.315 1.81(UX) 0.131 0.12(UX) 0.149 0.2(UX) 0.148 0.19(UX)
12 0.285 1.71(RZ) 0.102 0 0.124 0 0.123 0
Mode 1 Translational UY Mode 2 – Translational UX
1. The seismic responses of the buildings in both the directions are similar in terms of their intensity. These include base shear, storey displacements, and floor drifts. Theintensityoftheseresponsesvariessignificantlyacross differenttimeperiods.
2. Thevaluesofseismicresponsesarecomputedbytaking into account the varying intensities of seismic activities acrossdifferenttimeperiods.Theyshowthattheorderof seismicintensitychangeswithincreasingintensity.
3. The displacement of the X bracing structure (47mm) is greaterthanthatoftheV(37mm)andInvertedVbracing (41mm)inZoneV,andasimilarpatternisfollowedinallthe zones, according to the analysis. It is also noted that the displacement is quite high at the roof and very low at the base.
4. The base shear of the X bracing structure in Zone V is 1770kN,whichismorethantwiceasstrongastheV bracing andInvertedV bracingstructures.Similarpatternscanbe observedinallseismiczones.
5. Storey Drift mostly affects the middle of the building structure, and it is determined that it is higher in the X bracingthanintheotherbracingstructuresandthatitgets worse as the seismic zone gets bigger. It was 0.000407 in ZoneIIoftheXbracingstructureand0.00146inZoneVon thefifthfloor.Thisindicatesthat,whencomparingzoneIIto zone V, the storey drift increases by more than 50%. The storeydriftingroundfloorofallbracedsysteminallzone hasahugespike.Itisdueto softstoreyeffectwhereinthe lateralstiffnessoftheabovestoreyismorethanbelow.
6. Thefirsttwomodes,whichaccountformorethan60 65 percent of the mode participation ratio, are translational modes;thethirdmode,rotation,accountsfor93.22percent ofthebracingstructures.Exceptfortheabsenceofabracing structure, the modal Participating Ratio of X bracing, V bracing,andinvertedVbracingStructureallfollowasimilar pattern. It is also observed that natural period for braced structure is much less thanthe unbraced structure, hence lessdisplacementinbracedstructure.
7. Thedifferenceinbaseshearforallthebracedstructure (X,VandInvertedV)isnotmorethan10%.
8. Time Historyisa realistic seismic analysismethodthat offersa betterassurance of thesecurity ofstructuresthat havebeen examinedand developedinaccordancewith IS code.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e ISSN: 2395 0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p ISSN: 2395 0072
[1] Duggal S K (2010), “Earthquake Resistance Design of Structure”,FourthEdition,OxfordUniversityPress,New Delhi.
[2] HaseltonCBandWhittakerAS(2012),“Selectingand Scaling Earthquake Ground Motions for Performing Response History Analyses”, The 15th World ConferenceonEarthquakeEngineering.
[3] RomyMandPrabhaC(2011),“DynamicAnalysisofRCC Buildings with Shear Wall”, International Journal of EarthSciencesandEngineering,ISSN0974 5904,Vol. 04,659 662.
[4] Shaha V and Karve S (2010), “Illustrated Design of ReinforcedConcreteBuildings”,SixthEdition,Structures Publication,Pune.
[5] Patil A.S, Kumbhar P.D,“Time history analysis of multistoried RRC building for different seismic intensities”,InternationalJournalofStructuralandCivil EngineeringResearch,vol. 02,issue 03,Aug2013.
[6] BhagwatMayuriD,“ComparativestudyofPerformance ofmultistoriedbuildingforKoynaandBhujearthquake by THM and RSM”, International Journal of Advanced Technology in Engineering and Science, vol.no. 02, issue 07,ISSN:2348 7550,July2014.
[7] Dubey S.K, Sangamnerka Prakash, Agrawal Ankit, “Dynamicanalysisofstructuressubjectedtoearthquake load”,InternationalJournalofAdvanceEngineeringand Research Development, vol. 02, issue 09, ISSN: 2348 4470,Sep.2015.

[8] Rampure Aarti baburao, “Comparison between ResponseSpectrumMethodandTimeHistoryMethodof dynamicanalysisofconcretegravitydam”,OpenJournal ofCivilEngineering,June2016.
[9] HawaldarJyothiC,“EarthquakeanalysisofG+12storey building with and without infill for Bhuj and Koyna earthquakefunction”,InternationalResearchJournalof Engineering and Technology(IRJET), vol. 2, issue 05,ISSN:2395 0056,august2015.
[10] Harshita,“seismicAnalysisofsymmetricRCframeusing RSM and THM”, International Journal of Scientific ResearchandEducation,vol 02,issue 03,march2014.
[11] IS 1893 (Part 1):2002 Design Criteria for Earthquake ResistantdesignofStructure.
[12] CSI,(2016),extended3Danalysisofbuildingstructures (ETABS),ComputersandStructuresInc.,USA.
SantoshPotadar
M.Tech Department of Civil Engineering, Gogte Institute of TechnologyBelagavi
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page2600