International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Manish Rajput*1, Mayank Soni*1, Durgesh Bhardwaj*1, Abdul Aleem*1
*1School Of Computing Science And Engineering, Galgotias University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India. ***
Today, technology plays a significant role in every aspect of our life. Regardless of the use of gadgets like laptops, smartphones, etc., technology has been employed. It is also utilised in telemedicine, the creation of smart cities, agribusiness,autonomousdriving,andIOT,amongotherthings.Thefifthgeneration,alsoknownas5G,ismadetohandle data traffic,a largenumber oflinked nodes,latency,andfrequencyspectrum. With somanycutting edgecapabilities,5G technology is set to surpass all others in the near future. The 5G mobile network intends to get past the constraints of mobiletechnologiestoofferastrongbasisforIoTinthefuture(suchas2G,3Gand4G).5Giscomposedofmanyparts. Someof theseinclude public services,autonomousservices,smartservices,andso forth. We give a brief overview of 5G technical scenarios in this paper. The future of the 5G mobile network is next examined, followed by a summary of the articlesthathavebeenauthorisedforinclusioninourspecialeditions.Finally,weshallstatethis.
Duetoconsumerneedforflexiblestatistics,creativeimplementation,andpremiumportablestructures,mobilebroadband entertainmentisexpanding.Morerecently,inthepastthreeyears,wirelesscommunicationhasrapidlyincreasedfrom1G to4G.Themainguidingprincipleofthisstudybecametherequirementforverylowlatencyandenormousbandwidth.5G offers an abnormally cheap offer price, a significant improvement in the issuer's quality of service (QoS), low latency, extensive coverage, and excellent dependability. 3 sorts of services are offered by 5G: necessary cellular broadband (EMBB).Streaming UltraHD movies, virtual reality and augmented reality (AR/VR) media, increased bandwidth, medium latency, and many more features are all available with this independent architecture. Large System Verbal Exchange (eMTC),whichis the thirteenthspecification released by3GPP.It enables efficient, long distance,high bandwidthdevice communication while using significantly less electricity. For IoT initiatives, eMTC partners with mobile businesses to deliver a business with high data costs, low strength, and expanded coverage owing to simpler devices. A rich 86f68e4d402306ad3cd330d005134dac carrier (QoS) is available with ultra reliable low latency verbal exchange (URLLC), which is not possible with conventional cellular community design. Including remote surgery, car to vehicle (V2V), the 4.zero society, smart grids, and intelligent transportation systems, URLLC is built for on demand real time interaction.
TheITUrefersto3Gand4GtechnologiesasIMT 2000andIMT advanced,respectively.For5G,theIMT 2020timelineis utilised. All of us are referred to as IMT. IMT systems' capabilities are constantly being increased in accordance with societaldesiresandemergingtechnologytrends.4.IMTsystemshavehelpedtheworld'seconomyandsocietyadvance.
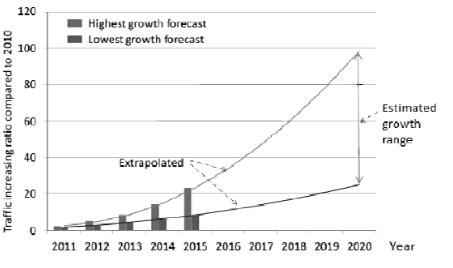
Visitors to websites can increase other spectrum resources using cell information, which will be important for future mobile broadband communication systems. The ITU R M.2290 0 report, Global Angle Estimate of Spectrum Needs for TerrestrialIMTin2020,isavailable.Toaccountforspectrumthatisalreadyinuseorisslatedforuse, theexpectedtotal demandforspectrumhasbeenchangedtobecomputedat1340MHzand1960MHz,respectively,atleastthroughtheend oftheyear.Domesticspectrumrequirementsinsomenationsmaybelessthanthoseestimatedusingsettingswithlower userdensities,whileinothernationstheymaybegreaterthanthoseestimatedusingsettingswithhigheruserdensities. InFig.1,theanticipatedmobiletrafficisdepicted.Withatleasta25 foldincreaseinexpectedtrafficfrom2010to2020, theaverageincreaseintrafficispredictedtorange betweentheminimumandthe biggestrise.Between2020 and2030, someestimates6forecastanincreaseinforeignvisitorstoIMT10to100sites.[1].
International Research Journal of Engineering
Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Fig. 1 Extrapolatedmobile
0
With the advent of 5G, the range of frequencies used for mobile communications will be expanded to accommodate the potential for record breakingvisitsandtheincreasingcapacityrequirementsforextraordinarilyhighdatacharges.More spectrum below 6 GHz as well as spectrum in higher frequency bands are included in this. Lower frequencies boost wirelesscoverage.AlmostallnationscurrentlyuseIMTsystemsintherangebelow6GHz.Therefore,the spectrumthatis appropriatefor5Gwirelessaccessliesbetween1GHzandabout100GHz.Itiscrucialtoensurethat5Gdeliversextensive locationinsurance,outdoorcoverage,andindoorcoverageinadditiontoreachinghighdatapricing.Therefore,spectrum below6GHzisacrucialcomponentofthe5Gspectrumsolution.Above1200MHzMobilebroadbanduseinEuropehasso farbeenstandardisedforarangeoffrequenciesbetween694MHzand3800MHz..[2].
The most suitable frequency band to begin using 5G in Europe before 2020 will be the 3400 3800 MHz range, which is now standardised for mobile networks and includes up to 400 MHz of continuous spectrum allowing for large channel capacity.Theimplementationof5Gorpre 5GcouldplaceEuropeintheforefrontthankstothisfrequency.
Thereisachancethat5Gnetworkswilloperateinthe1427 1518MHzfrequencyband[3].Thestudy'sfindingshavebeen usedtoupdatethismanuscript.[4].
In fact, 5G is anticipated to cost a lot more money and consume a lot more bandwidth than earlier technologies. Additionally, these incredibly high recordings can only be identified using higher frequency bands (above 6 GHz). New wireless solutions with improved frequencies in the millimetre wave (mm wave) band are anticipated to be implementedinordertoprovidefasterdatatransferandreducelatency.Therefore,itisstillnecessarytocreatefrequency bandsevenabove24GHz.consequencesformillimetrewaveinstallationsusingsmallcellsandhighlydirectionalantennas [4]inordertoreachall5Gperformancegoals,suchasmultigigabitinstepwith2.TheITU RM.2376 0study'smodelling, measurement,eradevelopment,andprototypeusingbandsbetween6and100GHzarereasonable.
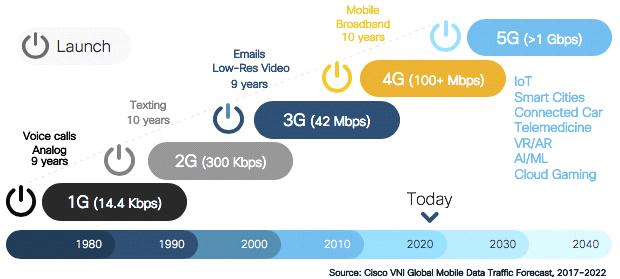
• First Generation (1G) Network The 1G network was introduced in the 1970s and 1984s. Technologies used in 1G areAMPS,NMTandTACS.Thefrequencyis30kHz.Thebandwidthwas2kbpsandtheaccesssystemwasFDMA.The coreofthe1GnetworkisthePSTN[5].
• dataonprices.implicationsforthedeploymentofmillimetrewaveswithhighlydirectedantennasandtinycellsizes [4].Usingthebandsbetween6and100GHz,themodelling,measurement,eradevelopment,andprototypeoutlined in the ITU R M.2376 0 report are practical for the examined IMT deployment scenarios and may be taken into consideration, according to the most recent ITU theoretical evaluation. IMT development factors for the years after 2020[5].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
• Third Generation (3G) Network: In the 1990s and 2002, the 3G network was first introduced. WCDMA is the technologyutilisedin3G.Therangeis1.6toGHz.TheaccessmechanismwasCDMA,andthebandwidthwas2Mbps. The3Gcorenetworkispacket.Establishanetwork[5].
• FourthGeneration(4G)Network The 4G network was introduced inthe 2000'sand2010's. Thetechnology used in 4GisLTE.Thefrequencyrangesfrom2to8GHz.Thebandwidthrangewasfrom2000Mbpsto1Gbpsandtheaccess systemwasCDMA.The4GcorenetworkistheInternet[5].
• FifthGeneration(5G)Network The5Gnetworkwasintroducedinthe2010'sand2015's.Thetechnologyusedin5G isMIMO,mm Waves. The frequency rangesfrom 3to 30GHz.The bandwidth rangedfrom 1Gbps& higherandthe accesssystemwasBDMA/OFDMThe5GcorenetworkistheInternet[5].
Figure 2: Caption Here
Infact,5Gisanticipated to be muchmore expensiveandbandwidth intensivethan priortechnologies.Additionally,only higherfrequencybandsmaybeusedtorecognisetheseextraordinarilyloudrecordings(above6GHz).Inordertoenable quickerdatatransferandlowerlatency,newwirelesssolutionswithenhancedfrequencies inthemillimetrewave(mm wave)band areanticipatedto beimplemented.Therefore,theneedtodevelopfrequencybandsabove24GHzpersists. implicationsforinstallingmillimetrewavesystemswithcompactcellsandhighlydirectionalantennas[4]tomeetall5G performance objectives,including multi gigabit instep with 2. It is reasonable to model, measure, develop, and research theITU RM.2376 0prototypeusingbandsbetween6and100GHz.IMTdevelopmentconsiderationsfor2020andlater.
Millimeter Wave: Utilizingthemm wavespectrumThefirststeptowarda1000 foldspeedupistouse(3 300GHzband) asacarrierfrequencyandperiodicallystoredatainunlicensedradio waves(5GHzWi Fi).Thesaturationspectrumused bytheauthorisedmobileoperatoratthetimespansfrom750MHzto2600MHz.Thephysicallayerdesignwastherefore completely underused. The mm wave spectrum (PHY layer) must be used. Furthermore, quicker data transfer and availability are ensured by massive MIMO, beamforming, transferring traffic to unlicensed bands, and cloudification of radio resources. Rappaport et al. demonstrated the route loss, penetration traits, and propagation behaviour of 28 GHz and 38 GHz carriers from a building. details displayed The subjects addressed in this thesis will undoubtedly aid in the design and PHY layer for 5G on mm waves implementation. Extremely low latency was developed by Levanen and coworkers.mm wave based5Gconnection[6].
5G Architecture: The 5G RAN and the core network will be closely integrated. High speed cable connections should be used for base station connections, and millimeter wave wireless communications may even replace optical fibre in the backbone network. The efficiency of a typical macrocell might decrease as more linked devices are added. be unfairly burdenedbythepriceofmanagingtheconnectionoftensofthousandsofdevices(about10,000percell).Thearchitecture mustthusbemorestraightforwardandadaptedtoenableincreasedsignalvolumesandoverheadpayloads.Efficiencyof
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
5G Giga KOREA's mm wave RAN's high end deployment architecture There was talk about the 5G initiative. The researchers in the study also highlighted how the beam steering mechanism enabled quick switching between different beams and generateda graphicrepresentation of the antenna arraytopologies for 3Dbeamforming. A2D arrayof patch antennas produces 3D light beams. Spatial multiple access is made possible by highly directional radio transmission beams that are generated from a 2D array of patch antennas in 3 dimensional environments (SDMA). (BDMA) is essentially beam division multiple access. They integrated NXM patch antenna arrays into the user equipment as patch antenna arrays.Radioaccesstechnologyisstrong,secure,andverydependable becauseitcancommunicateswiftlyover several beams.Additionally, "relay" transmission is employed to get around the RAN's constrained mm wave coverage, andbasestationsinsteadofthecorenodesmaynowhandlethehandoverprocess.In4GLTE,thebasestation,alsoknown as the eNB, does this resource allocation operation. To enhance LTE QoS, a variety of scheduling techniques have been suggested. Such an intelligent resource allocation technique for cognitive radio connections was given, based on calculations from game theory. This sort of ideal dispersed resource allocation method should be used by 5G while executing macrocell based operations when beamforming might not be practical.Along with boosting RAN capacity, it would be great to establish a core network that is adaptable, intelligent, simple to deploy, and affordable. Additionally, recentdevelopmentsincloudnetworkinghavemadeitpossibleforcorenetworkstobevirtualized.[6].
Modulation Method Superior to OFDM: The modulation system and multiple access mechanism utilised are important drivers of spectral efficiency. LTE Advanced uses the multiple access and modulation methods orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) and orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) (4G). Code Division Multiple Access(CDMA),whichwasutilisedin3Gmobiletelephony,isreplacedbyOFDMA.Thehighpeakpowerratio(PAPR)and the need for cyclic prefixes (CP) to prevent inter block interference should both be improved upon in OFDMA further. Furthermore,evenwiththerequisitehardwaresetup,itisuncertainifOFDMwilloperateonbroadbandmm waves.Ithas been publisheda comparisonofthe modulation methodsutilised by In5G,therearethreedifferentcarriertypes:FBMC, UFMC,andOFDM.TheFBMCsystemachieveshigherspectralefficiencythanOFDMbysuppressingsidelobesbyspreading thesubcarriersthroughoutthefilterbank.Internalasynchronybetweenthetransmitterandreceiverisnotaproblemfor FBMC.Thegoal ofthe5GNOWgroup istodevelopan effectiveairinterfacethatis notdependentonstrictorthogonality andsynchronisationconstraints.Thegroupiscurrentlyresearchingfourcurves:GFDM,UFMC,FBMC,andBFDM.[6]
RAN as a Service in the Cloud: A RAN can be regarded as a section of the front end network. In addition to extremely low bandwidthcontrolsignalsfortheInternetofThings,high qualityreal timevideowillbesentthroughtheairinterface of the 5G network. Although fundamental physical characteristics like Although RAN is closely related to modulation, coding, and massive MIMO, the quickly expanding field of cloud RAN is the primary emphasis of this chapter. The most important aspect of 5G that has been anticipated is the brand new use of cloud services in RAN implementation. The advantagesofRAN as a serviceintermsofnetworksustainabilityandenergyefficiencyweredemonstratedbySabellaet al(RANaaS).TheRANcapacityiscontrolledonasingleserverandmadeon demandavailabletousersundertheRANaaS cloud paradigm. Base stations need to be split into radio access units and baseband units for this reason, and a reserve poolofbasebandunitsneedstobeestablishedtosupportanycell.withasubstantialamountoftraffic.Tosaveenergyand make the reserved capacity of a cell available in case of an unexpected spike in traffic, low energy microcells should be placed.Additionally,theyshowedhowtheintroductionoffreshercloudcomputingplatformsandforthcomingdata centre servers will boost processing power and energy effectiveness even more. In addition to the RAN, core and backbone networkscanbevirtual.[6].
Usage of Less Energy: Energyuse hasa bigimpact on how new networksare deployed on a broad scale.More than 0.5 percent of the energy produced globally is being used by mobile networks. Tombaz and Sung statistically prove that a networkthathasbeendensifiedbyfewercellshasinevitableenergyrequirements.Theprimaryenergyusersinthegrid willbeidlepowerandbackhaulduetotheincreaseddeploymentofsmallercells.Inapotential5Garchitecture,network functional virtualization and software defined MAC have been incorporated. Tombaz and Sung want to create a 5G network with low latency and good energy effectiveness by combining these strategies. The 5GrEEn project seeks to providea heterogeneous network (HetNet)architecture thatis energy efficientand optimised in orderto boost capacity for a variety of requirements and traffic conditions. It's critical to carefully distribute cloud resources. "Anchor," a customizablecloudresourcemanagementsystem,wasdeveloped,putintouse,andassessed.[6].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
• • Despite cell types and RATs that mix and overlap macrocell BSs, small cell BSs, WLAN access points, and relay stations,seamlessmobilitymustbemadepossible[7].
• Regardless of the access network, a mobile terminal must be recognised by one ID for multiple access as a single entity[7].
• Inordertoaccommodatetheanticipated1000timesincreaseddemand,distributedarchitecturesupportsdispersed networkdesign..
• Portable signalling lightweight signalling that can accommodate a number of terminals, including the large MTC terminal[7].
• Inorderfor"FlowoverMulti RAT"todeliverhigh volumeserviceatafairpriceandensureservicecontinuitydespite constrainedwirelessaccessbandwidth,multipleRATinterworkingrequiresanarchitecture
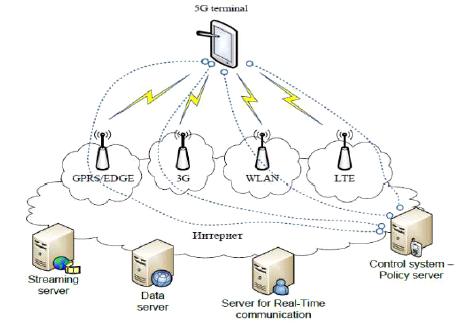
• To offer cutting edge location based services;To offer cutting edge location based services, fine grained location trackingmustbeabletotrackthelocationofthemobileterminalwithahighlevelofaccuracy[7].
Traffic Volumes in Data: Inspiteofconstrainedwirelessaccessbandwidth,multipleRATlinksmustbeabletodelivera wide range of services at a reasonable cost and ensure service continuity. Over the previous six years, there has been a 40%yearlyriseinthenumberofactivemobilebroadbandcustomers,whonownumberover2billionglobally.Asaresult of the proliferation of M2M devices, which have low bit requirements but substantial signalling overhead, new traffic characteristicswillalsobeintroducedintonetworks.Toenablenetworknodestoshutdownduringtimesoflowtraffic,an efficient signal management system will be necessary in this respect. According to this perspective, M2M traffic will providegreaterchallengesforgreennetworkdesignthatsupports"Flowover[7].
Diverse Requirements: Applicationsusing5Gwillhaveawiderangeoffeaturesandrequirements,someofwhichmaybe verydifferentfromthoseusedbycurrentmobilesystems.,accordingtotheevolutionaryscenariodescribedinthisstudy. Forsomeapplications,suchastime sensitiveindustrial control procedures,lowlatencymayberequired.Simplesensors areoneexampleofanapplicationwithreducedreliabilityneeds,yetthesamesortofapplicationsfrequentlydemandvery high dependability. Some applications, like security cameras, may need sending enormous volumes of data, while others may just require sending little amounts.The system architecture has to handle this issue. Since the right and effective management of QoS inside the system shouldn't be affected by the lowering of network energy consumption, the ecologicaldesignmaybesignificantlyimpacted.[7].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Consumption of Energy: Findinganeconomicalandlong termsolutiontotheaforementionedobjectivesanddifficulties maybethehardestobstacle.Priceisanimportantconsiderationnowandwillremainoneinthefuture.Fairpricingforthe end user and a compelling business case for mobile carriers must be attainable given the CAPEX and OPEX quantities. There is a clear danger that a mobile operator's energy expenses, which currently account for a sizeable and increasing portion of their OPEX, will increase drastically if nothing is done given future demands and expectations.We've already addressed how various variables impact energy use, which is why concentrating on low energy usage is crucial. Despite theriseintraffic,theenormousnumberofdevices,andthenewneeds,energyconsumptionshouldbekeptatleastatthe existing level; nevertheless, we think that it is feasible to go far further. In a recent news release, the GreenTouch Consortiumsaidthat,startingin2010,itcouldsignificantlycuttheenergyuseofcurrentsystems.Inordertoachievethe standards,5GrEEnseekstouse10timeslessenergythanexistingtechnologies.previoussubdivisions[7].
The Quantity of Connected Devices: Worldwide,therearecurrentlycloseto7billionmobilecustomers,andwiththem, wirelesslylinkeddevices.Themajorityofthemaretechnologicaldevicesthatpeopleutilise,suchcellphones,computers, ortablets.Asmoredevices, suchassmartgriddevices, sensors,andsecuritycameras,areconnectedto networks,thisis anticipated toalter inthe future. Machine to machine(M2M)connection, often known asthe Internet of Things(IoT), is thetheorythateverythingthatcanprofitfromwirelesscommunicationwill.Ifwemerelycountthenumberofgadgetsina normalhousehold,itcanalreadybeclaimedthatthere willbe10 100timesmorelinkeddevicesinthefuturethanthere arenow.[7].
Modulation patterns, software defined radios, and novel error control techniques for 5G terminals may all be downloadedviatheInternet.Theadvancementofuserterminalsistheprimaryobjectiveof5Gmobilenetworks. Sincethe terminalswillhavesimultaneousaccesstomanywirelesstechnologies,itshouldbepossibletocombinevariousstreams from various wireless technologies. Because they fail when there are several operators, technologies, and service providers, vertical handovers should be avoided. The management of user mobility will fall under the purview of each networkin5G,withtheterminalultimatelydecidingwhichwireless/mobileaccessnetworkprovidertoutiliseforagiven service. Everythingarounduswillbeconnectedbyanetworkthat isincrediblyquick,incrediblydependable,andtotally responsive thanks to fifth generation wireless technology. Thanks to IoT devices that are specifically connected to the Internet through mobile applications, people have more control over their surroundings. A smartphone may be used to manage a range of Internet of Things (IoT) devices from anywhere in the world, including baby monitors, intelligent securitysystems,thermostats,smarthomeappliances,motionsensors,andmore.Sincetherewillbemoretimeforleisure activities, travel, spending time with friends and family, etc., these technologies ought to make everyone's lives simpler andmorefun..[8].
Future 5G wireless networks will offer substantially higher data speeds, much larger coverage, very low latency, andsignificantlybetterqualityofservice(QoS).InternetofThings(IoT),pervasivemachine to machine(M2M),incredibly dependable, and reasonably priced Internet access for mobile portable devices, and cyber physical systems will all be madepossiblebyawiderangeofnewgadgetsfallingunderthe5Gbanner.Asopposedtowhatmostpeoplebelieve,these qualitiesdemonstratethat5Gisaconvergenceofcutting edgenewtechnologyrequiredtohandleusertraffic,increasing apps,andtheongoingneedforIoTdevices.5Gsecurityisevenmorecrucialgivenitsprojectedeffectsonsocietyandhow theywillaffectourdailylife.Therefore,mucheffortmustbeputintoensuringthethesystem,itsusers,andthe5Gnetwork itselfareallsecure.TheadvancementofLTEisnecessaryfor5G. However,5Gwillenhanceallnetworkelements,suchas radios,coreandcontrolsystems,andapps.Securitycanthusbecompromisedeverywhere..[8].
Futureadvancementsofthenanocorewilltremendouslybenefitfromtheintegrationofartificialintelligence(AI).A smartphonemaybeusedtocontroltheintelligentrobot.What'sgoingthroughyourmindcanbeimmediatelyenteredinto yourmobiledevice.Wemightbeabletocommunicateinsomesituationswithouttheuseofaspectrum.Thekeyword6G isnowthe17thmostpopularsearchphrase,perGoogleHotTrends.[8].
Businesses all around the world will make use of 5G technology to boost productivity, engage existing and future clients,andlaunchfresh businessstrategies.Theearlyyearsofthe5Geconomywillbedefinedbyeffortstocontinuously advancethetechnologyandinfrastructurebase,whichwillbefollowedbytheever increasingacceptanceof5Gusecases aroundtheworld,asexplainedinthe"5GTechnologyandUseCases."section.[8]
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
a variety of user terminals, wireless system possibilities, QoS, security, and network assistance Application level attacks, spoofing,jamming,andbillingandchargingEncryptionofdata[9].Thesystemcapacitymaybeboostedhundredsoftimes by adopting sophisticated antenna technology. Beamforming technology may be used to dynamically combine big antennassothatsignalstrengthItisdirectedinacertaindirection,andsmallerenergybeamscanbeconcentratedintoa more compact space, minimising self noise and local interference. The use of local hotspots in densely populated areas such as malls, shopping centres, transportation hubs, and other events and places is necessary for system application scenariosthatincludeseparateurbanandsuburbancabling.[9].
The amount of time it takes for a signal to complete one transaction is known as latency. To achieve high data speeds, energy savings, and long battery life, reducing latency becomes crucial. The 1ms subframe indicates that the current 4G delay is around 15ms. Although 5G will include innovations like haptic internet, real time two way gaming, cloud apps, and augmented reality that cannot be handled at present latencies, this latency is still regarded as ideal for currentuse.Therefore,5Gshouldbeabletoachievesub 1mslatencies,whichwillhaveabiginfluenceondesignchoicesat all levels.Two techniques for lowering latency are outlined above: D2D communication and dense tiny cells. D2D communication can manage two devices communicating while they are close to one another without using any network resources. D2D can manage local traffic with ease. This is a vital option for applications that demand minimal latency.D2D's adoption is driven by its significance for security and catastrophe applications as well as low latency applications.TheThirdGenerationPartnershipProject(3GPP)haspreviouslyreviewedD2Dasa4Gtechnology(version 12), and its adoption is driven by its evaluation as such. Obstacles in this field include effective proximity detection, networkintegration,andnativecompatibilityinforthcoming5Gnetworks.[9].
M2McommunicationhastremendouslyaidedtheintegrationofphysicalsystemswiththeInternet.Aemergingconceptis M2M communication over cellular networks. In order to enhance the present cellular standards and allow M2M communication,severalresearchershaveinvestigateduniqueandcutting edgeapproaches.Accordingtothewritersof5G hasthemostpromiseformobilebroadband.CriticalloTformission criticaluseswithmobilebroadbandM.Dighririetal. exploreslicecommunication,internet,logistics,agriculture,climate,automobiles,factories,and hugesegmentationofthe lo5G network for future M2M communication. The authors discussed mobile M2M communication and underlined the expandingM2Mtraffic.[10].
Millimeter wave technology isused inthe 5G network tohandle traffic. The millimetre wave technology issupported by the 5G network. The millimetre wave frequency band is roughly between 24GHz and 100GHz, whereas the 5G network operates at a frequency of 6GHz. We are aware that frequency and internet speed are directly inversely correlated; as internet speed increases, however, so does network range. Similarly, lower the frequency loq data rate while extending networkcoverage.Obstacleslikewalls,roofs,andothersurfacesinteractwithmillimetrewaves.ThespeedoftheInternet isalsoimpactedbythesechallenges.Aswestatedbefore,millimetrewaveshavea higherfrequencythatrangesfrom24 GHzto100GHz,thusinthiscaseweneedtosetthenetworkfrequencytocoverawiderangeofnetworkswithoutgoing toohighortoolow.[11].
Milimeterwavefrequencyin5gimprovesnetworkcapacitywithmulti gbpsspeed.Alsoimproveshigh speeddata transfer and wide bandwidth. Offer the user reliable experience and network efficiency benefits. 5G millimeter wave technologyhavebeenusedforcloudgamingandothermoredataconsumptionactivities[11],asdiscussednext.
• Increased capacity:Millimeterwavescancarrymoredatathantraditionalcellularfrequencies.Thishighercapacityis crucial forthe 5Gnetwork, whichwill needtohandle exponentiallymoretrafficthanprevious generationsof cellular networks[11].
• Increased speed: Millimeter waves can transmit data much faster than traditional cellular frequencies. This higher speedisnecessarytosupportthemanyhigh bandwidthapplicationsthatwillbeusedinthe5Gnetwork[11].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
• Increased reliability:Millimeterwavesarelesslikelytobeblockedbyobstaclesthantraditionalcellularfrequencies. Thisincreasedreliabilityisimportantforsupportingthemanybandwidth intensiveapplicationsthatwillbeusedin5G networks[11].
• Reduced latency:Comparedtoconventionalcellularfrequencies,millimetre wavesmaytransportdatamorequickly. Tosupportthemanylatency sensitiveapplicationsthatwillbedeployedin5Gnetworks,thisreducedlatencyiscrucial [11].].
Normal computers and laptops will face stiff competition from the new 5G technology, which will lower their market value. The market now offers the new 5G technology at cheap prices, with a high peak future, and with significantly greaterreliabilitythanitspredecessors.
[1].Lalwani,GauravChoudhary,Ilsunou,andGiovanniPau
[2].SpectrumConsiderationof5GMobileCommunicationsGuntisAncans(RigaTechnicalUniversity),VjaceslavsBobrovs (RigaTechnicalUniversity),DianaKalibatiene(VilniusGediminasUniversity).A10.1109/JSAC.2014.2328098.
[3].Internet Resource, Ericsson:http://www.ericsson.com/openarticle/mwc connected devices_1686565587_c
[4].Aleem,A.andKumar,A.,&Gore,M.M.,AStudyofManuscriptsEvolutiontoPerfection(March11,2019).Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computing and Software Engineering (ICACSE) 2019, Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3350277
[5]FP7 Integrating Project METIS (lCT 317669). [Online]. Available: https://www.metis2020.com/documents/deliverables/
[6].Singh,R.K.,Bisht,D.,&Prasad,R.C.(201 Aleem,AbdulandKumar,AkhileshandGore,M.M.,AStudyofManuscripts Evolution to Perfection (March 11, 2019). Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computing and Software Engineering (ICACSE) 2019, Available at SSRN:https://ssrn.com/abstract=3350277 Aleem, Abdul and Kumar, Akhilesh and Gore, M.M., A Study of Manuscripts Evolution to Perfection (March 11, 2019). Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computing and Software Engineering (ICACSE) 2019, Available at SSRN:https://ssrn.com/abstract=33502777). Development of 5G mobile network technology and its architecture. InternationalJournalofRecentTrendsinEngineering&Research(IJRTER),3(10),196 201.
[7].Mitra,R.N.,&Agrawal,D.P.(2015).5Gmobiletechnology:Asurvey.IctExpress,1(3),132 137.
[8].Yu,H.,Lee,H.,&Jeon,H.(2017).Whatis5G?Emerging5Gmobileservicesandnetworkrequirements.Sustainability, 9(10),1848.
[9]. Olsson, M., Cavdar, C., Frenger, P., Tombaz, S., Sabella, D., & Jantti, R.(2013, October). 5GrEEn: Towards Green 5G mobile networks. In 2013 IEEE 9th international conference on wireless and mobile computin networking and communications(WiMob)(pp.212 216).IEEE.
[10].Janevski,T.(2009,January).5Gmobilephoneconcept. In20096thIEEEconsumercommunicationsandnetworking conference(pp.1 2).IEEE.
[11]. Pisarov, J., & Mester, G. (2020). The impact of 5G technology on life in 21st century. IPSI BgD Transactions on AdvancedResearch(TAR),16(2),11 14.
[12]. Noohani, M. Z., & Magsi, K. U. (2020). A review of 5G technology: Architecture, security and wide applications. InternationalResearchJournalofEngineeringandTechnology(IRJET),7(05),3440 3471.
[13].Kachhavay,M.G.,&Thakare,A.P.(2014).5Gtechnology evolutionandrevolution.InternationalJournalofComputer ScienceandMobileComputing,3(3),1080 1087.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 07 | July 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[14].Campbell,K.,Diffley, J.,Flanagan,B.,Morelli,B.,O’Neil,B.,&Sideco,F.(2017).The5Geconomy:How5Gtechnology willcontributetotheglobaleconomy.IHSeconomicsandIHStechnology,4,16.
[15]. Gohil, A., Modi, H., & Patel, S. K. (2013, March). 5G technology of mobile communication: A survey. In 2013 internationalconferenceonintelligentsystemsandsignalprocessing(ISSP)(pp.288 292).IEEE.
[16].Ni,Y.,Liang,J.,Shi,X.,&Ban,D.(2019,January).Researchonkeytechnologyin5Gmobilecommunicationnetwork.In 2019InternationalConferenceonIntelligentTransportation,BigData&SmartCity(ICITBS)(pp.199 201).IEEE.
[17].Al Falahy,N.,&Alani,O.Y.(2017).Technologiesfor5Gnetworks:Challengesandopportunities. It Professional, 19(1), 12 20.
[18]. Dighriri, M., Lee, G. M., & Baker, T. (2018). Measurement and classification of smart systems data traffic over 5G mobilenetworks.InTechnologyforsmartfutures(pp.195 217).Springer,Cham.
[19].Xiao,M.,Mumtaz,S.,Huang,Y.,Dai,L.,Li,Y.,Matthaiou,M.,...&Ghosh,A.(2017).Millimeterwavecommunicationsfor futuremobilenetworks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 35(9),1909 1935.
[20].Dyadyuk,V.,Bunton,J.D.,Pathikulangara,J.,Kendall,R.,Sevimli,O.,Stokes,L.,&Abbott,D.A.(2007).Amultigigabit millimeter wave communication system with improved spectral efficiency. IEEE transactions on microwave theory and techniques, 55(12),2813 2821.
[21]. Thompson, J., Ge, X., Wu, H. C., Irmer, R., Jiang, H., Fettweis, G., & Alamouti, S. (2014). 5G wireless communication systems:Prospectsandchallenges[GuestEditorial]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(2),62 64.